Application of C-Terminal Clostridium Perfringens Enterotoxin in Treatment of Brain Metastasis from Breast Cancer
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
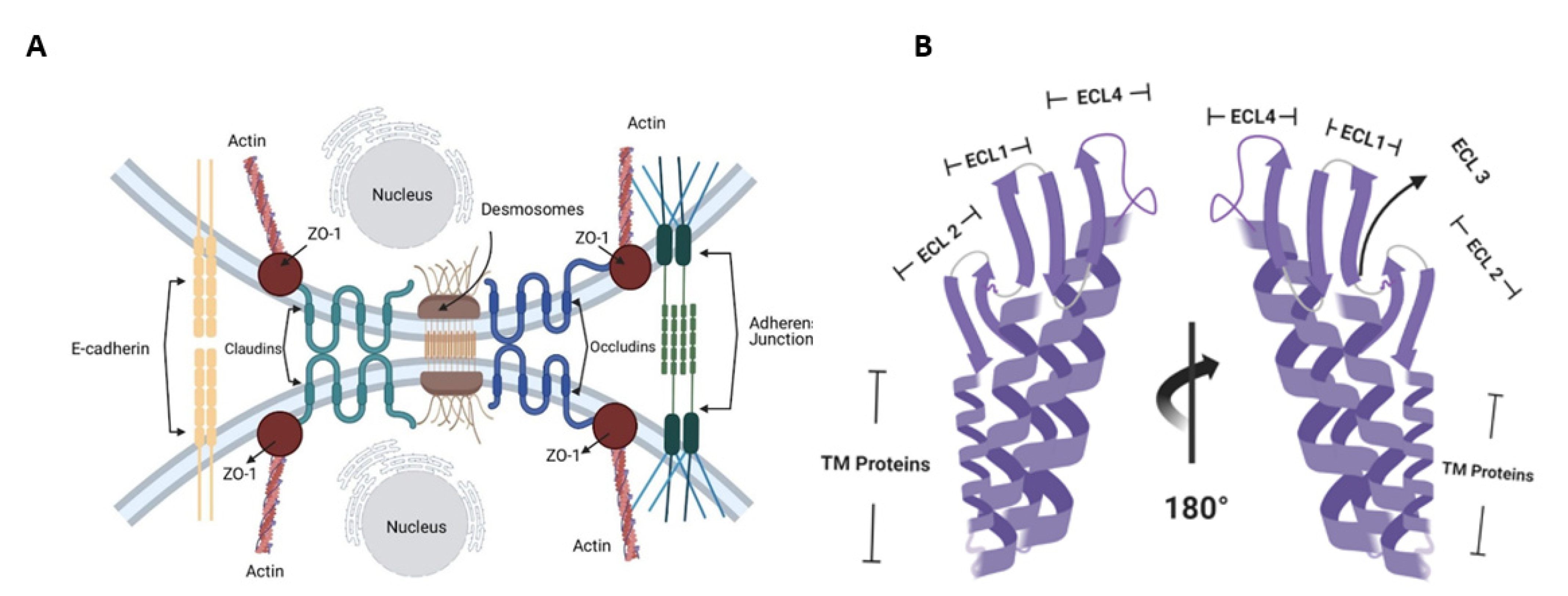
2. Molecular Targets of CPE in the Human Body
3. Application of CPE and Claudin-4 Interactions in Treatment of Brain Metastasis from Breast Cancer
3.1. Brain Metastasis Treatment Options
3.2. Claudin-4 Expression Patterns
4. Use of C-Terminal CPE as a Therapeutic Agent in Brain Metastasis from Breast Cancer
4.1. Claudin-4 and C-CPE Interactions in Cancer Cells
4.2. Crossing the Blood–Brain Barrier
5. Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shimizu, T.; Ohtani, K.; Hirakawa, H.; Ohshima, K.; Yamashita, A.; Shiba, T.; Ogasawara, N.; Hattori, M.; Kuhara, S.; Hayashi, H. Complete genome sequence of Clostridium perfringens, an anaerobic flesh-eater. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 996–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uzal, F.A.; Freedman, J.C.; Shrestha, A.; Theoret, J.R.; Garcia, J.; Awad, M.M.; Adams, V.; Moore, R.J.; Rood, J.I.; McClane, B.A. Towards an understanding of the role of Clostridium perfringens toxins in human and animal disease. Futur. Microbiol. 2014, 9, 361–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Uzal, F.A.; McClane, B.A. Clostridium perfringens Sialidases: Potential Contributors to Intestinal Pathogenesis and Therapeutic Targets. Toxins 2016, 8, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, W.A.; Hess, C.; Hess, M. Enteric Pathogens and Their Toxin-Induced Disruption of the Intestinal Barrier through Alteration of Tight Junctions in Chickens. Toxins 2017, 9, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vecchio, A.J.; Rathnayake, S.S.; Stroud, R.M. Structural basis for Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin targeting of claudins at tight junctions in mammalian gut. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebihara, C.; Kondoh, M.; Harada, M.; Fujii, M.; Mizuguchi, H.; Tsunoda, S.-I.; Horiguchi, Y.; Yagi, K.; Watanabe, Y. Role of Tyr306 in the C-terminal fragment of Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin for modulation of tight junction. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2007, 73, 824–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shrestha, A.; Uzal, F.A.; McClane, B.A. The interaction of Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin with receptor claudins. Anaerobe 2016, 41, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freedman, J.C.; Shrestha, A.; McClane, B.A. Clostridium perfringens Enterotoxin: Action, Genetics, and Translational Applications. Toxins 2016, 8, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujiwara-Tani, R.; Sasaki, T.; Luo, Y.; Goto, K.; Kawahara, I.; Nishiguchi, Y.; Kishi, S.; Mori, S.; Ohmori, H.; Kondoh, M.; et al. Anti-claudin-4 extracellular domain antibody enhances the antitumoral effects of chemotherapeutic and antibody drugs in colorectal cancer. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 37367–37378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.B.; Sharma, A.; Dhawan, P. Claudin Family of Proteins and Cancer: An Overview. J. Oncol. 2010, 2010, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; Rajagopal, M.; Yu, A.S. Claudins and the Kidney. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2013, 75, 479–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Xu, C.; Li, W.; Ding, L. Emerging clinical significance of claudin-7 in colorectal cancer: A review. Cancer Manag. Res. 2018, 10, 3741–3752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J. Context-Dependent Roles of Claudins in Tumorigenesis. Frontiers in Oncology. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 676781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Z.; McClane, B.A. Use of Clostridium perfringens Enterotoxin and the Enterotoxin Receptor-Binding Domain (C-CPE) for Cancer Treatment: Opportunities and Challenges. J. Toxicol. 2011, 2012, 981626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shrestha, A.; Robertson, S.L.; Garcia, J.; Beingasser, J.; McClane, B.A.; Uzal, F.A. A Synthetic Peptide Corresponding to the Extracellular Loop 2 Region of Claudin-4 Protects against Clostridium perfringens Enterotoxin In Vitro and In Vivo. Infect. Immun. 2014, 82, 4778–4788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Andrea, G.; Palombi, L.; Minniti, G.; Pesce, A.; Marchetti, P. Brain Metastases: Surgical Treatment and Overall Survival. World Neurosurg. 2016, 97, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amsbaugh, M.J.; Kim, C.S. Brain Metastasis. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK470246/# (accessed on 9 April 2022).
- Goetz, P.; Ebinu, J.O.; Roberge, D.; Zadeh, G. Current Standards in the Management of Cerebral Metastases. Int. J. Surg. Oncol. 2011, 2012, 493426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lin, X.; De Angelis, L.M. Treatment of Brain Metastases. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 3475–3484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, B.J.; Suki, D.; Fox, B.D.; Pelloski, C.E.; Maldaun, M.V.C.; Sawaya, R.E.; Lang, F.F.; Rao, G. Stereotactic radiosurgery for metastatic brain tumors: A comprehensive review of complications. J. Neurosurg. 2009, 111, 439–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, B.M. Experimental Methods and Transport Models for Drug Delivery Across the Blood-Brain Barrier. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2012, 13, 1346–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laksitorini, M.; Prasasty, V.D.; Kiptoo, P.K.; Siahaan, T.J. Pathways and progress in improving drug delivery through the intestinal mucosa and blood–brain barriers. Ther. Deliv. 2014, 5, 1143–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, A.; Komiya, E.; Kakutani, H.; Yoshida, T.; Fujii, M.; Horiguchi, Y.; Mizuguchi, H.; Tsutsumi, Y.; Tsunoda, S.-I.; Koizumi, N.; et al. Domain mapping of a claudin-4 modulator, the C-terminal region of C-terminal fragment of Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin, by site-directed mutagenesis. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2008, 75, 1639–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aungst, B.J. Absorption Enhancers: Applications and Advances. AAPS J. 2011, 14, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberts, B.; Johnson, A.; Lewis, J.; Raff, M.; Roberts, K.; Walter, P. Molecular Biology of the Cell, 4th ed.; Cell Junctions; Garland Science: New York, NY, USA, 2002. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK26857/ (accessed on 9 April 2022).
- Kwon, M.J. Emerging Roles of Claudins in Human Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 18148–18180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Sun, X.; Meng, X. Differences in the expression profiles of claudin proteins in human gastric carcinoma compared with non-neoplastic mucosa. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 18, 1271–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szász, M.A. Claudins as prognostic factors of breast cancer. Magy. Onkol. 2012, 56, 209–212. [Google Scholar]
- Abd-Elazeem, M.A.; Abd-Elazeem, M.A. Claudin 4 expression in triple-negative breast cancer: Correlation with androgen receptors and Ki-67 expression. Ann. Diagn. Pathol. 2015, 19, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abu-Farsakh, S.; Wu, T.; LaLonde, A.; Sun, J.; Zhou, Z. High expression of Claudin-2 in esophageal carcinoma and precancerous lesions is significantly associated with the bile salt receptors VDR and TGR5. BMC Gastroenterol. 2017, 17, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achari, C.; Winslow, S.; Larsson, C. Down Regulation of CLDND1 Induces Apoptosis in Breast Cancer Cells. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0130300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danilova, N.V.; Anikina, K.A.; Oleynikova, N.; Vychuzhanin, D.V.; Malkov, P.G. Claudin-3 expression in gastric cancer. Arkhiv Patol. 2020, 82, 5–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Li, M.; Xiang, R.; Zhou, X.; Zhu, L.; Zhai, Y. Expression of CLDN6 in tissues of gastric cancer patients: Association with clinical pathology and prognosis. Oncol. Lett. 2019, 17, 4621–4625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Li, J.; Qu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, L.; Chen, X.; Liu, B.; Zhu, Z. The expression of Claudin 1 correlates with β-catenin and is a prognostic factor of poor outcome in gastric cancer. Int. J. Oncol. 2014, 44, 1293–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinugasa, T.; Huo, Q.; Higashi, D.; Shibaguchi, H.; Kuroki, M.; Tanaka, T.; Futami, K.; Yamashita, Y.; Hachimine, K.; Maekawa, S.; et al. Selective up-regulation of claudin-1 and claudin-2 in colorectal cancer. Anticancer Res. 2007, 27, 3729–3734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleinberg, L.; Holth, A.; Fridman, E.; Schwartz, I.; Shih, I.-M.; Davidson, B. The Diagnostic Role of Claudins in Serous Effusions. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2007, 127, 928–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konecny, G.E.; Agarwal, R.; Keeney, G.A.; Winterhoff, B.; Jones, M.B.; Mariani, A.; Riehle, D.; Neuper, C.; Dowdy, S.C.; Wang, H.-J.; et al. Claudin-3 and claudin-4 expression in serous papillary, clear-cell, and endometrioid endometrial cancer. Gynecol. Oncol. 2008, 109, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morohashi, S.; Kusumi, T.; Sato, F.; Odagiri, H.; Chiba, H.; Yoshihara, S.; Hakamada, K.; Sasaki, M.; Kijima, H. Decreased expression of claudin-1 correlates with recurrence status in breast cancer. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2007, 20, 139–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paschoud, S.; Bongiovanni, M.; Pache, J.-C.; Citi, S. Claudin-1 and claudin-5 expression patterns differentiate lung squamous cell carcinomas from adenocarcinomas. Mod. Pathol. 2007, 20, 947–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Song, W.; Qian, L.; Zhu, J.; Li, Y.; Li, M.; Zhang, T.; Zhao, W.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, X. Effect of claudin 1 on cell proliferation, migration and apoptosis in human cervical squamous cell carcinoma. Oncol. Rep. 2020, 45, 606–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takala, H.; Saarnio, J.; Wiik, H.; Soini, Y. Claudins 1, 3, 4, 5 and 7 in esophageal cancer: Loss of claudin 3 and 4 expression is associated with metastatic behavior. APMIS 2007, 115, 838–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, J.B.; Mosley, M.; Koustoulidou, S.; Hopkins, S.; Knapp, S.; Chaikuad, A.; Kondoh, M.; Tachibana, K.; Kersemans, V.; Cornelissen, B. Radiolabeled cCPE Peptides for SPECT Imaging of Claudin-4 Overexpression in Pancreatic Cancer. J. Nucl. Med. 2020, 61, 1756–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, M.; Wei, M.; Dong, Q.; Xu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Gao, L.; et al. Claudin-3 expression increases the malignant potential of lung adenocarcinoma cells: Role of epidermal growth factor receptor activation. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 23033–23047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.-N.; Li, W.; Wang, X.-L.; Hu, Z.; Zhu, D.; Ding, W.-C.; Liu, D.; Li, K.-Z.; Ma, D.; Wang, H. CLDN1 expression in cervical cancer cells is related to tumor invasion and metastasis. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 87449–87461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eichner, M.; Augustin, C.; Fromm, A.; Piontek, A.; Walther, W.; Bücker, R.; Fromm, M.; Krause, G.; Schulzke, J.-D.; Günzel, D.; et al. In Colon Epithelia, Clostridium perfringens Enterotoxin Causes Focal Leaks by Targeting Claudins Which are Apically Accessible Due to Tight Junction Derangement. J. Infect. Dis. 2017, 217, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakrabarti, G.; McClane, B.A. The importance of calcium influx, calpain and calmodulin for the activation of CaCo-2 cell death pathways by Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin. Cell. Microbiol. 2004, 7, 129–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kominsky, S.L.; Vali, M.; Korz, D.; Gabig, T.G.; Weitzman, S.A.; Argani, P.; Sukumar, S. Clostridium perfringens Enterotoxin Elicits Rapid and Specific Cytolysis of Breast Carcinoma Cells Mediated through Tight Junction Proteins Claudin 3 and 4. Am. J. Pathol. 2004, 164, 1627–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kominsky, S.L.; Tyler, B.; Sosnowski, J.; Brady, K.; Doucet, M.; Nell, D.; Smedley, J.G., III; McClane, B.; Brem, H.; Sukumar, S. Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin as a novel-targeted therapeutic for brain metastasis. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 7977–7982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walther, W.; Petkov, S.; Kuvardina, O.N.; Aumann, J.; Kobelt, D.; Fichtner, I.; Lemm, M.; Piontek, J.; Blasig, I.E.; Stein, U.; et al. Novel Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin suicide gene therapy for selective treatment of claudin-3- and -4-overexpressing tumors. Gene Ther. 2011, 19, 494–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujiwara-Tani, R.; Fujii, K.; Mori, S.; Kishi, S.; Sasaki, T.; Ohmori, H.; Nakashima, C.; Kawahara, I.; Nishiguchi, Y.; Mori, T.; et al. Role of Clostridium perfringens Enterotoxin on YAP Activation in Colonic Sessile Serrated Adenoma/Polyps with Dysplasia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinoda, T.; Shinya, N.; Ito, K.; Ohsawa, N.; Terada, T.; Hirata, K.; Kawano, Y.; Yamamoto, M.; Kimura-Someya, T.; Yokoyama, S.; et al. Structural basis for disruption of claudin assembly in tight junctions by an enterotoxin. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 33632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojima, T.; Kondoh, M.; Keira, T.; Takano, K.-I.; Kakuki, T.; Kaneko, Y.; Miyata, R.; Nomura, K.; Obata, K.; Kohno, T.; et al. Claudin-binder C-CPE mutants enhance permeability of insulin across human nasal epithelial cells. Drug Deliv. 2015, 23, 2703–2710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, J.D.; Lopez, S.; Cocco, E.; Schwab, C.L.; English, D.P.; Santin, A.D. Clostridium Perfringens Enterotoxin (CPE) and CPE-Binding Domain (c-CPE) for the Detection and Treatment of Gynecologic Cancers. Toxins 2015, 7, 1116–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hewitt, K.J.; Agarwal, R.; Morin, P.J. The claudin gene family: Expression in normal and neoplastic tissues. BMC Cancer 2006, 6, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shim, M.K.; Na, J.; Cho, I.K.; Jang, E.H.; Park, J.; Lee, S.; Kim, J.-H. Targeting of claudin-4 by Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin-conjugated polysialic acid nanoparticles for pancreatic cancer therapy. J. Control. Release 2021, 331, 434–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cocco, E.; Deng, Y.; Shapiro, E.M.; Bortolomai, I.; Lopez, S.; Lin, K.; Bellone, S.; Cui, J.; Menderes, G.; Black, J.D.; et al. Dual-Targeting Nanoparticles for In Vivo Delivery of Suicide Genes to Chemotherapy-Resistant Ovarian Cancer Cells. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2017, 16, 323–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kono, T.; Kondoh, M.; Kyuno, D.; Ito, T.; Kimura, Y.; Imamura, M.; Kohno, T.; Konno, T.; Furuhata, T.; Sawada, N.; et al. Claudin-4 binder C-CPE 194 enhances effects of anticancer agents on pancreatic cancer cell lines via a MAPK pathway. Pharmacol. Res. Perspect. 2015, 3, e00196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebihara, C.; Kondoh, M.; Hasuike, N.; Harada, M.; Mizuguchi, H.; Horiguchi, Y.; Fujii, M.; Watanabe, Y. Preparation of a Claudin-Targeting Molecule Using a C-Terminal Fragment of Clostridium perfringens Enterotoxin. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2005, 316, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, Y.; Tachibana, K.; Krug, S.M.; Kunisawa, J.; Fromm, M.; Kondoh, M. Potential for Tight Junction Protein–Directed Drug Development Using Claudin Binders and Angubindin-1. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Lin, X.; Manorek, G.; Kanatani, I.; Cheung, L.H.; Rosenblum, M.G.; Howell, S.B. Recombinant CPE fused to tumor necrosis factor targets human ovarian cancer cells expressing the claudin-3 and claudin-4 receptors. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2009, 8, 1906–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuhaus, W.; Piontek, A.; Protze, J.; Eichner, M.; Mahringer, A.; Subileau, E.-A.; Lee, I.-F.M.; Schulzke, J.D.; Krause, G.; Piontek, J. Reversible opening of the blood-brain barrier by claudin-5-binding variants of Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin’s claudin-binding domain. Biomaterials 2018, 161, 129–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Protze, J.; Eichner, M.; Piontek, A.; Dinter, S.; Rossa, J.; Blecharz, K.G.; Vajkoczy, P.; Piontek, J.; Krause, G. Directed structural modification of Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin to enhance binding to claudin-5. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2014, 72, 1417–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Z.; Yang, Z.; Piontek, A.; Eichner, M.; Krause, G.; Li, L.; Piontek, J.; Zhang, J. Specific binding of a mutated fragment of Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin to endothelial claudin-5 and its modulation of cerebral vascular permeability. Neuroscience 2016, 327, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teleanu, D.M.; Chircov, C.; Grumezescu, A.M.; Volceanov, A.; Teleanu, R.I. Blood-Brain Delivery Methods Using Nanotechnology. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patra, J.K.; Das, G.; Fraceto, L.F.; Campos, E.V.R.; del Pilar Rodriguez-Torres, M.; Acosta-Torres, L.S.; Diaz-Torres, L.A.; Grillo, R.; Swamy, M.K.; Sharma, S.; et al. Nano based drug delivery systems: Recent developments and future prospects. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2018, 16, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, M.J.; Billingsley, M.M.; Haley, R.M.; Wechsler, M.E.; Peppas, N.A.; Langer, R. Engineering precision nanoparticles for drug delivery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2020, 20, 101–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabraji, S.; Ni, J.; Lin, N.U.; Xie, S.; Winer, E.P.; Zhao, J.J. Drug Resistance in HER2-Positive Breast Cancer Brain Metastases: Blame the Barrier or the Brain? Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 1795–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dijkers, E.C.; Oude Munnink, T.H.; Kosterink, J.G.; Brouwers, A.H.; Jager, P.L.; De Jong, J.R.; Van Dongen, G.A.; Schroder, C.P.; Lub-de Hooge, M.N.; de Vries, E.G. Biodistribution of 89Zr-trastuzumab and PET Imaging of HER2-Positive Lesions in Patients with Metastatic Breast Cancer. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2010, 87, 586–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taskar, K.S.; Rudraraju, V.; Mittapalli, R.K.; Samala, R.; Thorsheim, H.R.; Lockman, J.; Gril, B.; Hua, E.; Palmieri, D.; Polli, J.; et al. Lapatinib Distribution in HER2 Overexpressing Experimental Brain Metastases of Breast Cancer. Pharm. Res. 2011, 29, 770–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morikawa, A.; Peereboom, D.M.; Thorsheim, H.R.; Samala, R.; Balyan, R.; Murphy, C.G.; Lockman, P.R.; Simmons, A.; Weil, R.J.; Tabar, V.; et al. Capecitabine and lapatinib uptake in surgically resected brain metastases from metastatic breast cancer patients: A prospective study. Neuro-Oncology 2014, 17, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, G.D.L.; Nishimura, M.C.; Lacap, J.A.; Kharbanda, S.; Mai, E.; Tien, J.; Malesky, K.; Williams, S.P.; Marik, J.; Phillips, H.S. Trastuzumab uptake and its relation to efficacy in an animal model of HER2-positive breast cancer brain metastasis. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2017, 164, 581–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Banga, A.R.; Odiase, P.; Rachakonda, K.; Garg, A.P.; Adunyah, S.E.; Rachakonda, G. Application of C-Terminal Clostridium Perfringens Enterotoxin in Treatment of Brain Metastasis from Breast Cancer. Cancers 2022, 14, 4309. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14174309
Banga AR, Odiase P, Rachakonda K, Garg AP, Adunyah SE, Rachakonda G. Application of C-Terminal Clostridium Perfringens Enterotoxin in Treatment of Brain Metastasis from Breast Cancer. Cancers. 2022; 14(17):4309. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14174309
Chicago/Turabian StyleBanga, Amita R., Peace Odiase, Kartik Rachakonda, Amar P. Garg, Samuel E. Adunyah, and Girish Rachakonda. 2022. "Application of C-Terminal Clostridium Perfringens Enterotoxin in Treatment of Brain Metastasis from Breast Cancer" Cancers 14, no. 17: 4309. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14174309
APA StyleBanga, A. R., Odiase, P., Rachakonda, K., Garg, A. P., Adunyah, S. E., & Rachakonda, G. (2022). Application of C-Terminal Clostridium Perfringens Enterotoxin in Treatment of Brain Metastasis from Breast Cancer. Cancers, 14(17), 4309. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14174309






