Novel Insights into miR-944 in Cancer
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. miR-944 and Its Host Gene TP63
3. Aberrant Expression of miR-944 in Cancer
4. Co-Expression of TP63 Transcripts and miR-944
5. TP63 SNV and miR-944 Expression
6. TP63 Copy Number Variation (CNV) and miR-944
7. miR-944 and Cancer Cell Behaviors
8. Regulatory Effect of miR-944 on Cell Cycle
9. Regulatory Effect of miR-944 on Cancer Cell Proliferation
10. Regulatory Effect of miR-944 on Cancer Cell Apoptosis
11. Regulatory Effect of miR-944 on EMT
12. Regulatory Effect of miR-944 on Cancer Cell Invasion and Migration
13. The ceRNA Network of miR-944 in Cancer
14. Exogenous Regulators of miR-944
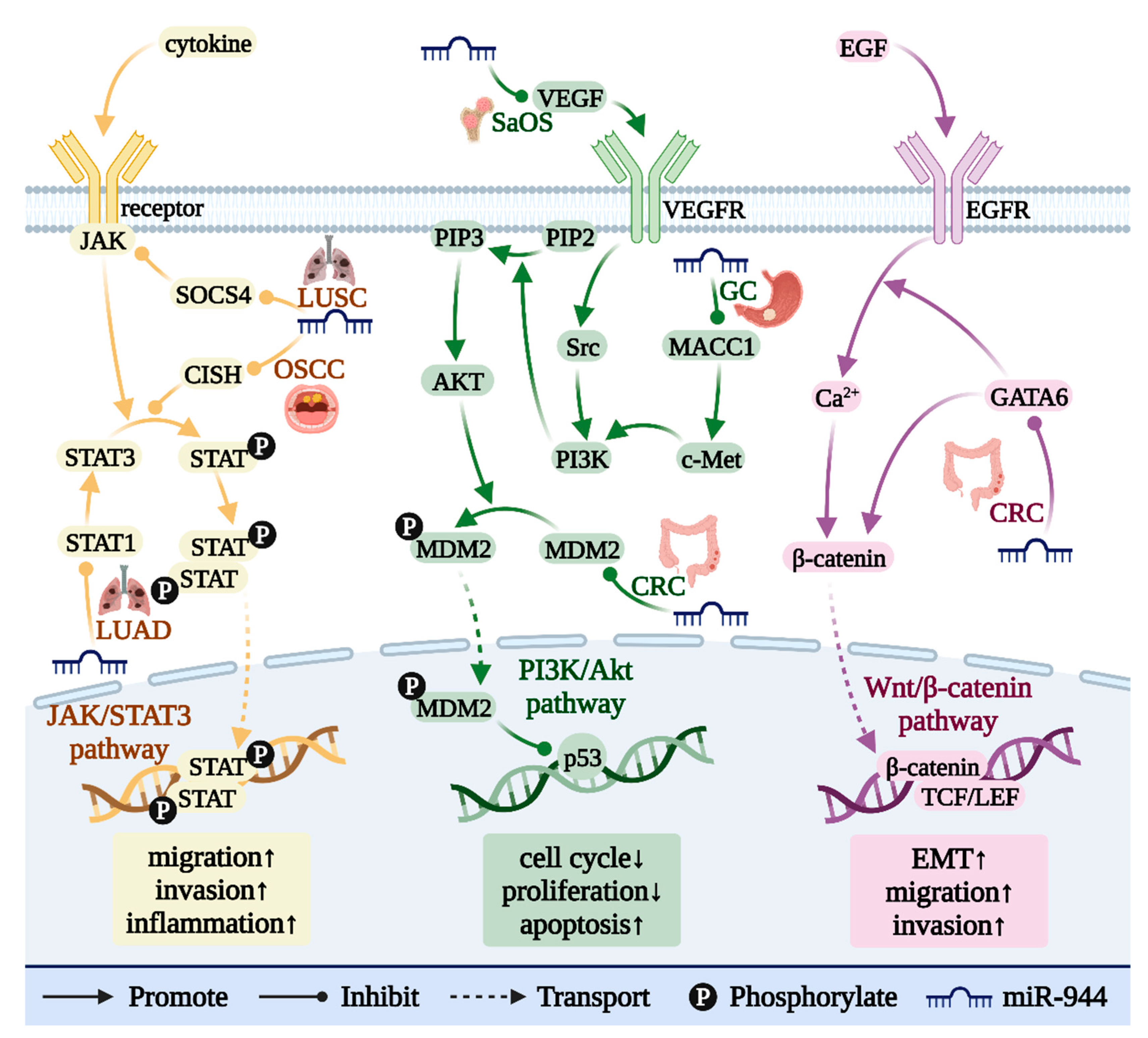
15. miR-944 Is Involved in a Variety of Cancer-Related Signaling Pathways
16. miR-944 and the Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway
17. miR-944 and the Jak/STAT Pathway
18. miR-944 and the PI3K/AKT Pathway
19. Prognostic Value of miR-944
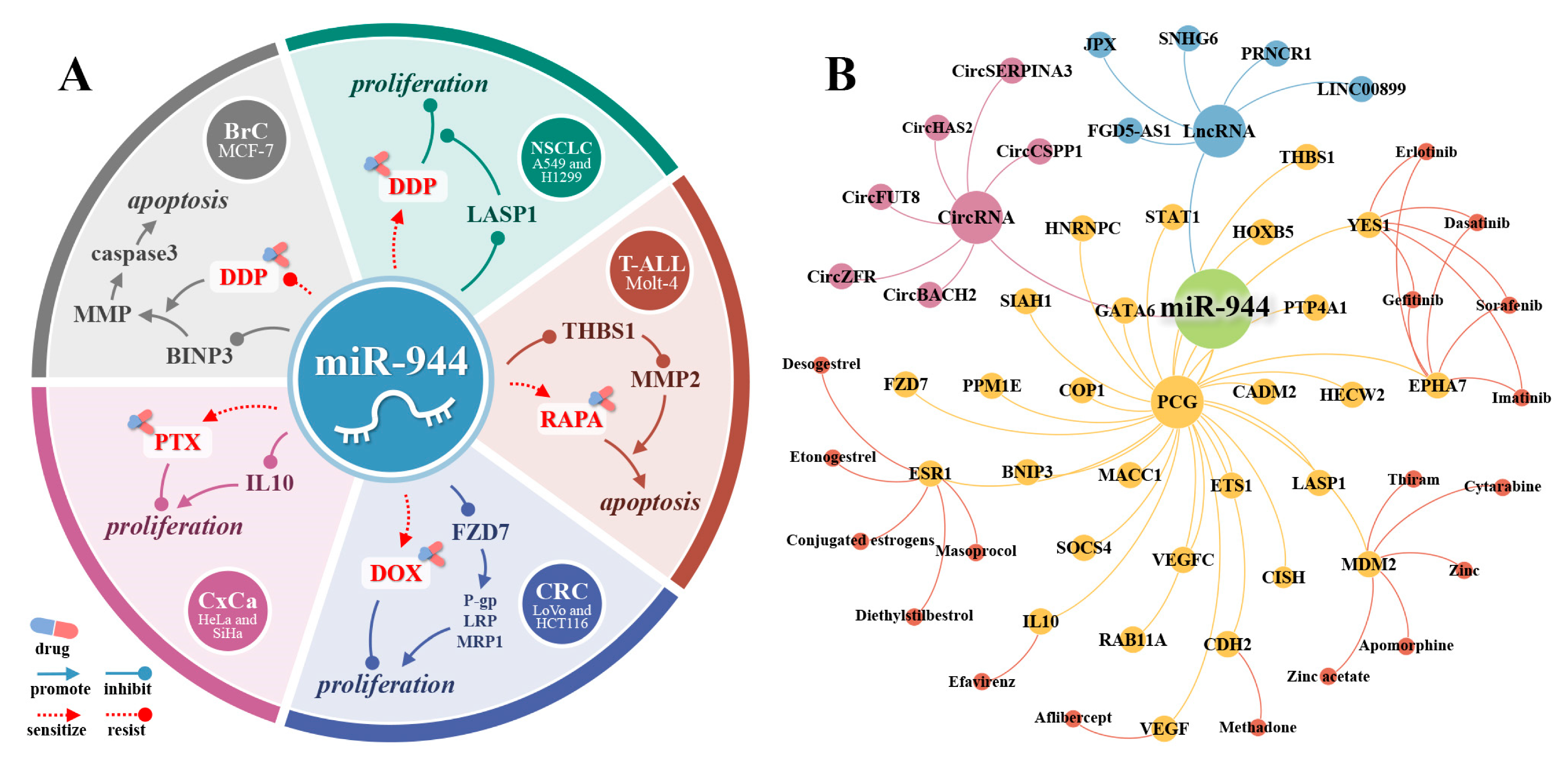
20. miR-944 and Its Therapeutic Value
21. miR-944 and Drug Resistance of Cancer Cells
22. miR-944 and Drug Therapy
23. The PCGs of miR-944 and Their Targeted Drugs
24. Discussion
25. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ha, M.; Kim, V.N. Regulation of microRNA biogenesis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2014, 15, 509–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.Y.; Han, S.S.; Rhee, H.; Park, J.H.; Lee, J.S.; Oh, Y.M.; Choi, S.S.; Shin, S.H.; Kim, W.J. Differential expression of microRNAs and their target genes in non-small-cell lung cancer. Mol. Med. Rep. 2015, 11, 2034–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Pereira, T.; Brito, J.A.R.; Guimaraes, A.L.S.; Gomes, C.C.; de Lacerda, J.C.T.; de Castro, W.H.; Coimbra, R.S.; Diniz, M.G.; Gomez, R.S. MicroRNA profiling reveals dysregulated microRNAs and their target gene regulatory networks in cemento-ossifying fibroma. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2018, 47, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, Y.; Zhong, C.; Hu, Z.; Duan, S. MiR-873-5p: A Potential Molecular Marker for Cancer Diagnosis and Prognosis. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 743701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Kim, J.; Eom, K.; Oh, S.; Kim, S.; Kim, G.; Ahn, S.; Park, K.H.; Chung, D.; Lee, H. microRNA-944 overexpression is a biomarker for poor prognosis of advanced cervical cancer. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, C.; Xie, Z.; Zeng, L.H.; Yuan, C.; Duan, S. MIR4435-2HG Is a Potential Pan-Cancer Biomarker for Diagnosis and Prognosis. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 855078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Zhou, M.; Zhang, P.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Y. Cell proliferation and invasion is promoted by circSERPINA3 in nasopharyngeal carcinoma by regulating miR-944/MDM2 axis. J. Cancer 2020, 11, 3910–3918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Gao, W.; Liu, G.; Sheng, W.; Zhou, J.; Dong, Q.; Dong, M. miR-944 Suppresses EGF-Induced EMT in Colorectal Cancer Cells by Directly Targeting GATA6. Oncol. Targets Ther. 2021, 14, 2311–2325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, L.; Li, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, B.; Han, F. miR-944 inhibits cell migration and invasion by targeting MACC1 in colorectal cancer. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 37, 3415–3422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, W.; Tan, Y.; Xiong, M.; Zhao, C.; Wang, Y.; Wu, M.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, Q. Analysis and validation of m6A regulatory network: A novel circBACH2/has-miR-944/HNRNPC axis in breast cancer progression. J. Transl. Med. 2021, 19, 527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wu, Y.; Hou, C.; Li, F. Circ_0072088 knockdown contributes to cisplatin sensitivity and inhibits tumor progression by miR-944/LASP1 axis in non-small cell lung cancer. J. Gene Med. 2022, 24, e3414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Guo, Z.; Fan, S.; Sun, L.; Li, H.; Zhou, J.; Li, Y. Integrating microRNA and mRNA expression in rapamycin-treated T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2019, 215, 152494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xi, L.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, W.; Luo, L.; Song, J.; Liu, R.; Wei, S.; Wang, Y. Circular RNA circCSPP1 knockdown attenuates doxorubicin resistance and suppresses tumor progression of colorectal cancer via miR-944/FZD7 axis. Cancer Cell Int. 2021, 21, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, X.; Zheng, M.; Yang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, H. circ_ZFR Is Linked to Paclitaxel Resistance in Cervical Cancer via miR-944 Sponging and IL-10 Upregulation. Anal. Cell Pathol. 2022, 2022, 4807287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, H.; Lu, Q.; Lu, Q.; Shen, X.; Yu, L. Matrine Regulates Proliferation, Apoptosis, Cell Cycle, Migration, and Invasion of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cells Through the circFUT8/miR-944/YES1 Axis. Cancer Manag. Res. 2021, 13, 3429–3442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.Z.; Wan, S.Y.; Lin, M.Y.; Chang, C.H.; Chen, T.W.; Yang, M.H.; Lee, Y.J. Involvement of Differentially Expressed microRNAs in the PEGylated Liposome Encapsulated (188)Rhenium-Mediated Suppression of Orthotopic Hypopharyngeal Tumor. Molecules 2020, 25, 3609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.H.; Cho, E.G.; Yu, S.J.; Kang, H.; Kim, Y.J.; Kim, S.H.; Lee, T.R. DeltaNp63 intronic miR-944 is implicated in the DeltaNp63-mediated induction of epidermal differentiation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, 7462–7479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prieto-Garcia, C.; Hartmann, O.; Reissland, M.; Braun, F.; Fischer, T.; Walz, S.; Schulein-Volk, C.; Eilers, U.; Ade, C.P.; Calzado, M.A.; et al. Maintaining protein stability of Np63 via USP28 is required by squamous cancer cells. EMBO Mol. Med. 2020, 12, e11101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Park, S.; Chang, Y.; Park, K.H.; Lee, H. Synergetic Effects of Intronic Mature miR-944 and DeltaNp63 Isoforms on Tumorigenesis in a Cervical Cancer Cell Line. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warnecke-Eberz, U.; Chon, S.H.; Holscher, A.H.; Drebber, U.; Bollschweiler, E. Exosomal onco-miRs from serum of patients with adenocarcinoma of the esophagus: Comparison of miRNA profiles of exosomes and matching tumor. Tumour Biol. 2015, 36, 4643–4653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Mannoor, K.; Gao, L.; Tan, A.; Guarnera, M.A.; Zhan, M.; Shetty, A.; Stass, S.A.; Xing, L.; Jiang, F. Characterization of microRNA transcriptome in lung cancer by next-generation deep sequencing. Mol. Oncol. 2014, 8, 1208–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Z.; Xu, H.; Meng, Y.; Kuang, Y. miR-944 acts as a prognostic marker and promotes the tumor progression in endometrial cancer. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 88, 902–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Gu, Y.; Gu, Y.; Wu, J. Long Noncoding RNA LINC00899/miR-944/ESR1 Axis Regulates Cervical Cancer Cell Proliferation, Migration, and Invasion. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 2021, 41, 220–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palatnik, A.; Ye, S.; Kendziorski, C.; Iden, M.; Zigman, J.S.; Hessner, M.J.; Rader, J.S. Identification of a serum-induced transcriptional signature associated with metastatic cervical cancer. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0181242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Lee, L.; Scicluna, P.; Kavak, E.; Larsson, C.; Sandberg, R.; Lui, W.O. Novel functions and targets of miR-944 in human cervical cancer cells. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 136, E230–E241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, H.; Tian, W.; Chen, H.; Jiang, K. MiR-944 functions as a novel oncogene and regulates the chemoresistance in breast cancer. Tumour Biol. 2016, 37, 1599–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores-Perez, A.; Marchat, L.A.; Rodriguez-Cuevas, S.; Bautista, V.P.; Fuentes-Mera, L.; Romero-Zamora, D.; Maciel-Dominguez, A.; de la Cruz, O.H.; Fonseca-Sanchez, M.; Ruiz-Garcia, E.; et al. Suppression of cell migration is promoted by miR-944 through targeting of SIAH1 and PTP4A1 in breast cancer cells. BMC Cancer 2016, 16, 379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Lu, J.; Wang, X.; Sun, B.; Liu, X.; Ding, Y.; Gao, G. Glioma stem cell-derived exosomal miR-944 reduces glioma growth and angiogenesis by inhibiting AKT/ERK signaling. Aging 2021, 13, 19243–19259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, J.; Peng, Y.; Niu, T.; Lin, Y.; Lin, Y.; Li, X.; Wu, X.; Huang, Z.; Zhong, L.; Zhang, S. miR-944 inhibits cell migration and invasion by targeting MACC1 in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2018, 11, 1167–1174. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- An, J.C.; Shi, H.B.; Hao, W.B.; Zhu, K.; Ma, B. miR-944 inhibits lung adenocarcinoma tumorigenesis by targeting STAT1 interaction. Oncol. Lett. 2019, 17, 3790–3798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, J.; Li, Q.; Ma, R.; Wang, Z.; Yu, Y.; Liu, H.; Miao, Y.; Jiang, S. Long Noncoding RNA FGD5-AS1 Knockdown Decrease Viability, Migration, and Invasion of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) Cells by Regulating the MicroRNA-944/MACC1 Axis. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2021, 20, 1533033821990090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, H.; Li, S.; Xu, M. Long Noncoding RNA SNHG6 Functions as an Oncogene in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer via Modulating ETS1 Signaling. Oncol. Targets Ther. 2020, 13, 921–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.; Zou, Y.; Li, R.; Liu, D. Long noncoding RNA PRNCR1 exerts oncogenic effects in tongue squamous cell carcinoma in vitro and in vivo by sponging microRNA944 and thereby increasing HOXB5 expression. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2020, 46, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, S.; Gu, X.; Shen, L.; Chen, Y.; Qian, C.; Shen, X.; Ju, S. CircHAS2 promotes the proliferation, migration, and invasion of gastric cancer cells by regulating PPM1E mediated by hsa-miR-944. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, T.; Chen, W.; Yuan, X.; Shen, J.; Qin, C.; Wang, L. miR-944 inhibits metastasis of gastric cancer by preventing the epithelial-mesenchymal transition via MACC1/Met/AKT signaling. FEBS Open Bio 2017, 7, 905–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Zou, A.E.; Saad, M.A.; Wang, X.Q.; Kwok, J.G.; Korrapati, A.; Li, P.; Kisseleva, T.; Wang-Rodriguez, J.; Ongkeko, W.M. Alcohol-dysregulated microRNAs in hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0178547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.J.; Lee, J.H.; Jin, S.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, S.H. Primate-specific miR-944 activates p53-dependent tumor suppression in human colorectal cancers. Cancer Lett. 2019, 440–441, 168–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.T.; Zhao, J.; Sheng, W.; Zhou, J.P.; Dong, Q.; Dong, M. Ectopic expression of miR-944 impairs colorectal cancer cell proliferation and invasion by targeting GATA binding protein 6. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2019, 23, 3483–3494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, T.; Zhu, S.; Zhang, J.; Lu, G.; Lv, C.; Wei, Y.; Luo, M. MicroRNA944 targets vascular endothelial growth factor to inhibit cell proliferation and invasion in osteosarcoma. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 18, 5221–5228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, C.C.; Selitsky, S.R.; Chai, S.; Armistead, P.M.; Vincent, B.G.; Serody, J.S. Alternative tumour-specific antigens. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2019, 19, 465–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steele, C.D.; Abbasi, A.; Islam, S.M.A.; Bowes, A.L.; Khandekar, A.; Haase, K.; Hames-Fathi, S.; Ajayi, D.; Verfaillie, A.; Dhami, P.; et al. Signatures of copy number alterations in human cancer. Nature 2022, 606, 984–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Zhou, K.; Cao, Y. MicroRNA-944 Affects Cell Growth by Targeting EPHA7 in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, Y.; Chen, S.; Lu, N.; Yin, Y.; Liu, Z. LncRNA JPX overexpressed in oral squamous cell carcinoma drives malignancy via miR-944/CDH2 axis. Oral Dis. 2021, 27, 924–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, H.Y.; Hsiao, J.R.; Chou, S.T.; Hsu, Y.M.; Wu, G.H.; Shieh, Y.S.; Shiah, S.G. MiR-944/CISH mediated inflammation via STAT3 is involved in oral cancer malignance by cigarette smoking. Neoplasia 2020, 22, 554–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, D.; Jie, Y.; Lv, Y. LncRNA SNHG6 Induces Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition of Pituitary Adenoma Via Suppressing MiR-944. Cancer Biother. Radiopharm. 2022, 37, 246–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, T.; Lin, Z. The Involvement of Ubiquitination Machinery in Cell Cycle Regulation and Cancer Progression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, G.H.; Stoeber, K. The cell cycle and cancer. J. Pathol. 2012, 226, 352–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Reyes, I.; Chandel, N.S. Cancer metabolism: Looking forward. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2021, 21, 669–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldar, S.; Khaniani, M.S.; Derakhshan, S.M.; Baradaran, B. Molecular mechanisms of apoptosis and roles in cancer development and treatment. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2015, 16, 2129–2144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastushenko, I.; Blanpain, C. EMT Transition States during Tumor Progression and Metastasis. Trends Cell Biol. 2019, 29, 212–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duff, D.; Long, A. Roles for RACK1 in cancer cell migration and invasion. Cell Signal. 2017, 35, 250–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.L.; Yang, L. Regulation of circRNA biogenesis. RNA Biol. 2015, 12, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, C.; Xie, Z.; Shen, J.; Jia, Y.; Duan, S. LINC00665: An Emerging Biomarker for Cancer Diagnostics and Therapeutics. Cells 2022, 11, 1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, J.; Wu, Y.; Ruan, W.; Zhu, F.; Duan, S. miR-1908 Dysregulation in Human Cancers. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 857743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri, A.; Nezafat, N.; Eslami, M.; Ghasemi, Y.; Negahdaripour, M. Designing a therapeutic and prophylactic candidate vaccine against human papillomavirus through vaccinomics approaches. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2021, 95, 105084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, X. Targeting the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway in cancer. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2020, 13, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nusse, R.; Clevers, H. Wnt/beta-Catenin Signaling, Disease, and Emerging Therapeutic Modalities. Cell 2017, 169, 985–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, D.E.; O’Keefe, R.A.; Grandis, J.R. Targeting the IL-6/JAK/STAT3 signalling axis in cancer. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 15, 234–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasidharan Nair, V.; Toor, S.M.; Ali, B.R.; Elkord, E. Dual inhibition of STAT1 and STAT3 activation downregulates expression of PD-L1 in human breast cancer cells. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2018, 22, 547–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, G.; Xie, H.; Yang, Z.; Li, L. Exosome-mediated miR-9-5p promotes proliferation and migration of renal cancer cells both in vitro and in vivo by targeting SOCS4. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2020, 529, 1216–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Jiang, W.; Hou, P. Emerging role of PI3K/AKT in tumor-related epigenetic regulation. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2019, 59, 112–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porta, C.; Paglino, C.; Mosca, A. Targeting PI3K/Akt/mTOR Signaling in Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2014, 4, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruan, G.X.; Kazlauskas, A. Axl is essential for VEGF-A-dependent activation of PI3K/Akt. EMBO J. 2012, 31, 1692–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Yan, J.; Cao, Y.; Yan, Y.; Shen, X.; Yu, B.; Tao, L.; Wang, S. Proliferation, migration and invasion of triple negative breast cancer cells are suppressed by berbamine via the PI3K/Akt/MDM2/p53 and PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathways. Oncol. Lett. 2021, 21, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Deng, H.; Zhao, Y.; Li, C.; Liang, Y. LncRNA XIST/miR-34a axis modulates the cell proliferation and tumor growth of thyroid cancer through MET-PI3K-AKT signaling. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 37, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miles, X.; Vandevoorde, C.; Hunter, A.; Bolcaen, J. MDM2/X Inhibitors as Radiosensitizers for Glioblastoma Targeted Therapy. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 703442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, M.; Xu, T.; Cui, X.; Li, H.; Li, X.; Xia, W. NCAPG upregulation mediated by four microRNAs combined with activation of the p53 signaling pathway is a predictor of poor prognosis in patients with breast cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2021, 21, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rupaimoole, R.; Slack, F.J. MicroRNA therapeutics: Towards a new era for the management of cancer and other diseases. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2017, 16, 203–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Yang, Z.; Nie, Y.; Shi, Y.; Fan, D. Multi-drug resistance in cancer chemotherapeutics: Mechanisms and lab approaches. Cancer Lett. 2014, 347, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnesano, F.; Natile, G. Interference between copper transport systems and platinum drugs. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2021, 76, 173–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S. Cisplatin: The first metal based anticancer drug. Bioorg. Chem. 2019, 88, 102925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arriola Apelo, S.I.; Lamming, D.W. Rapamycin: An InhibiTOR of Aging Emerges from the Soil of Easter Island. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2016, 71, 841–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Kim, S.G.; Blenis, J. Rapamycin: One drug, many effects. Cell. Metab. 2014, 19, 373–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.Y.; Sabatini, D.M. mTOR at the nexus of nutrition, growth, ageing and disease. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020, 21, 183–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalyanaraman, B. Teaching the basics of the mechanism of doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity: Have we been barking up the wrong tree? Redox Biol. 2020, 29, 101394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koleini, N.; Kardami, E. Autophagy and mitophagy in the context of doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 46663–46680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marupudi, N.I.; Han, J.E.; Li, K.W.; Renard, V.M.; Tyler, B.M.; Brem, H. Paclitaxel: A review of adverse toxicities and novel delivery strategies. Expert Opin. Drug Saf. 2007, 6, 609–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howell, W.M.; Rose-Zerilli, M.J. Cytokine gene polymorphisms, cancer susceptibility, and prognosis. J. Nutr. 2007, 137, 194S–199S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Xu, H. Matrine: Bioactivities and Structural Modifications. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2016, 16, 3365–3378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.H.; Liu, S.Y.; Chi, C.W.; Yu, H.L.; Chang, T.J.; Tsai, T.H.; Lee, T.W.; Chen, Y.J. External beam radiotherapy synergizes (1)(8)(8)Re-liposome against human esophageal cancer xenograft and modulates (1)(8)(8)Re-liposome pharmacokinetics. Int. J. Nanomed. 2015, 10, 3641–3649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartung, M.; Anastasi, E.; Mamdouh, Z.M.; Nogales, C.; Schmidt, H.; Baumbach, J.; Zolotareva, O.; List, M. Cancer driver drug interaction explorer. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, W138–W144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
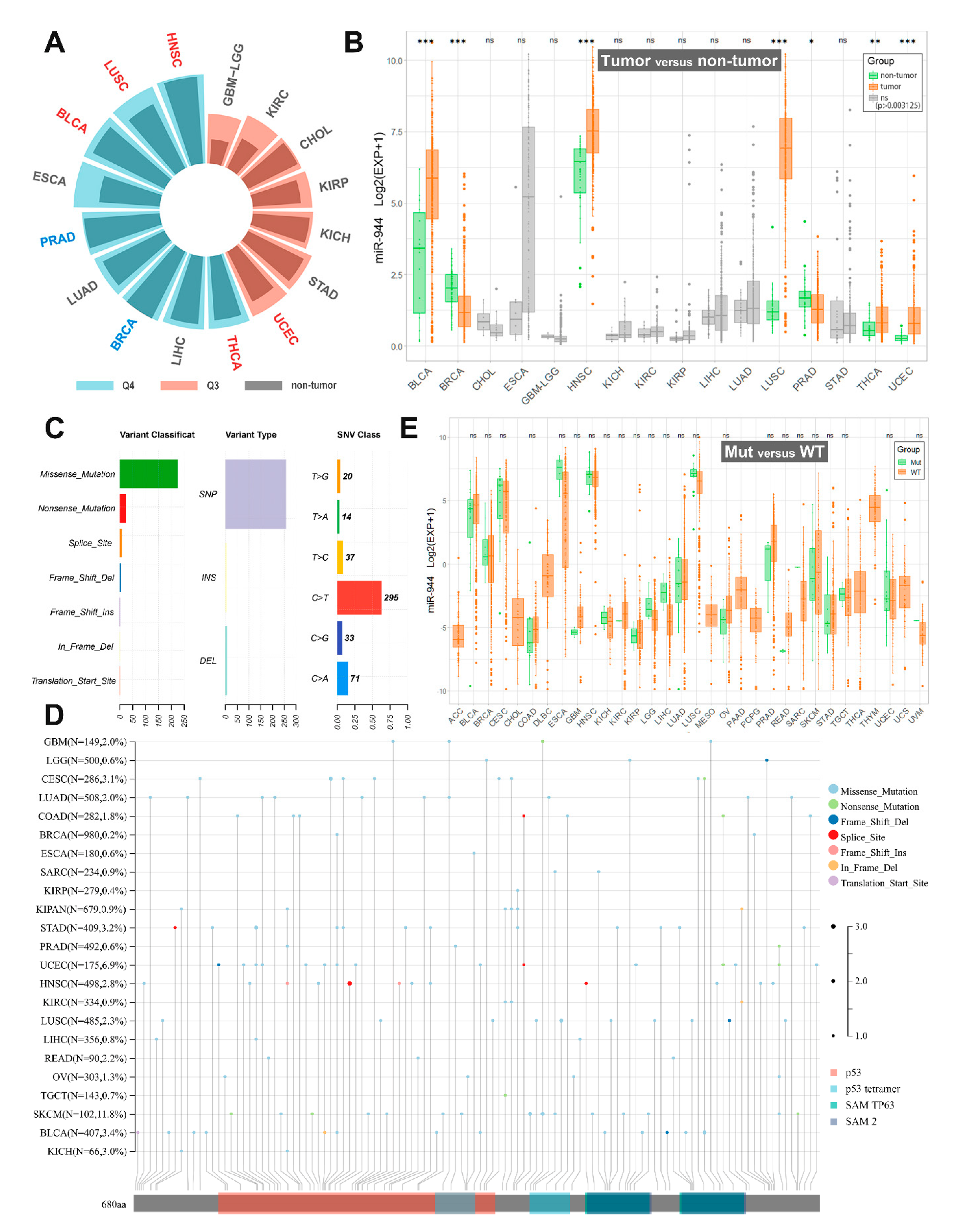
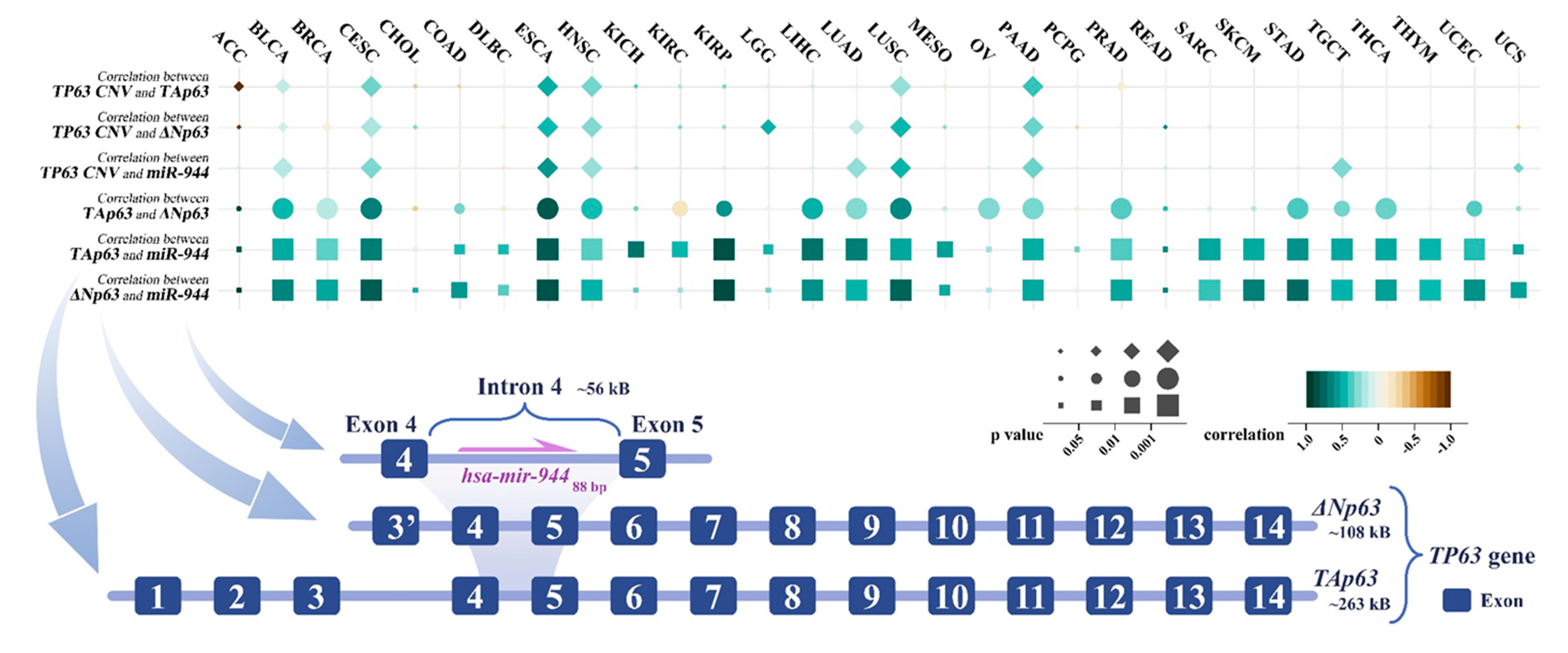
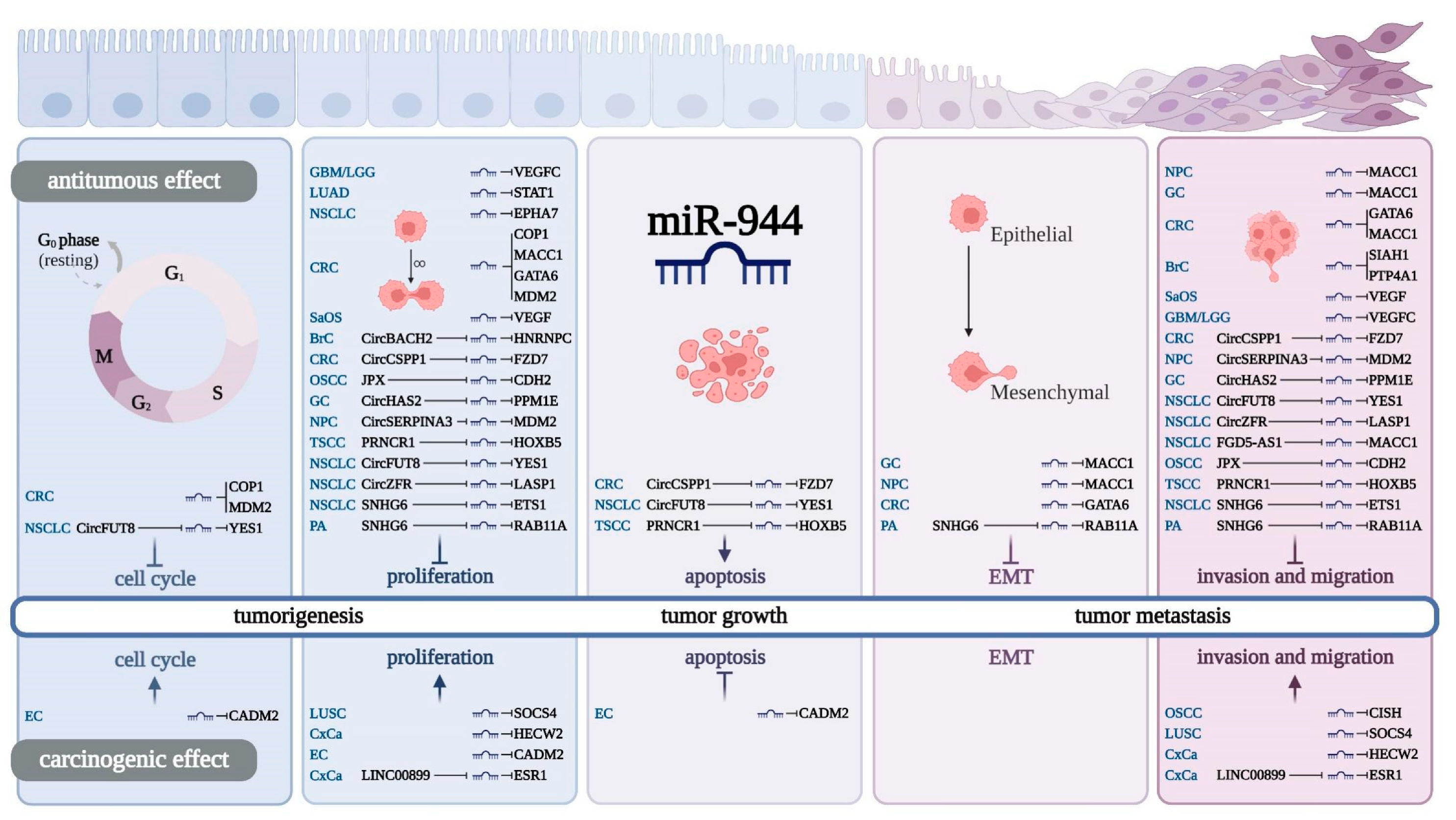

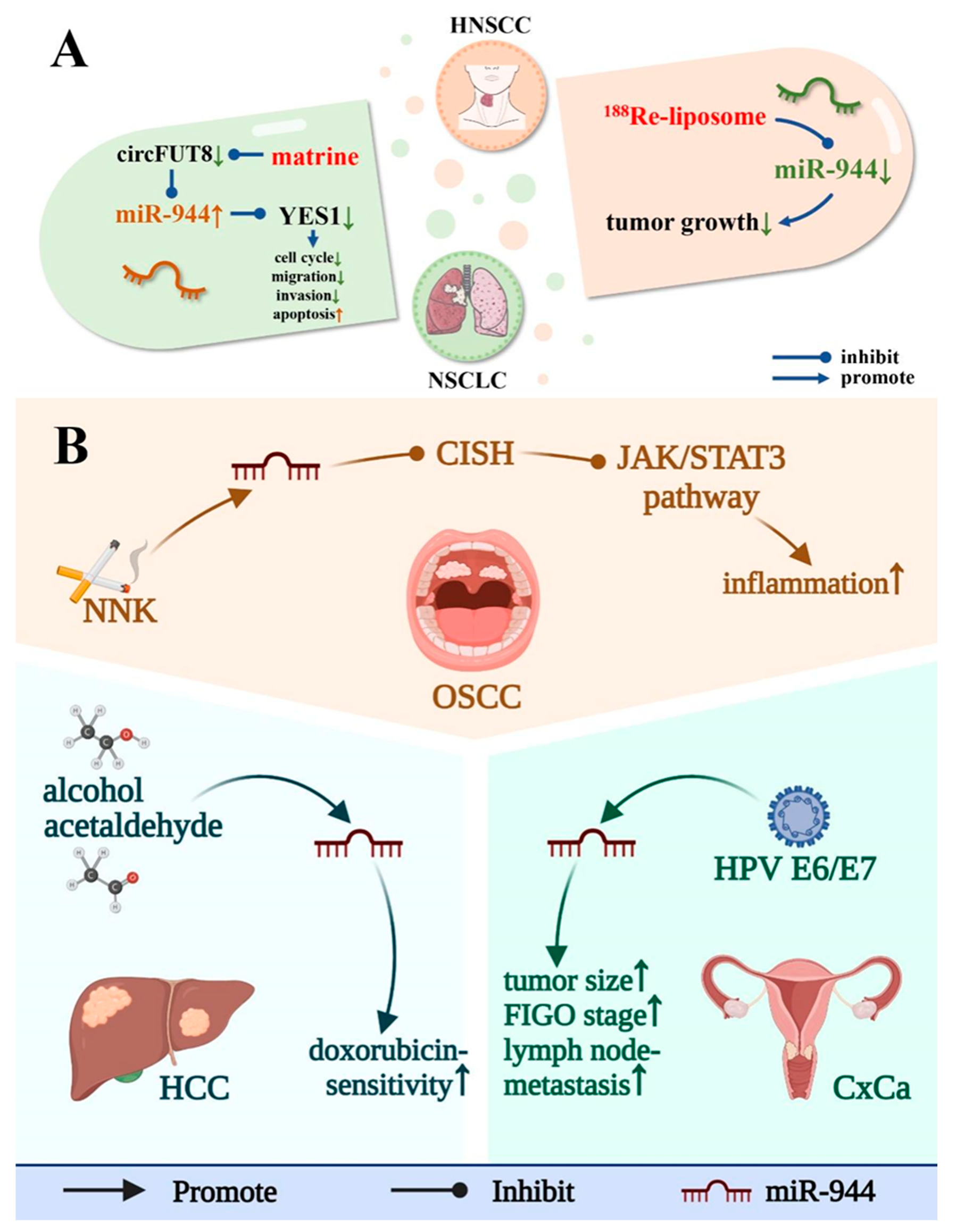
| Physiological System | Cancer | miR-944 Expression | Cell Line | Tissue or Serum | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nervous system | GBM/LGG | Downregulated | HA1800 versus SHG44, U87MG, and U251MG | Paracancerous tissues versus glioma tissues from 5 patients | [28] |
| Respiratory system | NPC | Downregulated | NP69 versus C666-1, CNE1, CNE2, and HNE1 | Paracancerous tissues versus tumor tissues from 20 NPC patients | [29] |
| Downregulated | NP69 versus CNU46, SUNE1, HONE1, 6–10 B, CNE1, CNE2, and HNE1 | Nasopharyngeal mucosa tissues from 30 healthy people versus primary tumor tissues from 30 NPC patients | [7] | ||
| LUAD | Downregulated | 16HBE versus A549, H1299, SK-Lu-1, and PC-9 | Paracancerous tissues versus LUAD tissues from 25 patients | [30] | |
| LUSC | Upregulated | — | Paracancerous tissues from patients versus SCC tissues from patients | [21] | |
| NSCLC | Downregulated | BEAS-2B versus H522 and H1975 | — | [15] | |
| Downregulated | BEAS-2B versus H358, H1299, PC-9, and A549 | Paracancerous tissues versus tumor tissues from 65 NSCLC patients | [31] | ||
| Downregulated | BEAS-2B versus A549, H226, H292, ANP973, and H1299 | Paracancerous tissues versus tumor tissues from 60 NSCLC patients | [32] | ||
| Downregulated | — | Paracancerous tissues versus tumor tissues from 9 NSCLC patients | [2] | ||
| Digestive system | TSCC | Downregulated | normal gingival epithelial cells versus SCC-9, CAL-27, and SCC-15 | Paracancerous tissues versus TSCC tissues from 57 patients | [33] |
| ECa | Downregulated | — | Paracancerous tissues versus adenocarcinoma tissues from 59 eca patients; serum exosomes from healthy persons versus serum exosomes from 59 eca patients | [20] | |
| GC | Downregulated | GES-1 versus AGS, MKN-1, HGC-27, MKN-45, SGC-7901, and BGC-823 | — | [34] | |
| Downregulated | GES-1 versus SGC-7901, MGC-803, MKN-28, and BGC-823 | Paracancerous tissues versus tumor tissues from 40 GC patients | [35] | ||
| HCC | Downregulated | L02 versus Hep3B, Bel-7402, SMMC-7721, Huh7, and SK-HEP-1 | Paracancerous tissues versus tumor tissues from 61 HCC patients | [36] | |
| CRC | Downregulated | HIEC and HEK293 versus HCT116, Caco-2, HT29, SW620, and SW480 | — | [9] | |
| Downregulated | COS7 versus HCT116, LoVo, RKO, HCT15, HT29, SW480, and SW620 | — | [37] | ||
| Downregulated | — | Paracancerous tissues versus fresh CRC tissues from 140 CRC patients | [8] | ||
| Downregulated | CCC-HIE-2 versus HT-29, HCT116, SW480, and SW620 | Paracancerous tissues versus fresh CRC tissues from 100 CRC patients | [38] | ||
| Reproductive system | EC | Upregulated | — | Normal endometrial tissues from 20 non-cancer patients versus tumor tissues from 68 EC patients | [22] |
| CxCa | Upregulated | — | Paracancerous tissues versus tumor tissues from 27 cxca patients | [25] | |
| Upregulated | — | Serum specimens from 24 women with localized disease versus serum specimens from 25 women with metastatic disease | [24] | ||
| Upregulated | HcerEpiC versus HeLa, CaSki, SiHa, and C33A | Paracancerous tissues versus fresh cxca tissues from 70 cxca patients | [23] | ||
| Upregulated | — | 50 FFPE normal cervical tissue samples versus 66 FFPE cxca tissue samples | [5] | ||
| BrC | Downregulated | MCF-10A versus MDA-MB-231, MCF-7, MDA-MB-453, ZR-75, and T47-D | Paracancerous tissues versus locally invasive breast tumors tissues from brc patients | [27] | |
| Upregulated | — | Paracancerous tissues versus tumor tissues from 40 brc patients; serum samples from 30 healthy people versus serum samples from 30 brc patients | [26] | ||
| Motor system | SaOS | Downregulated | hFOB1.19 versus MG-63, SAOS-2, HOS, and U2OS | Paracancerous tissues versus tumor tissues from 38 saos patients | [39] |
| COF | Downregulated | — | Bone tissues from 10 healthy people versus bone tissues from 9 COF patients | [3] |
| TCGA Cancers | Sample Size (T/N) | miR-944 Expression in TCGA | miR-944 Expression in the Present Studies |
|---|---|---|---|
| BLCA | 405/18 | Upregulated; Q4 | Not studied |
| BRCA | 624/74 | Downregulated; Q4 | Downregulated in BrC tissues and BrC cells (MDA-MB-231, MCF-7, MDA-MB-453, ZR-75, and T47-D) [27]; and Upregulated in BrC tissues and serum sample of BrC patients [26] |
| CHOL | 20/8 | ns; Q3 | Not studied |
| ESCA | 176/8 | ns; Q4 | Downregulated in ECa tissues and serums of ECa patients [20] |
| GBM/LGG | 209/3 | ns; Q3 | Downregulated in GBM/LGG tissues and GBM/LGG cells (SHG44, U87MG, and U251MG) [28] |
| HNSC | 485/44 | Upregulated; Q4 | Not studied |
| KICH | 49/8 | ns; Q3 | Not studied |
| KIRC | 108/19 | ns; Q3 | Not studied |
| KIRP | 155/23 | ns; Q3 | Not studied |
| LIHC | 324/47 | ns; Q4 | Downregulated in HCC tissues and HCC cells (Hep3B, Bel-7402, SMMC-7721, Huh7, and SK-HEP-1) [36] |
| LUAD | 430/40 | ns; Q4 | Downregulated in LUAD tissues and LUAD cells (A549, H1299, SK-Lu-1, and PC-9) [30] |
| LUSC | 334/44 | Upregulated; Q4 | Upregulated in LUSC tissues [21] |
| PRAD | 437/50 | Downregulated; Q4 | Not studied |
| STAD | 303/26 | ns; Q3 | Downregulated in GC tissues and GC cells (AGS, MKN-1, HGC-27, MKN-45, SGC-7901, MGC-803, BGC-823, and MKN-28) [34,35] |
| THCA | 420/50 | Upregulated; Q4 | Not studied |
| UCEC | 330/26 | Upregulated; Q3 | Upregulated in EC tissues [22] |
| Cancer | PCG | Effect in Vitro | Cell Line | Effect in Vivo | Xenograft Model | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BrC | BNIP3 | DDP-resistance↑ | MCF-7 | — | — | [26] |
| HNRNPC | Proliferation↓ | MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 | — | — | [10] | |
| PTP4A1 and SIAH1 | Invasion↓ and migration↓ | MDA-MB-231 | — | — | [27] | |
| CRC | COP1 and MDM2 | Cell cycle↓ and proliferation↓ | HCT116 | Tumor growth↓ | HCT116 cell xenograft in BALB/c nude mice | [37] |
| FZD7 | Proliferation↓, invasion↓, migration↓, apoptosis↑, and DOX-resistance↓ | LoVo and HCT116 | Tumor growth↓ | LoVo cell xenograft in nude mice | [13] | |
| GATA6 | Invasion↓, migration↓, and EMT↓ | SW480 and HCT116 | — | — | [8] | |
| Proliferation↓, invasion↓, and migration↓ | SW480 and HCT116 | — | — | [38] | ||
| MACC1 | Proliferation↓, invasion↓, and migration↓ | SW620 | — | — | [9] | |
| CxCa | ESR1 | Proliferation↑, invasion↑, and migration↑ | CaSki and SiHa | — | — | [23] |
| HECW2 | Proliferation↑, invasion↑, and migration↑ | HeLa | — | — | [25] | |
| IL10 | PTX-resistance↓ | HeLa and SiHa | — | — | [14] | |
| EC | CADM2 | Cell cycle↑, proliferation↑, and apoptosis↓ | Ishikawa and KLE | Tumor growth↑ | Ishikawa cell xenograft in BALB/c nude mice | [22] |
| GBM/LGG | VEGFC | Proliferation↓ and migration↓ | HUVECs | Tumor growth↓ and angiogenesis↓ | SHG44 cell xenograft in nude mice | [28] |
| GC | MACC1 | Invasion↓, migration↓, and EMT↓ | GES-1 and MGC-803 | — | — | [35] |
| PPM1E | Proliferation↓, invasion↓, and migration↓ | HGC-27 and MKN-45 | — | — | [34] | |
| LUAD | STAT1 | Proliferation↓ | A549 and H1299 | Tumor growth↓ | A549 cell xenograft in BALB/c nude mice | [30] |
| LUSC | SOCS4 | Growth↑, proliferation↑, invasion↑, and migration↑ | CALU-1 and H520 | — | — | [21] |
| NPC | MACC1 | Invasion↓, migration↓, and EMT↓ | 6–10B and C666-1 | — | — | [29] |
| MDM2 | Proliferation↓ and invasion↓ | HONE-1 | — | — | [7] | |
| NSCLC | LASP1 | Proliferation↓, invasion↓, migration↓, and DDP-resistance↓ | A549 and H1299 | Tumor growth↓ and DDP-resistance↓ | A549 cell xenograft in BALB/c nude mice | [11] |
| MACC1 | Invasion↓ and migration↓ | A549 and H1299 | — | — | [31] | |
| EPHA7 | Proliferation↓ | EPLC-32M1, A549, and XLA-07 | — | — | [42] | |
| ETS1 | Proliferation↓ and migration↓ | A549 | — | — | [32] | |
| YES1 | Cell cycle↓, proliferation↓, invasion↓, migration↓, and apoptosis↑ | H522 and H1975 | Tumor growth↓ | H522 cell xenograft in nude mice | [15] | |
| OSCC | CDH2 | Proliferation↓, invasion↓, and migration↓ | SCC-15 and SCC-9 | — | — | [43] |
| CISH | Invasion↑ and migration↑ | OEC-M1 and SCC-25 | — | — | [44] | |
| PA | RAB11A | Proliferation↓, invasion↓, migration↓, and EMT↓ | HP75 | — | — | [45] |
| SaOS | VEGF | Proliferation↓ and invasion↓ | MG-63 and U2OS | — | — | [39] |
| T-ALL | THBS1 | RAPA-resistance↓ | Molt-4 | — | — | [12] |
| TSCC | HOXB5 | proliferation↓, invasion↓, migration↓, and apoptosis↑ | SCC-9 and CAL-27 | Tumor growth↓ | SCC-9 cell xenograft in nude mice | [33] |
| CeRNA Axis | Cancer | Binding Site of ceRNA and miR-944 | Binding Site of miR-944 and PCG | Ref. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ceRNA (5’-…-3’) | miR-944 (3’-…-5’) | PCG (5’-…-3’) | miRNA (3’-…-5’) | |||
| CircBACH2/miR-944/HNRNPC | BrC | — | — | — | — | [10] |
| CircCSPP1/miR-944/FZD7 | CRC | CAAUAAUUU | GUUAUUAAA | UAAUUU | AUUAAA | [13] |
| CircFUT8/miR-944/YES1 | NSCLC | AcCaGAGAgAAUAAUU | UaGgCUaCaUgUUAUUAA | GAUuUcaAAUAAUU | CUAcAugUUAUUAA | [15] |
| CircHAS2/miR-944/PPM1E | GC | AgAATAATT | UgUUAUUAA | AAUAAUU | UUAUUAA | [34] |
| CircSERPINA3/miR-944/MDM2 | NPC | GUUUCAACA | CAAAGUUGU | uCUuCucUuUAguAUAAUU | gAGuAgGcuAcAUguUAUUAA | [7] |
| CircZFR/miR-944/IL10 | CxCa | CAAUAAUU | GUUAUUAA | AUAAUU | UAUUAA | [14] |
| CircZFR/miR-944/LASP1 | NSCLC | CAAUAAUU | GUUAUUAA | AUAAUU | UAUUAA | [11] |
| FGD5-AS1/miR-944/MACC1 | NSCLC | AUGUACuAAUAAUUU | UACAUGUUAUUAAA | AUAAUU | UAUUAA | [31] |
| JPX/miR-944/CDH2 | OSCC | AUcGgAgAAUAAUU | UACaUgUUAUUAA | AUAAUU | UAUUAA | [43] |
| LINC00899/miR-944/ESR1 | CxCa | AUuCugUuUACagaAAUAAUU | UAgGcuAcAUGUUAUUAA | AUAAUU | UAUUAA | [23] |
| PRNCR1/miR-944/HOXB5 | TSCC | AAUAAUU | UUAUUAA | AAUAAUU | UUAUUAA | [33] |
| SNHG6/miR-944/ETS1 | NSCLC | UuuGAaGAAAUAAUUU | AggCUaCaUgUUAUUAAA | ucCAUgaGAUuUgAAUAgAUUU | gaGUAggCUAcAugUUAUUAAA | [32] |
| SNHG6/miR-944/RAB11A | PA | UuuGAaGAAAUAAUU | AggCUaCaUgUUAUUAA | CAAUAAUU | GUUAUUAA | [45] |
| miR-944/BNIP3 | BrC | — | — | AAUAAUUU | UUAUUAAA | [26] |
| miR-944/CADM2 | EC | — | — | AAUAAUU | UUAUUAA | [22] |
| miR-944/CISH | OSCC | — | — | UuCAUGaaAuAAUAAUU | AgGcUACaUgUUAUUAA | [44] |
| miR-944/COP1 | CRC | — | — | UuGaaUAaAaAUAAAU | GgCuaCAuGuUAUUAA | [37] |
| miR-944/EPHA7 | NSCLC | — | — | AAUAAUU | UUAUUAA | [42] |
| miR-944/GATA6 | CRC | — | — | AAUAAUUU | UUAUUAAA | [38] |
| miR-944/HECW2 | CxCa | — | — | CUgugCaucUaaguAAUAAUUU | GAguaGgcuAcaugUUAUUAAA | [25] |
| miR-944/MACC1 | CRC | — | — | AAUAAUU | UUAUUAA | [9] |
| GC | — | — | AAUAAUU | UUAUUAA | [35] | |
| NPC | — | — | AAUAAUU | UUAUUAA | [29] | |
| miR-944/MDM2 | CRC | — | — | UaaUUuUaAAUAAUU | GcuACaUgUUAUUAA | [37] |
| miR-944/PTP4A1 | BrC | — | — | AAUAAUUU | UUAUUAAA | [27] |
| miR-944/SIAH1 | BrC | — | — | AAUAAUU | UUAUUAA | [27] |
| miR-944/SOCS4 | LUSC | — | — | GAUccaAAUAAUU | CUAcaugUUAUUAA | [21] |
| miR-944/STAT1 | LUAD | — | — | UAUcCaAaGcugAAUAcAUU | GUAgGcUaCaugUUAUUAA | [30] |
| miR-944/THBS1 | T-ALL | — | — | — | — | [12] |
| miR-944/VEGF | SaOS | — | — | AAUAAUU | UUAUUAA | [39] |
| miR-944/VEGFC | GBM/LGG | — | — | AAUAAUU | UUAUUAA | [28] |
| Cancer | Sample Size | miR-944 Expression | Clinicopathological Characteristics | Prognostic Values of miR-944 Overexpression | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BrC | 1061 | Downregulated | — | Longer OS | [67] |
| 1062 | Downregulated | Earlier clinical stages and TNM stage | Longer OS | [10] | |
| CRC | 86 | Downregulated | Earlier tumor stage, Earlier TNM stage, less lymph node metastasis and distant metastasis | Longer OS and PFS | [9] |
| 265 | Downregulated | — | Longer OS | [37] | |
| 140 | Downregulated | Earlier TNM stage, small lymph node status, and less liver metastasis | Longer OS | [8] | |
| CxCa | 66 | Upregulated | Advanced clinical stages | Shorter OS | [5] |
| EC | 68 | Upregulated | Advanced FIGO stages and poorer pathology classification | Shorter OS | [22] |
| HNSCC | 522 | Upregulated | — | Shorter OS | [16] |
| NPC | 30 | Downregulated | Earlier clinical stage | Longer OS | [7] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shen, J.; Wang, Q.; Liang, C.; Su, X.; Ke, Y.; Mao, Y.; Fang, J.; Duan, S. Novel Insights into miR-944 in Cancer. Cancers 2022, 14, 4232. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14174232
Shen J, Wang Q, Liang C, Su X, Ke Y, Mao Y, Fang J, Duan S. Novel Insights into miR-944 in Cancer. Cancers. 2022; 14(17):4232. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14174232
Chicago/Turabian StyleShen, Jinze, Qurui Wang, Chenhao Liang, Xinming Su, Yufei Ke, Yunan Mao, Jie Fang, and Shiwei Duan. 2022. "Novel Insights into miR-944 in Cancer" Cancers 14, no. 17: 4232. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14174232
APA StyleShen, J., Wang, Q., Liang, C., Su, X., Ke, Y., Mao, Y., Fang, J., & Duan, S. (2022). Novel Insights into miR-944 in Cancer. Cancers, 14(17), 4232. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14174232






