Evaluation of Angiogenesis in an Acellular Porous Biomaterial Based on Polyhydroxybutyrate and Chitosan Using the Chicken Ex Ovo Chorioallantoic Membrane Model
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation and Characterization of Composite Scaffold
2.2. Chick CAM Ex Ovo Model for Evaluation of the Biocompatibility and Angiogenic Response to Biomaterials
2.3. Macroscopic Evaluation of Angiogenic Response
2.4. Histological Examination
Morphometric Analysis
2.5. Immunohistochemical Analysis
2.6. Gene Expression Analysis
2.7. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Macroscopic Evidence of Angiogenic Response
3.2. Histological Evaluation of Angiogenic Response
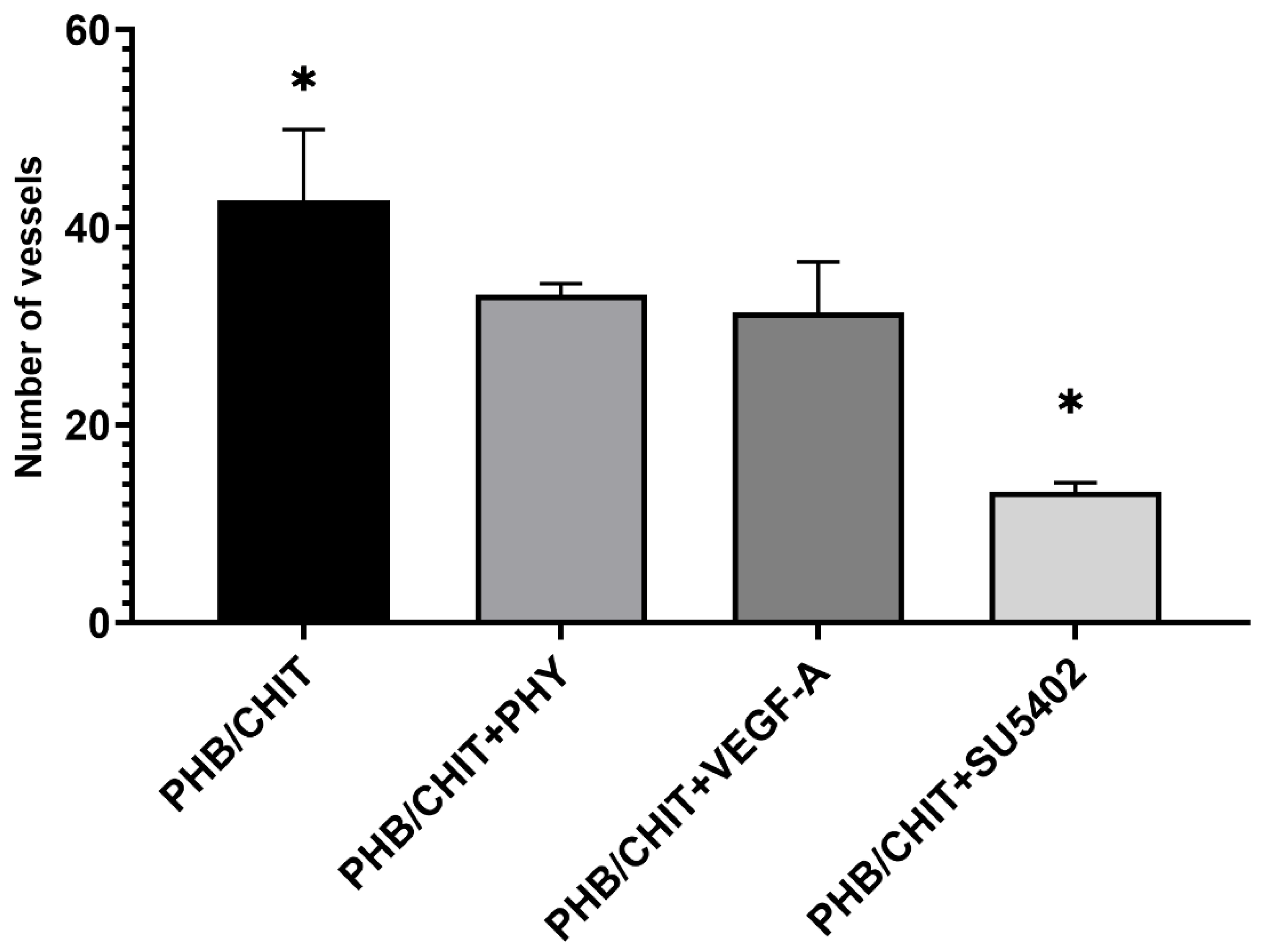
3.2.1. Number of Vessels
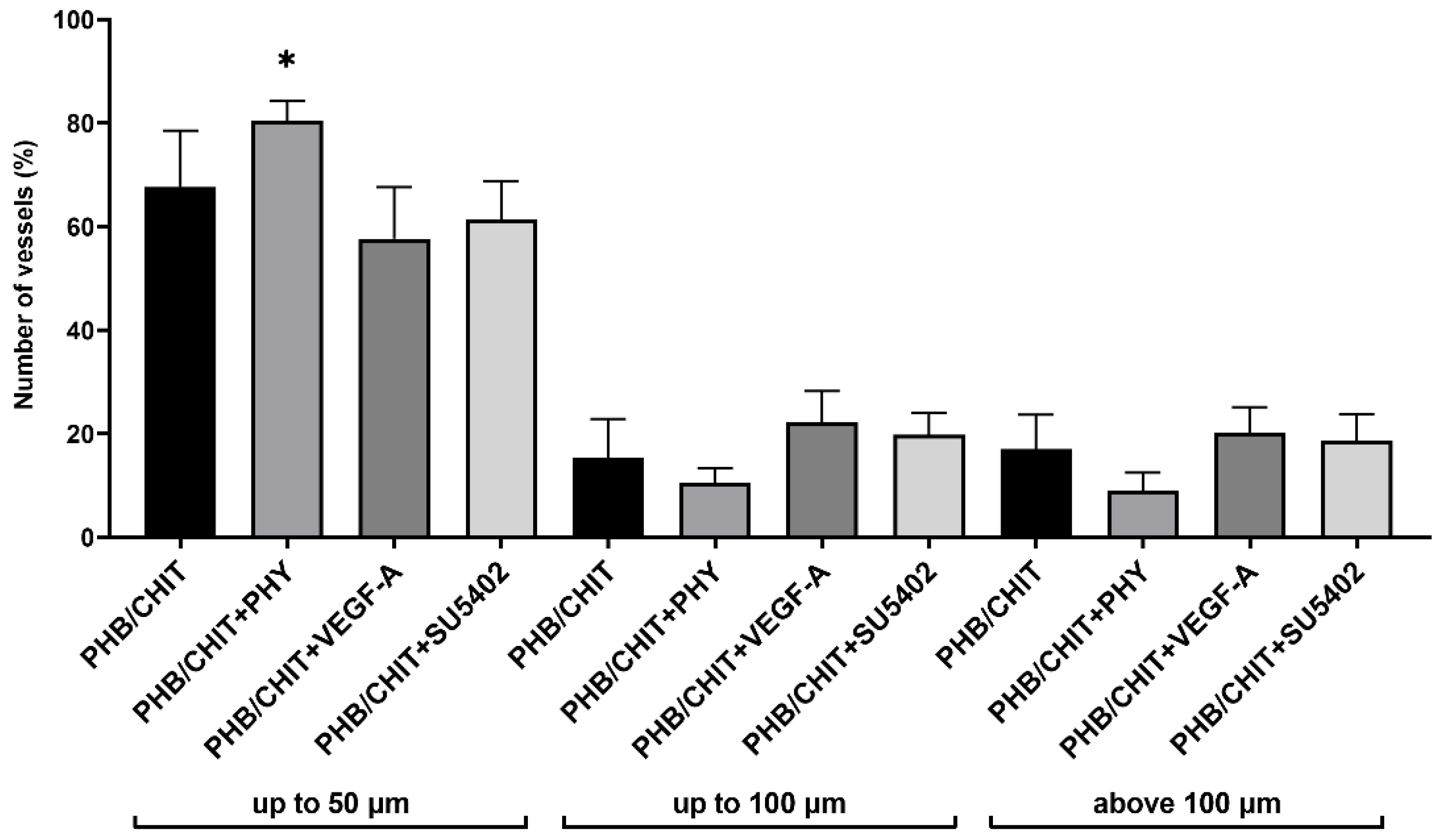
3.2.2. Diameter of Vessels
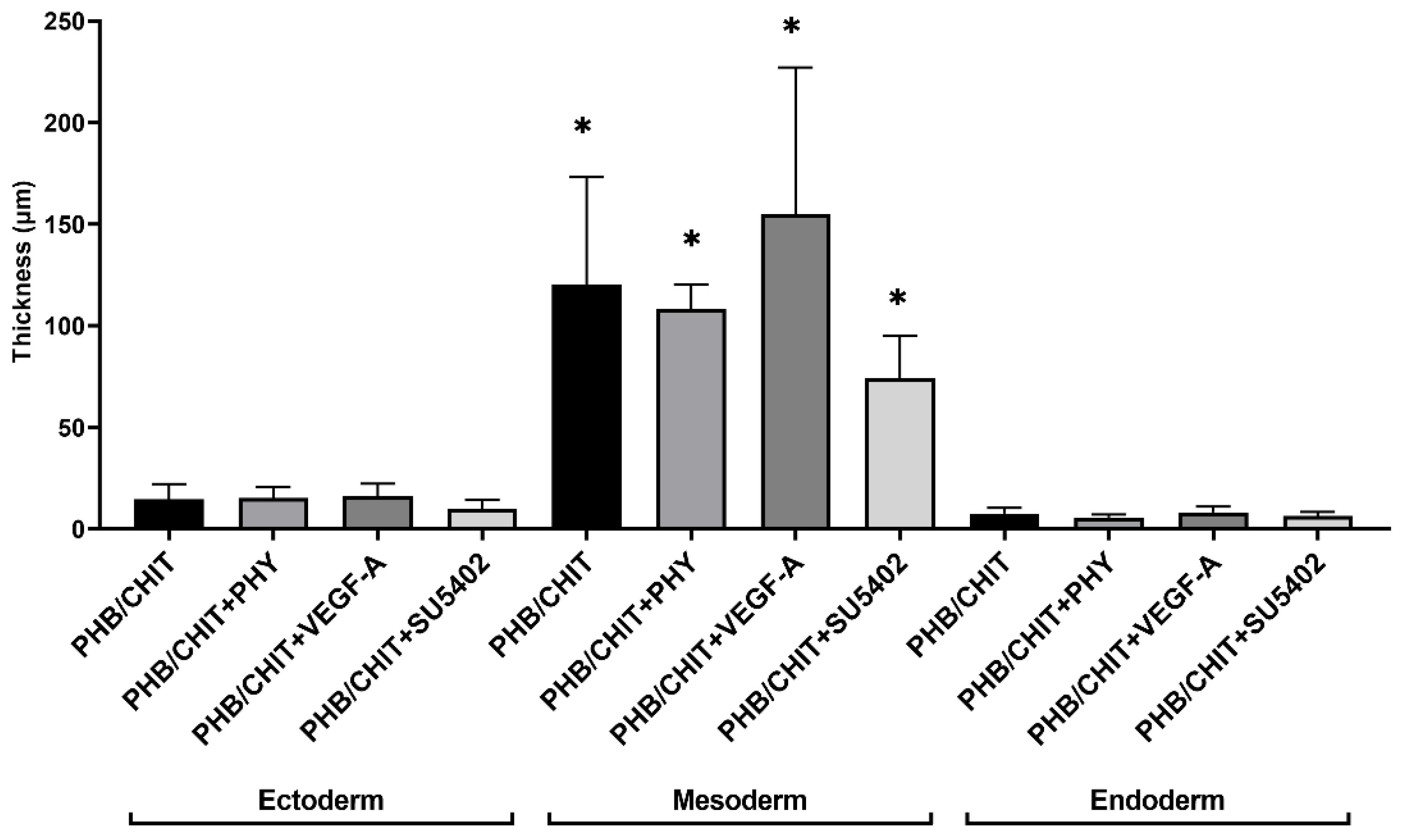
3.2.3. Thickness of the CAM Layers
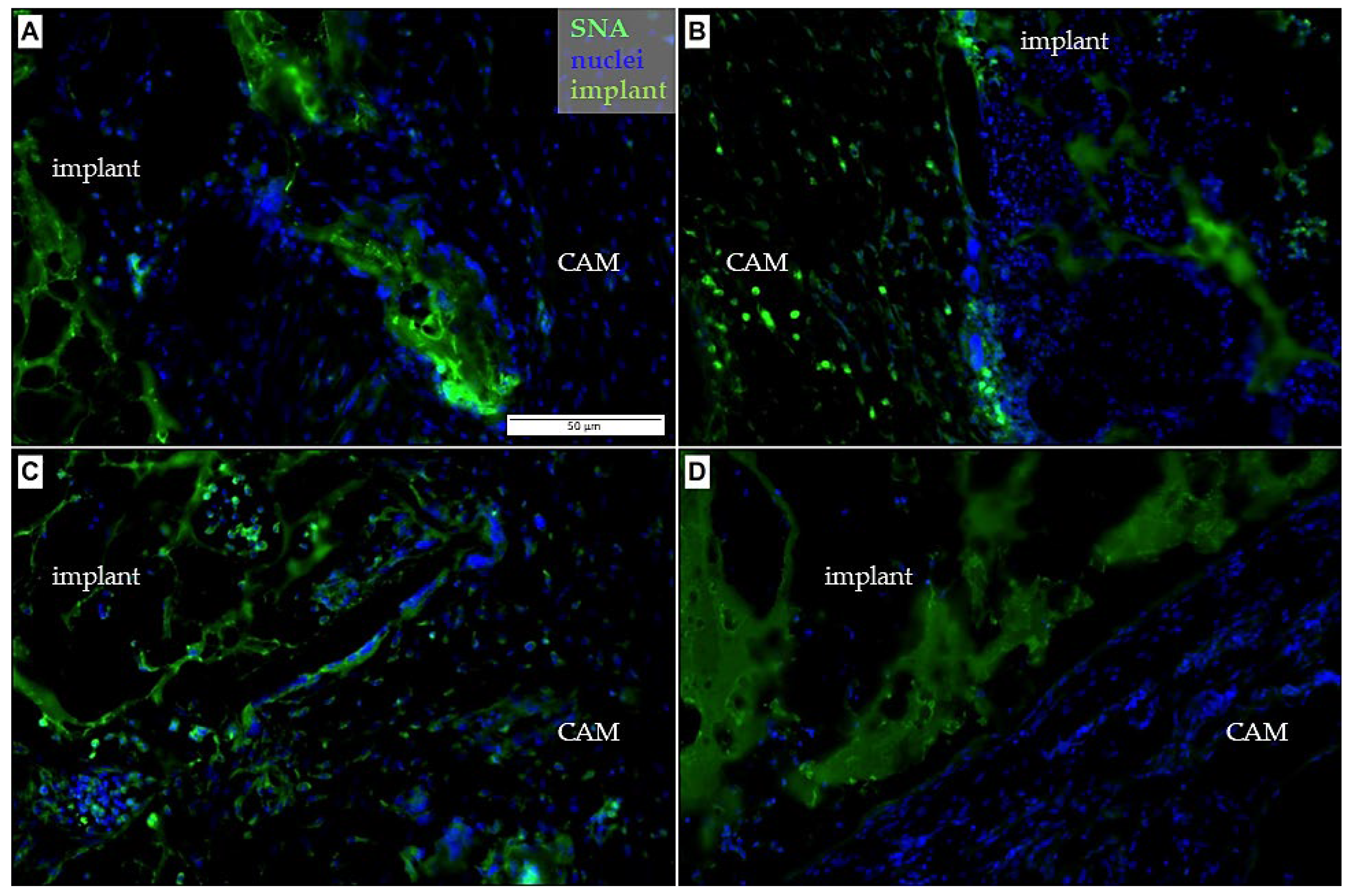
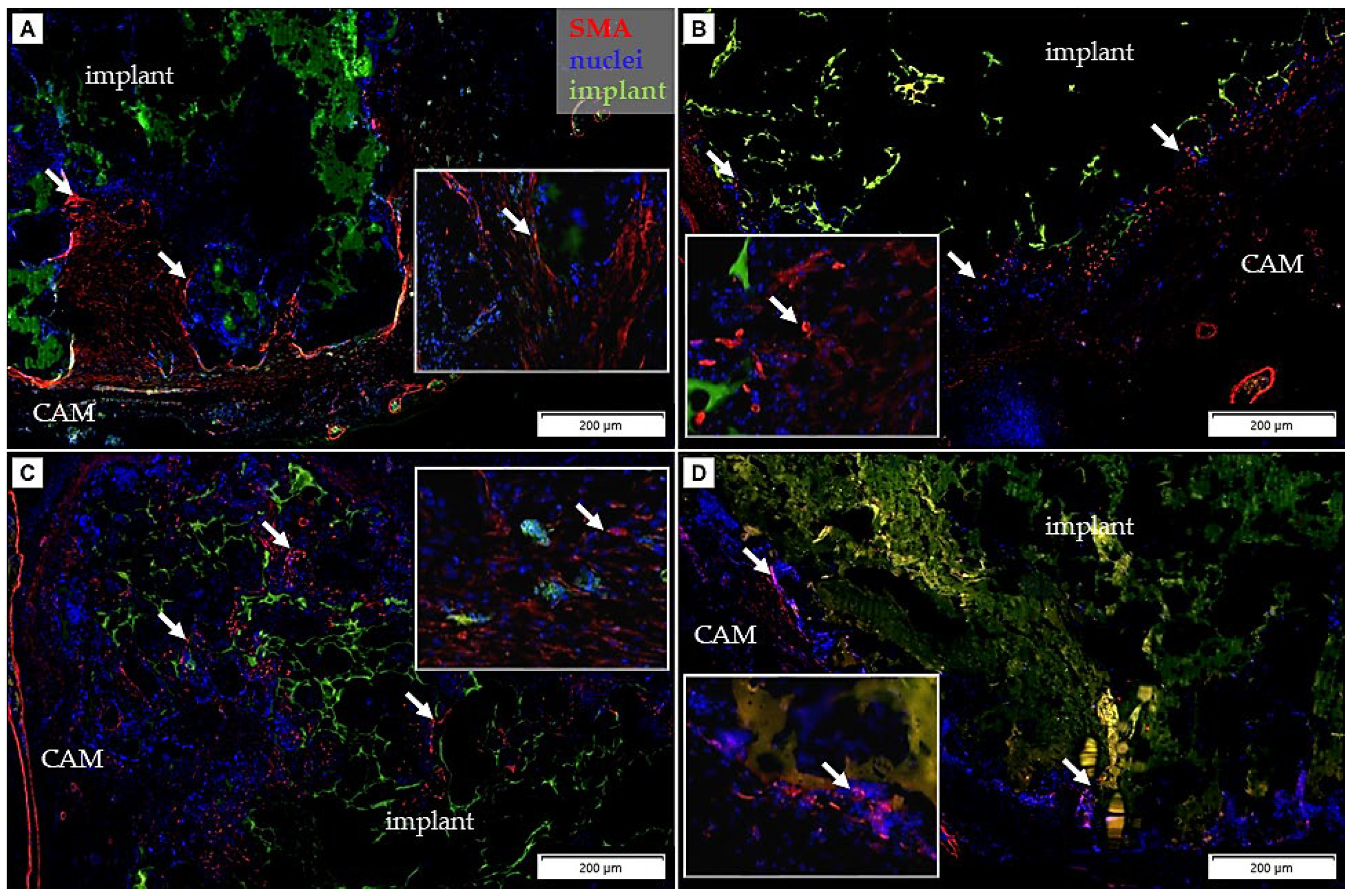
3.3. Immunohistochemical Analysis
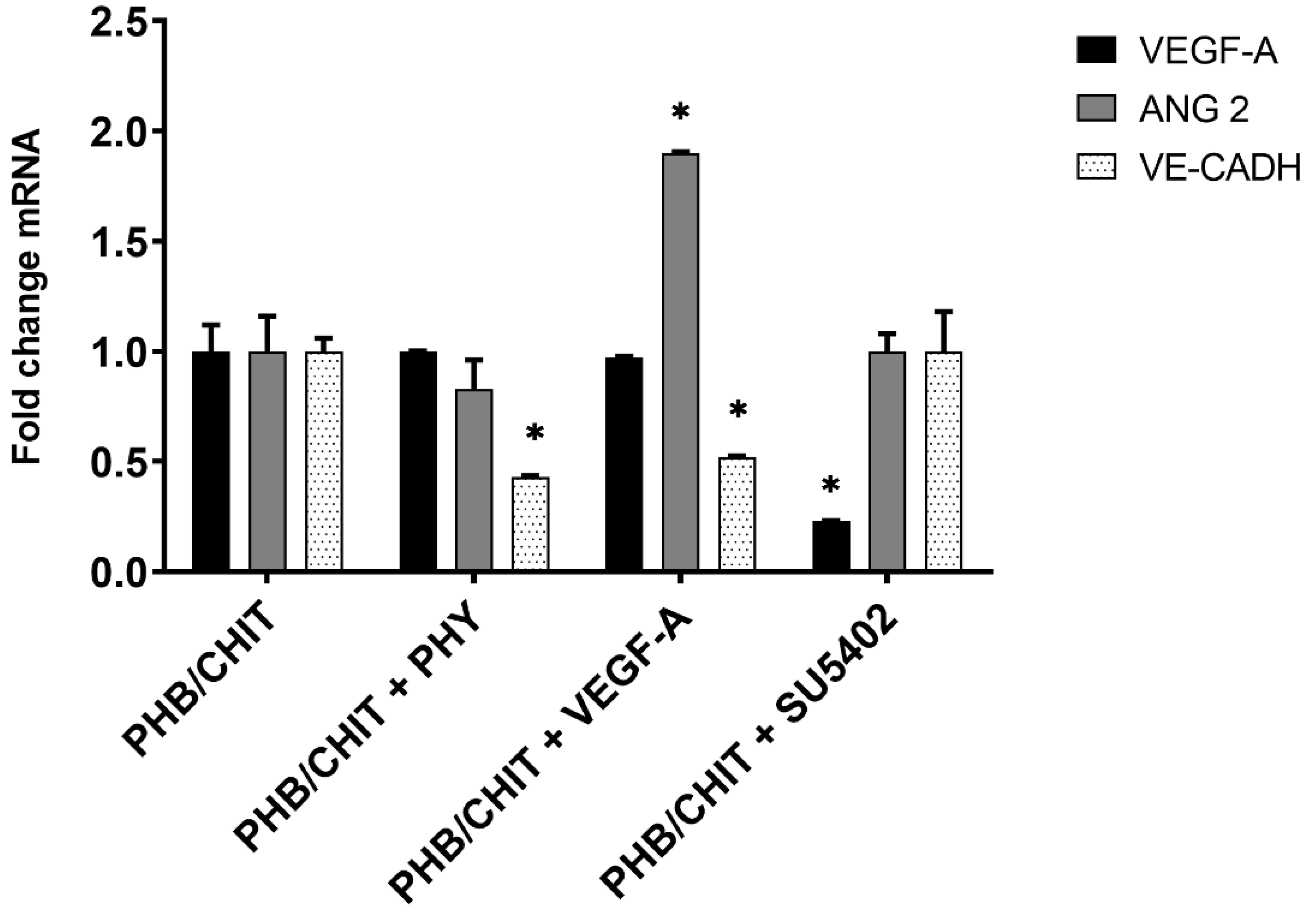
3.4. Gene Expression Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mangir, N.; Dikici, S.; Claeyssens, F.; MacNeil, S. Using ex ovo Chick Chorioallantoic Membrane (CAM) Assay To Evaluate the Biocompatibility and Angiogenic Response to Biomaterials. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 5, 3190–3200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribatti, D.; Annese, T.; Tamma, R. The use of the chick embryo CAM assay in the study of angiogenic activity of biomaterials. Microvasc. Res. 2020, 131, 104026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hinderer, S.; Layland, S.L.; Schenke-Layland, K. ECM and ECM-like materials—Biomaterials for applications in regenerative medicine and cancer therapy. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 97, 260–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ambrosio, L.; Raucci, M.; Vadalà, G.; Ambrosio, L.; Papalia, R.; Denaro, V. Innovative Biomaterials for the Treatment of Bone Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrovova, E.; Giretova, M.; Kvasilova, A.; Benada, O.; Danko, J.; Medvecky, L.; Sedmera, D. Preclinical alternative model for analysis of porous scaffold biocompatibility applicable in bone tissue engineering. Altex 2019, 36, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiran, A.S.K.; Ramakrishna, S. An Introduction to Biomaterials Science and Engineering; World Scientific Publishing: Singapore, 2021; pp. 82–93. [Google Scholar]
- Shahali, Z.; Karbasi, S.; Avadi, M.R.; Semnani, D.; Zargar, E.N.; Hashemibeni, B. Evaluation of structural, mechanical, and cellular behavior of electrospun poly-3-hydroxybutyrate scaffolds loaded with glucosamine sulfate to develop cartilage tissue engineering. Int. J. Polym. Mater. Polym. Biomater. 2017, 66, 589–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrovova, E.; Tomco, M.; Holovska, K.; Danko, J.; Kresakova, L.; Vdoviakova, K.; Simaiova, V.; Kolvek, F.; Hornakova, P.; Toth, T.; et al. PHB/CHIT Scaffold as a Promising Biopolymer in the Treatment of Osteochondral Defects—An Experimental Animal Study. Polymers 2021, 13, 1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhtiari, S.S.E.; Karbasi, S.; Toloue, E.B. Modified poly(3-hydroxybutyrate)-based scaffolds in tissue engineering applications: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 166, 986–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanova, D.G.; Yaneva, Z.L. Antioxidant Properties and Redox-Modulating Activity of Chitosan and Its Derivatives: Biomaterials with Application in Cancer Therapy. BioRes. Open Access 2020, 9, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.-S.; Cho, Y.-S.; Je, J.-Y. Antioxidant and Antibacterial Activities of Chitosan-Phloroglucinol Conjugate. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2013, 16, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, P.J.; Je, J.Y.; Kim, S.K. Free radical scavenging activities of differently deacylated chitosans using an ESR spectrometer. Carbohydr. Polym. 2004, 55, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-H.; Ryu, B.; Je, J.-Y.; Kim, S.-K. Diethylaminoethyl chitosan induces apoptosis in HeLa cells via activation of caspase-3 and p53 expression. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 84, 571–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Victor, R.D.S.; Santos, A.M.D.C.; De Sousa, B.V.; Neves, G.D.A.; Santana, L.N.D.L.; Menezes, R.R. A Review on Chitosan’s Uses as Biomaterial: Tissue Engineering, Drug Delivery Systems and Cancer Treatment. Materials 2020, 13, 4995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Y. Application progress of modified chitosan and its composite biomaterials for bone tissue engineering. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lizardi-Mendoza, J.; Monal, W.M.A.; Valencia, F.M.G. Chemical characteristics and functional properties of chitosan. In Chitosan in the Preservation of Agricultural Commodities; Bautista-Banos, S., Romanazzi, G., Jimenez-Aparicio, A., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 3–31. [Google Scholar]
- Olanipekun, E.O.; Ayodele, O.; Olatunde, O.C.; Olusegun, S.J. Comparative studies of chitosan and carboxymethyl chitosan doped with nickel and copper: Characterization and antibacterial potential. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 183, 1971–1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giretová, M.; Medvecky, L.; Petrovova, E.; Cizkova, D.; Danko, J.; Mudronova, D.; Slovinska, L.; Bures, R. Polyhydroxy-butyrate/Chitosan 3D scaffolds promote in vitro and in vivo chondrogenesis. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2019, 189, 556–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulingam, T.; Appaturi, J.N.; Parumasivam, T.; Ahmad, A.; Sudesh, K. Biomedical Applications of Polyhydroxyalkanoate in Tissue Engineering. Polymers 2022, 14, 2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nowak-Sliwinska, P.; Segura, T.; Iruela-Arispe, M.L. The chicken chorioallantoic membrane model in biology, medicine and bioengineering. Angiogenesis 2014, 17, 779–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chavakis, E.; Dimmer, S. Regulation of endothelial cell survival and apoptosis during angiogenesis. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2002, 22, 887–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, S.M.; Siegman, S.N.; Segura, T. The effect of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) presentation within fibrin matrices on endothelial cell branching. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 7432–7443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmeliet, P.; Jain, R.K. Molecular mechanisms and clinical applications of angiogenesis. Nature 2011, 473, 298–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribatti, D. The chick embryo chorioallantoic membrane as a model for tumor biology. Exp. Cell Res. 2014, 328, 314–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marinaccio, C.; Nico, B.; Ribatti, D. Differential expression of angiogenic and anti-angiogenic molecules in the chick embryo chorioallantoic membrane and selected organs during embryonic development. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 2013, 57, 907–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baiguera, S.; Macchiarini, P.; Ribatti, D. Chorioallantoic membrane for in vivo investigation of tissue-engineered construct biocompatibility. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2012, 100, 1425–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valdes, T.I.; Kreutzer, D.; Moussy, F. The chick chorioallantoic membrane as a novel in vivo model for the testing of bio-materials. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2002, 62, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tay, H.; Du Cheyne, C.; Demeyere, K.; De Craene, J.; De Bels, L.; Meyer, E.; Zijlstra, A.; De Spiegelaere, W. Depletion of Embryonic Macrophages Leads to a Reduction in Angiogenesis in the Ex Ovo Chick Chorioallantoic Membrane Assay. Cells 2020, 10, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Wang, S.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, J.; Du, Y.; Zhang, J.; Van Ongeval, C.H.; Ni, Y.; Li, Y. Utilisation of chick embryo chori-oallantoic membrane as a model platform for imaging-navigated biomedical research. Cells 2021, 10, 463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maina, J.N. Structure and Function of the Shell and the Chorioallantoic Membrane of the Avian Egg: Embryonic Respiration. In The Biology of the Avian Respiratory System; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 219–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maksimov, V.F.; Korostyshevskaya, I.M.; Kurganov, S.A. Functional morphology of chorioallantoic vascular network in chicken. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2006, 142, 367–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makanya, A.N.; Dimova, I.; Koller, T.; Styp-Rekowska, B.; Djonov, V. Dynamics of the Developing Chick Chorioallantoic Membrane Assessed by Stereology, Allometry, Immunohistochemistry and Molecular Analysis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0152821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribatti, D. The chick embryo chorioallantoic membrane (CAM) assay. Reprod. Toxicol. 2017, 70, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwadlo-Klarwasser, G.-C.; Görlitz, K.; Hafemann, B.; Klee, D.; Klosterhalfen, B. The chorioallantoic membrane of the chick embryo as a simple model for the study of the angiogenic and inflammatory response to biomaterials. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2001, 12, 195–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Xie, S.; Zhou, J. Use of animal models for the imaging and quantification of angiogenesis. Exp. Anim. 2018, 67, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, N.H.; Olsson, I.; Olsson, A. Scientists and the 3Rs: Attitudes to animal use in biomedical research and the effect of mandatory training in laboratory animal science. Lab. Anim. 2013, 48, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribatti, D. Chapter 5 Chick Embryo Chorioallantoic Membrane as a Useful Tool to Study Angiogenesis. Int. Rev. Cell Mol. Biol. 2008, 270, 181–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribatti, D. The chick embryo chorioallantoic membrane (CAM). A multifaceted experimental model. Mech. Dev. 2016, 141, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribatti, D.; Tamma, R.; Annese, T. Chorioallantoic membrane vascularization. A meta-analysis. Exp. Cell Res. 2021, 405, 112716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Zhou, X.; Ming, H.; Zhang, J.; Huang, G.; Zhang, Z.; Li, P. Chick Chorioallantoic Membrane Assay: A 3D Animal Model for Study of Human Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0130935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorustovich, A.A.; Vargas, G.E.; Bretcanu, O.; Mesones, R.V.; López, J.M.P.; Boccaccini, A.R. Novel bioassay to evaluate biocompatibility of bioactive glass scaffolds for tissue engineering. Adv. Appl. Ceram. 2008, 107, 274–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomco, M.; Petrovova, E.; Giretova, M.; Almasiova, V.; Holovska, K.; Cigankova, V.; Jenca, A.; Jencova, J.; Boldizar, M.; Balazs, K.; et al. In vitro and in vivo study of microporous ceramics using MC3T3 cells, CAM assay and a pig animal model. Anat. Sci. Int. 2016, 92, 569–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klueh, U.; Dorsky, D.I.; Moussy, F.; Kreutzer, D.L. Ex ova chick chorioallantoic membrane as a novel model for evaluation of tissue responses to biomaterials and implants. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2003, 67, 838–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oates, M.; Chen, R.; Duncan, M.; Hunt, J. The angiogenic potential of three-dimensional open porous synthetic matrix materials. Biomaterials 2007, 28, 3679–3686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samourides, A.; Browning, L.; Hearnden, V.; Chen, B. The effect of porous structure on the cell proliferation, tissue ingrowth and angiogenic properties of poly(glycerol sebacate urethane) scaffolds. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 108, 110384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medvecky, L.; Giretova, M.; Stulajterova, R. Properties and in vitro characterization of polyhydroxybutyrate–chitosan scaffolds prepared by modified precipitation method. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2013, 25, 777–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giretova, M.; Medvecky, L.; Stulajterova, R.; Sopcak, T.; Briancin, J.; Tatarkova, M. Effect of enzymatic degradation of chitosan in polyhydroxabutyrate/chitosan/calcium phosphate composites on in vitro osteoblast response. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2016, 27, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luptakova, L.; Dvorcakova, S.; Demcisakova, Z.; Belbahri, L.; Holovska, K.; Petrovova, E. Dimethyl Sulfoxide: Morphological, Histological, and Molecular View on Developing Chicken Liver. Toxics 2021, 9, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gheorghescu, A.; Thompson, J. Delayed vasculogenesis and impaired angiogenesis due to altered Ang-2 and VE-cadherin levels in the chick embryo model following exposure to cadmium. Pediatr. Surg. Int. 2015, 32, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stock, U.A.; Vacanti, J.P. Tissue Engineering: Current State and Prospects. Annu. Rev. Med. 2001, 52, 443–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klagsbrun, M.; Knighton, D.; Folkman, J. Tumor angiogenesis activity in cells grown in tissue culture. Cancer Res. 1976, 36, 110–114. [Google Scholar]
- Kohli, N.; Sawadkar, P.; Ho, S.; Sharma, V.; Snow, M.; Powell, S.; Woodruff, M.A.; Hook, L.; Garcia-Gareta, E. Pre-screening the intrinsic angiogenic capacity of biomaterials in an optimized ex ovo chorioallantoic membrane model. J. Tissue. Eng. 2020, 11, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosengren, A.; Bjursten, L.M. Pore size in implanted polypropylene filters is critical for tissue organization. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2003, 67A, 918–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnaudeix, A.; Usseglio, J.; Lasgorceix, M.; Lalloue, F.; Damia, C.; Brie, J.; Pascaud-Mathieu, P.; Champion, E. Quantitative analysis of vascular colonization and angio-conduction in porous silicon-substituted hydroxyapatite with various pore shapes in a chick chorioallantoic membrane (CAM) model. Acta. Biomater. 2016, 38, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Tienen, T.G.; Heijkants, R.G.; Buma, P.; de Groot, J.H.; Pennings, A.J.; Veth, R.P. Tissue ingrowth and degradation of two biodegradable porous polymers with different porosities and pore sizes. Biomaterials 2001, 23, 1731–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D´Arcy, P.F.; Howard, E.M. A new anti-inflammatory test, utilizing the chorio-allantoic membrane of the chick embryo. Br. J. Pharmac. Chemother. 1967, 29, 378–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribatti, D.; Nico, B.; Vacca, A.; Presta, M. The gelatin sponge–chorioallantoic membrane assay. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanka, O.; Peumans, W.J.; Van Damme, E.J.; Pfuller, U.; Valasek, P.; Halata, Z.; Schumacher, U.; Grim, M. Lectin histo-chemistry of microvascular endothelium in chick and quail musculature. Anat. Emrbyol. 2001, 204, 407–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jilani, S.M.; Murphy, T.J. Thai, S.N.M.; Eichmann, A.; Alva, J.A.; Iruela-Arispe, M.L. Selective binding of lectins to embryonic chicken vasculature. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2003, 51, 597–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, K.H.; Ryu, J.; Han, K.H. Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1–induced angiogenesis is mediated by vascular endothelial growth factor-A. Blood 2005, 105, 1405–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majd, H.; Scherer, S.S.; Boo, S.; Ramondetti, S.; Cambridge, E.; Raffoul, W.; Friedrich, M.; Pittet, B.; Pioletti, D.; Hinz, B.; et al. Novel micropatterns mechanically control fibrotic reactions at the surface of silicone implants. Biomaterials 2015, 54, 136–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emde, B.; Heinen, A.; Gödecke, A.; Bottermann, K. Wheat germ agglutinin staining as a suitable method for detection and quantification of fibrosis in cardiac tissue after myocardial infarction. Eur. J. Histochem. 2014, 58, 2448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du Chayne, C.H.; Smeets, M.; De Spiegelaere, W. Techniques used to asses intussusceptive angiogenesis: A systematic review. Dev. Dyn. 2021, 250, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Tavakkoli, H.; Attaran, R.; Khosravi, A.; Salari, Z.; Salarkia, E.; Dabiri, S.; Mosallanejad, S.S. Vascular alteration in relation to fosfomycine: In silico and in vivo investigations using a chick embryo model. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 118, 109240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizzi, A.; Benagiano, V.; Ribatti, D. Angiogenesis versus arteriogenesis. Rom. J. Morphol. Embryol. 2017, 58, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tufan, A.C.; Tufan, N.L.S. The Chick Embryo Chorioallantoic Membrane as a Model System for the Study of Tumor Angiogenesis, Invasion and Development of Anti-Angiogenic Agents. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2005, 5, 249–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talavera-Adame, D.; Xiong, Y.; Zhao, T.; Arias, A.E.; Sierra-Honigmann, M.R.; Farkas, D.L. Quantitative and morphometric evaluation of the angiogenic effects of leptin. J. Biomed. Opt. 2008, 13, 064017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zijlstra, A.; Lewis, J.D. Visualization and quantification of de novo angiogenesis in ex ovo chicken embryos. In The Textbook of Angiogenesis and Lymphangiogenesis: Methods and Application; Zudaire, E., Cuttitta, F., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 217–240. [Google Scholar]
- Ferra, N. Role of vascular endothelial growth factor in the regulation of angiogenesis. Kidney Int. 1999, 56, 794–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, P.F.; McClain, J.; Robinson, D.M.; Sato, T.N.; Yancopoulos, G.D. Identification and characterization of chicken cDNAs encoding the endothelial cell-specific receptor tyrosine kinase Tie2 and its ligands, the angiopoietins. Angiogenesis 1998, 2, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buríková, M.; Bilčík, B.; Máčajová, M.; Výboh, P.; Bizik, J.; Mateašík, A.; Čavarga, I.; Miškovský, P. Hypericin fluorescence kinetics in the presence of low density lipoproteins: Study on quail CAM assay for topical delivery. Gen. Physiol. Biophys. 2016, 35, 459–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
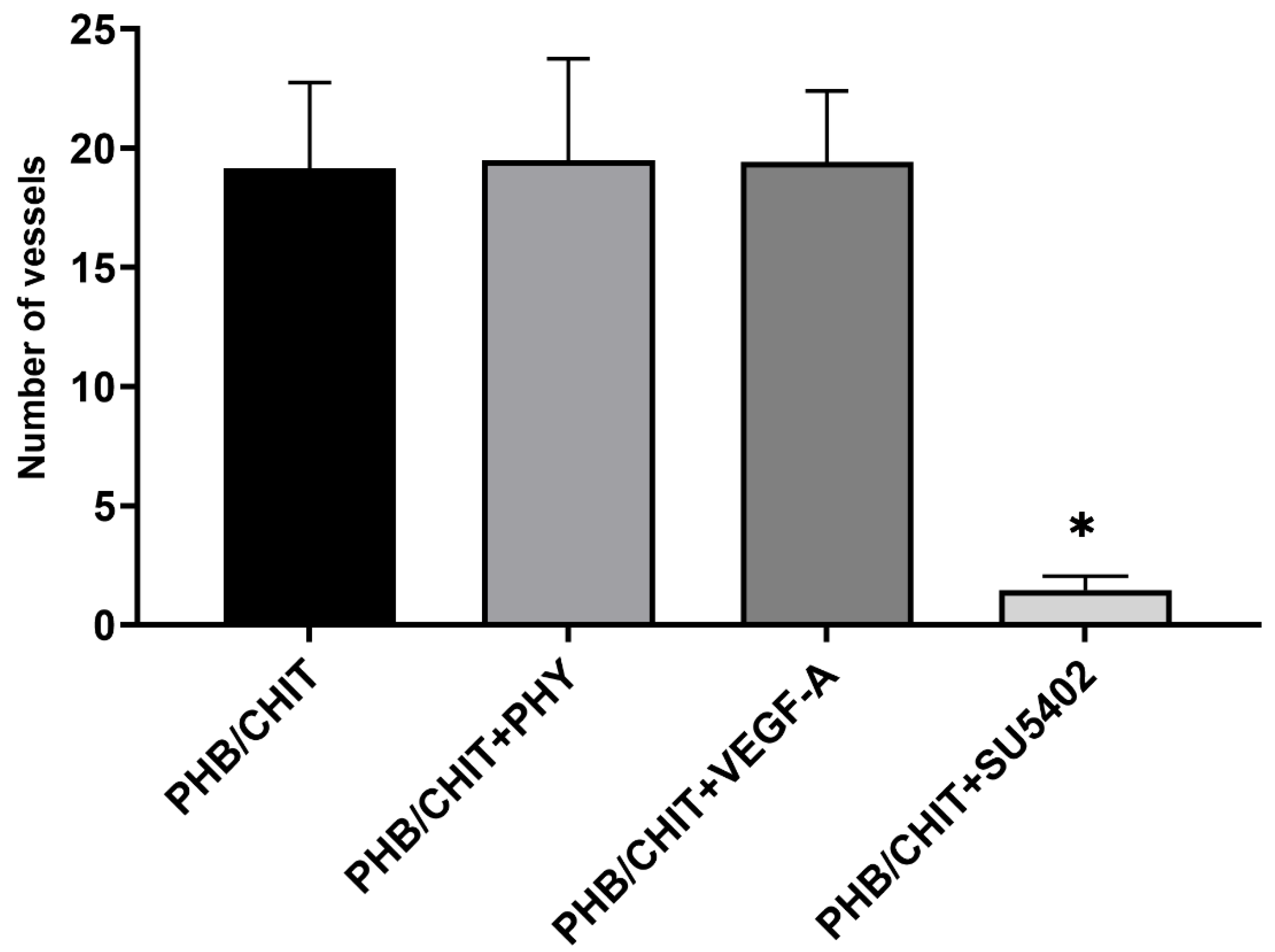
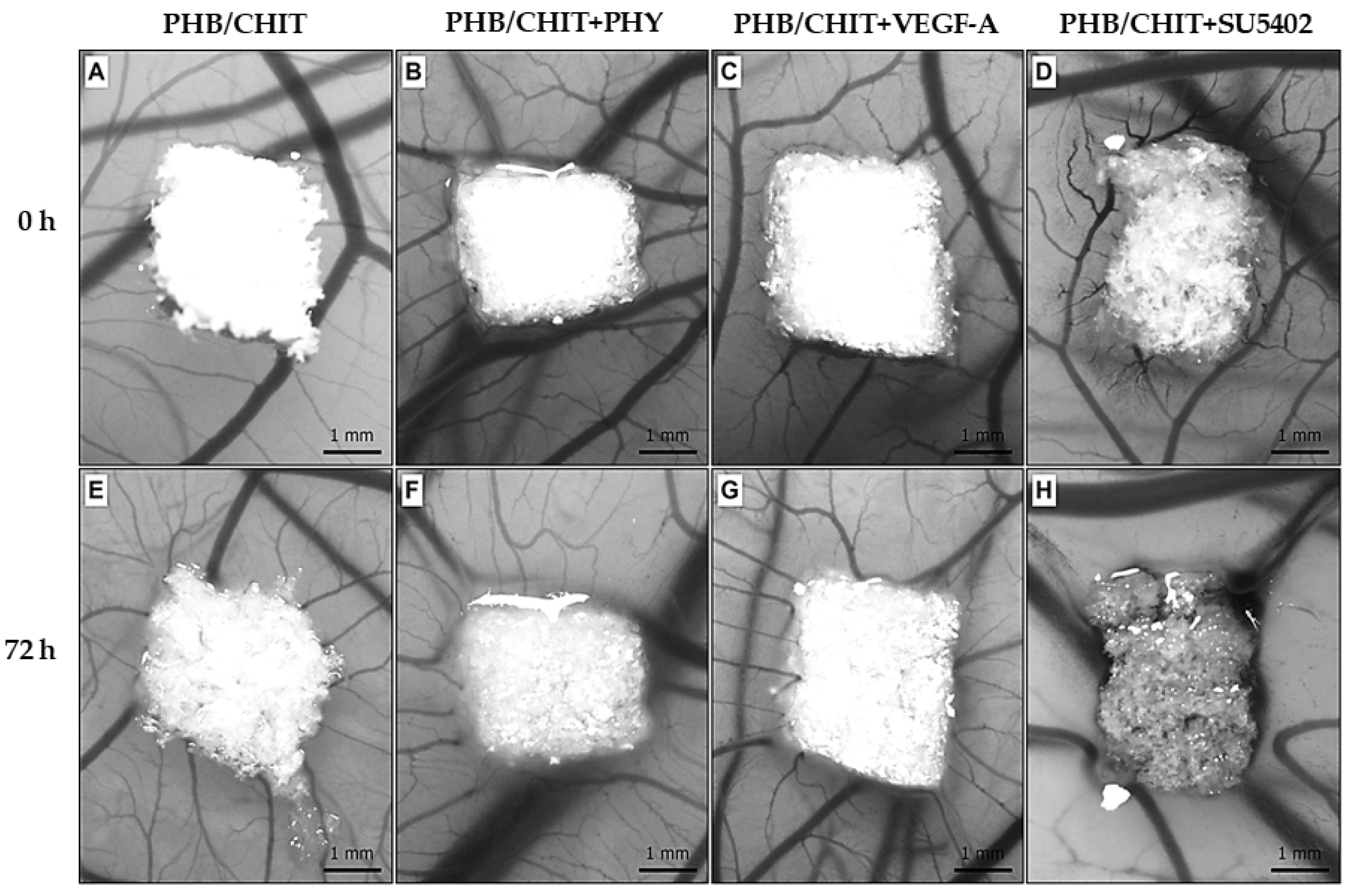


| Treated Material | Total Samples | Vascular Index |
|---|---|---|
| PHB/CHIT | 25 | 19.16 ± 3.59 |
| PHB/CHIT+PHY | 20 | 19.50 ± 4.25 |
| PHB/CHIT+VEGF-A | 24 | 19.42 ± 2.98 |
| PHB/CHIT+SU5402 | 24 | 1.46 ± 0.59 |
| Treated Material | Number of Vessels |
|---|---|
| PHB/CHIT | 42.72 ± 7.18 |
| PHB/CHIT+PHY | 33.22 ± 1.11 |
| PHB/CHIT+VEGF-A | 31.44 ± 5.07 |
| PHB/CHIT+SU5402 | 13.28 ± 0.89 |
| Treated Material | Diameter of the Vessels up to 50 µm | Diameter of the Vessels up to 100 µm | Diameter of the Vessels above 100 µm |
|---|---|---|---|
| PHB/CHIT | 67.68 ± 10.83 | 15.34 ± 7.49 | 16.98 ± 6.67 |
| PHB/CHIT+PHY | 80.45 ± 3.78 | 10.48 ± 2.87 | 9.07 ± 3.39 |
| PHB/CHIT+VEGF-A | 57.66 ± 9.93 | 22.21 ± 6.02 | 20.13 ± 4.97 |
| PHB/CHIT+SU5402 | 61.45 ± 7.28 | 19.83 ± 4.12 | 18.73 ± 4.99 |
| Treated Material | Ectoderm | Mesoderm | Endoderm |
|---|---|---|---|
| PHB/CHIT | 14.62 ± 7.49 | 120.22 ± 52.81 | 7.51 ± 2.86 |
| PHB/CHIT+PHY | 15.26 ± 5.28 | 108.06 ± 12.24 | 5.61 ± 1.50 |
| PHB/CHIT+VEGF-A | 16.27 ± 6.00 | 154.96 ± 72.11 | 8.20 ± 2.77 |
| PHB/CHIT+SU5402 | 9.91 ± 4.33 | 74.33 ± 20.61 | 6.41 ± 1.99 |
| Genes (Fold Change) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Treated Biomaterial | VEGF-A | ANG-2 | VE-CADH |
| PHB/CHIT (control) | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| PHB/CHIT+PHY | 1.00 | 0.83 | 0.43 * |
| PHB/CHIT+VEGF-A | 0.97 | 1.90 * | 0.52 * |
| PHB/CHIT+SU5402 | 0.23 * | 1.00 | 1.00 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Demcisakova, Z.; Luptakova, L.; Tirpakova, Z.; Kvasilova, A.; Medvecky, L.; De Spiegelaere, W.; Petrovova, E. Evaluation of Angiogenesis in an Acellular Porous Biomaterial Based on Polyhydroxybutyrate and Chitosan Using the Chicken Ex Ovo Chorioallantoic Membrane Model. Cancers 2022, 14, 4194. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14174194
Demcisakova Z, Luptakova L, Tirpakova Z, Kvasilova A, Medvecky L, De Spiegelaere W, Petrovova E. Evaluation of Angiogenesis in an Acellular Porous Biomaterial Based on Polyhydroxybutyrate and Chitosan Using the Chicken Ex Ovo Chorioallantoic Membrane Model. Cancers. 2022; 14(17):4194. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14174194
Chicago/Turabian StyleDemcisakova, Zuzana, Lenka Luptakova, Zuzana Tirpakova, Alena Kvasilova, Lubomir Medvecky, Ward De Spiegelaere, and Eva Petrovova. 2022. "Evaluation of Angiogenesis in an Acellular Porous Biomaterial Based on Polyhydroxybutyrate and Chitosan Using the Chicken Ex Ovo Chorioallantoic Membrane Model" Cancers 14, no. 17: 4194. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14174194
APA StyleDemcisakova, Z., Luptakova, L., Tirpakova, Z., Kvasilova, A., Medvecky, L., De Spiegelaere, W., & Petrovova, E. (2022). Evaluation of Angiogenesis in an Acellular Porous Biomaterial Based on Polyhydroxybutyrate and Chitosan Using the Chicken Ex Ovo Chorioallantoic Membrane Model. Cancers, 14(17), 4194. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14174194





