Hsa_circ_0044301 Regulates Gastric Cancer Cell’s Proliferation, Migration, and Invasion by Modulating the Hsa-miR-188-5p/DAXX Axis and MAPK Pathway
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Background
2. Methods
2.1. Tissues
2.2. Cells
2.3. Quantitative Reverse Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction (qRT-PCR)
2.4. Sanger Sequencing
2.5. Vector Construction and Cell Transfection
2.6. RNA Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization (FISH)
2.7. Actinomycin D
2.8. RNase R Assay
2.9. Cell Counting Kit-8 Proliferation Assay (CCK-8)
2.10. Transwell Assays
2.11. Wound Healing Assay
2.12. Microarray Analysis and ceRNA Network Analysis
2.13. Western Blotting (WB)
2.14. Dual Luciferase Reporter Assay
2.15. RNA Immunoprecipitation (RIP) Assay
2.16. Immunofluorescence (IF) Assay
2.17. Immunohistochemical Staining (IHC)
2.18. Mouse Tumorigenesis Model
2.19. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
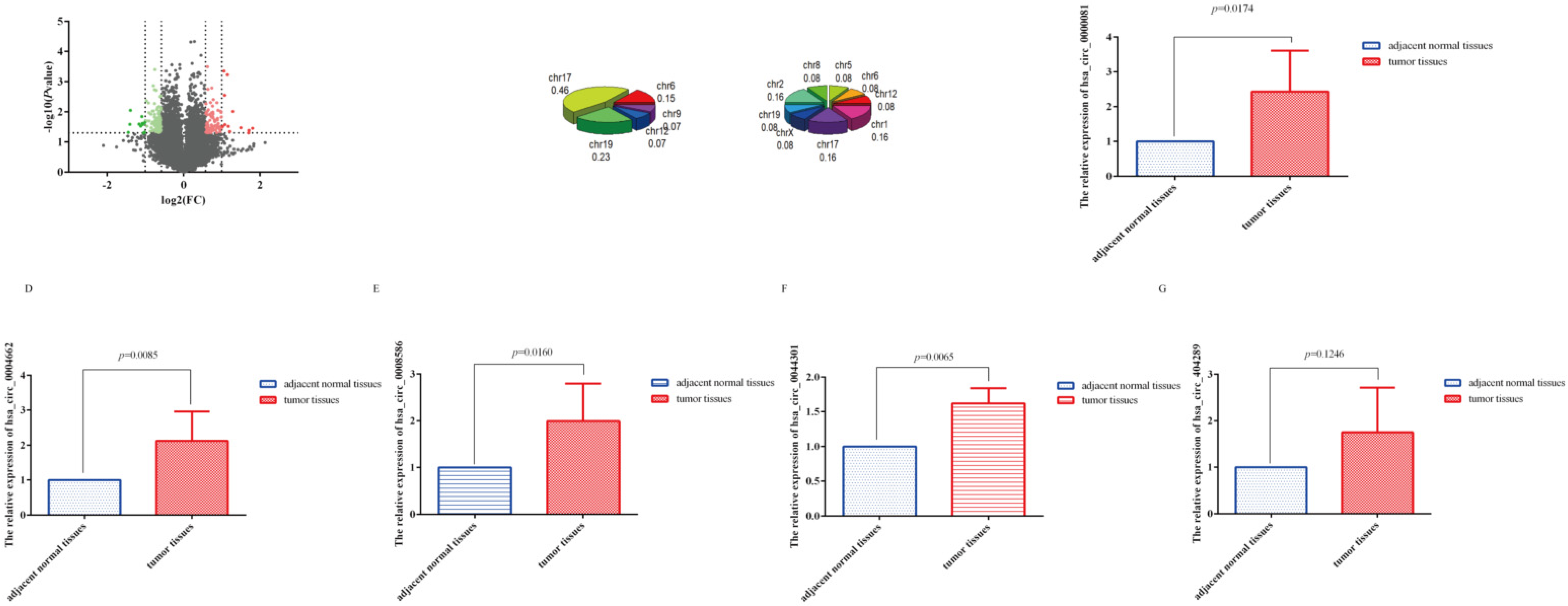
3.1. CircRNA Microarray Results
3.2. SDE-circRNA Were Shared between Our Results and GSE89143
3.3. CeRNA Network, GO, and KEGG Analyses of Shared circRNA
3.4. Correlation between circRNA-0044301 and Clinicopathological Indicators in Patients
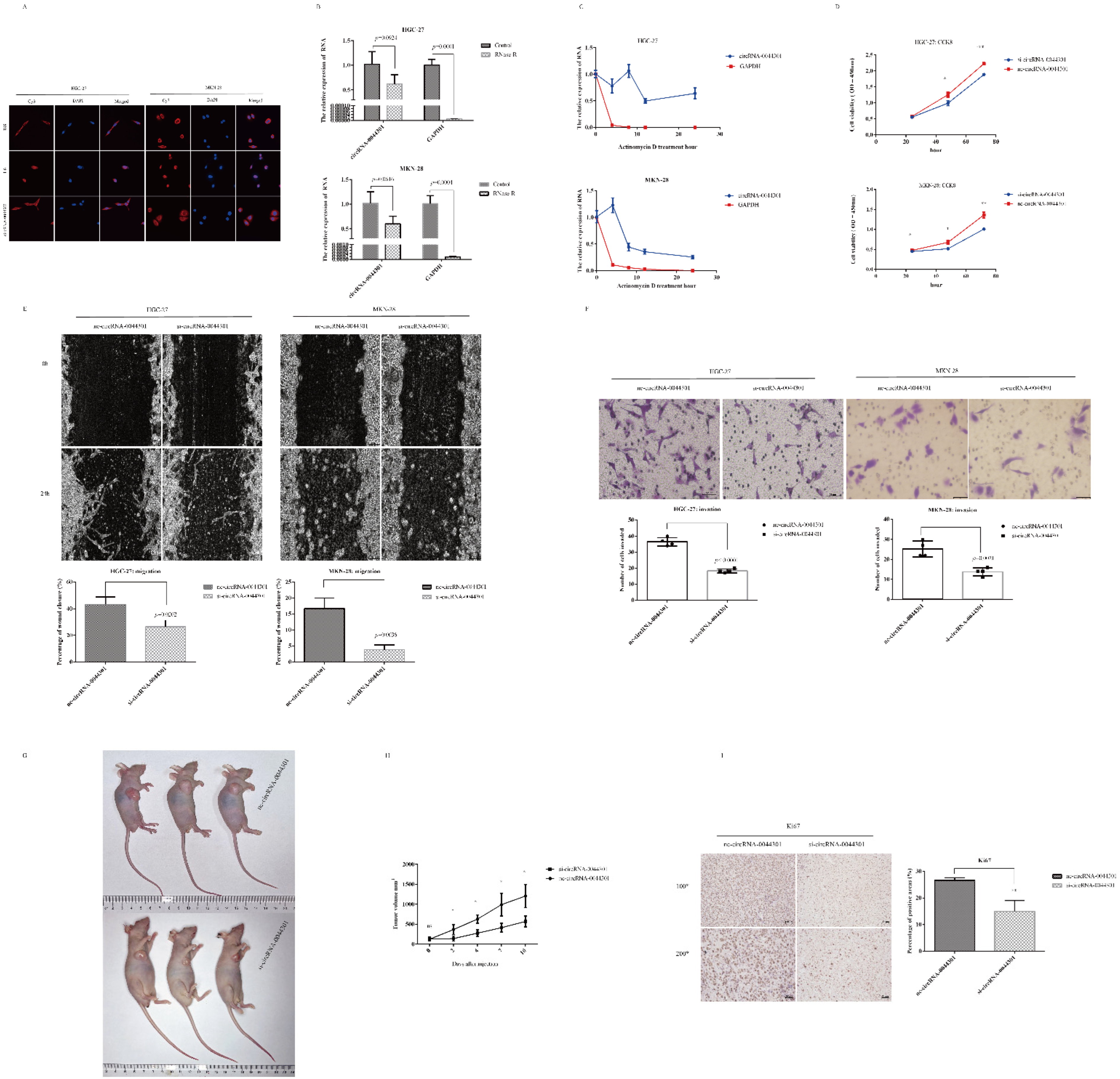
3.5. CircRNA-0044301 Influences the Function of GC Cells In Vitro and In Vivo
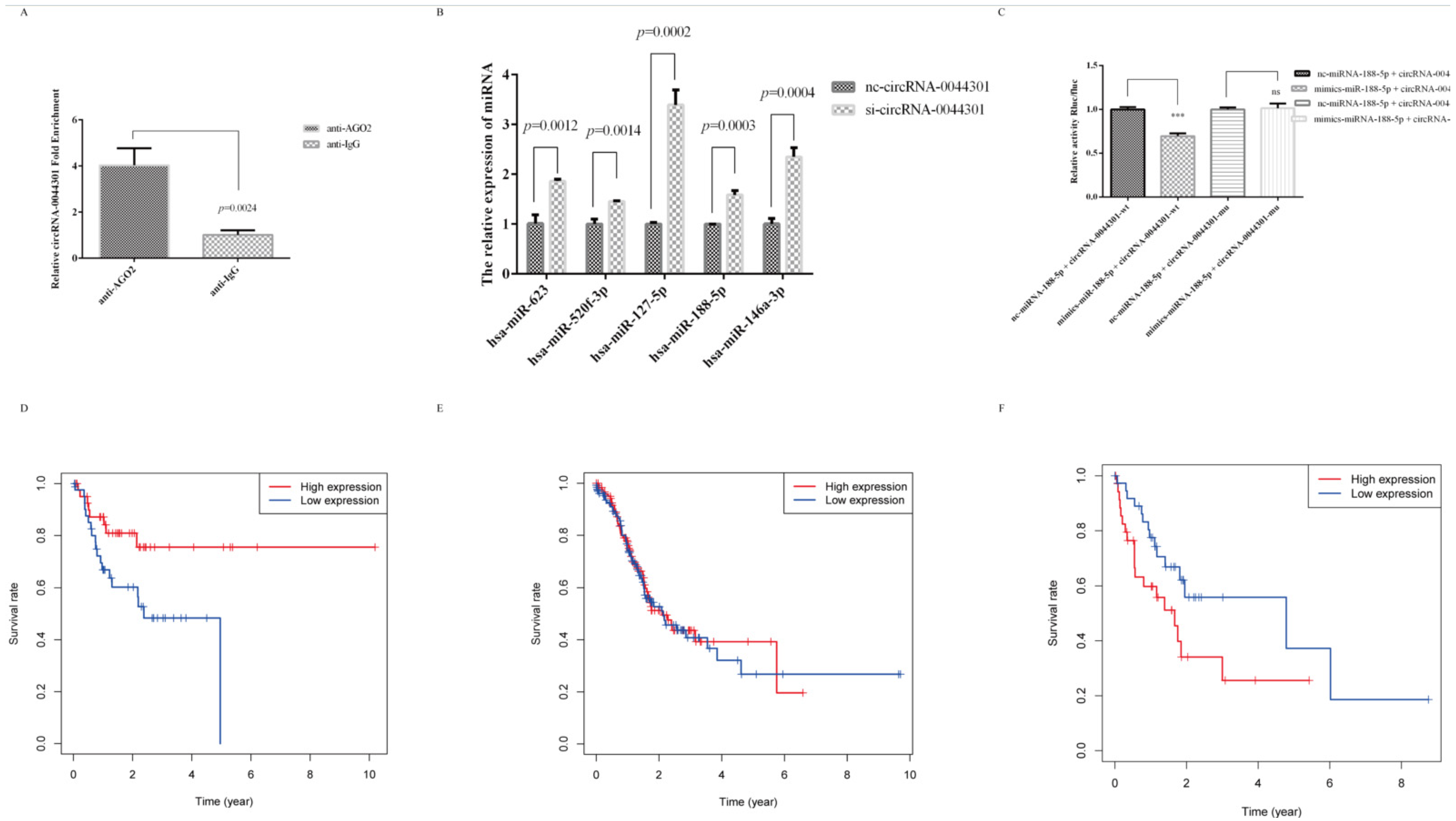
3.6. MiRNA-188-5p Was Sponged by circRNA-0044301 and Was Associated with GC Patients’ Prognosis
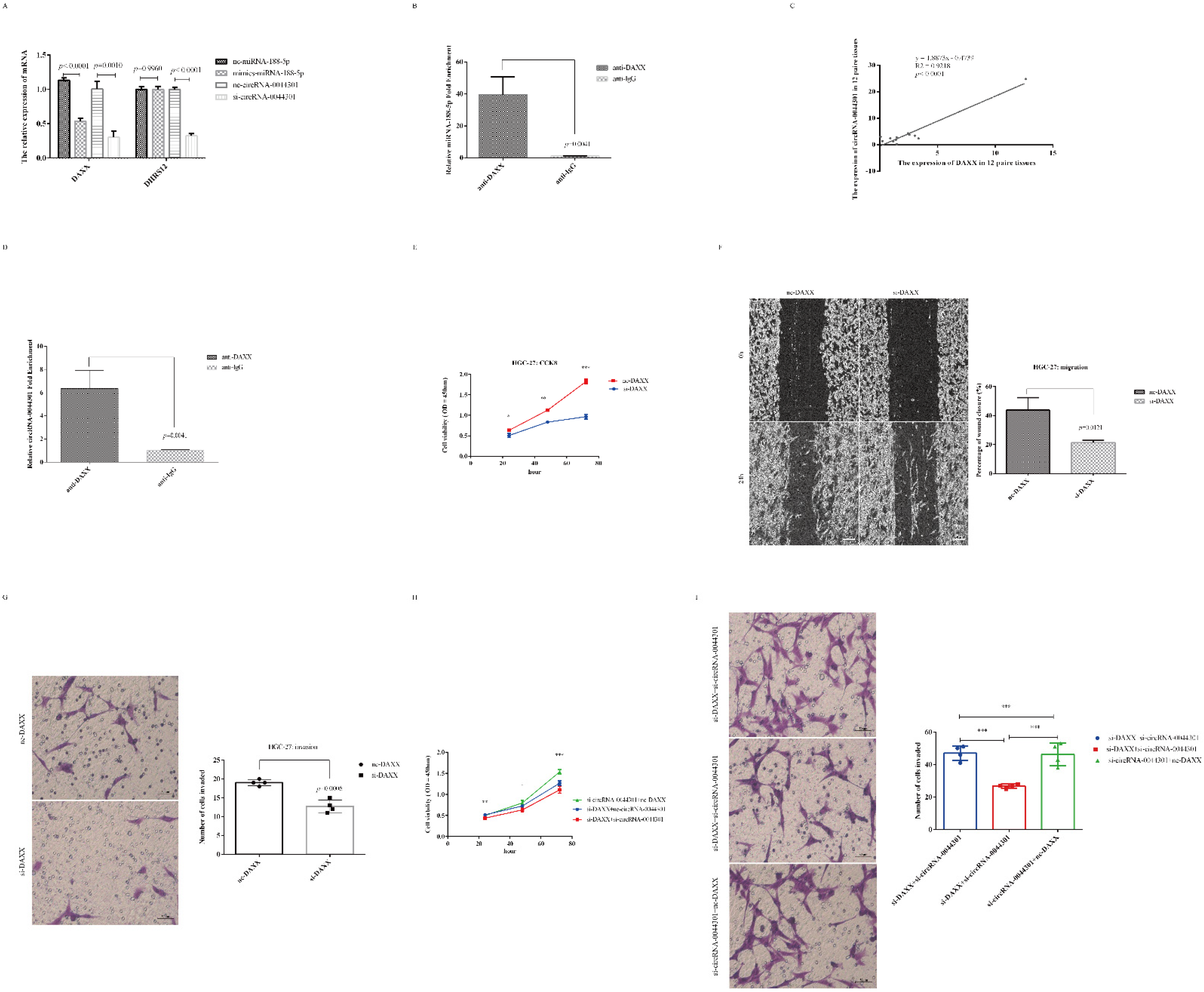
3.7. CircRNA-0044301 Participated in the Progression of GC via Regulating the miRNA-188-5p/DAXX Axis
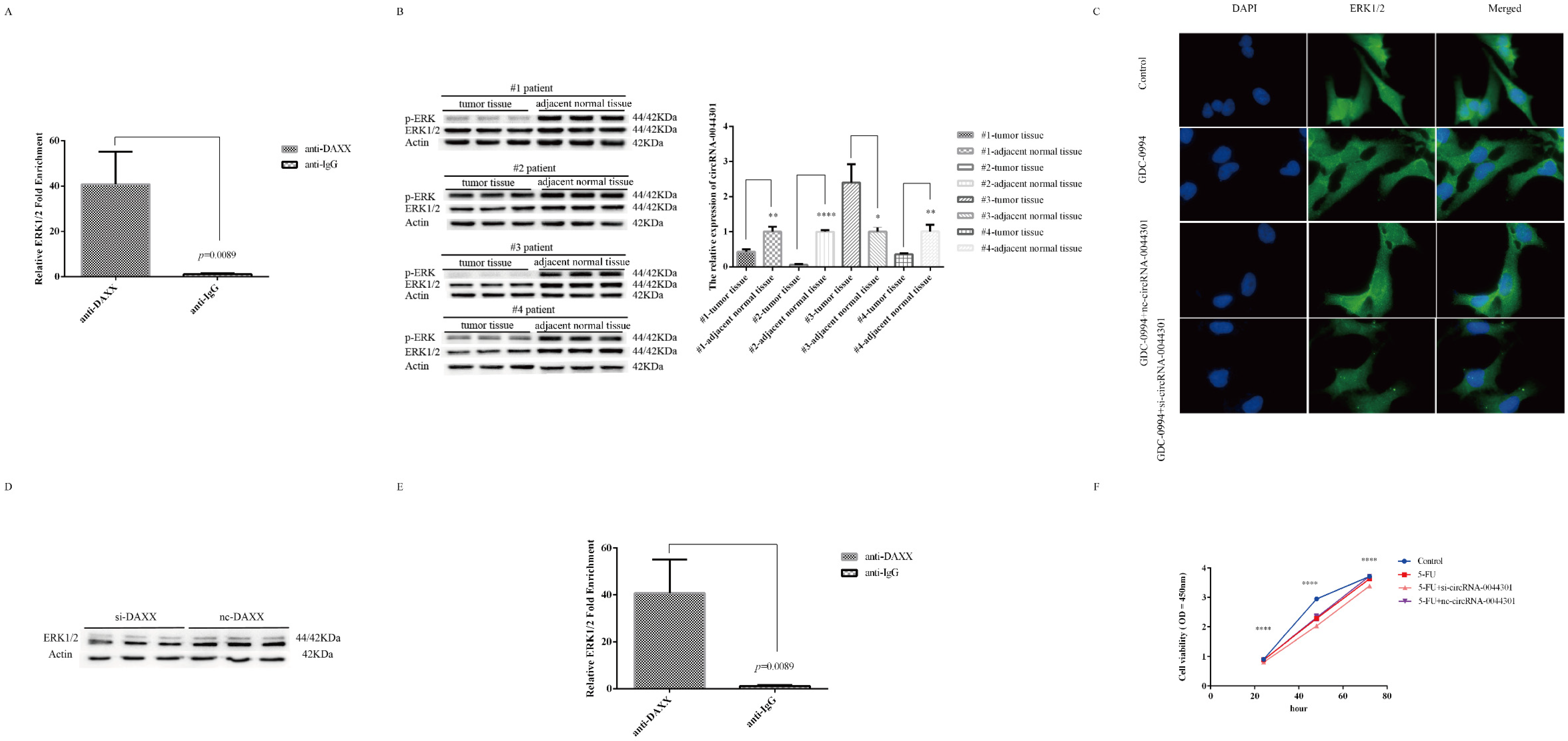
3.8. Knockdown of circRNA-0044301 Inhibited ERK1/2 Expression and Enhanced the Sensitivity of Cells to 5-FU
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| GC | gastric cancer |
| circRNA | circular RNA |
| miRNA | microRNA |
| qRT-PCR | quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction |
| 5-FU | 5-fluorouracil |
References
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torre, L.A.; Bray, F.; Siegel, R.L.; Ferlay, J.; Lortet-Tieulent, J.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2015, 65, 87–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrero, R.; Park, J.Y.; Forman, D. The fight against gastric cancer—The IARC Working Group report. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2014, 28, 1107–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferlay, J.; Steliarova-Foucher, E.; Lortet-Tieulent, J.; Rosso, S.; Coebergh, J.W.W.; Comber, H.; Forman, D.; Bray, F. Cancer incidence and mortality patterns in Europe: Estimates for 40 countries in 2012. Eur. J. Cancer 2013, 49, 1374–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkin, D.M. The global health burden of infection-associated cancers in the year 2002. Int. J. Cancer 2006, 118, 3030–3044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Necula, L.; Matei, L.; Dragu, D.; Neagu, A.I.; Mambet, C.; Nedeianu, S.; Bleotu, C.; Diaconu, C.C.; Chivu-Economescu, M. Recent advances in gastric cancer early diagnosis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 25, 2029–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Wang, Q.; Wang, W.; Wang, G.; Li, X.; Li, G.; Chen, J. A clinical analysis of systemic chemotherapy combined with radiotherapy for advanced gastric cancer. Medicine 2018, 97, e10786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salzman, J.; Gawad, C.; Wang, P.L.; Lacayo, N.; Brown, P.O. Circular RNAs are the predominant transcript isoform from hundreds of human genes in diverse cell types. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e30733. [Google Scholar]
- Rybak-Wolf, A.; Stottmeister, C.; Glažar, P.; Jens, M.; Pino, N.; Giusti, S.; Hanan, M.; Behm, M.; Bartok, O.; Ashwal-Fluss, R.; et al. Circular RNAs in the Mammalian Brain Are Highly Abundant, Conserved, and Dynamically Expressed. Mol. Cell 2015, 58, 870–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeck, W.R.; Sorrentino, J.A.; Wang, K.; Slevin, M.K.; Burd, C.E.; Liu, J.; Marzluff, W.F.; Sharpless, N.E. Circular RNAs are abundant, conserved, and associated with ALU repeats. RNA 2013, 19, 141–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.L.; Yang, L. Regulation of circRNA biogenesis. RNA Biol. 2015, 4, 381–388. [Google Scholar]
- Sanger, H.L.; Klotz, G.; Riesner, D.; Gross, H.J.; Kleinschmidt, A.K. Viroids are single-stranded covalently closed circular RNA molecules existing as highly base-paired rod-like structures. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1976, 73, 3852–3856. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Han, B.; Chao, J.; Yao, H. Circular RNA and its mechanisms in disease: From the bench to the clinic. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 187, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Han, P.; Zhou, T.; Guo, X.; Song, X.; Li, Y. circRNADb: A comprehensive database for human circular RNAs with protein-coding annotations. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 34985. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chu, Q.; Bai, P.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, X.; Mao, L.; Zhu, Q.; Fan, L.; Ye, C. Characteristics of plant circular RNAs. Brief. Bioinform. 2020, 21, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Ma, J.; Sun, T.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, W.; Wang, G.; Wu, P.; Wang, H.; Jiang, L.; et al. Exosomal circRNA: Biogenesis, effect and application in human diseases. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 116. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.; Chen, Z.; Song, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Dou, G.; Shen, X.; Zhou, Y.; Jiang, H.; Li, J.; Peng, Y. CircRNA_0005075 suppresses carcinogenesis via regulating miR-431/p53/epithelial-mesenchymal transition axis in gastric cancer. Cell Biochem. Funct. 2020, 38, 932–942. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Li, Y.; Zheng, Q.; Bao, C.; He, J.; Chen, B.; Lyu, D.; Zheng, B.; Xu, Y.; Long, Z.; et al. Circular RNA profile identifies circPVT1 as a proliferative factor and prognostic marker in gastric cancer. Cancer Lett. 2017, 388, 208–219. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, H.; Hou, L.; Wang, G.; Zhang, R.; Huang, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhu, J. Circular RNA_LARP4 inhibits cell proliferation and invasion of gastric cancer by sponging miR-424-5p and regulating LATS1 expression. Mol. Cancer 2017, 16, 151. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, F.; Hu, X.; Cao, H.; Shen, X. Hsa_circ_0000081 promotes the function of gastric cancer through sponging hsa-miR-423-5p to influence 3-phosphoinositide-dependent kinase 1 expression. Bioengineered 2022, 13, 8277–8290. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, C.; Ma, M.; Zhang, Y.; Li, L.; Long, F.; Xie, C.; Xiao, H.; Liu, T.; Tian, B.; Yang, K.; et al. The N6-methyladenosine modification of circALG1 promotes the metastasis of colorectal cancer mediated by the miR-342-5p/PGF signalling pathway. Mol. Cancer 2022, 21, 80. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pervouchine, D.D. Circular exonic RNAs: When RNA structure meets topology. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Gene Regul. Mech. 2019, 1862, 194384. [Google Scholar]
- Achyutuni, S.; Nadhan, R.; Sengodan, S.K.; Srinivas, P. The prodigious network of chromosome 17 miRNAs regulating cancer genes that influence the hallmarks of cancer. Semin. Oncol. 2017, 44, 254–264. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- López-Ochoa, S.; Ramírez-García, M.; Castro-Sierra, E.; Arenas-Huertero, F. Analysis of Chromosome 17 miRNAs and Their Importance in Medulloblastomas. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 717509. [Google Scholar]
- Koudelakova, V.; Trojanec, R.; Vrbkova, J.; Donevska, S.; Bouchalova, K.; Kolar, Z.; Varanasi, L.; Hajduch, M. Frequency of chromosome 17 polysomy in relation to CEP17 copy number in a large breast cancer cohort. Genes Chromosom. Cancer 2016, 55, 409–417. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Liang, G.; Yang, S.; Sui, J.; Wu, W.; Xu, S.; Ye, Y.; Shen, B.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y. LncRNA-LOC101928316 contributes to gastric cancer progression through regulating PI3K-Akt-mTOR signaling pathway. Cancer Med. 2019, 8, 4428–4440. [Google Scholar]
- Walczak, H. TNF and ubiquitin at the crossroads of gene activation, cell death, inflammation, and cancer. Immunol Rev. 2011, 244, 9–28. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Miao, L.; Xin, X.; Zhang, J.; Yang, S.; Miao, M.; Kong, X.; Jiao, B. Underexpressed CNDP2 participates in gastric cancer growth inhibition through activating the MAPK signaling pathway. Mol. Med. 2014, 20, 17–28. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, H.; Gao, F.; Liang, H.; Lv, Y.; Li, M.; Yao, L.; Zhang, J.; Dou, G.; Wang, Y. MicroRNA-188-5p regulates contribution of bone marrow-derived cells to choroidal neovascularization development by targeting MMP-2/13. Exp. Eye Res. 2018, 175, 115–123. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, K.; Kim, H.; An, K.; Kwon, O.; Park, S.; Cha, J.H.; Kim, M.; Lee, Y.; Kim, J.; Cho, K.; et al. Replenishment of microRNA-188-5p restores the synaptic and cognitive deficits in 5XFAD Mouse Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 34433. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, F.; Chang, R.M.; Yu, L.; Lei, X.; Xiao, S.; Yang, H.; Yang, L.Y. MicroRNA-188-5p suppresses tumor cell proliferation and metastasis by directly targeting FGF5 in hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2015, 63, 874–885. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cheng, N.; Wu, J.; Yin, M.; Xu, J.; Wang, Y.; Chen, X.; Nie, Z.; Yin, J. LncRNA CASC11 promotes cancer cell proliferation in hepatocellular carcinoma by inhibiting miRNA-188-5p. Biosci. Rep. 2019, 39, BSR20190251. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Washington, K. 7th Edition of the AJCC Cancer Staging Manual: Stomach. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2010, 17, 3077–3079. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, X.; Chen, L.; Yang, L. Complementary Sequence-Mediated Exon Circularization. Cell 2014, 159, 134–147. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.O.; Chen, T.; Xiang, J.F.; Yin, Q.F.; Xing, Y.H.; Zhu, S.; Yang, L.; Chen, L.L. Circular intronic long noncoding RNAs. Mol. Cell 2013, 51, 792–806. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Huang, C.; Bao, C.; Chen, L.; Lin, M.; Wang, X.; Zhong, G.; Yu, B.; Hu, W.; Dai, L.; et al. Exon-intron circular RNAs regulate transcription in the nucleus. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2015, 22, 256–264. [Google Scholar]
- Vicens, Q.; Westhof, E. Biogenesis of Circular RNAs. Cell 2014, 159, 13–14. [Google Scholar]
- Conn, S.J.; Pillman, K.A.; Toubia, J.; Conn, V.M.; Salmanidis, M.; Phillips, C.A.; Roslan, S.; Schreiber, A.W.; Gregory, P.A.; Goodall, G.J. The RNA Binding Protein Quaking Regulates Formation of circRNA. Cell 2015, 160, 1125–1134. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, I.; Chen, C.Y.; Chuang, T.J. Biogenesis, identification, and function of exonic circular RNAs. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. RNA 2015, 6, 563–579. [Google Scholar]
- Hansen, T.B.; Jensen, T.I.; Clausen, B.H.; Bramsen, J.B.; Finsen, B.; Damgaard, C.K.; Kjems, J. Natural RNA circles function as efficient microRNA sponges. Nature 2013, 495, 384–388. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, M.; Li, Y.; Wei, W. MicroRNA-188-5p Promotes Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition by Targeting ID4 Through Wnt/β-catenin Signaling in Retinoblastoma. OncoTargets Ther. 2019, 12, 10251–10262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shi, Y.; Jin, J.; Wang, X.; Ji, W.; Guan, X. DAXX, as a Tumor Suppressor, Impacts DNA Damage Repair and Sensitizes BRCA-Proficient TNBC Cells to PARP Inhibitors. Neoplasia 2019, 21, 533–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yost, K.E.; Soper, S.F.C.; Walker, R.L.; Pineda, M.A.; Zhu, Y.J.; Ester, C.D.; Showman, S.; Roschke, A.V.; Waterfall, J.J.; Meltzer, P.S. Rapid and reversible suppression of ALT by DAXX in osteosarcoma cells. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 4544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hechtman, J.F.; Klimstra, D.S.; Nanjangud, G.; Frosina, D.; Shia, J.; Jungbluth, A.A. Performance of DAXX Immunohistochemistry as a Screen for DAXX Mutations in Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors. Pancreas 2019, 48, 396–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, H.; Chen, C.; Chi, C.; Tsai, J.; Chiang, K.; Chang, Y.; Lin, S.; Harn, H. Targeting Telomerase and ATRX/DAXX Inducing Tumor Senescence and Apoptosis in the Malignant Glioma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Lin, X.; Xu, Y.; Shen, Z.; Pan, W. DAXX promotes ovarian cancer ascites cell proliferation and migration by activating the ERK signaling pathway. J. Ovarian Res. 2018, 11, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, W.W.; Yang, W.; Liu, E.; Yang, Z.; Dhaliwal, P.; Yang, B.B. Foxo3 circular RNA retards cell cycle progression via forming ternary complexes with p21 and CDK2. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, 2846–2858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varga, A.; Soria, J.; Hollebecque, A.; LoRusso, P.; Bendell, J.; Huang, S.A.; Wagle, M.; Okrah, K.; Liu, L.; Murray, E.; et al. A First-in-Human Phase I Study to Evaluate the ERK1/2 Inhibitor GDC-0994 in Patients with Advanced Solid Tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 1229–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Sun, C.; Tao, S.; Osunkoya, A.O.; Arnold, R.S.; Petros, J.A.; Zu, X.; Moreno, C.S. The JNK inhibitor AS602801 Synergizes with Enzalutamide to Kill Prostate Cancer Cells In Vitro and In Vivo and Inhibit Androgen Receptor Expression. Transl. Oncol. 2020, 13, 100751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuoka, T.; Yashiro, M. Molecular-targeted therapy toward precision medicine for gastrointestinal caner: Current progress and challenges. World J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2021, 13, 366–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokrejs, M. IRESite: The database of experimentally verified IRES structures (www.iresite.org). Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, D125–D130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, Y.; Gao, X.; Zhang, M.; Yan, S.; Sun, C.; Xiao, F.; Huang, N.; Yang, X.; Zhao, K.; Zhou, H.; et al. Novel Role of FBXW7 Circular RNA in Repressing Glioma Tumorigenesis. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2018, 110, 304–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.G.; Chen, R.; Ahmad, S.; Verma, R.; Kasturi, S.P.; Amaya, L.; Broughton, J.P.; Kim, J.; Cadena, C.; Pulendran, B.; et al. N6-Methyladenosine Modification Controls Circular RNA Immunity. Mol. Cell 2019, 76, 96–109.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Fu, K.; Sun, H.; Rong, D.; Wang, H.; Cao, H. CircRNA microarray profiling identifies a novel circulating biomarker for detection of gastric cancer. Mol. Cancer 2018, 17, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Shao, Y.; Fu, L.; Xie, Y.; Zhu, L.; Sun, W.; Yu, R.; Xiao, B.; Guo, J. Plasma circular RNA profiling of patients with gastric cancer and their droplet digital RT-PCR detection. J. Mol. Med. 2018, 96, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, W.W.; Zhang, C.; Yang, W.; Yong, T.; Awan, F.M.; Yang, B.B. Identifying and Characterizing circRNA-Protein Interaction. Theranostics 2017, 7, 4183–4191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Zhou, Q.; Li, A.; Li, S.; Greasley, A.; Skaro, A.; Quan, D.; Min, W.; Liu, K.; Zheng, X. Preventing alloimmune rejection using circular RNA FSCN1-silenced dendritic cells in heart transplantation. J. Heart Lung Transpl. 2021, 40, 584–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Han, B.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, S.; Bai, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, Y.; Du, L.; Xu, L.; Wu, F.; et al. Extracellular Vesicle–Mediated Delivery of Circular RNA SCMH1 Promotes Functional Recovery in Rodent and Nonhuman Primate Ischemic Stroke Models. Circulation 2020, 142, 556–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Liu, J.; Deng, H.; Ma, R.; Liao, J.; Liang, H.; Hu, J.; Li, J.; Guo, Z.; Cai, J.; et al. Targeting Mitochondria-Located circRNA SCAR Alleviates NASH via Reducing mROS Output. Cell 2020, 183, 76–93.e22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Cheng, Y.; Fu, K.; Lin, Q.; Zhao, T.; Tang, W.; Xi, L.; Sheng, L.; Zhang, H.; Sun, Y. Circ-PTPDC1 promotes the Progression of Gastric Cancer through Sponging Mir-139-3p by Regulating ELK1 and Functions as a Prognostic Biomarker. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 17, 4285–4304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badr, M.T.; Omar, M.; Häcker, G. Comprehensive Integration of Genome-Wide Association and Gene Expression Studies Reveals Novel Gene Signatures and Potential Therapeutic Targets for Helicobacter pylori-Induced Gastric Disease. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 624117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amieva, M.; Peek, R.M. Pathobiology of Helicobacter pylori–Induced Gastric Cancer. Gastroenterology 2016, 150, 64–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naumann, M.; Sokolova, O.; Tegtmeyer, N.; Backert, S. Helicobacter pylori: A Paradigm Pathogen for Subverting Host Cell Signal Transmission. Trends Microbiol. 2017, 25, 316–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Characteristics | Variable | Number (61) | CircRNA-0044301 Expression | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low | High | ||||
| Age (years) | ≤65 | 22 | 14 | 8 | 0.0862 |
| >65 | 37 | 15 | 22 | ||
| NA | 2 | ||||
| Gender | female | 20 | 7 | 13 | 0.1194 |
| male | 39 | 22 | 17 | ||
| NA | 2 | ||||
| AJCC (Version Type 8th) | stage I + II | 5 + 24 | 4 + 13 | 1 + 11 | 0.1892 |
| stage III + IV | 26 + 3 | 11 + 1 | 15 + 2 | ||
| NA | 3 | ||||
| Tumor size (cm) | ≤4.5 | 29 | 17 | 12 | 0.1444 |
| >4.5 | 28 | 11 | 17 | ||
| NA | 4 | ||||
| Family history | yes | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0.551 |
| no | 45 | 22 | 23 | ||
| NA | 13 | ||||
| History of hypertension | yes | 25 | 11 | 14 | 0.4129 |
| no | 29 | 16 | 13 | ||
| NA | 7 | ||||
| Blood type | A | 18 | 11 | 7 | 0.689 |
| AB | 4 | 2 | 2 | ||
| B | 10 | 4 | 6 | ||
| O | 22 | 10 | 12 | ||
| NA | 7 | ||||
| Parameters | Univariate Cox Regression | Multivariate Cox Regression | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR | 95% CI | p | HR | 95% CI | p | |
| Age | 10.363 | 2.114–50.804 | 0.004 | 6.781 | 1.281–35.909 | 0.024 |
| Gender | 0.744 | 0.177–3.134 | 0.687 | 0.531 | 0.110–2.576 | 0.432 |
| Stage | 8.118 | 1.828–30.042 | 0.006 | 4.832 | 0.972–24.033 | 0.054 |
| Tumor size (cm) | 6.323 | 1.475–27.101 | 0.013 | 2.353 | 0.430–12.882 | 0.324 |
| circRNA-0044301 | 2.301 | 1.331–3.978 | 0.003 | 1.640 | 0.855–3.144 | 0.136 |
| Characteristics | Variable | Number (436) | MiRNA-188 Expression | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low | High | ||||
| Age (years) | ≤65 | 194 | 99 | 95 | 0.6666 |
| >65 | 237 | 116 | 121 | ||
| NA | 5 | ||||
| Gender | female | 155 | 87 | 68 | 0.0573 |
| male | 281 | 131 | 150 | ||
| AJCC (Version Type 7th) | I + II | 57 + 163 | 22 + 77 | 35 + 86 | 0.1228 |
| III + IV | 158 + 30 | 84 + 15 | 74 + 15 | ||
| NA+ IIB or IIIB | 27 + 1 | ||||
| Longest dimension (cm) | ≤1.5 | 111 | 47 | 64 | 0.0255 |
| >1.5 | 121 | 69 | 52 | ||
| NA | 204 | ||||
| Family history | No | 317 | 158 | 159 | 0.9896 |
| Yes | 18 | 9 | 9 | ||
| NA | 101 | ||||
| Race category | White | 273 | 137 | 136 | 0.3484 |
| Asian | 88 | 46 | 42 | ||
| Black or African American | 13 | 4 | 9 | ||
| NA | 62 | ||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiang, F.; Liu, G.; Chen, X.; Li, Q.; Fang, F.; Shen, X. Hsa_circ_0044301 Regulates Gastric Cancer Cell’s Proliferation, Migration, and Invasion by Modulating the Hsa-miR-188-5p/DAXX Axis and MAPK Pathway. Cancers 2022, 14, 4183. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14174183
Jiang F, Liu G, Chen X, Li Q, Fang F, Shen X. Hsa_circ_0044301 Regulates Gastric Cancer Cell’s Proliferation, Migration, and Invasion by Modulating the Hsa-miR-188-5p/DAXX Axis and MAPK Pathway. Cancers. 2022; 14(17):4183. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14174183
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Fei, Guangxi Liu, Xiaowei Chen, Qiong Li, Fujin Fang, and Xiaobing Shen. 2022. "Hsa_circ_0044301 Regulates Gastric Cancer Cell’s Proliferation, Migration, and Invasion by Modulating the Hsa-miR-188-5p/DAXX Axis and MAPK Pathway" Cancers 14, no. 17: 4183. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14174183
APA StyleJiang, F., Liu, G., Chen, X., Li, Q., Fang, F., & Shen, X. (2022). Hsa_circ_0044301 Regulates Gastric Cancer Cell’s Proliferation, Migration, and Invasion by Modulating the Hsa-miR-188-5p/DAXX Axis and MAPK Pathway. Cancers, 14(17), 4183. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14174183







