Critical Role of Aquaporins in Cancer: Focus on Hematological Malignancies
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
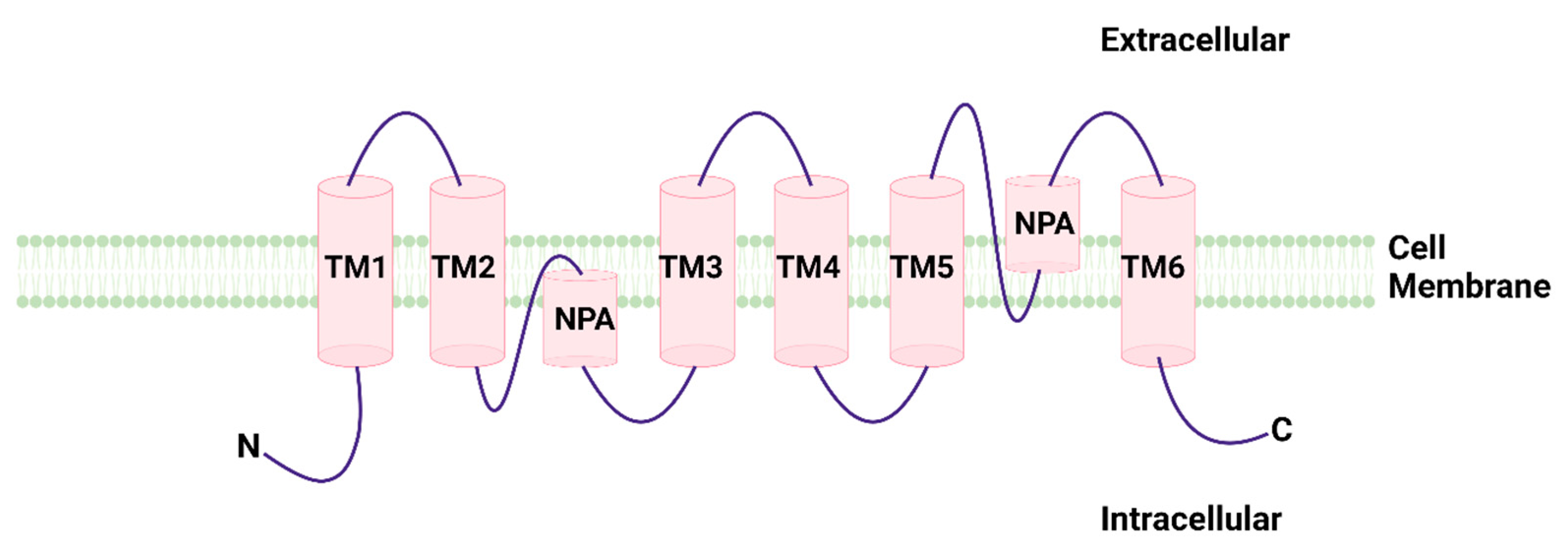
1. General Considerations on Aquaporins
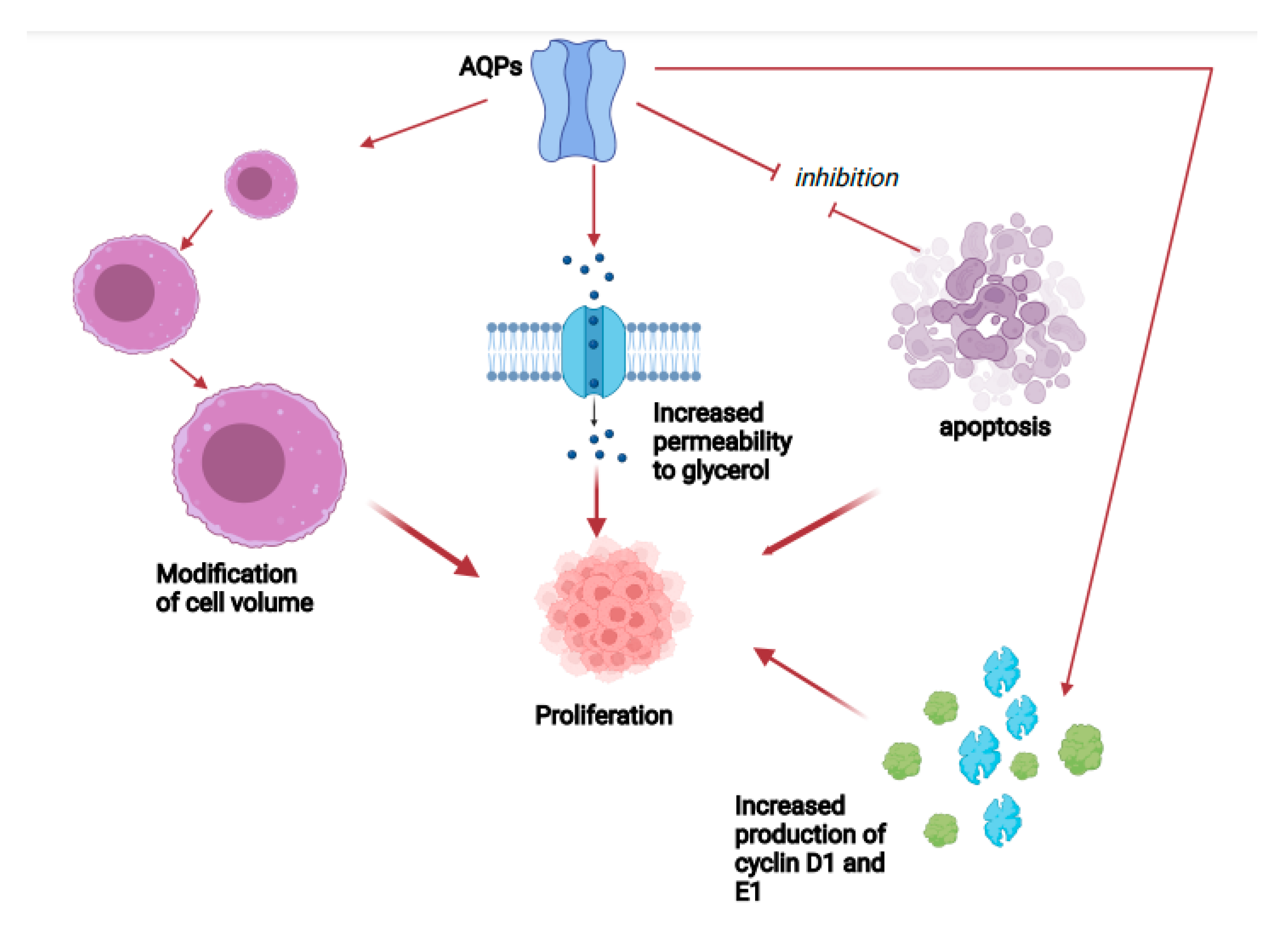
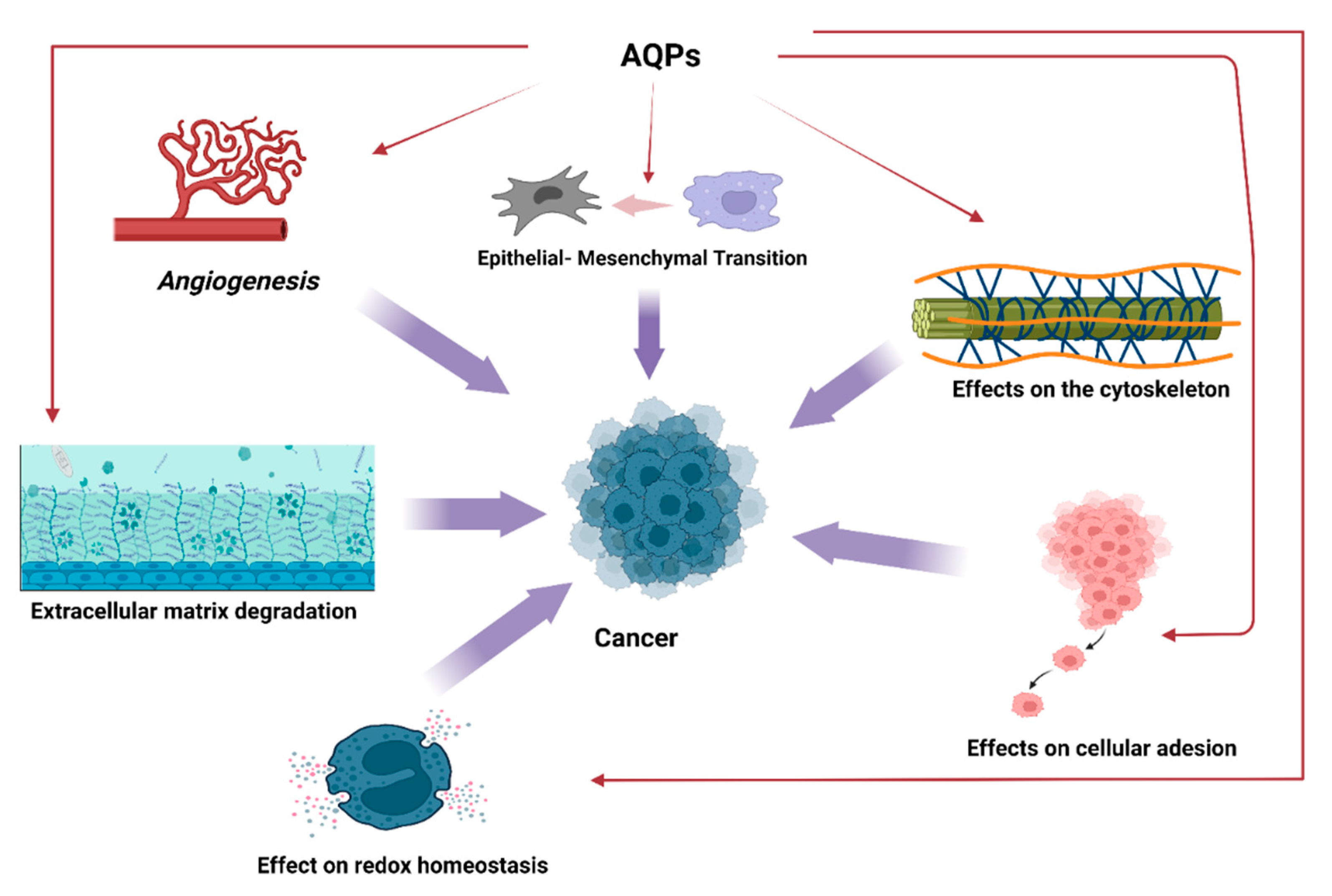
2. Aquaporins and Cancer
3. AQPs and Hematological Malignancies
4. AQPs and Lymphoproliferative Diseases
5. Future Perspectives
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Verkman, A. Aquaporins in Clinical Medicine. Annu. Rev. Med. 2012, 63, 303–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verkman, A.S.; Hara-Chikuma, M.; Papadopoulos, M.C. Aquaporins—New players in cancer biology. J. Mol. Med. 2008, 86, 523–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papadopoulos, M.C.; Saadoun, S. Key roles of aquaporins in tumor biology. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1848, 2576–2583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rojek, A.; Praetorius, J.; Frøkiaer, J.; Nielsen, S.; Fenton, R.A. A Current View of the Mammalian Aquaglyceroporins. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2008, 70, 301–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrami, L.; Berthonaud, V.; Rousselet, G.; Tacnet, F.; Ripoche, P.; Deen, P.M.T. Glycerol permeability of mutant aquaporin 1 and other AQP-MIP proteins: Inhibition studies. Pflugers Arch. 1996, 431, 408–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Echevarría, M.; Windhager, E.E.; Frindt, G. Selectivity of the Renal Collecting Duct Water Channel Aquaporin-3. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 25079–25082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasegawa, H.; Ma, T.; Skach, W.; Matthay, M.; Verkman, A. Molecular cloning of a mercurial-insensitive water channel expressed in selected water-transporting tissues. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 5497–5500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.D.; Bhakta, K.Y.; Raina, S.; Yonescu, R.; Griffin, C.A.; Copeland, N.G.; Gilbert, D.J.; Jenkins, N.A.; Preston, G.M.; Agre, P. The Human Aquaporin-5 Gene. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 8599–8604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Verkman, A.S. Water and Glycerol Permeabilities of Aquaporins 1–5 and MIP Determined Quantitatively by Expression of Epitope-tagged Constructs inXenopus Oocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 16140–16146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyama, N.; Ishibashi, K.; Kuwahara, M.; Inase, N.; Ichioka, M.; Sasaki, S.; Marumo, F. Cloning and Functional Expression of Human Aquaporin8 cDNA and Analysis of Its Gene. Genomics 1998, 54, 169–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishibashi, K.; Kuwahara, M.; Kageyama, Y.; Tohsaka, A.; Marumo, F.; Sasaki, S. Cloning and Functional Expression of a Second New Aquaporin Abundantly Expressed in Testis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1997, 237, 714–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Nagase, H.; Huang, C.G.; Calamita, G.; Agre, P. Purification and functional characterization of aquaporin-8. Biol. Cell 2006, 98, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Beitz, E. Aquaporins with selectivity for unconventional permeants. Experientia 2007, 64, 2413–2421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, M.; Garvin, J.L. Aquaporins as gas channels. Pflugers Arch. 2011, 462, 623–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verkman, A.S.; Mitra, A.K. Structure and function of aquaporin water channels. Am. J. Physiol. Physiol. Renal. 2000, 278, F13–F28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.; Preston, G.; Smith, B.; Guggino, W.; Agre, P. Molecular structure of the water channel through aquaporin CHIP. The hourglass model. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 14648–14654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreida, S.; Törnroth-Horsefield, S. Structural insights into aquaporin selectivity and regulation. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2015, 33, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, H.; Han, B.-G.; Lee, J.K.; Walian, P.J.; Jap, B.K. Structural basis of water-specific transport through the AQP1 water channel. Nature 2001, 414, 872–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, M.; Tajkhorshid, E.; Schulten, K. The Mechanism of Glycerol Conduction in Aquaglyceroporins. Structure 2001, 9, 1083–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markou, A.; Unger, L.; Abir-Awan, M.; Saadallah, A.; Halsey, A.; Balklava, Z.; Conner, M.; Törnroth-Horsefield, S.; Greenhill, S.D.; Conner, A.; et al. Molecular mechanisms governing aquaporin relocalisation. Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr 2021, 1864, 183853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vassiliou, A.G.; Manitsopoulos, N.; Kardara, M.; Maniatis, N.A.; Orfanos, S.E.; Kotanidou, A. Differential Expression of Aquaporins in Experimental Models of Acute Lung Injury. Vivo 2018, 31, 885–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Pires-Neto, R.C.; Bernardi, F.D.C.; De Araújo, P.A.; Mauad, T.; Dolhnikoff, M. The Expression of Water and Ion Channels in Diffuse Alveolar Damage Is Not Dependent on DAD Etiology. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0166184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Feng, Y.-L.; Wen, F.-Q.; Chen, X.-R.; Ou, X.-M.; Xu, D.; Yang, J.; Deng, Z.-P. Decreased expression of human aquaporin-5 correlated with mucus overproduction in airways of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2007, 28, 1166–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hussein, A.-A.M.; El-Dken, Z.H.; Barakat, N.; Abol-Enein, H. Renal ischaemia/reperfusion injury: Possible role of aquaporins. Acta Physiol. 2011, 204, 308–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galán-Cobo, A.; Ramírez-Lorca, R.; Serna, A.; Echevarría, M. Overexpression of AQP3 Modifies the Cell Cycle and the Proliferation Rate of Mammalian Cells in Culture. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0137692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cobo, A.G.; Lorca, R.R.; Toledo-Aral, J.J.; Echevarría, M. Aquaporin-1 plays important role in proliferation by affecting cell cycle progression. J. Cell. Physiol. 2015, 231, 243–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hara-Chikuma, M.; Verkman, A.S. Prevention of Skin Tumorigenesis and Impairment of Epidermal Cell Proliferation by Targeted Aquaporin-3 Gene Disruption. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2008, 28, 326–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marlar, S.; Jensen, H.H.; Login, F.H.; Nejsum, L.N. Aquaporin-3 in Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Li, S.; Liu, J.; Shi, Y.; Wang, J.; Chen, D.; Luo, L.; Qian, Y.; Huang, X.; Wang, H. RNAi-mediated silencing of AQP1 expression inhibited the proliferation, invasion and tumorigenesis of osteosarcoma cells. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2015, 16, 1332–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galan-Cobo, A.; Ramirez-Lorca, R.; Echevarria, M. Role of aquaporins in cell proliferation: What else beyond water permeability? Channels 2016, 10, 185–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kunzelmann, K. Ion Channels and Cancer. J. Membr. Biol. 2005, 205, 159–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, S.F.; Hoffmann, E.K.; Novak, I. Cell volume regulation in epithelial physiology and cancer. Front. Physiol. 2013, 4, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Ieso, M.L.; Yool, A.J. Mechanisms of Aquaporin-Facilitated Cancer Invasion and Metastasis. Front. Chem. 2018, 6, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delporte, C.; Chen, Z.J.; Baum, B.J. Aquaporin 1 Expression during the Cell Cycle in A5 Cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1996, 228, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, A.P.; Marrone, A.; Ciancetta, A.; Cobo, A.G.; Echevarría, M.; Moura, T.F.; Re, N.; Casini, A.; Soveral, G. Targeting Aquaporin Function: Potent Inhibition of Aquaglyceroporin-3 by a Gold-Based Compound. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e37435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serna, A.; Galán-Cobo, A.; Rodrigues, C.; Sánchez-Gomar, I.; Toledo-Aral, J.J.; Moura, T.F.; Casini, A.; Soveral, G.; Echevarría, M. Functional Inhibition of Aquaporin-3 With a Gold-Based Compound Induces Blockage of Cell Proliferation. J. Cell. Physiol. 2014, 229, 1787–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, H.; Shiozaki, A.; Ichikawa, D.; Fujiwara, H.; Konishi, H.; Ishii, H.; Komatsu, S.; Kubota, T.; Okamoto, K.; Kishimoto, M.; et al. The expression and role of Aquaporin 5 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 49, 655–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allegra, A.; Casciaro, M.; Barone, P.; Musolino, C.; Gangemi, S. Epigenetic Crosstalk between Malignant Plasma Cells and the Tumour Microenvironment in Multiple Myeloma. Cancers 2022, 14, 2597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alonci, A.; Allegra, A.; Bellomo, G.; Penna, G.; D’Angelo, A.; Quartarone, E.; Musolino, C. Evaluation of circulating endothelial cells, VEGF and VEGFR2 serum levels in patients with chronic myeloproliferative diseases. Hematol. Oncol. 2008, 26, 235–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allegra, A.; Coppolino, G.; Bolignano, D.; Giacobbe, M.S.; Alonci, A.; D’Angelo, A.; Bellomo, G.; Teti, D.; Loddo, S.; Musolino, C.; et al. Endothelial progenitor cells: Pathogenetic role and therapeutic perspectives. J. Nephrol. 2009, 22, 463–475. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pan, H.; Sun, C.-C.; Zhou, C.-Y.; Huang, H.-F. Expression of aquaporin-1 in normal, hyperplasic, and carcinomatous endometria. Int. J. Gynecol. Obstet. 2008, 101, 239–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esteva-Font, C.; Jin, B.; Verkman, A.S. Aquaporin-1 gene deletion reduces breast tumor growth and lung metastasis in tumor-producing MMTV-PyVT mice. FASEB J. 2013, 28, 1446–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Lu, D.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Fang, Y.; Li, F.; Sun, J. Critical role of aquaporin-3 in epidermal growth factor-induced migration of colorectal carcinoma cells and its clinical significance. Oncol. Rep. 2012, 29, 535–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pellavio, G.; Martinotti, S.; Patrone, M.; Ranzato, E.; Laforenza, U. Aquaporin-6 May Increase the Resistance to Oxidative Stress of Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma Cells. Cells 2022, 11, 1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, C.; Pimpão, C.; Mósca, A.F.; Coxixo, A.S.; Lopes, D.; da Silva, I.V.; Pedersen, P.A.; Antunes, F.; Soveral, G. Human Aquaporin-5 Facilitates Hydrogen Peroxide Permeation Affecting Adaption to Oxidative Stress and Cancer Cell Migration. Cancers 2019, 11, 932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, W.R.; Hay, M.P. Targeting hypoxia in cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2011, 11, 393–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, Y.; Edwards, N.A.; Proescholdt, M.A.; Oldfield, E.H.; Merrill, M.J. Regulation and Function of Aquaporin-1 in Glioma Cells. Neoplasia 2007, 9, 777–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potter, C.P.S.; Harris, A.L. Diagnostic, prognostic and therapeutic implications of carbonic anhydrases in cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2003, 89, 2–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foufelle, F.; Girard, J.; Ferré, P. Glucose regulation of gene expression. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 1998, 1, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dentin, R.; Denechaud, P.-D.; Benhamed, F.; Girard, J.; Postic, C. Hepatic Gene Regulation by Glucose and Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids: A Role for ChREBP. J. Nutr. 2006, 136, 1145–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-W.; Zeller, K.I.; Wang, Y.; Jegga, A.G.; Aronow, B.J.; O’Donnell, K.A.; Dang, C.V. Evaluation of Myc E-Box Phylogenetic Footprints in Glycolytic Genes by Chromatin Immunoprecipitation Assays. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2004, 24, 5923–5936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomita, Y.; Dorward, H.; Yool, A.J.; Smith, E.; Townsend, A.R.; Price, T.J.; Hardingham, J.E. Role of Aquaporin 1 Signalling in Cancer Development and Progression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koury, J.; Zhong, L.; Hao, J. Targeting Signaling Pathways in Cancer Stem Cells for Cancer Treatment. Stem Cells Int. 2017, 2017, 2925869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Shi, P.; Zhao, G.; Xu, J.; Peng, W.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, G.; Wang, X.; Dong, Z.; Chen, F.; et al. Targeting Cancer Stem Cell Pathways for Cancer Therapy. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2020, 5, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Liu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Jing, H. Molecular mechanism of AQP3 in regulating differentiation and apoptosis of lung cancer stem cells through Wnt/GSK3beta/beta-Catenin pathway. J. BUON 2020, 25, 1714–1720. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zheng, X.; Li, C.; Yu, K.; Shi, S.; Chen, H.; Qian, Y.; Mei, Z. Aquaporin-9, mediated by IGF2, suppresses liver cancer stem cell properties via augmenting ROS/beta-Catenin/FOXO3a signalling. Mol. Canc. Res. 2020, 18, 992–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wu, G.; Fu, X.; Xu, S.; Wang, T.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, Y. Aquaporin 3 maintains the stemness of CD133þ hepatocellular carcinoma cells by activating STAT3. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wang, T.; Zhou, Y.-C.; Gao, F.; Zhang, Z.-H.; Xu, H.; Wang, S.-L.; Shen, L.-Z. Aquaporin 3 promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition in gastric cancer. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 33, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Li, B.; Zhang, L.; Chen, L.; Sun, G.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, J.; Zhi, X.; Wang, L.; Xu, Z.; et al. The proliferation impairment induced by AQP3 deficiency is the result of glycerol uptake and metabolism inhibition in gastric cancer cells. Tumor Biol. 2016, 37, 9169–9179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Zhang, S.; Jiang, H.; Yang, Y.; Jiang, Y. Co-expression of AQP3 and AQP5 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma correlates with aggressive tumor progression and poor prognosis. Med Oncol. 2013, 30, 636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusayama, M.; Wada, K.; Nagata, M.; Ishimoto, S.; Takahashi, H.; Yoneda, M.; Nakajima, A.; Okura, M.; Kogo, M.; Kamisaki, Y. Critical role of aquaporin 3 on growth of human esophageal and oral squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Sci. 2011, 102, 1128–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, T.; Hojo, S.; Sekine, S.; Sawada, S.; Okumura, T.; Nagata, T.; Shimada, Y.; Tsukada, K. Expression of aquaporin-1 is a poor prognostic factor for stage II and III colon cancer. Mol. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 1, 953–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Sun, M.; Wang, J.; Guo, R.; Shen, L.; Wu, W. Critical role of aquaporin-3 in the human epidermal growth factor-induced migration and proliferation in the human gastric adenocarcinoma cells. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2010, 9, 1000–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magouliotis, D.E.; Tasiopoulou, V.S.; Dimas, K.; Sakellaridis, N.; Svokos, K.A.; Svokos, A.A.; Zacharoulis, D. Transcriptomic analysis of the Aquaporin (AQP) gene family interactome identifies a molecular panel of four prognostic markers in patients with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Pancreatology 2019, 19, 436–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.; Sun, T.; Yang, M.; Li, Z.; Li, Z.; Gao, Y. Prognostic Value of Combined Aquaporin 3 and Aquaporin 5 Overexpression in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. BioMed Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 206525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Z.; Zhang, T.; Luo, L.; Zhao, H.; Cheng, J.; Xiang, J.; Zhao, C. Aquaporins in human breast cancer: Identification and involvement in carcinogenesis of breast cancer. J. Surg. Oncol. 2011, 106, 267–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.J.; Chae, Y.S.; Kim, J.G.; Kim, W.W.; Jung, J.H.; Park, H.Y.; Jeong, J.Y.; Park, J.-Y.; Jung, H.J.; Kwon, T.-H. AQP5 Expression Predicts Survival in Patients with Early Breast Cancer. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2013, 21, 375–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Shi, Y.; Amiduo, R.; Tuokan, T.; Suzuk, L. Expression and Prognostic Value of Aquaporin 1, 3 in Cervical Carcinoma in Women of Uygur Ethnicity from Xinjiang, China. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e98576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magouliotisa, D.E.; Tasiopouloub, V.S.; Svokosc, A.A.; Svokos, K.A. Aquaporins in health and disease. Adv. Clin. Chem. 2020, 98, 149–171. [Google Scholar]
- Moosavi, M.-S.; Elham, Y. Aquaporins 1, 3 and 5 in Different Tumors, their Expression, Prognosis Value and Role as New Therapeutic Targets. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 2019, 26, 615–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensena, H.H.; Logina, F.H.; Koffmand, J.S.; Kwonc, T.-H.; Nejsum, L.N. The role of aquaporin-5 in cancer cell migration: A potential active participant. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2016, 79, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wen, J.; Zhao, H.; Dong, X.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, S.; Shen, L. Aquaporin 3 promotes the stem-like properties of gastric cancer cells via Wnt/GSK-3β/β-catenin pathway. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 16529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otto, W.; Rubenwolf, P.C.; Burger, M.; Fritsche, H.-M.; Rößler, W.; May, M.; Hartmann, A.; Hofstädter, F.; Wieland, W.F.; Denzinger, S. Loss of aquaporin 3 protein expression constitutes an independent prognostic factor for progression-free survival: An immunohistochemical study on stage pT1 urothelial bladder cancer. BMC Cancer 2012, 12, 459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagnan, A.; Bagger, F.O.; Piqué-Borràs, M.-R.; Ignacimouttou, C.; Caulier, A.; Lopez, C.K.; Robert, E.; Uzan, B.; Gelsi-Boyer, V.; Aid, Z.; et al. Human erythroleukemia genetics and transcriptomes identify master transcription factors as functional disease drivers. Blood 2020, 136, 698–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umenishi, F.; Verkman, A. Isolation of the Human Aquaporin-1 Promoter and Functional Characterization in Human Erythroleukemia Cell Lines. Genomics 1998, 47, 341–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, C.; King, L.S.; Agre, P. Aqp1 expression in erythroleukemia cells: Genetic regulation of glucocorticoid and chemical induction. Am. J. Physiol. Physiol. 1997, 273, C1562–C1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douer, D.; Koeffler, H.P. Retinoic acid enhances growth of human early erythroid progenitor cells in vitro. J. Clin. Investig. 1982, 69, 1039–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umenishi, F.; Schrier, R.W. Induction of human aquaporin-1 gene by retinoic acid in human erythroleukemia HEL cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2002, 293, 913–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharjee, R.; Ghosh, S.; Nath, A.; Basu, A.; Biswas, O.; Patil, C.R.; Kundu, C.N. Theragnostic strategies harnessing the self-renewal pathways of stem-like cells in the acute myeloid leukemia. Crit. Rev. Oncol. 2022, 177, 103753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Liu, H.-Q.; Wang, L.-N.; Yang, L.; Liu, X.-L. Current and emerging molecular and epigenetic disease entities in acute myeloid leukemia and a critical assessment of their therapeutic modalities. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2022, 83, 121–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, W.; Zhu, G.; Xu, L.; Liu, J.; Han, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Hou, J.; Zhao, H.; Zhong, H. G-CSF upregulates the expression of aquaporin-9 through CEBPB to enhance the cytotoxic activity of arsenic trioxide to acute myeloid leukemia cells. Cancer Cell Int. 2022, 22, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, J.; Pang, A.; Yuen, W.-H.; Kwong, Y.-L.; Tse, E.W.C. Relationship of expression of aquaglyceroporin 9 with arsenic uptake and sensitivity in leukemia cells. Blood 2006, 109, 740–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iriyama, N.; Yuan, B.; Yoshino, Y.; Hatta, Y.; Horikoshi, A.; Aizawa, S.; Takeuchi, J.; Toyoda, H. Aquaporin 9, a promising predictor for the cytocidal effects of arsenic trioxide in acute promyelocytic leukemia cell lines and primary blasts. Oncol. Rep. 2013, 29, 2362–2368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Z.; Hunter, T. Pin1 and cancer. Cell Res. 2014, 24, 1033–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.-L.; Cui, R.; Zhou, J.; Teng, K.-Y.; Hsiao, Y.-H.; Nakanishi, K.; Fassan, M.; Luo, Z.; Shi, G.; Tili, E.; et al. ERK Activation Globally Downregulates miRNAs through Phosphorylating Exportin-5. Cancer Cell 2016, 30, 723–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.-L.; Gong, C.; Chen, C.-H.; Lee, D.Y.; Hu, H.; Huang, P.; Yao, Y.; Guo, W.; Reinhardt, F.; Wulf, G.; et al. Prolyl Isomerase Pin1 Acts Downstream of miR200c to Promote Cancer Stem–like Cell Traits in Breast Cancer. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 3603–3616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.L.; Gong, C.; Chen, C.H.; Hu, H.; Huang, P.; Zheng, M.; Yao, Y.; Wei, S.; Wulf, G.; Lieberman, J.; et al. The Rab2A GTPase is a breast cancer stem-promoting gene that enhances tumorigenesis via activating Erk signaling. Cell Rep. 2015, 11, 111–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rustighi, A.; Zannini, A.; Tiberi, L.; Sommaggio, R.; Piazza, S.; Sorrentino, G.; Nuzzo, S.; Tuscano, A.; Eterno, V.; Benvenuti, F.; et al. Prolyl-isomerase Pin1 controls normal and cancer stem cells of the breast. EMBO Mol. Med. 2013, 6, 99–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozono, S.; Lin, Y.-M.; Seo, H.-S.; Pinch, B.; Lian, X.; Qiu, C.; Herbert, M.K.; Chen, C.-H.; Tan, L.; Gao, Z.J.; et al. Arsenic targets Pin1 and cooperates with retinoic acid to inhibit cancer-driving pathways and tumor-initiating cells. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iriyama, N.; Yuan, B.; Hatta, Y.; Horikoshi, A.; Yoshino, Y.; Toyoda, H.; Aizawa, S.; Takeuchi, J. Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor potentiates differentiation induction by all-trans retinoic acid and arsenic trioxide and enhances arsenic uptake in the acute promyelocytic leukemia cell line HT93A. Oncol. Rep. 2012, 28, 1875–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musolino, C.; Allegra, A.; Saija, A.; Alonci, A.; Russo, S.; Spatari, G.; Penna, G.; Gerace, D.; Cristani, M.; David, A.; et al. Changes in advanced oxidation protein products, advanced glycation end products, and s-nitrosylated proteins, in patients affected by polycythemia vera and essential thrombocythemia. Clin. Biochem. 2012, 45, 1439–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangemi, S.; Allegra, A.; Alonci, A.; Cristani, M.; Russo, S.; Speciale, A.; Penna, G.; Spatari, G.; Cannavò, A.; Bellomo, G.; et al. Increase of novel biomarkers for oxidative stress in patients with plasma cell disorders and in multiple myeloma patients with bone lesions. Agents Actions 2012, 61, 1063–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allegra, A.; Petrarca, C.; Di Gioacchino, M.; Casciaro, M.; Musolino, C.; Gangemi, S. Modulation of Cellular Redox Parameters for Improving Therapeutic Responses in Multiple Myeloma. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bienert, G.P.; Schjoerring, J.K.; Jahn, T.P. Membrane transport of hydrogen peroxide. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2006, 1758, 994–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, L.S.; Kozono, D.; Agre, P. From structure to disease: The evolving tale of aquaporin biology. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2004, 5, 687–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, E.W.; Dickinson, B.C.; Chang, C.J. Aquaporin-3 mediates hydrogen peroxide uptake to regulate downstream intracellular signaling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 15681–15686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agre, P. The aquaporin water channels. Proc. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2006, 3, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agre, P.; Smith, B.; Preston, G. ABH and Colton blood group antigens on Aquaporin-1, the human red cell water channel protein. Transfus. Clin. Biol. 1995, 2, 303–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roudier, N.; Ripoche, P.; Gane, P.; Le Pennec, P.Y.; Daniels, G.; Cartron, J.-P.; Bailly, P. AQP3 Deficiency in Humans and the Molecular Basis of a Novel Blood Group System, GIL. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 45854–45859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingsley, P.D.; Greenfest-Allen, E.; Frame, J.M.; Bushnell, T.P.; Malik, J.; McGrath, K.E.; Stoeckert, C.J., Jr.; Palis, J. Ontogeny of erythroid gene expression. Blood 2012, 121, e5–e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalla Sega, F.V.; Zambonin, L.; Fiorentini, D.; Rizzo, B.; Caliceti, C.; Landi, L.; Hrelia, S.; Prata, C. Specific aquaporins facilitate Nox-produced hydrogen peroxide transport through plasma membrane in leukaemia cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1843, 806–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sega, F.V.D.; Prata, C.; Zambonin, L.; Angeloni, C.; Rizzo, B.; Hrelia, S.; Fiorentini, D. Intracellular cysteine oxidation is modulated by aquaporin-8-mediated hydrogen peroxide channeling in leukaemia cells. BioFactors 2016, 43, 232–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ushio-Fukai, M. Compartmentalization of Redox Signaling Through NADPH Oxidase–Derived ROS. Antioxid. Redox Signal 2009, 11, 1289–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Han, W.; Villar, V.A.M.; Keever, L.B.; Lu, Q.; Hopfer, U.; Quinn, M.T.; Felder, R.A.; Jose, P.A.; Yu, P. D1-Like Receptors Regulate NADPH Oxidase Activity and Subunit Expression in Lipid Raft Microdomains of Renal Proximal Tubule Cells. Hypertension 2009, 53, 1054–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Li, F.; Sun, Y.; Lei, L.; Zhou, H.; Lei, T.; Xia, Y.; Verkman, A.S.; Yang, B. Aquaporin-1 retards renal cyst development in polycystic kidney disease by inhibition of Wnt signaling. FASEB J. 2015, 29, 1551–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metzeler, K.H.; Herold, T.; Rothenberg-Thurley, M.; Amler, S.; Sauerland, M.C.; Görlich, D.; Schneider, S.; Konstandin, N.P.; Dufour, A.; Bräundl, K.; et al. Spectrum and prognostic relevance of driver gene mutations in acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 2016, 128, 686–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.; Huang, H.; Huang, S.; Xu, A.; Fan, F.; Luo, S.; Yan, H.; Chen, L.; Sun, C.; Hu, Y. A Novel Scoring System for Risk Assessment of Elderly Patients With Cytogenetically Normal Acute Myeloid Leukemia Based on Expression of Three AQP1 DNA Methylation-Associated Genes. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahsan, F.; Shabbir, A.; Shahzad, M.; Mobashar, A.; Sharif, M.; Basheer, M.I.; Tareen, R.B.; Syed, N.-I. Amelioration of allergic asthma by Ziziphora clinopodioides via upregulation of aquaporins and downregulation of IL4 and IL5. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2019, 266, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, E.K.; Lambert, I.H.; Pedersen, S.F. Physiology of Cell Volume Regulation in Vertebrates. Physiol. Rev. 2009, 89, 193–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, F. Mechanisms and Significance of Cell Volume Regulation. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2007, 26, 613S–623S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, T.H.; Kwan, K.W.; Yip, T.T.C.; Fong, H.W.; Ngan, K.C.; Yu, M.; Yao, S.; Ngan, A.H.W.; Lin, Y. Regulating the Membrane Transport Activity and Death of Cells via Electroosmotic Manipulation. Biophys. J. 2016, 110, 2769–2778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenzi, M.; Fimognari, C.; Hrelia, P. Sulforaphane as a Promising Molecule for Fighting Cancer. Cancer Treat. Res. 2013, 159, 207–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langouët, S.; Furge, L.L.; Kerriguy, N.; Nakamura, K.; Guillouzo, A.; Guengerich, F.P. Inhibition of human cytochrome P 450 enzymes by 1, 2-dithiole-3-thione, oltipraz and its derivatives, and sulforaphane. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2000, 13, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, M.-K.; Wakabayashi, N.; Kensler, T.W. Chemoprevention through the Keap1–Nrf2 signaling pathway by phase 2 enzyme inducers. Mutat. Res. Mol. Mech. Mutagen. 2004, 555, 133–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokhtari, R.B.; Baluch, N.; Homayouni, T.S.; Morgatskaya, E.; Kumar, S.; Kazemi, P.; Yeger, H. The role of Sulforaphane in cancer chemoprevention and health benefits: A mini-review. J. Cell Commun. Signal 2017, 12, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertl, E.; Bartsch, H.; Gerhauser, C. Inhibition of angiogenesis and endothelial cell functions are novel sulforaphane-mediated mechanisms in chemoprevention. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2006, 5, 575–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.H.; Sung, B.; Kang, Y.J.; Hwang, S.Y.; Kim, M.J.; Yoon, J.-H.; Im, E.; Kim, N.D. Sulforaphane inhibits hypoxia-induced HIF-1α and VEGF expression and migration of human colon cancer cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2015, 47, 2226–2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jee, H.-G.; Lee, K.E.; Bin Kim, J.; Shin, H.-K.; Youn, Y.-K. Sulforaphane Inhibits Oral Carcinoma Cell Migration and Invasion In Vitro. Phytotherapy Res. 2011, 25, 1623–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.-S.; Cho, H.-J.; Jeong, Y.-J.; Shin, J.-M.; Park, K.-K.; Park, Y.-Y.; Bae, Y.-S.; Chung, I.-K.; Kim, M.; Kim, C.-H.; et al. Isothiocyanates inhibit the invasion and migration of C6 glioma cells by blocking FAK/JNK-mediated MMP-9 expression. Oncol. Rep. 2015, 34, 2901–2908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fimognari, C.; Turrini, E.; Sestili, P.; Calcabrini, C.; Carulli, G.; Fontanelli, G.; Rousseau, M.; Cantelli-Forti, G.; Hrelia, P. Antileukemic Activity of Sulforaphane in Primary Blasts from Patients Affected by Myelo- and Lympho-Proliferative Disorders and in Hypoxic Conditions. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e101991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, D.-O.; Kim, M.-O.; Kang, S.-H.; Choi, Y.H.; Kim, G.-Y. Sulforaphane suppresses TNF-α-mediated activation of NF-κB and induces apoptosis through activation of reactive oxygen species-dependent caspase-3. Cancer Lett. 2009, 274, 132–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, H.-S.; Shih, Y.-L.; Lee, C.-H.; Hsueh, S.-C.; Liu, J.-Y.; Liao, N.-C.; Chen, Y.-L.; Huang, Y.-P.; Lu, H.-F.; Chung, J.-G. Sulforaphane-induced apoptosis in human leukemia HL-60 cells through extrinsic and intrinsic signal pathways and altering associated genes expression assayed by cDNA microarray. Environ. Toxicol. 2016, 32, 311–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suppipat, K.; Park, C.S.; Shen, Y.; Zhu, X.; Lacorazza, H.D. Sulforaphane Induces Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptosis in Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Cells. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e51251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakubikova, J.; Bao, Y.; Sedlak, J. Isothiocyanates induce cell cycle arrest, apoptosis and mitochondrial potential depolarization in HL-60 and multidrug-resistant cell lines. Anticancer Res. 2005, 25, 3375–3386. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Prata, C.; Facchini, C.; Leoncini, E.; Lenzi, M.; Maraldi, T.; Angeloni, C.; Zambonin, L.; Hrelia, S.; Fiorentini, D. Sulforaphane Modulates AQP8-Linked Redox Signalling in Leukemia Cells. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2018, 2018, 4125297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poudel, G.; Tolland, M.G.; Hughes, T.P.; Pagani, I.S. Mechanisms of Resistance and Implications for Treatment Strategies in Chronic Myeloid Leukaemia. Cancers 2022, 14, 3300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chae, Y.K.; Kang, S.K.; Kim, M.S.; Woo, J.; Lee, J.; Chang, S.; Kim, D.-W.; Kim, M.; Park, S.; Kim, I.; et al. Human AQP5 Plays a Role in the Progression of Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia (CML). PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e2594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansouri, L.; Thorvaldsdottir, B.; Laidou, S.; Stamatopoulos, K.; Rosenquist, R. Precision diagnostics in lymphomas—Recent developments and future directions. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2021, 84, 170–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kay, N.E.; Hampel, P.J.; Van Dyke, D.L.; Parikh, S.A. CLL update 2022: A continuing evolution in care. Blood Rev. 2022, 54, 100930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangemi, S.; Allegra, A.; Aguennouz, M.; Alonci, A.; Speciale, A.; Cannavò, A.; Cristani, M.; Russo, S.; Spatari, G.; Alibrandi, A.; et al. Relationship Between Advanced Oxidation Protein Products, Advanced Glycation End Products, andS-Nitrosylated Proteins With Biological Risk and MDR-1 Polymorphisms in Patients Affected by B-Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Cancer Investig. 2012, 30, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.L.; Li, Y.; Xu, S.; Nie, Y.; Zhang, J. NFAT5 Regulated by STUB1, Facilitates Malignant Cell Survival and p38 MAPK Activation by Upregulating AQP5 in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Biochem. Genet. 2021, 59, 870–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nico, B.; Annese, T.; Tamma, R.; Longo, V.; Ruggieri, S.; Senetta, R.; Cassoni, P.; Specchia, G.; Vacca, A.; Ribatti, D. Aquaporin-4 expression in primary human central nervous system lymphomas correlates with tumour cell proliferation and phenotypic heterogeneity of the vessel wall. Eur. J. Cancer 2011, 48, 772–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, U.; Gloghini, A.; Gaidano, G.; Chadburn, A.; Cesarman, E.; Dalla-Favera, R.; Carbone, A. Gene expression profile analysis of AIDS-related primary effusion lymphoma (PEL) suggests a plasmablastic derivation and identifies PEL-specific transcripts. Blood 2003, 101, 4115–4121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, A.G.; Sharma-Walia, N.; Chandran, B. Targeting KSHV/HHV-8 Latency with COX-2 Selective Inhibitor Nimesulide: A Potential Chemotherapeutic Modality for Primary Effusion Lymphoma. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e24379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liu, W.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, B. Association of the Aquaporin 3 Gene Polymorphism (rs2231231) with Epstein-Barr Virus-Associated Cancers in China. Intervirology 2018, 61, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perini, T.; Materozzi, M.; Milan, E. The Immunity-malignancy equilibrium in multiple myeloma: Lessons from oncogenic events in plasma cells. FEBS J. 2021, 289, 4383–4397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vacca, A.; Ribatti, D.; Roccaro, A.M.; Frigeri, A.; Dammacco, F. Bone marrow angiogenesis in patients with active multiple myeloma. Semin. Oncol. 2001, 28, 543–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Hilsenbeck, S.; Gazitt, Y. Arsenic trioxide-induced apoptosis in myeloma cells: p53-dependent G1 or G2/M cell cycle arrest, activation of caspase-8 or caspase-9, and synergy with APO2/TRAIL. Blood 2003, 101, 4078–4087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allegra, A.; Speciale, A.; Molonia, M.S.; Guglielmo, L.; Musolino, C.; Ferlazzo, G.; Costa, G.; Saija, A.; Cimino, F. Curcumin ameliorates the in vitro efficacy of carfilzomib in human multiple myeloma U266 cells targeting p53 and NF-κB pathways. Toxicol. Vitr. 2018, 47, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.; Ma, G.; Gao, Y.; Su, Y. Curcumin Synergistically Enhances the Cytotoxicity of Arsenic Trioxide in U266 Cells by Increasing Arsenic Uptake. Evidence-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2021, 2021, 3083041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knepper, M.A.; Kwon, T.-H.; Nielsen, S. Molecular Physiology of Water Balance. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 1349–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abir-Awan, M.; Kitchen, P.; Salman, M.M.; Conner, M.T.; Conner, A.C.; Bill, R.M. Inhibitors of Mammalian Aquaporin Water Channels. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salman, M.M.; Kitchen, P.; Yool, A.J.; Bill, R.M. Recent breakthroughs and future directions in drugging aquaporins. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2021, 43, 30–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Feng, L.; Zhu, Z.; Zheng, M.; Wang, D.; Chen, Z.; Sun, H. Aquaporins as diagnostic and therapeutic targets in cancer: How far we are? J. Transl. Med. 2015, 13, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farr, G.W.; Hall, C.H.; Farr, S.M.; Wade, R.; Detzel, J.M.; Adams, A.G.; Buch, J.M.; Beahm, D.L.; Flask, C.A.; Xu, K.; et al. Functionalized Phenylbenzamides Inhibit Aquaporin-4 Reducing Cerebral Edema and Improving Outcome in Two Models of CNS Injury. Neuroscience 2019, 404, 484–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, C.; Cao, C.; Lu, S.; Kivlin, R.; Amaral, A.; Kouttab, N.; Yang, H.; Chu, W.; Bi, Z.; Di, W.; et al. Curcumin attenuates EGF-induced AQP3 up-regulation and cell migration in human ovarian cancer cells. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2008, 62, 857–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhou, G.-B.; Liu, P.; Song, J.-H.; Liang, Y.; Yan, X.-J.; Xu, F.; Wang, B.-S.; Mao, J.-H.; Shen, Z.-X.; et al. Dissection of mechanisms of Chinese medicinal formula Realgar-Indigo naturalis as an effective treatment for promyelocytic leukemia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 4826–4831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, J.V.; Kourghi, M.; De Ieso, M.L.; Campbell, E.M.; Dorward, H.S.; Hardingham, J.E.; Yool, A.J. Differential Inhibition of Water and Ion Channel Activities of Mammalian Aquaporin-1 by Two Structurally Related Bacopaside Compounds Derived from the Medicinal Plant Bacopa monnieri. Mol. Pharmacol. 2016, 90, 496–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Y.; Ma, B.; Li, T.; Gao, J.-W.; Yu, H.-M.; Li, X.-J. Acetazolamide inhibits aquaporin-1 protein expression and angiogenesis. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2004, 25, 812–816. [Google Scholar]
- Bin, K.; Shi-Peng, Z. Acetazolamide Inhibits Aquaporin-1 Expression and Colon Cancer Xenograft Tumor Growth. Hepatogastroenterology 2011, 58, 1502–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Detmers, F.J.; de Groot, B.L.; Müller, E.M.; Hinton, A.; Konings, I.B.; Sze, M.; Flitsch, S.L.; Grubmüller, H.; Deen, P.M. Quaternary Ammonium Compounds as Water Channel Blockers. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 14207–14214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, L.-B.; Zhang, R.-J.; Tan, Y.-J.; Ding, G.-L.; Shi, S.; Zhang, D.; He, R.-H.; Liu, A.-X.; Wang, T.-T.; Leung, P.; et al. Identification of Estrogen Response Element in the Aquaporin-2 Gene that Mediates Estrogen-Induced Cell Migration and Invasion in Human Endometrial Carcinoma. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 96, E1399–E1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migliati, E.; Meurice, N.; DuBois, P.; Fang, J.S.; Somasekharan, S.; Beckett, E.; Flynn, G.; Yool, A.J. Inhibition of Aquaporin-1 and Aquaporin-4 Water Permeability by a Derivative of the Loop Diuretic Bumetanide Acting at an Internal Pore-Occluding Binding Site. Mol. Pharmacol. 2009, 76, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Ieso, M.L.; Pei, J.V.; Nourmohammadi, S.; Smith, E.; Chow, P.H.; Kourghi, M.; Hardingham, J.E.; Yool, A.J. Combined pharmacological administration of AQP1 ion channel blocker AqB011 and water channel blocker Bacopaside II amplifies inhibition of colon cancer cell migration. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kourghi, M.; Pei, J.V.; De Ieso, M.L.; Flynn, G.; Yool, A.J. Bumetanide Derivatives AqB007 and AqB011 Selectively Block the Aquaporin-1 Ion Channel Conductance and Slow Cancer Cell Migration. Mol. Pharmacol. 2015, 89, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kourghi, M.; De Ieso, M.L.; Nourmohammadi, S.; Pei, J.V.; Yool, A.J. Identification of Loop D Domain Amino Acids in the Human Aquaporin-1 Channel Involved in Activation of the Ionic Conductance and Inhibition by AqB011. Front. Chem. 2018, 6, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, J.V. Drug discovery and therapeutic targets for pharmacological modulators of aquaporin channels. In Aquaporins in Health and Disease: New Molecular Targets For Drug Discovery; Soveral, G., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016; pp. 275–297. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Yan, C.; Zheng, W.; Chen, X. Proliferation inhibition of cisplatin and aquaporin 5 expression in human ovarian cancer cell CAOV3. Arch. Gynecol. Obstet. 2011, 285, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niemietz, C.M.; Tyerman, S.D. New potent inhibitors of aquaporins: Silver and gold compounds inhibit aquaporins of plant and human origin. FEBS Lett. 2002, 531, 443–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yukutake, Y.; Hirano, Y.; Suematsu, M.; Yasui, M. Rapid and Reversible Inhibition of Aquaporin-4 by Zinc. Biochemistry 2009, 48, 12059–12061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, X.; Yu, G. Aquaporins: New Targets for Cancer Therapy. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2016, 15, 821–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seeliger, D.; Zapater, C.; Krenc, D.; Haddoub, R.; Flitsch, S.; Beitz, E.; Cerdà, J.; De Groot, B.L. Discovery of Novel Human Aquaporin-1 Blockers. ACS Chem. Biol. 2012, 8, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliva, A.; Kang, Y.; Truettner, J.; Sanchez-Molano, J.; Furones, C.; Yool, A.; Atkins, C. Fluid-percussion brain injury induces changes in aquaporin channel expression. Neuroscience 2011, 180, 272–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yool, A.J.; Morelle, J.; Cnops, Y.; Verbavatz, J.-M.; Campbell, E.; Beckett, E.A.; Booker, G.W.; Flynn, G.; Devuyst, O. AqF026 Is a Pharmacologic Agonist of the Water Channel Aquaporin-1. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2013, 24, 1045–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mola, M.G.; Nicchia, G.P.; Svelto, M.; Spray, D.C.; Frigeri, A. Automated Cell-Based Assay for Screening of Aquaporin Inhibitors. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 8219–8229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- To, J.; Yeo, C.Y.; Soon, C.H.; Torres, J. A generic high-throughput assay to detect aquaporin functional mutants: Potential application to discovery of aquaporin inhibitors. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015, 1850, 1869–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, R.V.; Xu, S.; Van Hoek, A.N.; Rusinko, A.; Feng, Z.; May, J.; Hellberg, M.; Sharif, N.A.; Wax, M.B.; Irigoyen, M.; et al. Rapid Identification of Novel Inhibitors of the Human Aquaporin-1 Water Channel. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2016, 87, 794–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tradtrantip, L.; Zhang, H.; Saadoun, S.; Phuan, P.-W.; Lam, C.; Papadopoulos, M.C.; Bennett, J.L.; Verkman, A.S. Anti-Aquaporin-4 monoclonal antibody blocker therapy for neuromyelitis optica. Ann. Neurol. 2012, 71, 314–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tradtrantip, L.; Zhang, H.; Anderson, M.O.; Saadoun, S.; Phuan, P.W.; Papadopoulos, M.C.; Bennett, J.L.; Verkman, A.S. Small molecule inhibitors of NMO-IgG binding to aquaporin-4 reduce astrocyte cytotoxicity in neuromyelitis optica. FASEB J. 2012, 26, 2197–2208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tradtrantip, L.; Jin, B.-J.; Yao, X.; Anderson, M.O.; Verkman, A.S. Aquaporin-Targeted Therapeutics: State-of-the-Field. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2017, 969, 239–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baum, B.J.; Alevizos, I.; Zheng, C.; Cotrim, A.P.; Liu, S.; McCullagh, L.; Goldsmith, C.M.; Burbelo, P.D.; Citrin, D.E.; Mitchell, J.B.; et al. Early responses to adenoviral-mediated transfer of the aquaporin-1 cDNA for radiation-induced salivary hypofunction. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 19403–19407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Disease | Drug | Study | AQP | Effect | Mechanism | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AML | G-CSF + ATO | In vitro (HL-60, THP-1) | AQP9 | Apoptosis | Increased intracellular ATO | [81] |
| AML | GSF + ATO | In vivo xenograft animal model | AQP9 | Reduced tumor proliferation | CEBPB | [81] |
| AML (APL) | ATO | In vitro (HT93A, NB4) | AQP9 | Apoptosis | [83] | |
| AML | ATO + ATRA | In vitro | AQP9 | Reduced pro-oncogene effect | Effect on Pin1 | [89] |
| AML | ATO and/or ATRA and/or G-CSF | In vitro (HT93A) | AQP9 | Decreased cell viability | Increased arsenic uptake | [90] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Allegra, A.; Cicero, N.; Mirabile, G.; Cancemi, G.; Tonacci, A.; Musolino, C.; Gangemi, S. Critical Role of Aquaporins in Cancer: Focus on Hematological Malignancies. Cancers 2022, 14, 4182. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14174182
Allegra A, Cicero N, Mirabile G, Cancemi G, Tonacci A, Musolino C, Gangemi S. Critical Role of Aquaporins in Cancer: Focus on Hematological Malignancies. Cancers. 2022; 14(17):4182. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14174182
Chicago/Turabian StyleAllegra, Alessandro, Nicola Cicero, Giuseppe Mirabile, Gabriella Cancemi, Alessandro Tonacci, Caterina Musolino, and Sebastiano Gangemi. 2022. "Critical Role of Aquaporins in Cancer: Focus on Hematological Malignancies" Cancers 14, no. 17: 4182. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14174182
APA StyleAllegra, A., Cicero, N., Mirabile, G., Cancemi, G., Tonacci, A., Musolino, C., & Gangemi, S. (2022). Critical Role of Aquaporins in Cancer: Focus on Hematological Malignancies. Cancers, 14(17), 4182. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14174182








