Treatment of Recurrent Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma: A Sequential Challenge
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
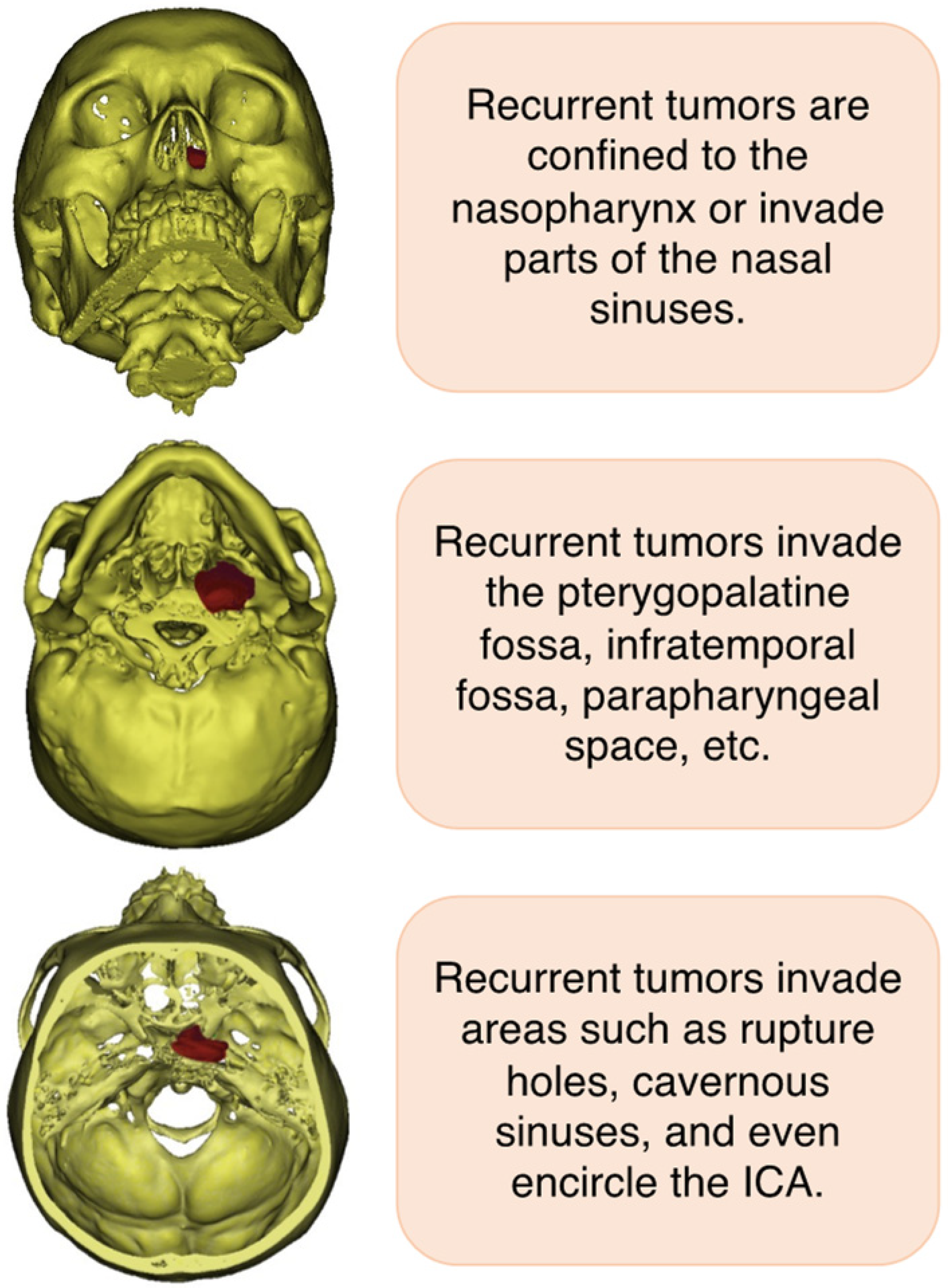
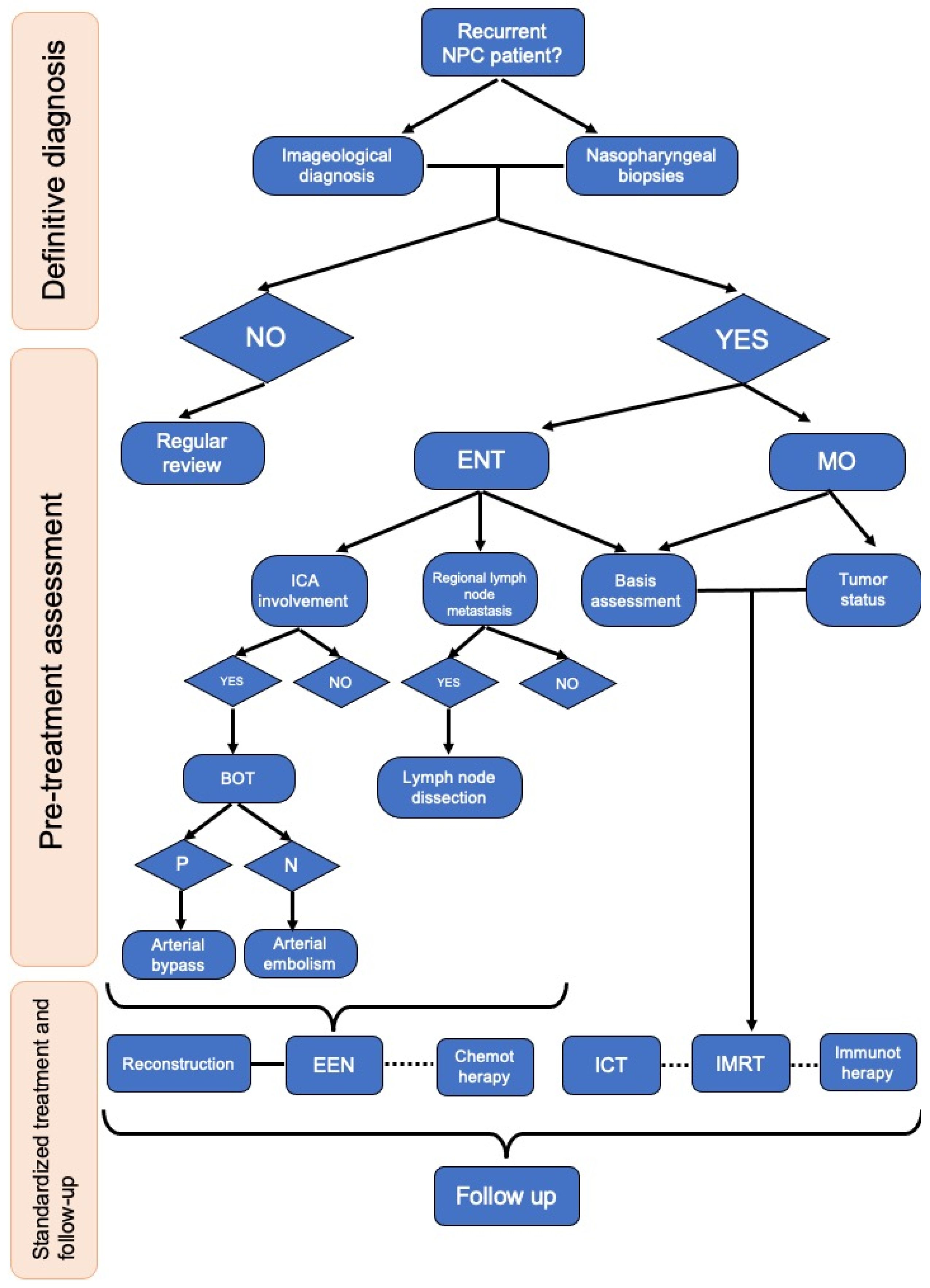
2. Clinical Symptom and Diagnosis of Recurrent NPC
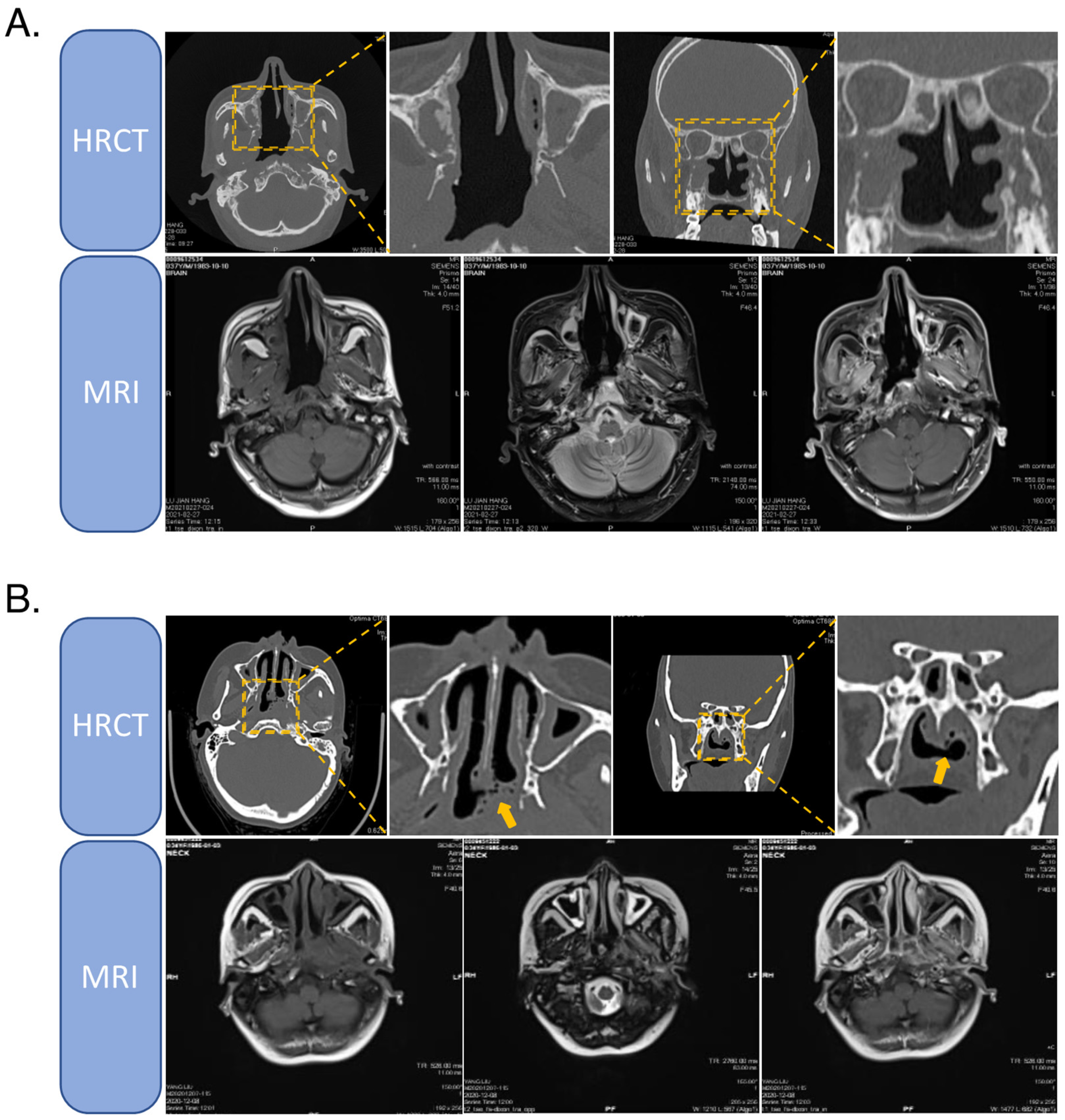
2.1. High-Resolution CT
2.2. Enhanced MRI
2.3. PET-CT
3. Treatment of Recurrent NPC
3.1. Re-Irradiation
3.2. Surgical Resection
3.3. Chemotherapy, Targeted Therapy, and Immunotherapy
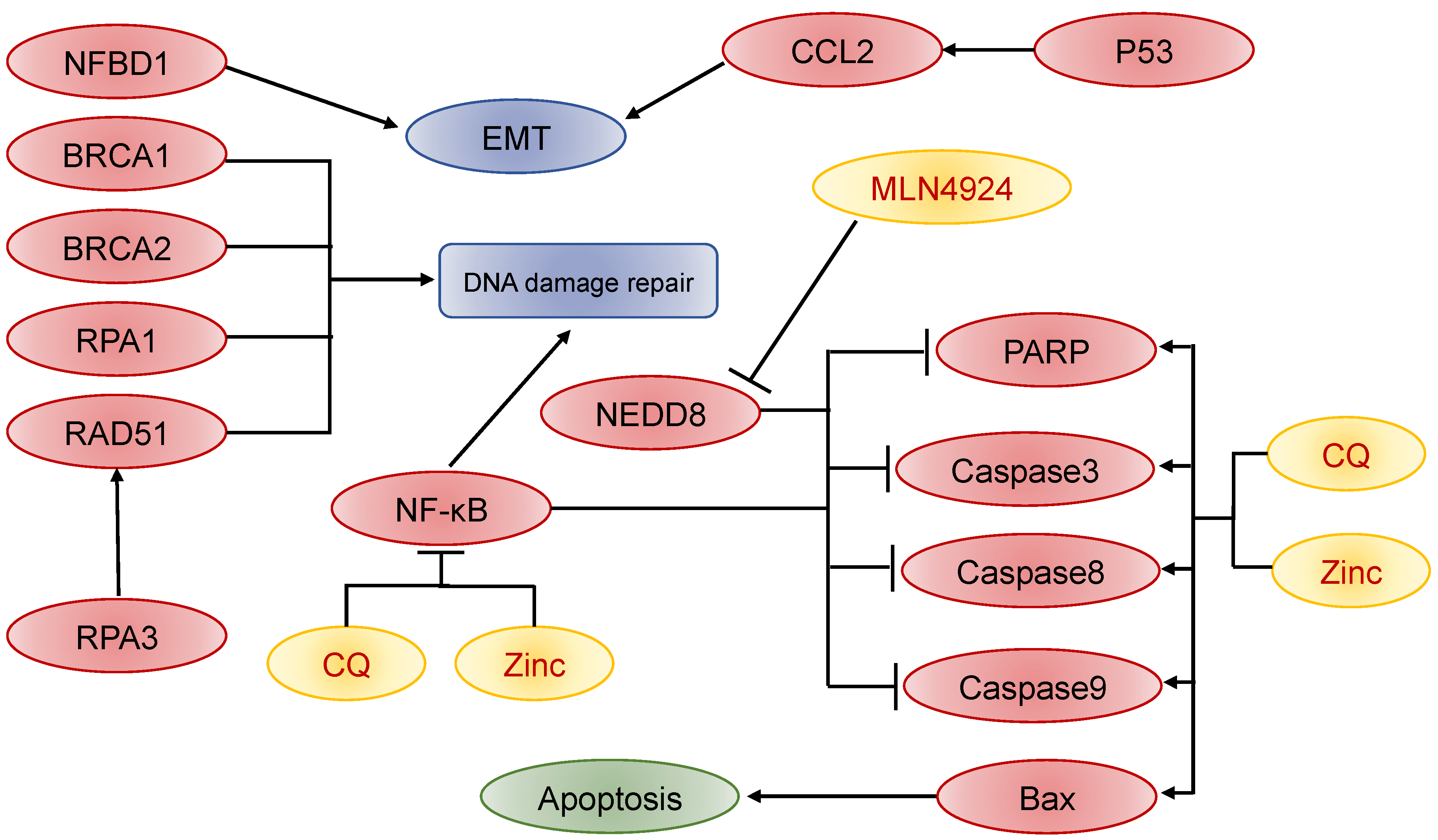
3.4. Biomarkers of Recurrent NPC
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, Y.P.; Chan, A.T.C.; Le, Q.T.; Blanchard, P.; Sun, Y.; Ma, J. Nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Lancet 2019, 394, 64–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Tang, J.; Gu, M.; Liu, L.; Wei, W.; Yang, H. Recurrent Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma: A Clinical Dilemma and Challenge. Curr. Oncol. 2013, 20, 406–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, S.; Fan, R.; Zhang, H.; Jiang, W. Application of radiomics and machine learning in head and neck cancers. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 17, 475–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Mo, Y.; Gong, Z.; Yang, X.; Yang, M.; Zhang, S.; Xiong, F.; Xiang, B.; Zhou, M.; Liao, Q.; et al. Circular RNAs in human cancer. Mol. Cancer 2017, 16, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, L.; Hu, G.Q.; Zhang, N.; Zhu, X.D.; Yang, K.Y.; Ma, J. Gemcitabine and Cisplatin Induction Chemotherapy in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 1124–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.-P.; Wen, Y.-H.; Tang, J.; Wei, Y.; You, R.; Zhu, X.-L.; Li, J.; Chen, L.; Ling, L.; Zhang, N.; et al. Endoscopic surgery compared with intensity-modulated radiotherapy in resectable locally recurrent nasopharyngeal carcinoma: A multicentre, open-label, randomised, controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2021, 22, 381–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Fan, R.; Gao, K.; Zhang, H.; Jiang, W. Preliminary Efficacy Report and Prognosis Analysis of Endoscopic Endonasal Nasopharyngectomy for Recurrent Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma. Front. Surg. 2021, 8, 713926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, C.-Y.; Hao, S.-P. The Management of rNPC: Salvage Surgery vs. Re-irradiation. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2020, 22, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Lu, H.; Wang, H.; Zhang, H.; Sun, X.; Hu, L.; Zhao, W.; Gu, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, D. Salvage Endoscopic Nasopharyngectomy in Recurrent Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma: Prognostic Factors and Treatment Outcomes. Am. J. Rhinol. Allergy 2020, 35, 458–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, J.Y.W.; Wei, W.I. Three-dimensional endoscopy for endoscopic salvage nasopharyngectomy: Preliminary report of experience. Laryngoscope 2017, 128, 1386–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.-P.; Lv, X.; Zou, X.; Hua, Y.-J.; You, R.; Yang, Q.; Xia, L.; Guo, S.-Y.; Hu, W.; Zhang, M.-X.; et al. Minimally invasive surgery alone compared with intensity-modulated radiotherapy for primary stage I nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer Commun. 2019, 39, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfister, D.G.; Spencer, S.; Adelstein, D.; Adkins, D.; Anzai, Y.; Brizel, D.M.; Darlow, S.D. Head and Neck Cancers, Version 2.2020, NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer. Netw. 2020, 18, 873–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, J.Y.W. Surgical management of recurrent nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Oral Oncol. 2014, 50, 913–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prawira, A.; Oosting, S.F.; Chen, T.W.; Santos, K.A.D.; Saluja, R.; Wang, L.; Siu, L.L.; Chan, K.K.W.; Hansen, A.R. Systemic therapies for recurrent or metastatic nasopharyngeal carcinoma: A systematic review. Br. J. Cancer 2017, 117, 1743–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, A.W.; Ng, W.T.; Chan, J.Y.; Corry, J.; Mäkitie, A.; Mendenhall, W.M.; Rinaldo, A.; Rodrigo, J.P.; Saba, N.F.; Strojan, P.; et al. Management of locally recurrent nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2019, 79, 101890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, R.; Zou, X.; Hua, Y.-J.; Han, F.; Li, L.; Zhao, C.; Hong, M.-H.; Chen, M.-Y. Salvage endoscopic nasopharyngectomy is superior to intensity-modulated radiation therapy for local recurrence of selected T1–T3 nasopharyngeal carcinoma–A case-matched comparison. Radiother. Oncol. 2015, 115, 399–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Fan, R.; Gao, K.; Zhang, H.; Jiang, W. Comparing the Effectiveness of Endoscopic Surgeries with Intensity-Modulated Radiotherapy for Recurrent rT3 and rT4 Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma: A Meta-Analysis. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 703954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.I.; Kwong, D.L. Recurrent nasopharyngeal carcinoma: Surgical salvage vs. additional chemoradiation. Curr. Opin. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2011, 19, 82–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, J.; Wei, J.; Si, J.; Qin, Y.; Li, M.; Liu, F.; Si, Y.; Su, J. Clinical outcomes of residual or recurrent nasopharyngeal carcinoma treated with endoscopic nasopharyngectomy plus chemoradiotherapy or with chemoradiotherapy alone: A retrospective study. PeerJ 2017, 5, 3912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, X.; Han, F.; Ma, W.-J.; Deng, M.-Q.; Jiang, R.; Guo, L.; Liu, Q.; Mai, H.-Q.; Hong, M.-H.; Chen, M.-Y. Salvage endoscopic nasopharyngectomy and intensity-modulated radiotherapy versus conventional radiotherapy in treating locally recurrent nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Head Neck 2014, 37, 1108–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, W.T.; Corry, J.; Langendijk, J.A.; Lee, A.W.; Mäkitie, A.; Mendenhall, W.M.; Rinaldo, A.; Rodrigo, J.P.; Saba, N.F.; Smee, R.; et al. Current management of stage IV nasopharyngeal carcinoma without distant metastasis. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2020, 85, 101995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, W.T.; Soong, Y.L.; Ahn, Y.C.; AlHussain, H.; Choi, H.C.; Corry, J.; Grégoire, V.; Harrington, K.J.; Hu, C.S.; Jensen, K.; et al. International Recommendations on Reirradiation by Intensity Modulated Radiation Therapy for Locally Recurrent Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2021, 110, 682–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, X.X.; Tong, L.H.; Chen, Y.F.; Li, F.L.; Tang, W.B.; Liu, Y.J.; Yang, W. A simplified T classification based on the 8th edition of the UICC/AJCC staging system for nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer Manag. Res. 2019, 11, 3163–3169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OuYang, P.-Y.; You, K.-Y.; Zhang, L.-N.; Xiao, Y.; Zhang, X.-M.; Xie, F.-Y. External validity of a prognostic nomogram for locoregionally advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma based on the 8th edition of the AJCC/UICC staging system: A retrospective cohort study. Cancer Commun. 2018, 38, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, E.H.C.; Liew, Y.T.; Loong, S.P.; Prepageran, N. Five-year Survival Data on the Role of Endoscopic Endonasal Nasopharyngectomy in Advanced Recurrent rT3 and rT4 Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 2019, 129, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, I.P.; Ngui, L.X.; Ramachandran, K.; Lim, L.Y.; Voon, P.J.; Yu, K.L.; Narayanan, P.; Carrau, R. A 4-year review of surgical and oncological outcomes of endoscopic endonasal transpterygoid nasopharyngectomy in salvaging locally recurrent nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Eur. Arch. Otorhinol. 2019, 276, 2475–2482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, E.H.C.; Liew, Y.T.; Lim, E.Y.L.; Abu Bakar, M.Z.; Prepageran, N. A preliminary report on the role of endoscopic endonasal nasopharyngectomy in recurrent rT3 and rT4 nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Eur. Arch. Otorhinol. 2016, 274, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, D.; Feng, H.; Lv, W.; Ashrafinia, S.; Yuan, Q.; Wang, Q.; Yang, W.; Feng, Q.; Chen, W.; Rahmim, A.; et al. Machine Learning Methods for Optimal Radiomics-Based Differentiation Between Recurrence and Inflammation: Application to Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Post-therapy PET/CT Images. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2019, 22, 730–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, S.; Lin, S.; Tham, I.W.; Pan, J.; Lu, J.; Lu, J.J. Intensity-Modulated Radiation Therapy in the Salvage of Locally Recurrent Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2012, 83, 676–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyata, T.; Yanagawa, M.; Hata, A.; Honda, O.; Yoshida, Y.; Kikuchi, N.; Tsubamoto, M.; Tsukagoshi, S.; Uranishi, A.; Tomiyama, N. Influence of field of view size on image quality: Ultra-high-resolution CT vs. conventional high-resolution CT. Eur. Radiol. 2020, 30, 3324–3333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vikgren, J.; Båth, M.; Johnsson, A.; Flinck, A.; Milde, H.; Thilander-Klang, A.; Kheddache, S. High-resolution computed tomography with single-slice computed tomography and 16-channel multidetector computed tomography: A comparison regarding visibility and motion artifacts. Acta Radiol. 2007, 48, 956–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Gao, K.L.; Xie, Z.H.; Zhang, J.Y.; Fan, R.H.; Wang, F.J.; Xie, S.M.; Jiang, W.H. Clinical study on endoscopic surgery for soft tissue necrosis of cranial base after radiotherapy for nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Zhonghua Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi 2021, 56, 26–32. [Google Scholar]
- Ng, S.H.; Chang, J.T.C.; Ko, S.F.; Wan, Y.L.; Tang, L.M.; Chen, W.C. MRI in recurrent nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Neuroradiology 1999, 41, 855–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olmi, P.; Fallai, C.; Colagrande, S.; Giannardi, G. Staging and follow-up of nasopharyngeal carcinoma: Magnetic resonance imaging versus computerized tomography. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 1995, 32, 795–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parlak, S.; Yazici, G.; Dolgun, A.; Ozgen, B. The evolution of bone marrow signal changes at the skull base in nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients treated with radiation therapy. Radiol. Med. 2021, 126, 818–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, K.; Tey, J.; Ho, F.C.H.; Asim, H.; Cheo, T. Utility of magnetic resonance imaging in determining treatment response and local recurrence in nasopharyngeal carcinoma treated curatively. BMC Cancer 2020, 20, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulaner, G.A.; Bodei, L. Hepatocellular Carcinoma Mimicking Neuroendocrine Tumor Metastasis on 68Ga-DOTATATE PET/CT. Clin. Nucl. Med. 2019, 44, 330–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, B.D.; Seetharam, M.; Ocal, T.I. 18F-FDG PET/CT Imaging of Trichoblastic Carcinoma with Nodal Metastasis. Clin. Nucl. Med. 2019, 44, e423–e424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, W.S.; Oh, J.S.; Roh, J.-L.; Kim, J.S.; Kim, S.-J.; Choi, S.-H.; Nam, S.Y.; Kim, S.Y. Prediction of distant metastasis and survival in adenoid cystic carcinoma using quantitative 18 F-FDG PET/CT measurements. Oral Oncol. 2017, 77, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.-M.; Liu, D.-F.; Xu, Y.-P.; Meng, T.; Zhu, F. PET/CT imaging in diagnosing lymph node metastasis of esophageal carcinoma and its comparison with pathological findings. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2016, 20, 1495–1500. [Google Scholar]
- Rahmim, A.; Lodge, M.A.; Karakatsanis, N.A.; Panin, V.Y.; Zhou, Y.; McMillan, A.; Cho, S.; Zaidi, H.; Casey, M.E.; Wahl, R.L. Dynamic whole-body PET imaging: Principles, potentials and applications. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2018, 46, 501–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kroenke, M.; Mirzoyan, L.; Horn, T.; Peeken, J.C.; Wurzer, A.; Wester, H.J.; Rauscher, I. Matched-Pair Comparison of 68Ga-PSMA-11 and 18F-rhPSMA-7 PET/CT in Patients with Primary and Biochemical Recurrence of Prostate Cancer: Frequency of Non-Tumor-Related Uptake and Tumor Positivity. J. Nucl. Med. 2021, 62, 1082–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusufaly, T.; Zou, J.; Nelson, T.; Williamson, C.; Simon, A.; Singhal, M.; Mell, L.K. Improved Prognosis of Treatment Failure in Cervical Cancer with Non-Tumor Positron Emission Tomography / Computed Tomography Radiomics. J. Nucl. Med. 2021, 63, 1087–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perlman, S.B.; Hall, B.S.; Reichelderfer, M. PET/CT Imaging of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Semin. Nucl. Med. 2013, 43, 420–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, B.; Hui, E.P.; King, A.; Leung, S.F.; Kam, M.K.; Mo, F.; Li, L.; Wang, K.; Loong, H.; Wong, A.; et al. Prospective evaluation of plasma Epstein–Barr virus DNA clearance and fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission scan in assessing early response to chemotherapy in patients with advanced or recurrent nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Br. J. Cancer 2018, 118, 1051–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Pang, Y.; Zheng, H.; Han, C.; Gu, J.; Sun, L.; Wu, H.; Wu, S.; Lin, Q.; Chen, H. Clinical utility of [68Ga]Ga-labeled fibroblast activation protein inhibitor (FAPI) positron emission tomography/computed tomography for primary staging and recurrence detection in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Eur. J. Med. Imaging 2021, 48, 3606–3617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, W.; Hu, J.; Lu, J.; Kong, L. RBE-weighted dose conversions for patients with recurrent nasopharyngeal carcinoma receiving carbon-ion radiotherapy from the local effect model to the microdosimetric kinetic model. Radiat. Oncol. 2020, 15, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.-L.; Huang, M.-Y.; Li, Y.; Liang, J.-H.; Gao, T.-S.; Deng, B.; Yao, J.-J.; Lin, L.; Chen, F.-P.; Huang, X.-D.; et al. Pretreatment MRI radiomics analysis allows for reliable prediction of local recurrence in non-metastatic T4 nasopharyngeal carcinoma. EBioMedicine 2019, 42, 270–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogan, C.A.; Rajpurkar, P.; Sowrirajan, H.; Phillips, N.A.; Le, A.T.; Wu, M.; Garamani, N.; Sahoo, M.K.; Wood, M.L.; Huang, C.; et al. Nasopharyngeal metabolomics and machine learning approach for the diagnosis of influenza. EBioMedicine 2021, 71, 103546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.; Lu, J.J. Reirradiation of locally recurrent nasopharyngeal cancer: History, advances, and promises for the future. Chin. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 5, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsang, R.K.; Wei, W.I. Salvage surgery for nasopharyngeal cancer. World J. Otorhinolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2015, 1, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Wang, J.; Tang, H.; Han, R.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhou, H. Comparing endoscopic surgeries with open surgeries in terms of effectiveness and safety in salvaging residual or recurrent nasopharyngeal cancer: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Head Neck 2020, 42, 3415–3426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Na’Ara, S.; Amit, M.; Billan, S.; Cohen, J.T.; Gil, Z. Outcome of Patients Undergoing Salvage Surgery for Recurrent Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma: A Meta-analysis. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2014, 21, 3056–3062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Song, X.; Sun, X.; Liu, Q.; Hu, L.; Yu, H.; Wang, D. Outcomes of recurrent nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients treated with endoscopic nasopharyngectomy: A meta-analysis. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2020, 10, 1001–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Q.; Zhang, M.; Chen, Y.; Zheng, D.; Chen, Y.; Feng, M. Establishment of prognostic factors in recurrent nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients who received salvage intensity-modulated radiotherapy: A meta-analysis. Oral Oncol. 2018, 81, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leong, Y.H.; Soon, Y.Y.; Lee, K.M.; Wong, L.C.; Tham, I.W.K.; Ho, F.C.H. Long-term outcomes after reirradiation in nasopharyngeal carcinoma with intensity-modulated radiotherapy: A meta-analysis. Head Neck 2017, 40, 622–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.C.; Cao, R.B.; Fu, C.; Chen, W.B.; Li, P.D.; Lin, G.H.; Liu, Q. The efficacy and safety of PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors in patients with recurrent or metastatic nasopharyngeal carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Oral Oncol. 2020, 104, 104640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyst, H.J.; Wildeman, M.A.; Indrasari, S.R.; Karakullukcu, B.; van Veen, R.L.; Adham, M.; Tan, I.B. Temoporfin mediated photodynamic therapy in patients with local persistent and recurrent nasopharyngeal carcinoma after curative radiotherapy: A feasibility study. Photodiagn. Photodyn. Ther. 2012, 9, 274–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Chen, X.; Wang, A.; Zhao, H.; Lin, Q.; Bao, H.; Zhang, Y.; Hong, S.; Tang, W.; Huang, Y.; et al. Copy number loss in granzyme genes confers resistance to immune checkpoint inhibitor in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. J. Immunother. Cancer 2021, 9, e002014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, T.; Zhang, Q.; Jin, Q.-F.; Hua, Y.-H.; Chen, X.-Z. Anti-PD1 checkpoint inhibitor with or without chemotherapy for patients with recurrent and metastatic nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Transl. Oncol. 2020, 14, 100989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, S.; Lu, J.; Zheng, W.; Xu, L.; Lin, S.; Huang, C.; Xu, Y.; Huang, L.; Pan, J. Advantages of intensity modulated radiotherapy in recurrent T1-2 nasopharyngeal carcinoma: A retrospective study. BMC Cancer 2014, 14, 797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dionisi, F.; Croci, S.; Giacomelli, I.; Cianchetti, M.; Caldara, A.; Bertolin, M.; Vanoni, V.; Pertile, R.; Widesott, L.; Farace, P.; et al. Clinical results of proton therapy reirradiation for recurrent nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Acta Oncol. 2019, 58, 1238–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Huang, Q.; Gao, J.; Guan, X.; Hu, W.; Yang, J.; Qiu, X.; Chen, M.; Kong, L.; Lu, J.J. Clinical outcomes of carbon-ion radiotherapy for patients with locoregionally recurrent nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer 2020, 126, 5173–5183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Bao, C.; Gao, J.; Guan, X.; Hu, W.; Yang, J.; Hu, C.; Kong, L.; Lu, J.J. Salvage treatment using carbon ion radiation in patients with locoregionally recurrent nasopharyngeal carcinoma: Initial results. Cancer 2018, 124, 2427–2437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Hu, J.; Liu, X.; Wang, W.; Kong, L.; Lu, J.J. Intensity-modulated carbon-ion radiation therapy versus intensity-modulated photon-based radiation therapy in locally recurrent nasopharyngeal carcinoma: A dosimetric comparison. Cancer Manag. Res. 2019, 11, 7767–7777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, F.; Zhao, C.; Huang, S.-M.; Lu, L.-X.; Huang, Y.; Deng, X.-W.; Mai, W.-Y.; Teh, B.S.; Butler, E.B.; Lu, T.-X. Long-term Outcomes and Prognostic Factors of Re-irradiation for Locally Recurrent Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma using Intensity-modulated Radiotherapy. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 24, 569–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, Y.-J.; Han, F.; Lu, L.-X.; Mai, H.-Q.; Guo, X.; Hong, M.-H.; Lu, T.-X.; Zhao, C. Long-term treatment outcome of recurrent nasopharyngeal carcinoma treated with salvage intensity modulated radiotherapy. Eur. J. Cancer 2012, 48, 3422–3428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.-Y.; Ma, X.-M.; Ye, M.; Hou, Y.-L.; Xie, H.-Y.; Bai, Y.-R. Effectiveness and Toxicities of Intensity-Modulated Radiotherapy for Patients with Locally Recurrent Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e73918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.-M.; Tian, Y.-H.; Zeng, L.; Liu, S.; Guan, Y.; Lu, T.-X.; Han, F. Prognostic model for survival of local recurrent nasopharyngeal carcinoma with intensity-modulated radiotherapy. Br. J. Cancer 2013, 110, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karam, I.; Huang, S.H.; McNiven, A.; Su, J.; Xu, W.; Waldron, J.; Bayley, A.J.; Kim, J.; Cho, J.; Ringash, J.; et al. Outcomes after reirradiation for recurrent nasopharyngeal carcinoma: North American experience. Head Neck 2015, 38, E1102–E1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.; Liu, S.; Tian, Y.; Guan, Y.; Huang, S.; Lin, C.; Zhao, C.; Lu, T.; Han, F. Prognostic Significance of Tumor Volume in Locally Recurrent Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Treated with Salvage Intensity-Modulated Radiotherapy. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0125351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, O.S.H.; Sze, H.C.K.; Lee, M.C.H.; Chan, L.L.K.; Chang, A.T.Y.; Lee, S.W.M.; Hung, W.M.; Lee, A.W.M.; Ng, W.T. Reirradiation with intensity-modulated radiotherapy for locally recurrent T3 to T4 nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Head Neck 2016, 39, 533–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.-M.; Huang, W.-Z.; Yuan, X.; Bai, L.; Zhao, C.; Han, F. The challenge in treating locally recurrent T3-4 nasopharyngeal carcinoma: The survival benefit and severe late toxicities of re-irradiation with intensity-modulated radiotherapy. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 43450–43457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, W.-T.; Ngan, R.K.; Kwong, D.L.; Tung, S.Y.; Yuen, K.-T.; Kam, M.K.; Sze, H.C.; Yiu, H.H.; Chan, L.L.; Lung, M.L.; et al. Prospective, Multicenter, Phase 2 Trial of Induction Chemotherapy Followed by Bio-Chemoradiotherapy for Locally Advanced Recurrent Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2017, 100, 630–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, F.; Zhou, J.; Du, C.; He, X.; Kong, L.; Hu, C.; Ying, H. Long-term survival and late complications of intensity-modulated radiotherapy for recurrent nasopharyngeal carcinoma. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.H.; Zhang, X.W.; Jiang, H. Clinical Efficacy and Prognostic Factors of Locally Recurrent Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma With Intensity- Modulated Radiotherapy. J. Shanghai Jiao Tong Univ. 2018, 38, 662–669. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshizaki, T.; Wakisaka, N.; Murono, S.; Shimizu, Y.; Furukawa, M. Endoscopic Nasopharyngectomy for Patients with Recurrent Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma at the Primary Site. Laryngoscope 2005, 115, 1517–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.-K.; Lai, J.-C.; Chang, C.-C.; Liu, M.-T. Minimally Invasive Endoscopic Nasopharyngectomy in the Treatment of Recurrent T1-2a Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma. Laryngoscope 2007, 117, 894–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.-Y.; Wen, W.-P.; Guo, X.; Yang, A.-K.; Qian, C.-N.; Hua, Y.-J.; Wan, X.-B.; Guo, Z.-M.; Li, T.-Y.; Hong, M.-H. Endoscopic nasopharyngectomy for locally recurrent nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Laryngoscope 2009, 119, 516–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, J.Y.W.; Wei, W.I. Critical appraisal of maxillary swing approach for nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2012, 16 (Suppl. 1), S111–S117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, H.-Q.; Mo, H.-Y.; Deng, J.-F.; Deng, M.-Q.; Mai, W.-Y.; Huang, X.-M.; Guo, X.; Hong, M.-H. Endoscopic microwave coagulation therapy for early recurrent T1 nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Eur. J. Cancer 2009, 45, 1107–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.; Weng, X.; Wu, X.; Wu, L. The efficacy and safety of apatinib in patients with recurrent or metastatic nasopharyngeal carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Transl. Cancer Res. 2022, 11, 1770–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, A.S.; Kaplan, M.J.; Fee, W.E., Jr.; Yao, M.; Sunwoo, J.B.; Hwang, P.H. Targeted endoscopic salvage nasopharyngectomy for recurrent nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2011, 2, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castelnuovo, P.; Nicolai, P.; Turri-Zanoni, M.; Battaglia, P.; Villaret, A.B.; Gallo, S.; Bignami, M.; Dallan, I. Endoscopic Endonasal Nasopharyngectomy in Selected Cancers. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2013, 149, 424–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emanuelli, E.; Albu, S.; Cazzador, D.; Pedruzzi, B.; Babighian, G.; Martini, A. Endoscopic Surgery for Recurrent Undifferentiated Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma. J. Craniofacial Surg. 2014, 25, 1003–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Qiu, Q. Analysis of Clinical Eifcacy and the Quality of Life After Endoscopic Nasopharyngectomy for Residual or Recurrent Nasopharyngela Carcinoma. Zhonghua Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi 2015, 50, 96–903. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vlantis, A.; Lee, D.L.; Wong, E.W.; Chow, S.M.; Ng, S.K.; Chan, J.Y. Endoscopic nasopharyngectomy in recurrent nasopharyngeal carcinoma: A case series, literature review, and pooled analysis. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2016, 7, 425–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Yu, H.; Sun, X.; Wang, D.; Gu, Y.; Liu, Q.; Wang, H.; Han, W.; Fry, A. Salvage endoscopic nasopharyngectomy for local recurrent or residual nasopharyngeal carcinoma: A 10-year experience. Int. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 22, 834–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Liu, J.; Wang, H.; Yu, H.; Wang, J.; Li, H.; Gu, Y.; Guo, L.; Wang, D. [Endoscopic nasopharyngectomy for recurrent nasopharyngeal carcinoma: A review of 71 patients and analysis of the prognostic factors]. Zhonghua Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi 2015, 50, 890–895. [Google Scholar]
- Thamboo, A.; Patel, V.S.; Hwang, P.H. 5-year outcomes of salvage endoscopic nasopharyngectomy for recurrent nasopharyngeal carcinoma. J. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2021, 50, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Wu, H.; Chen, B.; Sun, W.; Hu, X.; Wang, T.; Guo, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Dai, J. Balloon Test Occlusion of Internal Carotid Artery in Recurrent Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Before Endoscopic Nasopharyngectomy: A Single Center Experience. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 674889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hetzel, A.; Von Reutern, G.-M.; Wernz, M.; Droste, D.; Schumacher, M. The Carotid Compression Test for Therapeutic Occlusion of the Internal Carotid Artery. Comparison of angiography with transcranial Doppler sonography. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2000, 10, 194–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tani, S.; Imamura, H.; Asai, K.; Shimizu, K.; Adachi, H.; Tokunaga, S.; Sakai, N. Comparison of practical methods in clinical sites for estimating cerebral blood flow during balloon test occlusion. J. Neurosurg. 2018, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tayebi Meybodi, A.; Huang, W.; Benet, A.; Kola, O.; Lawton, M.T. Bypass surgery for complex middle cerebral artery aneurysms: An algorithmic approach to revascularization. J. Neurosurg. 2017, 127, 463–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nurminen, V.; Kivipelto, L.; Kivisaari, R.; Niemelä, M.; Lehecka, M. Bypass Surgery for Complex Internal Carotid Artery Aneurysms: 39 Consecutive Patients. World Neurosurg. 2019, 126, e453–e462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- A Laurie, S.; Ho, A.L.; Fury, M.G.; Sherman, E.; Pfister, D.G. Systemic therapy in the management of metastatic or locally recurrent adenoid cystic carcinoma of the salivary glands: A systematic review. Lancet Oncol. 2011, 12, 815–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birtle, A.; Johnson, M.; Chester, J.; Jones, R.; Dolling, D.; Bryan, R.T.; Harris, C.; Winterbottom, A.; Blacker, A.; Catto, J.; et al. Adjuvant chemotherapy in upper tract urothelial carcinoma (the POUT trial): A phase 3, open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2020, 395, 1268–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlachostergios, P.; Faltas, B.M. Treatment resistance in urothelial carcinoma: An evolutionary perspective. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 15, 495–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saygin, C.; Carraway, H.E. Emerging therapies for acute myeloid leukemia. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2017, 10, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Li, M.M.; Chen, W.H.; Zhao, J.F.; Chen, W.Q.; Dong, Y.H.; Zhang, S.X. Association of Chemoradiotherapy Regimens and Survival among Patients with Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA Netw. Open. 2019, 2, e1913619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Z.; Wang, Y.; Fang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yuan, X.; Shuai, M.; Xie, S.; Fan, R.; Zhang, H.; Xie, Z.; et al. Salvage Endoscopic Skull Base Surgery: Another Treatment Option after Immunotherapy for Recurrent Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 899932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruan, X.; Liang, J.; Pan, Y.; Cai, R.; Zhang, R.J.; He, Z.; Yang, X.; Niu, Z.; Jiang, W. Apatinib for the treatment of metastatic or locoregionally recurrent nasopharyngeal carcinoma after failure of chemotherapy: A multicenter, single-arm, prospective phase 2 study. Cancer 2021, 127, 3163–3171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, Z.; Lui, V.W.Y.; Li, Y.; Jia, L.; You, C.; Li, X.; Piao, W.; Yuan, H.; Khong, P.L.; Lo, K.W.; et al. Therapeutic evaluation of palbociclib and its compatibility with other chemotherapies for primary and recurrent nasopharyngeal carcinoma. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 39, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, W.; Lee, M.C.; Fung, N.T.; Wong, E.C.; Cheung, A.K.; Chow, J.C.; Au, K.; Mc Poon, D.; Lai, J.W.; Chiang, C.; et al. Dose volume effects of re-irradiation for locally recurrent nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Head Neck 2019, 42, 180–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.-L.; Guo, R.; Li, J.-Y.; Xu, C.; Mao, Y.-P.; Tian, L.; Lin, A.-H.; Sun, Y.; Ma, J.; Tang, L.-L. Nasopharyngeal carcinoma treated with intensity-modulated radiotherapy: Clinical outcomes and patterns of failure among subsets of 8th AJCC stage IVa. Eur. Radiol. 2019, 30, 816–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Z.-Q.; Jiang, Y.-X.; Wang, F.-H.; Luo, H.-Y.; Liang, Y.; Wang, D.-S.; Li, Y.-H. A triplet chemotherapy regimen of cisplatin, fluorouracil and paclitaxel for locoregionally recurrent nasopharyngeal carcinoma cases contraindicated for re-irradiation/surgery. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2016, 17, 1585–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.H.; Luo, S.D.; Wu, S.C.; Wu, C.N.; Chiu, T.J.; Wang, Y.M.; Yang, Y.H.; Chen, W.C. Clinical Characteristics and Predictive Outcomes of Recurrent Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma-A Lingering Pitfall of the Long Latency. Cancers 2022, 14, 3795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Wang, F.-H.; An, X.; Luo, H.-Y.; Wang, Z.-Q.; Liang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Li, Y.-H. Triplet combination with paclitaxel, cisplatin and 5-FU is effective in metastatic and/or recurrent nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2012, 71, 371–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, C.; Huang, Y.; Huang, P.Y.; Yu, Q.T.; Pan, J.J.; Liu, L.Z.; Song, X.Q.; Lin, S.J.; Wu, J.X.; Zhang, J.W.; et al. Phase II study of sorafenib in combination with cisplatin and 5-fluorouracil to treat recurrent or metastatic nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Ann. Oncol. 2012, 24, 1055–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, P.-J.; Cheng, H.; Ou, X.-Q.; Zeng, L.-J.; Wu, X.; Liu, Y.-M.; Lin, Z.; Tang, Y.-N.; Wang, S.-Y.; Zhang, H.-Y.; et al. Safety and efficacy of S-1 chemotherapy in recurrent and metastatic nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients after failure of platinum-based chemotherapy: Multi-institutional retrospective analysis. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2014, 8, 1083-7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, P.-J.; Lv, B.-J.; Wang, Z.-H.; Liao, H.; Liu, Y.-M.; Lin, Z.; Con, Y.-Y.; Huang, P.-Y. Multi-institutional prospective study of nedaplatin plus S-1 chemotherapy in recurrent and metastatic nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients after failure of platinum-containing regimens. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2016, 9, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Liang, W.; Wan, N.; Zhang, L.; Yang, Y.; Jiang, J.; Zhang, T. Cost-effectiveness analysis of gemcitabine plus cisplatin versus fluorouracil plus cisplatin for first-line treatment of recurrent or metastatic nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Oral Oncol. 2019, 94, 80–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, G.; Peng, P.; Peng, J.; Jia, J.; Wu, X.; Huang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Lin, Q.; et al. Gemcitabine Plus Cisplatin Versus Fluorouracil Plus Cisplatin as First-Line Therapy for Recurrent or Metastatic Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma: Final Overall Survival Analysis of GEM20110714 Phase III Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 3273–3282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Huang, Y.; Hong, S.; Yang, Y.; Yu, G.; Jia, J.; Peng, P.; Wu, X.; Lin, Q.; Xi, X.; et al. Gemcitabine plus cisplatin versus fluorouracil plus cisplatin in recurrent or metastatic nasopharyngeal carcinoma: A multicentre, randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2016, 388, 1883–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, J.-F.; Liang, Q.-D.; Lu, Q.-J.; Liu, Y.-H.; Xu, H.-C.; Chen, B.-J.; Guo, Q.-J.; Xu, Y.; Hu, C.-R.; Pan, J.-J.; et al. Comparison of radiotherapy combined with nimotuzumab vs. chemoradiotherapy for locally recurrent nasopharyngeal carcinoma. BMC Cancer 2021, 21, 1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, B.B.Y.; Lim, W.T.; Goh, B.C.; Hui, E.P.; Lo, K.W.; Pettinger, A.; Chan, A.T. Antitumor Activity of Nivolumab in Recurrent and Metastatic Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma: An International, Multicenter Study of the Mayo Clinic Phase 2 Consortium (NCI-9742). J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 1412–1418, Correction in J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 2360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, J.-W.; Li, J.-Y.; Luo, L.-N.; Wang, Z.-X.; Chen, Y.-P. Comparative safety and efficacy of anti-PD-1 monotherapy, chemotherapy alone, and their combination therapy in advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma: Findings from recent advances in landmark trials. J. Immunother. Cancer 2019, 7, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Yang, S.; Zhou, S.; Yang, J.; Qin, Y.; Gui, L.; Shi, Y.; He, X. Nimotuzumab plus platinum-based chemotherapy versus platinum-based chemotherapy alone in patients with recurrent or metastatic nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2020, 12, 1758835920953738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, W.Q.; Lim, C.M.; Sinha, A.K.; Tan, C.S.; Chan, G.H.J.; Huang, Y.; Kumarakulasinghe, N.B.; Sundar, R.; Jeyasekharan, A.D.; Loh, W.S.; et al. Integration of Antiangiogenic Therapy with Cisplatin and Gemcitabine Chemotherapy in Patients with Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 5320–5328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Qu, S.; Li, J.; Hu, C.; Xu, M.; Li, W.; Zhou, T.; Shen, L.; Wu, H.; Lang, J.; et al. Camrelizumab versus placebo in combination with gemcitabine and cisplatin as first-line treatment for recurrent or metastatic nasopharyngeal carcinoma (CAPTAIN-1st): A multicentre, randomised, double-blind, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2021, 22, 1162–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.-S.; Liu, R.; Wen, Y.-F.; Liu, L.-T.; Yuan, L.; Li, Y.-X.; Li, Y.; Hao, W.-W.; Peng, J.-Y.; Chen, D.-N.; et al. Endogenous production of C-C motif chemokine ligand 2 by nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells drives radioresistance-associated metastasis. Cancer Lett. 2020, 468, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zuo, W.; Zeng, Q.; Li, Y.; Lu, T.; Bu, Y.; Hu, G. The Homologous Recombination Repair Pathway is Associated with Resistance to Radiotherapy in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 16, 408–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, P.; Yang, J.-P.; Cao, Y.; Peng, L.-X.; Zheng, L.-S.; Sun, R.; Meng, D.-F.; Wang, M.-Y.; Mei, Y.; Qiang, Y.-Y.; et al. Promoting tumorigenesis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma, NEDD8 serves as a potential theranostic target. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e2834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.-C.; Hsu, T.; Chang, Y.-S.; Chung, A.-K.; Jiang, S.S.; Ouyang, C.-N.; Yuh, C.-H.; Hsueh, C.; Liu, Y.-P.; Tsang, N.-M. Cytoplasmic LIF reprograms invasive mode to enhance NPC dissemination through modulating YAP1-FAK/PXN signaling. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 5105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ke, Y.; Wu, C.; Zeng, Y.; Chen, M.; Li, Y.; Xie, C.; Zhou, Y.; Zhong, Y.; Yu, H. Radiosensitization of Clioquinol Combined with Zinc in the Nasopharyngeal Cancer Stem-like Cells by Inhibiting Autophagy In Vitro and In Vivo. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 16, 777–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valouev, A.; Weng, Z.; Sweeney, R.T.; Varma, S.; Le, Q.-T.; Kong, C.; Sidow, A.; West, R.B. Discovery of recurrent structural variants in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Genome Res. 2013, 24, 300–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, C.; Zhao, Y.; Feng, G.; Chen, C.; Tao, Y.; Zhou, S.; Liu, S.; Chang, H.; Zeng, M.; Xia, Y. RPA3 is a potential marker of prognosis and radioresistance for nasopharyngeal carcinoma. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2017, 21, 2872–2883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Year | No. of Patients | M/F | rT Classification | ReRT Mean Dose (Gy) | CCT | OS Rate (%) | DFS (%) | LCR/LRFS (%) | Median Follow-Up Time (Months) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rT1-2 | rT3-4 | 2-Year | 3-Year | 5-Year | 2-Year | 5-Year | 3-Year | 5-Year | |||||||
| Qiu et al. [29] | 2012 | 70 | 56/14 | 30 | 40 | 70.0 (50.0–77.4) | 18 | 67.4 | - | - | 65.8 | - | - | - | 25.0 (3.0–80.0) |
| Han et al. [66] | 2012 | 239 | 182/57 | 59 | 180 | 70.0 (61.7–77.5) | 117 | - | - | 44.9 | - | 45.4 | - | 85.8 | 12.0 (3.0–62.0) |
| Hua et al. [67] | 2012 | 151 | 122/29 | 29 | 122 | 70.4 (62.1–77.6) | 37 | - | 46.4 | 38.0 | - | - | 83.2 | 80.7 | 40.0 (7.2–116.9) |
| Chen et al. [68] | 2013 | 54 | 44/10 | 11 | 43 | 70.0 (49.8–76.6) | 18 | 44.3 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 16.5 (1.0–93.0) |
| Tian et al. [69] | 2013 | 251 | 195/56 | 53 | 198 | 70.7 (61.1–79.7) | 126 | - | 53.2 | 41.1 | - | - | 80.6 | 75.1 | 40.0 (3.0–147.0) |
| Karam et al. [70] | 2015 | 27 | 20/7 | 21 | 6 | 54.0 (39.0–97.0) | 23 | - | 53.0 | - | - | - | 53.0 | - | 36.0 |
| You et al. [16] | 2015 | 72 | 18/54 | 59 | 13 | - | 42 | - | - | 55.5 | 50.0 | - | - | 82.3 | 49.4 (3.1–149.0) |
| Zou et al. [20] | 2015 | 218 | 173/45 | 57 | 161 | - | 84 | - | - | 39.0 | - | - | - | - | 33.0 (2.0–146.0) |
| Xiao et al. [71] | 2015 | 291 | 225/66 | 47 | 244 | - | 120 | - | - | 33.2 | - | - | - | 66.6 | 29.0 (3.1–146.0) |
| Chan et al. [72] | 2016 | 38 | 31/7 | 0 | 38 | - | 8 | - | 47.2 | - | - | - | 44.3 | - | 47.8 (13.5–118.1) |
| Tian et al. [73] | 2017 | 245 | 196/49 | 0 | 245 | 70.0 (60.1–78.7) | 157 | - | - | 27.5 | - | - | - | 60.9 | 24.0 (2.0–132.0) |
| Ng et al. [74] | 2017 | 33 | - | 0 | 33 | - | - | - | 63.8 | - | - | - | 49.2 | - | 28.5 |
| Kong et al. [75] | 2018 | 184 | 133/51 | 64 | 120 | 66.7 (42.0–77) | 138 | - | 46.0 | 28.8 | - | - | 85.1 | 71.1 | 32.0 (3.0–125.0) |
| Zhang et al. [76] | 2019 | 44 | 33/11 | 21 | 23 | 66.0 (54.0–70.0) | 33 | - | 56.8 | - | - | - | 58.9 | - | 28.0 (5.0–168.0) |
| Liu et al. [6] | 2021 | 100 | 72/28 | 69 | 31 | - | - | 77.7 | 68.0 | 57.2 | 81.8 | 59.0 | 89.8 | 77.0 | - |
| Authors | Year | NO. of Patients | M/F | rT Classifications | Margin(+/−) | Margins+ Therapy | OS Rate (%) | DFS Rate (%) | Mean Follow-Up Time (Months) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rT1-2 | rT3-4 | 2-Year | 5-Year | 2-Year | 5-Year | |||||||
| Ho et al. [83] | 2012 | 13 | 9/4 | 11 | 2 | 4/9 | Y | 100 | - | - | 24.2 | |
| Castelnuovo et al. [84] | 2013 | 27 | - | 13 | 14 | 3/24 | - | 81.5 | 75.1 | 70.4 | 58.1 | 31.2 |
| Emanuelli et al. [85] | 2014 | 8 | 6/2 | 8 | 0 | - | - | 100 | - | 88.9 | - | 27.0 |
| You et al. [16] | 2015 | 72 | 54/18 | 59 | 13 | - | - | - | 77.1 | - | - | - |
| Zou et al. [20] | 2015 | 92 | 22/70 | 79 | 13 | - | - | - | 78.1 | - | - | - |
| Chen et al. [86] | 2015 | 96 | 72/24 | 38 | 58 | 51/44 | - | 51.7 | - | - | - | - |
| Wong et al. [27] | 2016 | 15 | - | 0 | 15 | 6/9 | Y | 66.7 | - | 40.0 | - | 28.7 |
| Vlantis et al. [87] | 2016 | 18 | 11/7 | 18 | 0 | 2/16 | N | 100 | 88.9 | 90.0 | - | 22.0 |
| Weng et al. [19] | 2017 | 36 | 26/10 | 17 | 19 | - | - | 66.5 | - | 64.0 | - | 54.0 |
| Liu et al. [88] | 2017 | 91 | 71/20 | 43 | 48 | - | - | 64.8 | 38.3 | 57.5 | 30.2 | median 23.0 |
| Sun et al. [89] | 2015 | 71 | 53/18 | 37 | 34 | 17/20 | - | 56.3 | - | - | - | - |
| Tang et al. [82] | 2019 | 55 | 44/11 | 45 | 10 | 4/51 | - | 98.2 | - | - | - | 18.0 |
| Wong et al. [25] | 2019 | 12 | - | 0 | 12 | - | - | - | 50 | - | 25 | 44.8 |
| Li et al. [9] | 2020 | 189 | 132/57 | 97 | 92 | 32/157 | - | 82.2 | 43.6 | - | - | median 24.0 |
| Thamboo et al. [90] | 2021 | 13 | 9/4 | 11 | 2 | 3/10 | Y | 100 | 84.6 | 76.9 | 53.8 | 74.3 |
| Liu et al. [6] | 2021 | 96 | - | 66 | 30 | 6/90 | - | 89.9 | 73.8 | 81.8 | 59.0 | median 56.0 |
| Peng et al. [7] | 2021 | 56 | 38/18 | 13 | 43 | - | - | 48.6 | - | 42.6 | - | 44.0 |
| Complications | No. of Patients in IMRT (Median, Range, %) | No. of Patients in EEN (Median, Range, %) |
|---|---|---|
| Cranial nerve palsies | 11.4 (7.1–28.6) | 13.9 |
| Headache | 17.3 (8.7–23.1) | 24.0 (9.7–25.0) |
| Trismus | 22.2 (7.9–46.2) | 9.7 |
| Deafness | 29.3 (4.5–65.4) | 11.1 (6.9–34.0) |
| Otitis media | 23.1 | 30.8 (25.0–70.0) |
| Necrosis (including ON, TLN, NN) | 46.2 (3.6–63.7) | 23.1 (6.9–44.4) |
| Dysphagia | 17.3 (5.5–26.3) | 8.3 (7.7–9.3) |
| Hemorrhage | 15.8 (11.5–17.2) | 6.0 (2.8–9.9) |
| Sinusitis | 40.6 | 12.0 (5.0–15.4) |
| Xerostomia | 30.8 | 11.1–17.9 |
| Neck fibrosis | 26.3 (0.5–34.6) | - |
| Cachexia | 15.3 | 4.2–10.7 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Peng, Z.; Wang, Y.; Fan, R.; Gao, K.; Xie, S.; Wang, F.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, H.; He, Y.; Xie, Z.; et al. Treatment of Recurrent Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma: A Sequential Challenge. Cancers 2022, 14, 4111. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14174111
Peng Z, Wang Y, Fan R, Gao K, Xie S, Wang F, Zhang J, Zhang H, He Y, Xie Z, et al. Treatment of Recurrent Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma: A Sequential Challenge. Cancers. 2022; 14(17):4111. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14174111
Chicago/Turabian StylePeng, Zhouying, Yumin Wang, Ruohao Fan, Kelei Gao, Shumin Xie, Fengjun Wang, Junyi Zhang, Hua Zhang, Yuxiang He, Zhihai Xie, and et al. 2022. "Treatment of Recurrent Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma: A Sequential Challenge" Cancers 14, no. 17: 4111. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14174111
APA StylePeng, Z., Wang, Y., Fan, R., Gao, K., Xie, S., Wang, F., Zhang, J., Zhang, H., He, Y., Xie, Z., & Jiang, W. (2022). Treatment of Recurrent Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma: A Sequential Challenge. Cancers, 14(17), 4111. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14174111






