Regulation and Function of Matrix Metalloproteinase-13 in Cancer Progression and Metastasis
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
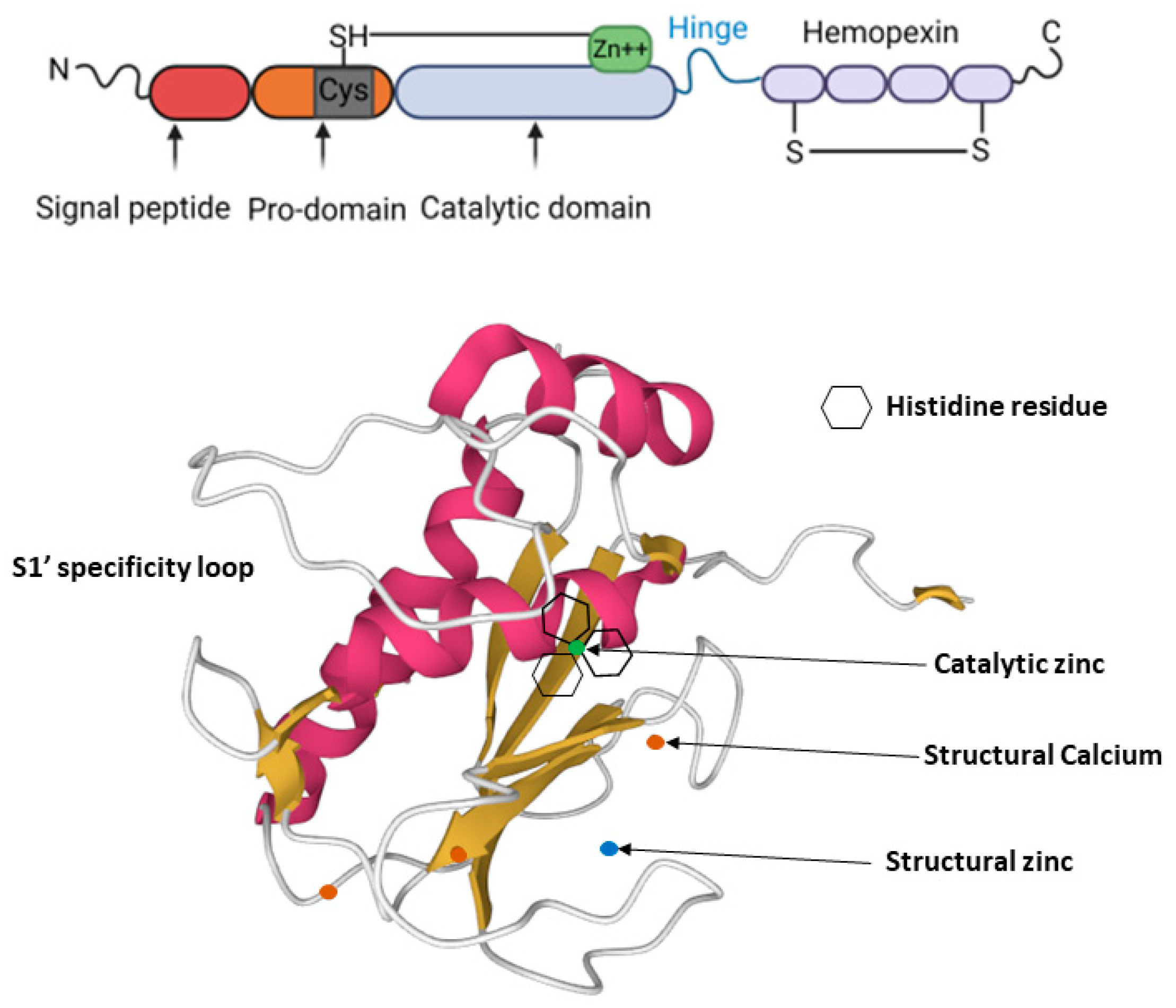
2. MMP-13 Structure
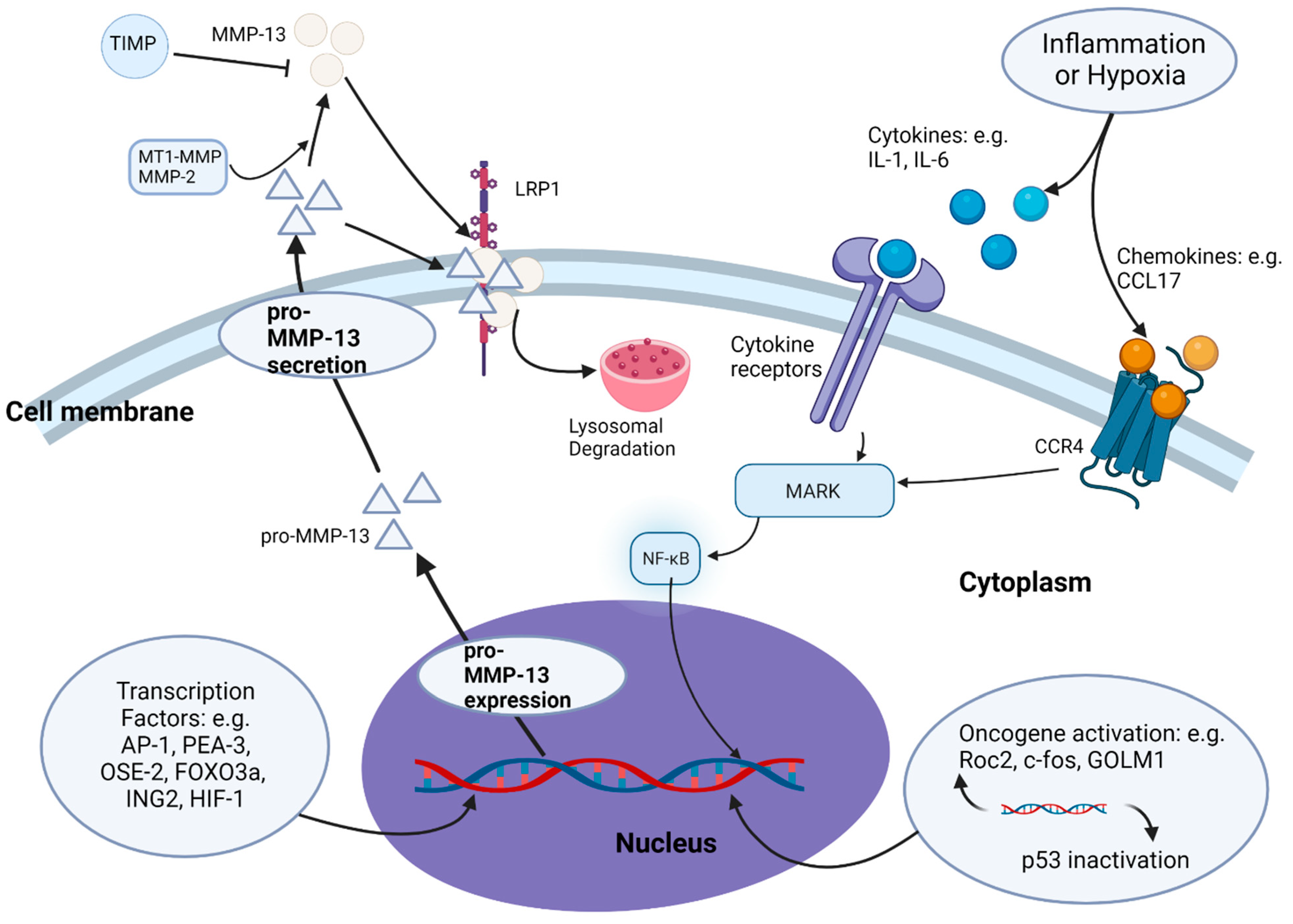
3. Regulation of MMP-13 Expression and Secretion
4. MMP-13 Expression in Cancer
5. MMP-13 in Tumour Growth
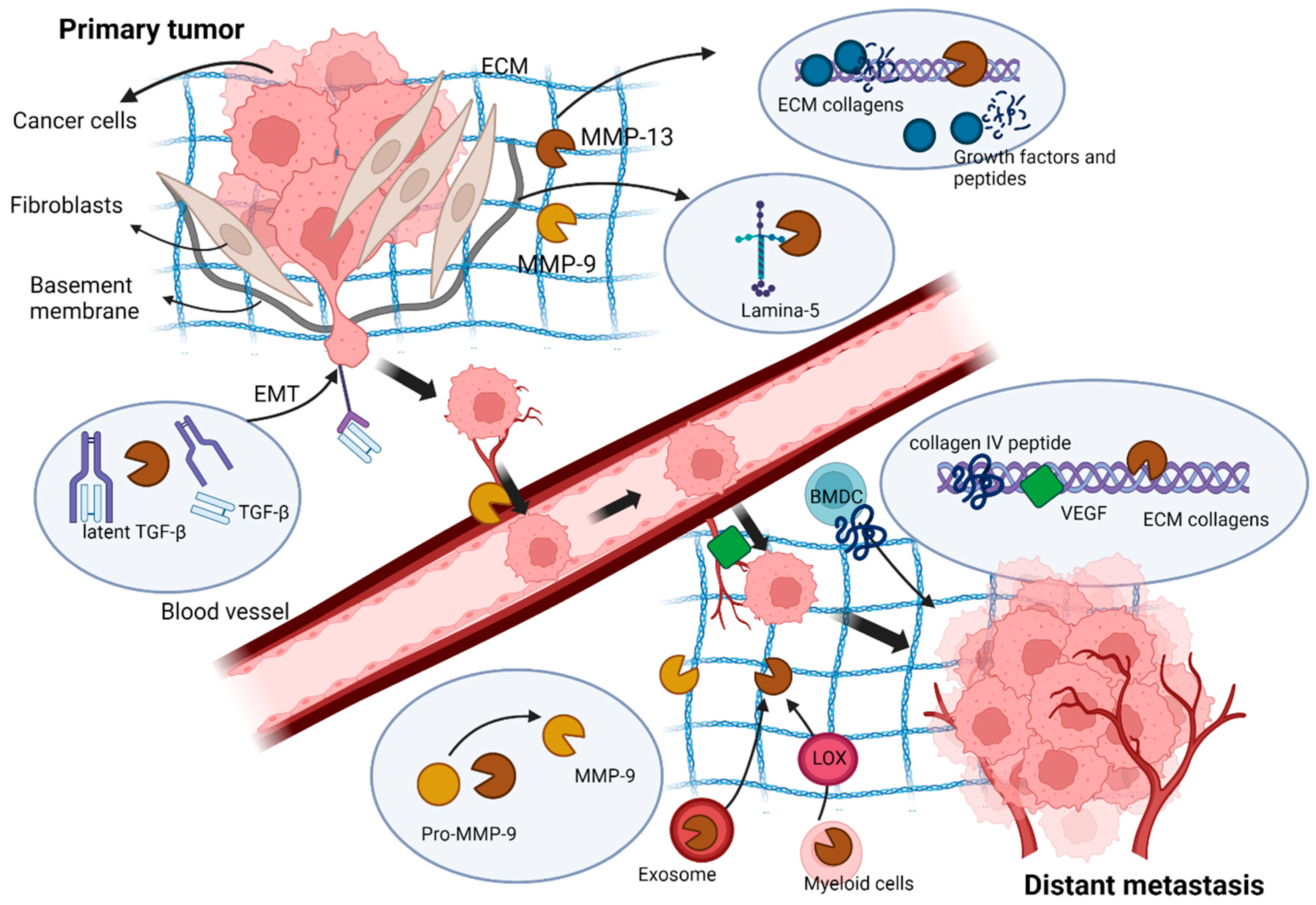
6. MMP-13 in Cancer Cell Invasion and Metastasis
7. MMP-13 in Angiogenesis
8. Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| bFGF | Basic fibroblast growth factor |
| BMDC | Bone marrow-derived cells |
| ECM | Extracellular matrix |
| EGF | Epidermal growth factor |
| EMT | Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition |
| ER | Extracellular signal-regulated kinase |
| ETV | ETS variant transcription factor 4 |
| FAK | Focal adhesion kinase |
| FHRE | Forkhead response element |
| FGF | Fibroblast growth factors |
| GOLM1 | Golgi membrane protein 1 |
| HIF | Hypoxia-inducible transcription factor |
| HNSCC | Squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck |
| IL | Interleukin |
| IFN-γ | Interferon gamma |
| ING2 | Inhibitor of growth 2 |
| IGF | Insulin-like growth factor |
| IFN-β | Interferon β |
| LOX | Lysl Oxidase |
| MMP | Matrix metalloproteinase |
| NF-κB | Nuclear factor kappa B |
| MM | Multiple Myeloma |
| OSE-2 | Osteoblast-specific element |
| PDGF | Platelet-derived growth factor |
| PTHrP | parathyroid hormone-related protein |
| PKC | Protein kinase C |
| SH | Zinc-interacting thiol |
| SUMO | Small ubiquitin related modifier |
| SENP2 | SUMO-specific protease 2 |
| TGF-β | Transforming growth factor-β1 |
| TIMPs | Tissue inhibitors of MMPs |
| TIE | Transforming growth factor-beta inhibitory element |
| TNF-α | Tumour necrosis factor alpha |
| VEGF | Vascular endothelial growth factor |
References
- Coussens, L.M.; Fingleton, B.; Matrisian, L.M. Matrix metalloproteinase inhibitors and cancer: Trials and tribulations. Science 2002, 295, 2387–2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puente, X.S.; Sánchez, L.M.; Overall, C.M.; López-Otín, C. Human and mouse proteases: A comparative genomic approach. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2003, 4, 544–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Javaid, M.A.; Abdallah, M.N.; Ahmed, A.S.; Sheikh, Z. Matrix metalloproteinases and their pathological upregulation in multiple sclerosis: An overview. Acta Neurol. Belg. 2013, 113, 381–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, Y.; Lu, Y.T.; Sun, Y.; Shi, Z.H.; Li, N.G.; Tang, Y.P.; Duan, J.A. Recent opportunities in matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor drug design for cancer. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2018, 13, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dufour, A.; Sampson, N.S.; Zucker, S.; Cao, J. Role of the hemopexin domain of matrix metalloproteinases in cell migration. J. Cell. Physiol. 2008, 217, 643–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egeblad, M.; Werb, Z. New functions for the matrix metalloproteinases in cancer progression. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2002, 2, 161–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapoor, C.; Vaidya, S.; Wadhwan, V.; Kaur, G.; Pathak, A. Seesaw of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs). J. Cancer Res. Ther. 2016, 12, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorsa, T.; Tervahartiala, T.; Leppilahti, J.; Hernandez, M.; Gamonal, J.; Tuomainen, A.M.; Lauhio, A.; Pussinen, P.J.; Mäntylä, P. Collagenase-2 (MMP-8) as a point-of-care biomarker in periodontitis and cardiovascular diseases. Therapeutic response to non-antimicrobial properties of tetracyclines. Pharmacol. Res. 2011, 63, 108–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burrage, P.S.; Mix, K.S.; Brinckerhoff, C.E. Matrix metalloproteinases: Role in arthritis. Front. Biosci. 2006, 11, 529–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H. Matrix Metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) as a Cancer Biomarker and MMP-9 Biosensors: Recent Advances. Sensors 2018, 18, 3249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCawley, L.J.; Matrisian, L.M. Matrix metalloproteinases: They’re not just for matrix anymore! Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2001, 13, 534–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freije, J.M.; Díez-Itza, I.; Balbín, M.; Sánchez, L.M.; Blasco, R.; Tolivia, J.; López-Otín, C. Molecular cloning and expression of collagenase-3, a novel human matrix metalloproteinase produced by breast carcinomas. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 16766–16773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotepui, M.; Punsawad, C.; Chupeerach, C.; Songsri, A.; Charoenkijkajorn, L.; Petmitr, S. Differential expression of matrix metalloproteinase-13 in association with invasion of breast cancer. Contemp. Oncol. 2016, 20, 225–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johansson, N.; Airola, K.; Grénman, R.; Kariniemi, A.L.; Saarialho-Kere, U.; Kähäri, V.M. Expression of collagenase-3 (matrix metalloproteinase-13) in squamous cell carcinomas of the head and neck. Am. J. Pathol. 1997, 151, 499–508. [Google Scholar]
- Uría, J.A.; Ståhle-Bäckdahl, M.; Seiki, M.; Fueyo, A.; López-Otín, C. Regulation of collagenase-3 expression in human breast carcinomas is mediated by stromal-epithelial cell interactions. Cancer Res. 1997, 57, 4882–4888. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Cheung, J.M.; Martel-Pelletier, J.; Pelletier, J.P.; Wenger, L.; Altman, R.D.; Howell, D.S.; Cheung, H.S. Wild type and mutant p53 differentially regulate the gene expression of human collagenase-3 (hMMP-13). J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 11327–11332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, Y.; Harvey, A.; Yu, X.P.; Chandrasekhar, S.; Thirunavukkarasu, K. Differential regulation of cytokine-induced MMP-1 and MMP-13 expression by p38 kinase inhibitors in human chondrosarcoma cells: Potential role of Runx2 in mediating p38 effects. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2006, 14, 749–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, S.W.; Chun, J.S.; Sung, M.H.; Kim, J.Y.; Poo, H. alpha-MSH inhibits TNF-alpha-induced matrix metalloproteinase-13 expression by modulating p38 kinase and nuclear factor kappaB signaling in human chondrosarcoma HTB-94 cells. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2008, 16, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowell, S.; Knäuper, V.; Stewart, M.L.; D’Ortho, M.P.; Stanton, H.; Hembry, R.M.; López-Otín, C.; Reynolds, J.J.; Murphy, G. Induction of matrix metalloproteinase activation cascades based on membrane-type 1 matrix metalloproteinase: Associated activation of gelatinase A, gelatinase B and collagenase 3. Biochem. J. 1998, 331 Pt 2, 453–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leeman, M.F.; Curran, S.; Murray, G.I. The structure, regulation, and function of human matrix metalloproteinase-13. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2002, 37, 149–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Wart, H.E.; Birkedal-Hansen, H. The cysteine switch: A principle of regulation of metalloproteinase activity with potential applicability to the entire matrix metalloproteinase gene family. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1990, 87, 5578–5582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rangasamy, L.; Geronimo, B.D.; Ortín, I.; Coderch, C.; Zapico, J.M.; Ramos, A.; de Pascual-Teresa, B. Molecular Imaging Probes Based on Matrix Metalloproteinase Inhibitors (MMPIs). Molecules 2019, 24, 2982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whittaker, M.; Floyd, C.D.; Brown, P.; Gearing, A.J. Design and therapeutic application of matrix metalloproteinase inhibitors. Chem. Rev. 1999, 99, 2735–2776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, G.; Nagase, H. Progress in matrix metalloproteinase research. Mol. Asp. Med. 2008, 29, 290–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, G.; Knäuper, V. Relating matrix metalloproteinase structure to function: Why the “hemopexin” domain? Matrix Biol. 1997, 15, 511–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bode, W. A helping hand for collagenases: The haemopexin-like domain. Structure 1995, 3, 527–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knäuper, V.; Will, H.; López-Otin, C.; Smith, B.; Atkinson, S.J.; Stanton, H.; Hembry, R.M.; Murphy, G. Cellular Mechanisms for Human Procollagenase-3 (MMP-13) Activation: Evidence that MT1-MMP (MMP-14) and gelatinase a (MMP-2) are able to generate active enzyme. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 17124–17131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grams, F.; Huber, R.; Kress, L.F.; Moroder, L.; Bode, W. Activation of snake venom metalloproteinases by a cysteine switch-like mechanism. FEBS Lett. 1993, 335, 76–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.P.; Patil, V.M. Specificity of binding with matrix metalloproteinases. Exp. Suppl. 2012, 103, 35–56. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Khalil, R.A. Matrix Metalloproteinase Inhibitors as Investigational and Therapeutic Tools in Unrestrained Tissue Remodeling and Pathological Disorders. Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci. 2017, 148, 355–420. [Google Scholar]
- Laronha, H.; Caldeira, J. Structure and Function of Human Matrix Metalloproteinases. Cells 2020, 9, 1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vincenti, M.P.; Brinckerhoff, C.E. Transcriptional regulation of collagenase (MMP-1, MMP-13) genes in arthritis: Integration of complex signaling pathways for the recruitment of gene-specific transcription factors. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2002, 4, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Sampson, E.R.; Jin, H.; Li, J.; Ke, Q.H.; Im, H.-J.; Chen, D. MMP13 is a critical target gene during the progression of osteoarthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2013, 15, R5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, K.; Okano, H.; Miyagawa, W.; Visse, R.; Shitomi, Y.; Santamaria, S.; Dudhia, J.; Troeberg, L.; Strickland, D.K.; Hirohata, S.; et al. MMP-13 is constitutively produced in human chondrocytes and co-endocytosed with ADAMTS-5 and TIMP-3 by the endocytic receptor LRP1. Matrix Biol. 2016, 56, 57–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, N.; Hu, M.; Khalil, R.A. Chapter One—Biochemical and Biological Attributes of Matrix Metalloproteinases. In Progress in Molecular Biology and Translational Science; Khalil, R.A., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017; Volume 147, pp. 1–73. [Google Scholar]
- Gutman, A.; Wasylyk, B. The collagenase gene promoter contains a TPA and oncogene-responsive unit encompassing the PEA3 and AP-1 binding sites. Embo J. 1990, 9, 2241–2246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiménez, M.J.; Balbín, M.; López, J.M.; Alvarez, J.; Komori, T.; López-Otín, C. Collagenase 3 is a target of Cbfa1, a transcription factor of the runt gene family involved in bone formation. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1999, 19, 4431–4442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tardif, G.; Reboul, P.; Dupuis, M.; Geng, C.; Duval, N.; Pelletier, J.P.; Martel-Pelletier, J. Transforming growth factor-beta induced collagenase-3 production in human osteoarthritic chondrocytes is triggered by Smad proteins: Cooperation between activator protein-1 and PEA-3 binding sites. J. Rheumatol. 2001, 28, 1631–1639. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Fellows, A.; Foote, K.; Yang, Z.; Figg, N.; Littlewood, T.; Bennett, M. FOXO3a (Forkhead Transcription Factor O Subfamily Member 3a) Links Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Apoptosis, Matrix Breakdown, Atherosclerosis, and Vascular Remodeling Through a Novel Pathway Involving MMP13 (Matrix Metalloproteinase 13). Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2018, 38, 555–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumortier, M.; Ladam, F.; Damour, I.; Vacher, S.; Bièche, I.; Marchand, N.; de Launoit, Y.; Tulasne, D.; Chotteau-Lelièvre, A. ETV4 transcription factor and MMP13 metalloprotease are interplaying actors of breast tumorigenesis. Breast Cancer Res. 2018, 20, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Kang, M.; Ko, J. Small leucine zipper protein promotes the metastasis of castration-resistant prostate cancer through transcriptional regulation of matrix metalloproteinase-13. Carcinogenesis 2021, 42, 1089–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borden, P.; Solymar, D.; Sucharczuk, A.; Lindman, B.; Cannon, P.; Heller, R.A. Cytokine control of interstitial collagenase and collagenase-3 gene expression in human chondrocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 23577–23581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, C.; Xu, M.; Kuang, X.; Xiao, J.; Tan, M.; Xie, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Zhao, F.; Wu, Y. Treponema pallidum flagellins stimulate MMP-9 and MMP-13 expression via TLR5 and MAPK/NF-κB signaling pathways in human epidermal keratinocytes. Exp. Cell. Res. 2017, 361, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delany, A.M.; Rydziel, S.; Canalis, E. Autocrine down-regulation of collagenase-3 in rat bone cell cultures by insulin-like growth factors. Endocrinology 1996, 137, 4665–4670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Uría, J.A.; Balbín, M.; López, J.M.; Alvarez, J.; Vizoso, F.; Takigawa, M.; López-Otín, C. Collagenase-3 (MMP-13) expression in chondrosarcoma cells and its regulation by basic fibroblast growth factor. Am. J. Pathol. 1998, 153, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knäuper, V.; Bailey, L.; Worley, J.R.; Soloway, P.; Patterson, M.L.; Murphy, G. Cellular activation of proMMP-13 by MT1-MMP depends on the C-terminal domain of MMP-13. FEBS Lett. 2002, 532, 127–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leeman, M.F.; McKay, J.A.; Murray, G.I. Matrix metalloproteinase 13 activity is associated with poor prognosis in colorectal cancer. J. Clin. Pathol. 2002, 55, 758–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moilanen, M.; Sorsa, T.; Stenman, M.; Nyberg, P.; Lindy, O.; Vesterinen, J.; Paju, A.; Konttinen, Y.T.; Stenman, U.H.; Salo, T. Tumor-associated trypsinogen-2 (trypsinogen-2) activates procollagenases (MMP-1, -8, -13) and stromelysin-1 (MMP-3) and degrades type I collagen. Biochemistry 2003, 42, 5414–5420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez, D.E.; Alonso, D.F.; Yoshiji, H.; Thorgeirsson, U.P. Tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases: Structure, regulation and biological functions. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 1997, 74, 111–122. [Google Scholar]
- Murphy, G. Tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases. Genome Biol. 2011, 12, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gokulnath, M.; Swetha, R.; Thejaswini, G.; Shilpa, P.; Selvamurugan, N. Transforming growth factor-β1 regulation of ATF-3, c-Jun and JunB proteins for activation of matrix metalloproteinase-13 gene in human breast cancer cells. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 94 Pt A, 370–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enomoto, M.; Hayakawa, S.; Itsukushima, S.; Ren, D.Y.; Matsuo, M.; Tamada, K.; Oneyama, C.; Okada, M.; Takumi, T.; Nishita, M.; et al. Autonomous regulation of osteosarcoma cell invasiveness by Wnt5a/Ror2 signaling. Oncogene 2009, 28, 3197–3208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Zhu, Z.; Shen, W.; Li, X.; Dhoomun, D.K.; Tian, Y. Golgi Membrane Protein 1 (GOLM1) Promotes Growth and Metastasis of Breast Cancer Cells via Regulating Matrix Metalloproteinase-13 (MMP13). Med. Sci. Monit. 2019, 25, 847–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ala-aho, R.; Grenman, R.; Seth, P.; Kähäri, V.-M. Adenoviral delivery of p53 gene suppresses expression of collagenase-3 (MMP-13) in squamous carcinoma cells. Oncogene 2002, 21, 1187–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaupel, P.; Multhoff, G. Fatal Alliance of Hypoxia-/HIF-1α-Driven Microenvironmental Traits Promoting Cancer Progression. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2020, 1232, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Furman, D.; Campisi, J.; Verdin, E.; Carrera-Bastos, P.; Targ, S.; Franceschi, C.; Ferrucci, L.; Gilroy, D.W.; Fasano, A.; Miller, G.W.; et al. Chronic inflammation in the etiology of disease across the life span. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 1822–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kusano, K.; Miyaura, C.; Inada, M.; Tamura, T.; Ito, A.; Nagase, H.; Kamoi, K.; Suda, T. Regulation of matrix metalloproteinases (MMP-2, -3, -9, and -13) by interleukin-1 and interleukin-6 in mouse calvaria: Association of MMP induction with bone resorption. Endocrinology 1998, 139, 1338–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mengshol, J.A.; Vincenti, M.P.; Coon, C.I.; Barchowsky, A.; Brinckerhoff, C.E. Interleukin-1 induction of collagenase 3 (matrix metalloproteinase 13) gene expression in chondrocytes requires p38, c-Jun N-terminal kinase, and nuclear factor kappaB: Differential regulation of collagenase 1 and collagenase 3. Arthritis Rheum. 2000, 43, 801–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibaragi, S.; Shimo, T.; Hassan, N.M.; Isowa, S.; Kurio, N.; Mandai, H.; Kodama, S.; Sasaki, A. Induction of MMP-13 expression in bone-metastasizing cancer cells by type I collagen through integrin α1β1 and α2β1-p38 MAPK signaling. Anticancer Res. 2011, 31, 1307–1313. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, L.; Rong, X.F.; Li, R.H.; Wu, X.Y. Icariin inhibits MMP-1, MMP-3 and MMP-13 expression through MAPK pathways in IL-1β-stimulated SW1353 chondrosarcoma cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 15, 2853–2858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Yang, Q.; Lian, X.; Jiang, P.; Cui, J. Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1α (HIF-1α) Promotes Hypoxia-Induced Invasion and Metastasis in Ovarian Cancer by Targeting Matrix Metallopeptidase 13 (MMP13). Med. Sci. Monit. 2019, 25, 7202–7208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Bo, Q.; Wang, W.; Wang, R.; Li, Y.; Chen, S.; Xia, Y.; Wang, W.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, K.; et al. CCL17-CCR4 axis promotes metastasis via ERK/MMP13 pathway in bladder cancer. J. Cell. Biochem. 2018, 120, 1979–1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ou, B.; Zhao, J.; Guan, S.; Feng, H.; Wangpu, X.; Zhu, C.; Zong, Y.; Ma, J.; Sun, J.; Shen, X.; et al. CCR4 promotes metastasis via ERK/NF-κB/MMP13 pathway and acts downstream of TNF-α in colorectal cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 47637–47649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumamoto, K.; Fujita, K.; Kurotani, R.; Saito, M.; Unoki, M.; Hagiwara, N.; Shiga, H.; Bowman, E.D.; Yanaihara, N.; Okamura, S.; et al. ING2 is upregulated in colon cancer and increases invasion by enhanced MMP13 expression. Int. J. Cancer 2009, 125, 1306–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, M.; Gong, H.; Wang, J.; Tao, L.; Xu, D.; Bao, E.; Liu, Z.; Qiu, J. SENP2 regulates MMP13 expression in a bladder cancer cell line through SUMOylation of TBL1/TBLR1. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 13996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Huang, M.; Chen, Z.; Chen, J.; Chao, Q.; Yin, X.; Quan, M. FTO promotes cell proliferation and migration in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma through up-regulation of MMP13. Exp. Cell Res. 2020, 389, 111894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, T.; Oshima, T.; Yoshihara, K.; Tamura, S.; Kanazawa, A.; Inagaki, D.; Yamamoto, N.; Sato, T.; Fujii, S.; Numata, K.; et al. Overexpression of MMP-13 Gene in Colorectal Cancer with Liver Metastasis. Anticancer Res. 2010, 30, 2693–2699. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, B.; Gao, J.; Rao, Z.; Shen, Q. Clinicopathological significance and prognostic value of MMP-13 expression in colorectal cancer. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Investig. 2012, 72, 501–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.W.; Tai, H.C.; Tang, C.H.; Lin, L.W.; Lin, T.H.; Chang, A.C.; Chen, P.C.; Chen, Y.H.; Wang, P.C.; Lai, Y.W.; et al. Melatonin impedes prostate cancer metastasis by suppressing MMP-13 expression. J. Cell. Physiol. 2021, 236, 3979–3990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etoh, T.; Inoue, H.; Yoshikawa, Y.; Barnard, G.F.; Kitano, S.; Mori, M. Increased expression of collagenase-3 (MMP-13) and MT1-MMP in oesophageal cancer is related to cancer aggressiveness. Gut 2000, 47, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, X.L.; Chen, D.; Wang, J.; Zhang, K. Clinical significance of serum matrix metalloproteinase-13 levels in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC). Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2014, 18, 509–515. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Li, X.; Gao, X.; An, S.; Liu, H.; Liang, J.; Zhang, K.; Liu, Z.; Wang, J.; Chen, Z. Expression of MMP-13 is associated with invasion and metastasis of papillary thyroid carcinoma. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2013, 17, 427–435. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- del Casar Lizcano, J.; LO, G.S.; Gava, R.; Santisteban, D. Expression and clinical significance of collagenase-3 (MMP-13) in gastric cancer. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2003, 26, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, C.H.; Shay, G.; McGuire, J.J.; Li, T.; Shain, K.H.; Choi, J.Y.; Fuerst, R.; Roush, W.R.; Knapinska, A.M.; Fields, G.B.; et al. Host-Derived Matrix Metalloproteinase-13 Activity Promotes Multiple Myeloma-Induced Osteolysis and Reduces Overall Survival. Cancer Res. 2021, 81, 2415–2428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boström, P.J.; Ravanti, L.; Reunanen, N.; Aaltonen, V.; Söderström, K.O.; Kähäri, V.M.; Laato, M. Expression of collagenase-3 (matrix metalloproteinase-13) in transitional-cell carcinoma of the urinary bladder. Int. J. Cancer 2000, 88, 417–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotepui, M.; Thawornkuno, C.; Chavalitshewinkoon-Petmitr, P.; Punyarit, P.; Petmitr, S. Quantitative real-time RT-PCR of ITGA7, SVEP1, TNS1, LPHN3, SEMA3G, KLB and MMP13 mRNA expression in breast cancer. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2012, 13, 5879–5882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Daja, M.M.; Niu, X.; Zhao, Z.; Brown, J.M.; Russell, P.J. Characterization of expression of matrix metalloproteinases and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases in prostate cancer cell lines. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2003, 6, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhang, B.; Cao, X.; Liu, Y.; Cao, W.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, S.; Li, H.; Ning, L.; Fu, L.; Niu, Y.; et al. Tumor-derived matrix metalloproteinase-13 (MMP-13) correlates with poor prognoses of invasive breast cancer. BMC Cancer 2008, 8, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luukkaa, M.; Vihinen, P.; Kronqvist, P.; Vahlberg, T.; Pyrhönen, S.; Kähäri, V.M.; Grénman, R. Association between high collagenase-3 expression levels and poor prognosis in patients with head and neck cancer. Head Neck 2006, 28, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, R.; Yu, S. Expression of MMP-13 and its correlation with prognosis in non-small cell lung cancer. Chin.-Ger. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 7, 142–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgia, G.; Falsaperla, M.; Malaponte, G.; Madonia, M.; Indelicato, M.; Travali, S.; Mazzarino, M.C. Matrix metalloproteinases as diagnostic (MMP-13) and prognostic (MMP-2, MMP-9) markers of prostate cancer. Urol. Res. 2005, 33, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalantari, E.; Abolhasani, M.; Roudi, R.; Farajollahi, M.M.; Farhad, S.; Madjd, Z.; Askarian-Amiri, S.; Mohsenzadegan, M. Co-expression of TLR-9 and MMP-13 is associated with the degree of tumour differentiation in prostate cancer. Int. J. Exp. Pathol. 2019, 100, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanzer, M.L. Current concepts of extracellular matrix. J. Orthop. Sci. 2006, 11, 326–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanzer, M.L. Collagens and elastin: Structure and interactions. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 1989, 1, 968–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iozzo, R.V. Matrix proteoglycans: From molecular design to cellular function. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1998, 67, 609–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aumailley, M.; Smyth, N. The role of laminins in basement membrane function. J. Anat. 1998, 193 Pt 1, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wierzbicka-Patynowski, I.; Schwarzbauer, J.E. The ins and outs of fibronectin matrix assembly. J. Cell Sci. 2003, 116 Pt 16, 3269–3276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mott, J.D.; Werb, Z. Regulation of matrix biology by matrix metalloproteinases. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2004, 16, 558–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, N.H. Extracellular matrix in development: Insights from mechanisms conserved between invertebrates and vertebrates. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2011, 3, a005082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrez, M.; Chen, A.; Cone, R.I.; Pytela, R.; Sheppard, D. The alpha v beta 6 integrin promotes proliferation of colon carcinoma cells through a unique region of the beta 6 cytoplasmic domain. J. Cell Biol. 1994, 127, 547–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deryugina, E.I.; Quigley, J.P. Matrix metalloproteinases and tumor metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2006, 25, 9–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knäuper, V.; López-Otin, C.; Smith, B.; Knight, G.; Murphy, G. Biochemical characterization of human collagenase-3. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 1544–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knäuper, V.; Cowell, S.; Smith, B.; López-Otin, C.; O’Shea, M.; Morris, H.; Zardi, L.; Murphy, G. The role of the C-terminal domain of human collagenase-3 (MMP-13) in the activation of procollagenase-3, substrate specificity, and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase interaction. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 7608–7616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fosang, A.J.; Last, K.; Knäuper, V.; Murphy, G.; Neame, P.J. Degradation of cartilage aggrecan by collagenase-3 (MMP-13). FEBS Lett. 1996, 380, 17–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashworth, J.L.; Murphy, G.; Rock, M.J.; Sherratt, M.J.; Shapiro, S.D.; Shuttleworth, C.A.; Kielty, C.M. Fibrillin degradation by matrix metalloproteinases: Implications for connective tissue remodelling. Biochem. J. 1999, 340 Pt 1, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, T.; Göhring, W.; Mann, K.; Maurer, P.; Hohenester, E.; Knäuper, V.; Murphy, G.; Timpl, R. Limited cleavage of extracellular matrix protein BM-40 by matrix metalloproteinases increases its affinity for collagens. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 9237–9243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abety, A.N.; Pach, E.; Giebeler, N.; Fromme, J.E.; Aramadhaka, L.R.; Mauch, C.; Fox, J.W.; Zigrino, P. Loss of ADAM9 Leads to Modifications of the Extracellular Matrix Modulating Tumor Growth. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McQuibban, G.A.; Butler, G.S.; Gong, J.-H.; Bendall, L.; Power, C.; Clark-Lewis, I.; Overall, C.M. Matrix metalloproteinase activity inactivates the CXC chemokine stromal cell-derived factor-1. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 43503–43508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McQuibban, G.A.; Gong, J.-H.; Tam, E.M.; McCulloch, C.A.; Clark-Lewis, I.; Overall, C.M. Inflammation dampened by gelatinase A cleavage of monocyte chemoattractant protein-3. Science 2000, 289, 1202–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, S.-J.; Bickett, D.M.; Mitchell, J.L.; Lambert, M.H.; Blackburn, R.K.; Carter, H.L.; Neugebauer, J.; Pahel, G.; Weiner, M.P.; Moss, M.L. Substrate specificity of human collagenase 3 assessed using a phage-displayed peptide library. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 31422–31427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.-Y.; Li, G.-C.; Wang, W.-M.; Zhu, J.-G.; Li, Y.-F.; Zhou, G.-H.; Sun, Q.-B. Transfection of colorectal cancer cells with chemokine MCP-3 (monocyte chemotactic protein-3) gene retards tumor growth and inhibits tumor metastasis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2002, 8, 1067–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viiklepp, K.; Nissinen, L.; Ojalill, M.; Riihilä, P.; Kallajoki, M.; Meri, S.; Heino, J.; Kähäri, V.M. C1r Upregulates Production of Matrix Metalloproteinase-13 and Promotes Invasion of Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2021, 142, 1478–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Y.; Gan, Y.; Shen, Y.; Cai, X.; Song, Y.; Zhao, F.; Yao, M.; Gu, J.; Tu, H. Leptin signaling enhances cell invasion and promotes the metastasis of human pancreatic cancer via increasing MMP-13 production. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 16120–16134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ala-aho, R.; Ahonen, M.; George, S.J.; Heikkilä, J.; Grenman, R.; Kallajoki, M.; Kähäri, V.-M. Targeted inhibition of human collagenase-3 (MMP-13) expression inhibits squamous cell carcinoma growth in vivo. Oncogene 2004, 23, 5111–5123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, M.; Huang, D.; Blick, T.; Connor, A.; Reiter, L.A.; Hardink, J.R.; Lynch, C.C.; Waltham, M.; Thompson, E.W. An MMP13-selective inhibitor delays primary tumor growth and the onset of tumor-associated osteolytic lesions in experimental models of breast cancer. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e29615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ala-aho, R.; Johansson, N.; Grenman, R.; Fusenig, N.E.; Lopez-Otin, C.; Kähäri, V.-M. Inhibition of collagenase-3 (MMP-13) expression in transformed human keratinocytes by interferon-γ is associated with activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase-1, 2 and STAT1. Oncogene 2000, 19, 248–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, P.; Takai, K.; Weaver, V.M.; Werb, Z. Extracellular matrix degradation and remodeling in development and disease. Cold Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2011, 3, a005058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitelock, J.M.; Murdoch, A.D.; Iozzo, R.V.; Underwood, P.A. The degradation of human endothelial cell-derived perlecan and release of bound basic fibroblast growth factor by stromelysin, collagenase, plasmin, and heparanases. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 10079–10086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marinkovich, M.P.; Verrando, P.; Keene, D.R.; Meneguzzi, G.; Lunstrum, G.P.; Ortonne, J.P.; Burgeson, R.E. Basement membrane proteins kalinin and nicein are structurally and immunologically identical. Lab. Investig. 1993, 69, 295–299. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Xia, Y.; Gil, S.G.; Carter, W.G. Anchorage mediated by integrin alpha6beta4 to laminin 5 (epiligrin) regulates tyrosine phosphorylation of a membrane-associated 80-kD protein. J. Cell Biol. 1996, 132, 727–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, J.C.; Kurpakus, M.A.; Cooper, H.M.; Quaranta, V. A function for the integrin alpha 6 beta 4 in the hemidesmosome. Cell Regul. 1991, 2, 427–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannelli, G.; Falk-Marzillier, J.; Schiraldi, O.; Stetler-Stevenson, W.G.; Quaranta, V. Induction of cell migration by matrix metalloprotease-2 cleavage of laminin-5. Science 1997, 277, 225–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koshikawa, N.; Giannelli, G.; Cirulli, V.; Miyazaki, K.; Quaranta, V. Role of cell surface metalloprotease MT1-MMP in epithelial cell migration over laminin-5. J. Cell Biol. 2000, 148, 615–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Sun, B.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, D.; Wang, X.; Gu, Q.; Zhao, J.; Dong, X.; Liu, Z.; et al. Dual effects of collagenase-3 on melanoma: Metastasis promotion and disruption of vasculogenic mimicry. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 8890–8899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knäuper, V.; Smith, B.; López-Otin, C.; Murphy, G. Activation of progelatinase B (proMMP-9) by active collagenase-3 (MMP-13). Eur. J. Biochem. 1997, 248, 369–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dreier, R.; Grässel, S.; Fuchs, S.; Schaumburger, J.; Bruckner, P. Pro-MMP-9 is a specific macrophage product and is activated by osteoarthritic chondrocytes via MMP-3 or a MT1-MMP/MMP-13 cascade. Exp. Cell Res. 2004, 297, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández Ríos, M.; Sorsa, T.; Obregón, F.; Tervahartiala, T.; Valenzuela, M.A.; Pozo, P.; Dutzan, N.; Lesaffre, E.; Molas, M.; Gamonal, J. Proteolytic roles of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-13 during progression of chronic periodontitis: Initial evidence for MMP-13/MMP-9 activation cascade. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2009, 36, 1011–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roche, J. The Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition in Cancer. Cancers 2018, 10, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, V. Epithelial Mesenchymal Transition in Tumor Metastasis. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2018, 13, 395–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.N.; Ahn, D.H.; Kang, N.; Yeo, C.D.; Kim, Y.K.; Lee, K.Y.; Kim, T.-J.; Lee, S.H.; Park, M.S.; Yim, H.W.; et al. TGF-β induced EMT and stemness characteristics are associated with epigenetic regulation in lung cancer. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 10597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illman, S.A.; Lehti, K.; Keski-Oja, J.; Lohi, J. Epilysin (MMP-28) induces TGF-beta mediated epithelial to mesenchymal transition in lung carcinoma cells. J. Cell Sci. 2006, 119 Pt 18, 3856–3865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Angelo, M.; Billings, P.C.; Pacifici, M.; Leboy, P.S.; Kirsch, T. Authentic matrix vesicles contain active metalloproteases (MMP). A role for matrix vesicle-associated MMP-13 in activation of transforming growth factor-beta. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 11347–11353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nannuru, K.C.; Futakuchi, M.; Varney, M.L.; Vincent, T.M.; Marcusson, E.G.; Singh, R.K. Matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-13 regulates mammary tumor-induced osteolysis by activating MMP9 and transforming growth factor-beta signaling at the tumor-bone interface. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 3494–3504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banyard, J.; Bielenberg, D.R. The role of EMT and MET in cancer dissemination. Connect. Tissue Res. 2015, 56, 403–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barillari, G. The Impact of Matrix Metalloproteinase-9 on the Sequential Steps of the Metastatic Process. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Folgueras, A.R.; Pendás, A.M.; Sánchez, L.M.; López-Otín, C. Matrix metalloproteinases in cancer: From new functions to improved inhibition strategies. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 2004, 48, 411–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mondal, S.; Adhikari, N.; Banerjee, S.; Amin, S.A.; Jha, T. Matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) and its inhibitors in cancer: A minireview. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 194, 112260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendonsa, A.M.; VanSaun, M.N.; Ustione, A.; Piston, D.W.; Fingleton, B.M.; Gorden, D.L. Host and tumor derived MMP13 regulate extravasation and establishment of colorectal metastases in the liver. Mol. Cancer 2015, 14, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolb, A.D.; Bussard, K.M. The Bone Extracellular Matrix as an Ideal Milieu for Cancer Cell Metastases. Cancers 2019, 11, 1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, P.; Weaver, V.M.; Werb, Z. The extracellular matrix: A dynamic niche in cancer progression. J. Cell Biol. 2012, 196, 395–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohshiba, T.; Miyaura, C.; Inada, M.; Ito, A. Role of RANKL-induced osteoclast formation and MMP-dependent matrix degradation in bone destruction by breast cancer metastasis. Br. J. Cancer 2003, 88, 1318–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page-McCaw, A.; Ewald, A.J.; Werb, Z. Matrix metalloproteinases and the regulation of tissue remodelling. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2007, 8, 221–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lafleur, M.A.; Drew, A.F.; de Sousa, E.L.; Blick, T.; Bills, M.; Walker, E.C.; Williams, E.D.; Waltham, M.; Thompson, E.W. Upregulation of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) in breast cancer xenografts: A major induction of stromal MMP-13. Int. J. Cancer 2005, 114, 544–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrison, C.; Mancini, S.; Cipollone, J.; Kappelhoff, R.; Roskelley, C.; Overall, C. Microarray and proteomic analysis of breast cancer cell and osteoblast co-cultures: Role of osteoblast matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-13 in bone metastasis. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 34271–34285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibaragi, S.; Shimo, T.; Iwamoto, M.; Hassan, N.M.; Kodama, S.; Isowa, S.; Sasaki, A. Parathyroid hormone-related peptide regulates matrix metalloproteinase-13 gene expression in bone metastatic breast cancer cells. Anticancer Res. 2010, 30, 5029–5036. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pivetta, E.; Scapolan, M.; Pecolo, M.; Wassermann, B.; Abu-Rumeileh, I.; Balestreri, L.; Borsatti, E.; Tripodo, C.; Colombatti, A.; Spessotto, P. MMP-13 stimulates osteoclast differentiation and activation in tumour breast bone metastases. Breast Cancer Res. 2011, 13, R105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Li, S.; Feng, R.; Ma, H.; Sabeh, F.; Roodman, G.D.; Mapara, M.; Weiss, S.J.; Lentzsch, S. Matrix Metalloproteinase 13 (MMP13) Upregulation Is Essential for Multiple Myeloma Related Bone Lytic Lesion. Blood 2012, 120, 4025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Li, S.; Feng, R.; Ma, H.; Sabeh, F.; Roodman, G.D.; Wang, J.; Robinson, S.; Guo, X.E.; Lund, T.; et al. Multiple myeloma-derived MMP-13 mediates osteoclast fusogenesis and osteolytic disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2016, 126, 1759–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuerst, R.; Yong Choi, J.; Knapinska, A.M.; Smith, L.; Cameron, M.D.; Ruiz, C.; Fields, G.B.; Roush, W.R. Development of matrix metalloproteinase-13 inhibitors—A structure-activity/structure-property relationship study. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2018, 26, 4984–4995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Cao, X. Characteristics and Significance of the Pre-metastatic Niche. Cancer Cell 2016, 30, 668–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiratsuka, S.; Watanabe, A.; Aburatani, H.; Maru, Y. Tumour-mediated upregulation of chemoattractants and recruitment of myeloid cells predetermines lung metastasis. Nat. Cell Biol. 2006, 8, 1369–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, R.N.; Riba, R.D.; Zacharoulis, S.; Bramley, A.H.; Vincent, L.; Costa, C.; MacDonald, D.D.; Jin, D.K.; Shido, K.; Kerns, S.A.; et al. VEGFR1-positive haematopoietic bone marrow progenitors initiate the pre-metastatic niche. Nature 2005, 438, 820–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiratsuka, S.; Watanabe, A.; Sakurai, Y.; Akashi-Takamura, S.; Ishibashi, S.; Miyake, K.; Shibuya, M.; Akira, S.; Aburatani, H.; Maru, Y. The S100A8-serum amyloid A3-TLR4 paracrine cascade establishes a pre-metastatic phase. Nat. Cell Biol. 2008, 10, 1349–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bond, M.; Fabunmi, R.P.; Baker, A.H.; Newby, A.C. Synergistic upregulation of metalloproteinase-9 by growth factors and inflammatory cytokines: An absolute requirement for transcription factor NF-kappa B. FEBS Lett. 1998, 435, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitamura, T.; Qian, B.-Z.; Pollard, J.W. Immune cell promotion of metastasis. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 15, 73–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heissig, B.; Hattori, K.; Dias, S.; Friedrich, M.; Ferris, B.; Hackett, N.R.; Crystal, R.G.; Besmer, P.; Lyden, D.; Moore, M.A.; et al. Recruitment of stem and progenitor cells from the bone marrow niche requires MMP-9 mediated release of kit-ligand. Cell 2002, 109, 625–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erler, J.T.; Bennewith, K.L.; Cox, T.R.; Lang, G.; Bird, D.; Koong, A.; Le, Q.-T.; Giaccia, A.J. Hypoxia-induced lysyl oxidase is a critical mediator of bone marrow cell recruitment to form the premetastatic niche. Cancer Cell 2009, 15, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boileau, C.; Pelletier, J.P.; Tardif, G.; Fahmi, H.; Laufer, S.; Lavigne, M.; Martel-Pelletier, J. The regulation of human MMP-13 by licofelone, an inhibitor of cyclo-oxygenases and 5-lipoxygenase, in human osteoarthritic chondrocytes is mediated by the inhibition of the p38 MAP kinase signalling pathway. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2005, 64, 891–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Yu, D. Exosomes in cancer development, metastasis, and immunity. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer 2019, 1871, 455–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Gu, Y.; Cao, X. The exosomes in tumor immunity. Oncoimmunology 2015, 4, e1027472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa-Silva, B.; Aiello, N.M.; Ocean, A.J.; Singh, S.; Zhang, H.; Thakur, B.K.; Becker, A.; Hoshino, A.; Mark, M.T.; Molina, H.; et al. Pancreatic cancer exosomes initiate pre-metastatic niche formation in the liver. Nat. Cell Biol. 2015, 17, 816–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, Y.; You, B.; Shi, S.; Shi, W.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Gu, M.; Chen, J.; Bao, L.; Liu, D.; et al. Hypoxia-Induced Matrix Metalloproteinase-13 Expression in Exosomes from Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Enhances Metastases. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, A.A.; Kamal, M.A.; Akhtar, S. Tumor Angiogenesis and VEGFR-2: Mechanism, Pathways and Current Biological Therapeutic Interventions. Curr. Drug Metab. 2021, 22, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Kang, G.; Wang, T.; Huang, H. Tumor angiogenesis and anti-angiogenic gene therapy for cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 16, 687–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishida, N.; Yano, H.; Nishida, T.; Kamura, T.; Kojiro, M. Angiogenesis in cancer. Vasc. Health Risk Manag. 2006, 2, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welti, J.; Loges, S.; Dimmeler, S.; Carmeliet, P. Recent molecular discoveries in angiogenesis and antiangiogenic therapies in cancer. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 3190–3200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Puente, P.; Muz, B.; Azab, F.; Azab, A.K. Cell trafficking of endothelial progenitor cells in tumor progression. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 3360–3368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrara, N.; Adamis, A.P. Ten years of anti-vascular endothelial growth factor therapy. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2016, 15, 385–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eelen, G.; de Zeeuw, P.; Simons, M.; Carmeliet, P. Endothelial cell metabolism in normal and diseased vasculature. Circ. Res. 2015, 116, 1231–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moschetta, M.; Mishima, Y.; Sahin, I.; Manier, S.; Glavey, S.; Vacca, A.; Roccaro, A.M.; Ghobrial, I.M. Role of endothelial progenitor cells in cancer progression. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1846, 26–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liekens, S.; De Clercq, E.; Neyts, J. Angiogenesis: Regulators and clinical applications. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2001, 61, 253–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milkiewicz, M.; Ispanovic, E.; Doyle, J.L.; Haas, T.L. Regulators of angiogenesis and strategies for their therapeutic manipulation. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2006, 38, 333–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quintero-Fabián, S.; Arreola, R.; Becerril-Villanueva, E.; Torres-Romero, J.C.; Arana-Argáez, V.; Lara-Riegos, J.; Ramírez-Camacho, M.A.; Alvarez-Sánchez, M.E. Role of Matrix Metalloproteinases in Angiogenesis and Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zijlstra, A.; Aimes, R.T.; Zhu, D.; Regazzoni, K.; Kupriyanova, T.; Seandel, M.; Deryugina, E.I.; Quigley, J.P. Collagenolysis-dependent angiogenesis mediated by matrix metalloproteinase-13 (collagenase-3). J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 27633–27645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perumal, S.; Antipova, O.; Orgel, J.P. Collagen fibril architecture, domain organization, and triple-helical conformation govern its proteolysis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 2824–2829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seandel, M.; Noack-Kunnmann, K.; Zhu, D.; Aimes, R.T.; Quigley, J.P. Growth factor-induced angiogenesis in vivo requires specific cleavage of fibrillar type I collagen. Blood 2001, 97, 2323–2332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rundhaug, J.E. Matrix metalloproteinases and angiogenesis. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2005, 9, 267–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudo, Y.; Iizuka, S.; Yoshida, M.; Tsunematsu, T.; Kondo, T.; Subarnbhesaj, A.; Deraz, E.M.; Siriwardena, S.B.; Tahara, H.; Ishimaru, N.; et al. Matrix metalloproteinase-13 (MMP-13) directly and indirectly promotes tumor angiogenesis. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 38716–38728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lederle, W.; Hartenstein, B.; Meides, A.; Kunzelmann, H.; Werb, Z.; Angel, P.; Mueller, M.M. MMP13 as a stromal mediator in controlling persistent angiogenesis in skin carcinoma. Carcinogenesis 2010, 31, 1175–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Sun, K.; Xia, M.; Li, X.; Lu, Y. MMP13 Regulates Aggressiveness of Pediatric Multiple Myeloma Through VEGF-C. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2015, 36, 509–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Cancer Type | Expression Level | Function and Clinical Significance | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Breast cancer | Increased | Increased tumour growth, invasion and metastasis; potential diagnostic biomarker | [13] |
| Prostate cancer | Increased | Increased tumour differentiation, invasion and metastasis; diagnostic biomarker; poor prognosis | [69,81,82] |
| Bladder cancer | Increased | Increased tumour invasion and metastasis; poor prognosis | [75] |
| Colorectal cancer | Increased | Increased tumour growth, invasion and metastasis; poor prognosis | [47,68] |
| Oesophageal cancer | Increased | Promoted cancer aggressiveness; poor prognosis | [70,71] |
| Head and neck cancer | Increased | Increased tumour invasion and metastasis; poor prognosis | [14] |
| Lung cancer | Increased | Promoted lymph node metastasis; poor survival | [80] |
| Oesophageal cancer | Increased | Promoted cancer aggressiveness; poor prognosis | [70] |
| Gastric cancer | Increased | Increased tumour invasion and metastasis; poor prognosis | [73] |
| Thyroid cancer | Increased | Increased tumour invasion and metastasis; poor prognosis | [72] |
| Multiple Myeloma | Increased | Promoted tumour growth and MM-induced osteolysis; poor prognosis | [74] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, S.; Pritchard, D.M.; Yu, L.-G. Regulation and Function of Matrix Metalloproteinase-13 in Cancer Progression and Metastasis. Cancers 2022, 14, 3263. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14133263
Li S, Pritchard DM, Yu L-G. Regulation and Function of Matrix Metalloproteinase-13 in Cancer Progression and Metastasis. Cancers. 2022; 14(13):3263. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14133263
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Shun, David Mark Pritchard, and Lu-Gang Yu. 2022. "Regulation and Function of Matrix Metalloproteinase-13 in Cancer Progression and Metastasis" Cancers 14, no. 13: 3263. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14133263
APA StyleLi, S., Pritchard, D. M., & Yu, L.-G. (2022). Regulation and Function of Matrix Metalloproteinase-13 in Cancer Progression and Metastasis. Cancers, 14(13), 3263. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14133263







