Theranostic Potential of Adaptive Cold Atmospheric Plasma with Temozolomide to Checkmate Glioblastoma: An In Vitro Study
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Kits
2.2. Cell Culture
2.3. CAP Jet Device Configuration
2.4. Preparation of Temozolomide (TMZ) Dilutions and IC50 of GBM Cell Lines
2.5. Time-Dependent CAP Sensitization of GBM Cell Lines
2.6. CAP-Induced TMZ-Supported Apoptosis Detection in GBM Cells by DAPI Staining
2.7. Estimation of Lactate Dehydrogenase (LDH) and Caspase-3 Activity in GBM Cells
2.8. Definition of Control
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
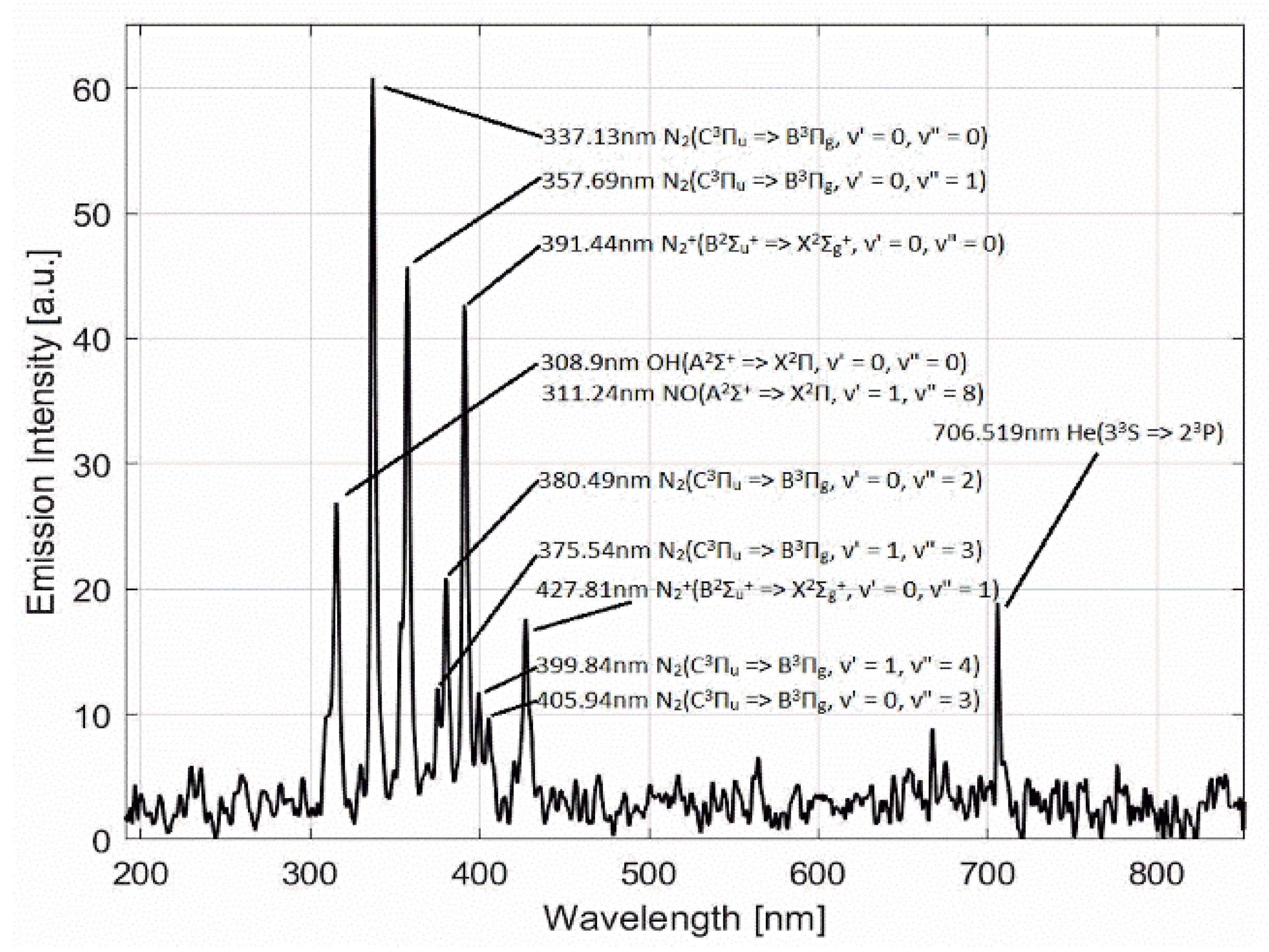
3.1. CAP Jet and Characterization
3.2. Cytotoxic (IC50) Dose of TMZ on T98G and A172 Cells

3.3. Combination Effect of CAP and TMZ (CAP Sensitization Phenomena)

3.4. Effect of Combination Therapy of CAP and TMZ in Different Parameters (for Short and Long Treatments)
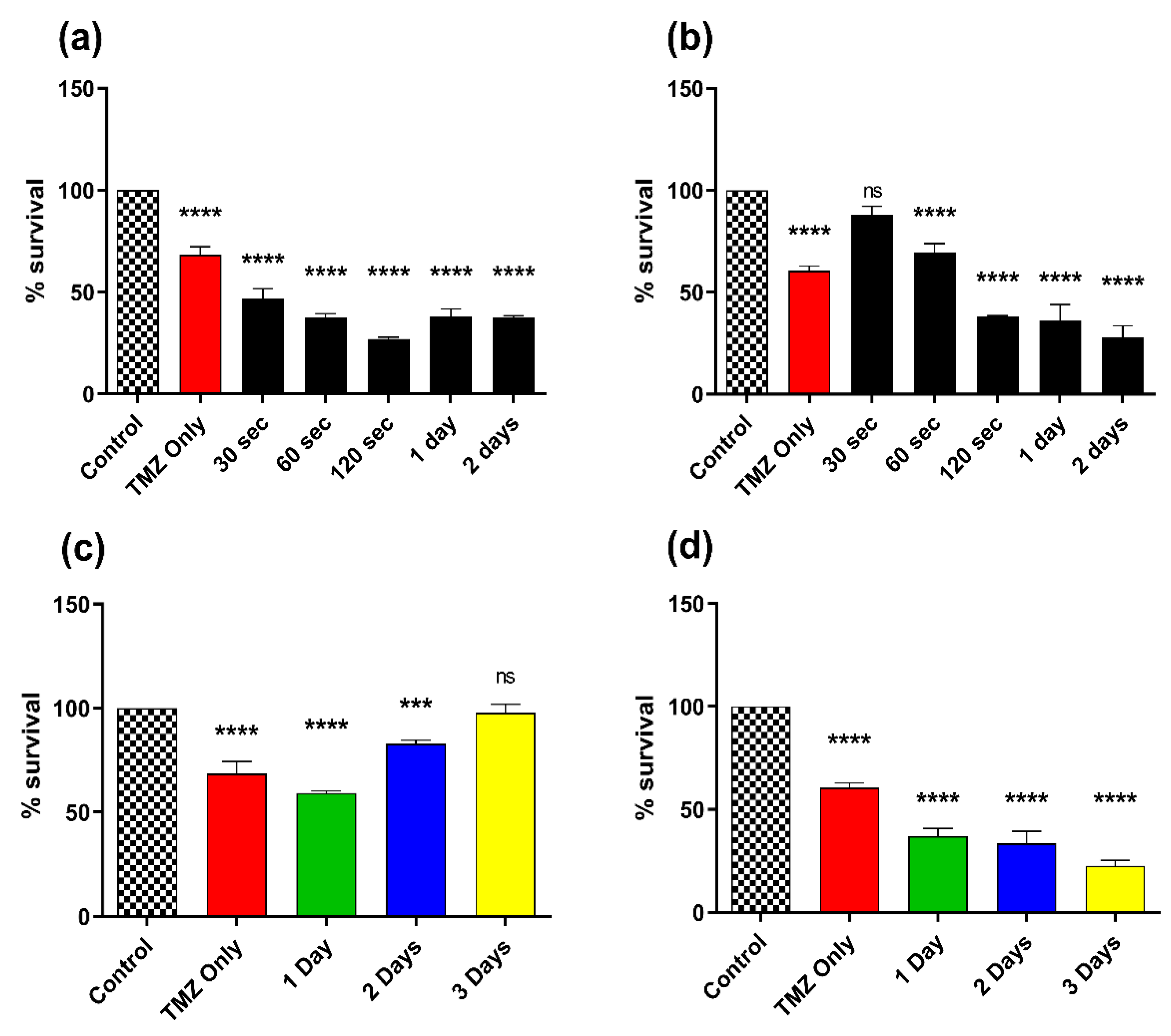
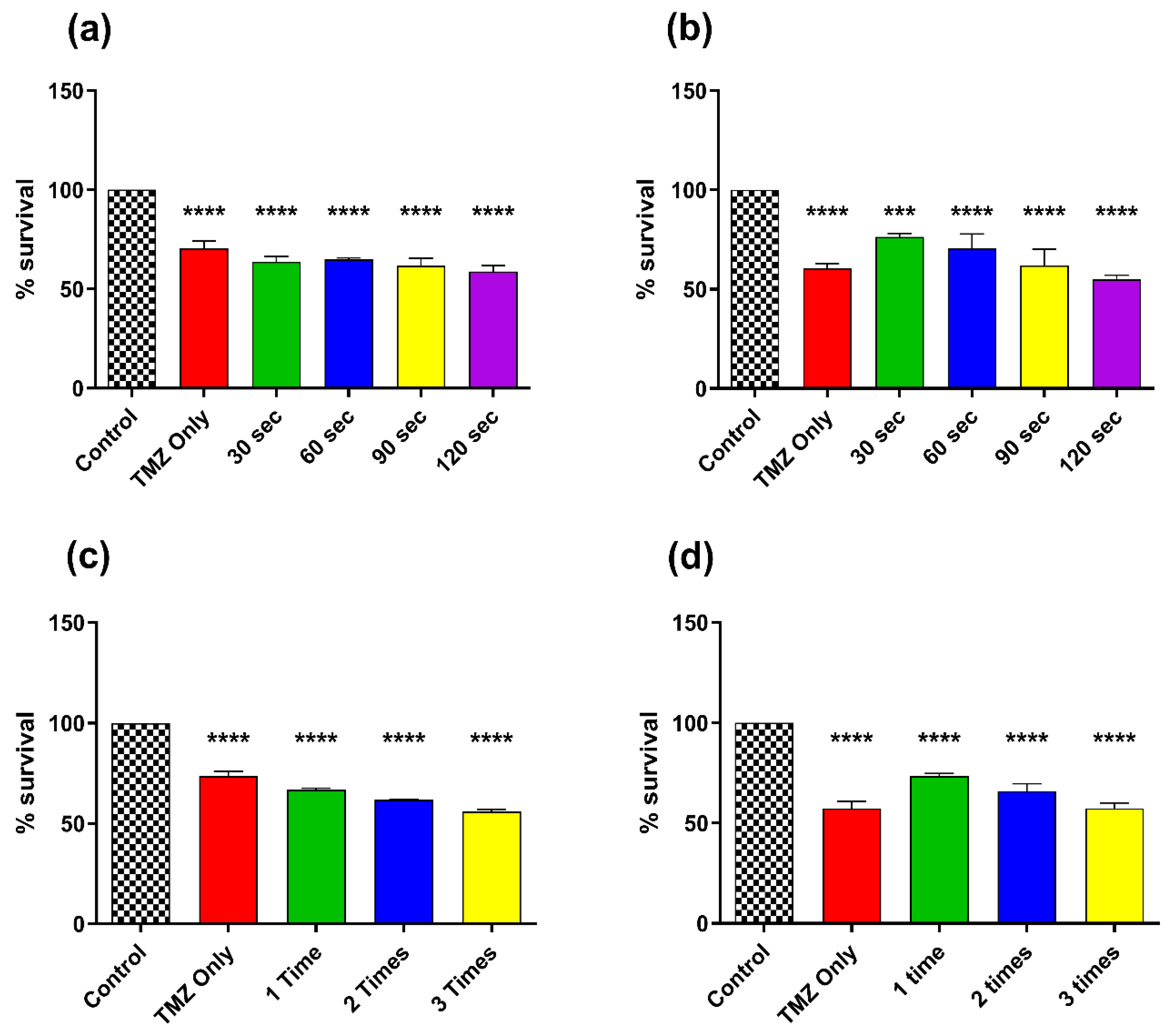
3.5. Effect of Combination Therapy of CAP and TMZ Using Different Parameters (for Shorter Time Intervals and Multiple Treatments)
3.6. Apoptosis Detection by DAPI Staining Using Confocal Microscopy

3.7. Effect of CAP and TMZ Combination on LDH and Caspase-3 Levels

4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Persaud-Sharma, D.; Burns, J.; Trangle, J.; Moulik, S. Disparities in Brain Cancer in the United States: A Literature Review of Gliomas. Med. Sci. 2017, 5, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hayat, M.A. Tumors of the Central Nervous System; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; Volume 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, V.; Kochar, P. Brain Cancer: Implication to Disease, Therapeutic Strategies and Tumor Targeted Drug Delivery Approaches. Recent Pat. Anti-Cancer Drug Discov. 2018, 13, 70–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2020, 70, 7–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laquintana, V.; Trapani, A.; Denora, N.; Wang, F.; Gallo, J.M.; Trapani, G. New strategies to deliver anticancer drugs to brain tumors. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2009, 6, 1017–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harder, B.G.; Blomquist, M.R.; Wang, J.; Kim, A.J.; Woodworth, G.F.; Winkles, J.A.; Loftus, J.C.; Tran, N.L. Developments in Blood-Brain Barrier Penetrance and Drug Repurposing for Improved Treatment of Glioblastoma. Front. Oncol. 2018, 8, 462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shergalis, A.; Bankhead, A., III; Luesakul, U.; Muangsin, N.; Neamati, N. Current Challenges and Opportunities in Treating Glioblastoma. Pharmacol. Rev. 2018, 70, 412–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carter, T.C.; Medina-Flores, R.; Lawler, B.E. Glioblastoma Treatment with Temozolomide and Bevacizumab and Overall Survival in a Rural Tertiary Healthcare Practice. BioMed Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Strobel, H.; Baisch, T.; Fitzel, R.; Schilberg, K.; Siegelin, M.D.; Karpel-Massler, G.; Debatin, K.-M.; Westhoff, M.-A. Temozolomide and Other Alkylating Agents in Glioblastoma Therapy. Biomedicines 2019, 7, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Stevens, M.F.; Bradshaw, T.D. Temozolomide: Mechanisms of Action, Repair and Resistance. Curr. Mol. Pharmacol. 2012, 5, 102–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegi, M.E.; Diserens, A.-C.; Gorlia, T.; Hamou, M.-F.; De Tribolet, N.; Weller, M.; Kros, J.M.; Hainfellner, J.A.; Mason, W.; Mariani, L.; et al. MGMT Gene Silencing and Benefit from Temozolomide in Glioblastoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 997–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Woo, P.Y.; Li, Y.; Chan, A.H.; Ng, S.C.; Loong, H.H.; Chan, D.T.; Wong, G.K.; Poon, W.S. A multifaceted review of temozolomide resistance mechanisms in glio-blastoma beyond O-6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase. Glioma 2019, 2, 68–82. [Google Scholar]
- Yi, G.-Z.; Huang, G.; Guo, M.; Zhang, X.; Wang, H.; Deng, S.; Li, Y.; Xiang, W.; Chen, Z.; Pan, J.; et al. Acquired temozolomide resistance in MGMT-deficient glioblastoma cells is associated with regulation of DNA repair by DHC2. Brain 2019, 142, 2352–2366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soni, V.; Adhikari, M.; Simonyan, H.; Lin, L.; Sherman, J.H.; Young, C.N.; Keidar, M. In Vitro and In Vivo Enhancement of Temozolomide Effect in Human Glioblastoma by Non-Invasive Application of Cold Atmospheric Plasma. Cancers 2021, 13, 4485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keidar, M.; Shashurin, A.; Volotskova, O.; Stepp, M.A.; Srinivasan, P.; Sandler, A.; Trink, B. Cold atmospheric plasma in cancer therapy. Phys. Plasmas 2013, 20, 057101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keidar, M.; Yan, D.; Beilis, I.I.; Trink, B.; Sherman, J.H. Plasmas for Treating Cancer: Opportunities for Adaptive and Self-Adaptive Approaches. Trends Biotechnol. 2018, 36, 586–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernhardt, T.; Semmler, M.L.; Schäfer, M.; Bekeschus, S.; Emmert, S.; Boeckmann, L. Plasma Medicine: Applications of Cold Atmospheric Pressure Plasma in Dermatology. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiong, Z. Cold Atmospheric Pressure Plasmas (COLD PLASMAs) for Skin Wound Healing; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Sakudo, A.; Yagyu, Y.; Onodera, T. Disinfection and Sterilization Using Plasma Technology: Fundamentals and Future Perspectives for Biological Applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adhikari, B.; Adhikari, M.; Ghimire, B.; Park, G.; Choi, E.H. Cold Atmospheric Plasma-Activated Water Irrigation Induces Defense Hormone and Gene expression in Tomato seedlings. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adhikari, B.; Adhikari, M.; Ghimire, B.; Adhikari, B.C.; Park, G.; Choi, E.H. Cold plasma seed priming modulates growth, redox homeostasis and stress response by inducing reactive species in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum). Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2020, 156, 57–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keidar, M. A prospectus on innovations in the plasma treatment of cancer. Phys. Plasmas 2018, 25, 083504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, M.; Kaushik, N.; Ghimire, B.; Adhikari, B.; Baboota, S.; Al-Khedhairy, A.A.; Wahab, R.; Lee, S.-J.; Kaushik, N.K.; Choi, E.H. Cold atmospheric plasma and silymarin nanoemulsion synergistically inhibits human melanoma tumorigenesis via targeting HGF/c-MET downstream pathway. Cell Commun. Signal. 2019, 17, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Adhikari, M.; Adhikari, B.; Adhikari, A.; Yan, D.; Soni, V.; Sherman, J.; Keidar, M. Cold Atmospheric Plasma as a Novel Therapeutic Tool for the Treatment of Brain Cancer. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2020, 26, 2195–2206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akter, M.; Jangra, A.; Choi, S.A.; Choi, E.H.; Han, I. Non-Thermal Atmospheric Pressure Bio-Compatible Plasma Stimulates Apoptosis via p38/MAPK Mechanism in U87 Malignant Glioblastoma. Cancers 2020, 12, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Adhikari, M.; Adhikari, B.; Kaushik, N.; Lee, S.-J.; Kaushik, N.K.; Choi, E.H. Melanoma Growth Analysis in Blood Serum and Tissue Using Xenograft Model with Response to Cold Atmospheric Plasma Activated Medium. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 4227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gjika, E.; Pal-Ghosh, S.; Tang, A.; Kirschner, M.; Tadvalkar, G.; Canady, J.; Stepp, M.A.; Keidar, M. Adaptation of Operational Parameters of Cold Atmospheric Plasma for in Vitro Treatment of Cancer Cells. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 9269–9279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, M.; Adhikari, B.; Ghimire, B.; Baboota, S.; Choi, E.H. Cold Atmospheric Plasma and Silymarin Nanoemulsion Activate Autophagy in Human Melanoma Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fridman, G.; Friedman, G.; Gutsol, A.; Shekhter, A.B.; Vasilets, V.N.; Fridman, A. Applied Plasma Medicine. Plasma Process. Polym. 2008, 5, 503–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dikalov, S.I.; Harrison, D.G. Methods for Detection of Mitochondrial and Cellular Reactive Oxygen Species. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2014, 20, 372–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leduc, M.; Guay, D.; Coulombe, S.; Leask, R.L. Effects of Non-thermal Plasmas on DNA and Mammalian Cells. Plasma Process. Polym. 2010, 7, 899–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Lin, L.; Soni, V.; Gjika, E.; Sherman, J.H.; Yan, D.; Keidar, M. Sensitization of glioblastoma cells to temozolomide by a helium gas discharge tube. Phys. Plasmas 2020, 27, 114502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shashurin, A.; Keidar, M.; Bronnikov, S.; Jurjus, R.A.; Stepp, M.A. Living tissue under treatment of cold plasma atmospheric jet. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 93, 181501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zucker, S.N.; Zirnheld, J.; Bagati, A.; Disanto, T.M.; Soye, B.D.; Wawrzyniak, J.A.; Etemadi, K.; Nikiforov, M.; Berezney, R. Preferential induction of apoptotic cell death in melanoma cells as compared with normal keratinocytes using a non-thermal plasma torch. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2012, 13, 1299–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iseki, S.; Nakamura, K.; Hayashi, M.; Tanaka, H.; Kondo, H.; Kajiyama, H.; Kano, H.; Kikkawa, F.; Hori, M. Selective killing of ovarian cancer cells through induction of apoptosis by nonequilibrium atmospheric pressure plasma. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2012, 100, 113702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushik, N.K.; Kaushik, N.; Yoo, K.C.; Uddin, N.; Kim, J.S.; Lee, S.J.; Choi, E.H. Low doses of PEG-coated gold nanoparticles sensitize solid tumors to cold plasma by blocking the PI3K/AKT-driven signaling axis to suppress cellular transformation by inhibiting growth and EMT. Biomaterials 2016, 87, 118–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Yu, H.; Ding, D.; Chen, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, S.; Li, X.; Keidar, M.; Zhang, W. Cold atmospheric plasma and iron oxide-based magnetic nanoparticles for synergetic lung cancer therapy. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2018, 130, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, W.; Lee, S.-J.; Castro, N.J.; Yan, D.; Keidar, M.; Zhang, L.G. Synergistic Effect of Cold Atmospheric Plasma and Drug Loaded Core-shell Nanoparticles on Inhibiting Breast Cancer Cell Growth. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 21974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Young, R.M.; Jamshidi, A.; Davis, G.; Sherman, J.H. Current trends in the surgical management and treatment of adult glioblastoma. Ann. Transl. Med. 2015, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gjika, E.; Pal-Ghosh, S.; Kirschner, M.E.; Lin, L.; Sherman, J.H.; Stepp, M.A.; Keidar, M. Combination therapy of cold atmospheric plasma (CAP) with temozolomide in the treatment of U87MG glioblastoma cells. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 16495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krautwald, S.; Ziegler, E.; Rölver, L.; Linkermann, A.; Keyser, K.A.; Steen, P.; Wollert, K.C.; Klingebiel, M.K.; Kunzendorf, U. Effective Blockage of Both the Extrinsic and Intrinsic Pathways of Apoptosis in Mice by TAT-crmA. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 19997–20005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bahadur, S.; Sahu, A.K.; Baghel, P.; Saha, S. Current promising treatment strategy for glioblastoma multiform: A review. Oncol. Rev. 2019, 13, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, P.; Du, X.L.; Lu, G.; Zhu, J.-J. Survival benefit of glioblastoma patients after FDA approval of temozolomide concomitant with radiation and bevacizumab: A population-based study. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 44015–44031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fridman, G.; Shereshevsky, A.; Jost, M.M.; Brooks, A.D.; Fridman, A.; Gutsol, A.; Vasilets, V.; Friedman, G. Floating Electrode Dielectric Barrier Discharge Plasma in Air Promoting Apoptotic Behavior in Melanoma Skin Cancer Cell Lines. Plasma Chem. Plasma Process. 2007, 27, 163–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Ito, F.; Wang, Y.; Okazaki, Y.; Tanaka, H.; Mizuno, M.; Hori, M.; Hirayama, T.; Nagasawa, H.; Richardson, D.R.; et al. Non-thermal plasma induces a stress response in mesothelioma cells resulting in increased endocytosis, lysosome biogenesis and autophagy. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2017, 108, 904–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semmler, M.L.; Bekeschus, S.; Schäfer, M.; Bernhardt, T.; Fischer, T.; Witzke, K.; Seebauer, C.; Rebl, H.; Grambow, E.; Vollmar, B.; et al. Molecular Mechanisms of the Efficacy of Cold Atmospheric Pressure Plasma (CAP) in Cancer Treatment. Cancers 2020, 12, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Domonkos, M.; Tichá, P.; Trejbal, J.; Demo, P. Applications of Cold Atmospheric Pressure Plasma Technology in Medicine, Agriculture and Food Industry. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 4809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Shi, X.; Wu, X. Applications and challenges of low temperature plasma in pharmaceutical field. J. Pharm. Anal. 2020, 11, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.Y. Temozolomide resistance in glioblastoma multiforme. Genes Dis. 2016, 3, 198–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stupp, R.; Mason, W.P.; van den Bent, M.J.; Weller, M.; Fisher, B.; Taphoorn, M.J.B.; Belanger, K.; Brandes, A.A.; Marosi, C.; Bogdahn, U.; et al. Radiotherapy plus Concomitant and Adjuvant Temozolomide for Glioblastoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 987–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parisi, S.; Corsa, P.; Raguso, A.; Perrone, A.; Cossa, S.; Munafò, T.; Sanpaolo, G.; Donno, E.; Clemente, M.A.; Piombino, M.; et al. Temozolomide and Radiotherapy versus Radiotherapy Alone in High Grade Gliomas: A Very Long Term Comparative Study and Literature Review. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Combs, S.E.; Gutwein, S.; Schulz-Ertner, D.; van Kampen, M.; Thilmann, C.; Edler, L.; Wannenmacher, M.M.; Debus, J. Temozolomide Combined with Irradiation as Postoperative Treatment of Primary Glioblastoma Multiforme. Strahlenther. und Onkol. 2005, 181, 372–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Goldstein, I.; Lin, L.; Sherman, J.H.; Keidar, M. Comparative Study of Cancer Treatment Potential Effects of Tumor-Treating Fields and Cold Atmospheric Plasma. Plasma Med. 2020, 10, 45–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rominiyi, O.; Vanderlinden, A.; Clenton, S.J.; Bridgewater, C.; Al-Tamimi, Y.; Collis, S.J. Tumour treating fields therapy for glioblastoma: Current advances and future directions. Br. J. Cancer 2020, 124, 697–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrieri, F.A.; Smack, C.; Siddiqui, I.; Kleinberg, L.R.; Tran, P.T. Tumor Treating Fields: At the Crossroads Between Physics and Biology for Cancer Treatment. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 575992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.J.; Chung, T.H. Cold atmospheric plasma jet-generated RONS and their selective effects on normal and carcinoma cells. Sci, Rep. 2016, 6, 20332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bauer, G. The synergistic effect between hydrogen peroxide and nitrite, two long-lived molecular species from cold atmospheric plasma, triggers tumor cells to induce their own cell death. Redox Biol. 2019, 26, 101291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köritzer, J.; Boxhammer, V.; Schäfer, A.; Shimizu, T.; Klämpfl, T.G.; Li, Y.-F.; Welz, C.; Schwenk-Zieger, S.; Morfill, G.E.; Zimmermann, J.L.; et al. Restoration of Sensitivity in Chemo—Resistant Glioma Cells by Cold Atmospheric Plasma. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e64498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yadav, D.K.; Adhikari, M.; Kumar, S.; Ghimire, B.; Han, I.; Kim, M.-H.; Choi, E.-H. Cold atmospheric plasma generated reactive species aided inhibitory effects on human melanoma cells: An in vitro and in silico study. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 3396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, S.R.; Erickson, L.A.; Ichetovkin, I.; Knauer, D.J.; Markovic, S.N. Circulating Serologic and Molecular Biomarkers in Malignant Melanoma. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2011, 86, 981–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goldman, R.D.; O’Kaplan, N.; Hall, T.C. Lactic Dehydrogenase in Human Neoplastic Tissues. Cancer Res. 1964, 24, 389–399. [Google Scholar]
- Buchanan, J.D.; Armstrong, D. Free radical inactivation of lactate dehydrogenase. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. Relat. Stud. Phys. Chem. Med. 1976, 30, 115–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Soni, V.; Adhikari, M.; Lin, L.; Sherman, J.H.; Keidar, M. Theranostic Potential of Adaptive Cold Atmospheric Plasma with Temozolomide to Checkmate Glioblastoma: An In Vitro Study. Cancers 2022, 14, 3116. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14133116
Soni V, Adhikari M, Lin L, Sherman JH, Keidar M. Theranostic Potential of Adaptive Cold Atmospheric Plasma with Temozolomide to Checkmate Glioblastoma: An In Vitro Study. Cancers. 2022; 14(13):3116. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14133116
Chicago/Turabian StyleSoni, Vikas, Manish Adhikari, Li Lin, Jonathan H. Sherman, and Michael Keidar. 2022. "Theranostic Potential of Adaptive Cold Atmospheric Plasma with Temozolomide to Checkmate Glioblastoma: An In Vitro Study" Cancers 14, no. 13: 3116. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14133116
APA StyleSoni, V., Adhikari, M., Lin, L., Sherman, J. H., & Keidar, M. (2022). Theranostic Potential of Adaptive Cold Atmospheric Plasma with Temozolomide to Checkmate Glioblastoma: An In Vitro Study. Cancers, 14(13), 3116. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14133116







