The Systemic Inflammatory Response Identifies Patients with Adverse Clinical Outcome from Immunotherapy in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
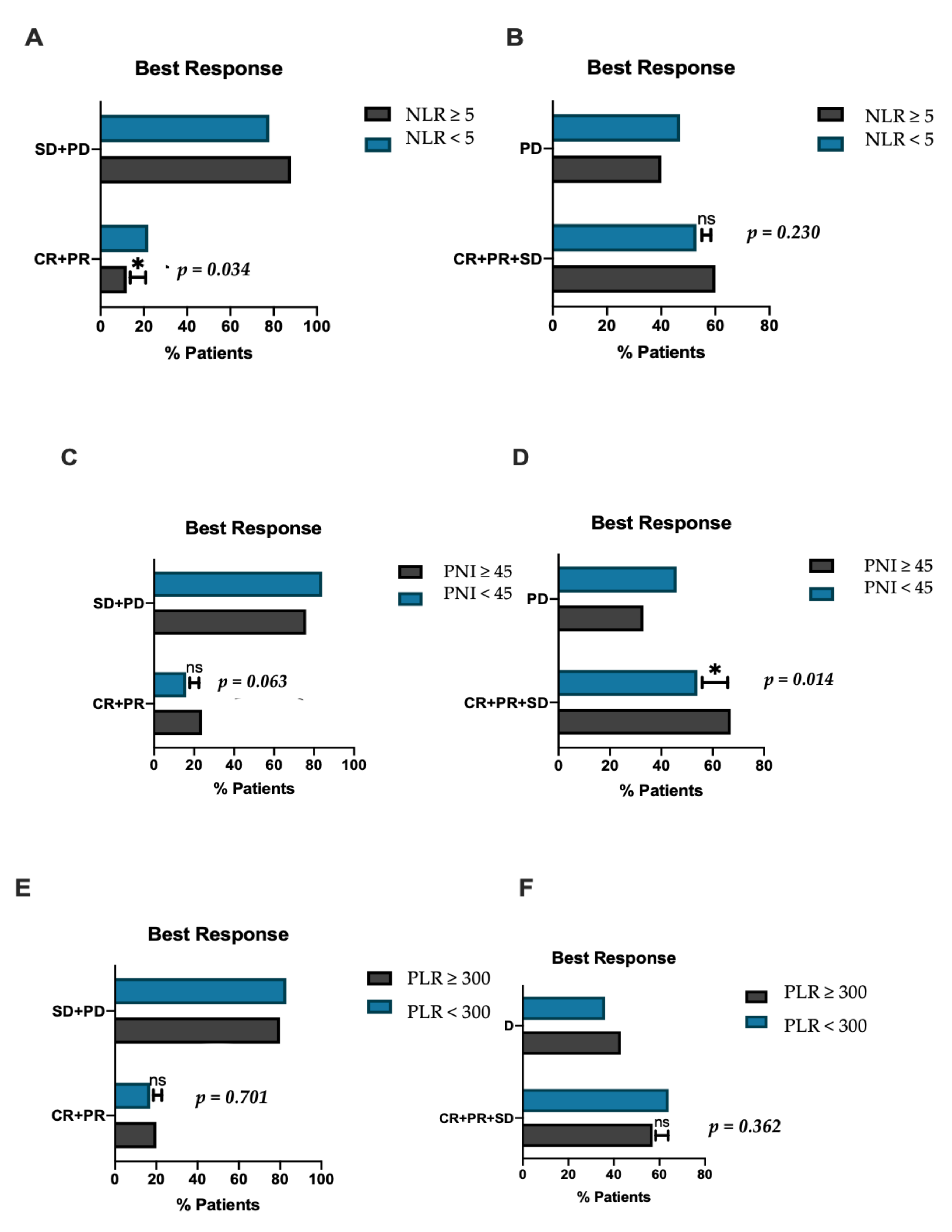
3. Results
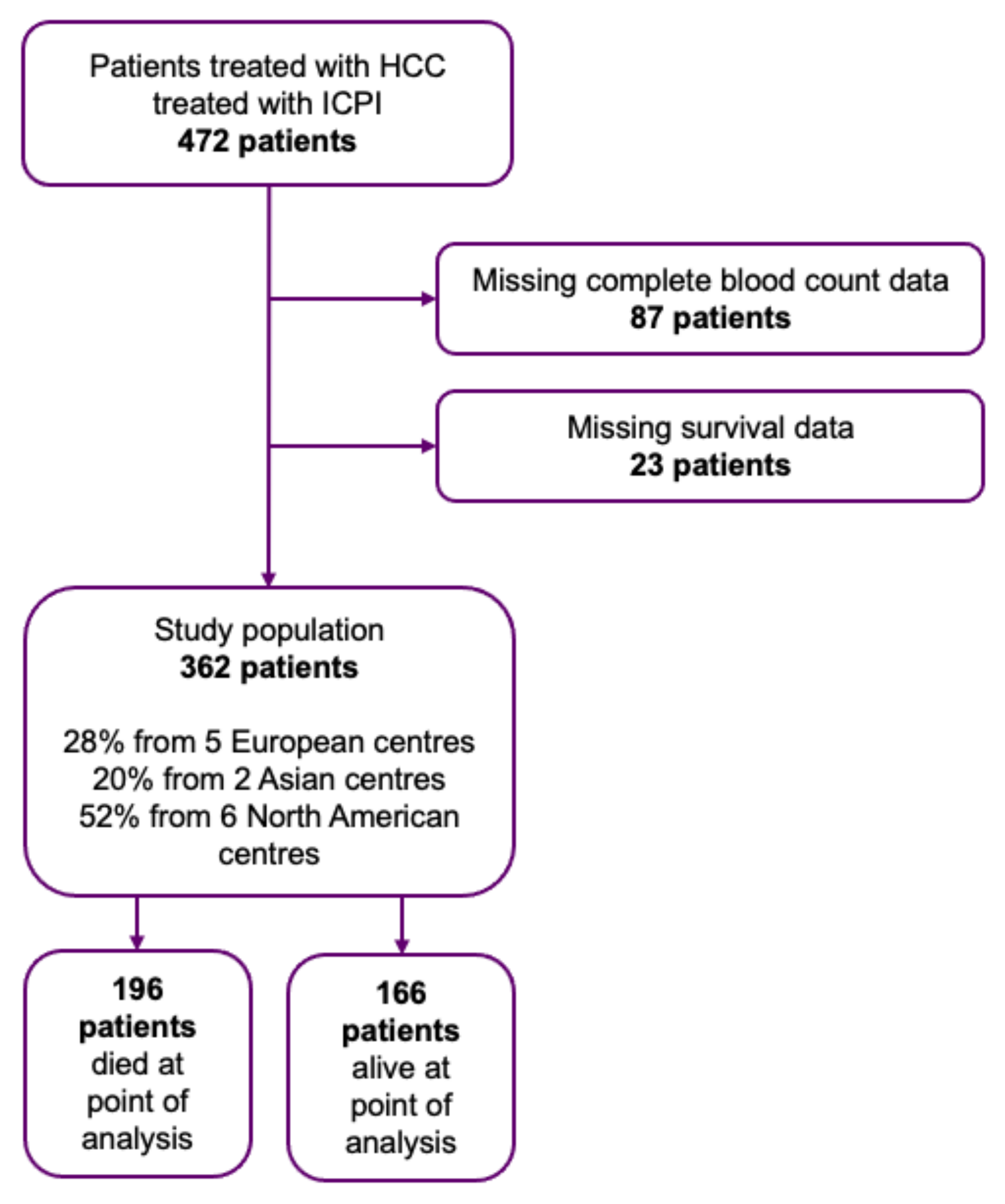
3.1. Patient and Disease Characteristics
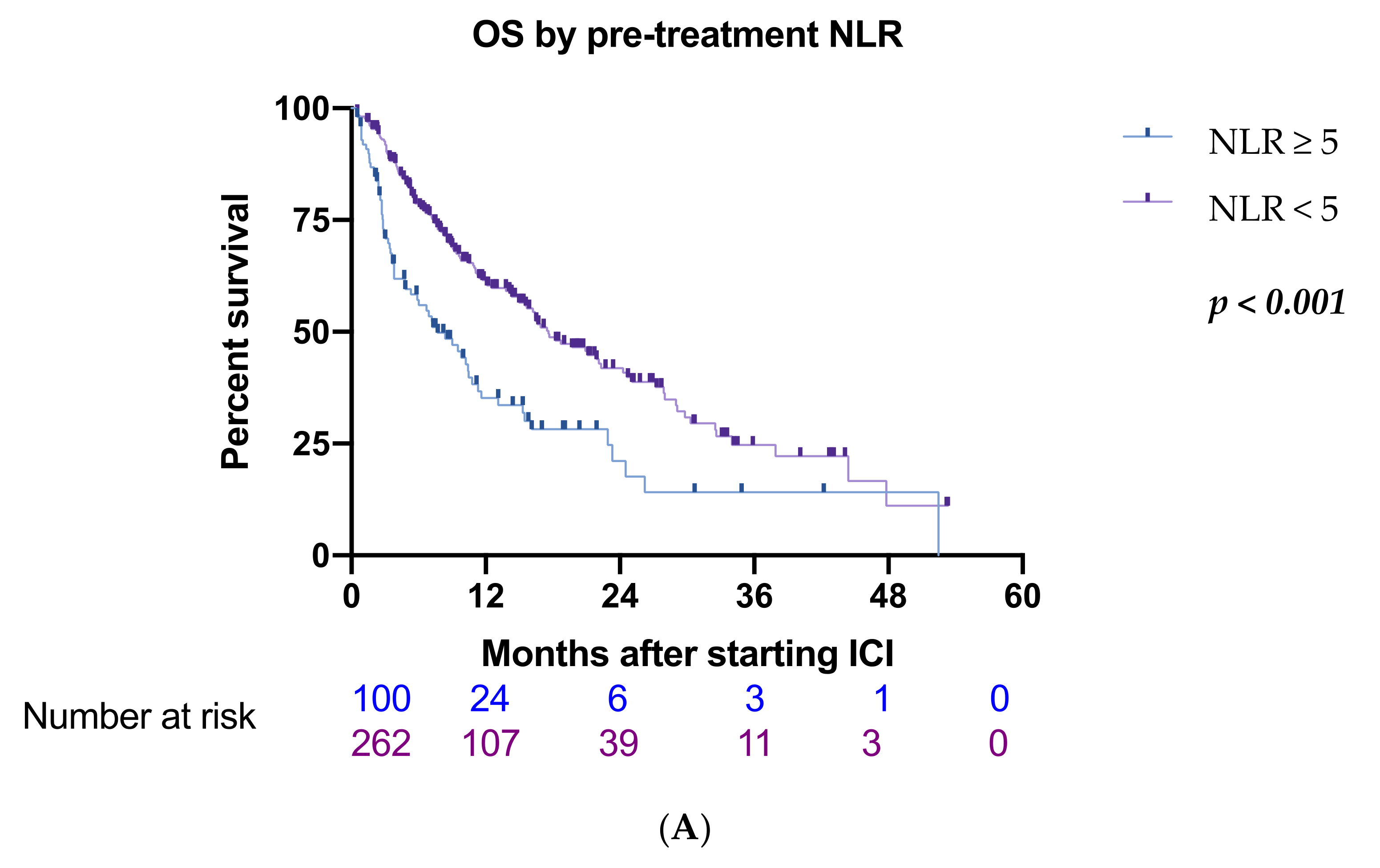
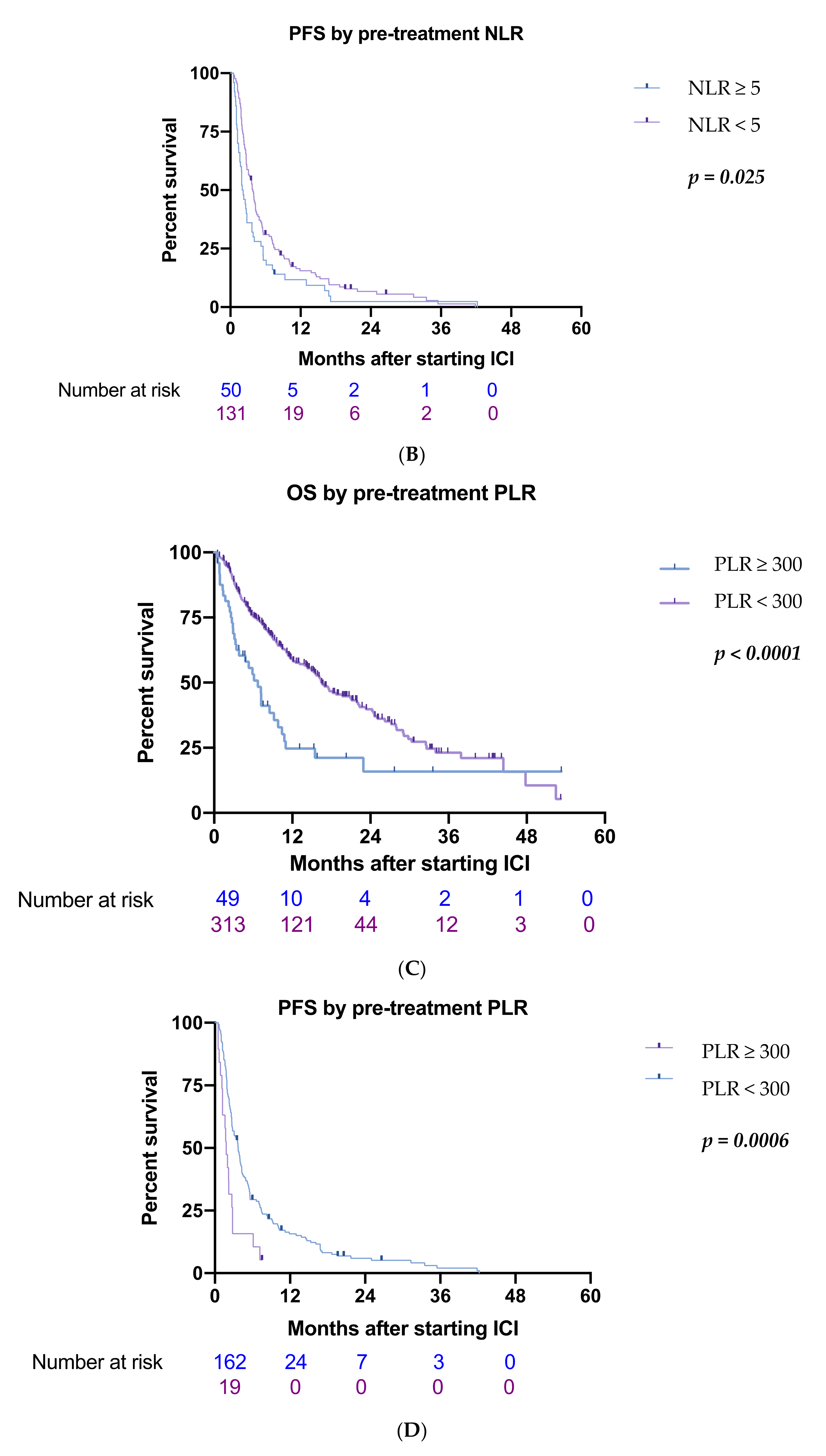
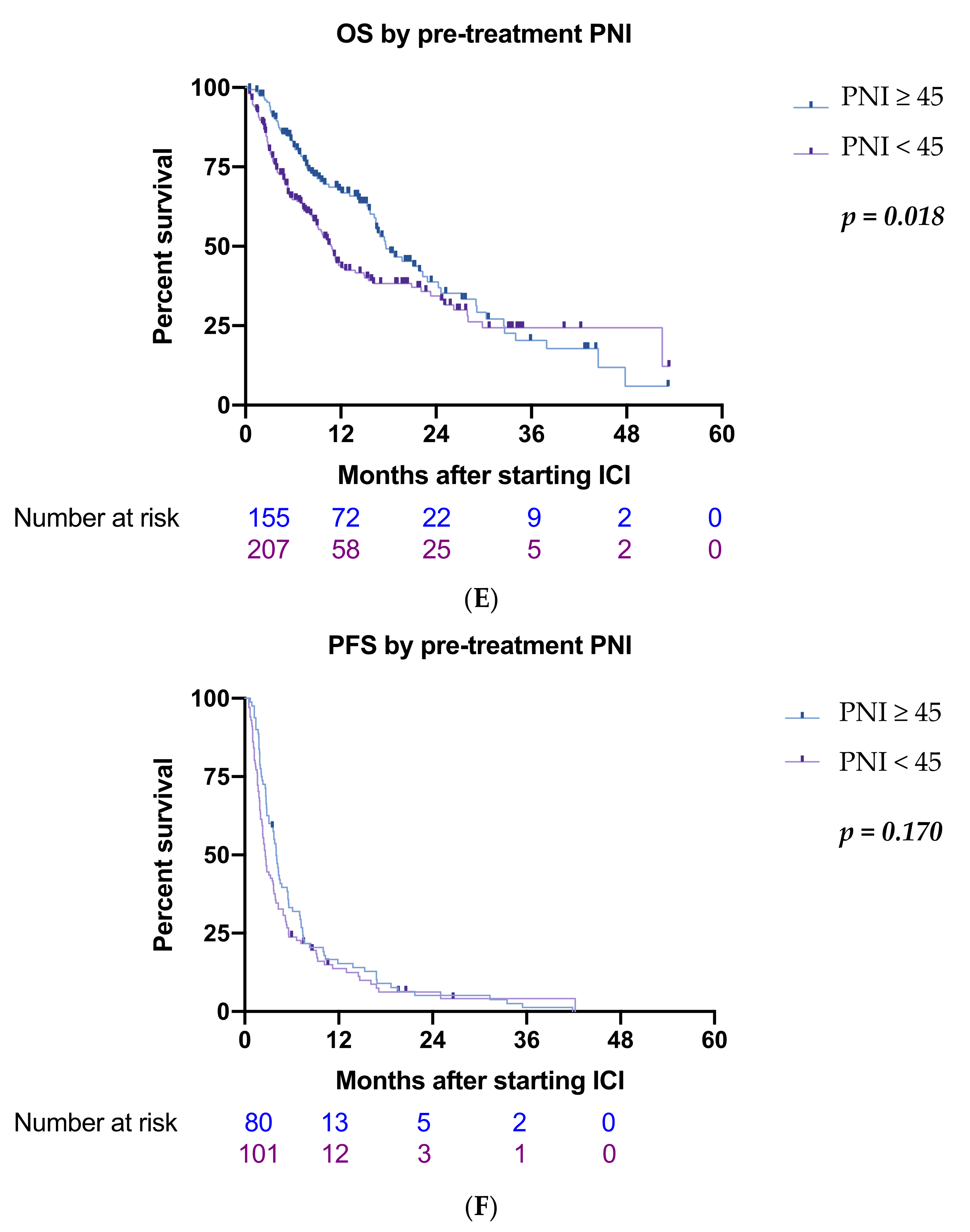
3.2. Inflammatory Biomarkers
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yegin, E.G.; Oymaci, E.; Karatay, E.; Coker, A. Progress in surgical and nonsurgical approaches for hepatocellular carcinoma treatment. Hepatobiliary Pancreat. Dis. Int. 2016, 15, 234–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinato, D.J.; Guerra, N.; Fessas, P.; Murphy, R.; Mineo, T.; Mauri, F.A.; Mukherjee, S.K.; Thursz, M.; Wong, C.N.; Sharma, R.; et al. Immune-based therapies for hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene 2020, 39, 3620–3637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yau, T.; Kang, Y.K.; Kim, T.Y.; El-Khoueiry, A.B.; Santoro, A.; Sangro, B.; Melero, I.; Kudo, M.; Hou, M.M.; Matilla, A.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Nivolumab Plus Ipilimumab in Patients With Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma Previously Treated With Sorafenib: The CheckMate 040 Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Oncol. 2020, 6, e204564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yau, T.; Park, J.W.; Finn, R.S.; Cheng, A.L.; Mathurin, P.; Edeline, J.; Kudo, M.; Han, K.H.; Harding, J.J.; Merle, P.; et al. CheckMate 459: A randomized, multi-center phase III study of nivolumab (NIVO) vs. sorafenib (SOR) as first-line (1L) treatment in patients (pts) with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (aHCC). Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, 874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finn, R.S.; Ryoo, B.Y.; Merle, P.; Kudo, M.; Bouattour, M.; Lim, H.Y.; Breder, V.; Edeline, J.; Chao, Y.; Ogasawara, S.; et al. Pembrolizumab As Second-Line Therapy in Patients With Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma in KEYNOTE-240: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Phase III Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finn, R.S.; Qin, S.; Ikeda, M.; Galle, P.R.; Ducreux, M.; Kim, T.Y.; Kudo, M.; Breder, V.; Merle, P.; Kaseb, A.O.; et al. Atezolizumab plus Bevacizumab in Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma. N Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1894–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finn, R.S.; Qin, S.; Ikeda, M.; Galle, P.R.; Ducreux, M.; Kim, T.-Y.; Lim, H.Y.; Kudo, M.; Breder, V.V.; Merle, P.; et al. IMbrave150: Updated overall survival (OS) data from a global, randomized, open-label phase III study of atezolizumab (atezo) + bevacizumab (bev) versus sorafenib (sor) in patients (pts) with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Alessio, A.; Fulgenzi, C.A.M. Treating patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma and impaired liver function: Broadening the reach of anti-cancer therapy. Liver Cancer Int. 2021, 2, 31–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinter, M.; Jain, R.K.; Duda, D.G. The Current Landscape of Immune Checkpoint Blockade in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Review. JAMA Oncol. 2021, 7, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinato, D.J.; Mauri, F.A.; Spina, P.; Cain, O.; Siddique, A.; Goldin, R.; Victor, S.; Pizio, C.; Akarca, A.U.; Boldorini, R.L.; et al. Clinical implications of heterogeneity in PD-L1 immunohistochemical detection in hepatocellular carcinoma: The Blueprint-HCC study. Br. J. Cancer 2019, 120, 1033–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ang, C.; Klempner, S.J.; Ali, S.M.; Madison, R.; Ross, J.S.; Severson, E.A.; Fabrizio, D.; Goodman, A.; Kurzrock, R.; Suh, J.; et al. Prevalence of established and emerging biomarkers of immune checkpoint inhibitor response in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget 2019, 10, 4018–4025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pinato, D.J.; Stebbing, J.; Ishizuka, M.; Khan, S.A.; Wasan, H.S.; North, B.V.; Kubota, K.; Sharma, R. A novel and validated prognostic index in hepatocellular carcinoma: The inflammation based index (IBI). J. Hepatol. 2012, 57, 1013–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanghera, C.; Teh, J.J.; Pinato, D.J. The systemic inflammatory response as a source of biomarkers and therapeutic targets in hepatocellular carcinoma. Liver Int. 2019, 39, 2008–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sangro, B.; Melero, I.; Wadhawan, S.; Finn, R.S.; Abou-Alfa, G.K.; Cheng, A.L.; Yau, T.; Furuse, J.; Park, J.W.; Boyd, Z.; et al. Association of inflammatory biomarkers with clinical outcomes in nivolumab-treated patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2020, 73, 1460–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelley, R.K.; Sangro, B.; Harris, W.; Ikeda, M.; Okusaka, T.; Kang, Y.K.; Qin, S.; Tai, D.W.; Lim, H.Y.; Yau, T.; et al. Safety, Efficacy, and Pharmacodynamics of Tremelimumab Plus Durvalumab for Patients with Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Randomized Expansion of a Phase I/II Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 27, 2991–3001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diakos, C.I.; Charles, K.A.; McMillan, D.C.; Clarke, S.J. Lancet Oncol. 2014, 15, e493–e503. [CrossRef]
- Personeni, N.; Giordano, L.; Abbadessa, G.; Porta, C.; Borbath, I.; Daniele, B.; Van Laethem, J.L.; Van Vlierberghe, H.; Trojan, J.; De Toni, E.N.; et al. Prognostic value of the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in the ARQ 197-215 second-line study for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 14408–14415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caputo, F.; Dadduzio, V.; Tovoli, F.; Bertolini, G.; Cabibbo, G.; Cerma, K.; Vivaldi, C.; Faloppi, L.; Rizzato, M.D.; Piscaglia, F.; et al. The role of PNI to predict survival in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma treated with Sorafenib. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0232449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinato, D.J.; North, B.V.; Sharma, R. A novel, externally validated inflammation-based prognostic algorithm in hepatocellular carcinoma: The prognostic nutritional index (PNI). Br. J. Cancer 2012, 106, 1439–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dharmapuri, S.; Ozbek, U.; Lin, J.Y.; Sung, M.; Schwartz, M.; Branch, A.D.; Ang, C. Predictive value of neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio and platelet to lymphocyte ratio in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma patients treated with anti-PD-1 therapy. Cancer Med. 2020, 9, 4962–4970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanemura, A.; Mizuno, S.; Hayasaki, A.; Gyoten, K.; Fujii, T.; Iizawa, Y.; Kato, H.; Murata, Y.; Kuriyama, N.; Kishiwada, M.; et al. Onodera’s prognostic nutritional index is a strong prognostic indicator for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma after initial hepatectomy, especially patients with preserved liver function. BMC Surg. 2020, 20, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulgenzi, C.A.M.; Talbot, T.; Murray, S.M.; Silletta, M.; Vincenzi, B.; Cortellini, A.; Pinato, D.J. Immunotherapy in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Curr. Treat. Options Oncol. 2021, 22, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Q.; Wang, X.Y.; Qiu, S.J.; Yamato, I.; Sho, M.; Nakajima, Y.; Zhou, J.; Li, B.Z.; Shi, Y.H.; Xiao, Y.S.; et al. Overexpression of PD-L1 significantly associates with tumor aggressiveness and postoperative recurrence in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 971–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yamamoto, H.; Itoh, F.; Fukushima, H.; Kaneto, H.; Sasaki, S.; Ohmura, T.; Satoh, T.; Karino, Y.; Endo, T.; Toyota, J.; et al. Infrequent widespread microsatellite instability in hepatocellular carcinomas. Int. J. Oncol. 2000, 16, 543–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luke, J.J.; Bao, R.; Sweis, R.F.; Spranger, S.; Gajewski, T.F. WNT/beta-catenin Pathway Activation Correlates with Immune Exclusion across Human Cancers. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 3074–3083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sia, D.; Jiao, Y.; Martinez-Quetglas, I.; Kuchuk, O.; Villacorta-Martin, C.; Castro de Moura, M.; Putra, J.; Camprecios, G.; Bassaganyas, L.; Akers, N.; et al. Identification of an Immune-specific Class of Hepatocellular Carcinoma, Based on Molecular Features. Gastroenterology 2017, 153, 812–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Van der Windt, D.J.; Sud, V.; Zhang, H.; Varley, P.R.; Goswami, J.; Yazdani, H.O.; Tohme, S.; Loughran, P.; O’Doherty, R.M.; Minervini, M.I.; et al. Neutrophil extracellular traps promote inflammation and development of hepatocellular carcinoma in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatology 2018, 68, 1347–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhou, S.L.; Yin, D.; Hu, Z.Q.; Luo, C.B.; Zhou, Z.J.; Xin, H.Y.; Yang, X.R.; Shi, Y.H.; Wang, Z.; Huang, X.W.; et al. A Positive Feedback Loop Between Cancer Stem-Like Cells and Tumor-Associated Neutrophils Controls Hepatocellular Carcinoma Progression. Hepatology 2019, 70, 1214–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarker, D.; Plummer, R.; Meyer, T.; Sodergren, M.H.; Basu, B.; Chee, C.E.; Huang, K.W.; Palmer, D.H.; Ma, Y.T.; Evans, T.R.J.; et al. MTL-CEBPA, a Small Activating RNA Therapeutic Upregulating C/EBP-alpha, in Patients with Advanced Liver Cancer: A First-in-Human, Multicenter, Open-Label, Phase I Trial. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 3936–3946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashimoto, A.; Sarker, D.; Reebye, V.; Jarvis, S.; Sodergren, M.H.; Kossenkov, A.; Sanseviero, E.; Raulf, N.; Vasara, J.; Andrikakou, P.; et al. Upregulation of C/EBPalpha Inhibits Suppressive Activity of Myeloid Cells and Potentiates Antitumor Response in Mice and Patients with Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 27, 5961–5978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Gender | |
| Male | 284 (78.5) |
| Female | 78 (21.5) |
| Age | Median (LQ-UQ) = 65 (58–70) |
| <65 | 180 (49.7) |
| ≥65 | 182 (50.3) |
| Aetiology | |
| HBV | 81 (22.4) |
| HCV | 121 (33.4) |
| Alcohol induced | 81 (22.4) |
| NASH | 43 (11.9) |
| Other | 36 (9.94) |
| Cirrhosis | |
| Present | 259 (71.5) |
| Absent | 103 (28.5) |
| Portal vein thrombosis | |
| Present | 247 (68.2) |
| Absent | 115 (31.5) |
| Child-Pugh Class | |
| A | 272 (75.1) |
| B | 90 (24.9) |
| ALBI grade | |
| 1 | 129 (35.6) |
| 2 | 137 (29) |
| 3 | 96 (25.4) |
| ECOG Performance status | |
| 0 | 168 (46.4) |
| 1 | 174 (48.1) |
| 2 | 17 (4.7) |
| 3 | 3 (0.8) |
| Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer stage | |
| A | 13 (3.6) |
| B | 80 (22.1) |
| C | 269 (74.3) |
| Mean tumour diameter | Median (LQ-UQ) = 6.0 (3.0 −10.8) |
| Extrahepatic metastasis | |
| Present | 193 (53.3) |
| Absent | 169 (46.7) |
| Immunotherapy | |
| Nivolumab | 218 (60.2) |
| Pembrolizumab | 45 (12.4) |
| Ipilimumab | 1 (0.3) |
| Ipilimumab/Nivolumab | 13 (3.6) |
| Avelumab | 1 (0.3) |
| Atezolizumab | 11 (3.0) |
| Durvalumab | 8 (2.2) |
| Other PD-1 single agents | 13 (3.6) |
| PD-1, CTLA-4 combination | 14 (3.9) |
| PD-1, TKI combination | 24 (6.6) |
| Other PD-1 combinations | 14 (3.9) |
| Variable | NLR | p-Value | PLR | p-Value | PNI | p-Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| <5 | ≥5 | <300 | ≥300 | <45 | ≥45 | ||||
| Portal-vein thrombosis Absent/ Present | 194/68 (74%)(26%) | 53/47 (53%)(47%) | ≤0.001 *** | 217/92 (70.2%) (29.8%) | 26/27 (49%)(51%) | 0.004 ** | 126/81 (61%)(39%) | 121/34 (78%) (22%) | 0.001 ** |
| Child-Pugh class A/B | 202/60 (77%)(23%) | 70/30 (70%)(30%) | 0.162 | 239/70 (77.3%) (22.7%) | 33/20 (62.3%) (37.7%) | 0.025 * | 135/72 (65%)(35%) | 137/18 (88%) (12%) | <0.001 *** |
| ECOG performance status 0/1/2/3 | 135/116/9/2 (51.5%) (44.2%) (3.4%)(0.9%) | 33/58/8/1 (33%)(58%) (8%)(1%) | 0.009 ** | 152/143/14/0 (49%) (46%) (5%) | 16/29/8/0 (30.2%) (54.7%) (5.1%) | 0.011 * | 72/117/16/2 (34.8)(56%) (7.7%) (9.2%) | 96/57/1/1 (61.9%) (36.7%) (0.7%) | <0.001 *** |
| BCLC stage A/B/C | 10/67/185 (3.8%) (25.6%) (70.6%) | 3/13/84 (3%)(13%) (84%) | 0.029 * | 7/75/227 (2.3%) (24.2%) (73.5%) | 3/8/42 (5.6%) (15%) (79.4%) | <0.001 *** | 11/34/162 (5.3%) (16.4%) (78.3%) | 2/46/107 (1.4%) (29.6%) (69%) | 0.002 ** |
| ALBI grade 1/2/3 | 99/90/73 (37.8%)(34%) (28.2%) | 31/49/20 (31%)(49%) (20%) | 0.334 | 114/74/121 (36.8%) (24%) (39.2%) | 18/28/7 (33.9%) (52.8%) (13.3%) | 0.758 | 61/92/54 (29.5%) (44.4%) (26.1%) | 71/38/46 (45.8%) (24.5%) (29.7%) | 0.279 |
| Extrahepatic spread Absent/ Present | 127/135 (48%)(52%) | 42/58 (42%)(58%) | 0.270 | 146/163 (47.2%) (52.8%) | 23/30 (43.4%) (56.6%) | 0.656 | 94/113 (45%)(55%) | 75/80 (48%) (52%) | 0.574 |
| Aetiology Viral/ Non-viral | 180/107 (62%)(38%) | 44/45 (49%)(51%) | 0.04 * | 169/144 (54%)(46%) | 23/24 (49%)(51%) | 0.53 | 115/91 (56%)(44%) | 85/69 (55%)(45%) | 0.92 |
| Prognostic Factor | Univariate Analysis | Multivariate Analysis | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n = 362 | HR (95% CI) | p Value | HR (95%) | p Value | |
| NLR | |||||
| ≥5/<5 | 100/262 | 1.95 (1.45–2.64) | <0.001 *** | 1.73 (1.23–2.42) | 0.002 ** |
| PLR | |||||
| ≥300/<300 | 53/309 | 2.05 (1.42–2.98) | <0.001 *** | 1.60 (1.6–2.40) | 0.020 * |
| PNI | |||||
| ≥45/<45 | 207/155 | 0.71 (0.53–0.94) | 0.018 * | 0.99 (0.71–1.37) | 0.940 |
| PVT | |||||
| Present/Absent | 247/115 | 1.78 (1.34–2.38) | <0.001 *** | 1.49 (1.02–2.02) | 0.010 * |
| ECOG performance score | |||||
| 0–1/2–3 | 342/20 | 1.49 (0.83–2.67) | 0.186 | ||
| ALBI grade | |||||
| 1/2–3 | 129/233 | 1.30 (0.90–1.89) | 0.151 | ||
| BCLC stage | |||||
| C/A-B | 269/93 | 1.19 (0.85–1.64) | 0.309 | ||
| Child-Pugh class | |||||
| B/A | 90/272 | 1.81 (1.33–2.46) | <0.001 *** | 1.62 (1.17–2.25) | 0.004 ** |
| Extrahepatic metastasis | |||||
| Present/Absent | 193/169 | 1.17 (0.88–1.55) | 0.275 | ||
| HCC Aetiology | |||||
| Viral/Non-viral | 197/164 | 0.93 (0.70−1.24) | 0.620 | ||
| Prognostic Factor | Univariate Analysis | Multivariate Analysis | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n = 362 | HR (95% CI) | p Value | HR (95%) | p Value | |
| NLR | |||||
| ≥5/<5 | 100/262 | 1.54 (1.03–2.30) | 0.036 * | 1.21 (0.82–1.78) | 0.331 |
| PLR | |||||
| ≥ 300/<300 | 53/309 | 2.33 (1.41–3.83) | 0.001 ** | 1.99 (1.11–3.49) | 0.021 * |
| PNI | |||||
| ≥ 45/<45 | 207/155 | 0.86 (0.60–1.24) | 0.423 | ||
| PVT | |||||
| Present/Absent | 247/115 | 1.53 (1.04–2.24) | 0.030 * | 1.12 (0.81–1.58) | 0.480 |
| ECOG performance score | |||||
| 0–1/2–3 | 342/20 | 1.18 (0.58–2.43) | 0.649 | ||
| ALBI grade | |||||
| 1/2–3 | 129/233 | 0.72 (0.50–1.04) | 0.091 | ||
| Child-Pugh class | |||||
| B/A | 90/272 | 1.39 (0.92–2.09) | 0.115 | ||
| Extrahepatic metastasis | |||||
| Present/Absent | 193/169 | 0.97 (0.67–1.39) | 0.855 | ||
| HCC Aetiology | |||||
| Viral/Non-viral | 197/164 | 0.85 (0–62-1.15) | 0.290 | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Muhammed, A.; Fulgenzi, C.A.M.; Dharmapuri, S.; Pinter, M.; Balcar, L.; Scheiner, B.; Marron, T.U.; Jun, T.; Saeed, A.; Hildebrand, H.; et al. The Systemic Inflammatory Response Identifies Patients with Adverse Clinical Outcome from Immunotherapy in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancers 2022, 14, 186. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14010186
Muhammed A, Fulgenzi CAM, Dharmapuri S, Pinter M, Balcar L, Scheiner B, Marron TU, Jun T, Saeed A, Hildebrand H, et al. The Systemic Inflammatory Response Identifies Patients with Adverse Clinical Outcome from Immunotherapy in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancers. 2022; 14(1):186. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14010186
Chicago/Turabian StyleMuhammed, Ambreen, Claudia Angela Maria Fulgenzi, Sirish Dharmapuri, Matthias Pinter, Lorenz Balcar, Bernhard Scheiner, Thomas U. Marron, Tomi Jun, Anwaar Saeed, Hannah Hildebrand, and et al. 2022. "The Systemic Inflammatory Response Identifies Patients with Adverse Clinical Outcome from Immunotherapy in Hepatocellular Carcinoma" Cancers 14, no. 1: 186. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14010186
APA StyleMuhammed, A., Fulgenzi, C. A. M., Dharmapuri, S., Pinter, M., Balcar, L., Scheiner, B., Marron, T. U., Jun, T., Saeed, A., Hildebrand, H., Muzaffar, M., Navaid, M., Naqash, A. R., Gampa, A., Ozbek, U., Lin, J.-Y., Perone, Y., Vincenzi, B., Silletta, M., ... Pinato, D. J. (2022). The Systemic Inflammatory Response Identifies Patients with Adverse Clinical Outcome from Immunotherapy in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancers, 14(1), 186. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14010186













