Classification of Clinically Significant Prostate Cancer on Multi-Parametric MRI: A Validation Study Comparing Deep Learning and Radiomics
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Data Sets
2.2. MR Imaging and Pre-Processing
2.3. Development of the Models
2.3.1. Deep-Learning Network
2.3.2. Radiomics Model Development
2.4. Methods Performance Comparison
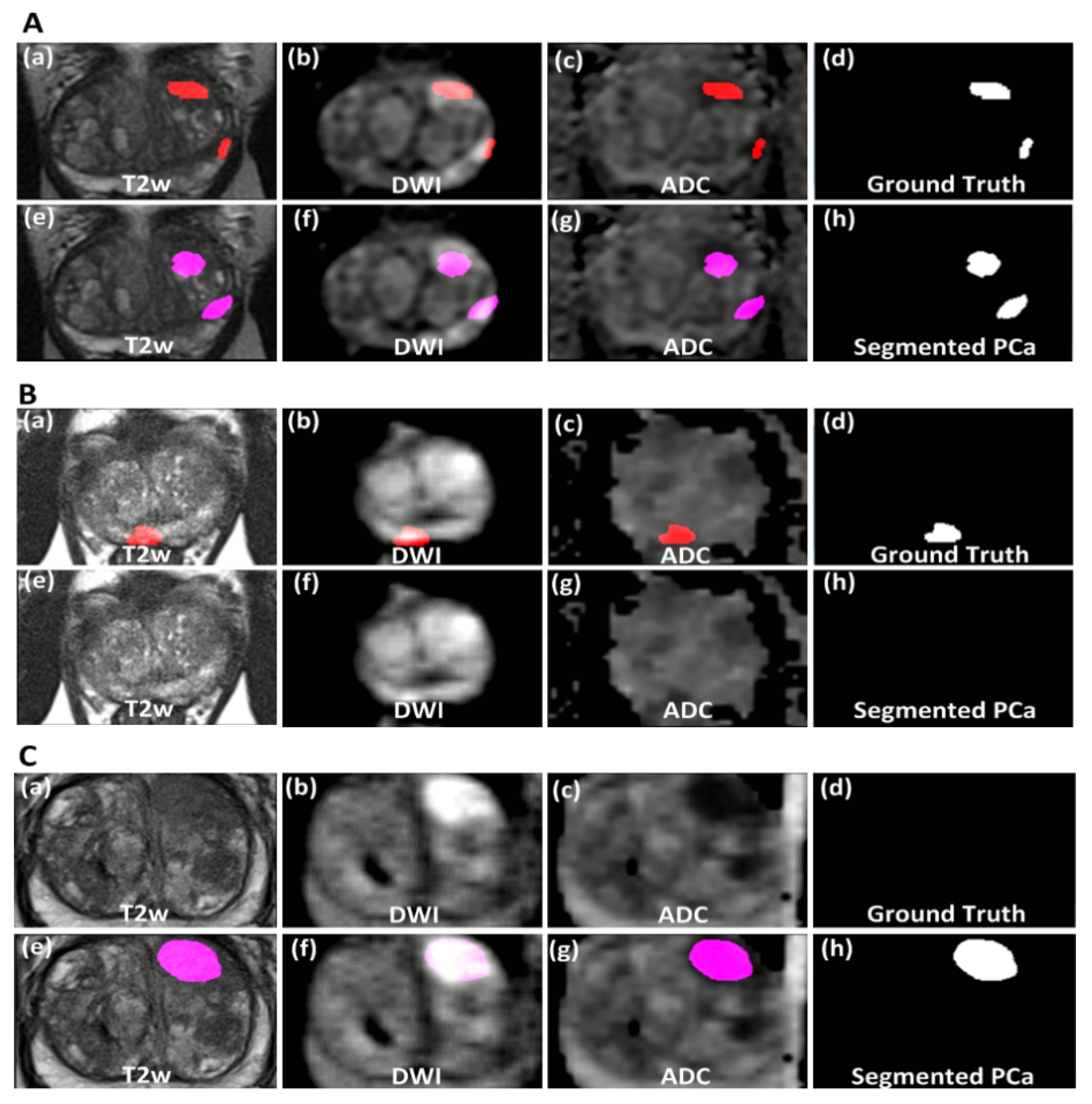
3. Results
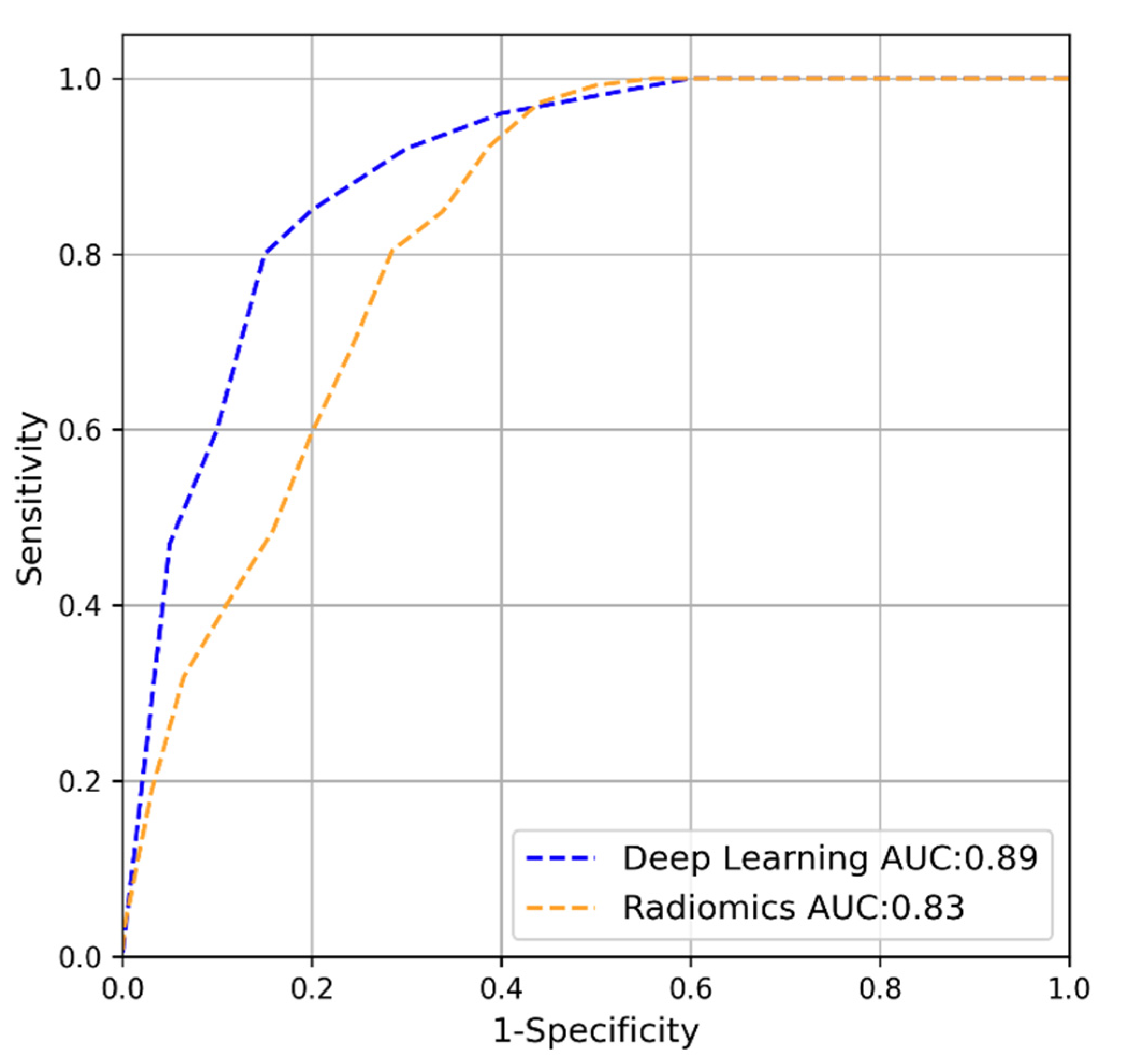
3.1. Internal Cross-Validation
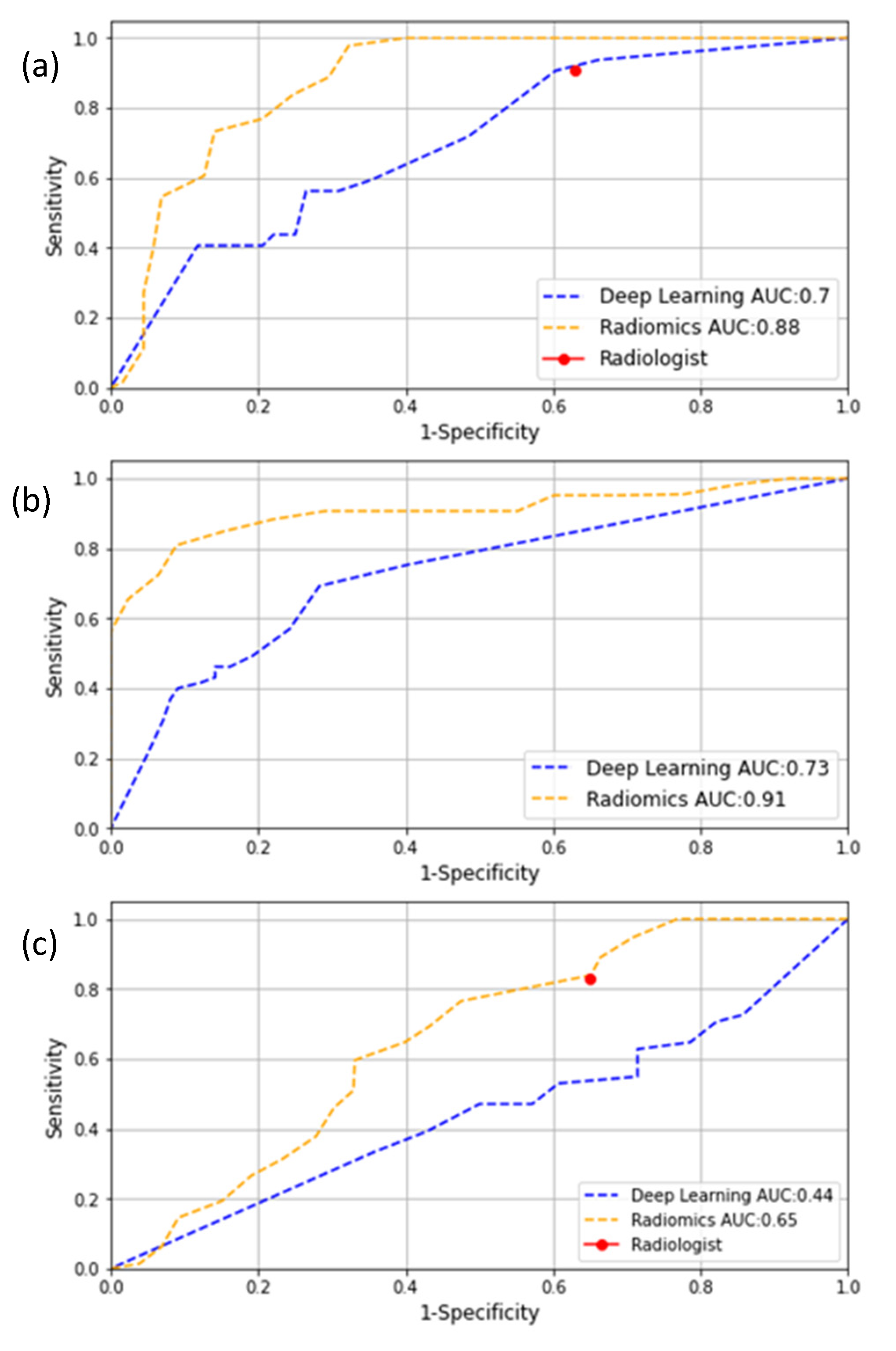
3.2. External-Validation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Radiomics Features Extraction
Appendix B. Adaptive Workflow Optimization for Automatic Decision-Model Creation
References
- Heidenreich, A.; Bastian, P.J.; Bellmunt, J.; Bolla, M.; Joniau, S.; Van Der Kwast, T.; Mason, M.; Matveev, V.; Wiegel, T.; Zattoni, F.; et al. EAU Guidelines on Prostate Cancer. Part 1: Screening, Diagnosis, and Local Treatment with Curative Intent—Update 2013. Eur. Urol. 2014, 65, 124–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drost, F.-J.H.; Osses, D.F.; Nieboer, D.; Steyerberg, E.W.; Bangma, C.H.; Roobol, M.J.; Schoots, I.G. Prostate MRI, with or without MRI-Targeted Biopsy, and Systematic Biopsy for Detecting Prostate Cancer. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2019, 4, CD012663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoots, I.G.; Roobol, M.J.; Nieboer, D.; Bangma, C.H.; Steyerberg, E.W.; Hunink, M.G.M. Magnetic Resonance Imaging–Targeted Biopsy May Enhance the Diagnostic Accuracy of Significant Prostate Cancer Detection Compared to Standard Transrectal Ultrasound-Guided Biopsy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Eur. Urol. 2015, 68, 438–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, H.U.; El-Shater Bosaily, A.; Brown, L.C.; Gabe, R.; Kaplan, R.; Parmar, M.K.; Collaco-Moraes, Y.; Ward, K.; Hindley, R.G.; Freeman, A.; et al. Diagnostic Accuracy of Multi-Parametric MRI and TRUS Biopsy in Prostate Cancer (PROMIS): A Paired Validating Confirmatory Study. Lancet 2017, 389, 815–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahdoot, M.; Wilbur, A.R.; Reese, S.E.; Lebastchi, A.H.; Mehralivand, S.; Gomella, P.T.; Bloom, J.; Gurram, S.; Siddiqui, M.; Pinsky, P.; et al. MRI-Targeted, Systematic, and Combined Biopsy for Prostate Cancer Diagnosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 917–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valerio, M.; Donaldson, I.; Emberton, M.; Ehdaie, B.; Hadaschik, B.A.; Marks, L.S.; Mozer, P.; Rastinehad, A.R.; Ahmed, H.U. Detection of Clinically Significant Prostate Cancer Using Magnetic Resonance Imaging-Ultrasound Fusion Targeted Biopsy: A Systematic Review. Eur. Urol. 2015, 68, 8–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penzkofer, T.; Padhani, A.R.; Turkbey, B.; Haider, M.A.; Huisman, H.; Walz, J.; Salomon, G.; Schoots, I.G.; Richenberg, J.; Villeirs, G.; et al. ESUR/ESUI Position Paper: Developing Artificial Intelligence for Precision Diagnosis of Prostate Cancer Using Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Eur. Radiol. 2021, 31, 9567–9578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouvière, O.; Schoots, I.G.; Mottet, N. Multiparametric Magnetic Resonance Imaging Before Prostate Biopsy: A Chain Is Only as Strong as Its Weakest Link. Eur. Urol. 2019, 75, 889–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padhani, A.R.; Barentsz, J.; Villeirs, G.; Rosenkrantz, A.B.; Margolis, D.J.; Turkbey, B.; Thoeny, H.C.; Cornud, F.; Haider, M.A.; Macura, K.J.; et al. PI-RADS Steering Committee: The PI-RADS Multiparametric MRI and MRI-Directed Biopsy Pathway. Radiology 2019, 292, 464–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arif, M.; Schoots, I.G.; Castillo Tovar, J.; Bangma, C.H.; Krestin, G.P.; Roobol, M.J.; Niessen, W.; Veenland, J.F. Clinically Significant Prostate Cancer Detection and Segmentation in Low-Risk Patients Using a Convolutional Neural Network on Multi-Parametric MRI. Eur. Radiol. 2020, 30, 6582–6592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.; Carver, E.; Liu, C.; Lee, J.; Feldman, A.; Zong, W.; Pantelic, M.; Elshaikh, M.; Wen, N. Segmentation of the Prostatic Gland and the Intraprostatic Lesions on Multiparametic Magnetic Resonance Imaging Using Mask Region-Based Convolutional Neural Networks. Adv. Radiat. Oncol. 2020, 5, 473–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pellicer-Valero, O.J.; Jiménez, J.L.M.; Gonzalez-Perez, V.; Ramón-Borja, J.L.C.; García, I.M.; Benito, M.B.; Gómez, P.P.; Rubio-Briones, J.; Rupérez, M.J.; Martín-Guerrero, J.D. Deep Learning for Fully Automatic Detection, Segmentation, and Gleason Grade Estimation of Prostate Cancer in Multiparametric Magnetic Resonance Images. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2103.12650. Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/2103 (accessed on 19 August 2021).
- Aldoj, N.; Lukas, S.; Dewey, M.; Penzkofer, T. Semi-Automatic Classification of Prostate Cancer on Multi-Parametric MR Imaging Using a Multi-Channel 3D Convolutional Neural Network. Eur. Radiol. 2020, 30, 1243–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schelb, P.; Kohl, S.; Radtke, J.P.; Wiesenfarth, M.; Kickingereder, P.; Bickelhaupt, S.; Kuder, T.A.; Stenzinger, A.; Hohenfellner, M.; Schlemmer, H.-P.; et al. Classification of Cancer at Prostate MRI: Deep Learning versus Clinical PI-RADS Assessment. Radiology 2019, 293, 607–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starmans, M.P.; Niessen, W.J.; Schoots, I.; Klein, S.; Veenland, J.F. Classification of Prostate Cancer: High Grade Versus Low Grade Using A Radiomics Approach. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 16th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI 2019), Venice, Italy, 8–11 April 2019; pp. 1319–1322. [Google Scholar]
- Starmans, M.P.A.; van der Voort, S.R.; Tovar, J.M.C.; Veenland, J.F.; Klein, S.; Niessen, W.J. Chapter 18—Radiomics: Data Mining Using Quantitative Medical Image Features. In Handbook of Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention; Zhou, S.K., Rueckert, D., Fichtinger, G., Eds.; The Elsevier and MICCAI Society Book Series; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020; pp. 429–456. ISBN 978-0-12-816176-0. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Wang, L.; Lee, E.H.; Zheng, J.; Zhang, W.; Halabi, S.; Liu, C.; Deng, K.; Song, J.; Yeom, K.W. Decoding COVID-19 Pneumonia: Comparison of Deep Learning and Radiomics CT Image Signatures. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2021, 48, 1478–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo T., J.M.; Starmans, M.P.A.; Arif, M.; Niessen, W.J.; Klein, S.; Bangma, C.H.; Schoots, I.G.; Veenland, J.F. A Multi-Center, Multi-Vendor Study to Evaluate the Generalizability of a Radiomics Model for Classifying Prostate Cancer: High Grade vs. Low Grade. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armato, S.G.; Huisman, H.; Drukker, K.; Hadjiiski, L.; Kirby, J.S.; Petrick, N.; Redmond, G.; Giger, M.L.; Cha, K.; Mamonov, A.; et al. PROSTATEx Challenges for Computerized Classification of Prostate Lesions from Multiparametric Magnetic Resonance Images. J. Med. Imaging 2018, 5, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mottet, N.; Cornford, P.; Briers, E.; Gillessen, S.; Grummet, J.; Henry, A.M.; Lam, T.B.; Mason, M.D. Eau-Eanm-Estro-Esur-Siog Guidelines On Prostate Cancer. Eur. Urol. 2020, 79, 26. [Google Scholar]
- Van den Bergh, R.C.N.; Roemeling, S.; Roobol, M.J.; Roobol, W.; Schröder, F.H.; Bangma, C.H. Prospective Validation of Active Surveillance in Prostate Cancer: The PRIAS Study. Eur. Urol. 2007, 52, 1560–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PROSTATEx Challenge 2017—The Cancer Imaging Archive (TCIA) Public Access—Cancer Imaging Archive Wiki. Available online: https://wiki.cancerimagingarchive.net/display/Public/PROSTATEx+Challenge+2017 (accessed on 13 July 2021).
- Clark, K.; Vendt, B.; Smith, K.; Freymann, J.; Kirby, J.; Koppel, P.; Moore, S.; Phillips, S.; Maffitt, D.; Pringle, M.; et al. The Cancer Imaging Archive (TCIA): Maintaining and Operating a Public Information Repository. J. Digit. Imaging 2013, 26, 1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Turkbey, B.; Rosenkrantz, A.B.; Haider, M.A.; Padhani, A.R.; Villeirs, G.; Macura, K.J.; Tempany, C.M.; Choyke, P.L.; Cornud, F.; Margolis, D.J.; et al. Prostate Imaging Reporting and Data System Version 2.1: 2019 Update of Prostate Imaging Reporting and Data System Version 2. Eur. Urol. 2019, 76, 340–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoots, I.G.; Osses, D.F.; Drost, F.J.H.; Verbeek, J.F.M.; Remmers, S.; van Leenders, G.J.L.H.; Bangma, C.H.; Roobol, M.J. Reduction of MRI-Targeted Biopsies in Men with Low-Risk Prostate Cancer on Active Surveillance by Stratifying to PI-RADS and PSAdensity, with Different Thresholds for Significant Disease. Transl. Androl. Urol. 2018, 7, 132–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weinreb, J.C.; Barentsz, J.O.; Choyke, P.L.; Cornud, F.; Haider, M.A.; Macura, K.J.; Margolis, D.; Schnall, M.D.; Shtern, F.; Tempany, C.M.; et al. PI-RADS Prostate Imaging—Reporting and Data System: 2015, Version 2. Eur. Urol. 2016, 69, 16–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Epstein, J.I.; Egevad, L.; Amin, M.B.; Delahunt, B.; Srigley, J.R.; Humphrey, P.A. The 2014 International Society of Urological Pathology (ISUP) Consensus Conference on Gleason Grading of Prostatic Carcinoma: Definition of Grading Patterns and Proposal for a New Grading System. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2016, 40, 244–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Starmans, M.P.A. MStarmans91/WORC. 2021. Available online: https://github.com/MStarmans91/WORCDatabase (accessed on 6 August 2021).
- Castillo T., J. M.; Arif, M.; Niessen, W.J.; Schoots, I.G.; Veenland, J.F. Automated Classification of Significant Prostate Cancer on MRI: A Systematic Review on the Performance of Machine Learning Applications. Cancers 2020, 12, 1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castaldo, R.; Cavaliere, C.; Soricelli, A.; Salvatore, M.; Pecchia, L.; Franzese, M. Radiomic and Genomic Machine Learning Method Performance for Prostate Cancer Diagnosis: Systematic Literature Review. J. Med. Internet. Res. 2021, 23, e22394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferro, M.; de Cobelli, O.; Vartolomei, M.D.; Lucarelli, G.; Crocetto, F.; Barone, B.; Sciarra, A.; Del Giudice, F.; Muto, M.; Maggi, M.; et al. Prostate Cancer Radiogenomics—From Imaging to Molecular Characterization. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vos, M.; Starmans, M.P.A.; Timbergen, M.J.M.; van der Voort, S.R.; Padmos, G.A.; Kessels, W.; Niessen, W.J.; van Leenders, G.J.L.H.; Grünhagen, D.J.; Sleijfer, S.; et al. Radiomics Approach to Distinguish between Well Differentiated Liposarcomas and Lipomas on MRI. Br. J. Surg. 2019, 106, 1800–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van der Voort, S.R.; Incekara, F.; Wijnenga, M.M.J.; Kapas, G.; Gardeniers, M.; Schouten, J.W.; Starmans, M.P.A.; Tewarie, R.N.; Lycklama, G.J.; French, P.J.; et al. Predicting the 1p/19q Codeletion Status of Presumed Low-Grade Glioma with an Externally Validated Machine Learning Algorithm. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 7455–7462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, Z.-H. Ensemble Learning. In Encyclopedia of Biometrics; Li, S.Z., Jain, A., Eds.; Springer US: Boston, MA, USA, 2009; pp. 270–273. ISBN 978-0-387-73003-5. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Yue, W.; Li, X.; Liu, S.; Guo, L.; Xu, H.; Zhang, H.; Yang, G. Comparison Study of Radiomics and Deep Learning-Based Methods for Thyroid Nodules Classification Using Ultrasound Images. IEEE Access. 2020, 8, 52010–52017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truhn, D.; Schrading, S.; Haarburger, C.; Schneider, H.; Merhof, D.; Kuhl, C. Radiomic versus Convolutional Neural Networks Analysis for Classification of Contrast-Enhancing Lesions at Multiparametric Breast MRI. Radiology 2019, 290, 290–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Lin, X.; Zhao, Y.; Li, L.; Yan, K.; Liang, D.; Sun, D.; Li, Z.-C. Deep Learning vs. Radiomics for Predicting Axillary Lymph Node Metastasis of Breast Cancer Using Ultrasound Images: Don’t Forget the Peritumoral Region. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xia, X.; Gong, J.; Hao, W.; Yang, T.; Lin, Y.; Wang, S.; Peng, W. Comparison and Fusion of Deep Learning and Radiomics Features of Ground-Glass Nodules to Predict the Invasiveness Risk of Stage-I Lung Adenocarcinomas in CT Scan. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perdana, N.R.; Mochtar, C.A.; Umbas, R.; Hamid, A.R.A. The Risk Factors of Prostate Cancer and Its Prevention: A Literature Review. Acta Med. Indones 2016, 48, 228–238. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Timbergen, M.J.M.; Starmans, M.P.A.; Padmos, G.A.; Grünhagen, D.J.; van Leenders, G.J.L.H.; Hanff, D.F.; Verhoef, C.; Niessen, W.J.; Sleijfer, S.; Klein, S.; et al. Differential Diagnosis and Mutation Stratification of Desmoid-Type Fibromatosis on MRI Using Radiomics. Eur. J. Radiol. 2020, 131, 109266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starmans, M.P.A. WORC v3.4.5; 2021. Available online: https://worc.readthedocs.io/en/v3.3.4/ (accessed on 18 December 2021).
- MStarmans91; Svdvoort. Svdvoort/PREDICTFastr: V3.1.12. 2020. Available online: https://zenodo.org/record/4045375#.Yb8HtdDMJPY (accessed on 18 December 2021).
- Zwanenburg, A.; Vallières, M.; Abdalah, M.A.; Aerts, H.J.W.L.; Andrearczyk, V.; Apte, A.; Ashrafinia, S.; Bakas, S.; Beukinga, R.J.; Boellaard, R.; et al. The Image Biomarker Standardization Initiative: Standardized Quantitative Radiomics for High-Throughput Image-Based Phenotyping. Radiology 2020, 295, 328–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Frangi, A.F.; Niessen, W.J.; Vincken, K.L.; Viergever, M.A. Multiscale Vessel Enhancement Filtering. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention—MICCAI’98; Wells, W.M., Colchester, A., Delp, S., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1998; pp. 130–137. [Google Scholar]
- Ojala, T.; Pietikainen, M.; Maenpaa, T. Multiresolution Gray-Scale and Rotation Invariant Texture Classification with Local Binary Patterns. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2002, 24, 971–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovesi, P. Phase Congruency Detects Corners and Edges. In Proceedings of the in The Australian Pattern Recognition Society Conference; Sun, C., Talbot, H., Ourselin, S., Adriaansen, T., Eds.; Csiro Publishing: Collingwood, VIC, Australia, 2003; pp. 309–318. [Google Scholar]
- Lemaître, G.; Nogueira, F.; Aridas, C.K. Imbalanced-Learn: A Python Toolbox to Tackle the Curse of Imbalanced Datasets in Machine Learning. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2017, 18, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
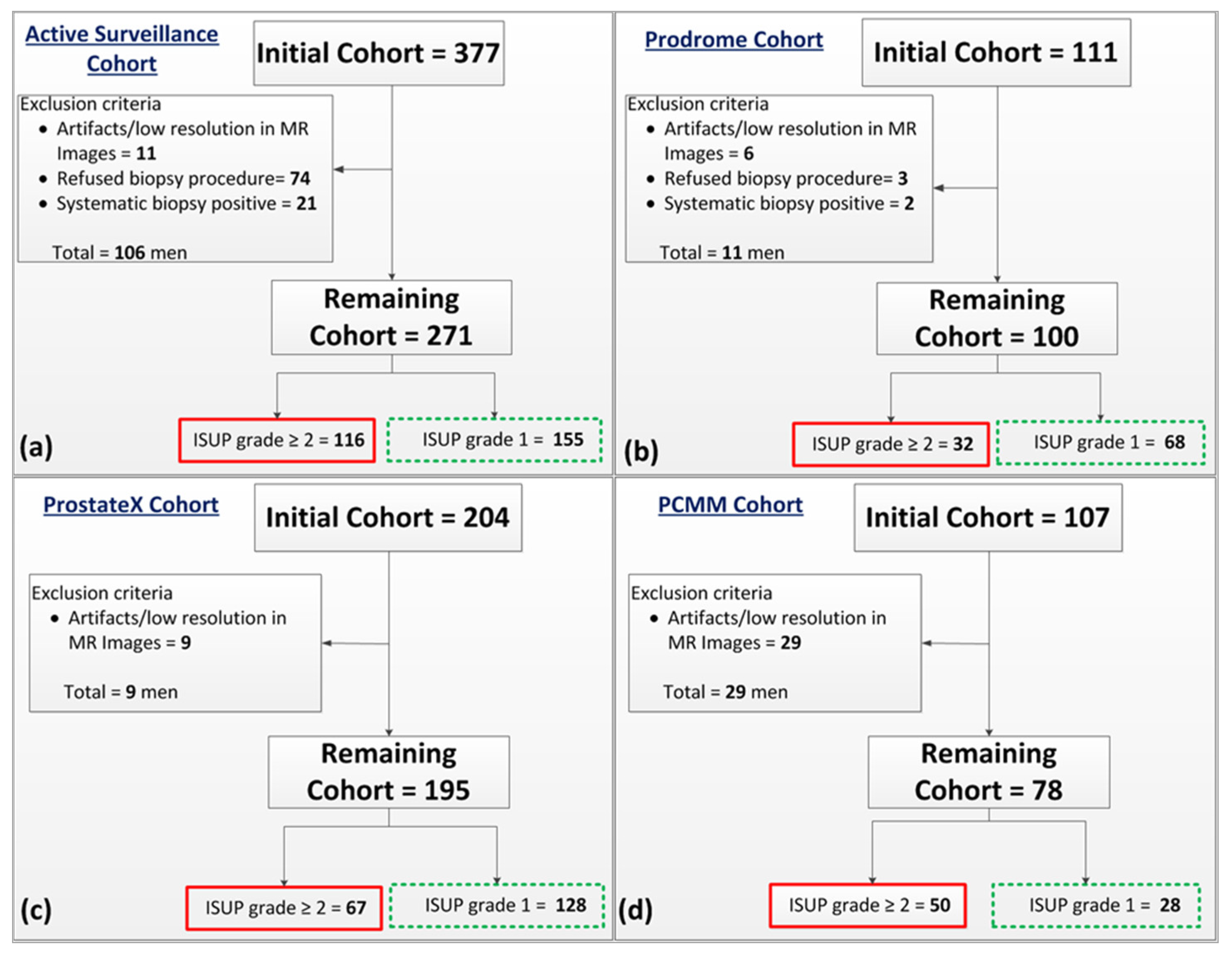
| Training Cohort | Testing Cohort | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Patient Cohort | Active Surveillance | Prodrome | ProstateX * | PCMM |
| Total Number of patients | 271 | 100 | 195 | 78 |
| Patients with a lesion ISUP grade = 1 | 155 | 68 | 128 | 28 |
| Patients with a lesion ISUP grade ≥ 2 | 116 | 32 | 67 | 50 |
| Total number of lesions | 233 | 104 | 328 | 156 |
| ISUP grade 1 | 100 | 52 | 254 | 77 |
| ISUP grade ≥ 2 | 133 | 52 | 74 | 79 |
| ISUP grade 2 | 124 | 45 | NA | 68 |
| ISUP grade 3 | 3 | 6 | NA | 8 |
| ISUP grade 4 & 5 | 6 | 1 | NA | 3 |
| Lesions in PZ | 150 | 60 | 191 | 104 |
| Lesions in TZ | 33 | 41 | 82 | 49 |
| Lesions in other zones (central, anterior stroma) | 38 | 3 | 55 | 3 |
| Lesion volume (mL) | 0.3(0.2–0.8) | 0.61 (0.3–1.0) | 1.42 (1.4–3.2) | 0.80 (0.2–1.1) |
| Prostate Volume(mL) | 43.1 (30.5–76.2) | 50. (33–67) | NA | NA |
| Age (year) | 67 ± 7 | 68 ± 4 | NA | NA |
| PSA(mean ± std ng/mL) | 10 ± 6 | 12 ± 4 | NA | 9 ± 7 |
| Active Surveillance | Prodrome | ProstateX | PCMM | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Metrics | DL | Radiomics | DL | Radiomics | DL | Radiomics | DL | Radiomics |
| AUC | 0.89 | 0.83 | 0.70 | 0.88 | 0.73 | 0.91 | 0.44 | 0.65 |
| Accuracy | 0.76 | 0.63 | 0.58 | 0.78 | 0.71 | 0.85 | 0.52 | 0.55 |
| Sensitivity | 0.85 | 1.00 | 0.72 | 1.00 | 0.70 | 0.72 | 0.70 | 0.44 |
| Specificity | 0.52 | 0.54 | 0.51 | 0.68 | 0.71 | 0.94 | 0.18 | 0.71 |
| F1-score | 0.74 | 0.66 | 0.52 | 0.78 | 0.65 | 0.85 | 0.66 | 0.55 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Castillo T., J.M.; Arif, M.; Starmans, M.P.A.; Niessen, W.J.; Bangma, C.H.; Schoots, I.G.; Veenland, J.F. Classification of Clinically Significant Prostate Cancer on Multi-Parametric MRI: A Validation Study Comparing Deep Learning and Radiomics. Cancers 2022, 14, 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14010012
Castillo T. JM, Arif M, Starmans MPA, Niessen WJ, Bangma CH, Schoots IG, Veenland JF. Classification of Clinically Significant Prostate Cancer on Multi-Parametric MRI: A Validation Study Comparing Deep Learning and Radiomics. Cancers. 2022; 14(1):12. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14010012
Chicago/Turabian StyleCastillo T., Jose M., Muhammad Arif, Martijn P. A. Starmans, Wiro J. Niessen, Chris H. Bangma, Ivo G. Schoots, and Jifke F. Veenland. 2022. "Classification of Clinically Significant Prostate Cancer on Multi-Parametric MRI: A Validation Study Comparing Deep Learning and Radiomics" Cancers 14, no. 1: 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14010012
APA StyleCastillo T., J. M., Arif, M., Starmans, M. P. A., Niessen, W. J., Bangma, C. H., Schoots, I. G., & Veenland, J. F. (2022). Classification of Clinically Significant Prostate Cancer on Multi-Parametric MRI: A Validation Study Comparing Deep Learning and Radiomics. Cancers, 14(1), 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14010012






