Obesity and Androgen Receptor Signaling: Associations and Potential Crosstalk in Breast Cancer Cells
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
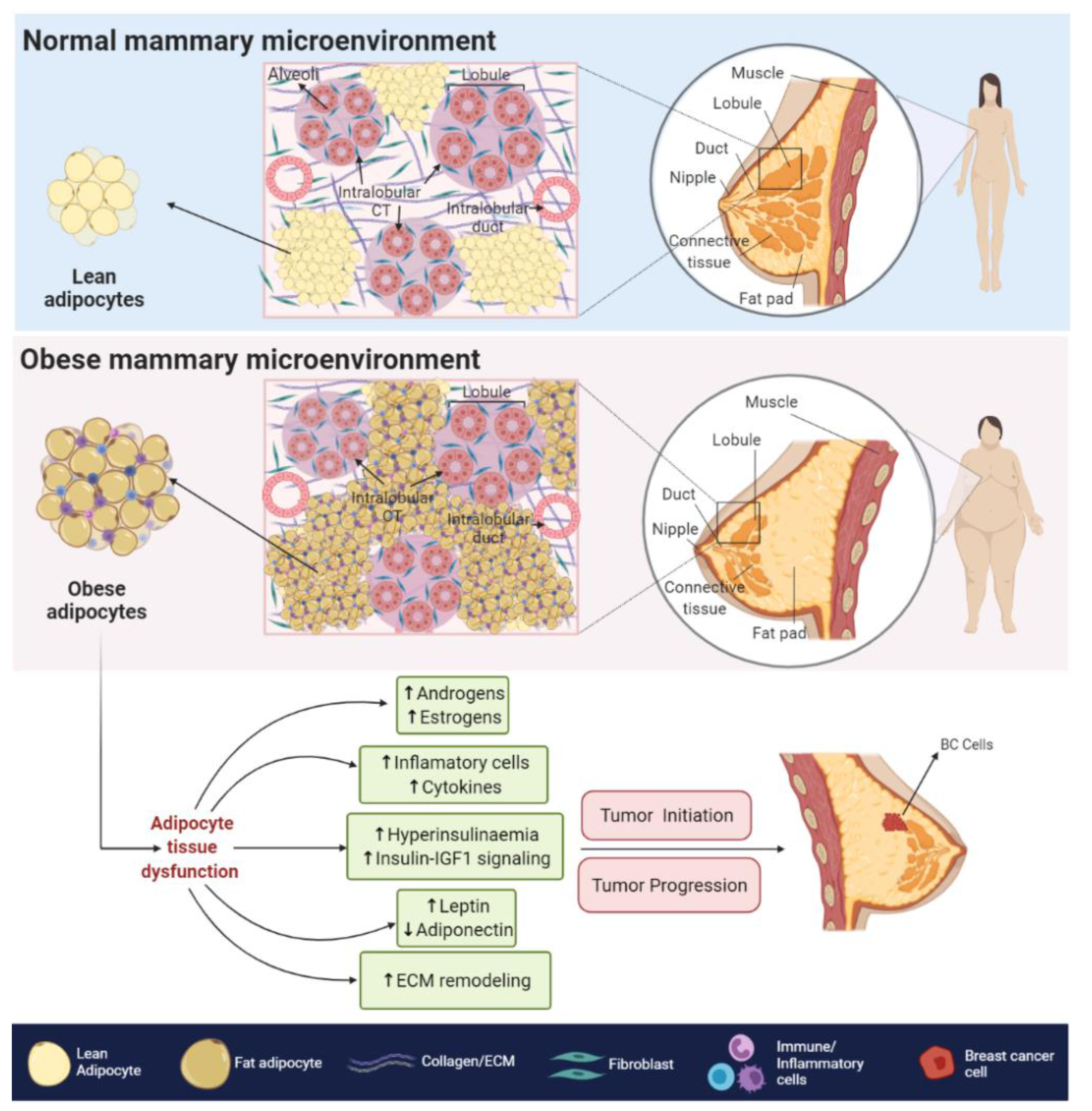
2. Obesity and BC
2.1. Biological Associations
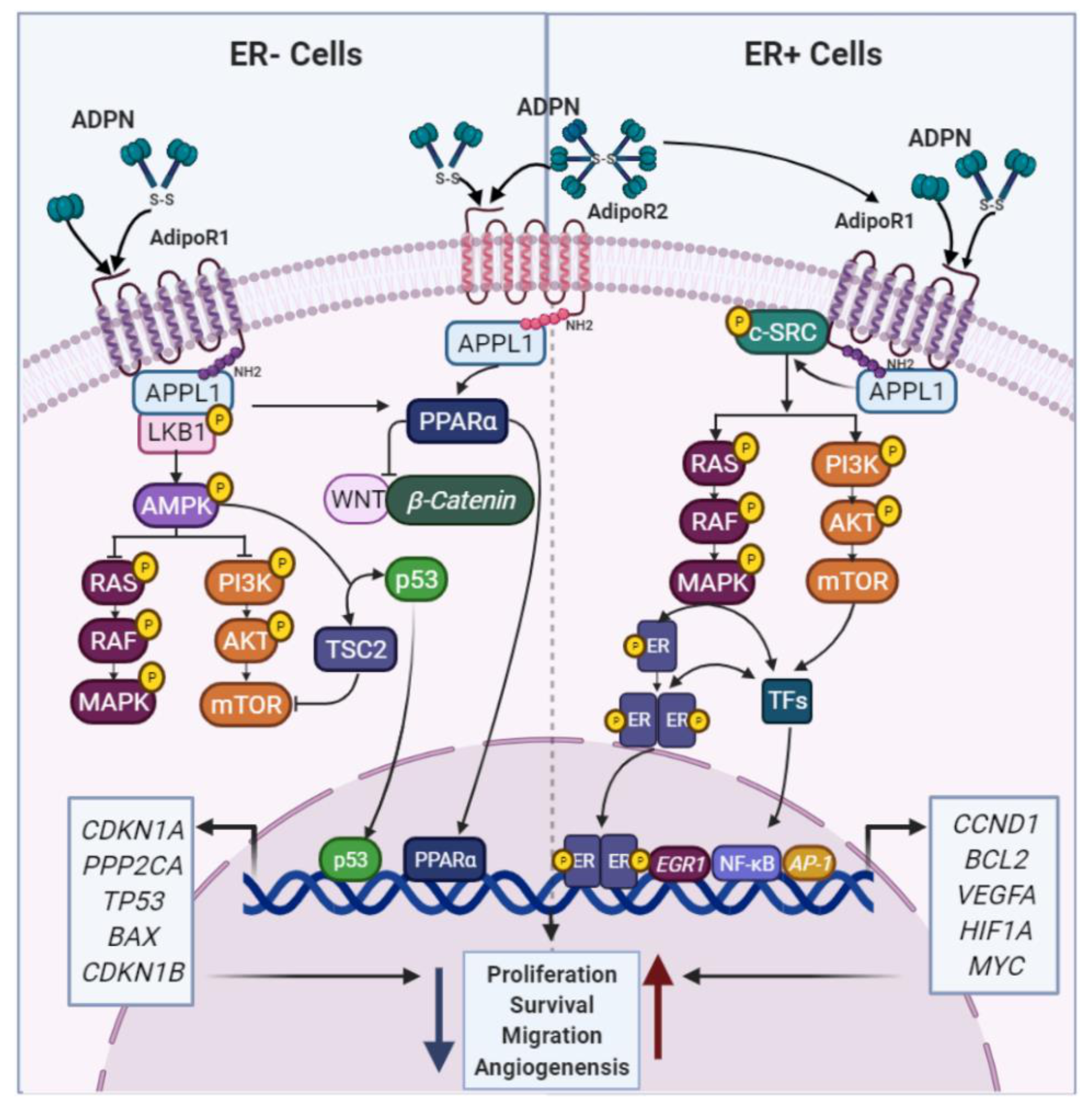
2.1.1. ADPN and BC
2.1.2. LEP and BC
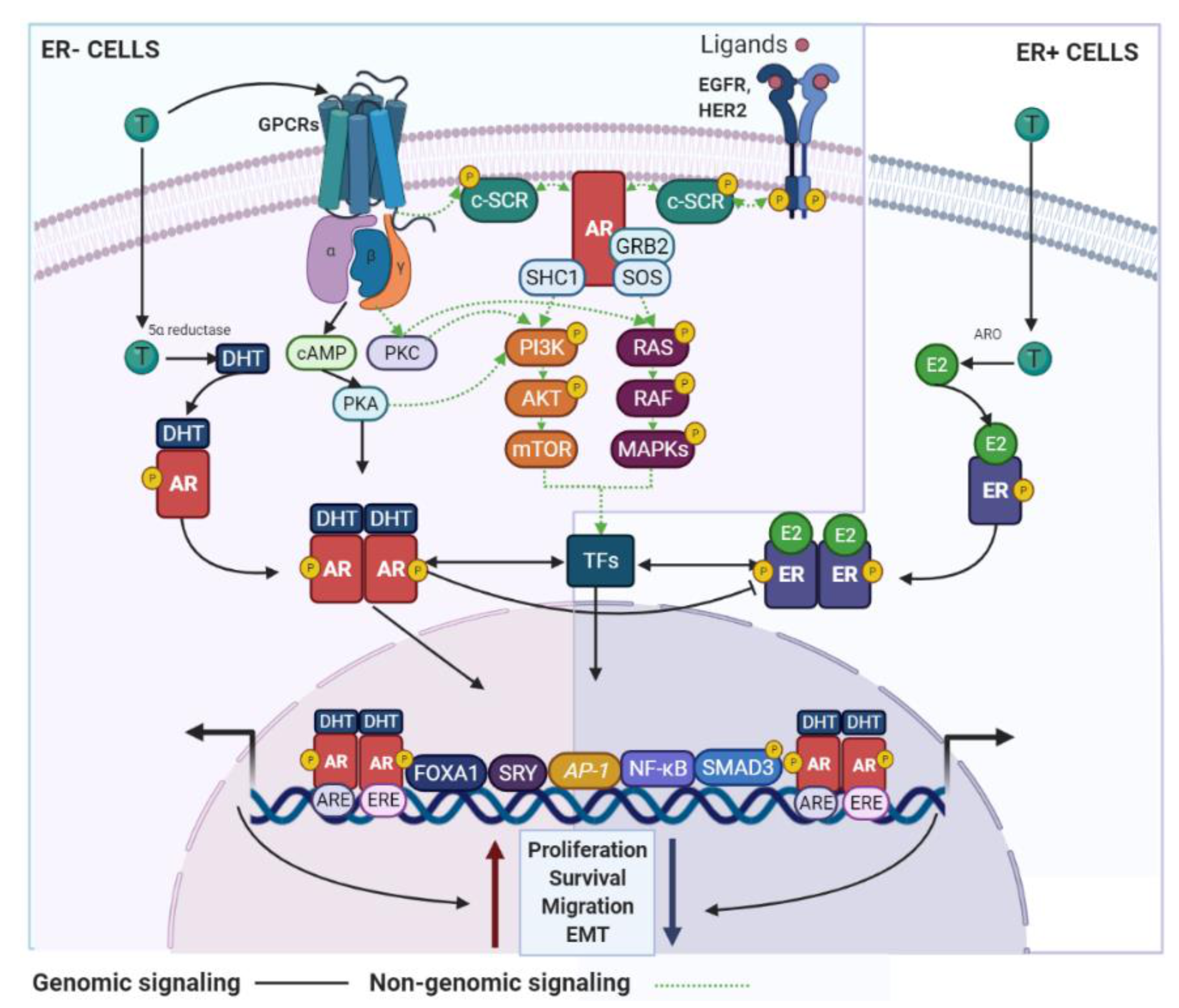
3. AR Signaling and BC
3.1. Biological Associations
3.1.1. The AR in ER+ BC
3.1.2. AR in ER− BC
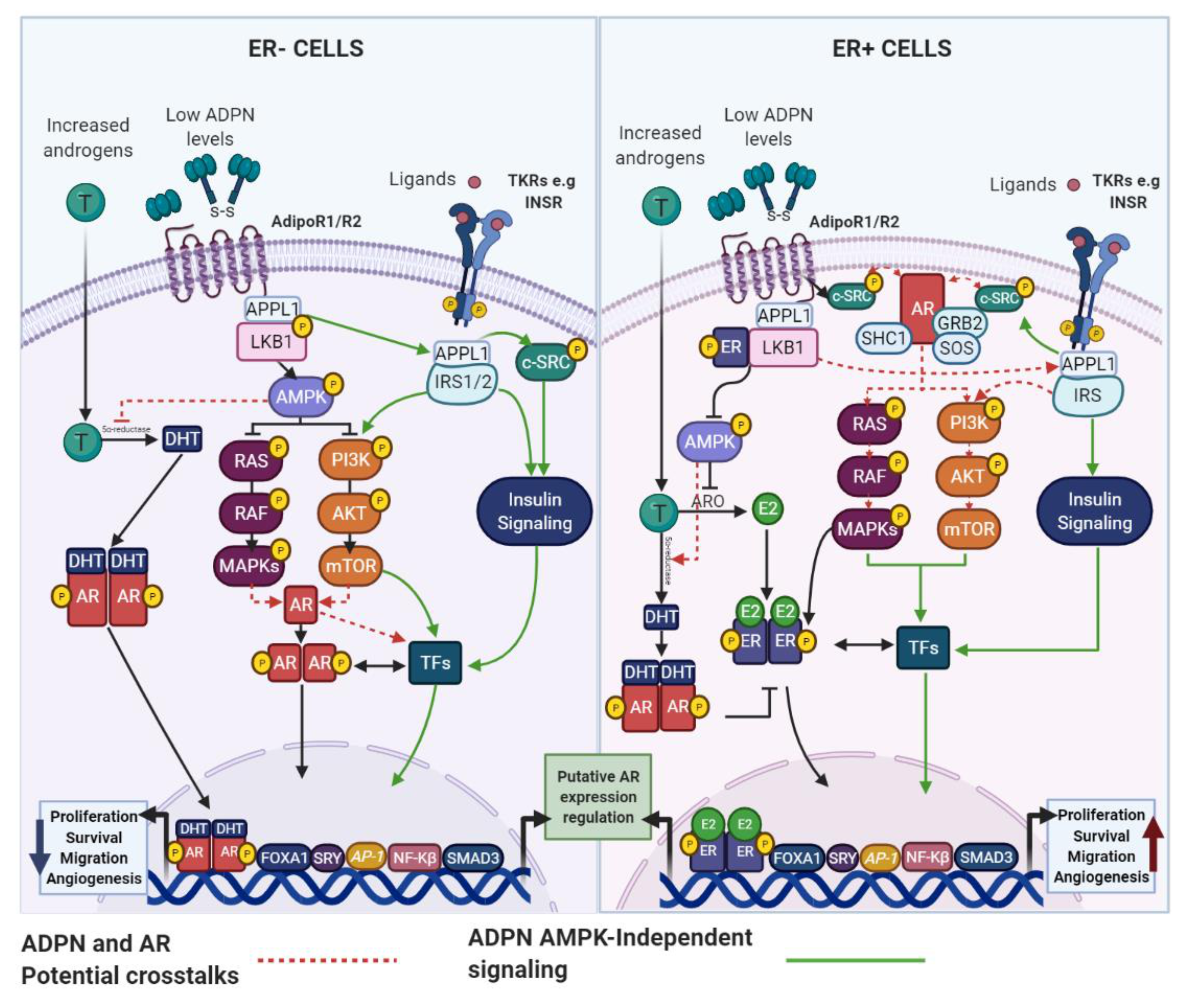
4. Obesity, AR Signaling and BC
4.1. Adipokines and the AR: Potential Links in BC
4.1.1. ADPN and AR
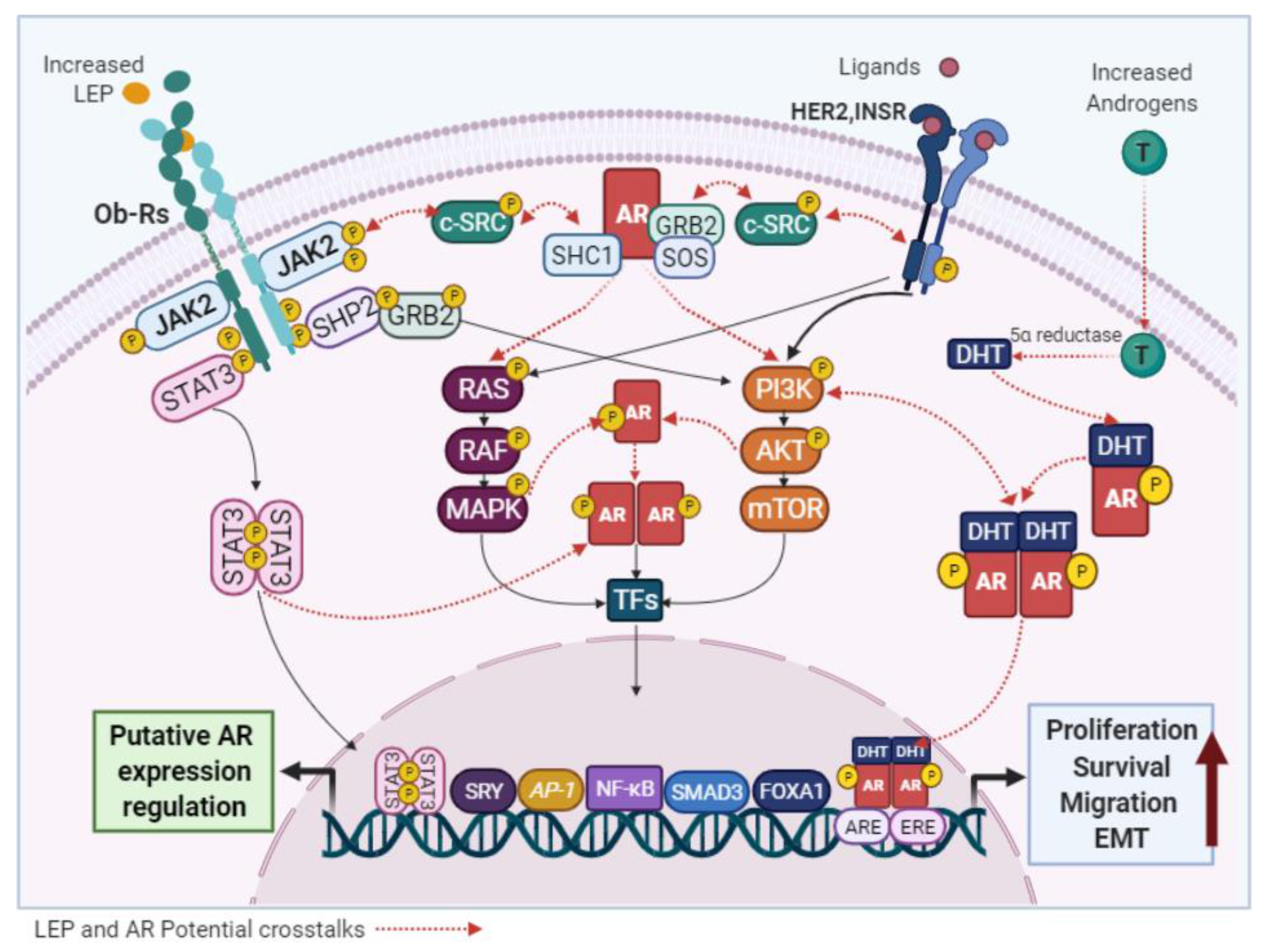
4.1.2. LEP and AR
5. Concluding Remarks and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ferlay, J.; Colombet, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Mathers, C.; Parkin, D.M.; Piñeros, M.; Znaor, A.; Bray, A.F. Estimating the Global Cancer Incidence and Mortality in 2018: GLOBOCAN Sources and Methods. Int. J. Cancer 2018, 144, 1941–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauby-Secretan, B.; Scoccianti, C.; Loomis, D.; Grosse, Y.; Bianchini, F.; Straif, K. Body Fatness and Cancer—Viewpoint of the IARC Working Group. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lapeire, L.; Denys, H.; Cocquyt, V.; De Wever, O. When fat becomes an ally of the enemy: Adipose tissue as collaborator in human breast cancer. Horm. Mol. Biol. Clin. Investig. 2015, 23, 21–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Euhus, D.M.; Scherer, P.E. Paracrine and endocrine effects of adipose tissue on cancer development and progression. Endocr. Rev. 2011, 32, 550–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Early Breast Cancer Trialists’ Collaborative Group; Davies, C.; Godwin, J.; Gray, R.; Clarke, M.; Cutter, D.; Darby, S.; McGale, P.; Pan, H.C.; Taylor, C.; et al. Relevance of breast cancer hormone receptors and other factors to the efficacy of adjuvant tamoxifen: Patient-level meta-analysis of randomised trials. Lancet 2011, 378, 771–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amaral, C.; Augusto, T.V.; Almada, M.; Cunha, S.C.; Correia-da-Silva, G.; Teixeira, N. The potential clinical benefit of targeting androgen receptor (AR) in estrogen-receptor positive breast cancer cells treated with Exemestane. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis. Dis. 2020, 1866, 165661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, M.; Yuan, Y.; Yan, P.; Jiang, J.; Ma, P.; Niu, X.; Ma, S.; Cai, H.; Yang, K. Prognostic Significance of Androgen Receptor Expression in Triple Negative Breast Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Clin. Breast Cancer 2020, 20, e385–e396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasquali, R. Obesity and androgens: Facts and perspectives. Fertil. Steril. 2006, 85, 1319–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schapira, D.V.; Kumar, N.B.; GH, L. Obesity, body fat distribution, and sex hormones in breast cancer patients. Cancer 1991, 67, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NCD Risk Factor Collaboration. Worldwide trends in body-mass index, underweight, overweight, and obesity from 1975 to 2016: A pooled analysis of 2416 population-based measurement studies in 128.9 million children, adolescents, and adults. Lancet 2017, 390, 2627–2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, Z.J.; Bleich, S.N.; Cradock, A.L.; Barrett, J.L.; Giles, C.M.; Flax, C.; Long, M.W.; Gortmaker, S.L.; Projected, U.S. State-Level Prevalence of Adult Obesity and Severe Obesity. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 2440–2450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, E.K.; Park, H.B.; Lee, K.H.; Park, J.H.; Eisenhut, M.; van der Vliet, H.J.; Kim, G.; Shin, J.I. Body mass index and 20 specific cancers: Re-analyses of dose-response meta-analyses of observational studies. Ann. Oncol. 2018, 29, 749–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Wei, J.; He, X.; Lian, J.; Han, D.; An, P.; Zhou, T.; Liu, S.; Wang, F.; Min, J. Quantitative association between body mass index and the risk of cancer: A global Meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. Int. J. Cancer 2018, 143, 1595–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freisling, H.; Arnold, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; O’Doherty, M.G.; Ordonez-Mena, J.M.; Bamia, C.; Kampman, E.; Leitzmann, M.; Romieu, I.; Kee, F.; et al. Comparison of general obesity and measures of body fat distribution in older adults in relation to cancer risk: Meta-analysis of individual participant data of seven prospective cohorts in Europe. Br. J. Cancer 2017, 116, 1486–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyrgiou, M.; Kalliala, I.; Markozannes, G.; Gunter, M.J.; Paraskevaidis, E.; Gabra, H.; Martin-Hirsch, P.; Tsilidis, K.K. Adiposity and cancer at major anatomical sites: Umbrella review of the literature. BMJ 2017, 356, j477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yang, D.L.; Chen, Z.Z.; Gou, B.F. Associations of body mass index with cancer incidence among populations, genders, and menopausal status: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Cancer Epidemiol 2016, 42, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Premenopausal Breast Cancer Collaborative Group; Schoemaker, M.J.; Nichols, H.B.; Wright, L.B.; Brook, M.N.; Jones, M.E.; O’Brien, K.M.; Adami, H.O.; Baglietto, L.; Bernstein, L.; et al. Association of Body Mass Index and Age With Subsequent Breast Cancer Risk in Premenopausal Women. JAMA Oncol 2018, 4, e181771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayoub, N.M.; Yaghan, R.J.; Abdo, N.M.; Matalka, I.I.; Akhu-Zaheya, L.M.; Al-Mohtaseb, A.H. Impact of Obesity on Clinicopathologic Characteristics and Disease Prognosis in Pre- and Postmenopausal Breast Cancer Patients: A Retrospective Institutional Study. J. Obes. 2019, 2019, 3820759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blair, C.K.; Wiggins, C.L.; Nibbe, A.M.; Storlie, C.B.; Prossnitz, E.R.; Royce, M.; Lomo, L.C.; Hill, D.A. Obesity and survival among a cohort of breast cancer patients is partially mediated by tumor characteristics. NPJ Breast Cancer 2019, 5, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, S.; Liu, Y.; Yu, K.D.; Chen, S.; Yang, W.T.; Shao, Z.M. Overweight as a Prognostic Factor for Triple-Negative Breast Cancers in Chinese Women. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0129741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ademuyiwa, F.O.; Groman, A.; O’Connor, T.; Ambrosone, C.; Watroba, N.; Edge, S.B. Impact of body mass index on clinical outcomes in triple-negative breast cancer. Cancer 2011, 117, 4132–4140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Cook, L.S.; Tang, M.T.; Porter, P.L.; Hill, D.A.; Wiggins, C.L.; Li, C.I. Body mass index and risk of luminal, HER2-overexpressing, and triple negative breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2016, 157, 545–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, S.H.; An, Y.; Ahn, C.; Park, B.; Lee, M.H.; Noh, D.Y.; Park, S.K. Body mass index and risk of breast cancer molecular subtypes in Korean women: A case-control study. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2020, 179, 459–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bandera, E.V.; Chandran, U.; Hong, C.C.; Troester, M.A.; Bethea, T.N.; Adams-Campbell, L.L.; Haiman, C.A.; Park, S.Y.; Olshan, A.F.; Ambrosone, C.B.; et al. Obesity, body fat distribution, and risk of breast cancer subtypes in African American women participating in the AMBER Consortium. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2015, 150, 655–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canchola, A.J.; Anton-Culver, H.; Bernstein, L.; Clarke, C.A.; Henderson, K.; Ma, H.; Ursin, G.; Horn-Ross, P.L. Body size and the risk of postmenopausal breast cancer subtypes in the California Teachers Study cohort. Cancer Causes Control. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwan, M.L.; Kroenke, C.H.; Sweeney, C.; Bernard, P.S.; Weltzien, E.K.; Castillo, A.; Factor, R.E.; Maxfield, K.S.; Stijleman, I.J.; Kushi, L.H.; et al. Association of high obesity with PAM50 breast cancer intrinsic subtypes and gene expression. BMC Cancer 2015, 15, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamidi, T.K.K.; Wu, J.; Tchounwou, P.B.; Miele, L.; Hicks, C. Whole Genome Transcriptome Analysis of the Association between Obesity and Triple-Negative Breast Cancer in Caucasian Women. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bluher, M. Adipose tissue dysfunction in obesity. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 2009, 117, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Andrade, I.; Moraes, J.; Brandao-Costa, R.M.; Vargas da Silva, S.; de Souza, A.; da Silva, C.; Renovato-Martins, M.; Barja-Fidalgo, C. Obese adipose tissue extracellular vesicles raise breast cancer cell malignancy. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2020, 27, 571–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Li, S.; He, J.; Du, H.; Liu, Y.; Yu, W.; Hu, H.; Han, L.; Wang, C.; Li, H.; et al. Tumor-secreted PAI-1 promotes breast cancer metastasis via the induction of adipocyte-derived collagen remodeling. Cell Commun. Signal. 2019, 17, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engin, A. Adipose Tissue Hypoxia in Obesity and Its Impact on Preadipocytes and Macrophages: Hypoxia Hypothesis. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2017, 960, 305–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Z.; Zhu, X.; Yang, S.; Guo, Z.; Li, K.; Ren, C.; Zhou, Y.; Dou, J. Yin-yang effect of tumour cells in breast cancer: From mechanism of crosstalk between tumour-associated macrophages and cancer-associated adipocytes. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2020, 10, 383–392. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yee, L.D.; Mortimer, J.E.; Natarajan, R.; Dietze, E.C.; Seewaldt, V.L. Metabolic Health, Insulin, and Breast Cancer: Why Oncologists Should Care About Insulin. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne) 2020, 11, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega, M.A.; Fraile-Martinez, O.; Asunsolo, A.; Bujan, J.; Garcia-Honduvilla, N.; Coca, S. Signal Transduction Pathways in Breast Cancer: The Important Role of PI3K/Akt/mTOR. J. Oncol. 2020, 2020, 9258396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treins, C.; Giorgetti-Peraldi, S.; Murdaca, J.; Semenza, G.L.; Van Obberghen, E. Insulin stimulates hypoxia-inducible factor 1 through a phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/target of rapamycin-dependent signaling pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 27975–27981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Tang, C.; Cao, H.; Li, K.; Pang, X.; Zhong, L.; Dang, W.; Tang, H.; Huang, Y.; Wei, L.; et al. Activation of IL-8 via PI3K/Akt-dependent pathway is involved in leptin-mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition in human breast cancer cells. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2015, 16, 1220–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascale, R.M.; Calvisi, D.F.; Simile, M.M.; Feo, C.F.; Feo, F. The Warburg Effect 97 Years after Its Discovery. Cancers 2020, 12, 2819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehr, S.; Hartwig, S.; Sell, H. Adipokines: A treasure trove for the discovery of biomarkers for metabolic disorders. Proteomics Clin. Appl. 2012, 6, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Booth, A.; Magnuson, A.; Fouts, J.; Foster, M. Adipose tissue, obesity and adipokines: Role in cancer promotion. Horm. Mol. Biol. Clin. Investig. 2015, 21, 57–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Bateman, A. Progranulin (granulin-epithelin precursor, PC-cell-derived growth factor, acrogranin) mediates tissue repair and tumorigenesis. J. Mol. Med. 2003, 81, 600–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsubara, T.; Mita, A.; Minami, K.; Hosooka, T.; Kitazawa, S.; Takahashi, K.; Tamori, Y.; Yokoi, N.; Watanabe, M.; Matsuo, E.; et al. PGRN is a key adipokine mediating high fat diet-induced insulin resistance and obesity through IL-6 in adipose tissue. Cell Metab. 2012, 15, 38–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tangkeangsirisin, W.; Serrero, G. PC cell-derived growth factor (PCDGF/GP88, progranulin) stimulates migration, invasiveness and VEGF expression in breast cancer cells. Carcinogenesis 2004, 25, 1587–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tkaczuk, K.H.R.; Hawkins, D.; Yue, B.; Hicks, D.; Tait, N.; Serrero, G. Association of Serum Progranulin Levels With Disease Progression, Therapy Response and Survival in Patients With Metastatic Breast Cancer. Clin. Breast Cancer 2020, 20, 220–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, G.W.; Wang, J.; Hug, C.; Tsao, T.S.; Lodish, H.F. A family of Acrp30/adiponectin structural and functional paralogs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 10302–10307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Zazzo, E.; Polito, R.; Bartollino, S.; Nigro, E.; Porcile, C.; Bianco, A.; Daniele, A.; Moncharmont, B. Adiponectin as Link Factor between Adipose Tissue and Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosogai, N.; Fukuhara, A.; Oshima, K.; Miyata, Y.; Tanaka, S.; Segawa, K.; Furukawa, S.; Tochino, Y.; Komuro, R.; Matsuda, M.; et al. Adipose tissue hypoxia in obesity and its impact on adipocytokine dysregulation. Diabetes 2007, 56, 901–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Tang, S.; Ma, H.; Duan, H.; Zeng, Y. Association of serum adiponectin with breast cancer: A meta-analysis of 27 case-control studies. Medicine 2019, 98, e14359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arditi, J.D.; Venihaki, M.; Karalis, K.P.; Chrousos, G.P. Antiproliferative effect of adiponectin on MCF7 breast cancer cells: A potential hormonal link between obesity and cancer. Horm. Metab. Res. 2007, 39, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos, E.; Benaitreau, D.; Dieudonne, M.N.; Leneveu, M.C.; Serazin, V.; Giudicelli, Y.; Pecquery, R. Adiponectin mediates an antiproliferative response in human MDA-MB 231 breast cancer cells. Oncol. Rep. 2008, 20, 971–977. [Google Scholar]
- Nakayama, S.; Miyoshi, Y.; Ishihara, H.; Noguchi, S. Growth-inhibitory effect of adiponectin via adiponectin receptor 1 on human breast cancer cells through inhibition of S-phase entry without inducing apoptosis. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2008, 112, 405–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamauchi, T.; Kamon, J.; Ito, Y.; Tsuchida, A.; Yokomizo, T.; Kita, S.; Sugiyama, T.; Miyagishi, M.; Hara, K.; Tsunoda, M.; et al. Cloning of adiponectin receptors that mediate antidiabetic metabolic effects. Nature 2003, 423, 762–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, W.; Li, J.; Hao, Q.; Vadgama, J.V.; Wu, Y. AMP-activated protein kinase: A potential therapeutic target for triple-negative breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2019, 21, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shackelford, D.B.; Shaw, R.J. The LKB1-AMPK pathway: Metabolism and growth control in tumour suppression. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2009, 9, 563–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grossmann, M.E.; Nkhata, K.J.; Mizuno, N.K.; Ray, A.; Cleary, M.P. Effects of adiponectin on breast cancer cell growth and signaling. Br. J. Cancer 2008, 98, 370–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, K.A.; Simpson, E.R. Obesity and breast cancer: Progress to understanding the relationship. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 4–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandran, K.; Goswami, S.; Sharma-Walia, N. Implications of a peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPARα) ligand clofibrate in breast cancer. Oncotarget 2015, 7, 23. [Google Scholar]
- Lecarpentier, Y.; Claes, V.; Vallee, A.; Hebert, J.L. Thermodynamics in cancers: Opposing interactions between PPAR gamma and the canonical WNT/beta-catenin pathway. Clin. Transl. Med. 2017, 6, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauro, L.; Naimo, G.D.; Gelsomino, L.; Malivindi, R.; Bruno, L.; Pellegrino, M.; Tarallo, R.; Memoli, D.; Weisz, A.; Panno, M.L.; et al. Uncoupling effects of estrogen receptor alpha on LKB1/AMPK interaction upon adiponectin exposure in breast cancer. FASEB J. 2018, 32, 4343–4355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauro, L.; Pellegrino, M.; De Amicis, F.; Ricchio, E.; Giordano, F.; Rizza, P.; Catalano, S.; Bonofiglio, D.; Sisci, D.; Panno, M.L.; et al. Evidences that estrogen receptor alpha interferes with adiponectin effects on breast cancer cell growth. Cell Cycle 2014, 13, 553–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauro, L.; Pellegrino, M.; Giordano, F.; Ricchio, E.; Rizza, P.; De Amicis, F.; Catalano, S.; Bonofiglio, D.; Panno, M.L.; Ando, S. Estrogen receptor-alpha drives adiponectin effects on cyclin D1 expression in breast cancer cells. FASEB J. 2015, 29, 2150–2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naimo, G.D.; Gelsomino, L.; Catalano, S.; Mauro, L.; Ando, S. Interfering Role of ERalpha on Adiponectin Action in Breast Cancer. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne) 2020, 11, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeiler, G.H.; Buechler, C.; Neumeier, M.; Schaffler, A.; Schmitz, G.; Ortmann, O.; Treeck, O. Adiponectin effects on human breast cancer cells are dependent on 17-beta estradiol. Oncol. Rep. 2008, 19, 787–793. [Google Scholar]
- Landskroner-Eiger, S.; Qian, B.; Muise, E.S.; Nawrocki, A.R.; Berger, J.P.; Fine, E.J.; Koba, W.; Deng, Y.; Pollard, J.W.; Scherer, P.E. Proangiogenic contribution of adiponectin toward mammary tumor growth in vivo. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 3265–3276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markowska, A.; Malendowicz, K.; Drews, K. The role of leptin in breast cancer. Eur. J. Gynaecol Oncol. 2004, 25, 192–194. [Google Scholar]
- Friedman, J.M.; Halaas, J.L. Leptin and the regulation of body weight in mammals. Nature 1998, 395, 763–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Himbert, C.; Delphan, M.; Scherer, D.; Bowers, L.W.; Hursting, S.; Ulrich, C.M. Signals from the Adipose Microenvironment and the Obesity-Cancer Link-A Systematic Review. Cancer Prev. Res. (Phila) 2017, 10, 494–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, M.; Kitayama, J.; Nagawa, H. Enhanced expression of leptin and leptin receptor (OB-R) in human breast cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 4325–4331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.; Deng, L.L.; Cui, J.Q.; Shi, L.; Yang, Y.C.; Luo, J.H.; Qin, D.; Wang, L. Association between serum leptin levels and breast cancer risk: An updated systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine 2018, 97, e11345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigo, C.; Tennekoon, K.H.; Karunanayake, E.H.; De Silva, K.; Amarasinghe, I.; Wijayasiri, A. Circulating leptin, soluble leptin receptor, free leptin index, visfatin and selected leptin and leptin receptor gene polymorphisms in sporadic breast cancer. Endocr. J. 2017, 64, 393–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khabaz, M.N.; Abdelrahman, A.; Butt, N.; Damnhory, L.; Elshal, M.; Aldahlawi, A.M.; Ashoor, S.; Al-Maghrabi, B.; Dobson, P.; Brown, B.; et al. Immunohistochemical staining of leptin is associated with grade, stage, lymph node involvement, recurrence, and hormone receptor phenotypes in breast cancer. BMC Womens Health 2017, 17, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giordano, C.; Chemi, F.; Panza, S.; Barone, I.; Bonofiglio, D.; Lanzino, M.; Cordella, A.; Campana, A.; Hashim, A.; Rizza, P.; et al. Leptin as a mediator of tumor-stromal interactions promotes breast cancer stem cell activity. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 1262–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linares, R.L.; Benitez, J.G.S.; Reynoso, M.O.; Romero, C.G.; Sandoval-Cabrera, A. Modulation of the leptin receptors expression in breast cancer cell lines exposed to leptin and tamoxifen. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 19189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, A.; Nkhata, K.J.; Cleary, M.P. Effects of leptin on human breast cancer cell lines in relationship to estrogen receptor and HER2 status. Int. J. Oncol. 2007, 30, 1499–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabol, R.A.; Bowles, A.C.; Cote, A.; Wise, R.; O’Donnell, B.; Matossian, M.D.; Hossain, F.M.; Burks, H.E.; Del Valle, L.; Miele, L.; et al. Leptin produced by obesity-altered adipose stem cells promotes metastasis but not tumorigenesis of triple-negative breast cancer in orthotopic xenograft and patient-derived xenograft models. Breast Cancer Res. 2019, 21, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez-Jimenez, F.; Perez-Perez, A.; de la Cruz-Merino, L.; Sanchez-Margalet, V. Obesity and Breast Cancer: Role of Leptin. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saxena, N.K.; Vertino, P.M.; Anania, F.A.; Sharma, D. leptin-induced growth stimulation of breast cancer cells involves recruitment of histone acetyltransferases and mediator complex to CYCLIN D1 promoter via activation of Stat3. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 13316–13325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, H.J.; Sun, K.W.; Yu, K. Leptin promotes the proliferation and migration of human breast cancer through the extracellular-signal regulated kinase pathway. Mol. Med. Rep. 2014, 9, 350–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catalano, S.; Mauro, L.; Marsico, S.; Giordano, C.; Rizza, P.; Rago, V.; Montanaro, D.; Maggiolini, M.; Panno, M.L.; Ando, S. Leptin induces, via ERK1/ERK2 signal, functional activation of estrogen receptor alpha in MCF-7 cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 19908–19915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahid, H.; Subbaramaiah, K.; Iyengar, N.M.; Zhou, X.K.; Chen, I.C.; Bhardwaj, P.; Gucalp, A.; Morrow, M.; Hudis, C.A.; Dannenberg, A.J.; et al. Leptin regulation of the p53-HIF1alpha/PKM2-aromatase axis in breast adipose stromal cells: A novel mechanism for the obesity-breast cancer link. Int. J. Obes. 2018, 42, 711–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Perez, R.R.; Xu, Y.; Guo, S.; Watters, A.; Zhou, W.; Leibovich, S.J. Leptin upregulates VEGF in breast cancer via canonic and non-canonical signalling pathways and NFkappaB/HIF-1alpha activation. Cell Signal. 2010, 22, 1350–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.Y.; Wei, X.H.; Li, S.J.; Liu, Y.; Hu, H.L.; Li, Z.Z.; Kuang, X.H.; Wang, L.; Shi, X.; Yuan, S.T.; et al. Adipocyte-derived IL-6 and leptin promote breast Cancer metastasis via upregulation of Lysyl Hydroxylase-2 expression. Cell Commun. Signal. 2018, 16, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Jin, Q.; Su, M.; Ji, F.; Wang, N.; Zhong, C.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, J.; et al. Leptin promotes the migration and invasion of breast cancer cells by upregulating ACAT2. Cell Oncol. (Dordr) 2017, 40, 537–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.W.; Zhao, L.; Willingham, M.C.; Cheng, S.Y. Inhibition of STAT3 signaling blocks obesity-induced mammary hyperplasia in a mouse model. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2017, 7, 727–739. [Google Scholar]
- Basu, S.; Nachat-Kappes, R.; Caldefie-Chezet, F.; Vasson, M.P. Eicosanoids and adipokines in breast cancer: From molecular mechanisms to clinical considerations. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2013, 18, 323–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.C.; Wu, M.J.; Yang, J.Y.; Camarillo, I.G.; Chang, C.J. Leptin-STAT3-G9a Signaling Promotes Obesity-Mediated Breast Cancer Progression. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 2375–2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorgan, J.F.; Stanczyk, F.Z.; Kahle, L.L.; Brinton, L.A. Prospective case-control study of premenopausal serum estradiol and testosterone levels and breast cancer risk. Breast Cancer Res. 2010, 12, R98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Honma, N.; Saji, S.; Hirose, M.; Horiguchi, S.; Kuroi, K.; Hayashi, S.; Utsumi, T.; Harada, N. Sex steroid hormones in pairs of tumor and serum from breast cancer patients and pathobiological role of androstene-3beta, 17beta-diol. Cancer Sci. 2011, 102, 1848–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikora, M.J.; Strumba, V.; Lippman, M.E.; Johnson, M.D.; Rae, J.M. Mechanisms of estrogen-independent breast cancer growth driven by low estrogen concentrations are unique versus complete estrogen deprivation. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2012, 134, 1027–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doane, A.S.; Danso, M.; Lal, P.; Donaton, M.; Zhang, L.; Hudis, C.; Gerald, W.L. An estrogen receptor-negative breast cancer subset characterized by a hormonally regulated transcriptional program and response to androgen. Oncogene 2006, 25, 3994–4008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangel, N.; Rondon-Lagos, M.; Annaratone, L.; Aristizabal-Pachon, A.F.; Cassoni, P.; Sapino, A.; Castellano, I. AR/ER Ratio Correlates with Expression of Proliferation Markers and with Distinct Subset of Breast Tumors. Cells 2020, 9, 1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burger, H.G. Androgen production in women. Fertil. Steril. 2002, 77 (Suppl. S4), S3–S5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanan, R.; Coss, C.C.; Dalton, J.T. Development of selective androgen receptor modulators (SARMs). Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2018, 465, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baglietto, L.; Severi, G.; English, D.R.; Krishnan, K.; Hopper, J.L.; McLean, C.; Morris, H.A.; Tilley, W.D.; Giles, G.G. Circulating steroid hormone levels and risk of breast cancer for postmenopausal women. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev. 2010, 19, 492–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woolcott, C.G.; Shvetsov, Y.B.; Stanczyk, F.Z.; Wilkens, L.R.; White, K.K.; Caberto, C.; Henderson, B.E.; Le Marchand, L.; Kolonel, L.N.; Goodman, M.T. Plasma sex hormone concentrations and breast cancer risk in an ethnically diverse population of postmenopausal women: The Multiethnic Cohort Study. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2010, 17, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeleniuch-Jacquotte, A.; Afanasyeva, Y.; Kaaks, R.; Rinaldi, S.; Scarmo, S.; Liu, M.; Arslan, A.A.; Toniolo, P.; Shore, R.E.; Koenig, K.L. Premenopausal serum androgens and breast cancer risk: A nested case-control study. Breast Cancer Res. 2012, 14, R32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kensler, K.H.; Eliassen, A.H.; Rosner, B.A.; Hankinson, S.E.; Brown, M.; Tamimi, R.M. Pre-diagnostic sex hormone levels and survival among breast cancer patients. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2019, 174, 749–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellano, I.; Allia, E.; Accortanzo, V.; Vandone, A.M.; Chiusa, L.; Arisio, R.; Durando, A.; Donadio, M.; Bussolati, G.; Coates, A.S.; et al. Androgen receptor expression is a significant prognostic factor in estrogen receptor positive breast cancers. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2010, 124, 607–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Min, A.; Lee, K.H.; Ryu, H.S.; Kim, T.Y.; Woo, G.U.; Suh, K.J.; Lee, D.W.; Lee, H.B.; Moon, H.G.; et al. Prognostic Role of Androgen Receptor Expression in Surgically Resected Early Breast Cancer Patients. J. Breast Cancer 2020, 23, 182–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozovic-Spasojevic, I.; Zardavas, D.; Brohee, S.; Ameye, L.; Fumagalli, D.; Ades, F.; de Azambuja, E.; Bareche, Y.; Piccart, M.; Paesmans, M.; et al. The Prognostic Role of Androgen Receptor in Patients with Early-Stage Breast Cancer: A Meta-analysis of Clinical and Gene Expression Data. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricciardelli, C.; Bianco-Miotto, T.; Jindal, S.; Butler, L.M.; Leung, S.; McNeil, C.M.; O’Toole, S.A.; Ebrahimie, E.; Millar, E.K.A.; Sakko, A.J.; et al. The Magnitude of Androgen Receptor Positivity in Breast Cancer Is Critical for Reliable Prediction of Disease Outcome. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 2328–2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vera-Badillo, F.E.; Templeton, A.J.; de Gouveia, P.; Diaz-Padilla, I.; Bedard, P.L.; Al-Mubarak, M.; Seruga, B.; Tannock, I.F.; Ocana, A.; Amir, E. Androgen receptor expression and outcomes in early breast cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2014, 106, djt319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.; Koo, J.; Park, H.S.; Kim, J.H.; Choi, S.Y.; Lee, J.H.; Park, B.W.; Lee, K.S. Expression of androgen receptors in primary breast cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2010, 21, 488–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Govindan, S.; Siraganahalli Eswaraiah, M.; Basavaraj, C.; Adinarayan, M.; Sankaran, S.; Bakre, M. Androgen Receptor mRNA levels determine the prognosis in triple-negative breast cancer patients. BMC Cancer 2020, 20, 745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Eliassen, A.H.; Tamimi, R.M.; Hazra, A.; Beck, A.H.; Brown, M.; Collins, L.C.; Rosner, B.; Hankinson, S.E. Adult body size and physical activity in relation to risk of breast cancer according to tumor androgen receptor status. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev. 2015, 24, 962–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilborn, E.; Gacic, J.; Fornander, T.; Nordenskjold, B.; Stal, O.; Jansson, A. Androgen receptor expression predicts beneficial tamoxifen response in oestrogen receptor-alpha-negative breast cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2016, 114, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Shi, Y.X.; Li, Z.M.; Jiang, W.Q. Expression and clinical significance of androgen receptor in triple negative breast cancer. Chin. J. Cancer 2010, 29, 585–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van de Stolpe, A.; Wesseling-Rozendaal, Y.; Alves de Inda, M.; Van Ooijen, H.; Verhaegh, W. Androgen receptor pathway activity and the ratio between androgen and estrogen receptor pathway activity in breast cancer subtypes. In Proceedings of the San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium, San Antonio, TX, USA, 14 February 2020; AACR publications: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Anestis, A.; Zoi, I.; Papavassiliou, A.G.; Karamouzis, M.V. Androgen Receptor in Breast Cancer-Clinical and Preclinical Research Insights. Molecules 2020, 25, 358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claessens, F.; Verrijdt, G.; Schoenmakers, E.; Haelens, A.; Peeters, B.; Verhoeven, G.; Rombauts, W. Selective DNA binding by the androgen receptor as a mechanism for hormone-specific gene regulation. J. Steroid Biochem Mol. Biol. 2001, 76, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinlein, C.A.; Chang, C. The roles of androgen receptors and androgen-binding proteins in nongenomic androgen actions. Mol. Endocrinol. 2002, 16, 2181–2187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birrell, S.N.; Bentel, J.M.; Hickey, T.E.; Ricciardelli, C.; Weger, M.A.; Horsfall, D.J.; Tilley, W.D. Androgens induce divergent proliferative responses in human breast cancer cell lines. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1995, 52, 459–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, Y.; Li, Z.L.; Shih, Y.J.; Chen, Y.R.; Wang, K.; Whang-Peng, J.; Lin, H.Y.; Davis, P.J. Integrin alphavbeta3 in the Mediating Effects of Dihydrotestosterone and Resveratrol on Breast Cancer Cell Proliferation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonne-Hansen, K.; Lykkesfeldt, A.E. Endogenous aromatization of testosterone results in growth stimulation of the human MCF-7 breast cancer cell line. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2005, 93, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macedo, L.F.; Guo, Z.; Tilghman, S.L.; Sabnis, G.J.; Qiu, Y.; Brodie, A. Role of androgens on MCF-7 breast cancer cell growth and on the inhibitory effect of letrozole. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 7775–7782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cops, E.J.; Bianco-Miotto, T.; Moore, N.L.; Clarke, C.L.; Birrell, S.N.; Butler, L.M.; Tilley, W.D. Antiproliferative actions of the synthetic androgen, mibolerone, in breast cancer cells are mediated by both androgen and progesterone receptors. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2008, 110, 236–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortmann, J.; Prifti, S.; Bohlmann, M.K.; Rehberger-Schneider, S.; Strowitzki, T.; Rabe, T. Testosterone and 5 alpha-dihydrotestosterone inhibit in vitro growth of human breast cancer cell lines. Gynecol. Endocrinol. 2002, 16, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, J.Y.; McNamara, K.M.; Lee, J.J.; Chung, B.C.; Sasano, H.; Choi, M.H. Improved detectability of sex steroids from frozen sections of breast cancer tissue using GC-triple quadrupole-MS. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2018, 178, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velie, E.M.; Nechuta, S.; Osuch, J.R. Lifetime reproductive and anthropometric risk factors for breast cancer in postmenopausal women. Breast Dis. 2005, 24, 17–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandouz, M.; Lombet, A.; Perrot, J.Y.; Jacob, D.; Carvajal, S.; Kazem, A.; Rostene, W.; Therwath, A.; Gompel, A. Proapoptotic effects of antiestrogens, progestins and androgen in breast cancer cells. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1999, 69, 463–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, A.A.; Buchanan, G.; Ricciardelli, C.; Bianco-Miotto, T.; Centenera, M.M.; Harris, J.M.; Jindal, S.; Segara, D.; Jia, L.; Moore, N.L.; et al. Androgen receptor inhibits estrogen receptor-alpha activity and is prognostic in breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 6131–6140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanzino, M.; Sisci, D.; Morelli, C.; Garofalo, C.; Catalano, S.; Casaburi, I.; Capparelli, C.; Giordano, C.; Giordano, F.; Maggiolini, M.; et al. Inhibition of cyclin D1 expression by androgen receptor in breast cancer cells--identification of a novel androgen response element. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, 5351–5365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; He, X.; Yu, Q.; Eng, C. Androgen receptor-induced tumor suppressor, KLLN, inhibits breast cancer growth and transcriptionally activates p53/p73-mediated apoptosis in breast carcinomas. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2013, 22, 2263–2272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Romigh, T.; He, X.; Tan, M.H.; Orloff, M.S.; Silverman, R.H.; Heston, W.D.; Eng, C. Differential regulation of PTEN expression by androgen receptor in prostate and breast cancers. Oncogene 2011, 30, 4327–4338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanzino, M.; De Amicis, F.; McPhaul, M.J.; Marsico, S.; Panno, M.L.; Ando, S. Endogenous coactivator ARA70 interacts with estrogen receptor alpha (ERalpha) and modulates the functional ERalpha/androgen receptor interplay in MCF-7 cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 20421–20430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Need, E.F.; Selth, L.A.; Harris, T.J.; Birrell, S.N.; Tilley, W.D.; Buchanan, G. Research resource: Interplay between the genomic and transcriptional networks of androgen receptor and estrogen receptor alpha in luminal breast cancer cells. Mol. Endocrinol. 2012, 26, 1941–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanzino, M.; Maris, P.; Sirianni, R.; Barone, I.; Casaburi, I.; Chimento, A.; Giordano, C.; Morelli, C.; Sisci, D.; Rizza, P.; et al. DAX-1, as an androgen-target gene, inhibits aromatase expression: A novel mechanism blocking estrogen-dependent breast cancer cell proliferation. Cell Death. Dis. 2013, 4, e724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciupek, A.; Rechoum, Y.; Gu, G.; Gelsomino, L.; Beyer, A.R.; Brusco, L.; Covington, K.R.; Tsimelzon, A.; Fuqua, S.A. Androgen receptor promotes tamoxifen agonist activity by activation of EGFR in ERalpha-positive breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2015, 154, 225–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migliaccio, A.; Di Domenico, M.; Castoria, G.; Nanayakkara, M.; Lombardi, M.; de Falco, A.; Bilancio, A.; Varricchio, L.; Ciociola, A.; Auricchio, F. Steroid receptor regulation of epidermal growth factor signaling through Src in breast and prostate cancer cells: Steroid antagonist action. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 10585–10593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shou, J.; Massarweh, S.; Osborne, C.K.; Wakeling, A.E.; Ali, S.; Weiss, H.; Schiff, R. Mechanisms of tamoxifen resistance: Increased estrogen receptor-HER2/neu cross-talk in ER/HER2-positive breast cancer. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2004, 96, 926–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thrane, S.; Lykkesfeldt, A.E.; Larsen, M.S.; Sorensen, B.S.; Yde, C.W. Estrogen receptor alpha is the major driving factor for growth in tamoxifen-resistant breast cancer and supported by HER/ERK signaling. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2013, 139, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chia, K.; Milioli, H.; Portman, N.; Laven-Law, G.; Coulson, R.; Yong, A.; Segara, D.; Parker, A.; Caldon, C.E.; Deng, N.; et al. Non-canonical AR activity facilitates endocrine resistance in breast cancer. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2019, 26, 251–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Amicis, F.; Thirugnansampanthan, J.; Cui, Y.; Selever, J.; Beyer, A.; Parra, I.; Weigel, N.L.; Herynk, M.H.; Tsimelzon, A.; Lewis, M.T.; et al. Androgen receptor overexpression induces tamoxifen resistance in human breast cancer cells. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2010, 121, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, R.; Hanamura, T.; Suzuki, T.; Gohno, T.; Shibahara, Y.; Niwa, T.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Ohnuki, K.; Kakugawa, Y.; Hirakawa, H.; et al. Increased androgen receptor activity and cell proliferation in aromatase inhibitor-resistant breast carcinoma. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2014, 144 Pt B, 513–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rechoum, Y.; Rovito, D.; Iacopetta, D.; Barone, I.; Ando, S.; Weigel, N.L.; O’Malley, B.W.; Brown, P.H.; Fuqua, S.A. AR collaborates with ERalpha in aromatase inhibitor-resistant breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2014, 147, 473–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cochrane, D.R.; Bernales, S.; Jacobsen, B.M.; Cittelly, D.M.; Howe, E.N.; D’Amato, N.C.; Spoelstra, N.S.; Edgerton, S.M.; Jean, A.; Guerrero, J.; et al. Role of the androgen receptor in breast cancer and preclinical analysis of enzalutamide. Breast Cancer Res. 2014, 16, R7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangel, N.; Rondon-Lagos, M.; Annaratone, L.; Osella-Abate, S.; Metovic, J.; Mano, M.P.; Bertero, L.; Cassoni, P.; Sapino, A.; Castellano, I. The role of the AR/ER ratio in ER-positive breast cancer patients. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2018, 25, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coss, C.C.; Jones, A.; Dalton, J.T. Selective androgen receptor modulators as improved androgen therapy for advanced breast cancer. Steroids 2014, 90, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanan, R.; Ahn, S.; Cheney, M.D.; Yepuru, M.; Miller, D.D.; Steiner, M.S.; Dalton, J.T. Selective androgen receptor modulators (SARMs) negatively regulate triple-negative breast cancer growth and epithelial:mesenchymal stem cell signaling. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e103202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.; Xia, W.; Lee, K.; Zhang, J.; Yuan, H.; Yuan, Z.; Shi, Y.; Wang, S.; Xu, F. Bicalutamide plus Aromatase Inhibitor in Patients with Estrogen Receptor-Positive/Androgen Receptor-Positive Advanced Breast Cancer. Oncologist 2020, 25, 21-e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krop, I.; Abramson, V.; Colleoni, M.; Traina, T.; Holmes, F.; Garcia-Estevez, L.; Hart, L.; Awada, A.; Zamagni, C.; Morris, P.G.; et al. A Randomized Placebo Controlled Phase II Trial Evaluating Exemestane with or without Enzalutamide in Patients with Hormone Receptor-Positive Breast Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 6149–6157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D. AR pathway activity correlates with AR expression in a HER2-dependent manner and serves as a better prognostic factor in breast cancer. Cell Oncol. (Dordr) 2020, 43, 321–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hackenberg, R.; Luttchens, S.; Hofmann, J.; Kunzmann, R.; Holzel, F.; Schulz, K.D. Androgen sensitivity of the new human breast cancer cell line MFM-223. Cancer Res. 1991, 51, 5722–5727. [Google Scholar]
- Lehmann, B.D.; Bauer, J.A.; Chen, X.; Sanders, M.E.; Chakravarthy, A.B.; Shyr, Y.; Pietenpol, J.A. Identification of human triple-negative breast cancer subtypes and preclinical models for selection of targeted therapies. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 2750–2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, J.L.; Macarthur, S.; Ross-Innes, C.S.; Tilley, W.D.; Neal, D.E.; Mills, I.G.; Carroll, J.S. Androgen receptor driven transcription in molecular apocrine breast cancer is mediated by FoxA1. EMBO J. 2011, 30, 3019–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barton, V.N.; D’Amato, N.C.; Gordon, M.A.; Lind, H.T.; Spoelstra, N.S.; Babbs, B.L.; Heinz, R.E.; Elias, A.; Jedlicka, P.; Jacobsen, B.M.; et al. Multiple molecular subtypes of triple-negative breast cancer critically rely on androgen receptor and respond to enzalutamide in vivo. Mol. Cancer. Ther. 2015, 14, 769–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Angulo, A.M.; Stemke-Hale, K.; Palla, S.L.; Carey, M.; Agarwal, R.; Meric-Berstam, F.; Traina, T.A.; Hudis, C.; Hortobagyi, G.N.; Gerald, W.L.; et al. Androgen receptor levels and association with PIK3CA mutations and prognosis in breast cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 2472–2478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuenca-Lopez, M.D.; Montero, J.C.; Morales, J.C.; Prat, A.; Pandiella, A.; Ocana, A. Phospho-kinase profile of triple negative breast cancer and androgen receptor signaling. BMC Cancer 2014, 14, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Bolton, E.C.; Jones, J.O. Androgens and androgen receptor signaling in prostate tumorigenesis. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2015, 54, R15–R29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bareche, Y.; Buisseret, L.; Gruosso, T.; Girard, E.; Venet, D.; Dupont, F.; Desmedt, C.; Larsimont, D.; Park, M.; Rothe, F.; et al. Unraveling Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Tumor Microenvironment Heterogeneity: Towards an Optimized Treatment Approach. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2020, 112, 708–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teschendorff, A.E.; Miremadi, A.; Pinder, S.E.; Ellis, I.O.; Caldas, C. An immune response gene expression module identifies a good prognosis subtype in estrogen receptor negative breast cancer. Genome Biol. 2007, 8, R157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vranic, S.; Marchio, C.; Castellano, I.; Botta, C.; Scalzo, M.S.; Bender, R.P.; Payan-Gomez, C.; di Cantogno, L.V.; Gugliotta, P.; Tondat, F.; et al. Immunohistochemical and molecular profiling of histologically defined apocrine carcinomas of the breast. Hum. Pathol. 2015, 46, 1350–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coussy, F.; Lavigne, M.; de Koning, L.; Botty, R.E.; Nemati, F.; Naguez, A.; Bataillon, G.; Ouine, B.; Dahmani, A.; Montaudon, E.; et al. Response to mTOR and PI3K inhibitors in enzalutamide-resistant luminal androgen receptor triple-negative breast cancer patient-derived xenografts. Theranostics 2020, 10, 1531–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehmann-Che, J.; Hamy, A.S.; Porcher, R.; Barritault, M.; Bouhidel, F.; Habuellelah, H.; Leman-Detours, S.; de Roquancourt, A.; Cahen-Doidy, L.; Bourstyn, E.; et al. Molecular apocrine breast cancers are aggressive estrogen receptor negative tumors overexpressing either HER2 or GCDFP15. Breast Cancer Res. 2013, 15, R37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Yang, Y.; Xu, K.; Li, L.; Huang, J.; Qiu, F. Androgen Receptor in Breast Cancer: From Bench to Bedside. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne) 2020, 11, 573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerratana, L.; Basile, D.; Buono, G.; De Placido, S.; Giuliano, M.; Minichillo, S.; Coinu, A.; Martorana, F.; De Santo, I.; Del Mastro, L.; et al. Androgen receptor in triple negative breast cancer: A potential target for the targetless subtype. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2018, 68, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michmerhuizen, A.R.; Spratt, D.E.; Pierce, L.J.; Speers, C.W. ARe we there yet? Understanding androgen receptor signaling in breast cancer. NPJ Breast Cancer 2020, 6, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gucalp, A.; Tolaney, S.; Isakoff, S.J.; Ingle, J.N.; Liu, M.C.; Carey, L.A.; Blackwell, K.; Rugo, H.; Nabell, L.; Forero, A.; et al. Phase ii trial of bicalutamide in patients with androgen receptor-positive, estrogen, receptor-negative metastatic breast cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 5505–5512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traina, T.A.; Miller, K.; Yardley, D.A.; Eakle, J.; Schwartzberg, L.S.; O’Shaughnessy, J.; Gradishar, W.; Schmid, P.; Winer, E.; Kelly, C.; et al. Enzalutamide for the Treatment of Androgen Receptor-Expressing Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 884–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, B.D.; Bauer, J.A.; Schafer, J.M.; Pendleton, C.S.; Tang, L.; Johnson, K.C.; Chen, X.; Balko, J.M.; Gomez, H.; Arteaga, C.L.; et al. PIK3CA mutations in androgen receptor-positive triple negative breast cancer confer sensitivity to the combination of PI3K and androgen receptor inhibitors. Breast Cancer Res. 2014, 16, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, B.D.; Abramson, V.G.; Sanders, M.E.; Mayer, E.L.; Haddad, T.C.; Nanda, R.; Van Poznak, C.; Storniolo, A.M.; Nangia, J.R.; Gonzalez-Ericsson, P.I.; et al. TBCRC 032 IB/II Multicenter Study: Molecular Insights to AR Antagonist and PI3K Inhibitor Efficacy in Patients with AR(+) Metastatic Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 2111–2123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, L.R.; Bulun, S.E. Estrogen production and action. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2001, 45, S116–S124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, E.R. Sources of estrogen and their importance. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2003, 86, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feher, T.; Bodrogi, L.; Vallent, K.; Ribai, Z. Role of human adipose tissue in the production and metabolism of steroid hormones. Endokrinologie 1982, 80, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Venturelli, E.; Orenti, A.; Fabricio, A.S.C.; Garrone, G.; Agresti, R.; Paolini, B.; Bonini, C.; Gion, M.; Berrino, F.; Desmedt, C.; et al. Observational study on the prognostic value of testosterone and adiposity in postmenopausal estrogen receptor positive breast cancer patients. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krusinska, B.; Wadolowska, L.; Slowinska, M.A.; Biernacki, M.; Drozdowski, M.; Chadzynski, T. Associations of Dietary Patterns and Metabolic-Hormone Profiles with Breast Cancer Risk: A Case-Control Study. Nutrients 2018, 10, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wellberg, E.A.; Checkley, L.A.; Giles, E.D.; Johnson, S.J.; Oljira, R.; Wahdan-Alaswad, R.; Foright, R.M.; Dooley, G.; Edgerton, S.M.; Jindal, S.; et al. The Androgen Receptor Supports Tumor Progression After the Loss of Ovarian Function in a Preclinical Model of Obesity and Breast Cancer. Horm. Cancer 2017, 8, 269–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwyer, A.R.; Truong, T.H.; Ostrander, J.H.; Lange, C.A. 90 YEARS OF PROGESTERONE: Steroid receptors as MAPK signaling sensors in breast cancer: Let the fates decide. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2020, 65, T35–T48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panno, M.L.; Naimo, G.D.; Spina, E.; Ando, S.; Mauro, L. Different molecular signaling sustaining adiponectin action in breast cancer. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2016, 31, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stelzer, G.; Rosen, N.; Plaschkes, I.; Zimmerman, S.; Twik, M.; Fishilevich, S.; Stein, T.I.; Nudel, R.; Lieder, I.; Mazor, Y.; et al. The GeneCards Suite: From Gene Data Mining to Disease Genome Sequence Analyses. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2016, 54, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizokami, A.; Gotoh, A.; Yamada, H.; Keller, E.T.; Matsumoto, T. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha represses androgen sensitivity in the LNCaP prostate cancer cell line. J. Urol. 2000, 164, 800–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenks, M.Z.; Fairfield, H.E.; Johnson, E.C.; Morrison, R.F.; Muday, G.K. Sex Steroid Hormones Regulate Leptin Transcript Accumulation and Protein Secretion in 3T3-L1 Cells. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 8232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fruhbeck, G. Intracellular signalling pathways activated by leptin. Biochem. J. 2006, 393, 7–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, R.S.; Ma, S.; Miao, L.; Li, R.; Yin, Y.; Raj, G.V. Androgen receptor-mediated non-genomic regulation of prostate cancer cell proliferation. Transl. Androl. Urol. 2013, 2, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pietri, E.; Conteduca, V.; Andreis, D.; Massa, I.; Melegari, E.; Sarti, S.; Cecconetto, L.; Schirone, A.; Bravaccini, S.; Serra, P.; et al. Androgen receptor signaling pathways as a target for breast cancer treatment. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2016, 23, R485–R498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, T.; Wang, L.H.; Farrar, W.L. Interleukin 6 activates androgen receptor-mediated gene expression through a signal transducer and activator of transcription 3-dependent pathway in LNCaP prostate cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2000, 60, 2132–2135. [Google Scholar]
- De Miguel, F.; Lee, S.O.; Onate, S.A.; Gao, A.C. Stat3 enhances transactivation of steroid hormone receptors. Nucl. Recept. 2003, 1, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gupta, N.; Mayer, D. Interaction of JAK with steroid receptor function. JAKSTAT 2013, 2, e24911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobisch, A.; Eder, I.E.; Putz, T.; Horninger, W.; Bartsch, G.; Klocker, H.; Culig, Z. Interleukin-6 regulates prostate-specific protein expression in prostate carcinoma cells by activation of the androgen receptor. Cancer Res. 1998, 58, 4640–4645. [Google Scholar]
- Hosney, M.; Sabet, S.; El-Shinawi, M.; Gaafar, K.M.; Mohamed, M.M. Leptin is overexpressed in the tumor microenvironment of obese patients with estrogen receptor positive breast cancer. Exp. Ther. Med. 2017, 13, 2235–2246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorio, E.; Mercanti, A.; Terrasi, M.; Micciolo, R.; Remo, A.; Auriemma, A.; Molino, A.; Parolin, V.; Di Stefano, B.; Bonetti, F.; et al. Leptin/HER2 crosstalk in breast cancer: In vitro study and preliminary in vivo analysis. BMC Cancer 2008, 8, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochsner, S.A.; Abraham, D.; Martin, K.; Ding, W.; McOwiti, A.; Kankanamge, W.; Wang, Z.; Andreano, K.; Hamilton, R.A.; Chen, Y.; et al. The Signaling Pathways Project, an integrated ‘omics knowledgebase for mammalian cellular signaling pathways. Sci. Data 2019, 6, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidel, H.M.; Milocco, L.H.; Lamb, P.; Darnell, J.E., Jr.; Stein, R.B.; Rosen, J. Spacing of palindromic half sites as a determinant of selective STAT (signal transducers and activators of transcription) DNA binding and transcriptional activity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szyszka, M.; Paschke, L.; Tyczewska, M.; Jopek, K.; Celichowski, P.; Milecka, P.; Sultanova, G.; Stelcer, E.; Malinska, A.; Malendowicz, L.K.; et al. Analysis of Transcriptome, Selected Intracellular Signaling Pathways, Proliferation and Apoptosis of LNCaP Cells Exposed to High Leptin Concentrations. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rangel, N.; Villegas, V.E.; Rondón-Lagos, M. Obesity and Androgen Receptor Signaling: Associations and Potential Crosstalk in Breast Cancer Cells. Cancers 2021, 13, 2218. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13092218
Rangel N, Villegas VE, Rondón-Lagos M. Obesity and Androgen Receptor Signaling: Associations and Potential Crosstalk in Breast Cancer Cells. Cancers. 2021; 13(9):2218. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13092218
Chicago/Turabian StyleRangel, Nelson, Victoria E. Villegas, and Milena Rondón-Lagos. 2021. "Obesity and Androgen Receptor Signaling: Associations and Potential Crosstalk in Breast Cancer Cells" Cancers 13, no. 9: 2218. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13092218
APA StyleRangel, N., Villegas, V. E., & Rondón-Lagos, M. (2021). Obesity and Androgen Receptor Signaling: Associations and Potential Crosstalk in Breast Cancer Cells. Cancers, 13(9), 2218. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13092218





