Clinical Implications of Geometric and Dosimetric Uncertainties of Inter- and Intra-Fractional Movement during Volumetric Modulated Arc Therapy for Breast Cancer Patients
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
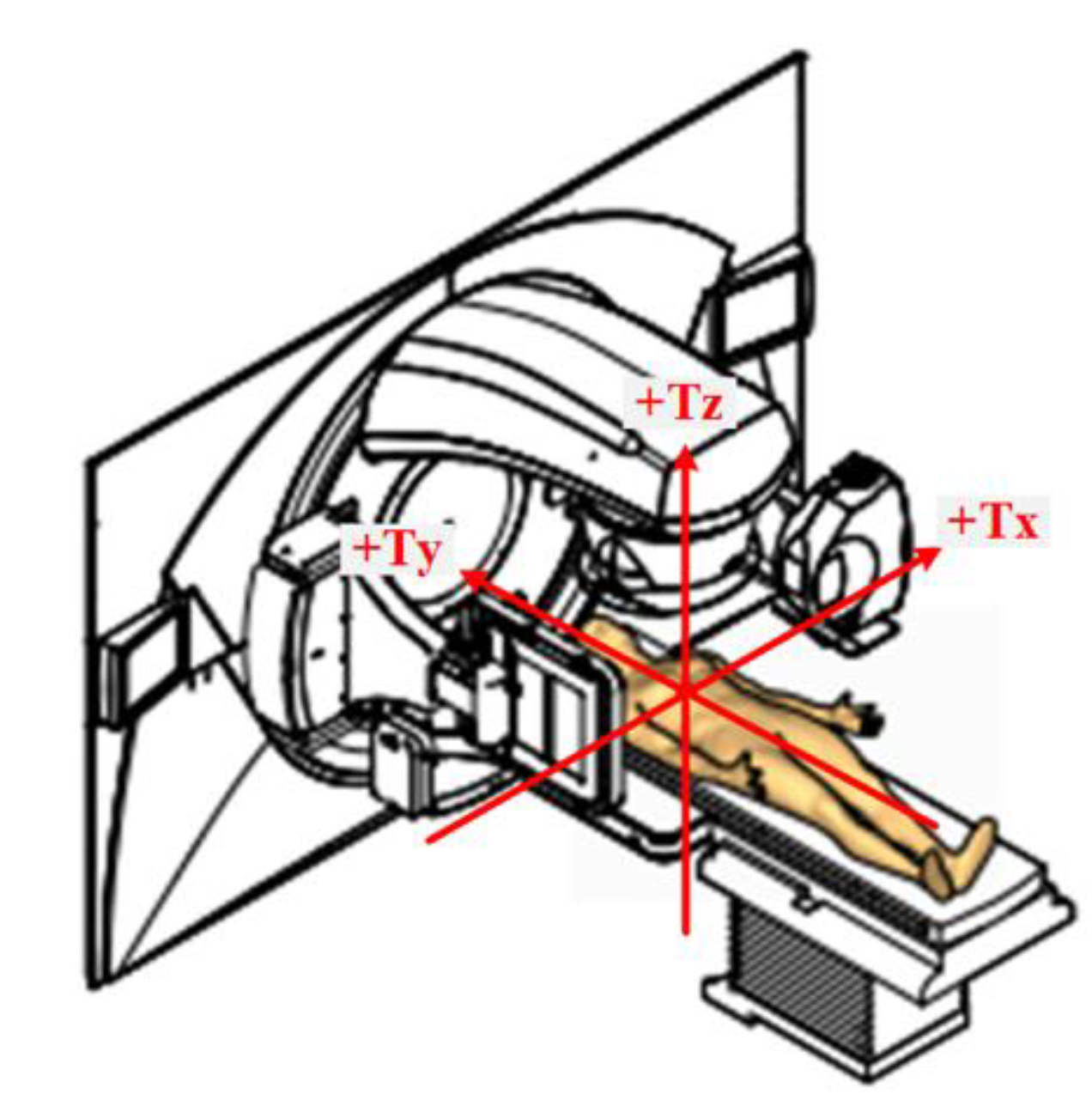
2.2. CBCT Data Acquisition
2.3. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patients and Treatment
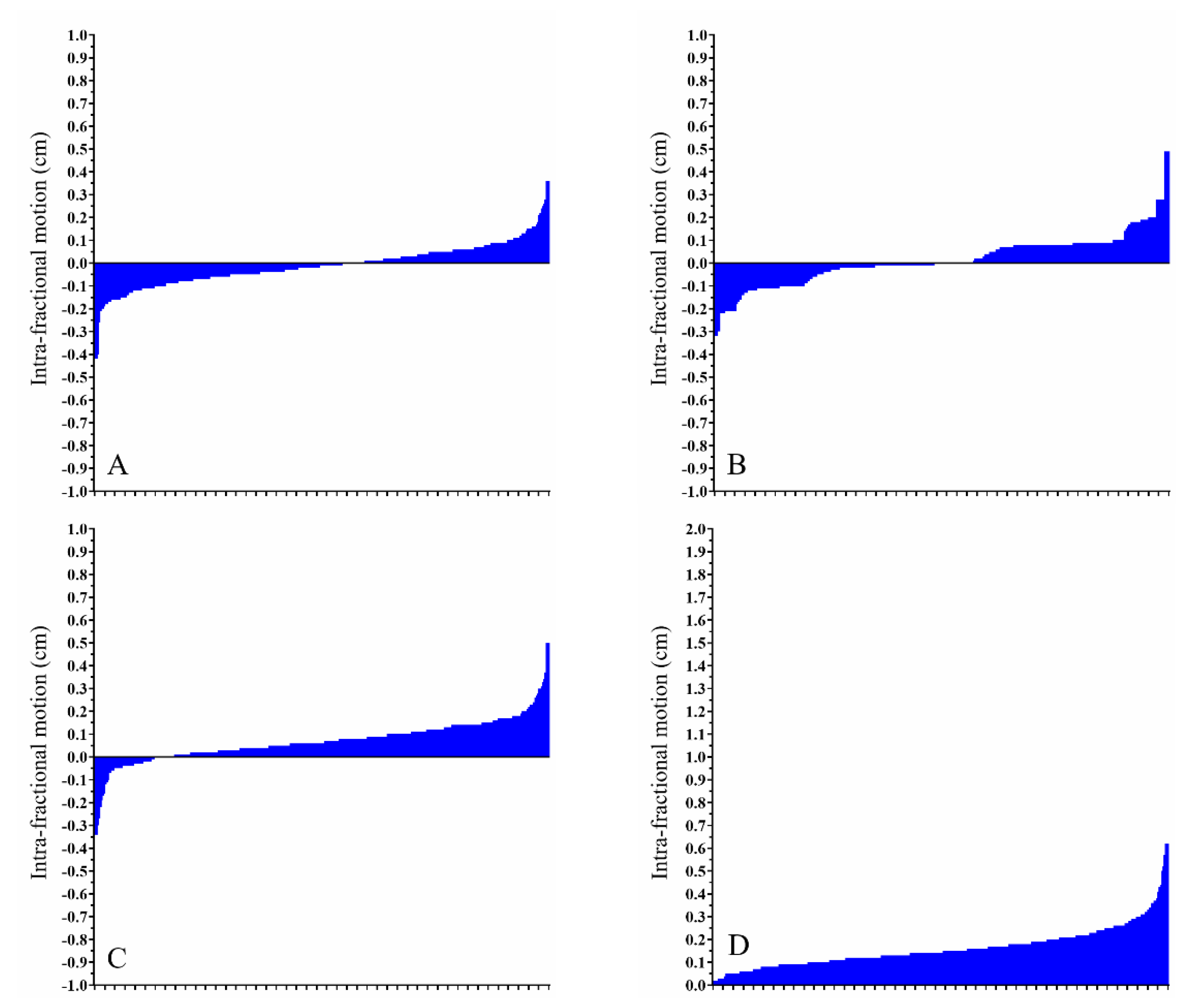
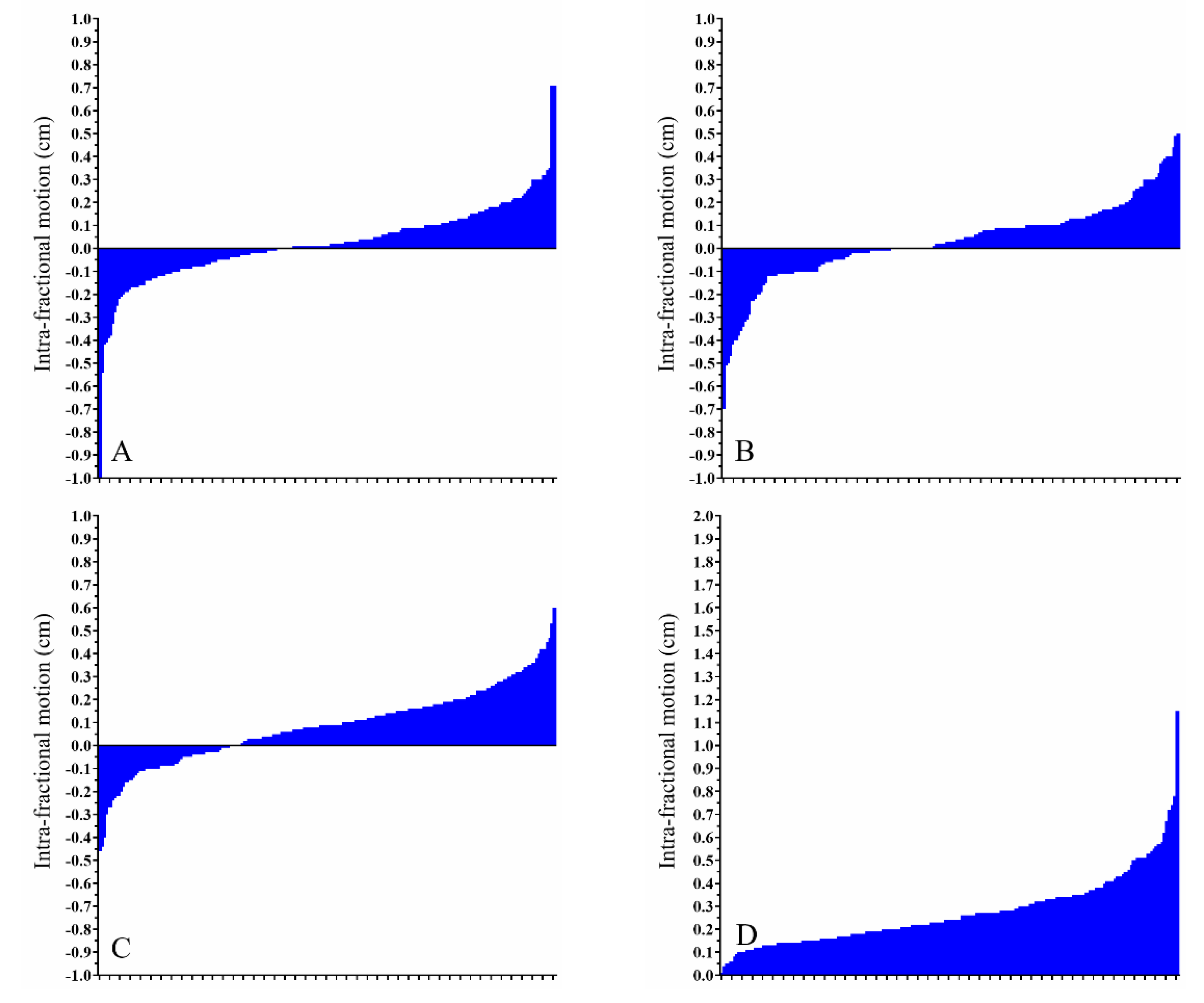
3.2. Pre-Treatment and Intra-Fractional CBCT
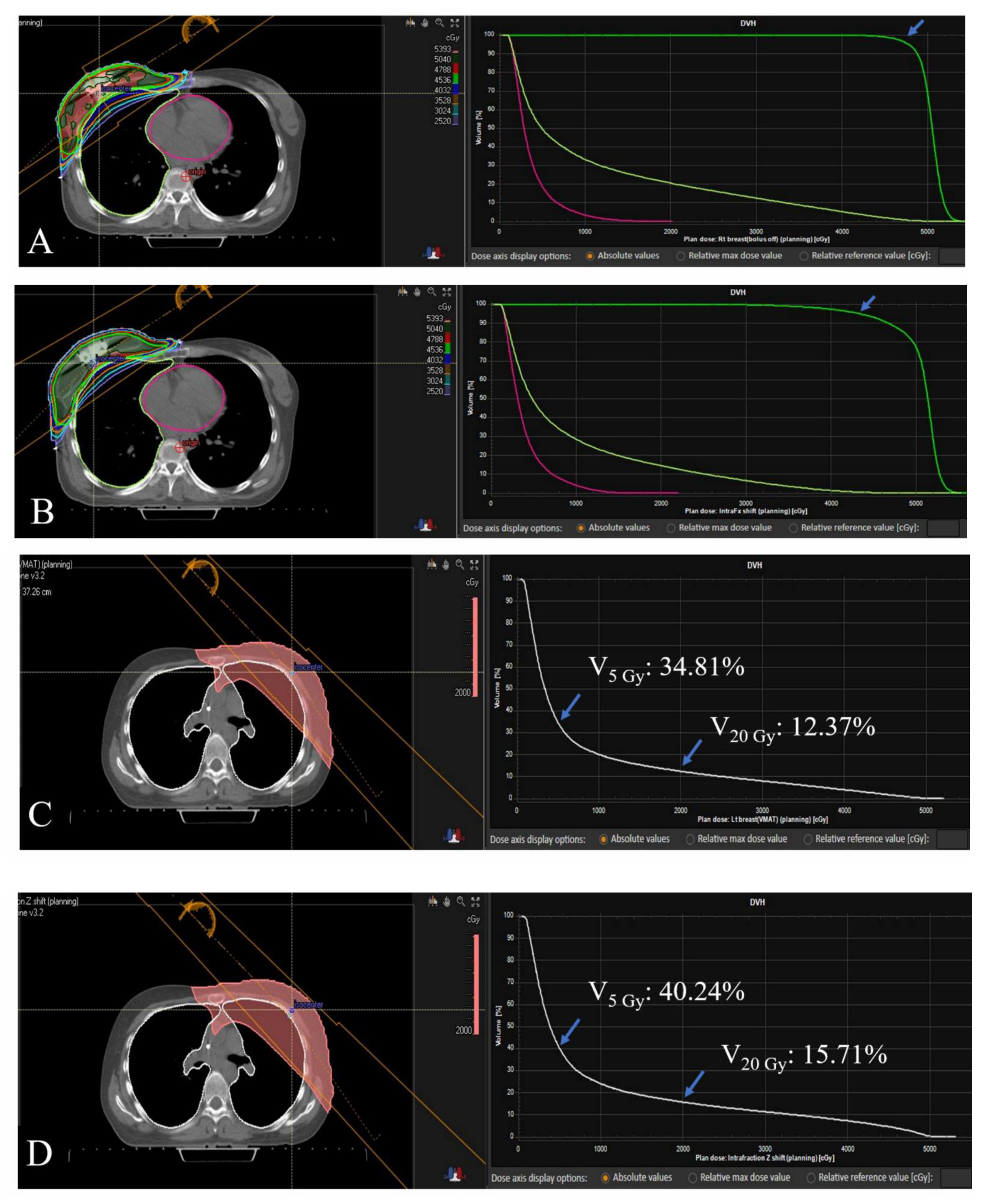
3.3. Dose-Volume Histogram Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Baskar, R.; Lee, K.A.; Yeo, R.; Yeoh, K.W. Cancer and radiation therapy: Current advances and future directions. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2012, 9, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabavizadeh, N.; Elliott, D.A.; Chen, Y.; Kusano, A.S.; Mitin, T.; Thomas, C.R., Jr.; Holland, J.M. Image Guided Radiation Therapy (IGRT) Practice Patterns and IGRT’s Impact on Workflow and Treatment Planning: Results From a National Survey of American Society for Radiation Oncology Members. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2016, 94, 850–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adamson, J.; Wu, Q.; Yan, D. Dosimetric effect of intrafraction motion and residual setup error for hypofractionated prostate intensity-modulated radiotherapy with online cone beam computed tomography image guidance. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2011, 80, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Litzenberg, D.W.; Balter, J.M.; Hadley, S.W.; Sandler, H.M.; Willoughby, T.R.; Kupelian, P.A.; Levine, L. Influence of intrafraction motion on margins for prostate radiotherapy. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2006, 65, 548–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Han, B.; Meng, B.; Maxim, P.G.; Xing, L.; Koong, A.C.; Diehn, M.; Loo, B.W., Jr. Clinical implementation of intrafraction cone beam computed tomography imaging during lung tumor stereotactic ablative radiation therapy. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2013, 87, 917–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Purdie, T.G.; Bissonnette, J.P.; Franks, K.; Bezjak, A.; Payne, D.; Sie, F.; Sharpe, M.B.; Jaffray, D.A. Cone-beam computed tomography for on-line image guidance of lung stereotactic radiotherapy: Localization, verification, and intrafraction tumor position. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2007, 68, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, F.; Wang, J.; Bai, S.; Li, Y.; Shen, Y.; Zhong, R.; Jiang, X.; Xu, Q. Detection of intrafractional tumour position error in radiotherapy utilizing cone beam computed tomography. Radiother. Oncol. 2008, 89, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Offersen, B.V.; Overgaard, J. Breast cancer radiation therapy. Lancet 2020, 396, 1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theberge, V.; Whelan, T.; Shaitelman, S.F.; Vicini, F.A. Altered fractionation: Rationale and justification for whole and partial breast hypofractionated radiotherapy. Semin. Radiat. Oncol. 2011, 21, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanders, M.E.; Scroggins, T.; Ampil, F.L.; Li, B.D. Accelerated partial breast irradiation in early-stage breast cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2007, 25, 996–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Offersen, B.V.; Boersma, L.J.; Kirkove, C.; Hol, S.; Aznar, M.C.; Biete Sola, A.; Kirova, Y.M.; Pignol, J.P.; Remouchamps, V.; Verhoeven, K.; et al. ESTRO consensus guideline on target volume delineation for elective radiation therapy of early stage breast cancer. Radiother. Oncol. 2015, 114, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergom, C.; Currey, A.; Desai, N.; Tai, A.; Strauss, J.B. Deep Inspiration Breath Hold: Techniques and Advantages for Cardiac Sparing During Breast Cancer Irradiation. Front. Oncol. 2018, 8, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Pan, T.; Pinnix, C.; Zhang, S.X.; Salehpour, M.; Sun, T.L.; Gladish, G.; Strom, E.A.; Perkins, G.H.; Tereffe, W.; et al. Cardiac motion during deep-inspiration breath-hold: Implications for breast cancer radiotherapy. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2012, 82, 708–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betgen, A.; Alderliesten, T.; Sonke, J.J.; van Vliet-Vroegindeweij, C.; Bartelink, H.; Remeijer, P. Assessment of set-up variability during deep inspiration breath hold radiotherapy for breast cancer patients by 3D-surface imaging. Radiother. Oncol. 2013, 106, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, A.M.; Ceder, Y.K.; Shochat, T.; Fenig, E.; Popovtzer, A.; Bragilofsky, D.; Alfassy, A.; Allon, H. CPAP (Continuous Positive Airway Pressure) is an effective and stable solution for heart sparing radiotherapy of left sided breast cancer. Radiat. Oncol. 2020, 15, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Virk, J.S.; Kotecha, B. When continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) fails. J. Thorac. Dis. 2016, 8, E1112–E1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teoh, M.; Clark, C.H.; Wood, K.; Whitaker, S.; Nisbet, A. Volumetric modulated arc therapy: A review of current literature and clinical use in practice. Br. J. Radiol. 2011, 84, 967–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Connell, P.P.; Hellman, S. Advances in radiotherapy and implications for the next century: A historical perspective. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 383–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powell, S. Radiotherapy for breast cancer in the 21st Century. Breast J. 2010, 16 (Suppl. 1), S34–S38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whelan, T.J.; Julian, J.A.; Berrang, T.S.; Kim, D.H.; Germain, I.; Nichol, A.M.; Akra, M.; Lavertu, S.; Germain, F.; Fyles, A.; et al. External beam accelerated partial breast irradiation versus whole breast irradiation after breast conserving surgery in women with ductal carcinoma in situ and node-negative breast cancer (RAPID): A randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2019, 394, 2165–2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meattini, I.; Marrazzo, L.; Saieva, C.; Desideri, I.; Scotti, V.; Simontacchi, G.; Bonomo, P.; Greto, D.; Mangoni, M.; Scoccianti, S.; et al. Accelerated Partial-Breast Irradiation Compared With Whole-Breast Irradiation for Early Breast Cancer: Long-Term Results of the Randomized Phase III APBI-IMRT-Florence Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 4175–4183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray Brunt, A.; Haviland, J.S.; Wheatley, D.A.; Sydenham, M.A.; Alhasso, A.; Bloomfield, D.J.; Chan, C.; Churn, M.; Cleator, S.; Coles, C.E.; et al. Hypofractionated breast radiotherapy for 1 week versus 3 weeks (FAST-Forward): 5-year efficacy and late normal tissue effects results from a multicentre, non-inferiority, randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2020, 395, 1613–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, E.A.; Cho, J.; Vallis, K.A.; Sharpe, M.B.; Lee, G.; Blackburn, H.; Nageeti, T.; McGibney, C.; Jaffray, D.A. Cone beam computed tomography guidance for setup of patients receiving accelerated partial breast irradiation. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2007, 68, 547–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topolnjak, R.; Sonke, J.J.; Nijkamp, J.; Rasch, C.; Minkema, D.; Remeijer, P.; van Vliet-Vroegindeweij, C. Breast patient setup error assessment: Comparison of electronic portal image devices and cone-beam computed tomography matching results. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2010, 78, 1235–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazelaar, C.; Dahele, M.; Scheib, S.; Slotman, B.J.; Verbakel, W. Verifying tumor position during stereotactic body radiation therapy delivery using (limited-arc) cone beam computed tomography imaging. Radiother. Oncol. 2017, 123, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.; Palma, D.A.; Scott, D.; McGregor, D.; Gaede, S.; Yartsev, S.; Bauman, G.; Louie, A.V.; Rodrigues, G. Inter- and intrafraction uncertainty in prostate bed image-guided radiotherapy. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2012, 84, 402–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boda-Heggemann, J.; Kohler, F.M.; Wertz, H.; Ehmann, M.; Hermann, B.; Riesenacker, N.; Kupper, B.; Lohr, F.; Wenz, F. Intrafraction motion of the prostate during an IMRT session: A fiducial-based 3D measurement with Cone-beam CT. Radiat. Oncol. 2008, 3, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Reitz, D.; Carl, G.; Schonecker, S.; Pazos, M.; Freislederer, P.; Niyazi, M.; Ganswindt, U.; Alongi, F.; Reiner, M.; Belka, C.; et al. Real-time intra-fraction motion management in breast cancer radiotherapy: Analysis of 2028 treatment sessions. Radiat. Oncol. 2018, 13, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, G.; Hu, W.G.; Chen, J.Y.; Yu, X.L.; Pan, Z.Q.; Yang, Z.Z.; Guo, X.M.; Shao, Z.M.; Jiang, G.L. Impact of residual and intrafractional errors on strategy of correction for image-guided accelerated partial breast irradiation. Radiat. Oncol. 2010, 5, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalski, A.; Atyeo, J.; Cox, J.; Rinks, M. Inter- and intra-fraction motion during radiation therapy to the whole breast in the supine position: A systematic review. J. Med. Imaging Radiat. Oncol. 2012, 56, 499–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyran, M.; Tallet, A.; Resbeut, M.; Ferre, M.; Favrel, V.; Fau, P.; Moureau-Zabotto, L.; Darreon, J.; Gonzague, L.; Benkemouche, A.; et al. Safety and benefit of using a virtual bolus during treatment planning for breast cancer treated with arc therapy. J. Appl. Clin. Med. Phys. 2018, 19, 463–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gagliardi, G.; Constine, L.S.; Moiseenko, V.; Correa, C.; Pierce, L.J.; Allen, A.M.; Marks, L.B. Radiation dose-volume effects in the heart. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2010, 76, S77–S85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kugele, M.; Edvardsson, A.; Berg, L.; Alkner, S.; Andersson Ljus, C.; Ceberg, S. Dosimetric effects of intrafractional isocenter variation during deep inspiration breath-hold for breast cancer patients using surface-guided radiotherapy. J. Appl. Clin. Med. Phys. 2018, 19, 25–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoganathan, S.A.; Maria Das, K.J.; Maria Midunvaleja, K.; Gowtham Raj, D.; Agarwal, A.; Velmurugan, J.; Kumar, S. Evaluating the image quality of cone beam CT acquired during rotational delivery. Br. J. Radiol. 2015, 88, 20150425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazelaar, C.; Dahele, M.; Mostafavi, H.; van der Weide, L.; Slotman, B.; Verbakel, W. Markerless positional verification using template matching and triangulation of kV images acquired during irradiation for lung tumors treated in breath-hold. Phys. Med. Biol. 2018, 63, 115005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, M.; Zolfaghari, R.; Briggs, A.; Furtado, H.; Booth, J.; Keall, P.; Nguyen, D.; O’Brien, R.; Shieh, C.C. The first prospective implementation of markerless lung target tracking in an experimental quality assurance procedure on a standard linear accelerator. Phys. Med. Biol. 2020, 65, 025008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.; Fahimian, B.P.; Xing, L. Binary moving-blocker-based scatter correction in cone-beam computed tomography with width-truncated projections: Proof of concept. Phys. Med. Biol. 2017, 62, 2176–2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youn, I.; Choi, S.; Kook, S.H.; Choi, Y.J. Mammographic Breast Density Evaluation in Korean Women Using Fully Automated Volumetric Assessment. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2016, 31, 457–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, H.M.; Lee, E.H.; Ko, K.; Kang, B.J.; Cha, J.H.; Yi, A.; Jung, H.K.; Jun, J.K.; Alliance for Breast Cancer Screening in, K. Prevalence of Women with Dense Breasts in Korea: Results from a Nationwide Cross-sectional Study. Cancer Res. Treat. 2019, 51, 1295–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| x-Axis | y-Axis | z-Axis | Absolute Difference | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Treatment Location and Radiotherapy Technique | Median (Range) | Median (Range) | Median (Range) | Median (Range) |
| Rt. breast pre-treatment CBCT, Free-breathing (cm) | −0.07 (−0.78–0.64) | 0.14 (−2.92–1.30) | 0.29 (−1.69–0.94) | 0.53 (0.06–2.98) |
| Rt. breast intra-fractional CBCT, Free-breathing (cm) | −0.01 (−0.42–0.36) | 0.00 (−0.32–0.49) | 0.06 (−0.34–0.50) | 0.14 (0.00–0.62) |
| Lt. breast pre-treatment CBCT, DIBH (cm) | 0.12 (−1.32–0.84) | -0.03 (−1.86–4.26) | 0.29 (−1.97–1.83) | 0.66 (0.08–4.41) |
| Lt. breast intra-fractional CBCT, DIBH (cm) | 0.00 (−0.63–0.50) | -0.01 (−0.62–0.81) | 0.03 (−0.50–0.80) | 0.23 (0.02–0.96) |
| Lt. breast pre-treatment CBCT, CPAP (cm) | 0.03 (−1.83–1.41) | 0.00 (−3.72–3.18) | 0.07 (−1.92–1.50) | 0.69 (0.04–3.80) |
| Lt. breast intra-fractional CBCT, CPAP (cm) | 0.01 (−1.11–0.71) | 0.03 (−0.70–0.50) | 0.09 (−0.46–0.60) | 0.24 (0.00–1.15) |
| Patients (Location; Technique) | D95% of the PTV (% of Prescribed Dose) | V95% of the prescribed dose (% of the PTV) | Mean Lung Dose (Gy) | Ipsilateral Lung V5 Gy (%) | Ipsilateral Lung V20 Gy (%) | Heart D0.2 cc (Gy) | Heart V25 Gy (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Patient 1 (Right-sided) | |||||||
| Original | 96.1 | 96.9 | 9.53 | 56.07 | 12.15 | 24.49 | 0.51 |
| Modified | 94.9 | 95 | 9.05 | 55.33 | 10.9 | 22.21 | 0.48 |
| Patient 2 (Right-sided) | |||||||
| Original | 95.47 | 95.83 | 8.23 | 45.27 | 11.2 | 14.15 | 0 |
| Modified | 86.03 | 87.41 | 7.01 | 42.52 | 8 | 12.86 | 0 |
| Patient 3 (Right-sided) | |||||||
| Original | 98.02 | 99 | 11.05 | 73.1 | 13.44 | 23.61 | 0.62 |
| Modified | 93.53 | 94 | 9.82 | 71.38 | 9.78 | 21.57 | 0.18 |
| Patient 4 (Left-sided; DIBH) | |||||||
| Original | 96.77 | 97.28 | 8.01 | 34.81 | 12.37 | 21.39 | 0.15 |
| Modified | 86.88 | 88.41 | 9.68 | 40.24 | 15.71 | 31.62 | 3.32 |
| Patient 5 (Left-sided; DIBH) | |||||||
| Original | 94.03 | 93.54 | 6.27 | 38.31 | 5.95 | 11.71 | 0 |
| Modified | 80.45 | 81.55 | 5.75 | 38.2 | 3.85 | 10.87 | 0 |
| Patient 6 (Left-sided; DIBH) | |||||||
| Original | 94.76 | 94.88 | 8.43 | 57.51 | 8.84 | 19.02 | 0.01 |
| Modified | 86.41 | 83.64 | 10.05 | 61.73 | 12.64 | 22.35 | 0.36 |
| Patient 7 (Left-sided; DIBH) | |||||||
| Original | 91.67 | 90.02 | 9.67 | 62.38 | 11.57 | 26.35 | 1.48 |
| Modified | 87.26 | 88.07 | 9.75 | 64.93 | 11.53 | 32.41 | 3.87 |
| Patient 8 (Left-sided; CPAP) | |||||||
| Original | 95.75 | 96.25 | 7.89 | 43.06 | 11.25 | 14.39 | 0 |
| Modified | 90.3 | 89.02 | 6.61 | 39.66 | 8.09 | 13.16 | 0 |
| Patient 9 (Left-sided; CPAP) | |||||||
| Original | 93.19 | 92.43 | 7.83 | 41.44 | 11.27 | 13.74 | 0 |
| Modified | 90.52 | 90.62 | 9.39 | 45.37 | 14.92 | 14.75 | 0.02 |
| Patient10(Left-sided; CPAP) | |||||||
| Original | 93.77 | 93.4 | 8 | 41.66 | 11.55 | 16.09 | 0 |
| Modified | 90.44 | 89.6 | 7.08 | 39.18 | 9.27 | 15.52 | 0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, J.J.B.; Lee, I.J.; Choi, Y.; Jeon, M.J.; Jung, I.H.; Lee, H. Clinical Implications of Geometric and Dosimetric Uncertainties of Inter- and Intra-Fractional Movement during Volumetric Modulated Arc Therapy for Breast Cancer Patients. Cancers 2021, 13, 1651. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13071651
Lee JJB, Lee IJ, Choi Y, Jeon MJ, Jung IH, Lee H. Clinical Implications of Geometric and Dosimetric Uncertainties of Inter- and Intra-Fractional Movement during Volumetric Modulated Arc Therapy for Breast Cancer Patients. Cancers. 2021; 13(7):1651. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13071651
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Jason Joon Bock, Ik Jae Lee, Yeonho Choi, Mi Jin Jeon, Il Hun Jung, and Ho Lee. 2021. "Clinical Implications of Geometric and Dosimetric Uncertainties of Inter- and Intra-Fractional Movement during Volumetric Modulated Arc Therapy for Breast Cancer Patients" Cancers 13, no. 7: 1651. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13071651
APA StyleLee, J. J. B., Lee, I. J., Choi, Y., Jeon, M. J., Jung, I. H., & Lee, H. (2021). Clinical Implications of Geometric and Dosimetric Uncertainties of Inter- and Intra-Fractional Movement during Volumetric Modulated Arc Therapy for Breast Cancer Patients. Cancers, 13(7), 1651. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13071651






