FTIR Spectroscopic Imaging Supports Urine Cytology for Classification of Low- and High-Grade Bladder Carcinoma
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
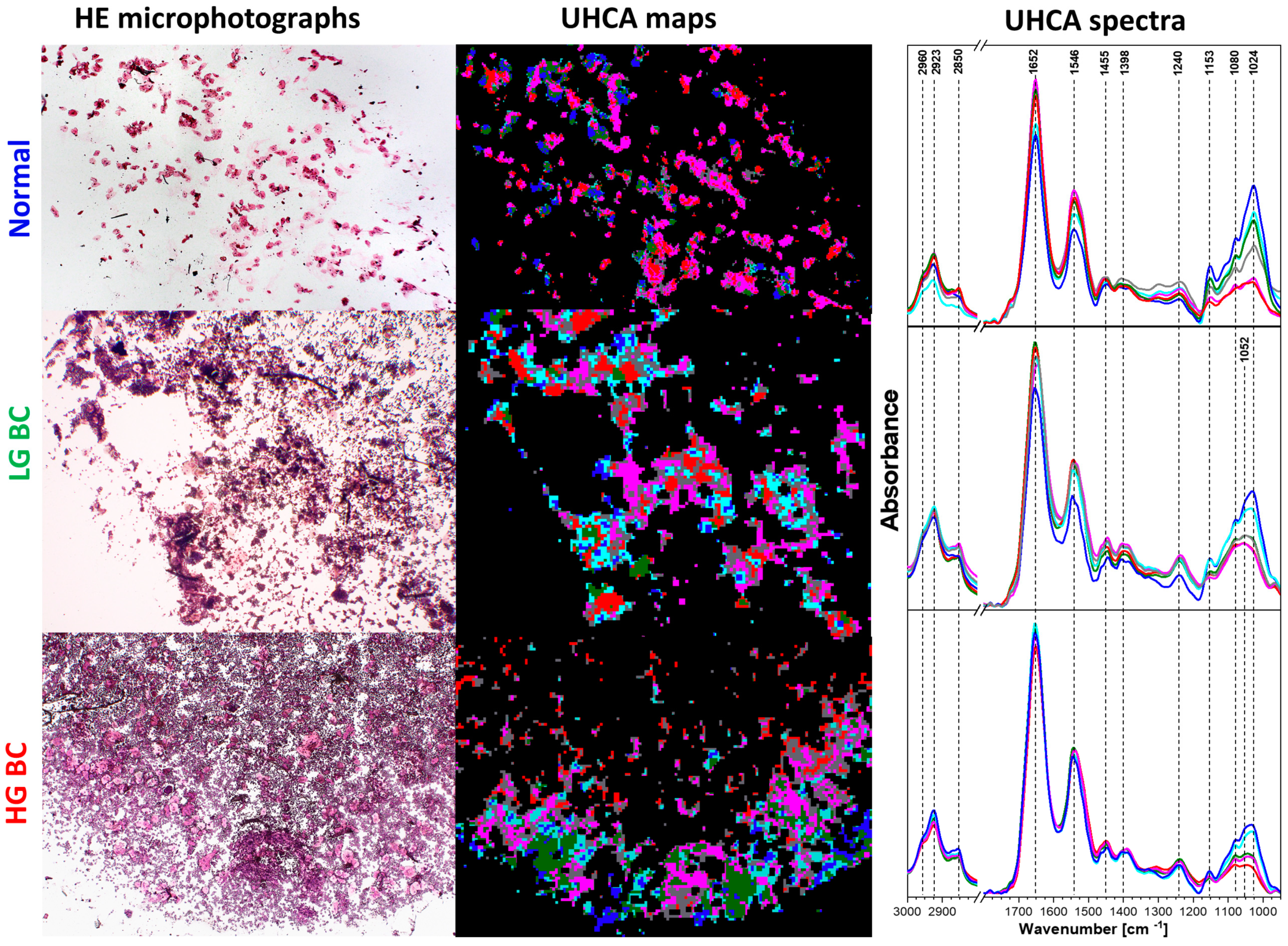
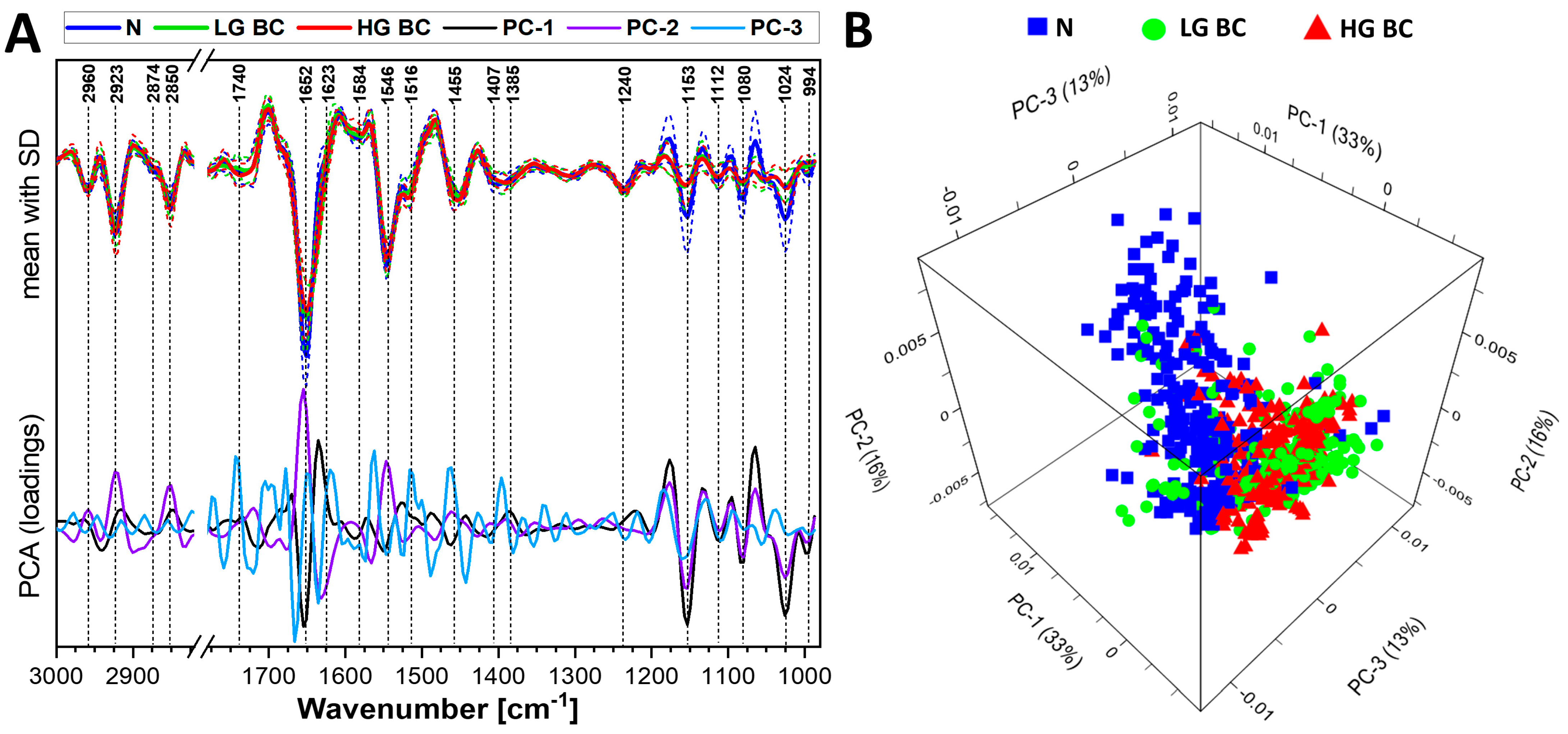
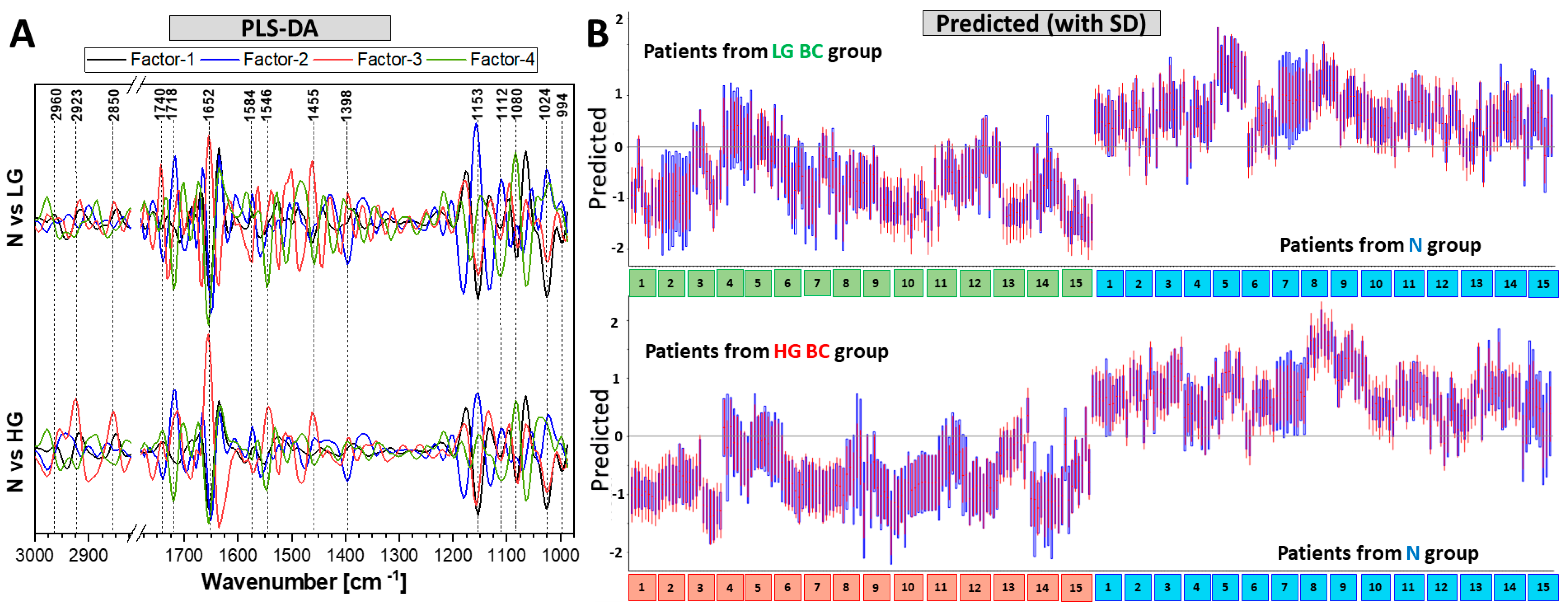
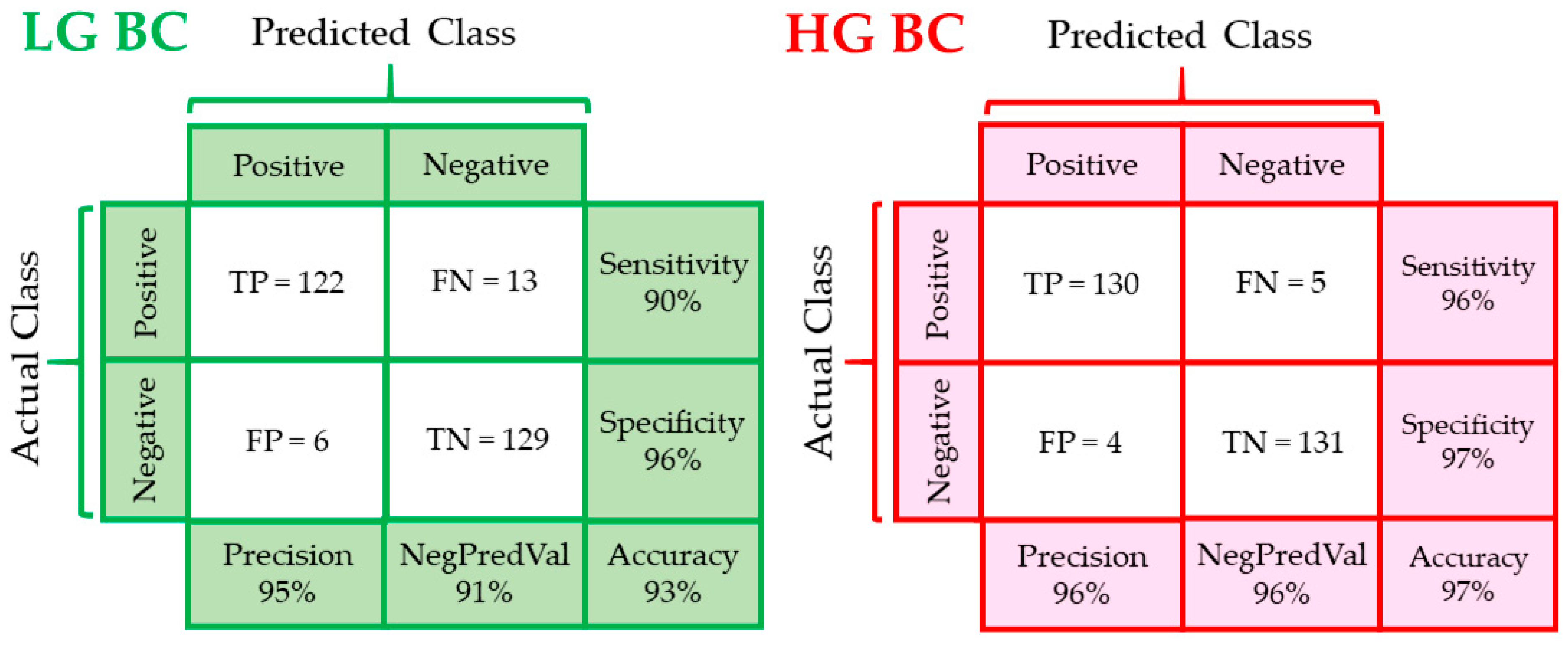
3. Results
3.1. Clinic-Pathological Profile of Patients
3.2. Cluster and Principal Component Analysis of Spectral Database
3.3. PLS Discrimination Analysis of Patients’ Groups
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kurtycz, D.F.I.; Sundling, K.E.; Barkan, G.A. The Paris system of Reporting Urinary Cytology: Strengths and opportunities. Diagn. Cytopathol. 2020, 48, 890–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, M.; He, G.; Goh, S.; Low, A.W.X.; Tay, K.J.; Lim, T.K.H.; Yeong, J.; Khor, L.Y.; Lim, T.S. Biomarkers for precision urothelial carcinoma diagnosis: Current approaches and the application of single-cell technologies. Cancers 2021, 13, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koss, L.G.; Hoda, R.S. Koss’s Cytology of the Urinary Tract with Histopathologic Correlations; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; ISBN 1461420555. [Google Scholar]
- Hartman, R.; Kawashima, A. Lower tract neoplasm: Update of imaging evaluation. Eur. J. Radiol. 2017, 97, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abouelkheir, R.T.; Abdelhamid, A.; El-Ghar, M.A.; Tarek, E.-D. Imaging of Bladder Cancer: Standard Applications and Future Trends. Medicina (B. Aires) 2021, 57, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenthal, D.L.; Wojcik, E.M.; Kurtycz, D.F.I. (Eds.) The Paris System for Reporting Urinary Cytology, 1st ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; ISBN 978-3-319-22864-8. [Google Scholar]
- Hughes, C.; Iqbal-Wahid, J.; Brown, M.; Shanks, J.H.; Eustace, A.; Denley, H.; Hoskin, P.J.; West, C.; Clarke, N.W.; Gardner, P. FTIR microspectroscopy of selected rare diverse sub-variants of carcinoma of the urinary bladder. J. Biophotonics 2013, 6, 73–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.C.; Czerniak, B. Bladder cancer in the genomic era. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2019, 143, 695–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bird, B.; Romeo, M.J.; Diem, M.; Bedrossian, K.; Laver, N.; Naber, S. Cytology by infrared micro-spectroscopy: Automatic distinction of cell types in urinary cytology. Vib. Spectrosc. 2008, 48, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gill, G. Cytopreparation Principles & Practice; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2013; ISBN 978-1-4614-4932-4. [Google Scholar]
- Kujdowicz, M.; Placha, W.; Mech, B.; Chrabaszcz, K.; Okoń, K.; Malek, K. In Vitro Spectroscopy-Based Profiling of Urothelial Carcinoma: A Fourier Transform Infrared and Raman Imaging Study. Cancers 2021, 13, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soh, J.Y.; Chueng, A.; Adio, A.; Cooper, A.J.; Birch, B.R.; Lwaleed, B.A. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy imaging of live epithelial cancer cells under non-aqueous media. J. Clin. Pathol. 2013, 66, 312–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gok, S.; Aydin, O.Z.; Sural, Y.S.; Zorlu, F.; Bayol, U.; Severcan, F. Bladder cancer diagnosis from bladder wash by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy as a novel test for tumor recurrence. J. Biophotonics 2016, 9, 967–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kujdowicz, M.; Perez Guaita, D.; Chłosta, P.; Okon, K.; Malek, K. Towards the Point of Care and noninvasive classification of bladder cancer from urine sediment infrared spectroscopy. Spectral differentiation of normal, abnormal and cancer patients. Microchem. J. 2021, 168, 106460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bensaid, S.; Kachenoura, A.; Costet, N.; Bensalah, K.; Tariel, H.; Senhadji, L. Noninvasive detection of bladder cancer using mid-infrared spectra classification. Expert Syst. Appl. 2017, 89, 333–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jin, H.; Lin, T.; Han, P.; Yao, Y.; Zheng, D.; Hao, J.; Hu, Y.; Zeng, R. Efficacy of Raman spectroscopy in the diagnosis of bladder cancer. Medicine 2019, 98, e18066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, M.J.; Trevisan, J.; Bassan, P.; Bhargava, R.; Butler, H.J.; Dorling, K.M.; Fielden, P.R.; Fogarty, S.W.; Fullwood, N.J.; Heys, K.A.; et al. Using Fourier transform IR spectroscopy to analyze biological materials. Nat. Protoc. 2014, 9, 1771–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Balan, V.; Mihai, C.T.; Cojocaru, F.D.; Uritu, C.M.; Dodi, G.; Botezat, D.; Gardikiotis, I. Vibrational spectroscopy fingerprinting in medicine: From molecular to clinical practice. Materials (Basel) 2019, 12, 2884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brandenburg, K.; Seydel, U. Infrared spectroscopy of glycolipids. Chem. Phys. Lipids 1998, 96, 23–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bongiovanni, G.A.; Eynard, A.R.; Calderón, R.O. Altered lipid profile and changes in uroplakin properties of rat urothelial plasma membrane with diets of different lipid composition. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2005, 271, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taladrid, D.; Marín, D.; Alemán, A.; Álvarez-Acero, I.; Montero, P.; Gómez-Guillén, M.C. Effect of chemical composition and sonication procedure on properties of food-grade soy lecithin liposomes with added glycerol. Food Res. Int. 2017, 100, 541–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Atkins, P.; de Paula, J. Physical Chemistry, 9th ed.; OUP Oxford: Oxford, UK, 2009; ISBN 0199543372. [Google Scholar]
- Staniszewska, E.; Malek, K.; Baranska, M. Rapid approach to analyze biochemical variation in rat organs by ATR FTIR spectroscopy. Spectrochim. Acta—Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2014, 118, 981–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreissig, I.; Machill, S.; Salzer, R.; Krafft, C. Quantification of brain lipids by FTIR spectroscopy and partial least squares regression. Spectrochim. Acta—Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2009, 71, 2069–2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsztyńska-Janus, S. Specific Applications of Vibrational Spectroscopy in Biomedical Engineering. In Biomedical Engineering, Trends, Research and Technologies; Gąsior-Głogowska, M., Ed.; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, L.C.; Liong, C.-Y.; Jemain, A.A. Partial least squares-discriminant analysis (PLS-DA) for classification of high-dimensional (HD) data: A review of contemporary practice strategies and knowledge gaps. Analyst 2018, 143, 3526–3539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diem, M.; Mazur, A.; Lenau, K.; Schubert, J.; Bird, B.; Miljković, M.; Krafft, C.; Popp, J. Molecular pathology via IR and Raman spectral imaging. J. Biophotonics 2013, 6, 855–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajjar, K.; Ahmadzai, A.A.; Valasoulis, G.; Trevisan, J.; Founta, C.; Nasioutziki, M.; Loufopoulos, A.; Kyrgiou, M.; Stasinou, S.M.; Karakitsos, P.; et al. Histology verification demonstrates that biospectroscopy analysis of cervical cytology identifies underlying disease more accurately than conventional screening: Removing the confounder of discordance. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e82416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Appiah, B.; Nammalvar, V.; Drezek, R. Statistical analysis of FTIR spectra of cervical tissues and diagnostic algorithms for cervical cancer. In Proceedings of the SPIE BiOS 2008, San Jose, CA, USA, 13 May 2008; Volume 6863. [Google Scholar]
- Crow, P.; Uff, J.S.; Farmer, J.A.; Wright, M.P.; Stone, N. The use of Raman spectroscopy to identify and characterize transitional cell carcinoma in vitro. BJU Int. 2004, 93, 1232–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shapiro, A.; Gofrit, O.N.; Pizov, G.; Cohen, J.K.; Maier, J. Raman molecular imaging: A novel spectroscopic technique for diagnosis of bladder cancer in urine specimens. Eur. Urol. 2011, 59, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| N | LG BC | HG BC | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender [M/F] | 3/12 | 8/7 | 14/1 |
| Age [ys ± SD] | 64.9 (13.7) | 70.8 (5.6) | 70.9 (6.0) |
| Hematuria | 1 | 3 | 0 |
| Urine pH [±SD] | 5.57 (0.56) | 5.57 (0.65) | 5.57 (0.56) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kujdowicz, M.; Mech, B.; Chrabaszcz, K.; Chlosta, P.; Okon, K.; Malek, K. FTIR Spectroscopic Imaging Supports Urine Cytology for Classification of Low- and High-Grade Bladder Carcinoma. Cancers 2021, 13, 5734. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13225734
Kujdowicz M, Mech B, Chrabaszcz K, Chlosta P, Okon K, Malek K. FTIR Spectroscopic Imaging Supports Urine Cytology for Classification of Low- and High-Grade Bladder Carcinoma. Cancers. 2021; 13(22):5734. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13225734
Chicago/Turabian StyleKujdowicz, Monika, Brygida Mech, Karolina Chrabaszcz, Piotr Chlosta, Krzysztof Okon, and Kamilla Malek. 2021. "FTIR Spectroscopic Imaging Supports Urine Cytology for Classification of Low- and High-Grade Bladder Carcinoma" Cancers 13, no. 22: 5734. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13225734
APA StyleKujdowicz, M., Mech, B., Chrabaszcz, K., Chlosta, P., Okon, K., & Malek, K. (2021). FTIR Spectroscopic Imaging Supports Urine Cytology for Classification of Low- and High-Grade Bladder Carcinoma. Cancers, 13(22), 5734. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13225734







