ADAM9-Responsive Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Targeted Drug Delivery in Pancreatic Cancer
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
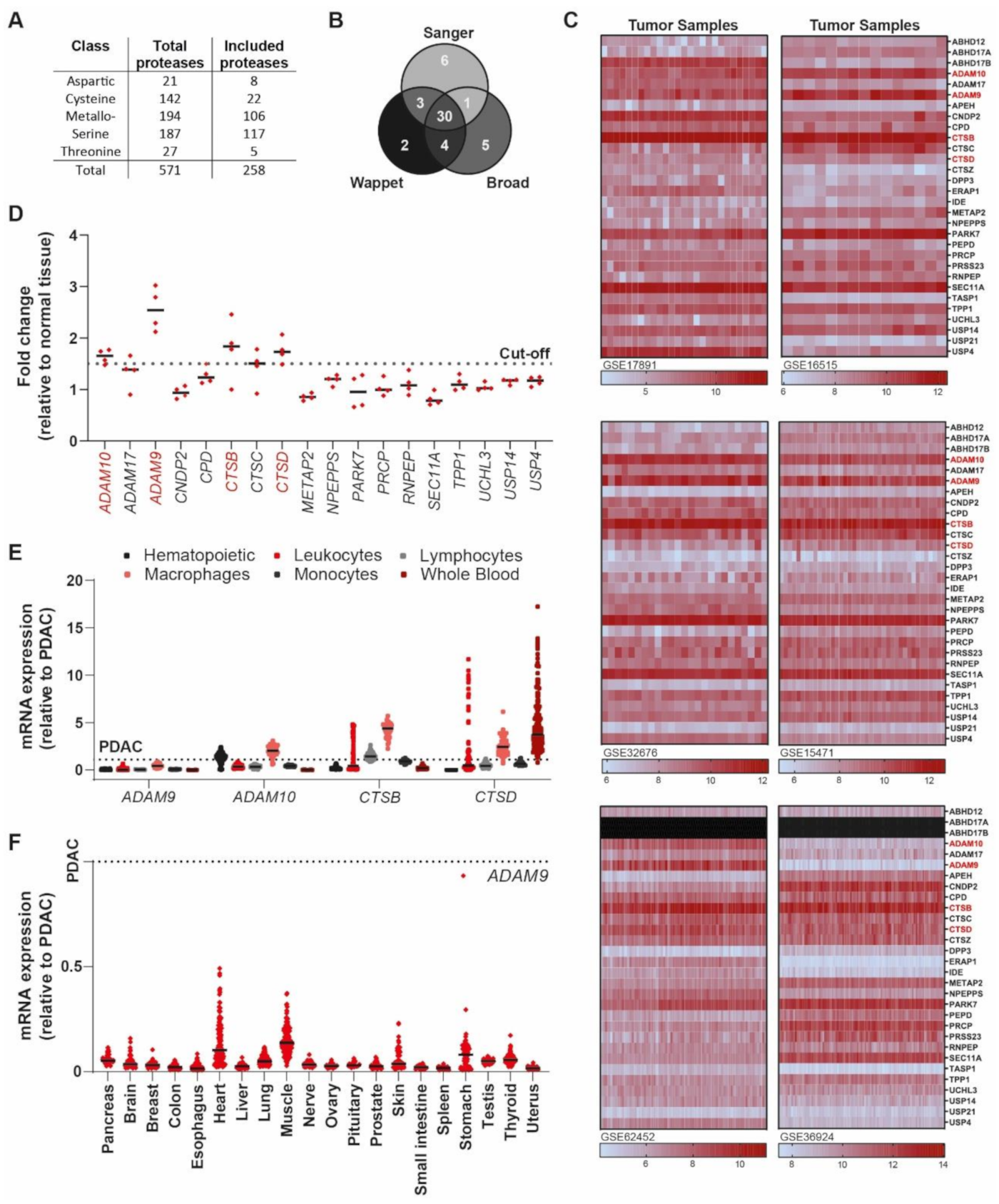
2.1. Identification of PDAC-Enriched Proteases
2.2. An ADAM9 Substrate Is Specifically Cleaved by PDAC Cells
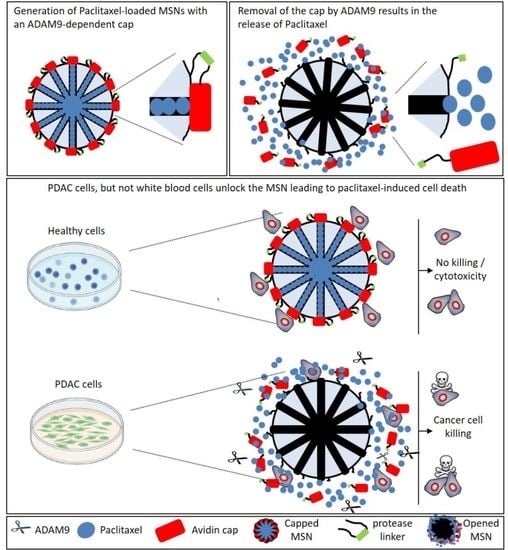
2.3. Generation and Validation of ADAM9-Responsive Avidin-Capped MSNs
2.4. ADAM9-Dependent Removal of the Avidin Cap
2.5. Drug Release after CAP Removal
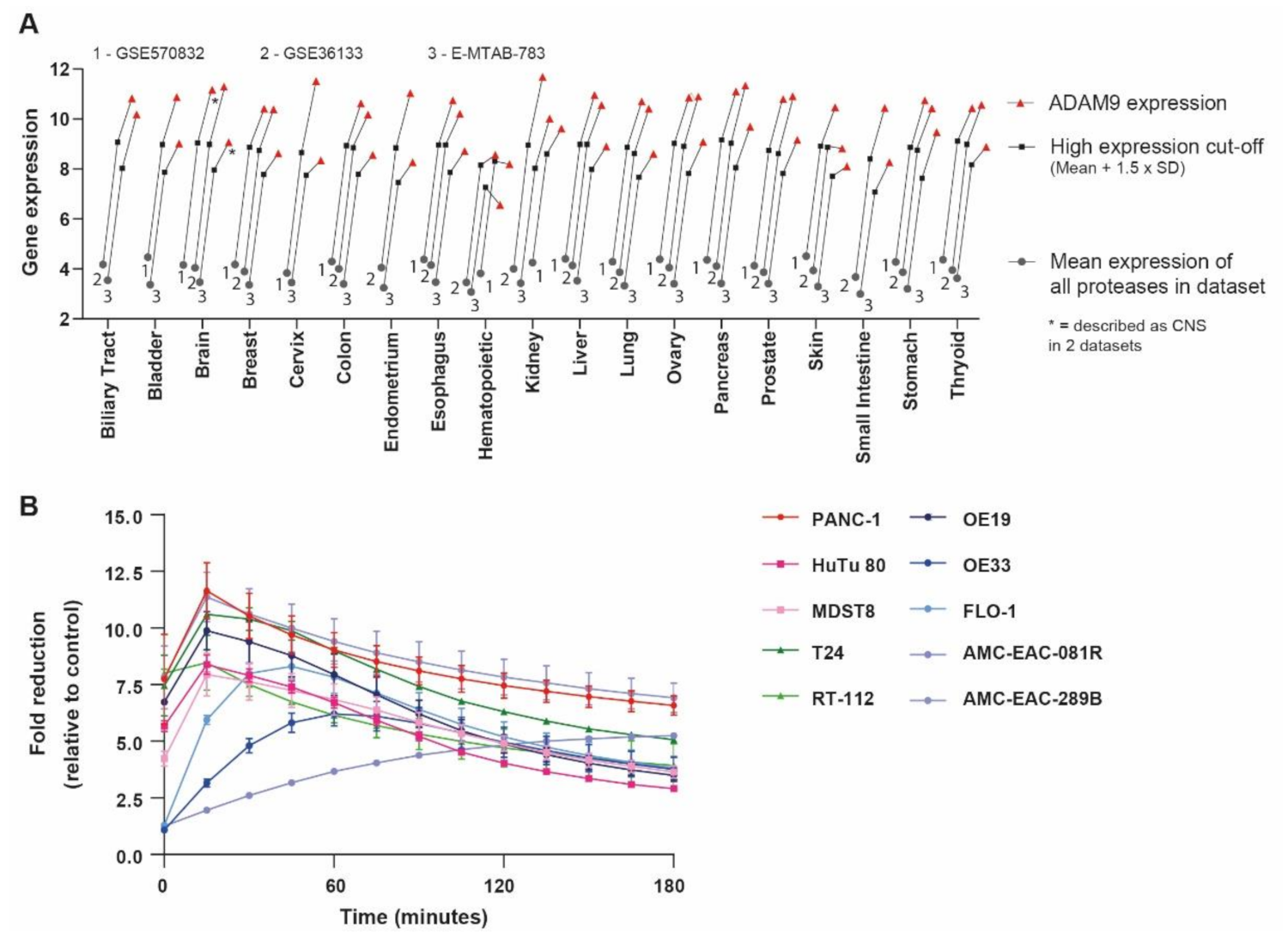
2.6. Pan-Cancer Applicability of the ADAM9-Responsive Nanoplatform
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Analysis of Publicly Available Gene Expression Datasets
4.2. Cell lines, Tissue Culture, and Conditioned Medium Collection
4.3. Peptide Cleavage Assay
4.4. Synthesis of MSNs
4.5. Surface Modification of the MSNs
4.6. Synthesis of Linker Peptides
4.7. Conjugation of MSNs with Linker Peptides
4.8. Characterization of MSNs
4.9. Flow Cytometric Analysis of Capping Efficiency
4.10. Paclitaxel Loading of ADAM9-MSNs
4.11. Avidin Capping of MSNs
4.12. MSN-Induced Cytotoxicity
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2019, 69, 7–34. [Google Scholar]
- McBride, A.; Bonafede, M.; Cai, Q.; Princic, N.; Tran, O.; Pelletier, C.; Parisi, M.; Patel, M. Comparison of treatment patterns and economic outcomes among metastatic pancreatic cancer patients initiated on nab-paclitaxel plus gemcitabine versus FOLFIRINOX. Expert Rev. Clin. Pharmacol. 2017, 10, 1153–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bharti, C.; Gulati, N.; Nagaich, U.; Pal, A.K. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles in target drug delivery system: A review. Int. J. Pharm. Investig. 2015, 5, 124–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Porta, F.; Lamers, G.E.M.; Morrhayim, J.; Chatzopoulou, A.; Schaaf, M.; Dulk, H.D.; Backendorf, C.; Zink, J.I.; Kros, A. Folic Acid-Modified Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Cellular and Nuclear Targeted Drug Delivery. Adv. Health Mater. 2012, 2, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watermann, A.; Brieger, J. Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles as Drug Delivery Vehicles in Cancer. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yu, Q.; Deng, T.; Lin, F.-C.; Zhang, B.; Zink, J.I. Supramolecular Assemblies of Heterogeneous Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles to Co-deliver Antimicrobial Peptides and Antibiotics for Synergistic Eradication of Pathogenic Biofilms. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 5926–5937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Rijt, S.H.; Bölükbaş, D.A.; Argyo, C.; Datz, S.; Lindner, M.; Eickelberg, O.; Königshoff, M.; Bein, T.; Meiners, S. Protease-Mediated Release of Chemotherapeutics from Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles to ex Vivo Human and Mouse Lung Tumors. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 2377–2389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kappelhoff, R.; Puente, X.S.; Wilson, C.H.; Seth, A.; López-Otín, C.; Overall, C.M. Overview of transcriptomic analysis of all human proteases, non-proteolytic homologs and inhibitors: Organ, tissue and ovarian cancer cell line expression profiling of the human protease degradome by the CLIP-CHIP™ DNA microarray. Biochim Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2017, 1864, 2210–2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garnett, M.J.; Edelman, E.J.; Heidorn, S.J.; Greenman, C.D.; Dastur, A.; Lau, K.W.; Greninger, P.; Thompson, I.R.; Luo, X.; Soares, J.; et al. Systematic identification of genomic markers of drug sensitivity in cancer cells. Nature 2012, 483, 570–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barretina, J.; Caponigro, G.; Stransky, N.; Venkatesan, K.; Margolin, A.A.; Kim, S.; Wilson, C.J.; Lehár, J.; Kryukov, G.V.; Sonkin, D.; et al. The Cancer Cell Line Encyclopedia enables predictive modelling of anticancer drug sensitivity. Nature 2012, 483, 603–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collisson, E.A.; Sadanandam, A.; Olson, P.; Gibb, W.J.; Truitt, M.; Gu, S.; Cooc, J.; Weinkle, J.; Kim, G.E.; Jakkula, L.; et al. Subtypes of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma and their differing responses to therapy. Nat. Med. 2011, 17, 500–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellsworth, K.A.; Eckloff, B.W.; Li, L.; Moon, I.; Fridley, B.L.; Jenkins, G.D.; Carlson, E.; Brisbin, A.; Abo, R.; Bamlet, W.; et al. Contribution of FKBP5 Genetic Variation to Gemcitabine Treatment and Survival in Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e70216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donahue, T.R.; Tran, L.M.; Hill, R.; Li, Y.; Kovochich, A.; Calvopina, J.H.; Patel, S.G.; Wu, N.; Hindoyan, A.; Farrell, J.J.; et al. Integrative Survival-Based Molecular Profiling of Human Pancreatic Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 1352–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Idichi, T.; Seki, N.; Kurahara, H.; Yonemori, K.; Osako, Y.; Arai, T.; Okato, A.; Kita, Y.; Arigami, T.; Mataki, Y.; et al. Regulation of actin-binding protein ANLN by antitumor miR-217 inhibits cancer cell aggressiveness in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 53180–53193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, S.; He, P.; Wang, J.; Schetter, A.; Tang, W.; Funamizu, N.; Yanaga, K.; Uwagawa, T.; Satoskar, A.R.; Gaedcke, J.; et al. A Novel MIF Signaling Pathway Drives the Malignant Character of Pancreatic Cancer by Targeting NR3C2. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 3838–3850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pérez-Mancera, P.A.; Initiative, A.P.C.G.; Rust, A.G.; Van Der Weyden, L.; Kristiansen, G.; Li, A.; Sarver, A.L.; Silverstein, K.A.T.; Grützmann, R.; Aust, D.; et al. The deubiquitinase USP9X suppresses pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Nat. Cell Biol. 2012, 486, 266–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novershtern, N.; Subramanian, A.; Lawton, L.N.; Mak, R.H.; Haining, W.N.; McConkey, M.E.; Habib, N.; Yosef, N.; Chang, C.Y.; Shay, T.; et al. Densely Interconnected Transcriptional Circuits Control Cell States in Human Hematopoiesis. Cell 2011, 144, 296–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abbas, A.R.; Baldwin, D.; Ma, Y.; Ouyang, W.; Gurney, A.; Martin, F.; Fong, S.; Campagne, M.V.L.; Godowski, P.; Williams, P.M.; et al. Immune response in silico (IRIS): Immune-specific genes identified from a compendium of microarray expression data. Genes Immun. 2005, 6, 319–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heng, Y.J.; Pennell, C.; Chua, H.N.; Perkins, J.E.; Lye, S.J. Whole Blood Gene Expression Profile Associated with Spontaneous Preterm Birth in Women with Threatened Preterm Labor. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e96901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodruff, P.G.; Koth, L.L.; Yang, J.; Rodriguez, M.W.; Favoreto, S.; Dolganov, G.M.; Paquet, A.C.; Erle, D. A Distinctive Alveolar Macrophage Activation State Induced by Cigarette Smoking. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2005, 172, 1383–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Consortium, G.T. The Genotype-Tissue Expression (GTEx) project. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 580–585. [Google Scholar]
- Moss, M.L.; Rasmussen, F.H.; Nudelman, R.; Dempsey, P.J.; Williams, J. Fluorescent substrates useful as high-throughput screening tools for ADAM9. Comb. Chem. High Throughput Screen. 2010, 13, 358–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trewyn, B.G.; Slowing, I.; Giri, S.; Chen, H.-T.; Lin, V.S.-Y. Synthesis and Functionalization of a Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticle Based on the Sol–Gel Process and Applications in Controlled Release. Accounts Chem. Res. 2007, 40, 846–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chou, C.-W.; Huang, Y.-K.; Kuo, T.-T.; Liu, J.-P.; Sher, Y.-P. An Overview of ADAM9: Structure, Activation, and Regulation in Human Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latenstein, A.E.J.; van der Geest, L.G.M.; Bonsing, B.A.; Groot Koerkamp, B.; Haj Mohammad, N.; de Hingh, I.; de Meijer, V.E.; Molenaar, I.Q.; van Santvoort, H.C.; van Tienhoven, G.; et al. Nationwide trends in incidence, treatment and survival of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Eur. J. Cancer. 2020, 125, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mantoni, T.S.; Schendel, R.R.; Rödel, F.; Niedobitek, G.; Al-Assar, O.; Masamune, A.; Brunner, T.B. Stromal SPARC expression and patient survival after chemoradiation for non-resectable pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2008, 7, 1806–1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, H.; Samuel, S.; Lopez-Casas, P.P.; Grizzle, W.; Hidalgo, M.; Kovar, J.; Oelschlager, D.; Zinn, K.; Warram, J.; Buchsbaum, D. SPARC-Independent Delivery of Nab-Paclitaxel without Depleting Tumor Stroma in Patient-Derived Pancreatic Cancer Xenografts. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2016, 15, 680–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Neesse, A.; Frese, K.K.; Chan, D.S.; Bapiro, T.E.; Howat, W.J.; Richards, F.M.; Ellenrieder, V.; Jodrell, D.I.; Tuveson, D.A. SPARC independent drug delivery and antitumour effects of nab-paclitaxel in genetically engineered mice. Gut 2014, 63, 974–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Henderson, I.C.; Bhatia, V. Nab-paclitaxel for breast cancer: A new formulation with an improved safety profile and greater efficacy. Expert Rev. Anticancer. Ther. 2007, 7, 919–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.; Karambelkar, A.D.; Gu, L.; Lin, K.Y.-M.; Miller, J.; Chen, C.; Sailor, M.J.; Bhatia, S.N. Bioresponsive Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Triggered Drug Release. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 19582–19585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yuan, Z.-F.; Wang, Y.; Chen, W.-H.; Luo, G.-F.; Cheng, S.-X.; Zhuo, R.-X.; Zhang, X.-Z. Multifunctional Envelope-Type Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Tumor-Triggered Targeting Drug Delivery. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 5068–5073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.-H.; Gao, F.-P.; Li, L.-L.; Ma, H.L.; Fan, Y.-S.; Liu, W.; Guo, S.-S.; Zhao, X.-Z.; Wang, H. Gelatin–mesoporous silica nanoparticles as matrix metalloproteinases-degradable drug delivery systems in vivo. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2013, 182, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaghasiya, K.; Ray, E.; Sharma, A.; Katare, O.P.; Verma, R.K. Matrix Metalloproteinase-Responsive Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles Cloaked with Cleavable Protein for “Self-Actuating” On-Demand Controlled Drug Delivery for Cancer Therapy. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2020, 3, 4987–4999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Meng, Q.; Sun, H.; Su, J.; Yin, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, H.; Chen, L.; Chen, Y.; Gu, W.; et al. Tumor-Microenvironment-Adaptive Nanoparticles Codeliver Paclitaxel and siRNA to Inhibit Growth and Lung Metastasis of Breast Cancer. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2016, 26, 6033–6046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slapak, E.J.; Duitman, J.; Tekin, C.; Bijlsma, M.F.; Spek, C.A. Matrix Metalloproteases in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma: Key Drivers of Disease Progression? Biology 2020, 9, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gobin, E.; Bagwell, K.; Wagner, J.; Mysona, D.; Sandirasegarane, S.; Smith, N.; Bai, S.; Sharma, A.; Schleifer, R.; She, J.-X. A pan-cancer perspective of matrix metalloproteases (MMP) gene expression profile and their diagnostic/prognostic potential. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bar-Or, A.; Nuttall, R.K.; Duddy, M.; Alter, A.; Kim, H.J.; Ifergan, I.; Pennington, C.J.; Bourgoin, P.; Edwards, D.R.; Yong, V.W. Analyses of all matrix metalloproteinase members in leukocytes emphasize monocytes as major inflammatory mediators in multiple sclerosis. Brain 2003, 126, 2738–2749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grünwald, B.; Vandooren, J.; Gerg, M.; Ahomaa, K.; Hunger, A.; Berchtold, S.; Akbareian, S.; Schaten, S.; Knolle, P.A.; Edwards, D.; et al. Systemic Ablation of MMP-9 Triggers Invasive Growth and Metastasis of Pancreatic Cancer via Deregulation of IL6 Expression in the Bone Marrow. Mol. Cancer Res. 2016, 14, 1147–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haas, S.L.; Jesnowski, R.; Steiner, M.; Hummel, F.; Ringel, J.; Burstein, C.; Nizze, H.; Liebe, S.; Löhr, J.M. Expression of tissue factor in pancreatic adenocarcinoma is associated with activation of coagulation. World J. Gastroenterol. 2006, 12, 4843–4849. [Google Scholar]
- Lo, J.H.; Hao, L.; Muzumdar, M.D.; Raghavan, S.; Kwon, E.J.; Pulver, E.M.; Hsu, F.; Aguirre, A.J.; Wolpin, B.M.; Fuchs, C.S.; et al. iRGD-guided Tumor-penetrating Nanocomplexes for Therapeutic siRNA Delivery to Pancreatic Cancer. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2018, 17, 2377–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meng, H.; Wang, M.; Liu, H.; Liu, X.; Situ, A.; Wu, B.; Ji, Z.; Chang, C.H.; Nel, A.E. Use of a Lipid-Coated Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticle Platform for Synergistic Gemcitabine and Paclitaxel Delivery to Human Pancreatic Cancer in Mice. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 3540–3557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, X.; Situ, A.; Kang, Y.; Villabroza, K.R.; Liao, Y.; Chang, C.H.; Donahue, T.; Nel, A.E.; Meng, H. Irinotecan Delivery by Lipid-Coated Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles Shows Improved Efficacy and Safety over Liposomes for Pancreatic Cancer. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 2702–2715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, L.; She, X.; Wang, T.; He, L.; Shigdar, S.; Duan, W.; Kong, L. Overcoming acquired drug resistance in colorectal cancer cells by targeted delivery of 5-FU with EGF grafted hollow mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 14080–14092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castillo, R.R.; Lozano, D.; Vallet-Regí, M. Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles as Carriers for Therapeutic Biomolecules. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, J.; Boyle, A.; Friedrich, H.; Bomans, P.H.H.; Bussmann, J.; Sommerdijk, N.A.J.M.; Jiskoot, W.; Kros, A. Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles with Large Pores for the Encapsulation and Release of Proteins. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 32211–32219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damhofer, H.; Ebbing, E.A.; Steins, A.; Welling, L.; Tol, J.A.; Krishnadath, K.K.; Van Leusden, T.; Van De Vijver, M.J.; Besselink, M.G.; Busch, O.R.; et al. Establishment of patient-derived xenograft models and cell lines for malignancies of the upper gastrointestinal tract. J. Transl. Med. 2015, 13, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Porta, F.; Lamers, G.E.; Zink, J.I.; Kros, A. Peptide modified mesoporous silica nanocontainers. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2011, 13, 9982–9985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Liu, Y.; Wu, C. Effect of Paclitaxel-Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles with a Core-Shell Structure on the Human Lung Cancer Cell Line A549. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2017, 12, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Slapak, E.J.; Kong, L.; el Mandili, M.; Nieuwland, R.; Kros, A.; Bijlsma, M.F.; Spek, C.A. ADAM9-Responsive Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Targeted Drug Delivery in Pancreatic Cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 3321. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13133321
Slapak EJ, Kong L, el Mandili M, Nieuwland R, Kros A, Bijlsma MF, Spek CA. ADAM9-Responsive Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Targeted Drug Delivery in Pancreatic Cancer. Cancers. 2021; 13(13):3321. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13133321
Chicago/Turabian StyleSlapak, Etienne J., Lily Kong, Mouad el Mandili, Rienk Nieuwland, Alexander Kros, Maarten F. Bijlsma, and C. Arnold Spek. 2021. "ADAM9-Responsive Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Targeted Drug Delivery in Pancreatic Cancer" Cancers 13, no. 13: 3321. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13133321
APA StyleSlapak, E. J., Kong, L., el Mandili, M., Nieuwland, R., Kros, A., Bijlsma, M. F., & Spek, C. A. (2021). ADAM9-Responsive Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Targeted Drug Delivery in Pancreatic Cancer. Cancers, 13(13), 3321. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13133321