Ancillary Diagnostic Investigations in Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Pleural Fluid (PF) Cytology
3. PF Immunohistochemistry (IHC) and Molecular Techniques
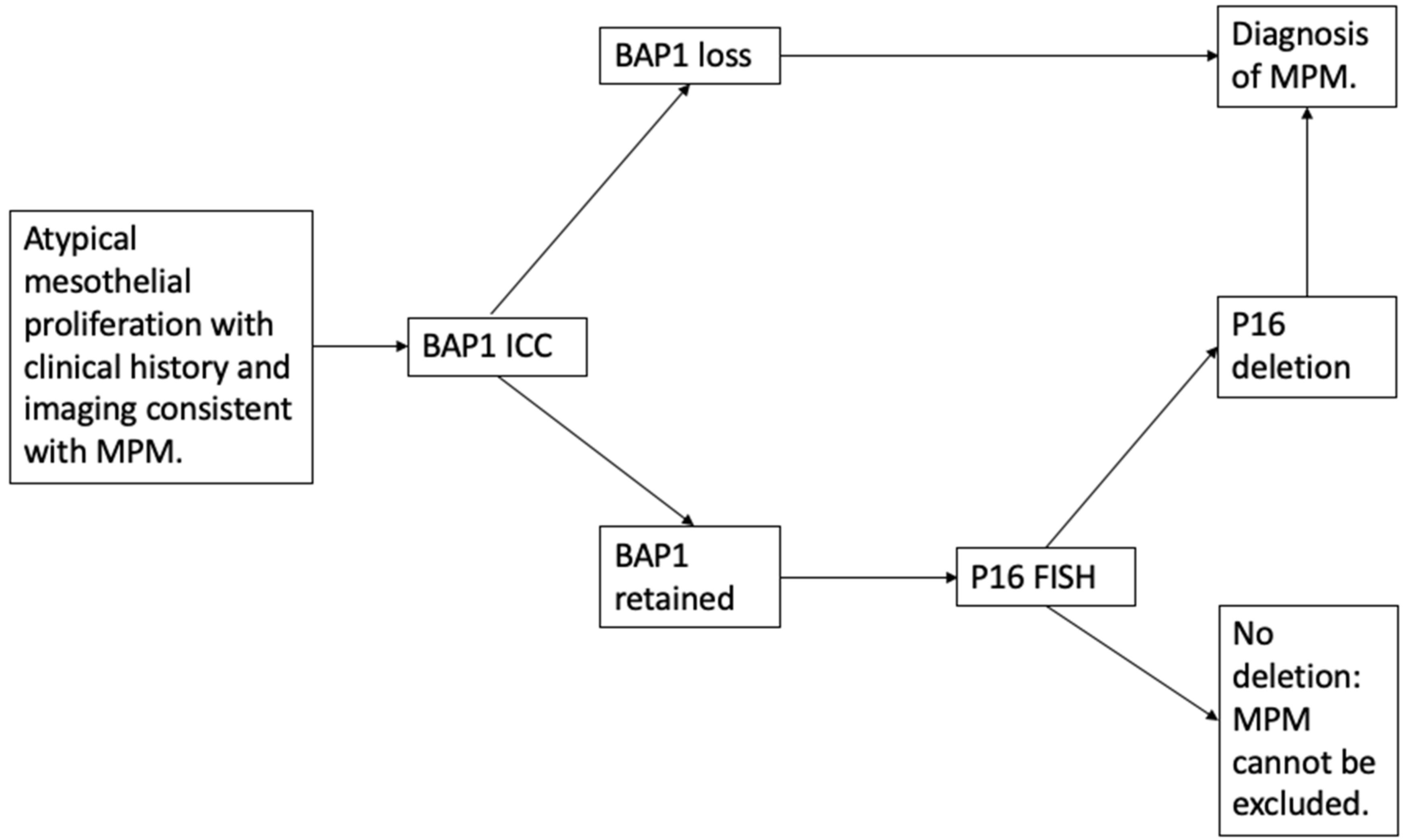
3.1. Discriminating Benign from Malignant Mesothelial Populations
3.1.1. BAP1 Loss
3.1.2. p16 Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization (FISH)
3.2. Distinguishing Mesothelioma from Carcinoma
3.3. Distinguishing Mesothelioma from Other Malignant Cell Neoplasms
4. Diagnostic Biomarkers
4.1. Mesothelin
4.2. Other Diagnostic Biomarkers
5. Imaging Techniques
6. Future Directions
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Woolhouse, I.; Bishop, L.; Darlison, L.; De Fonseka, D.; Edey, A.; Edwards, J.; Faivre-Finn, C.; Fennell, D.A.; Holmes, S.; Kerr, K.M.; et al. British Thoracic Society Guideline for the investigation and management of malignant pleural mesothelioma. Thorax 2018, 73, i1–i30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sekido, Y. Molecular pathogenesis of malignant mesothelioma. Carcinogenesis 2013, 34, 1413–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, J.C.; Sleggs, C.A.; Marchand, P. Diffuse pleural mesothelioma and asbestos exposure in the North Western Cape Province. Br. J. Ind. Med. 1960, 17, 260–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bibby, A.C.; Tsim, S.; Kanellakis, N.; Ball, H.; Talbot, D.C.; Blyth, K.G.; Maskell, N.A.; Psallidas, I. Malignant pleural mesothelioma: An update on investigation, diagnosis and treatment. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2016, 25, 472–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- LaDou, J.; Castleman, B.; Frank, A.; Gochfeld, M.; Greenberg, M.; Huff, J.; Joshi, T.K.; Landrigan, P.J.; Lemen, R.; Myers, J.; et al. The Case for a Global Ban on Asbestos. Environ. Heal Perspect. 2010, 118, 897–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Odgerel, C.-O.; Takahashi, K.; Sorahan, T.; Driscoll, T.; Fitzmaurice, C.; Yoko, O.M.; Sawanyawisuth, K.; Furuya, S.; Tanaka, F.; Horie, S.; et al. Estimation of the global burden of mesothelioma deaths from incomplete national mortality data. Occup. Environ. Med. 2017, 74, 851–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Testa, J.R.; Cheung, M.; Pei, J.; Below, J.E.; Tan, Y.; Sementino, E.; Cox, N.J.; Dogan, A.U.; Pass, H.I.; Trusa, S.; et al. P1 mutations predispose to malignant mesothelioma. Nat. Genet. 2011, 43, 1022–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scherpereel, A.; Opitz, I.; Berghmans, T.; Psallidas, I.; Glatzer, M.; Rigau, D.; Astoul, P.; Bölükbas, S.; Boyd, J.; Coolen, J.; et al. ERS/ESTS/EACTS/ESTRO guidelines for the management of malignant pleural mesothelioma. Eur. Respir. J. 2020, 55, 1900953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, B.W.S.; Lake, R.A. Advances in Malignant Mesothelioma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 353, 1591–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carbone, M.; Adusumilli, P.S.; Alexander, H.R., Jr.; Baas, P.; Bardelli, F.; Bononi, A.; Bueno, R.; Felley-Bosco, E.; Galateau-Salle, F.; Jablons, D.; et al. Mesothelioma: Scientific clues for prevention, diagnosis, and therapy. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2019, 69, 402–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arnold, D.T.; Maskell, N.A. Biomarkers in mesothelioma. Ann. Clin. Biochem 2018, 55, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beckett, P.; Edwards, J.; Fennell, D.; Hubbard, R.; Woolhouse, I.; Peake, M. Demographics, management and survival of patients with malignant pleural mesothelioma in the National Lung Cancer Audit in England and Wales. Lung Cancer 2015, 88, 344–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abo E-Magd, G.H.; Abouissa, A.H.; Abbass, I. Diagnostic yield and safety of medical thoraco-scopic versus CT guided percutaneous tru-cut pleural biopsy. Eur. Respir. J. 2019, 54, PA3085. [Google Scholar]
- Roberts, M.; Neville, E.; Berrisford, R.G.; Antunes, G.; Ali, N.J.; on behalf of the BTS Pleural Disease Guideline Group. Management of a malignant pleural effusion: British Thoracic Society pleural disease guideline 2010. Thorax 2010, 65, II32–II40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kindler, H.L.; Ismaila, N.; Armato, S.G., III; Bueno, R.; Hesdorffer, M.; Jahan, T.; Jones, C.M.; Miettinen, M.; Pass, H.; Rimner, A.; et al. Treatment of Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma: American Society of Clinical Oncology Clinical Practice Guideline. J. Clin. Oncol 2018, 36, 1343–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Physicians RCo. National Mesothelioma Audit Report 2020 (for the Audit Period 2016–18); National Mesothelioma Audit: London, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Damhuis, R.; Khakwani, A.; De Schutter, H.; Rich, A.; Burgers, J.; Van Meerbeeck, J. Treatment patterns and survival analysis in 9014 patients with malignant pleural mesothelioma from Belgium, the Netherlands and England. Lung Cancer 2015, 89, 212–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bibby, A.C.; Williams, K.; Smith, S.; Bhatt, N.; A Maskell, N. What is the role of a specialist regional mesothelioma multidisciplinary team meeting? A service evaluation of one tertiary referral centre in the UK. BMJ Open 2016, 6, e012092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hooper, C.; Lee, Y.C.G.; Maskell, N. Investigation of a unilateral pleural effusion in adults: British Thoracic Society pleural disease guideline 2010. Thorax 2010, 65, ii4-ii17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arnold, D.T.; De Fonseka, D.; Perry, S.; Morley, A.; Harvey, J.E.; Medford, A.; Brett, M.; Maskell, N.A. Investigating unilateral pleural effusions: The role of cytology. Eur. Respir. J. 2018, 52, 1801254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porcel, J.M. Biomarkers in the diagnosis of pleural diseases: A 2018 update. Ther. Adv. Respir. Dis. 2018, 12, 1753466618808660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hjerpe, A.; Ascoli, V.; Bedrossian, C.W.M.; Boon, M.E.; Creaney, J.; Davidson, B.; Dejmek, A.; Dobra, K.; Fassina, A.; Field, A.; et al. Guidelines for the Cytopathologic Diagnosis of Epithelioid and Mixed-Type Malignant Mesothelioma: A secondary publication. Cytopathology 2015, 26, 142–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monaco, S.; Mehrad, M.; Dacic, S. Recent Advances in the Diagnosis of Malignant Mesothelioma: Focus on Approach in Challenging Cases and in Limited Tissue and Cytologic Samples. Adv. Anat. Pathol. 2018, 25, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husain, A.N.; Colby, T.V.; Ordóñez, N.G.; Allen, T.C.; Attanoos, R.L.; Beasley, M.B.; Butnor, K.J.; Chirieac, L.R.; Churg, A.M.; Dacic, S.; et al. Guidelines for Pathologic Diagnosis of Malignant Mesothelioma 2017 Update of the Consensus Statement From the International Mesothelioma Interest Group. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2018, 142, 89–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pinelli, V.; Laroumagne, S.; Sakr, L.; Marchetti, G.P.; Tassi, G.F.; Astoul, P. Pleural Fluid Cytological Yield and Visceral Pleural Invasion in Patients with Epithelioid Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2012, 7, 595–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chapel, D.B.; Schulte, J.J.; Husain, A.N.; Krausz, T. Application of immunohistochemistry in diagnosis and management of malignant mesothelioma. Trans. Lung Cancer Res. 2020, 9, S3-S27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeren, E.H.; Demirag, F. Benign and Malignant Mesothelial Proliferation. Surg. Pathol. Clin. 2010, 3, 83–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attanoos, R.L.; Griffin, A.; Gibbs, A.R. The use of immunohistochemistry in distinguishing reactive from neoplastic mesothelium. A novel use for desmin and comparative evaluation with epithelial membrane antigen, p53, platelet-derived growth factor-receptor, P-glycoprotein and Bcl-2. Histopathology 2003, 43, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Churg, A.; Sheffield, B.S.; Galateau-Salle, F. New Markers for Separating Benign From Malignant Mesothelial Proliferations: Are We There Yet? Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2016, 140, 318–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ikeda, K.; Tate, G.; Suzuki, T.; Kitamura, T.; Mitsuya, T. Diagnostic usefulness of EMA, IMP3, and GLUT-1 for the immunocytochemical distinction of malignant cells from reactive mesothelial cells in effusion cytology using cytospin preparations. Diagn. Cytopathol. 2011, 39, 395–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Pinkus, G.S.; Deshpande, V.; Cibas, E.S. Usefulness of EMA, GLUT-1, and XIAP for the cytologic diagnosis of malignant mesothelioma in body cavity fluids. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2009, 131, 516–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pulford, E.; Huilgol, K.; Moffat, D.; Henderson, D.W.; Klebe, S. Malignant Mesothelioma, BAP1 Immunohistochemistry, and VEGFA: Does BAP1 Have Potential for Early Diagnosis and Assessment of Prognosis? Dis. Markers 2017, 2017, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.-M.; Shi, Z.-W.; Wang, J.-L.; Lv, Z.; Du, F.-B.; Yang, Q.-B.; Wang, Y. Diagnostic accuracy of BRCA1-associated protein 1 in malignant mesothelioma: A meta-analysis. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 68863–68872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Murali, R.; Wiesner, T.; Scolyer, R.A. Tumours associated with BAP1 mutations. Pathology 2013, 45, 116–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hida, T.; Matsumoto, S.; Hamasaki, M.; Kawahara, K.; Tsujimura, T.; Hiroshima, K.; Kamei, T.; Taguchi, K.; Iwasaki, A.; Oda, Y.; et al. Deletion status of p16 in effusion smear preparation correlates with that of underlying malignant pleural mesothelioma tissue. Cancer Sci 2015, 106, 1635–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hida, T.; Hamasaki, M.; Matsumoto, S.; Sato, A.; Tsujimura, T.; Kawahara, K.; Iwasaki, A.; Okamoto, T.; Oda, Y.; Honda, H.; et al. Immunohistochemical detection of MTAP and BAP1 protein loss for mesothelioma diagnosis: Comparison with 9p21 FISH and BAP1 immunohistochemistry. Lung Cancer 2017, 104, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinoshita, Y.; Hamasaki, M.; Yoshimura, M.; Matsumoto, S.; Sato, A.; Tsujimura, T.; Ueda, H.; Makihata, S.; Kato, F.; Iwasaki, A.; et al. A combination of MTAP and BAP1 immunohistochemistry is effective for distinguishing sarcomatoid mesothelioma from fibrous pleuritis. Lung Cancer 2018, 125, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinoshita, Y.; Hida, T.; Hamasaki, M.; Matsumoto, S.; Sato, A.; Tsujimura, T.; Kawahara, K.; Hiroshima, K.; Oda, Y.; Nabeshima, K. A combination of MTAP and BAP1 immunohistochemistry in pleural effusion cytology for the diagnosis of mesothelioma. Cancer Cytopathol 2018, 126, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapel, D.B.; Schulte, J.J.; Berg, K.; Churg, A.; Dacic, S.; Fitzpatrick, C.; Galateau-Salle, F.; Hiroshima, K.; Krausz, T.; Le Stang, N.; et al. MTAP immunohistochemistry is an accurate and reproducible surrogate for CDKN2A fluorescence in situ hybridization in diagnosis of malignant pleural mesothelioma. Mod. Pathol 2020, 33, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alì, G.; Bruno, R.; Poma, A.M.; Proietti, A.; Ricci, S.; Chella, A.; Melfi, F.; Ambrogi, M.C.; Lucchi, M.; Fontanini, G. A gene-expression-based test can outperform bap1 and p16 analyses in the differential diagnosis of pleural mesothelial proliferations. Oncol. Lett. 2020, 19, 1060–1065. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Davidson, B.; Tötsch, M.; Wohlschlaeger, J.; Hager, T.; Pinamonti, M. The diagnostic role of BAP1 in serous effusions. Hum. Pathol. 2018, 79, 122–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selves, J.; Long-Mira, E.; Mathieu, M.-C.; Rochaix, P.; Ilié, M. Immunohistochemistry for Diagnosis of Metastatic Carcinomas of Unknown Primary Site. Cancers 2018, 10, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fels, E.D.R.; Jones, K.D. Diagnosis of Mesothelioma. Surg. Pathol. Clin. 2020, 13, 73–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bibby, A.C.; Dorn, P.; Psallidas, I.; Porcel, J.M.; Janssen, J.; Froudarakis, M.; Subotic, D.; Astoul, P.; Licht, P.; Schmid, R.; et al. ERS/EACTS statement on the management of malignant pleural effusions. Eur. J. Cardio-Thoracic Surg. 2019, 55, 116–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledda, C.; Senia, P.; Rapisarda, V. Biomarkers for Early Diagnosis and Prognosis of Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma: The Quest Goes on. Cancers 2018, 10, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Robinson, B.W.; Creaney, J.; Lake, R.; Nowak, A.; Musk, A.W.; de Klerk, N.; Winzell, P.; Hellstrom, K.E.; Hellstrom, I. Mesothelin-family proteins and diagnosis of mesothelioma. Lancet 2003, 362, 1612–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creaney, J.; Robinson, B.W.S. Malignant Mesothelioma Biomarkers: From Discovery to Use in Clinical Practice for Diagnosis, Monitoring, Screening, and Treatment. Chest 2017, 152, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cui, A.; Jin, X.-G.; Zhai, K.; Tong, Z.-H.; Shi, H.-Z. Diagnostic values of soluble mesothelin-related peptides for malignant pleural mesothelioma: Updated meta-analysis. BMJ Open 2014, 4, e004145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pass, H.I.; Wolaniuk, D.; Wali, A.; Thiel, R.; Hellstrom, I.; Sardesai, N.Y. Soluble mesothelin related peptides: A potential biomarker for malignant pleural mesothelioma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2005, 23, 9532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, H.E.; Sadler, R.S.; Bielsa, S.; Maskell, N.A.; Rahman, N.M.; Davies, R.J.O.; Ferry, B.L.; Lee, Y.C.G. Clinical Impact and Reliability of Pleural Fluid Mesothelin in Undiagnosed Pleural Effusions. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2009, 180, 437–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hooper, C.E.; Morley, A.J.; Virgo, P.; Harvey, J.E.; Kahan, B.; Maskell, N.A. A prospective trial evaluating the role of mesothelin in undiagnosed pleural effusions. Eur. Respir. J. 2013, 41, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, Z.-D.; Liu, X.-F.; Ding, C.-M.; Hu, C.-J. Diagnostic accuracy of osteopontin for malignant pleural mesothelioma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Chim. Acta 2014, 433, 44–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pass, H.I.; Levin, S.M.; Harbut, M.R.; Melamed, J.; Chiriboga, L.; Donington, J.; Huflejt, M.; Carbone, M.; Chia, D.; Goodglick, L.; et al. Fibulin-3 as a Blood and Effusion Biomarker for Pleural Mesothelioma. New Engl. J. Med. 2012, 367, 1417–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Creaney, J.; Dick, I.M.; Meniawy, T.; Leong, S.L.; Leon, J.S.; Demelker, Y.; Segal, A.; Musk, A.W.B.; Lee, Y.C.G.; Skates, S.J.; et al. Comparison of fibulin-3 and mesothelin as markers in malignant mesothelioma. Thorax 2014, 69, 895–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kirschner, M.B.; Pulford, E.; Hoda, M.A.; Rozsas, A.; Griggs, K.; Cheng, Y.Y.; Edelman, J.J.B.; Kao, S.C.; Hyland, R.; Dong, Y.; et al. Fibulin-3 levels in malignant pleural mesothelioma are associated with prognosis but not diagnosis. Br. J. Cancer 2015, 113, 963–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ren, R.; Yin, P.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Zhou, Y.; Xu, R.; Lin, H.; Huang, C. Diagnostic value of fibulin-3 for malignant pleural mesothelioma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 84851–84859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pei, D.; Li, Y.; Liu, X.; Yan, S.; Guo, X.; Xu, X.; Guo, X. Diagnostic and prognostic utilities of humoral fibulin-3 in malignant pleural mesothelioma: Evidence from a meta-analysis. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 13030–13038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsim, S.; Kelly, C.; Alexander, L.; McCormick, C.; Thomson, F.; Woodward, R.; Foster, J.E.; Stobo, D.B.; Paul, J.; Maskell, N.A.; et al. Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarkers in the Rational Assessment of Mesothelioma (DIAPHRAGM) study: Protocol of a prospective, multicentre, observational study. BMJ Open 2016, 6, e013324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usuda, K.; Iwai, S.; Funasaki, A.; Sekimura, A.; Motono, N.; Matoba, M.; Doai, M.; Yamada, S.; Ueda, Y.; Uramoto, H. Diffusion-Weighted Imaging Can Differentiate between Malignant and Benign Pleural Diseases. Cancers 2019, 11, 811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Leung, A.N.; Müller, N.L.; Miller, R.R. CT in differential diagnosis of diffuse pleural disease. Am. J. Roentgenol. 1990, 154, 487–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blyth, K.G.; Murphy, D. Progress and challenges in Mesothelioma: From bench to bedside. Respir. Med. 2018, 134, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Treglia, G.; Sadeghi, R.; Annunziata, S.; Lococo, F.; Cafarotti, S.; Bertagna, F.; Prior, J.O.; Ceriani, L.; Giovanella, L. Diagnostic accuracy of 18F-FDG-PET and PET/CT in the differential diagnosis between malignant and benign pleural lesions: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Acad. Radiol. 2014, 21, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeFonseka, D. PET-CT in the Undiagnosed Effusion: Results of the TARGET Study. In Proceedings of the British Thoracic Society Winter Meeting, London, UK, 4–6 December 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Tsim, S.; Cowell, G.W.; Kidd, A.; Woodward, R.; Alexander, L.; Kelly, C.; E Foster, J.; Blyth, K.G. A comparison between MRI and CT in the assessment of primary tumour volume in mesothelioma. Lung Cancer 2020, 150, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacerenza, S.; Ciregia, F.; Giusti, L.; Bonotti, A.; Greco, V.; Giannaccini, G.; D’Antongiovanni, V.; Fallahi, P.; Pieroni, L.; Cristaudo, A.; et al. Putative Biomarkers for Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma Suggested by Proteomic Analysis of Cell Secretome. Cancer Genom. Proteom. 2020, 17, 225–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sage, A.P.; Martinez, V.D.; Minatel, B.C.; Pewarchuk, M.E.; Marshall, E.A.; Macaulay, G.M.; Hubaux, R.; Pearson, D.D.; Goodarzi, A.A.; Dellaire, G.; et al. Genomics and Epigenetics of Malignant Mesothelioma. High Throughput 2018, 7, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Joseph, N.M.; Chen, Y.-Y.; Nasr, A.; Yeh, I.; Talevich, E.; Onodera, C.; Bastian, B.; Rabban, J.T.; Garg, K.; Zaloudek, C.; et al. Genomic profiling of malignant peritoneal mesothelioma reveals recurrent alterations in epigenetic regulatory genes BAP1, SETD2, and DDX3X. Mod. Pathol. 2017, 30, 246–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cakiroglu, E.; Senturk, S. Genomics and Functional Genomics of Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber, D.G.; Gawrych, K.; Casjens, S.; Brik, A.; Lehnert, M.; Taeger, D.; Pesch, B.; Kollmeier, J.; Bauer, T.T.; Johnen, G.; et al. Circulating miR-132-3p as a Candidate Diagnostic Biomarker for Malignant Mesothelioma. Dis. Markers 2017, 2017, 9280170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.-M.; He, C.-C.; Liu, Y.-M.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, D.; Du, Y.; Zheng, W.-Y.; Li, J.-X. Metabonomic classification and detection of small molecule biomarkers of malignant pleural effusions. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2012, 404, 3123–3133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zennaro, L.; Vanzani, P.; Nicolè, L.; Cappellesso, R.; Fassina, A. Metabonomics by proton nuclear magnetic resonance in human pleural effusions: A route to discriminate between benign and malignant pleural effusions and to target small molecules as potential cancer biomarkers. Cancer Cytopathol. 2017, 125, 341–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsim, S.; Paterson, S.; Cartwright, D.; Fong, C.J.; Alexander, L.; Kelly, C.; Holme, J.; Evison, M.; Blyth, K.G. Baseline predictors of negative and incomplete pleural cytology in patients with suspected pleural malignancy—Data supporting ‘Direct to LAT’ in selected groups. Lung Cancer 2019, 133, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Mesothelial Markers | Adenocarcinoma Markers | Other Markers |
|---|---|---|
| Calretinin | TTF1 (lung and thyroid) | Squamous cell lung cancer: p40, p63 and claudin 4 |
| CK 5/6 | CEA | Renal cell carcinoma: PAX8, PAX2 and claudin 4 |
| WT1 | Ber–EP4 | Pancreas: CA19-9 |
| D2-40 | Gastrointestinal: CD20 and CDX-2 | |
| Gynaecological: PAX-8 and WT1 Prostate: PSA and PSMA | ||
| Breast: mammaglobin, GCDFP-15, ER, PR and GATA3 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dipper, A.; Maskell, N.; Bibby, A. Ancillary Diagnostic Investigations in Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma. Cancers 2021, 13, 3291. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13133291
Dipper A, Maskell N, Bibby A. Ancillary Diagnostic Investigations in Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma. Cancers. 2021; 13(13):3291. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13133291
Chicago/Turabian StyleDipper, Alex, Nick Maskell, and Anna Bibby. 2021. "Ancillary Diagnostic Investigations in Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma" Cancers 13, no. 13: 3291. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13133291
APA StyleDipper, A., Maskell, N., & Bibby, A. (2021). Ancillary Diagnostic Investigations in Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma. Cancers, 13(13), 3291. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13133291





