Copy Number Alteration Profile Provides Additional Prognostic Value for Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Patients Treated on BFM Protocols
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Diagnosis; Morphologic, Molecular and Cytogenetic Testing
2.3. Flow Cytometry (FC)
2.4. G-Banding, FISH and RT-PCR
2.5. MLPA (Multiple Ligation Probe Amplification)
2.6. Conventional Risk Stratification, Therapy Groups and Treatment Protocol
2.7. Copy Number Alterations (CNA)-Profile Risk Stratification
- (1)
- Good risk (GR) CNA profile with:
- a.
- no deletion of IKZF1, CDKN2A/B, PAR1, BTG1, EBF1, PAX5, ETV6, RB1 or
- b.
- isolated deletions of ETV6, PAX5, BTG1 or
- c.
- ETV6 deletions with a single additional deletion of BTG1, PAX5 or CDKN2A/B.
- (2)
- Poor risk (PR) CNA profile with:
- a.
- any deletion of IKZF1, PAR1, EBF1, RB1 or
- b.
- any other CΝA-profile not mentioned above.
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics and Conventional Risk Stratification
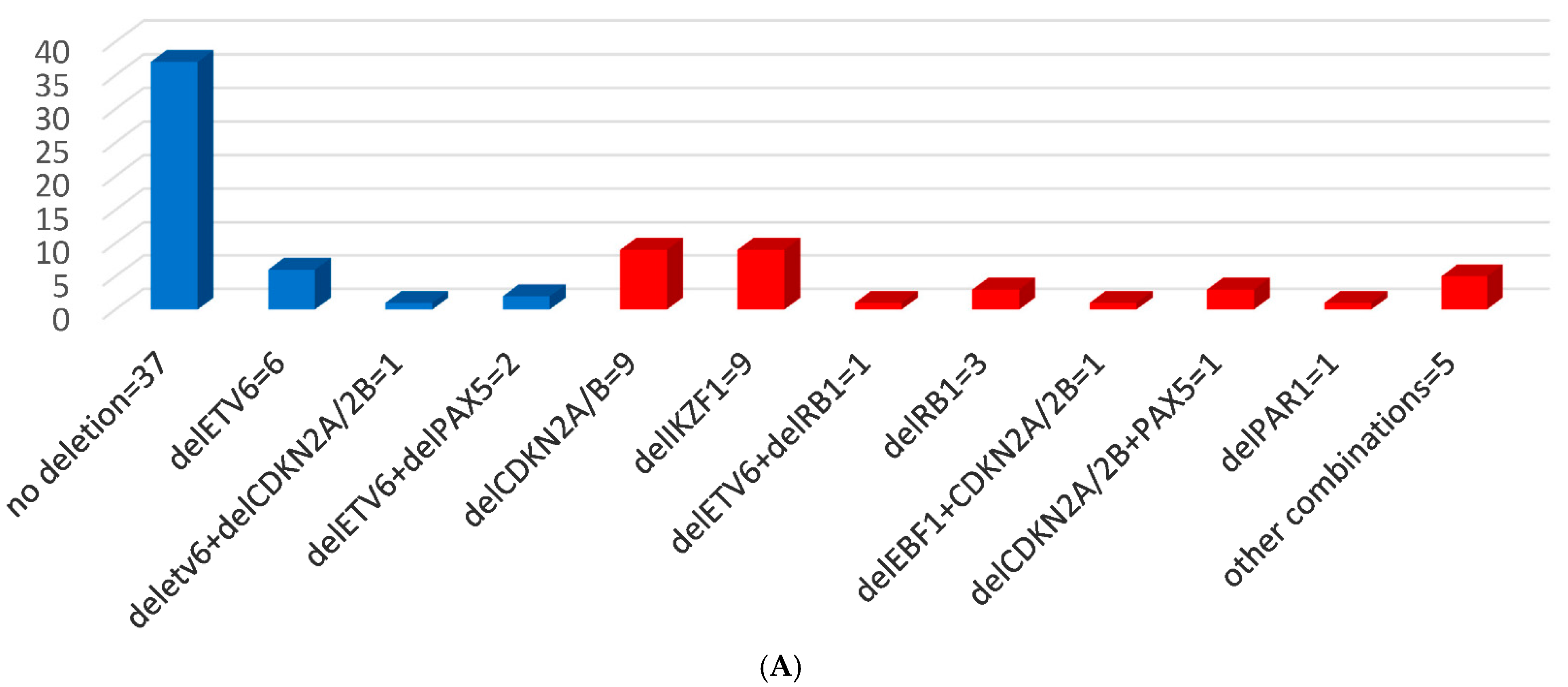
3.2. MLPA Results and CNAs
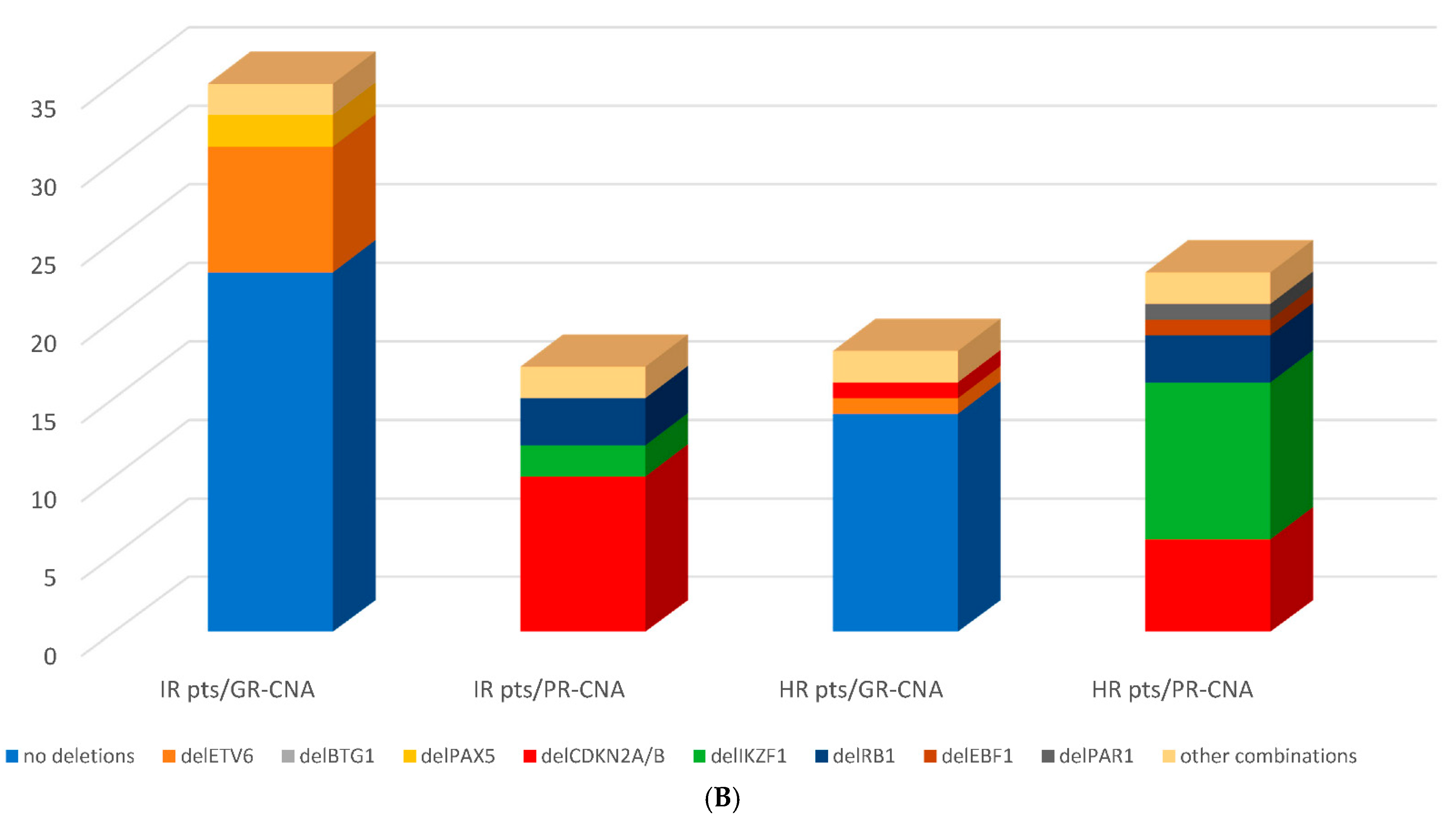
3.3. Genomic Risk Stratification—Detected CNA Profiles within Conventional Risk Groups
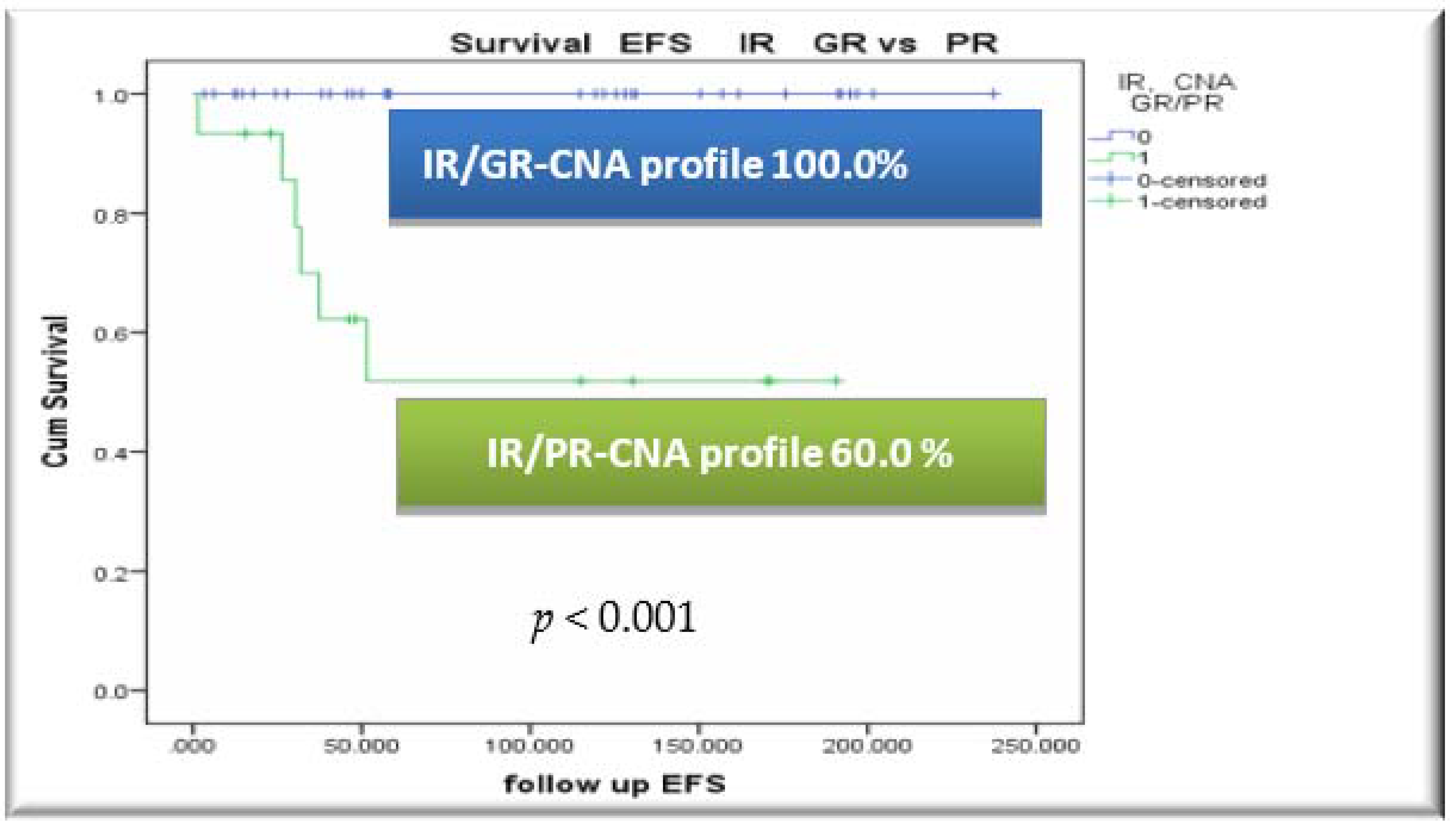
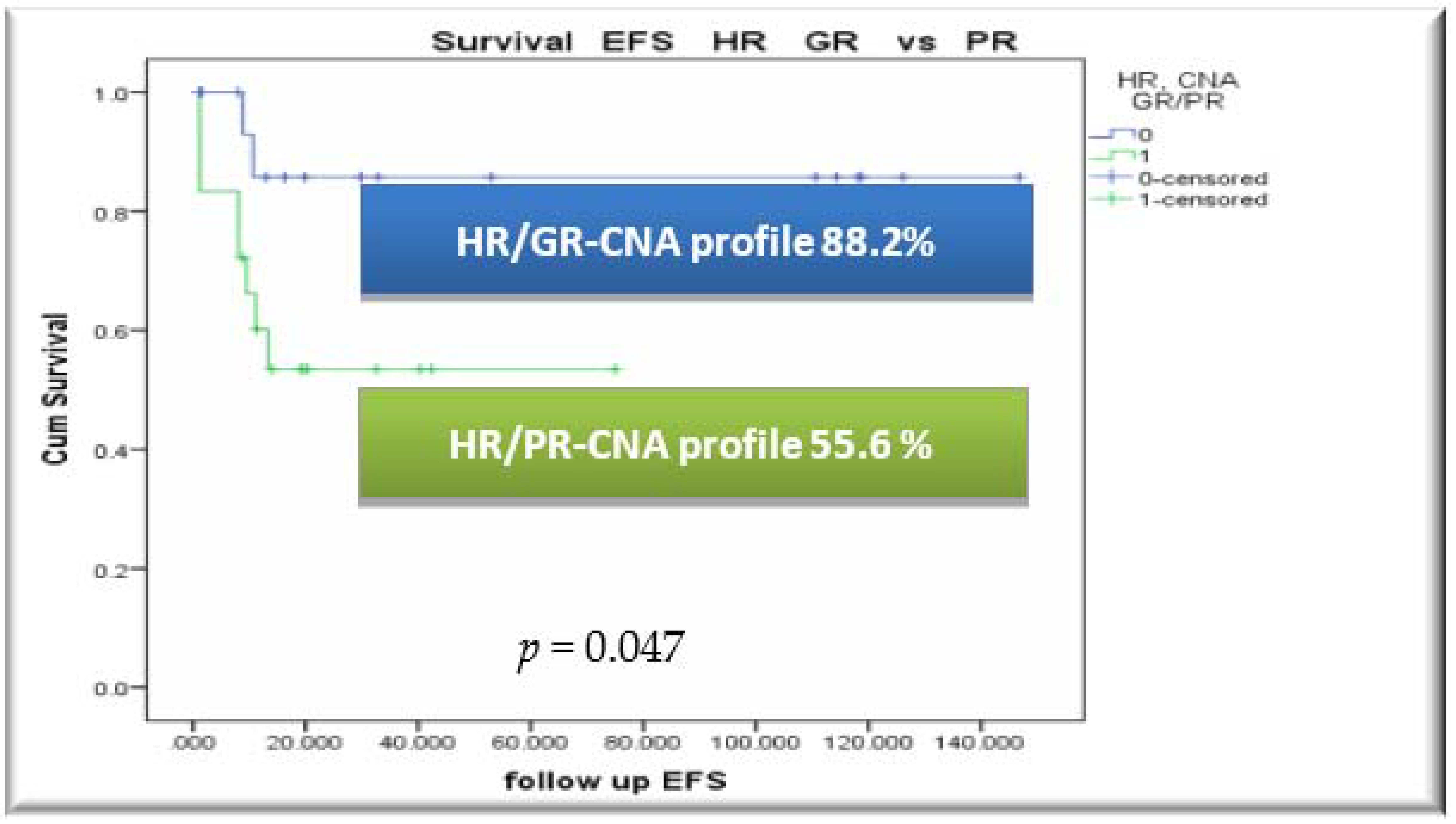
3.4. Outcome, Relapses and Survival Rates by CNA Profile
3.5. CNA Profile and MRD Integration
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ALL | Acute Lymphoblastic leukemia |
| CNA | Copy Number Alterations |
| FC | Flow Cytometry |
| MRD | Minimal Residual Disease |
| MRDd15 | Minimal Residual Disease on day 15 of induction therapy |
| MRDd33 | Minimal Residual Disease on day 33 of induction therapy |
| EOI | End of Induction |
| SR | Standard Risk |
| IR | Intermediate Risk |
| HR | High Risk |
| GR | Good Risk |
| PR | Poor Risk |
| MLPA | Multiple ligation probe amplification |
| OS | Overall Survival |
| EFS | Event-free survival |
| PCR | Polymerase chain reaction |
| BM | Bone marrow |
References
- Ampatzidou, M.; Panagiotou, J.P.; Paterakis, G.; Papadakis, V.; Papadhimitriou, S.I.; Parcharidou, A.; Papargyri, S.; Rigatou, E.; Avgerinou, G.; Tsitsikas, K.; et al. Childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia: 12 years of experience, using a Berlin-Frankfurt-Münster approach, in a Greek center. Leuk. Lymphoma 2014, 27, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conter, V.; Arico, M.; Basso, G.; Biondi, A.; Barisone, E.; Messina, C.; Parasole, R.; De Rossi, G.; Locatelli, F.; Pession, A.; et al. Long-term results of the Italian Association of Pediatric Hematology and Oncology (AIEOP) Studies 82, 87, 88, 91 and 95 for childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leukemia 2010, 24, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ampatzidou, M.; Kelaidi, C.; Dworzak, M.N.; Polychronopoulou, S. Adolescents and young adults with acute lymphoblastic and acute myeloid leukemia. MEMO-Mag. Eur. Med. Oncol. 2018, 11, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Möricke, A.; Zimmermann, M.; Reiter, A.; Henze, G.; Schrauder, A.; Gadner, H.; Ludwig, W.D.; Ritter, J.; Harbott, J.; Mann, G.; et al. Long-term results of five consecutive trials in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia performed by the ALL-BFM study group from 1981 to 2000. Leukemia 2010, 24, 265–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ampatzidou, M.; Paterakis, G.; Vasdekis, V.; Papadhimitriou, S.I.; Papadakis, V.; Vassilopoulos, G.; Polychronopoulou, S. Prognostic significance of flow cytometry MRD log reduction during induction treatment of childhood ALL. Leuk. Lymphoma 2018, 2, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ampatzidou, Μ.; Papadhimitriou, S.I.; Paterakis, G.; Pavlidis, D.; Tsitsikas, Κ.; Kostopoulos, I.V.; Papadakis, V.; Vassilopoulos, G.; Polychronopoulou, S. ETV6/RUNX1-positive childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL): The spectrum of clonal heterogeneity and its impact on prognosis. Cancer Genet. 2018, 224–225, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escherich, G.; Horstmann, M.A.; Zimmermann, M.; Janka-Schaub, G.E. Cooperative study group for childhood acute lymphoblastic leukaemia (COALL): Long-term results of trials 82, 85, 89, 92 and 97. Leukemia 2010, 24, 298–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Silverman, L.B.; Stevenson, K.E.; O’Brien, J.E.; Asselin, B.L.; Barr, R.D.; Clavell, L.; Colle, P.D.; Kelly, K.M.; Laverdiere, C.; Michon, B.; et al. Long-term results of Dana-Farber Cancer Institute ALL Consortium protocols for children with newly diagnosed acute lymphoblastic leukemia (1985–2000). Leukemia 2010, 24, 320–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmiegelow, K.; Forestier, E.; Hellebostad, M.; Heyman, M.; Kristinsson, J.; Soderhall, S.; Taskinen, M. Nordic Society of Paediatric Haematology and Oncology. Long-term results of NOPHO ALL-92 and ALL-2000 studies of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leukemia 2010, 24, 345–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salzer, W.L.; Devidas, M.; Carroll, W.L.; Winick, N.; Pullen, J.; Hunger, S.P.; Camitta, B.A. Long-term results of the pediatric oncology group studies for childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia 1984–2001: A report from the children’s oncology group. Leukemia 2010, 24, 55–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pui, C.H.; Pei, D.; Sandlund, J.T.; Ribeiro, R.C.; Rubnitz, J.E.; Raimondi, S.C.; Onciu, M.; Campana, D.; Kun, L.E.; Jeha, S.; et al. Long-term results of St Jude Total Therapy Studies 11, 12, 13A, 13B, and 14 for childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leukemia 2010, 24, 371–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Papadakis, V.; Panagiotou, J.P.; Polychronopoulou-Androulakaki, S.; Mikraki, V.; Parcharidou, A.; Tsitsikas, C.; Vrachnou, E.; Paterakis, G.; Mavrou, A.; Sambanis, C.; et al. Results of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia treatment in Greek patients using a BFM-based protocol. Haema 2003, 6, 208–216. [Google Scholar]
- Conter, V.; Bartram, C.R.; Valsecchi, M.G.; Aricò, M.; Zimmermann, M.; Mann, G.; Giulio De Rossi, G. Molecular response to treatment redefines all prognostic factors in children and adolescents with B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia: Results in 3184 patients of the AIEOP-BFM ALL 2000 study. Blood 2010, 115, 3206–3214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanulla, M.; Dagdan, E.; Zaliova, M.; Möricke, A.; Palmi, C.; Cazzaniga, G.; Eckert, C.; Te Kronnie, G.; Bourquin, J.P.; Bornhauser, B.; et al. IKZF1 plus defines a new minimal residual disease dependent very-poor prognostic profile in pediatric b-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 1240–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rosales-Rodríguez, B.; Núñez-Enríquez, J.C.; Mejía-Aranguré, J.M.; Rosas-Vargas, H. Prognostic Impact of Somatic Copy Number Alterations in Childhood B-Lineage Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2021, 23, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pui, C.H.; Nichols, K.E.; Yang, J.J. Somatic and germline genomics in paediatric acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 16, 227–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forero-Castro, M.; Robledo, C.; Benito, R.; Abáigar, M.; África Martín, A.; Arefi, M.; Fuster, J.L.; de Las Heras, N.; Rodriguez, J.N.; Quintero, J.; et al. Genome-wide DNA copy number analysis of acute lymphoblastic leukemia identifies new genetic markers associated with clinical outcome. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0148972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakral, D.; Kaur, G.; Gupta, R.; Benard-Slagter, A.; Savola, S.; Kumar, I.; Anand, R.; Rani, L.; Verma, P.; Joshi, S.; et al. Rapid identification of key copy number alterations in B- and T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia by digital multiplex ligation dependent probe amplification. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zaliova, M.; Stuchly, J.; Winkowska, L.; Musilova, A.; Fiser, K.; Slamova, M.; Starkova, J.; Vaskova, M.; Hrusak, O.; Sramkova, L.; et al. Genomic landscape of pediatric B-other acute lymphoblastic leukemia in a consecutive European cohort. Haematologica 2019, 104, 1396–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steeghs, E.M.P.; Boer, J.M.; Hoogkamer, A.Q.; Boeree, A.; de Haas, V.; de Groot-Kruseman, H.A.; Horstmann, M.A.; Escheriche, G.; Pieters, R.; den Boer, M.L. Copy number alterations in B-cell development genes, drug resistance, and clinical outcome in pediatric B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 4634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutton, R.; Venn, N.C.; Law, T.; Boer, J.M.; Trahair, T.N.; Ng, A.; den Boer, M.L.; Dissanayake, A.; Giles, J.E.; Dalzell, P.; et al. A risk score including microdeletions improves relapse prediction for standard and medium risk precursor B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukaemia in children. Br. J. Haematol. 2018, 180, 550–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.K.; Bakhshi, S.; Kumar, L.; Kamal, V.K.; Kumar, R. Gene copy number alteration profile and its clinical correlation in B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leuk. Lymphoma 2017, 58, 333–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwab, C.J.; Jones, L.R.; Morrison, H.; Ryan, S.L.; Yigittop, H.; Schouten, J.P.; Harrison, C.J. Evaluation of multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification as a method for the detection of copy number abnormalities in B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Genes Chromosom. Cancer 2009, 49, 1104–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benard-Slagter, A.; Zondervan, I.; de Groot, K.; Ghazavi, F.; Sarhadi, V.; Van Vlierberghe, P.; de Moerloose, B.; Schwab, C.; Vettenranta, K.; Harrison, C.J.; et al. Digital multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification for detection of key copy number alterations in T- and B-cell lymphoblastic leukemia. J. Mol. Diagn. 2017, 19, 659–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moorman, A.V.; Enshaei, A.; Schwab, C.; Wade, R.; Chilton, L.; Elliott, A.; Richardson, S.; Hancock, J.; Kinsey, S.E.; Mitchell, C.D.; et al. A novel integrated cytogenetic and genomic classification refines risk stratification in pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood 2014, 124, 1434–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hamadeh, L.; Enshaei, A.; Schwab, C.; Alonso, C.N.; Attarbaschi, A.; Barbany, G.; den Boer, M.L.; Boer, J.M.; Braun, M.; Pozza, L.D.; et al. Validation of the United Kingdom copy-number alteration classifier in 3239 children with B-cell precursor ALL. Blood Adv. 2019, 3, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiss, R.; Gángó, A.; Benard-Slagter, A.; Egyed, B.; Haltrich, I.; Hegyi, L.; de Groot, K.; Kiraly, P.A.; Krizsan, S.; Kajtar, B.; et al. Comprehensive profiling of disease-relevant copy number aberrations for advanced clinical diagnostics of pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Mod. Pathol. 2020, 33, 812–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dworzak, M.; Buldini, B.; Gaipa, G.; Ratei, R.; Hrusak, O.; Luria, D.; Rosenthal, E.; Bourquin, J.P.; Sartor, M.; Schumich, A.; et al. AIEOP-BFM Consensus Guidelines 2016 for Flow Cytometric Immunophenotyping of Pediatric Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Cytom. Part B Clin. Cytom. 2018, 94, 82–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Riehm, H.; Schrappe, M.; Reiter, A. Trial ALL-BFM 95. Treatment protocol ALL-BFM 95 for children and adolescents with acute lymphoblastic leukemia: A cooperative multicenter trial of the German Society for Pediatric Hematology and Oncology. Blood 2008, 111, 4477–4489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- ALL IC 2009 Trial of the I-BFM Study Group. 2009. Available online: https://bfminternational.wordpress.com/clinical-trials/ongoing-trials/ (accessed on 28 June 2021).
- Moorman, A.V. The clinical relevance of chromosomal and genomic abnormalities in B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Blood Rev. 2012, 26, 123–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moorman, A.V. New and emerging prognostic and predictive genetic biomarkers in B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Haematologica 2016, 101, 407–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mullighan, C.G.; Su, X.; Zhang, J.; Radtke, I.; Phillips, L.A.A.; Miller, C.B.; Ma, J.; Liu, W.; Cheng, C.; Schulman, B.A.; et al. Deletion of IKZF1 and prognosis in acute lymphoblastic leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 360, 470–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olsson, L.; Ivanov Öfverholm, I.; Norén-Nyström, U.; Zachariadis, V.; Nordlund, J.; Sjögren, H.; Golovleva, I.; Nordgren, A.; Paulsson, K.; Heyman, M.; et al. The clinical impact of IKZF1 deletions in paediatric B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukaemia is independent of minimal residual disease stratification in Nordic Society for Paediatric Haematology and Oncology treatment protocols used between 1992 and 2013. Br. J. Haematol. 2015, 170, 847–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Öfverholm, I.; Tran, A.N.; Heyman, M.; Zachariadis, V.; Nordenskjöld, M.; Nordgren, A.; Barbany, G. Impact of IKZF1 deletions and PAX5 amplifications in pediatric B-cell precursor ALL treated according to NOPHO protocols. Leukemia 2013, 27, 1936–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanulla, M.; Cavé, H.; Moorman, A.V. IKZF1 deletions in pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia: Still a poor prognostic marker? Blood 2020, 135, 252–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vitanza, N.A.; Zaky, W.; Blum, R.; Meyer, J.A.; Wang, J.; Bhatla, T.; Morrison, D.J.; Raetz, E.A.; Caroll, W.L. Ikaros deletions in BCR-ABL-negative childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia are associated with a distinct gene expression signature but do not result in intrinsic chemoresistance. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2014, 61, 1779–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marke, R.; Havinga, J.; Cloos, J.; Demkes, M.; Poelmans, G.; Yuniati, L.; van Ingen Schenau, D.; Sonneveld, E.; Waanders, E.; Pieters, R.; et al. Tumor suppressor IKZF1 mediates glucocorticoid resistance in B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leukemia 2016, 30, 1599–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vesely, C.; Frech, C.; Eckert, C.; Cario, G.; Mecklenbräuker, A.; Zur Stadt, U.; Nebral, K.; Kraler, F.; Fischer, S.; Attarbashi, A.; et al. Genomic and transcriptional landscape of P2RY8CRLF2-positive childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leukemia 2017, 31, 1491–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mirebeau, D.; Acquaviva, C.; Suciu, S.; Bertin, R.; Dastugue, N.; Robert, A.; Boutard, P.; Mechinaud, F.; Plouvier, E.; Otten, J.; et al. The prognostic significance of CDKN2A, CDKN2B and MTAP inactivation in B-lineage acute lymphoblastic leukemia of childhood. Results of the EORTC studies 58881 and 58951. Haematologica 2006, 91, 881–885. [Google Scholar]
- Braun, M.; Pastorczak, A.; Fendler, W.; Madzio, J.; Tomasik, B.; Taha, J.; Bielska, M.; Sedek, L.; Szczepanski, T.; Matysiak, M.; et al. Biallelic loss of CDKN2A is associated with poor response to treatment in pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leuk. Lymphoma 2017, 58, 1162–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Kuang, P.; Liu, T. Prognostic significance of CDKN2A/B deletions in acute lymphoblastic leukaemia: A meta-analysis. Ann. Med. 2019, 51, 28–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulong, S.; Moorman, A.V.; Irving, J.A.E.; Strefford, J.C.; Konn, Z.J.; Case, M.C.; Minto, L.; Barber, K.E.; Parker, H.; Wright, S.L.; et al. A comprehensive analysis of the CDKN2A gene in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia reveals genomic deletion, copy number neutral loss of heterozygosity, and association with specific cytogenetic subgroups. Blood 2009, 113, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Messina, M.; Chiaretti, S.; Fedullo, A.L.; Piciocchi, A.; Puzzolo, M.C.; Lauretti, A.; Gianfelici, V.; Apicella, V.; Fazi, P.; Te Kronnie, G.; et al. Clinical significance of recurrent copy number aberrations in B-lineage acute lymphoblastic leukaemia without recurrent fusion genes across age cohorts. Br. J. Haematol. 2017, 178, 583–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dagdan, E.; Zaliova, M.; Zimmermann, M.; Dörge, P.; Möricke, A.; Teigler-Schlegel, A.; Koehler, R.; Bartram, C.R.; Ratei, R.; Ludwig, W.D.; et al. Concurrent deIetions of IKZF1 and PAX5, CDKN2A, CDKN2B or PAR1 (IKZF1plus) confer a very poor prognosis in pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Klin. Pädiatr. 2014, 226, A10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, D.; Enshaei, A.; Bartram, J.; Hancock, J.; Harrison, C.J.; Hough, R.; Samarasinghe, S.; Schwab, C.; Vora, A.; Wade, R.; et al. Genotype-specific minimal residual disease interpretation improves stratification in pediatric acute lymhoblastic leukemia. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 34–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.K.; Bakhshi, S.; Chopra, A.; Kamal, V.K. Molecular genetic profile in BCR-ABL1 negative pediatric B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia can further refine outcome prediction in addition to that by end-induction minimal residual disease detection. Leuk. Lymphoma 2017, 59, 1899–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

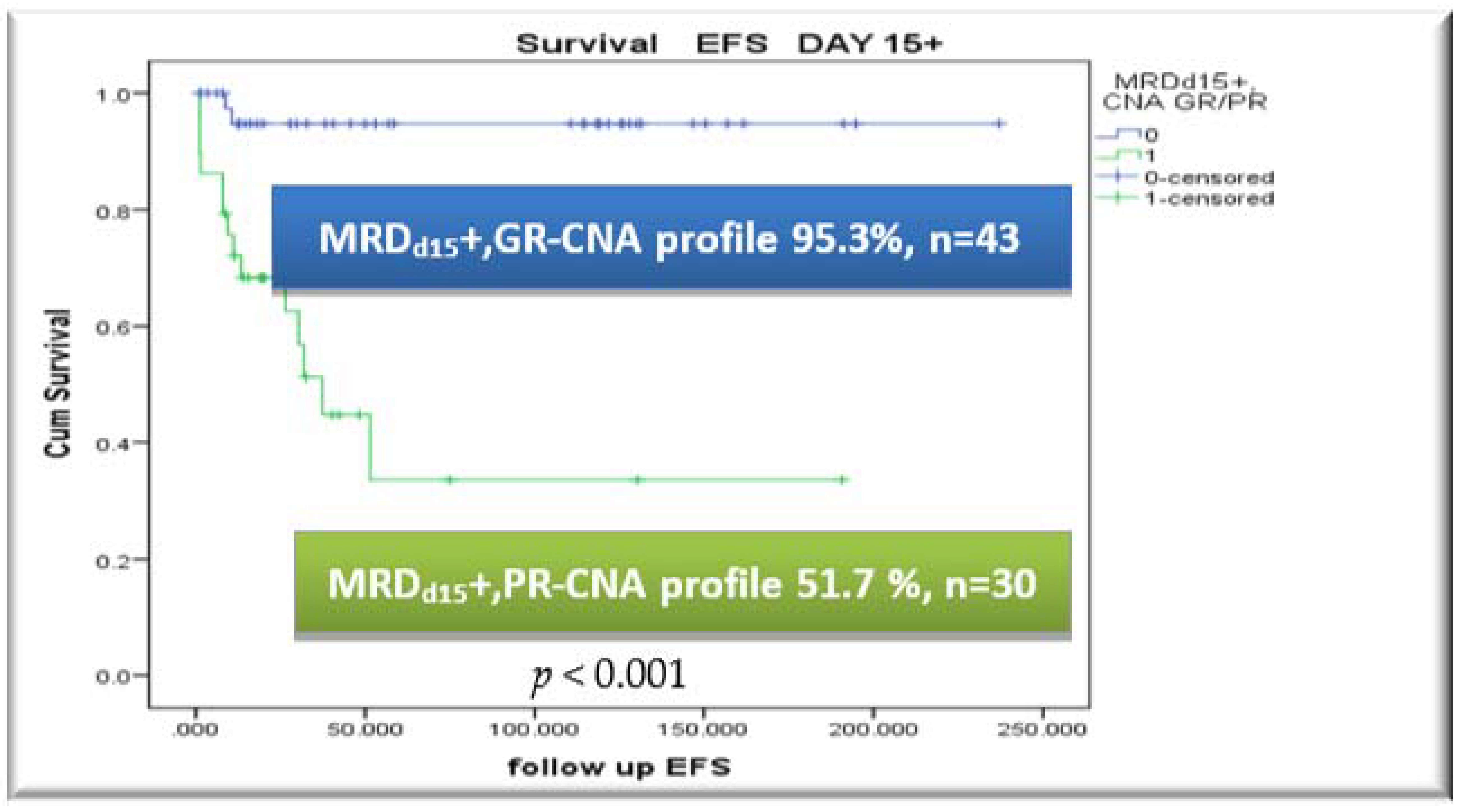
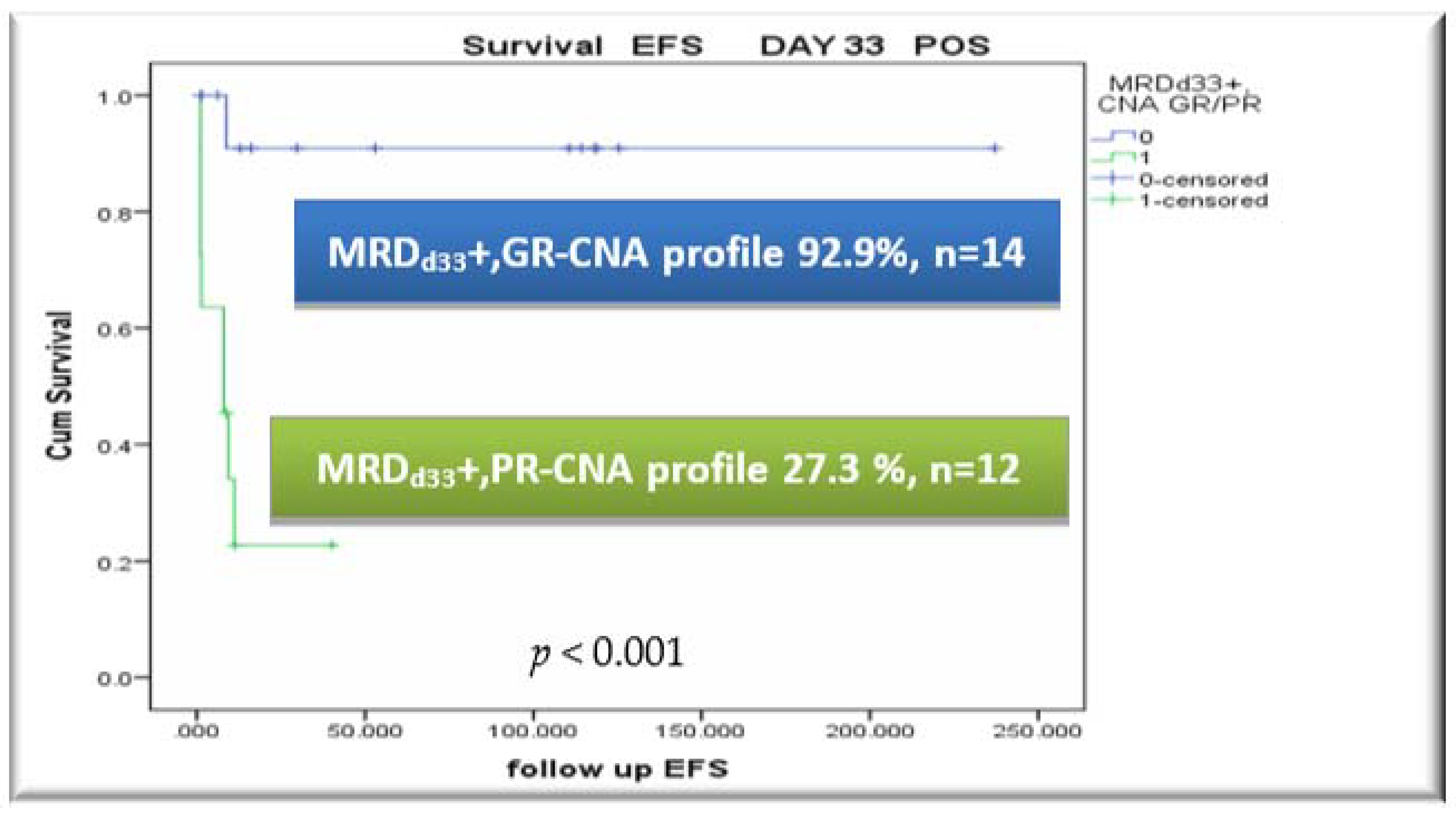
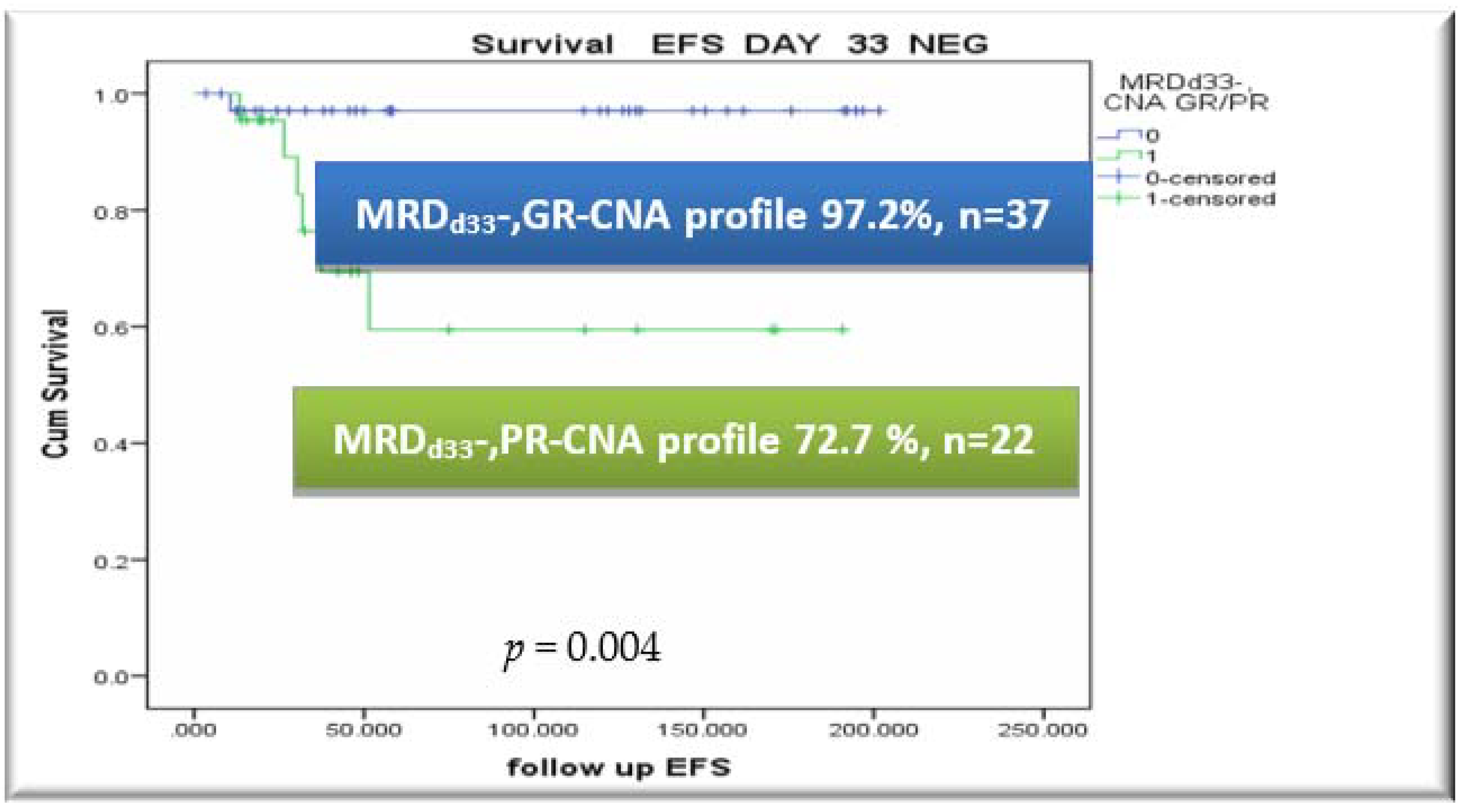
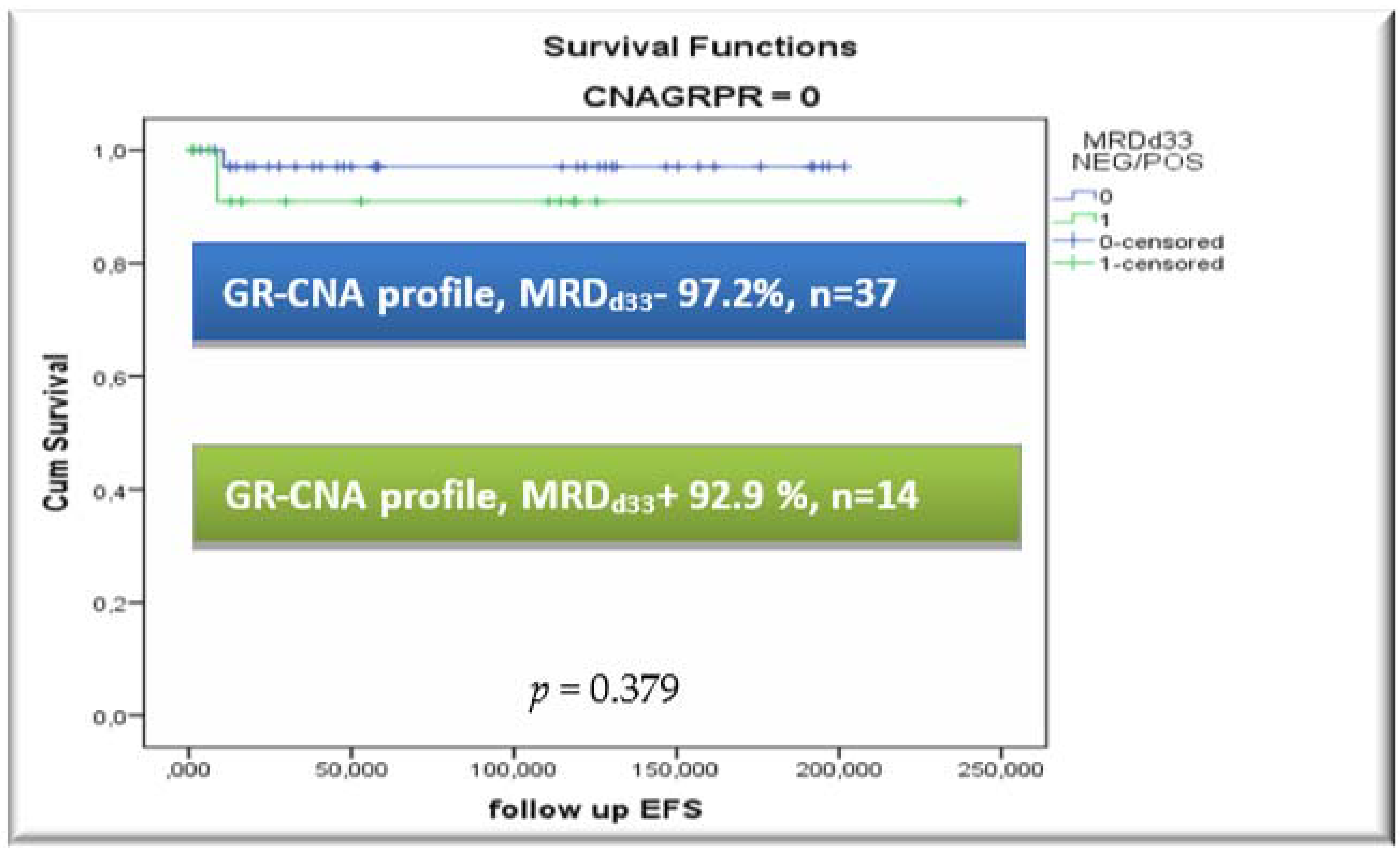

| Characteristics | Number (%) |
|---|---|
| Total | 85 |
| Gender | |
| Male | 48 (56.5) |
| Female | 37 (43.5) |
| Immunophenotype | |
| B-ALL | 77 (90.6) |
| Pro-B ALL | 6 (7.1) |
| Common-B ALL | 51 (60.0) |
| Pre-B ALL | 20 (23.5) |
| T-ALL | 8 (9.4) |
| ETP-ALL | 2 (2.4) |
| Genetics | |
| ETV6/RUNX1 | 19 (22.3) |
| KMT2A rearrangements | 3 (3.5) |
| BCR/ABL1 | 1 (1.2) |
| TCF3/PBX1 | 1 (1.2) |
| iAMP21 | 2 (2.3) |
| TCF3/HLF | 0 (0) |
| Hyperdiploidy | 18 (21.2) |
| Hypodiploidy | 0 (0) |
| Treatment Protocol | |
| BFM 95/2000 modified | 22 (25.9) |
| ALLIC BFM 2009 | 63 (74.1) |
| Protocol Risk Group | |
| Intermediate Risk | 48 (56.5) |
| High Risk | 37 (43.5) |
| FC-MRD Status | |
| FC-MRDd15 positive (MRDd15 ≥ 10−4) | 73 (85.9) |
| FC-MRDd15 positive (MRDd15 ≥ 10−3) | 66 (77.6) |
| FC-MRDd33 positive (MRDd33 ≥ 10−4) | 26 (30.6) |
| Complete Remission (EOI-CR *) | |
| Yes | 80 (94.1) |
| No | 5 (5.9) |
| Allo-HSCT | 17 (20.0) |
| Salvage Regimens # | 15 (17.6) |
| Variable | Total (n = 85) | IR Group (n = 48) | HR Group (n = 37) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GR-CNA, n (%) | PR-CNA n (%) | GR-CNA n (%) | PR-CNA n (%) | GR-CNA n (%) | PR-CNA N (%) | |
| Total n of patients Complete Remission * | 51 (60.0) | 34 (40.0) | 33 (68.8) | 15 (31.2) | 18 (48.6) | 19 (51.4) |
| n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | |
| Yes | 50 (98.0) | 30 (88.2) | 33 (100.0) | 15(100.0) | 17 (94.4) | 15 (78.9) |
| No | 1 (2.0) | 4 (11.8) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (5.6) | 4 (21.1) |
| Event | ||||||
| Yes | 3 (5.9) | 15 (44.1) | 0 (0.0) | 6 (40.0) | 3 (16.7) | 9 (47.4) |
| No | 48 (94.1) | 19 (55.9) | 33 (100.0) | 9 (60.0) | 15 (83.3) | 10 (52.6) |
| Relapse | ||||||
| Yes | 1 (2.0) | 12 (35.3) | 0 (0.0) | 5 (33.3) | 1 (5.6) | 8 (42.1) |
| No | 50 (98.0) | 22 (64.7) | 33 (100.0) | 10 (66.7) | 17 (94.4) | 11 (57.9) |
| Death | ||||||
| Yes | 3 (5.9) | 8 (23.5) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (6.7) | 3 (16.7) | 7 (36.8) |
| No | 48 (94.1) | 26 (76.5) | 33 (100.0) | 14 (93.3) | 15 (83.3) | 12 (63.2) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Αmpatzidou, Μ.; Florentin, L.; Papadakis, V.; Paterakis, G.; Tzanoudaki, M.; Bouzarelou, D.; Papadhimitriou, S.I.; Polychronopoulou, S. Copy Number Alteration Profile Provides Additional Prognostic Value for Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Patients Treated on BFM Protocols. Cancers 2021, 13, 3289. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13133289
Αmpatzidou Μ, Florentin L, Papadakis V, Paterakis G, Tzanoudaki M, Bouzarelou D, Papadhimitriou SI, Polychronopoulou S. Copy Number Alteration Profile Provides Additional Prognostic Value for Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Patients Treated on BFM Protocols. Cancers. 2021; 13(13):3289. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13133289
Chicago/Turabian StyleΑmpatzidou, Μirella, Lina Florentin, Vassilios Papadakis, Georgios Paterakis, Marianna Tzanoudaki, Dimitra Bouzarelou, Stefanos I. Papadhimitriou, and Sophia Polychronopoulou. 2021. "Copy Number Alteration Profile Provides Additional Prognostic Value for Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Patients Treated on BFM Protocols" Cancers 13, no. 13: 3289. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13133289
APA StyleΑmpatzidou, Μ., Florentin, L., Papadakis, V., Paterakis, G., Tzanoudaki, M., Bouzarelou, D., Papadhimitriou, S. I., & Polychronopoulou, S. (2021). Copy Number Alteration Profile Provides Additional Prognostic Value for Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Patients Treated on BFM Protocols. Cancers, 13(13), 3289. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13133289






