The Janus Face of IL-33 Signaling in Tumor Development and Immune Escape
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
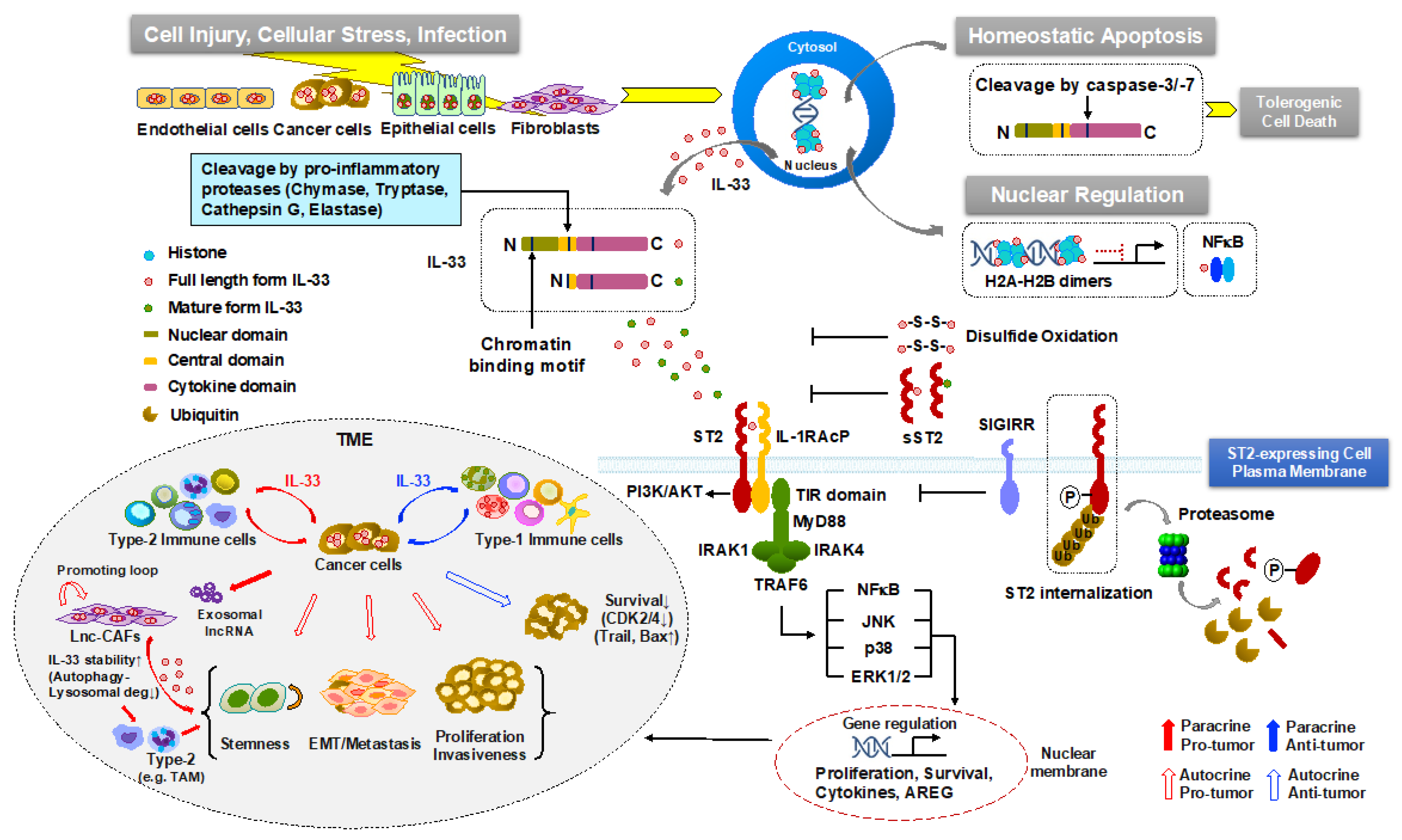
2. Molecular Features of IL-33
2.1. Gene and Protein
2.2. Nuclear Localization and Release of Isoforms
2.3. Signaling Cascade
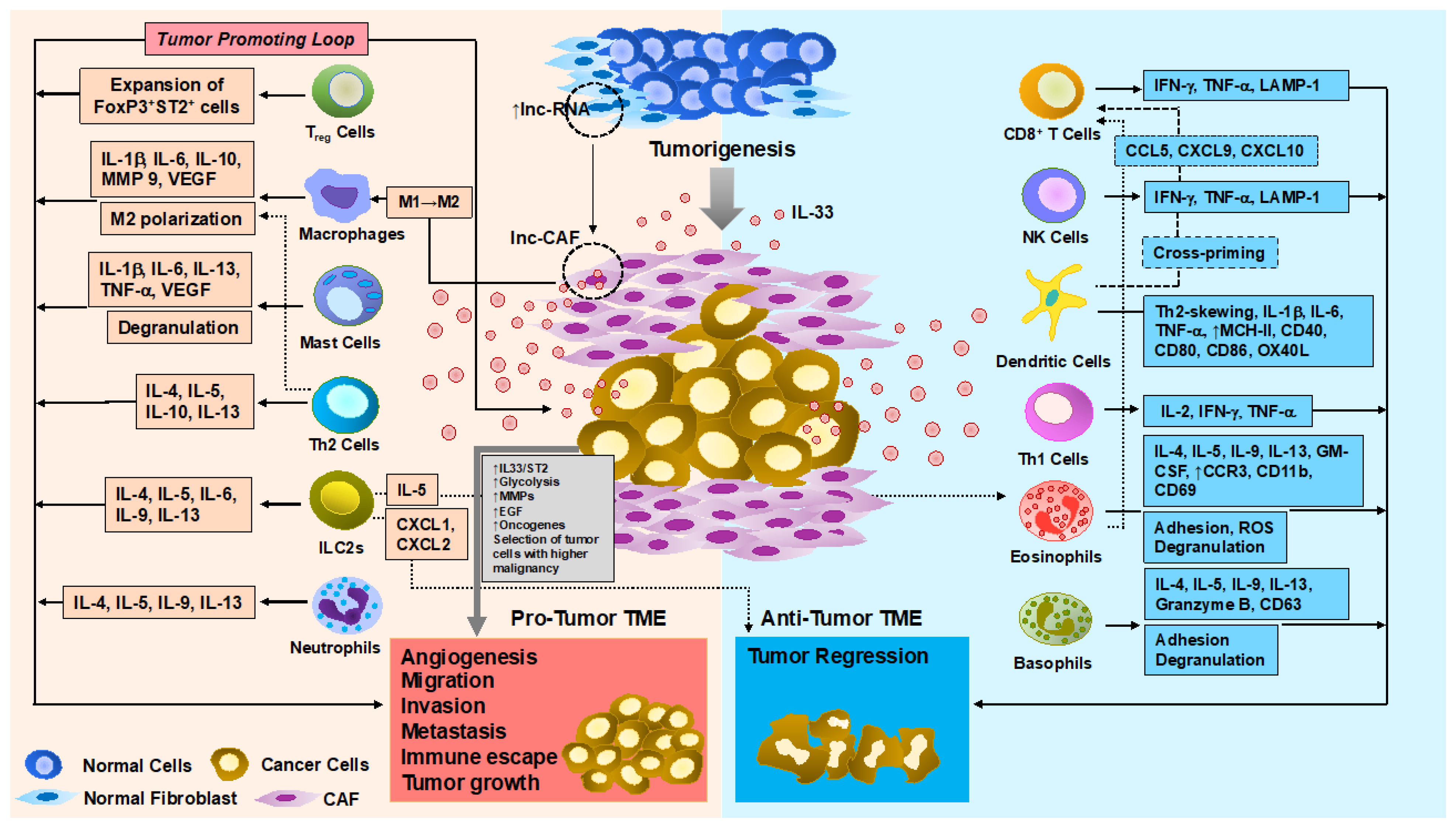
3. Pro-Tumorigenic Function of IL-33
3.1. Tumor Cells
3.2. Stromal Cells
3.3. Immune Cells
3.3.1. CD4+ Treg Cells
3.3.2. Macrophages
3.3.3. Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells (MDSCs)
3.3.4. Neutrophils
3.3.5. Mast Cells
3.3.6. ILC2
4. Anti-Tumorigenic Function of IL-33
4.1. Tumor Cells
4.2. Immune Cells
4.2.1. CD4+ Th Cells
4.2.2. CD8+ T Cells
4.2.3. NK and NKT Cells
4.2.4. DCs
4.2.5. Eosinophils
4.2.6. Basophils
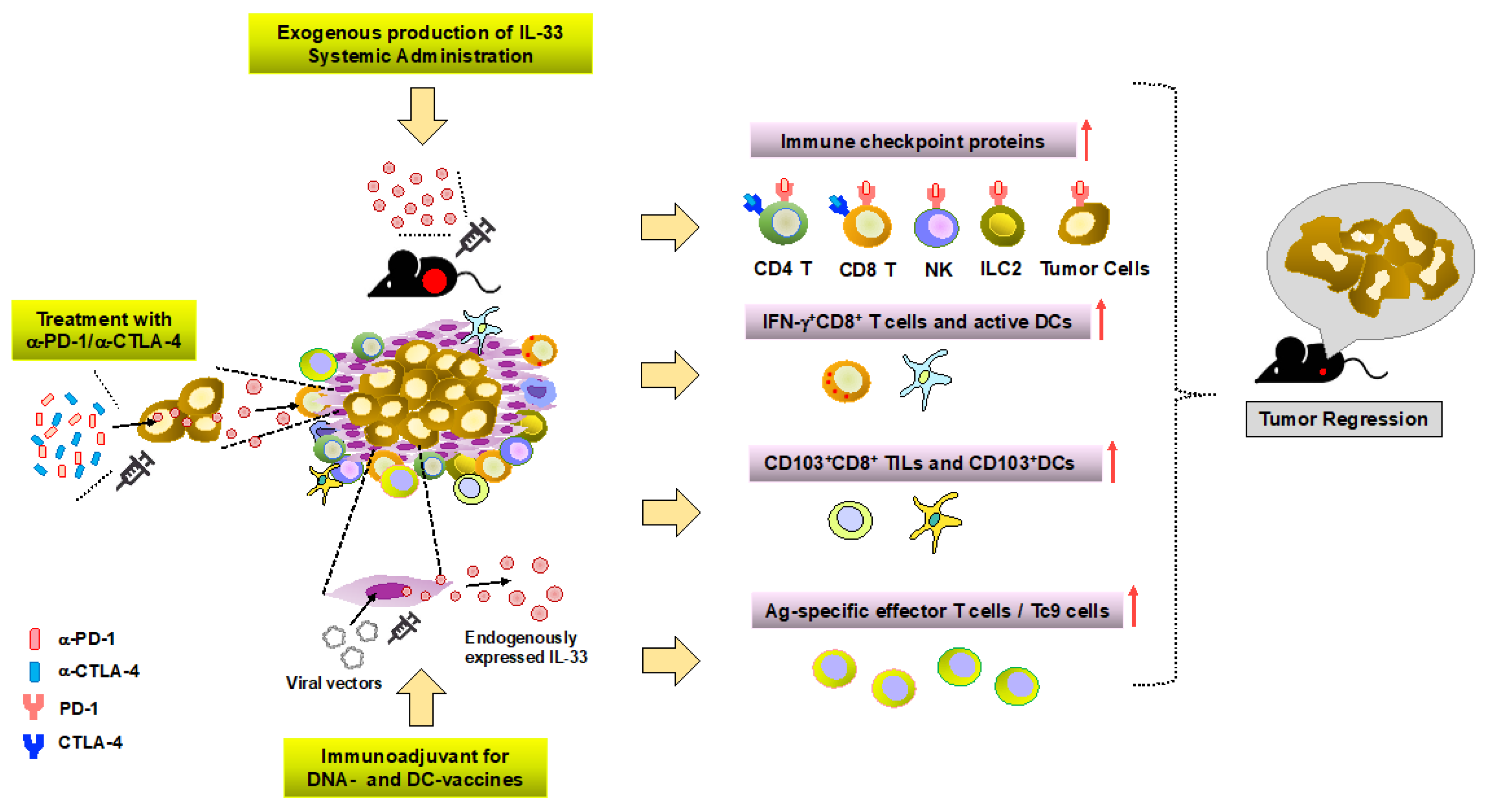
5. Targeting IL-33/ST2 to Augment Cancer Immunotherapy
6. Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schmitz, J.; Owyang, A.; Oldham, E.; Song, Y.; Murphy, E.; McClanahan, T.K.; Zurawski, G.; Moshrefi, M.; Qin, J.; Li, X.; et al. IL-33, an interleukin-1-like cytokine that signals via the IL-1 receptor-related protein ST2 and induces T helper type 2-associated cytokines. Immunity 2005, 23, 479–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, D.; Chan, W.L.; Leung, B.P.; Huang, F.; Wheeler, R.; Piedrafita, D.; Robinson, J.H.; Liew, F.Y. Selective expression of a stable cell surface molecule on type 2 but not type 1 helper T cells. J. Exp. Med. 1998, 187, 787–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roh, J.S.; Sohn, D.H. Damage-Associated Molecular Patterns in Inflammatory Diseases. Immune Netw. 2018, 18, e27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Showalter, A.; Limaye, A.; Oyer, J.L.; Igarashi, R.; Kittipatarin, C.; Copik, A.J.; Khaled, A.R. Cytokines in immunogenic cell death: Applications for cancer immunotherapy. Cytokine 2017, 97, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cayrol, C.; Girard, J.P. IL-33: An alarmin cytokine with crucial roles in innate immunity, inflammation and allergy. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2014, 31, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Inoue, H.; Tani, K. Multimodal immunogenic cancer cell death as a consequence of anticancer cytotoxic treatments. Cell Death Differ. 2014, 21, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cassel, S.L.; Joly, S.; Sutterwala, F.S. The NLRP3 inflammasome: A sensor of immune danger signals. Semin. Immunol. 2009, 21, 194–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ghiringhelli, F.; Apetoh, L.; Tesniere, A.; Aymeric, L.; Ma, Y.; Ortiz, C.; Vermaelen, K.; Panaretakis, T.; Mignot, G.; Ullrich, E.; et al. Activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome in dendritic cells induces IL-1beta-dependent adaptive immunity against tumors. Nat. Med. 2009, 15, 1170–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liew, F.Y.; Pitman, N.I.; McInnes, I.B. Disease-associated functions of IL-33: The new kid in the IL-1 family. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2010, 10, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liew, F.Y.; Girard, J.P.; Turnquist, H.R. Interleukin-33 in health and disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2016, 16, 676–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millar, N.L.; O’Donnell, C.; McInnes, I.B.; Brint, E. Wounds that heal and wounds that don’t—The role of the IL-33/ST2 pathway in tissue repair and tumorigenesis. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2017, 61, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wasmer, M.H.; Krebs, P. The Role of IL-33-Dependent Inflammation in the Tumor Microenvironment. Front Immunol. 2016, 7, 682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akimoto, M.; Maruyama, R.; Takamaru, H.; Ochiya, T.; Takenaga, K. Soluble IL-33 receptor sST2 inhibits colorectal cancer malignant growth by modifying the tumour microenvironment. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 13589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, M.; Li, Y.; Huang, K.; Qi, S.; Zhang, J.; Zgodzinski, W.; Majewski, M.; Wallner, G.; Gozdz, S.; Macek, P.; et al. IL33 Promotes Colon Cancer Cell Stemness via JNK Activation and Macrophage Recruitment. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 2735–2745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, H.; Sun, J.; Wang, C.; Bu, X.; Liu, X.; Mao, Y.; Wang, H. IL-33 facilitates endocrine resistance of breast cancer by inducing cancer stem cell properties. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 485, 643–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhu, L.; Lu, X.; Bian, H.; Wu, X.; Yang, W.; Qin, Q. IL-33/ST2 pathway contributes to metastasis of human colorectal cancer. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 453, 486–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Chen, Z.; Bu, X.; Han, Y.; Shan, S.; Ren, T.; Song, W. IL-33 signaling fuels outgrowth and metastasis of human lung cancer. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 47, 461–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Gao, X.; Wang, J.; Xu, L.; Zheng, Y.; Xu, Y. Interleukin-33 enhanced the migration and invasiveness of human lung cancer cells. OncoTargets Ther. 2018, 11, 843–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Razumilava, N.; Gores, G.J.; Walters, S.; Mizuochi, T.; Mourya, R.; Bessho, K.; Wang, Y.H.; Glaser, S.S.; Shivakumar, P.; et al. Biliary repair and carcinogenesis are mediated by IL-33-dependent cholangiocyte proliferation. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 3241–3251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akimoto, M.; Hayashi, J.I.; Nakae, S.; Saito, H.; Takenaga, K. Interleukin-33 enhances programmed oncosis of ST2L-positive low-metastatic cells in the tumour microenvironment of lung cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2016, 7, e2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yamada, D.; Rizvi, S.; Razumilava, N.; Bronk, S.F.; Davila, J.I.; Champion, M.D.; Borad, M.J.; Bezerra, J.A.; Chen, X.; Gores, G.J. IL-33 facilitates oncogene-induced cholangiocarcinoma in mice by an interleukin-6-sensitive mechanism. Hepatology 2015, 61, 1627–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.F.; Nieh, S.; Jao, S.W.; Wu, M.Z.; Liu, C.L.; Chang, Y.C.; Lin, Y.S. The paracrine effect of cancer-associated fibroblast-induced interleukin-33 regulates the invasiveness of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. J. Pathol. 2013, 231, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, L.; Ren, J.; Zhang, D.; Li, Y.; Huang, X.; Hu, Q.; Wang, H.; Song, Y.; Ni, Y.; Hou, Y. A novel stromal lncRNA signature reprograms fibroblasts to promote the growth of oral squamous cell carcinoma via LncRNA-CAF/interleukin-33. Carcinogenesis 2018, 39, 397–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersson, P.; Yang, Y.; Hosaka, K.; Zhang, Y.; Fischer, C.; Braun, H.; Liu, S.; Yu, G.; Liu, S.; Beyaert, R.; et al. Molecular mechanisms of IL-33-mediated stromal interactions in cancer metastasis. JCI Insight 2018, 3, e122375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maywald, R.L.; Doerner, S.K.; Pastorelli, L.; De Salvo, C.; Benton, S.M.; Dawson, E.P.; Lanza, D.G.; Berger, N.A.; Markowitz, S.D.; Lenz, H.J.; et al. IL-33 activates tumor stroma to promote intestinal polyposis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E2487–E2496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jovanovic, I.; Radosavljevic, G.; Mitrovic, M.; Juranic, V.L.; McKenzie, A.N.; Arsenijevic, N.; Jonjic, S.; Lukic, M.L. ST2 deletion enhances innate and acquired immunity to murine mammary carcinoma. Eur. J. Immunol. 2011, 41, 1902–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jovanovic, I.P.; Pejnovic, N.N.; Radosavljevic, G.D.; Pantic, J.M.; Milovanovic, M.Z.; Arsenijevic, N.N.; Lukic, M.L. Interleukin-33/ST2 axis promotes breast cancer growth and metastases by facilitating intratumoral accumulation of immunosuppressive and innate lymphoid cells. Int. J. Cancer 2014, 134, 1669–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Chen, L.; Souto, F.O.; Canasto-Chibuque, C.; Bongers, G.; Deshpande, M.; Harpaz, N.; Ko, H.M.; Kelley, K.; Furtado, G.C.; et al. Epithelial-derived IL-33 promotes intestinal tumorigenesis in Apc (Min/+) mice. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 5520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fang, Y.; Zhao, L.; Xiao, H.; Cook, K.M.; Bai, Q.; Herrick, E.J.; Chen, X.; Qin, C.; Zhu, Z.; Wakefield, M.R.; et al. IL-33 acts as a foe to MIA PaCa-2 pancreatic cancer. Med. Oncol. 2017, 34, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Lu, K.; Timko, N.J.; Weir, D.M.; Zhu, Z.; Qin, C.; Mann, J.D.; Bai, Q.; Xiao, H.; Nicholl, M.B.; et al. IL-33 notably inhibits the growth of colon cancer cells. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 16, 769–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eissmann, M.F.; Dijkstra, C.; Wouters, M.A.; Baloyan, D.; Mouradov, D.; Nguyen, P.M.; Davalos-Salas, M.; Putoczki, T.L.; Sieber, O.M.; Mariadason, J.M.; et al. Interleukin 33 Signaling Restrains Sporadic Colon Cancer in an Interferon-gamma-Dependent Manner. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2018, 6, 409–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saranchova, I.; Han, J.; Zaman, R.; Arora, H.; Huang, H.; Fenninger, F.; Choi, K.B.; Munro, L.; Pfeifer, C.G.; Welch, I.; et al. Type 2 Innate Lymphocytes Actuate Immunity Against Tumours and Limit Cancer Metastasis. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 2924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Li, H.; Liang, F.; Hong, Y.; Jiang, S.; Xiao, L. Examining IL-33 expression in the cervix of HPV-infected patients: A preliminary study comparing IL-33 levels in different stages of disease and analyzing its potential association with IFN-gamma. Med. Oncol. 2014, 31, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saranchova, I.; Han, J.; Huang, H.; Fenninger, F.; Choi, K.B.; Munro, L.; Pfeifer, C.; Welch, I.; Wyatt, A.W.; Fazli, L.; et al. Discovery of a Metastatic Immune Escape Mechanism Initiated by the Loss of Expression of the Tumour Biomarker Interleukin-33. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 30555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, X.; Wang, X.; Yang, Q.; Zhao, X.; Wen, W.; Li, G.; Lu, J.; Qin, W.; Qi, Y.; Xie, F.; et al. Tumoral expression of IL-33 inhibits tumor growth and modifies the tumor microenvironment through CD8+ T and NK cells. J. Immunol. 2015, 194, 438–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Malik, A.; Sharma, D.; Zhu, Q.; Karki, R.; Guy, C.S.; Vogel, P.; Kanneganti, T.D. IL-33 regulates the IgA-microbiota axis to restrain IL-1alpha-dependent colitis and tumorigenesis. J. Clin. Investig. 2016, 126, 4469–4481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucarini, V.; Ziccheddu, G.; Macchia, I.; La Sorsa, V.; Peschiaroli, F.; Buccione, C.; Sistigu, A.; Sanchez, M.; Andreone, S.; D’Urso, M.T.; et al. IL-33 restricts tumor growth and inhibits pulmonary metastasis in melanoma-bearing mice through eosinophils. Oncoimmunology 2017, 6, e1317420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.; Kim, W.; Moon, U.J.; Kim, H.J.; Choi, H.J.; Sin, J.I.; Park, N.H.; Cho, H.R.; Kwon, B. Intratumorally Establishing Type 2 Innate Lymphoid Cells Blocks Tumor Growth. J. Immunol. 2016, 196, 2410–2423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qin, L.; Dominguez, D.; Chen, S.; Fan, J.; Long, A.; Zhang, M.; Fang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Kuzel, T.M.; Zhang, B. Exogenous IL-33 overcomes T cell tolerance in murine acute myeloid leukemia. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 61069–61080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dominguez, D.; Ye, C.; Geng, Z.; Chen, S.; Fan, J.; Qin, L.; Long, A.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Exogenous IL-33 Restores Dendritic Cell Activation and Maturation in Established Cancer. J. Immunol. 2017, 198, 1365–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, K.; Li, X.; Zhang, L.; Bai, L.; Dong, W.; Gao, K.; Shi, G.; Xia, X.; Wu, L.; Zhang, L. Transgenic expression of IL-33 activates CD8(+) T cells and NK cells and inhibits tumor growth and metastasis in mice. Cancer Lett. 2013, 335, 463–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duault, C.; Betous, D.; Bezombes, C.; Roga, S.; Cayrol, C.; Girard, J.P.; Fournie, J.J.; Poupot, M. IL-33-expanded human Vgamma9Vdelta2 T cells have anti-lymphoma effect in a mouse tumor model. Eur. J. Immunol. 2017, 47, 2137–2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baekkevold, E.S.; Roussigne, M.; Yamanaka, T.; Johansen, F.E.; Jahnsen, F.L.; Amalric, F.; Brandtzaeg, P.; Erard, M.; Haraldsen, G.; Girard, J.P. Molecular characterization of NF-HEV, a nuclear factor preferentially expressed in human high endothelial venules. Am. J. Pathol. 2003, 163, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carriere, V.; Roussel, L.; Ortega, N.; Lacorre, D.A.; Americh, L.; Aguilar, L.; Bouche, G.; Girard, J.P. IL-33, the IL-1-like cytokine ligand for ST2 receptor, is a chromatin-associated nuclear factor in vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 282–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Afferni, C.; Buccione, C.; Andreone, S.; Galdiero, M.R.; Varricchi, G.; Marone, G.; Mattei, F.; Schiavoni, G. The Pleiotropic Immunomodulatory Functions of IL-33 and Its Implications in Tumor Immunity. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moussion, C.; Ortega, N.; Girard, J.P. The IL-1-like cytokine IL-33 is constitutively expressed in the nucleus of endothelial cells and epithelial cells in vivo: A novel ‘alarmin’? PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e3331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sanada, S.; Hakuno, D.; Higgins, L.J.; Schreiter, E.R.; McKenzie, A.N.; Lee, R.T. IL-33 and ST2 comprise a critical biomechanically induced and cardioprotective signaling system. J. Clin. Investig. 2007, 117, 1538–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miller, A.M.; Xu, D.; Asquith, D.L.; Denby, L.; Li, Y.; Sattar, N.; Baker, A.H.; McInnes, I.B.; Liew, F.Y. IL-33 reduces the development of atherosclerosis. J. Exp. Med. 2008, 205, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roussel, L.; Erard, M.; Cayrol, C.; Girard, J.P. Molecular mimicry between IL-33 and KSHV for attachment to chromatin through the H2A-H2B acidic pocket. EMBO Rep 2008, 9, 1006–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ali, S.; Mohs, A.; Thomas, M.; Klare, J.; Ross, R.; Schmitz, M.L.; Martin, M.U. The dual function cytokine IL-33 interacts with the transcription factor NF-kappaB to dampen NF-kappaB-stimulated gene transcription. J. Immunol. 2011, 187, 1609–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lefrancais, E.; Cayrol, C. Mechanisms of IL-33 processing and secretion: Differences and similarities between IL-1 family members. Eur. Cytokine Netw. 2012, 23, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefrancais, E.; Duval, A.; Mirey, E.; Roga, S.; Espinosa, E.; Cayrol, C.; Girard, J.P. Central domain of IL-33 is cleaved by mast cell proteases for potent activation of group-2 innate lymphoid cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 15502–15507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lefrancais, E.; Roga, S.; Gautier, V.; Gonzalez-de-Peredo, A.; Monsarrat, B.; Girard, J.P.; Cayrol, C. IL-33 is processed into mature bioactive forms by neutrophil elastase and cathepsin G. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 1673–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luzina, I.G.; Pickering, E.M.; Kopach, P.; Kang, P.H.; Lockatell, V.; Todd, N.W.; Papadimitriou, J.C.; McKenzie, A.N.; Atamas, S.P. Full-length IL-33 promotes inflammation but not Th2 response in vivo in an ST2-independent fashion. J. Immunol. 2012, 189, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villarreal, D.O.; Wise, M.C.; Walters, J.N.; Reuschel, E.L.; Choi, M.J.; Obeng-Adjei, N.; Yan, J.; Morrow, M.P.; Weiner, D.B. Alarmin IL-33 acts as an immunoadjuvant to enhance antigen-specific tumor immunity. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 1789–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gordon, E.D.; Simpson, L.J.; Rios, C.L.; Ringel, L.; Lachowicz-Scroggins, M.E.; Peters, M.C.; Wesolowska-Andersen, A.; Gonzalez, J.R.; MacLeod, H.J.; Christian, L.S.; et al. Alternative splicing of interleukin-33 and type 2 inflammation in asthma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 8765–8770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hong, J.; Bae, S.; Jhun, H.; Lee, S.; Choi, J.; Kang, T.; Kwak, A.; Hong, K.; Kim, E.; Jo, S.; et al. Identification of constitutively active interleukin 33 (IL-33) splice variant. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 20078–20086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tsuda, H.; Komine, M.; Karakawa, M.; Etoh, T.; Tominaga, S.; Ohtsuki, M. Novel splice variants of IL-33: Differential expression in normal and transformed cells. J. Invest. Dermatol. 2012, 132, 2661–2664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, I.S.; Son, H.; Kim, S.; Kim, S. ISOexpresso: A web-based platform for isoform-level expression analysis in human cancer. BMC Genom. 2016, 17, 631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ali, S.; Nguyen, D.Q.; Falk, W.; Martin, M.U. Caspase 3 inactivates biologically active full length interleukin-33 as a classical cytokine but does not prohibit nuclear translocation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 391, 1512–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cayrol, C.; Girard, J.P. The IL-1-like cytokine IL-33 is inactivated after maturation by caspase-1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 9021–9026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luthi, A.U.; Cullen, S.P.; McNeela, E.A.; Duriez, P.J.; Afonina, I.S.; Sheridan, C.; Brumatti, G.; Taylor, R.C.; Kersse, K.; Vandenabeele, P.; et al. Suppression of interleukin-33 bioactivity through proteolysis by apoptotic caspases. Immunity 2009, 31, 84–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, E.S.; Scott, I.C.; Majithiya, J.B.; Rapley, L.; Kemp, B.P.; England, E.; Rees, D.G.; Overed-Sayer, C.L.; Woods, J.; Bond, N.J.; et al. Oxidation of the alarmin IL-33 regulates ST2-dependent inflammation. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Molofsky, A.B.; Savage, A.K.; Locksley, R.M. Interleukin-33 in Tissue Homeostasis, Injury, and Inflammation. Immunity 2015, 42, 1005–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oshikawa, K.; Yanagisawa, K.; Tominaga, S.; Sugiyama, Y. Expression and function of the ST2 gene in a murine model of allergic airway inflammation. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2002, 32, 1520–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Homsak, E.; Gruson, D. Soluble ST2: A complex and diverse role in several diseases. Clin. Chim. Acta 2020, 507, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.P.; Hu, M.H.; Hsiao, Y.P.; Wang, Y.C. ST2 Signaling in the Tumor Microenvironment. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2020, 1240, 83–93. [Google Scholar]
- Bulek, K.; Swaidani, S.; Qin, J.; Lu, Y.; Gulen, M.F.; Herjan, T.; Min, B.; Kastelein, R.A.; Aronica, M.; Kosz-Vnenchak, M.; et al. The essential role of single Ig IL-1 receptor-related molecule/Toll IL-1R8 in regulation of Th2 immune response. J. Immunol. 2009, 182, 2601–2609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lingel, A.; Weiss, T.M.; Niebuhr, M.; Pan, B.; Appleton, B.A.; Wiesmann, C.; Bazan, J.F.; Fairbrother, W.J. Structure of IL-33 and its interaction with the ST2 and IL-1RAcP receptors--insight into heterotrimeric IL-1 signaling complexes. Structure 2009, 17, 1398–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, X.; Hammel, M.; He, Y.; Tainer, J.A.; Jeng, U.S.; Zhang, L.; Wang, S.; Wang, X. Structural insights into the interaction of IL-33 with its receptors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 14918–14923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pinto, S.M.; Subbannayya, Y.; Rex, D.A.B.; Raju, R.; Chatterjee, O.; Advani, J.; Radhakrishnan, A.; Keshava Prasad, T.S.; Wani, M.R.; Pandey, A. A network map of IL-33 signaling pathway. J. Cell Commun. Signal. 2018, 12, 615–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balkwill, F.; Mantovani, A. Inflammation and cancer: Back to Virchow? Lancet 2001, 357, 539–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crusz, S.M.; Balkwill, F.R. Inflammation and cancer: Advances and new agents. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 12, 584–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kundu, J.K.; Surh, Y.J. Inflammation: Gearing the journey to cancer. Mutat. Res. 2008, 659, 15–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aggarwal, B.B.; Vijayalekshmi, R.V.; Sung, B. Targeting inflammatory pathways for prevention and therapy of cancer: Short-term friend, long-term foe. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 425–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, P.; Ben, Q.; Tu, S.; Dong, W.; Qi, X.; Wu, Y. Serum interleukin-33 levels in patients with gastric cancer. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2011, 56, 3596–3601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergis, D.; Kassis, V.; Ranglack, A.; Koeberle, V.; Piiper, A.; Kronenberger, B.; Zeuzem, S.; Waidmann, O.; Radeke, H.H. High Serum Levels of the Interleukin-33 Receptor Soluble ST2 as a Negative Prognostic Factor in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Transl. Oncol. 2013, 6, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ishikawa, K.; Yagi-Nakanishi, S.; Nakanishi, Y.; Kondo, S.; Tsuji, A.; Endo, K.; Wakisaka, N.; Murono, S.; Yoshizaki, T. Expression of interleukin-33 is correlated with poor prognosis of patients with squamous cell carcinoma of the tongue. Auris Nasus Larynx 2014, 41, 552–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.; Shen, J.X.; Hu, J.L.; Huang, W.H.; Zhang, G.J. Significance of interleukin-33 and its related cytokines in patients with breast cancers. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, L.A.; Fu, Y.; Zhang, D.N.; Zhang, J. Serum IL-33 as a diagnostic and prognostic marker in non- small cell lung cancer. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2013, 14, 2563–2566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Z.P.; Ling, D.Y.; Xie, Y.H.; Wu, W.X.; Li, J.R.; Jiang, J.; Zheng, J.L.; Fan, Y.H.; Zhang, Y. The Association of Serum IL-33 and sST2 with Breast Cancer. Dis. Markers 2015, 2015, 516895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jovanovic, I.P.; Pejnovic, N.N.; Radosavljevic, G.D.; Arsenijevic, N.N.; Lukic, M.L. IL-33/ST2 axis in innate and acquired immunity to tumors. Oncoimmunology 2012, 1, 229–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tong, X.; Barbour, M.; Hou, K.; Gao, C.; Cao, S.; Zheng, J.; Zhao, Y.; Mu, R.; Jiang, H.R. Interleukin-33 predicts poor prognosis and promotes ovarian cancer cell growth and metastasis through regulating ERK and JNK signaling pathways. Mol. Oncol. 2016, 10, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Islam, M.S.; Horiguchi, K.; Iino, S.; Kaji, N.; Mikawa, S.; Hori, M.; Ozaki, H. Epidermal growth factor is a critical regulator of the cytokine IL-33 in intestinal epithelial cells. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 173, 2532–2542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Shi, J.; Qi, S.; Zhang, J.; Peng, D.; Chen, Z.; Wang, G.; Wang, Z.; Wang, L. IL-33 facilitates proliferation of colorectal cancer dependent on COX2/PGE2. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 37, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mager, L.F.; Riether, C.; Schurch, C.M.; Banz, Y.; Wasmer, M.H.; Stuber, R.; Theocharides, A.P.; Li, X.; Xia, Y.; Saito, H.; et al. IL-33 signaling contributes to the pathogenesis of myeloproliferative neoplasms. J. Clin. Investig. 2015, 125, 2579–2591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.Y.; Lim, S.C.; Kim, G.; Yun, H.J.; Ahn, S.G.; Choi, H.S. Interleukin-33/ST2 axis promotes epithelial cell transformation and breast tumorigenesis via upregulation of COT activity. Oncogene 2015, 34, 4928–4938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weerasinghe, P.; Buja, L.M. Oncosis: An important non-apoptotic mode of cell death. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2012, 93, 302–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsen, K.M.; Minaya, M.K.; Vaish, V.; Pena, M.M.O. The Role of IL-33/ST2 Pathway in Tumorigenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hu, W.T.; Li, M.Q.; Liu, W.; Jin, L.P.; Li, D.J.; Zhu, X.Y. IL-33 enhances proliferation and invasiveness of decidual stromal cells by up-regulation of CCL2/CCR2 via NF-kappaB and ERK1/2 signaling. Mol. Hum. Reprod. 2014, 20, 358–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shani, O.; Vorobyov, T.; Monteran, L.; Lavie, D.; Cohen, N.; Raz, Y.; Tsarfaty, G.; Avivi, C.; Barshack, I.; Erez, N. Fibroblast-Derived IL33 Facilitates Breast Cancer Metastasis by Modifying the Immune Microenvironment and Driving Type 2 Immunity. Cancer Res. 2020, 80, 5317–5329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lott, J.M.; Sumpter, T.L.; Turnquist, H.R. New dog and new tricks: Evolving roles for IL-33 in type 2 immunity. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2015, 97, 1037–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohning, M.; Stroehmann, A.; Coyle, A.J.; Grogan, J.L.; Lin, S.; Gutierrez-Ramos, J.C.; Levinson, D.; Radbruch, A.; Kamradt, T. T1/ST2 is preferentially expressed on murine Th2 cells, independent of interleukin 4, interleukin 5, and interleukin 10, and important for Th2 effector function. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 6930–6935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, L.; Wei, G.; Zhu, J.; Liao, W.; Leonard, W.J.; Zhao, K.; Paul, W. IL-1 family members and STAT activators induce cytokine production by Th2, Th17, and Th1 cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 13463–13468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moro, K.; Yamada, T.; Tanabe, M.; Takeuchi, T.; Ikawa, T.; Kawamoto, H.; Furusawa, J.; Ohtani, M.; Fujii, H.; Koyasu, S. Innate production of T(H)2 cytokines by adipose tissue-associated c-Kit(+)Sca-1(+) lymphoid cells. Nature 2010, 463, 540–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monticelli, L.A.; Osborne, L.C.; Noti, M.; Tran, S.V.; Zaiss, D.M.; Artis, D. IL-33 promotes an innate immune pathway of intestinal tissue protection dependent on amphiregulin-EGFR interactions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 10762–10767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lloyd, C.M. IL-33 family members and asthma—Bridging innate and adaptive immune responses. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2010, 22, 800–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Price, A.E.; Liang, H.E.; Sullivan, B.M.; Reinhardt, R.L.; Eisley, C.J.; Erle, D.J.; Locksley, R.M. Systemically dispersed innate IL-13-expressing cells in type 2 immunity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 11489–11494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Neill, D.R.; Wong, S.H.; Bellosi, A.; Flynn, R.J.; Daly, M.; Langford, T.K.; Bucks, C.; Kane, C.M.; Fallon, P.G.; Pannell, R.; et al. Nuocytes represent a new innate effector leukocyte that mediates type-2 immunity. Nature 2010, 464, 1367–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mjosberg, J.; Bernink, J.; Golebski, K.; Karrich, J.J.; Peters, C.P.; Blom, B.; te Velde, A.A.; Fokkens, W.J.; van Drunen, C.M.; Spits, H. The transcription factor GATA3 is essential for the function of human type 2 innate lymphoid cells. Immunity 2012, 37, 649–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yagi, R.; Zhong, C.; Northrup, D.L.; Yu, F.; Bouladoux, N.; Spencer, S.; Hu, G.; Barron, L.; Sharma, S.; Nakayama, T.; et al. The transcription factor GATA3 is critical for the development of all IL-7Ralpha-expressing innate lymphoid cells. Immunity 2014, 40, 378–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Spits, H.; Artis, D.; Colonna, M.; Diefenbach, A.; Di Santo, J.P.; Eberl, G.; Koyasu, S.; Locksley, R.M.; McKenzie, A.N.; Mebius, R.E.; et al. Innate lymphoid cells--a proposal for uniform nomenclature. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 13, 145–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eberl, G.; Di Santo, J.P.; Vivier, E. The brave new world of innate lymphoid cells. Nat. Immunol. 2015, 16, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burzyn, D.; Kuswanto, W.; Kolodin, D.; Shadrach, J.L.; Cerletti, M.; Jang, Y.; Sefik, E.; Tan, T.G.; Wagers, A.J.; Benoist, C.; et al. A special population of regulatory T cells potentiates muscle repair. Cell 2013, 155, 1282–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zaiss, D.M.W.; Gause, W.C.; Osborne, L.C.; Artis, D. Emerging functions of amphiregulin in orchestrating immunity, inflammation, and tissue repair. Immunity 2015, 42, 216–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Matta, B.M.; Lott, J.M.; Mathews, L.R.; Liu, Q.; Rosborough, B.R.; Blazar, B.R.; Turnquist, H.R. IL-33 is an unconventional Alarmin that stimulates IL-2 secretion by dendritic cells to selectively expand IL-33R/ST2+ regulatory T cells. J. Immunol. 2014, 193, 4010–4020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Turnquist, H.R.; Sumpter, T.L.; Tsung, A.; Zahorchak, A.F.; Nakao, A.; Nau, G.J.; Liew, F.Y.; Geller, D.A.; Thomson, A.W. IL-1beta-driven ST2L expression promotes maturation resistance in rapamycin-conditioned dendritic cells. J. Immunol. 2008, 181, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rank, M.A.; Kobayashi, T.; Kozaki, H.; Bartemes, K.R.; Squillace, D.L.; Kita, H. IL-33-activated dendritic cells induce an atypical TH2-type response. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2009, 123, 1047–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Turnquist, H.R.; Cardinal, J.; Macedo, C.; Rosborough, B.R.; Sumpter, T.L.; Geller, D.A.; Metes, D.; Thomson, A.W. mTOR and GSK-3 shape the CD4+ T-cell stimulatory and differentiation capacity of myeloid DCs after exposure to LPS. Blood 2010, 115, 4758–4769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morita, H.; Arae, K.; Unno, H.; Miyauchi, K.; Toyama, S.; Nambu, A.; Oboki, K.; Ohno, T.; Motomura, K.; Matsuda, A.; et al. An Interleukin-33-Mast Cell-Interleukin-2 Axis Suppresses Papain-Induced Allergic Inflammation by Promoting Regulatory T Cell Numbers. Immunity 2015, 43, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Galon, J.; Costes, A.; Sanchez-Cabo, F.; Kirilovsky, A.; Mlecnik, B.; Lagorce-Pages, C.; Tosolini, M.; Camus, M.; Berger, A.; Wind, P.; et al. Type, density, and location of immune cells within human colorectal tumors predict clinical outcome. Science 2006, 313, 1960–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, Y.; Ju, S.; Chen, E.; Dai, S.; Li, C.; Morel, P.; Liu, L.; Zhang, X.; Lu, B. T-bet and eomesodermin are required for T cell-mediated antitumor immune responses. J. Immunol. 2010, 185, 3174–3183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pastille, E.; Wasmer, M.H.; Adamczyk, A.; Vu, V.P.; Mager, L.F.; Phuong, N.N.T.; Palmieri, V.; Simillion, C.; Hansen, W.; Kasper, S.; et al. The IL-33/ST2 pathway shapes the regulatory T cell phenotype to promote intestinal cancer. Mucosal Immunol. 2019, 12, 990–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, A.; Herbst, R.H.; Canner, D.; Schenkel, J.M.; Smith, O.C.; Kim, J.Y.; Hillman, M.; Bhutkar, A.; Cuoco, M.S.; Rappazzo, C.G.; et al. IL-33 Signaling Alters Regulatory T Cell Diversity in Support of Tumor Development. Cell Rep. 2019, 29, 2998–3008.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hatzioannou, A.; Banos, A.; Sakelaropoulos, T.; Fedonidis, C.; Vidali, M.S.; Kohne, M.; Handler, K.; Boon, L.; Henriques, A.; Koliaraki, V.; et al. An intrinsic role of IL-33 in Treg cell-mediated tumor immunoevasion. Nat. Immunol. 2020, 21, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, J.; Cho, J.W.; Park, H.J.; Moon, J.; Park, S.; Lee, H.; Lee, J.; Kim, G.; Park, S.M.; Lira, S.A.; et al. Tumor-Infiltrating Regulatory T Cell Accumulation in the Tumor Microenvironment is Mediated by IL33/ST2 Signaling. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biton, J.; Khaleghparast Athari, S.; Thiolat, A.; Santinon, F.; Lemeiter, D.; Herve, R.; Delavallee, L.; Levescot, A.; Roga, S.; Decker, P.; et al. In Vivo Expansion of Activated Foxp3+ Regulatory T Cells and Establishment of a Type 2 Immune Response upon IL-33 Treatment Protect against Experimental Arthritis. J. Immunol. 2016, 197, 1708–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, Y.; Ji, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, H. IL-33 Promotes the Development of Colorectal Cancer Through Inducing Tumor-Infiltrating ST2L (+) Regulatory T Cells in Mice. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2018, 17, 1533033818780091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yue, Y.; Lian, J.; Wang, T.; Luo, C.; Yuan, Y.; Qin, G.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, Y. Interleukin-33-nuclear factor-kappaB-CCL2 signaling pathway promotes progression of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by directing regulatory T cells. Cancer Sci. 2020, 111, 795–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Shan, S.; Yang, Z.; Gu, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, C.; Ren, T. IL-33 blockade suppresses tumor growth of human lung cancer through direct and indirect pathways in a preclinical model. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 68571–68582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- O’Donnell, C.; Mahmoud, A.; Keane, J.; Murphy, C.; White, D.; Carey, S.; O’Riordain, M.; Bennett, M.W.; Brint, E.; Houston, A. An antitumorigenic role for the IL-33 receptor, ST2L, in colon cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2016, 114, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Y.; Andersson, P.; Hosaka, K.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, R.; Iwamoto, H.; Yang, X.; Nakamura, M.; Wang, J.; Zhuang, R.; et al. The PDGF-BB-SOX7 axis-modulated IL-33 in pericytes and stromal cells promotes metastasis through tumour-associated macrophages. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ariyoshi, W.; Okinaga, T.; Chaweewannakorn, W.; Akifusa, S.; Nisihara, T. Mechanisms involved in enhancement of matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression in macrophages by interleukin-33. J. Cell. Physiol. 2017, 232, 3481–3495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taniguchi, S.; Elhance, A.; Van Duzer, A.; Kumar, S.; Leitenberger, J.J.; Oshimori, N. Tumor-initiating cells establish an IL-33-TGF-beta niche signaling loop to promote cancer progression. Science 2020, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tcyganov, E.; Mastio, J.; Chen, E.; Gabrilovich, D.I. Plasticity of myeloid-derived suppressor cells in cancer. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2018, 51, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, P.; Wan, X.; Cui, B.; Liu, Y.; Qiu, C.; Rong, J.; Zheng, M.; Song, Y.; Chen, L.; He, J.; et al. Interleukin 33 in tumor microenvironment is crucial for the accumulation and function of myeloid-derived suppressor cells. Oncoimmunology 2016, 5, e1063772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lim, H.X.; Choi, S.; Cho, D.; Kim, T.S. IL-33 inhibits the differentiation and immunosuppressive activity of granulocytic myeloid-derived suppressor cells in tumor-bearing mice. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2017, 95, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Zhu, L.; Tao, Y.; Sun, H.X.; Li, Y.; Wang, P.; Hou, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, L.; et al. Characterization and allergic role of IL-33-induced neutrophil polarization. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2018, 15, 782–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Yi, P.; Yuan, D.M.K.; Jie, Z.; Kwota, Z.; Soong, L.; Cong, Y.; Sun, J. IL-33 induces immunosuppressive neutrophils via a type 2 innate lymphoid cell/IL-13/STAT6 axis and protects the liver against injury in LCMV infection-induced viral hepatitis. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2019, 16, 126–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guabiraba, R.; Besnard, A.G.; Menezes, G.B.; Secher, T.; Jabir, M.S.; Amaral, S.S.; Braun, H.; Lima-Junior, R.C.; Ribeiro, R.A.; Cunha, F.Q.; et al. IL-33 targeting attenuates intestinal mucositis and enhances effective tumor chemotherapy in mice. Mucosal Immunol. 2014, 7, 1079–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Galdiero, M.R.; Varricchi, G.; Seaf, M.; Marone, G.; Levi-Schaffer, F.; Marone, G. Bidirectional Mast Cell-Eosinophil Interactions in Inflammatory Disorders and Cancer. Front. Med. 2017, 4, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sammarco, G.; Varricchi, G.; Ferraro, V.; Ammendola, M.; De Fazio, M.; Altomare, D.F.; Luposella, M.; Maltese, L.; Curro, G.; Marone, G.; et al. Mast Cells, Angiogenesis and Lymphangiogenesis in Human Gastric Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iikura, M.; Suto, H.; Kajiwara, N.; Oboki, K.; Ohno, T.; Okayama, Y.; Saito, H.; Galli, S.J.; Nakae, S. IL-33 can promote survival, adhesion and cytokine production in human mast cells. Lab. Invest. 2007, 87, 971–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Silver, M.R.; Margulis, A.; Wood, N.; Goldman, S.J.; Kasaian, M.; Chaudhary, D. IL-33 synergizes with IgE-dependent and IgE-independent agents to promote mast cell and basophil activation. Inflamm. Res. 2010, 59, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theoharides, T.C.; Zhang, B.; Kempuraj, D.; Tagen, M.; Vasiadi, M.; Angelidou, A.; Alysandratos, K.D.; Kalogeromitros, D.; Asadi, S.; Stavrianeas, N.; et al. IL-33 augments substance P-induced VEGF secretion from human mast cells and is increased in psoriatic skin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 4448–4453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Marone, G.; Varricchi, G.; Loffredo, S.; Granata, F. Mast cells and basophils in inflammatory and tumor angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 778, 146–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrne, S.N.; Beaugie, C.; O’Sullivan, C.; Leighton, S.; Halliday, G.M. The immune-modulating cytokine and endogenous Alarmin interleukin-33 is upregulated in skin exposed to inflammatory UVB radiation. Am. J. Pathol. 2011, 179, 211–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mertz, K.D.; Mager, L.F.; Wasmer, M.H.; Thiesler, T.; Koelzer, V.H.; Ruzzante, G.; Joller, S.; Murdoch, J.R.; Brummendorf, T.; Genitsch, V.; et al. The IL-33/ST2 pathway contributes to intestinal tumorigenesis in humans and mice. Oncoimmunology 2016, 5, e1062966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gounaris, E.; Erdman, S.E.; Restaino, C.; Gurish, M.F.; Friend, D.S.; Gounari, F.; Lee, D.M.; Zhang, G.; Glickman, J.N.; Shin, K.; et al. Mast cells are an essential hematopoietic component for polyp development. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 19977–19982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Blatner, N.R.; Bonertz, A.; Beckhove, P.; Cheon, E.C.; Krantz, S.B.; Strouch, M.; Weitz, J.; Koch, M.; Halverson, A.L.; Bentrem, D.J.; et al. In colorectal cancer mast cells contribute to systemic regulatory T-cell dysfunction. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 6430–6435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cheon, E.C.; Khazaie, K.; Khan, M.W.; Strouch, M.J.; Krantz, S.B.; Phillips, J.; Blatner, N.R.; Hix, L.M.; Zhang, M.; Dennis, K.L.; et al. Mast cell 5-lipoxygenase activity promotes intestinal polyposis in APCDelta468 mice. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 1627–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Varricchi, G.; Galdiero, M.R.; Loffredo, S.; Marone, G.; Iannone, R.; Marone, G.; Granata, F. Are Mast Cells MASTers in Cancer? Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mjosberg, J.M.; Trifari, S.; Crellin, N.K.; Peters, C.P.; van Drunen, C.M.; Piet, B.; Fokkens, W.J.; Cupedo, T.; Spits, H. Human IL-25- and IL-33-responsive type 2 innate lymphoid cells are defined by expression of CRTH2 and CD161. Nat. Immunol. 2011, 12, 1055–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, B.S.; Siracusa, M.C.; Saenz, S.A.; Noti, M.; Monticelli, L.A.; Sonnenberg, G.F.; Hepworth, M.R.; Van Voorhees, A.S.; Comeau, M.R.; Artis, D. TSLP elicits IL-33-independent innate lymphoid cell responses to promote skin inflammation. Sci. Transl. Med. 2013, 5, 170ra16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, Y.; Guo, L.; Qiu, J.; Chen, X.; Hu-Li, J.; Siebenlist, U.; Williamson, P.R.; Urban, J.F., Jr.; Paul, W.E. IL-25-responsive, lineage-negative KLRG1(hi) cells are multipotential ‘inflammatory’ type 2 innate lymphoid cells. Nat. Immunol. 2015, 16, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Flamar, A.L.; Klose, C.S.N.; Moeller, J.B.; Mahlakoiv, T.; Bessman, N.J.; Zhang, W.; Moriyama, S.; Stokic-Trtica, V.; Rankin, L.C.; Putzel, G.G.; et al. Interleukin-33 Induces the Enzyme Tryptophan Hydroxylase 1 to Promote Inflammatory Group 2 Innate Lymphoid Cell-Mediated Immunity. Immunity 2020, 52, 606–619.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dancescu, M.; Rubio-Trujillo, M.; Biron, G.; Bron, D.; Delespesse, G.; Sarfati, M. Interleukin 4 protects chronic lymphocytic leukemic B cells from death by apoptosis and upregulates Bcl-2 expression. J. Exp. Med. 1992, 176, 1319–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bie, Q.; Zhang, P.; Su, Z.; Zheng, D.; Ying, X.; Wu, Y.; Yang, H.; Chen, D.; Wang, S.; Xu, H. Polarization of ILC2s in peripheral blood might contribute to immunosuppressive microenvironment in patients with gastric cancer. J. Immunol. Res. 2014, 2014, 923135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaiss, D.M.; van Loosdregt, J.; Gorlani, A.; Bekker, C.P.; Grone, A.; Sibilia, M.; van Bergen en Henegouwen, P.M.; Roovers, R.C.; Coffer, P.J.; Sijts, A.J. Amphiregulin enhances regulatory T cell-suppressive function via the epidermal growth factor receptor. Immunity 2013, 38, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Long, A.; Dominguez, D.; Qin, L.; Chen, S.; Fan, J.; Zhang, M.; Fang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Kuzel, T.M.; Zhang, B. Type 2 Innate Lymphoid Cells Impede IL-33-Mediated Tumor Suppression. J. Immunol. 2018, 201, 3456–3464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moral, J.A.; Leung, J.; Rojas, L.A.; Ruan, J.; Zhao, J.; Sethna, Z.; Ramnarain, A.; Gasmi, B.; Gururajan, M.; Redmond, D.; et al. ILC2s amplify PD-1 blockade by activating tissue-specific cancer immunity. Nature 2020, 579, 130–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikutani, M.; Yanagibashi, T.; Ogasawara, M.; Tsuneyama, K.; Yamamoto, S.; Hattori, Y.; Kouro, T.; Itakura, A.; Nagai, Y.; Takaki, S.; et al. Identification of innate IL-5-producing cells and their role in lung eosinophil regulation and antitumor immunity. J. Immunol. 2012, 188, 703–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wagner, M.; Ealey, K.N.; Tetsu, H.; Kiniwa, T.; Motomura, Y.; Moro, K.; Koyasu, S. Tumor-Derived Lactic Acid Contributes to the Paucity of Intratumoral ILC2s. Cell Rep. 2020, 30, 2743–2757.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Katkoori, V.R.; Shanmugam, C.; Jia, X.; Vitta, S.P.; Sthanam, M.; Callens, T.; Messiaen, L.; Chen, D.; Zhang, B.; Bumpers, H.L.; et al. Prognostic significance and gene expression profiles of p53 mutations in microsatellite-stable stage III colorectal adenocarcinomas. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e30020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Musolino, C.; Allegra, A.; Profita, M.; Alonci, A.; Saitta, S.; Russo, S.; Bonanno, A.; Innao, V.; Gangemi, S. Reduced IL-33 plasma levels in multiple myeloma patients are associated with more advanced stage of disease. Br. J. Haematol. 2013, 160, 709–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.S.; Kim, E.; Heo, J.S.; Bae, D.J.; Lee, J.U.; Lee, T.H.; Lee, H.J.; Chang, H.S.; Park, J.S.; Jang, A.S.; et al. Circulating IL-33 level is associated with the progression of lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2015, 90, 346–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourgeois, E.; Van, L.P.; Samson, M.; Diem, S.; Barra, A.; Roga, S.; Gombert, J.M.; Schneider, E.; Dy, M.; Gourdy, P.; et al. The pro-Th2 cytokine IL-33 directly interacts with invariant NKT and NK cells to induce IFN-gamma production. Eur. J. Immunol. 2009, 39, 1046–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smithgall, M.D.; Comeau, M.R.; Yoon, B.R.; Kaufman, D.; Armitage, R.; Smith, D.E. IL-33 amplifies both Th1- and Th2-type responses through its activity on human basophils, allergen-reactive Th2 cells, iNKT and NK cells. Int. Immunol. 2008, 20, 1019–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Q.; Li, G.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, L.; Chen, E.; Turnquist, H.; Zhang, X.; Finn, O.J.; Chen, X.; Lu, B. IL-33 synergizes with TCR and IL-12 signaling to promote the effector function of CD8+ T cells. Eur. J. Immunol. 2011, 41, 3351–3360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ngoi, S.M.; St Rose, M.C.; Menoret, A.M.; Smith, D.E.; Tovey, M.G.; Adler, A.J.; Vella, A.T. Presensitizing with a Toll-like receptor 3 ligand impairs CD8 T-cell effector differentiation and IL-33 responsiveness. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 10486–10491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bonilla, W.V.; Frohlich, A.; Senn, K.; Kallert, S.; Fernandez, M.; Johnson, S.; Kreutzfeldt, M.; Hegazy, A.N.; Schrick, C.; Fallon, P.G.; et al. The alarmin interleukin-33 drives protective antiviral CD8(+) T cell responses. Science 2012, 335, 984–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichenbach, D.K.; Schwarze, V.; Matta, B.M.; Tkachev, V.; Lieberknecht, E.; Liu, Q.; Koehn, B.H.; Pfeifer, D.; Taylor, P.A.; Prinz, G.; et al. The IL-33/ST2 axis augments effector T-cell responses during acute GVHD. Blood 2015, 125, 3183–3192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baumann, C.; Bonilla, W.V.; Frohlich, A.; Helmstetter, C.; Peine, M.; Hegazy, A.N.; Pinschewer, D.D.; Lohning, M. T-bet- and STAT4-dependent IL-33 receptor expression directly promotes antiviral Th1 cell responses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 4056–4061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xia, Y.; Ohno, T.; Nishii, N.; Bhingare, A.; Tachinami, H.; Kashima, Y.; Nagai, S.; Saito, H.; Nakae, S.; Azuma, M. Endogenous IL-33 exerts CD8(+) T cell antitumor responses overcoming pro-tumor effects by regulatory T cells in a colon carcinoma model. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2019, 518, 331–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, P.; Deng, S.; Ye, H.; Yu, X.; Deng, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, L.; Li, J.; Yu, Y.; Han, W. The IL-33/ST2 pathway suppresses murine colon cancer growth and metastasis by upregulating CD40 L signaling. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 127, 110232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Z.; Lei, L.; Lin, D.; Liu, Y.; Song, Y.; Gong, H.; Zhu, Y.; Mei, Y.; Hu, B.; Wu, Y.; et al. IL-33 Released in the Liver Inhibits Tumor Growth via Promotion of CD4(+) and CD8(+) T Cell Responses in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Immunol. 2018, 201, 3770–3779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Komai-Koma, M.; Wang, E.; Kurowska-Stolarska, M.; Li, D.; McSharry, C.; Xu, D. Interleukin-33 promoting Th1 lymphocyte differentiation dependents on IL-12. Immunobiology 2016, 221, 412–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kearley, J.; Silver, J.S.; Sanden, C.; Liu, Z.; Berlin, A.A.; White, N.; Mori, M.; Pham, T.H.; Ward, C.K.; Criner, G.J.; et al. Cigarette smoke silences innate lymphoid cell function and facilitates an exacerbated type I interleukin-33-dependent response to infection. Immunity 2015, 42, 566–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rivera Vargas, T.; Humblin, E.; Vegran, F.; Ghiringhelli, F.; Apetoh, L. TH9 cells in anti-tumor immunity. Semin. Immunopathol. 2017, 39, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liang, Y.; Jie, Z.; Hou, L.; Yi, P.; Wang, W.; Kwota, Z.; Salvato, M.; de Waal Malefyt, R.; Soong, L.; Sun, J. IL-33 promotes innate IFN-gamma production and modulates dendritic cell response in LCMV-induced hepatitis in mice. Eur. J. Immunol. 2015, 45, 3052–3063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabekura, T.; Girard, J.P.; Lanier, L.L. IL-33 receptor ST2 amplifies the expansion of NK cells and enhances host defense during mouse cytomegalovirus infection. J. Immunol. 2015, 194, 5948–5952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qi, L.; Zhang, Q.; Miao, Y.; Kang, W.; Tian, Z.; Xu, D.; Xiao, W.; Fang, F. Interleukin-33 activates and recruits natural killer cells to inhibit pulmonary metastatic cancer development. Int. J. Cancer 2020, 146, 1421–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabriele, L.; Schiavoni, G.; Mattei, F.; Sanchez, M.; Sestili, P.; Butteroni, C.; Businaro, R.; Mirchandani, A.; Niedbala, W.; Liew, F.Y.; et al. Novel allergic asthma model demonstrates ST2-dependent dendritic cell targeting by cypress pollen. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2013, 132, 686–695.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Besnard, A.G.; Togbe, D.; Guillou, N.; Erard, F.; Quesniaux, V.; Ryffel, B. IL-33-activated dendritic cells are critical for allergic airway inflammation. Eur. J. Immunol. 2011, 41, 1675–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurokawa, M.; Matsukura, S.; Kawaguchi, M.; Ieki, K.; Suzuki, S.; Watanabe, S.; Homma, T.; Yamaguchi, M.; Takeuchi, H.; Adachi, M. Interleukin-33-activated dendritic cells induce the production of thymus and activation-regulated chemokine and macrophage-derived chemokine. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2013, 161, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayuzumi, N.; Matsushima, H.; Takashima, A. IL-33 promotes DC development in BM culture by triggering GM-CSF production. Eur. J. Immunol. 2009, 39, 3331–3342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Z.; Lin, J.; Lu, F.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, L.; Gandhi, N.B.; de Paiva, C.S.; Pflugfelder, S.C.; Li, D.Q. Potential autocrine regulation of interleukin-33/ST2 signaling of dendritic cells in allergic inflammation. Mucosal Immunol. 2013, 6, 921–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, L.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, J.; Xu, Y.; Xie, Y.; Yang, Z.P. IL33 activates CD8+T and NK cells through MyD88 pathway to suppress the lung cancer cell growth in mice. Biotechnol. Lett. 2020, 42, 1113–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varricchi, G.; Galdiero, M.R.; Loffredo, S.; Lucarini, V.; Marone, G.; Mattei, F.; Marone, G.; Schiavoni, G. Eosinophils: The unsung heroes in cancer? Oncoimmunology 2018, 7, e1393134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Simson, L.; Ellyard, J.I.; Dent, L.A.; Matthaei, K.I.; Rothenberg, M.E.; Foster, P.S.; Smyth, M.J.; Parish, C.R. Regulation of carcinogenesis by IL-5 and CCL11: A potential role for eosinophils in tumor immune surveillance. J. Immunol. 2007, 178, 4222–4229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Johansson, K.; Malmhall, C.; Ramos-Ramirez, P.; Radinger, M. Bone marrow type 2 innate lymphoid cells: A local source of interleukin-5 in interleukin-33-driven eosinophilia. Immunology 2018, 153, 268–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreone, S.; Spadaro, F.; Buccione, C.; Mancini, J.; Tinari, A.; Sestili, P.; Gambardella, A.R.; Lucarini, V.; Ziccheddu, G.; Parolini, I.; et al. IL-33 Promotes CD11b/CD18-Mediated Adhesion of Eosinophils to Cancer Cells and Synapse-Polarized Degranulation Leading to Tumor Cell Killing. Cancers 2019, 11, 1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kienzl, M.; Hasenoehrl, C.; Valadez-Cosmes, P.; Maitz, K.; Sarsembayeva, A.; Sturm, E.; Heinemann, A.; Kargl, J.; Schicho, R. IL-33 reduces tumor growth in models of colorectal cancer with the help of eosinophils. Oncoimmunology 2020, 9, 1776059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondo, Y.; Yoshimoto, T.; Yasuda, K.; Futatsugi-Yumikura, S.; Morimoto, M.; Hayashi, N.; Hoshino, T.; Fujimoto, J.; Nakanishi, K. Administration of IL-33 induces airway hyperresponsiveness and goblet cell hyperplasia in the lungs in the absence of adaptive immune system. Int. Immunol. 2008, 20, 791–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Willebrand, R.; Voehringer, D. IL-33-Induced Cytokine Secretion and Survival of Mouse Eosinophils Is Promoted by Autocrine GM-CSF. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0163751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hollande, C.; Boussier, J.; Ziai, J.; Nozawa, T.; Bondet, V.; Phung, W.; Lu, B.; Duffy, D.; Paradis, V.; Mallet, V.; et al. Inhibition of the dipeptidyl peptidase DPP4 (CD26) reveals IL-33-dependent eosinophil-mediated control of tumor growth. Nat. Immunol. 2019, 20, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carretero, R.; Sektioglu, I.M.; Garbi, N.; Salgado, O.C.; Beckhove, P.; Hammerling, G.J. Eosinophils orchestrate cancer rejection by normalizing tumor vessels and enhancing infiltration of CD8(+) T cells. Nat. Immunol. 2015, 16, 609–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Legrand, F.; Driss, V.; Delbeke, M.; Loiseau, S.; Hermann, E.; Dombrowicz, D.; Capron, M. Human eosinophils exert TNF-alpha and granzyme A-mediated tumoricidal activity toward colon carcinoma cells. J. Immunol. 2010, 185, 7443–7451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Legrand, F.; Tomasevic, N.; Simakova, O.; Lee, C.C.; Wang, Z.; Raffeld, M.; Makiya, M.A.; Palath, V.; Leung, J.; Baer, M.; et al. The eosinophil surface receptor epidermal growth factor-like module containing mucin-like hormone receptor 1 (EMR1): A novel therapeutic target for eosinophilic disorders. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2014, 133, 1439–1447.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suzukawa, M.; Iikura, M.; Koketsu, R.; Nagase, H.; Tamura, C.; Komiya, A.; Nakae, S.; Matsushima, K.; Ohta, K.; Yamamoto, K.; et al. An IL-1 cytokine member, IL-33, induces human basophil activation via its ST2 receptor. J. Immunol. 2008, 181, 5981–5989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pecaric-Petkovic, T.; Didichenko, S.A.; Kaempfer, S.; Spiegl, N.; Dahinden, C.A. Human basophils and eosinophils are the direct target leukocytes of the novel IL-1 family member IL-33. Blood 2009, 113, 1526–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rivellese, F.; Suurmond, J.; de Paulis, A.; Marone, G.; Huizinga, T.W.; Toes, R.E. IgE and IL-33-mediated triggering of human basophils inhibits TLR4-induced monocyte activation. Eur. J. Immunol. 2014, 44, 3045–3055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blom, L.; Poulsen, B.C.; Jensen, B.M.; Hansen, A.; Poulsen, L.K. IL-33 induces IL-9 production in human CD4+ T cells and basophils. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e21695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wan, J.; Wu, Y.; Ji, X.; Huang, L.; Cai, W.; Su, Z.; Wang, S.; Xu, H. IL-9 and IL-9-producing cells in tumor immunity. Cell Commun. Signal. 2020, 18, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sektioglu, I.M.; Carretero, R.; Bulbuc, N.; Bald, T.; Tuting, T.; Rudensky, A.Y.; Hammerling, G.J. Basophils Promote Tumor Rejection via Chemotaxis and Infiltration of CD8+ T Cells. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 291–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wei, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, G.; Zhou, Y.; Luo, M.; Wang, S.; Hong, C. The impacts of pretreatment circulating eosinophils and basophils on prognosis of stage—Colorectal cancer. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 14, e243–e251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marone, G.; Gambardella, A.R.; Mattei, F.; Mancini, J.; Schiavoni, G.; Varricchi, G. Basophils in Tumor Microenvironment and Surroundings. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2020, 1224, 21–34. [Google Scholar]
- Marone, G.; Schroeder, J.T.; Mattei, F.; Loffredo, S.; Gambardella, A.R.; Poto, R.; de Paulis, A.; Schiavoni, G.; Varricchi, G. Is There a Role for Basophils in Cancer? Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Zhao, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Gao, S.; Wang, Y.; Wang, D.; Wang, A.; Yi, H.; Gu, R.; Yi, Q.; et al. Interleukin-33 Contributes to the Induction of Th9 Cells and Antitumor Efficacy by Dectin-1-Activated Dendritic Cells. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Taylor, S.; Huang, Y.; Mallett, G.; Stathopoulou, C.; Felizardo, T.C.; Sun, M.A.; Martin, E.L.; Zhu, N.; Woodward, E.L.; Elias, M.S.; et al. PD-1 regulates KLRG1(+) group 2 innate lymphoid cells. J. Exp. Med. 2017, 214, 1663–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oldenhove, G.; Boucquey, E.; Taquin, A.; Acolty, V.; Bonetti, L.; Ryffel, B.; Le Bert, M.; Englebert, K.; Boon, L.; Moser, M. PD-1 Is Involved in the Dysregulation of Type 2 Innate Lymphoid Cells in a Murine Model of Obesity. Cell Rep. 2018, 25, 2053–2060.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, L.; Sun, R.; Xu, J.; Zhai, W.; Zhang, D.; Yang, M.; Yue, C.; Chen, Y.; Li, S.; Turnquist, H.; et al. Tumor-Derived IL33 Promotes Tissue-Resident CD8(+) T Cells and Is Required for Checkpoint Blockade Tumor Immunotherapy. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2020, 8, 1381–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keilholz, U. CTLA-4: Negative regulator of the immune response and a target for cancer therapy. J. Immunother. 2008, 31, 431–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jevtovic, A.; Pantic, J.; Jovanovic, I.; Milovanovic, M.; Stanojevic, I.; Vojvodic, D.; Arsenijevic, N.; Lukic, M.L.; Radosavljevic, G.D. Interleukin-33 pretreatment promotes metastatic growth of murine melanoma by reducing the cytotoxic capacity of CD8(+) T cells and enhancing regulatory T cells. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2020, 69, 1461–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buder-Bakhaya, K.; Hassel, J.C. Biomarkers for Clinical Benefit of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Treatment-A Review From the Melanoma Perspective and Beyond. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, S.C.S.; Hu, X.; Panten, J.; Grees, M.; Renders, S.; Thomas, D.; Weber, R.; Schulze, T.J.; Utikal, J.; Umansky, V. Eosinophil accumulation predicts response to melanoma treatment with immune checkpoint inhibitors. Oncoimmunology 2020, 9, 1727116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kallert, S.M.; Darbre, S.; Bonilla, W.V.; Kreutzfeldt, M.; Page, N.; Muller, P.; Kreuzaler, M.; Lu, M.; Favre, S.; Kreppel, F.; et al. Replicating viral vector platform exploits alarmin signals for potent CD8(+) T cell-mediated tumour immunotherapy. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Jiang, Y.; Chen, J.; Nan, H.; Zhao, Y.; Chu, X.; Wang, A.; Wang, D.; Qin, T.; Gao, S.; et al. IL-33 drives the antitumor effects of dendritic cells via the induction of Tc9 cells. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2019, 16, 644–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudo-Saito, C.; Miyamoto, T.; Imazeki, H.; Shoji, H.; Aoki, K.; Boku, N. IL33 Is a Key Driver of Treatment Resistance of Cancer. Cancer Res. 2020, 80, 1981–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Van der Jeught, K.; Sun, Y.; Fang, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Jiang, H.; Yu, T.; Yang, J.; Kamocka, M.M.; So, K.M.; Li, Y.; et al. ST2 as checkpoint target for colorectal cancer immunotherapy. JCI Insight 2020, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, R.N.; Riba, R.D.; Zacharoulis, S.; Bramley, A.H.; Vincent, L.; Costa, C.; MacDonald, D.D.; Jin, D.K.; Shido, K.; Kerns, S.A.; et al. VEGFR1-positive haematopoietic bone marrow progenitors initiate the pre-metastatic niche. Nature 2005, 438, 820–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andtbacka, R.H.; Kaufman, H.L.; Collichio, F.; Amatruda, T.; Senzer, N.; Chesney, J.; Delman, K.A.; Spitler, L.E.; Puzanov, I.; Agarwala, S.S.; et al. Talimogene Laherparepvec Improves Durable Response Rate in Patients with Advanced Melanoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 2780–2788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerkar, S.P.; Muranski, P.; Kaiser, A.; Boni, A.; Sanchez-Perez, L.; Yu, Z.; Palmer, D.C.; Reger, R.N.; Borman, Z.A.; Zhang, L.; et al. Tumor-specific CD8+ T cells expressing interleukin-12 eradicate established cancers in lymphodepleted hosts. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 6725–6734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schrama, D.; Reisfeld, R.A.; Becker, J.C. Antibody targeted drugs as cancer therapeutics. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2006, 5, 147–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Role | Mechanism of Action of IL-33/ST2 | Cancer Type (H, Human) (M, Mouse) | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pro-tumorigenic | Immune cell-independent | ||
| -Promote tumor angiogenesis. | CRC (H/M) | [13] | |
| -Induce cancer cell stemness via activation of JNK or NF-kB pathway. | Breast (H/M) CRC (H/M) | [14,15] | |
| -Promote EMT and tumor cell proliferation, invasion, and metastasis by elevating MMP2/9 and other inflammatory cytokines (e.g., IL-6 and IL-17) and/or soluble mediators (e.g., COX2/PGE). | Breast (H) CCA (H/M) CRC (H/M) Lung (H/M) | [13,16,17,18,19,20,21] | |
| -Mediate CAF-induced tumor invasiveness and metastasis. | CRC (H/M) HNSCC (H) OSCC (H/M) Pancreatic (H/M) | [22,23,24,25] | |
| Immune cell-dependent | |||
| -Favor recruitment and inhibitory activities of immunosuppressive myeloid cells (e.g., TAM, MDSCs, and neutrophils), Tregs, and ILC2s. | Breast (H/M) CRC (H/M) | [13,15,16,26,27,28] | |
| Anti-tumorigenic | Immune cell-independent | ||
| -Inhibit cancer cell growth by downregulation of proteins involved in cellular proliferation and by upregulation of pro-apoptotic molecules. | Colon (H) Pancreatic (H) | [29,30] | |
| Immune cell-dependent | |||
| -Promote the MHC-I and IFN-γ-mediated immune surveillance. | Breast (M) Cervical (H) Colon (M) Lung (M) Prostate (H/M) | [31,32,33,34,35] | |
| -Inhibit tumorigenesis via modulation of B cell-produced IgA, IL-1α, and the microbiota. | CAC (M) | [36] | |
| -Inhibit tumor cell propagation and metastasis via the cooperation of Th1, CD8+ T cells, NK, DCs, and eosinophils. | AML (M) Breast (M) Lung (M) Lymphoma (H/M) Melanoma (M) Prostate (H/M) | [32,34,35,37,38,39,40,41,42] | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Choi, M.-R.; Sosman, J.A.; Zhang, B. The Janus Face of IL-33 Signaling in Tumor Development and Immune Escape. Cancers 2021, 13, 3281. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13133281
Choi M-R, Sosman JA, Zhang B. The Janus Face of IL-33 Signaling in Tumor Development and Immune Escape. Cancers. 2021; 13(13):3281. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13133281
Chicago/Turabian StyleChoi, Mi-Ran, Jeffrey A. Sosman, and Bin Zhang. 2021. "The Janus Face of IL-33 Signaling in Tumor Development and Immune Escape" Cancers 13, no. 13: 3281. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13133281
APA StyleChoi, M.-R., Sosman, J. A., & Zhang, B. (2021). The Janus Face of IL-33 Signaling in Tumor Development and Immune Escape. Cancers, 13(13), 3281. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13133281





