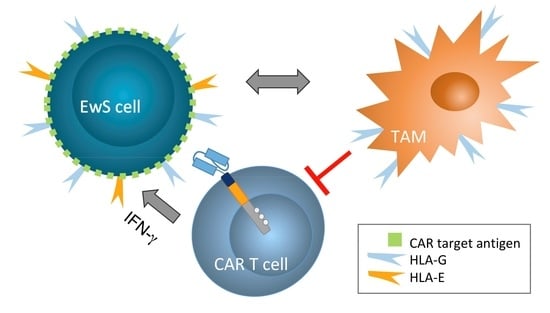
HLA-G and HLA-E Immune Checkpoints Are Widely Expressed in Ewing Sarcoma but Have Limited Functional Impact on the Effector Functions of Antigen-Specific CAR T Cells
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
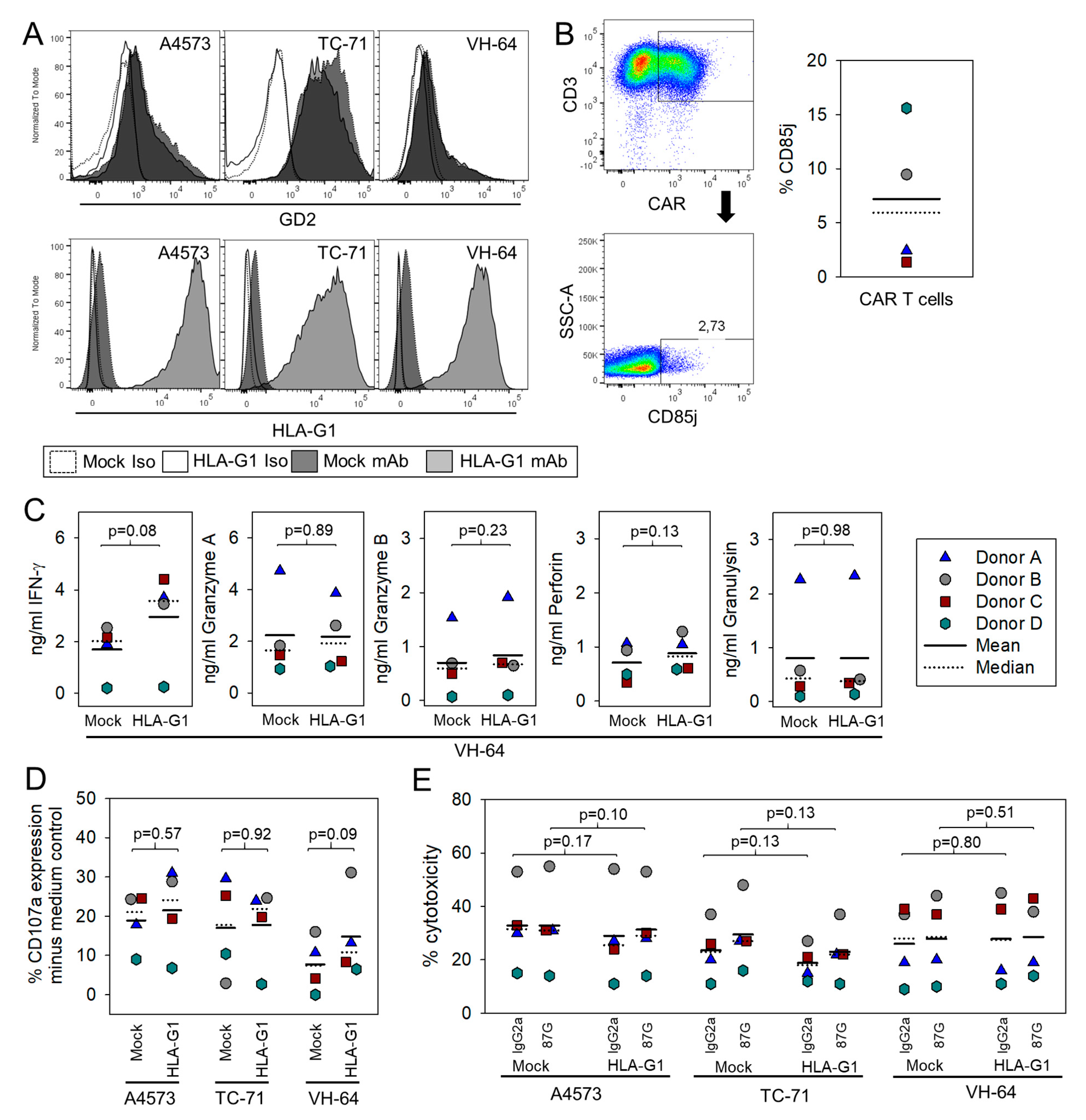
3.1. IFN-γ Cytokine Stimulated EwS Cells Express HLA-G Isoform HLA-G1
3.2. HLA-G Expression on EwS Cells Does Not Directly Impair Cytolysis by GD2-Specific CART
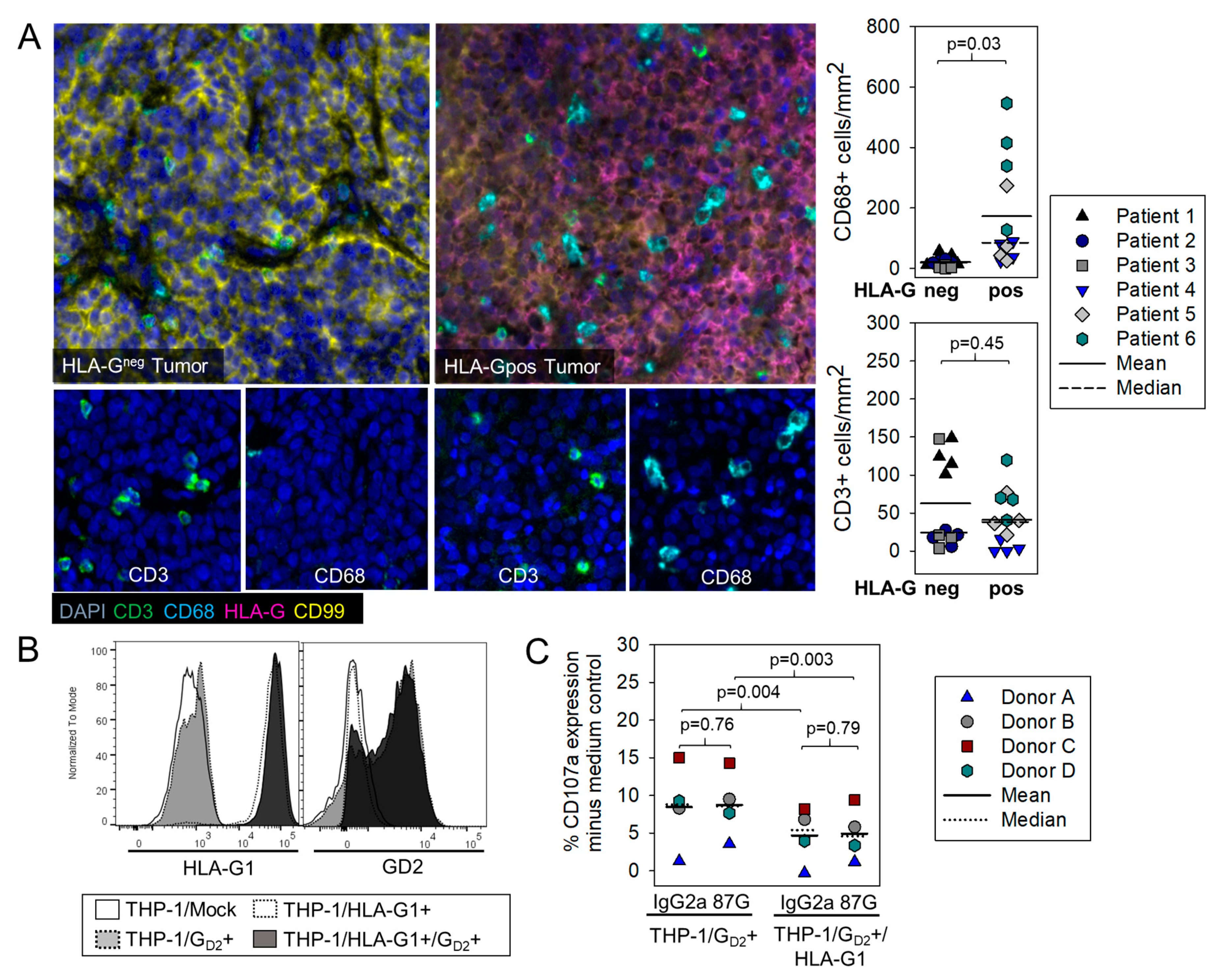
3.3. HLA-G Expression on Myeloid Bystander Cells Reduces the Degranulation Response of GD2-Specific CART
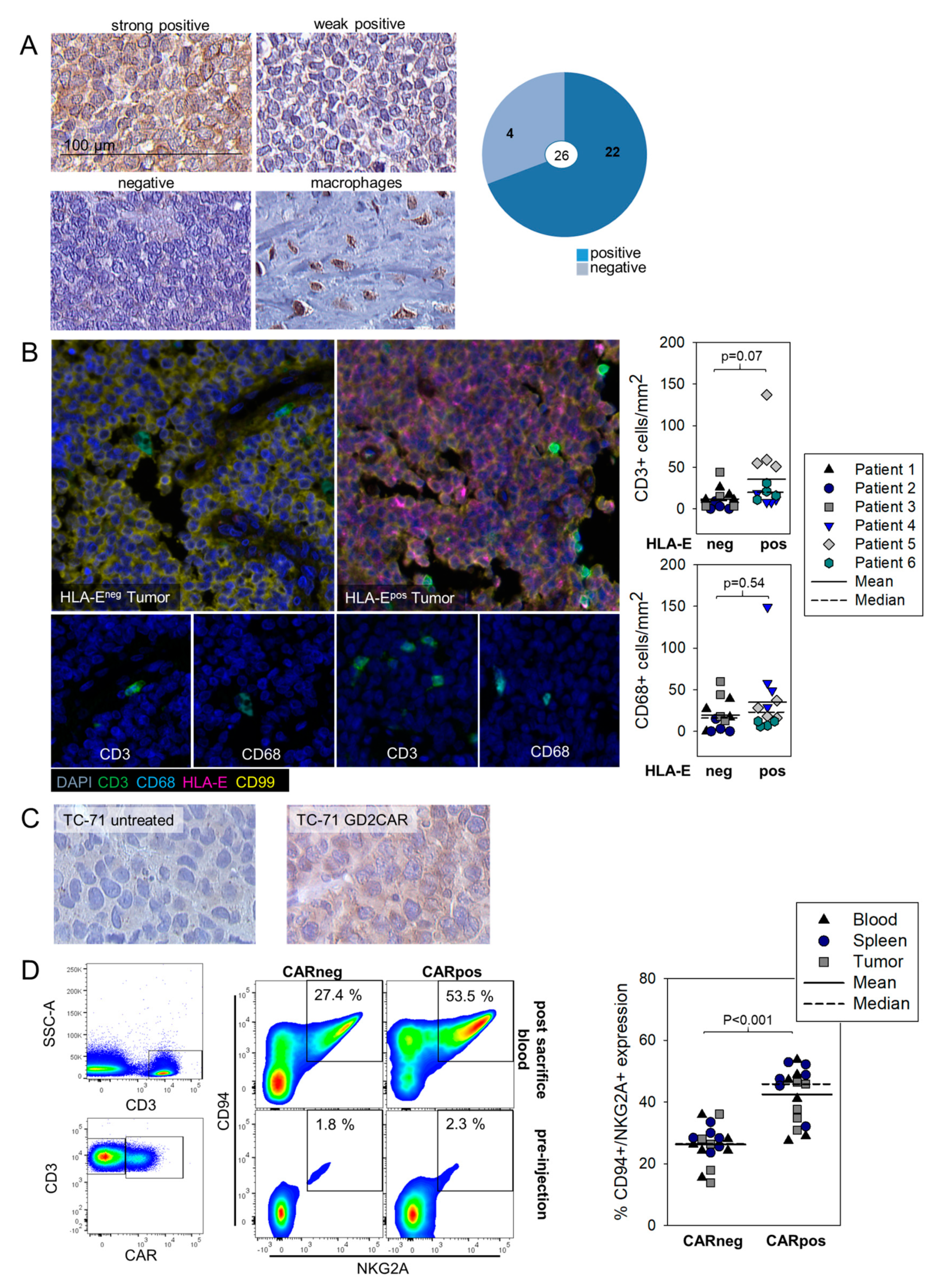
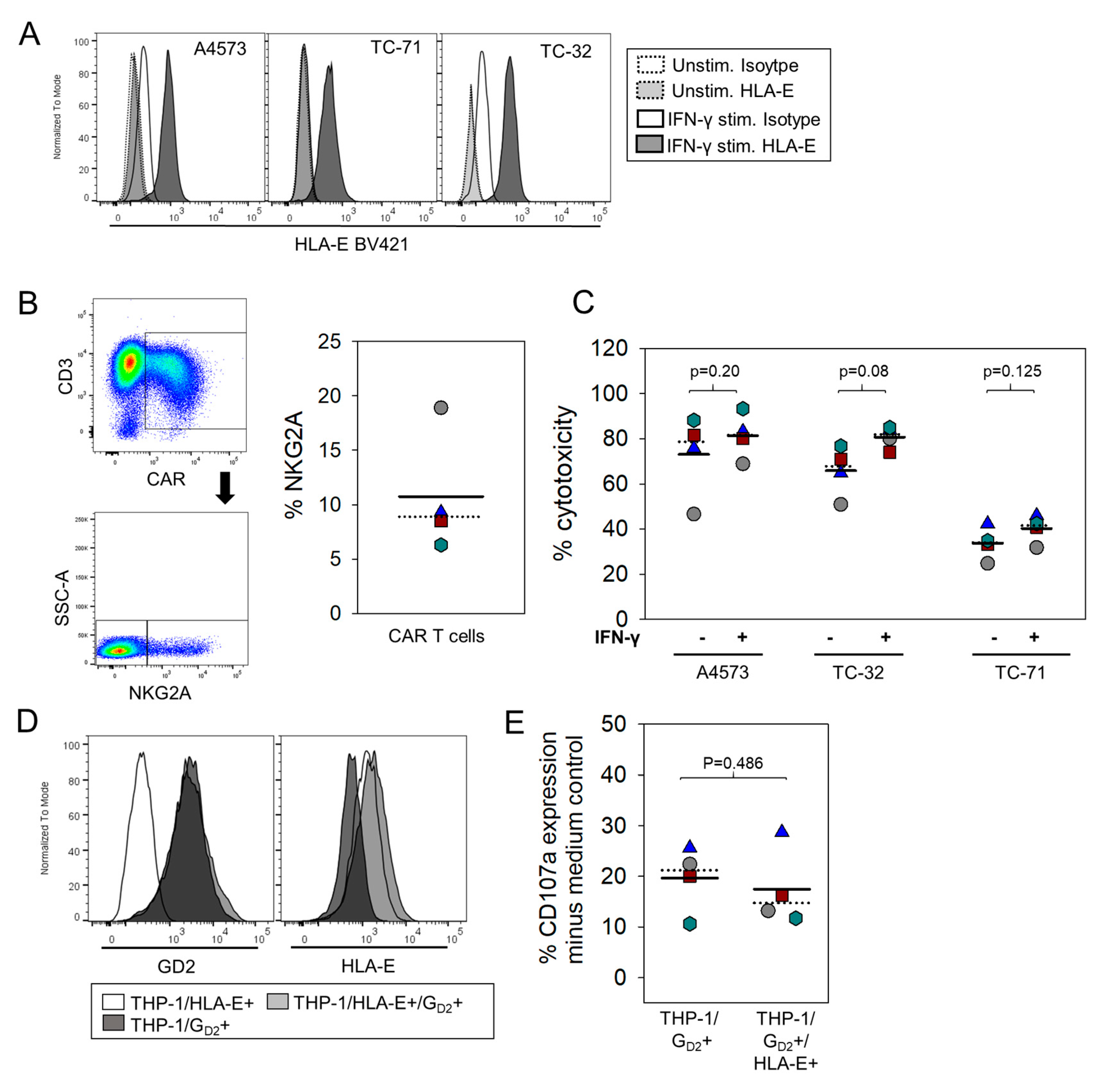
3.4. HLA-E Is Expressed in EwS and Associated with Infiltrating T Cells Both in Human Pretherapeutic Biopsies and in Murine EwS Xenografts Treated with GD2.BBζ CART In Vivo, and CART Recovered from Treated Mice Express the HLA-E Receptor NKG2A
3.5. HLA-E Does Not Impair Degranulation Responses against EwS Cells or Myeloid Cells by GD2-Specific CART
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
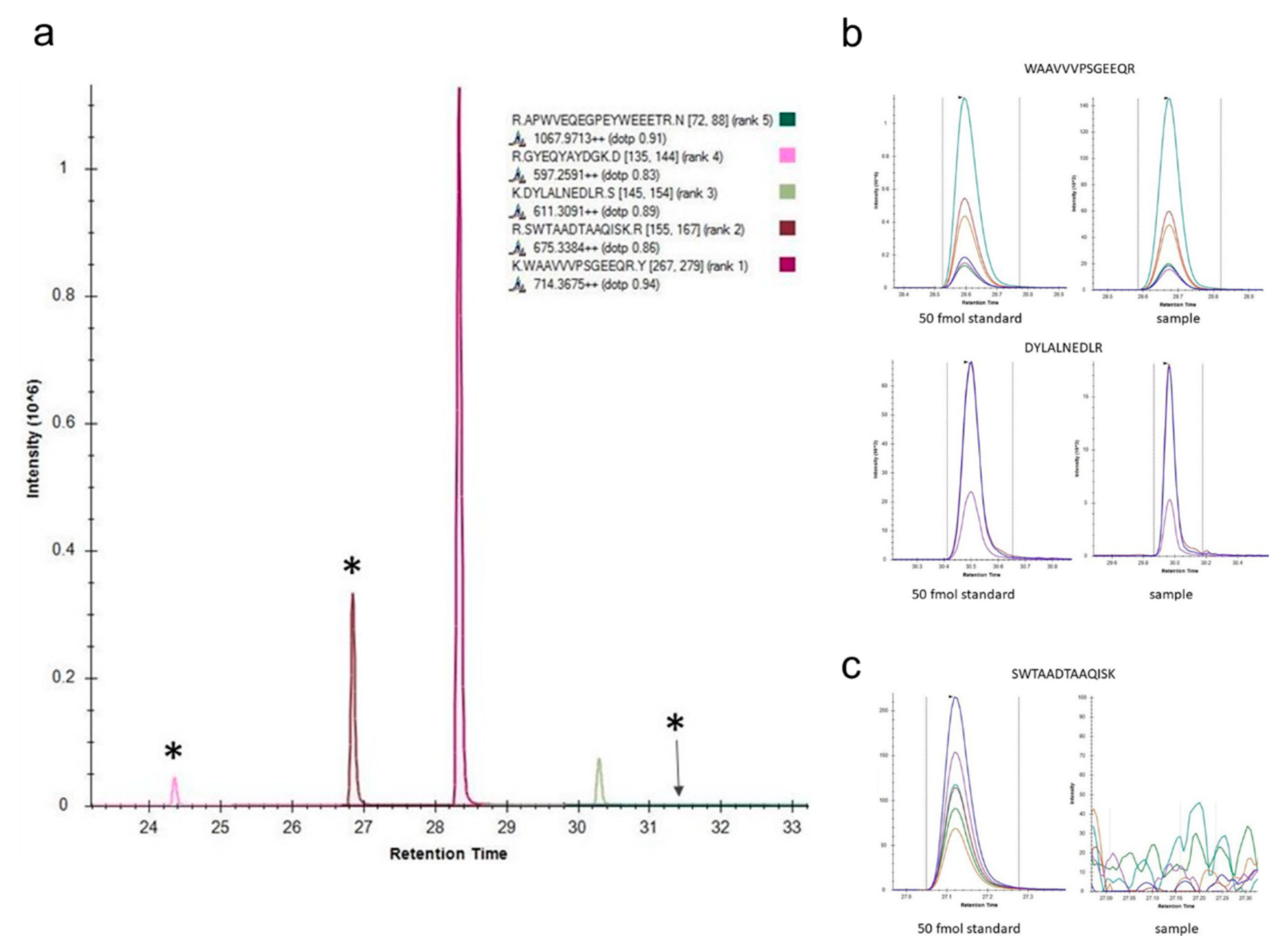
Appendix B
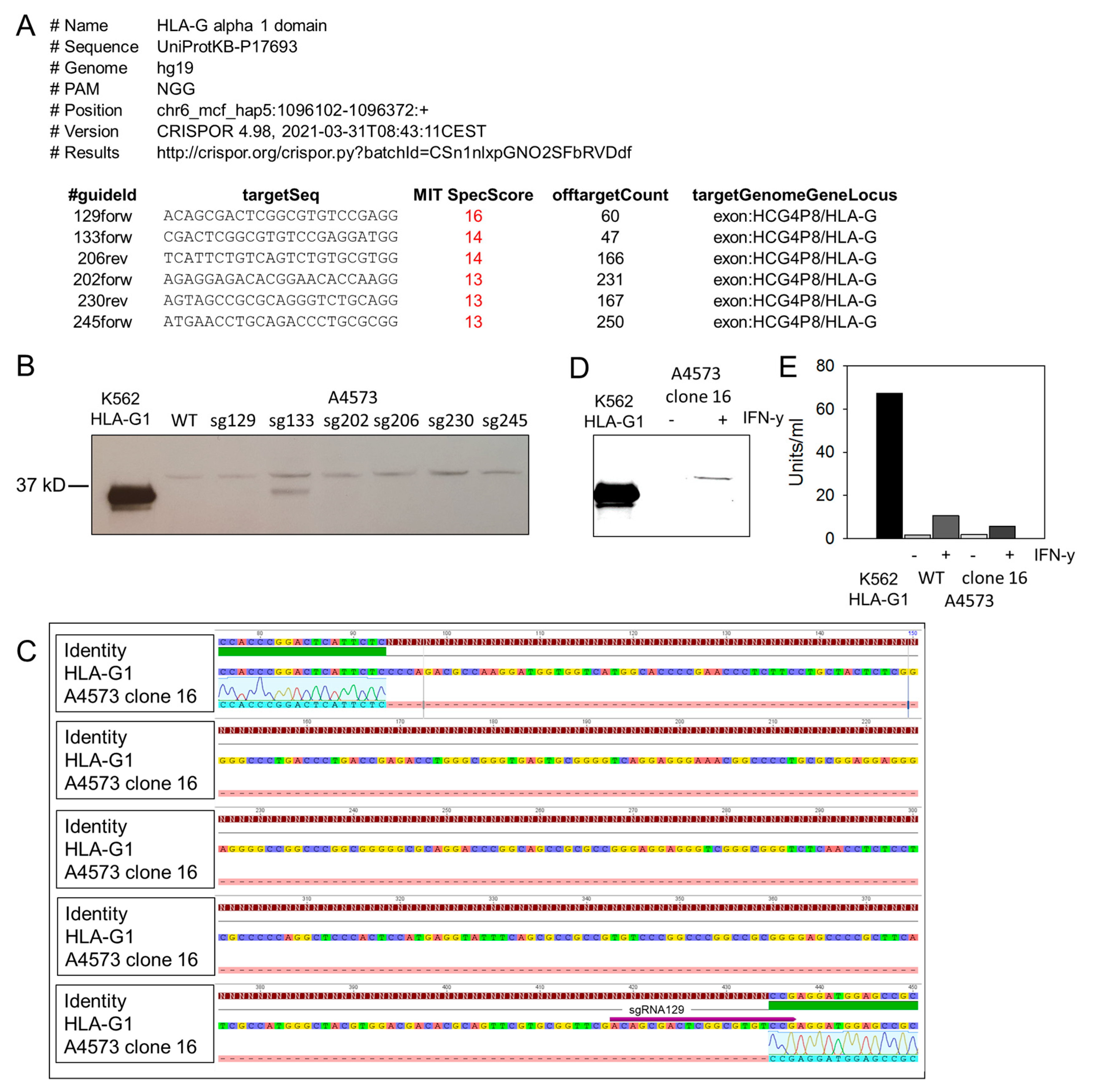
Appendix C

References
- Ladenstein, R.; Potschger, U.; Le Deley, M.C.; Whelan, J.; Paulussen, M.; Oberlin, O.; van den Berg, H.; Dirksen, U.; Hjorth, L.; Michon, J.; et al. Primary Disseminated Multifocal Ewing Sarcoma: Results of the Euro-EWING 99 Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 3284–3291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grier, H.E.; Krailo, M.D.; Tarbell, N.J.; Link, M.P.; Fryer, C.J.; Pritchard, D.J.; Gebhardt, M.C.; Dickman, P.S.; Perlman, E.J.; Meyers, P.A.; et al. Addition of ifosfamide and etoposide to standard chemotherapy for Ewing’s sarcoma and primitive neuroectodermal tumor of bone. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 348, 694–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maude, S.L.; Laetsch, T.W.; Buechner, J.; Rives, S.; Boyer, M.; Bittencourt, H.; Bader, P.; Verneris, M.R.; Stefanski, H.E.; Myers, G.D.; et al. Tisagenlecleucel in Children and Young Adults with B-Cell Lymphoblastic Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 439–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neelapu, S.S.; Locke, F.L.; Bartlett, N.L.; Lekakis, L.J.; Miklos, D.B.; Jacobson, C.A.; Braunschweig, I.; Oluwole, O.O.; Siddiqi, T.; Lin, Y.; et al. Axicabtagene Ciloleucel CAR T-Cell Therapy in Refractory Large B-Cell Lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 2531–2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kailayangiri, S.; Altvater, B.; Meltzer, J.; Pscherer, S.; Luecke, A.; Dierkes, C.; Titze, U.; Leuchte, K.; Landmeier, S.; Hotfilder, M.; et al. The ganglioside antigen G(D2) is surface-expressed in Ewing sarcoma and allows for MHC-independent immune targeting. Br. J. Cancer 2012, 106, 1123–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kailayangiri, S.; Altvater, B.; Spurny, C.; Jamitzky, S.; Schelhaas, S.; Jacobs, A.H.; Wiek, C.; Roellecke, K.; Hanenberg, H.; Hartmann, W.; et al. Targeting Ewing sarcoma with activated and GD2-specific chimeric antigen receptor-engineered human NK cells induces upregulation of immune-inhibitory HLA-G. Oncoimmunology 2017, 6, e1250050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liebsch, L.; Kailayangiri, S.; Beck, L.; Altvater, B.; Koch, R.; Dierkes, C.; Hotfilder, M.; Nagelmann, N.; Faber, C.; Kooijman, H.; et al. Ewing sarcoma dissemination and response to T-cell therapy in mice assessed by whole-body magnetic resonance imaging. Br. J. Cancer 2013, 109, 658–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, A.H.; Highfill, S.L.; Cui, Y.; Smith, J.P.; Walker, A.J.; Ramakrishna, S.; El-Etriby, R.; Galli, S.; Tsokos, M.G.; Orentas, R.J.; et al. Reduction of MDSCs with All-trans Retinoic Acid Improves CAR Therapy Efficacy for Sarcomas. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2016, 4, 869–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binnewies, M.; Roberts, E.W.; Kersten, K.; Chan, V.; Fearon, D.F.; Merad, M.; Coussens, L.M.; Gabrilovich, D.I.; Ostrand-Rosenberg, S.; Hedrick, C.C.; et al. Understanding the tumor immune microenvironment (TIME) for effective therapy. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 541–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmadzadeh, M.; Johnson, L.A.; Heemskerk, B.; Wunderlich, J.R.; Dudley, M.E.; White, D.E.; Rosenberg, S.A. Tumor antigen-specific CD8 T cells infiltrating the tumor express high levels of PD-1 and are functionally impaired. Blood 2009, 114, 1537–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spurny, C.; Kailayangiri, S.; Jamitzky, S.; Altvater, B.; Wardelmann, E.; Dirksen, U.; Hardes, J.; Hartmann, W.; Rossig, C. Programmed cell death ligand 1 (PD-L1) expression is not a predominant feature in Ewing sarcomas. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2018, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geoerger, B.; Kang, H.J.; Yalon-Oren, M.; Marshall, L.V.; Vezina, C.; Pappo, A.; Laetsch, T.W.; Petrilli, A.S.; Ebinger, M.; Toporski, J.; et al. Pembrolizumab in paediatric patients with advanced melanoma or a PD-L1-positive, advanced, relapsed, or refractory solid tumour or lymphoma (KEYNOTE-051): Interim analysis of an open-label, single-arm, phase 1-2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2020, 21, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouas-Freiss, N.; Goncalves, R.M.; Menier, C.; Dausset, J.; Carosella, E.D. Direct evidence to support the role of HLA-G in protecting the fetus from maternal uterine natural killer cytolysis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 11520–11525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Drean, E.; Vely, F.; Olcese, L.; Cambiaggi, A.; Guia, S.; Krystal, G.; Gervois, N.; Moretta, A.; Jotereau, F.; Vivier, E. Inhibition of antigen-induced T cell response and antibody-induced NK cell cytotoxicity by NKG2A: Association of NKG2A with SHP-1 and SHP-2 protein-tyrosine phosphatases. Eur. J. Immunol. 1998, 28, 264–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riteau, B.; Rouas-Freiss, N.; Menier, C.; Paul, P.; Dausset, J.; Carosella, E.D. HLA-G2, -G3, and -G4 isoforms expressed as nonmature cell surface glycoproteins inhibit NK and antigen-specific CTL cytolysis. J. Immunol. 2001, 166, 5018–5026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agaugue, S.; Carosella, E.D.; Rouas-Freiss, N. Role of HLA-G in tumor escape through expansion of myeloid-derived suppressor cells and cytokinic balance in favor of Th2 versus Th1/Th17. Blood 2011, 117, 7021–7031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rapaport, A.S.; Schriewer, J.; Gilfillan, S.; Hembrador, E.; Crump, R.; Plougastel, B.F.; Wang, Y.; Le Friec, G.; Gao, J.; Cella, M.; et al. The Inhibitory Receptor NKG2A Sustains Virus-Specific CD8(+) T Cells in Response to a Lethal Poxvirus Infection. Immunity 2015, 43, 1112–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andre, P.; Denis, C.; Soulas, C.; Bourbon-Caillet, C.; Lopez, J.; Arnoux, T.; Blery, M.; Bonnafous, C.; Gauthier, L.; Morel, A.; et al. Anti-NKG2A mAb Is a Checkpoint Inhibitor that Promotes Anti-tumor Immunity by Unleashing Both T and NK Cells. Cell 2018, 175, 1731–1743.e1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gooden, M.; Lampen, M.; Jordanova, E.S.; Leffers, N.; Trimbos, J.B.; van der Burg, S.H.; Nijman, H.; van Hall, T. HLA-E expression by gynecological cancers restrains tumor-infiltrating CD8(+) T lymphocytes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 10656–10661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talebian Yazdi, M.; van Riet, S.; van Schadewijk, A.; Fiocco, M.; van Hall, T.; Taube, C.; Hiemstra, P.S.; van der Burg, S.H. The positive prognostic effect of stromal CD8+ tumor-infiltrating T cells is restrained by the expression of HLA-E in non-small cell lung carcinoma. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 3477–3488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouas-Freiss, N.; Moreau, P.; Menier, C.; Carosella, E.D. HLA-G in cancer: A way to turn off the immune system. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2003, 13, 325–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, E.C.; Guerra, N.; Lacombe, M.J.; Angevin, E.; Chouaib, S.; Carosella, E.D.; Caignard, A.; Paul, P. Tumor-specific up-regulation of the nonclassical class I HLA-G antigen expression in renal carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 6838–6845. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Paul, P.; Rouas-Freiss, N.; Khalil-Daher, I.; Moreau, P.; Riteau, B.; Le Gal, F.A.; Avril, M.F.; Dausset, J.; Guillet, J.G.; Carosella, E.D. HLA-G expression in melanoma: A way for tumor cells to escape from immunosurveillance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 4510–4515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiendl, H.; Mitsdoerffer, M.; Hofmeister, V.; Wischhusen, J.; Bornemann, A.; Meyermann, R.; Weiss, E.H.; Melms, A.; Weller, M. A functional role of HLA-G expression in human gliomas: An alternative strategy of immune escape. J. Immunol. 2002, 168, 4772–4780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morandi, F.; Levreri, I.; Bocca, P.; Galleni, B.; Raffaghello, L.; Ferrone, S.; Prigione, I.; Pistoia, V. Human neuroblastoma cells trigger an immunosuppressive program in monocytes by stimulating soluble HLA-G release. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 6433–6441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spurny, C.; Kailayangiri, S.; Altvater, B.; Jamitzky, S.; Hartmann, W.; Wardelmann, E.; Ranft, A.; Dirksen, U.; Amler, S.; Hardes, J.; et al. T cell infiltration into Ewing sarcomas is associated with local expression of immune-inhibitory HLA-G. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 6536–6549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanjana, N.E.; Shalem, O.; Zhang, F. Improved vectors and genome-wide libraries for CRISPR screening. Nat. Methods 2014, 11, 783–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kailayangiri, S.; Altvater, B.; Lesch, S.; Balbach, S.; Gottlich, C.; Kuhnemundt, J.; Mikesch, J.H.; Schelhaas, S.; Jamitzky, S.; Meltzer, J.; et al. EZH2 Inhibition in Ewing Sarcoma Upregulates GD2 Expression for Targeting with Gene-Modified T Cells. Mol. Ther. 2019, 27, 933–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lila, N.; Rouas-Freiss, N.; Dausset, J.; Carpentier, A.; Carosella, E.D. Soluble HLA-G protein secreted by allo-specific CD4+ T cells suppresses the allo-proliferative response: A CD4+ T cell regulatory mechanism. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 12150–12155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cherkassky, L.; Morello, A.; Villena-Vargas, J.; Feng, Y.; Dimitrov, D.S.; Jones, D.R.; Sadelain, M.; Adusumilli, P.S. Human CAR T cells with cell-intrinsic PD-1 checkpoint blockade resist tumor-mediated inhibition. J. Clin. Investig. 2016, 126, 3130–3144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fanger, N.A.; Cosman, D.; Peterson, L.; Braddy, S.C.; Maliszewski, C.R.; Borges, L. The MHC class I binding proteins LIR-1 and LIR-2 inhibit Fc receptor-mediated signaling in monocytes. Eur. J. Immunol. 1998, 28, 3423–3434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustafson, C.E.; Qi, Q.; Hutter-Saunders, J.; Gupta, S.; Jadhav, R.; Newell, E.; Maecker, H.; Weyand, C.M.; Goronzy, J.J. Immune Checkpoint Function of CD85j in CD8 T Cell Differentiation and Aging. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saverino, D.; Fabbi, M.; Ghiotto, F.; Merlo, A.; Bruno, S.; Zarcone, D.; Tenca, C.; Tiso, M.; Santoro, G.; Anastasi, G.; et al. The CD85/LIR-1/ILT2 inhibitory receptor is expressed by all human T lymphocytes and down-regulates their functions. J. Immunol. 2000, 165, 3742–3755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabri, B.; Selby, J.M.; Negulescu, H.; Lee, L.; Roberts, A.I.; Beavis, A.; Lopez-Botet, M.; Ebert, E.C.; Winchester, R.J. TCR specificity dictates CD94/NKG2A expression by human CTL. Immunity 2002, 17, 487–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colonna, M.; Navarro, F.; Bellon, T.; Llano, M.; Garcia, P.; Samaridis, J.; Angman, L.; Cella, M.; Lopez-Botet, M. A common inhibitory receptor for major histocompatibility complex class I molecules on human lymphoid and myelomonocytic cells. J. Exp. Med. 1997, 186, 1809–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertone, S.; Schiavetti, F.; Bellomo, R.; Vitale, C.; Ponte, M.; Moretta, L.; Mingari, M.C. Transforming growth factor-beta-induced expression of CD94/NKG2A inhibitory receptors in human T lymphocytes. Eur. J. Immunol. 1999, 29, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mingari, M.C.; Ponte, M.; Bertone, S.; Schiavetti, F.; Vitale, C.; Bellomo, R.; Moretta, A.; Moretta, L. HLA class I-specific inhibitory receptors in human T lymphocytes: Interleukin 15-induced expression of CD94/NKG2A in superantigen- or alloantigen-activated CD8+ T cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 1172–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derre, L.; Corvaisier, M.; Pandolfino, M.C.; Diez, E.; Jotereau, F.; Gervois, N. Expression of CD94/NKG2-A on human T lymphocytes is induced by IL-12: Implications for adoptive immunotherapy. J. Immunol. 2002, 168, 4864–4870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujiwara, T.; Fukushi, J.; Yamamoto, S.; Matsumoto, Y.; Setsu, N.; Oda, Y.; Yamada, H.; Okada, S.; Watari, K.; Ono, M.; et al. Macrophage infiltration predicts a poor prognosis for human ewing sarcoma. Am. J. Pathol. 2011, 179, 1157–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rouas-Freiss, N.; Moreau, P.; Menier, C.; LeMaoult, J.; Carosella, E.D. Expression of tolerogenic HLA-G molecules in cancer prevents antitumor responses. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2007, 17, 413–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yie, S.M.; Yang, H.; Ye, S.R.; Li, K.; Dong, D.D.; Lin, X.M. Expression of HLA-G is associated with prognosis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2007, 128, 1002–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, M.Y.; Xu, Y.F.; Qiu, S.J.; Ju, M.J.; Gao, Q.; Li, Y.W.; Zhang, B.H.; Zhou, J.; Fan, J. Human leukocyte antigen-G protein expression is an unfavorable prognostic predictor of hepatocellular carcinoma following curative resection. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 4686–4693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Kruijf, E.M.; Sajet, A.; van Nes, J.G.; Natanov, R.; Putter, H.; Smit, V.T.; Liefers, G.J.; van den Elsen, P.J.; van de Velde, C.J.; Kuppen, P.J. HLA-E and HLA-G expression in classical HLA class I-negative tumors is of prognostic value for clinical outcome of early breast cancer patients. J. Immunol. 2010, 185, 7452–7459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiraoka, N.; Ino, Y.; Hori, S.; Yamazaki-Itoh, R.; Naito, C.; Shimasaki, M.; Esaki, M.; Nara, S.; Kishi, Y.; Shimada, K.; et al. Expression of classical human leukocyte antigen class I antigens, HLA-E and HLA-G, is adversely prognostic in pancreatic cancer patients. Cancer Sci. 2020, 111, 3057–3070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chmielewski, M.; Abken, H. CAR T Cells Releasing IL-18 Convert to T-Bet(high) FoxO1(low) Effectors that Exhibit Augmented Activity against Advanced Solid Tumors. Cell Rep. 2017, 21, 3205–3219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- König, S.; Spurny, C.; Rössig, C. Pseudo-MRM method for the selective detection of human HLA-G. MERCATOR J. Biomol. Anal. 2017, 1, 12–21. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Altvater, B.; Kailayangiri, S.; Pérez Lanuza, L.F.; Urban, K.; Greune, L.; Flügge, M.; Meltzer, J.; Farwick, N.; König, S.; Görlich, D.; et al. HLA-G and HLA-E Immune Checkpoints Are Widely Expressed in Ewing Sarcoma but Have Limited Functional Impact on the Effector Functions of Antigen-Specific CAR T Cells. Cancers 2021, 13, 2857. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13122857
Altvater B, Kailayangiri S, Pérez Lanuza LF, Urban K, Greune L, Flügge M, Meltzer J, Farwick N, König S, Görlich D, et al. HLA-G and HLA-E Immune Checkpoints Are Widely Expressed in Ewing Sarcoma but Have Limited Functional Impact on the Effector Functions of Antigen-Specific CAR T Cells. Cancers. 2021; 13(12):2857. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13122857
Chicago/Turabian StyleAltvater, Bianca, Sareetha Kailayangiri, Lina F. Pérez Lanuza, Katja Urban, Lea Greune, Maike Flügge, Jutta Meltzer, Nicole Farwick, Simone König, Dennis Görlich, and et al. 2021. "HLA-G and HLA-E Immune Checkpoints Are Widely Expressed in Ewing Sarcoma but Have Limited Functional Impact on the Effector Functions of Antigen-Specific CAR T Cells" Cancers 13, no. 12: 2857. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13122857
APA StyleAltvater, B., Kailayangiri, S., Pérez Lanuza, L. F., Urban, K., Greune, L., Flügge, M., Meltzer, J., Farwick, N., König, S., Görlich, D., Hartmann, W., & Rossig, C. (2021). HLA-G and HLA-E Immune Checkpoints Are Widely Expressed in Ewing Sarcoma but Have Limited Functional Impact on the Effector Functions of Antigen-Specific CAR T Cells. Cancers, 13(12), 2857. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13122857