Simple Summary
Cancer is one of the major public health burdens in the world. To date, various conventional cancer therapies have been used, but these therapies are less effective and have severe side effects. Currently, in order to find a better cure for cancer, researchers have tried to explore new approaches with minimal toxicity and fewer side effects. In recent years, nanotechnology has been widely used in diseases management and holds a promising future in curing complex incurable diseases, in particular cancer. Biosynthesized metallic nanoparticles are eco-friendly and biocompatible, and can be used in cancer diagnostics, novel treatments, and drug delivery systems. This review gives an overview of the recent advancements in the biosynthesis of metallic nanoparticles (silver (Ag), gold (Au), zinc (Zn) and copper (Cu)) and their possible anti-cancer activities, with particular emphasis on the mechanisms of action, and future research prospects of nano-therapeutics are also discussed.
Abstract
Cancer is one of the foremost causes of death worldwide. Cancer develops because of mutation in genes that regulate normal cell cycle and cell division, thereby resulting in uncontrolled division and proliferation of cells. Various drugs have been used to treat cancer thus far; however, conventional chemotherapeutic drugs have lower bioavailability, rapid renal clearance, unequal delivery, and severe side effects. In the recent years, nanotechnology has flourished rapidly and has a multitude of applications in the biomedical field. Bio-mediated nanoparticles (NPs) are cost effective, safe, and biocompatible and have got substantial attention from researchers around the globe. Due to their safe profile and fewer side effects, these nanoscale materials offer a promising cure for cancer. Currently, various metallic NPs have been designed to cure or diagnose cancer; among these, silver (Ag), gold (Au), zinc (Zn) and copper (Cu) are the leading anti-cancer NPs. The anticancer potential of these NPs is attributed to the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in cellular compartments that eventually leads to activation of autophagic, apoptotic and necrotic death pathways. In this review, we summarized the recent advancements in the biosynthesis of Ag, Au, Zn and Cu NPs with emphasis on their mechanism of action. Moreover, nanotoxicity, as well as the future prospects and opportunities of nano-therapeutics, are also highlighted.
1. Cancer: A Global Public Health Issue
Cancer is one of the leading causes of death, resulting in about 10.0 million deaths in 2020 alone [1]. Additionally, according to the World Health Organization (WHO), it is anticipated that it will increase up to three folds by the end of 2040 [2,3]. Cancer causes one in six deaths globally, resulting in more deaths than tuberculosis, malaria and acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) [4]. Around 70% of these deaths occur in low- and middle-income countries owing to their lifestyle adaptations [3]. Chemotherapy, surgery, radiations, immunotherapy, and hormone therapy are commonly used for cancer treatment, but these approaches pose severe side effects in patients [5,6]. Chemotherapeutic agents cause various toxicities, for example, a commonly used drug, 5-fluorouracil, is generally associated with myelotoxicity, leukopenia, cardiotoxicity, and blood vessels constriction [7]. Similarly, cyclophosphamide and bleomycin, often used in combination therapy, are associated with bladder toxicity, pulmonary toxicity, and cutaneous toxicity [7,8,9]. Doxorubicin, another anticancer drug, is reported for cardiotoxicity, myelotoxicity, and renal toxicity, respectively [10]. In order to find a better cure with minimal toxicity, scientists are on a quest to explore novel approaches and discover potent anticancer agents for effective treatment against cancer with minimal side effects.
In the recent years, nanotechnology based therapeutic and diagnostic approaches have shown significant potential to ameliorate cancer therapy [3,11]. Cancer nanotechnology developed a new area of integrative research in biology, chemistry, engineering, and medicine, and is concerned with major advances in cancer diagnosis, prevention and treatment [12]. In past few years, nanoparticles (NPs) have become a subject of attraction for scientists due to their maximal efficacy and safety [13]. Due to these applications, recently, the US FDA has approved nanotechnology based anticancer drugs such as, Myocet™ (Perrigo, Dublin, Ireland), DaunoXome® (Gilead Sciences, Foster City, CA, USA), Doxil® (Johnson & Johnson, New Brunswick, NJ, USA) and Abraxane® (Celgene, Summit, NJ, USA) [14].
This article provides an insight into the green synthesis of metallic NPs and their potential applications as therapeutics in cancer therapy. This review has mainly focused on biosynthesis of silver, gold, zinc and copper NPs for cancer therapy and their in vitro anticancer activities against cell lines. The basic mechanism behind cancer development and a proposed mechanism involved in metallic NPs-mediated cytotoxicity in cancerous cells have also been discussed in the current review.
2. Genome Instability: A Basic Mechanism in Cancer Development
The fundamental abnormality that leads to the development of cancer is the abnormal cellular proliferation and division, which arise when their regulatory genes are mutated [15]. The protein product of these mutated genes can cause cancer by accelerated cell division rates or inhibiting normal cell cycle control, such as programmed cell death or cell cycle arrest [16]. The genes that mainly contributed to development of cancer fall into three broad categories, involving proto-oncogenes, oncogenes, and tumor suppressor genes. The proto-oncogenes (normal version of genes), when activated or mutated, become oncogenes (mutated version of genes) and produce various onco-proteins that can affect cell division, proliferation and survival, and results in cancer development [17,18]. A few of the many known proto-oncogenes include HER-2/neu, RAS, MYC, SRC, BCL-2 and hTERT, and these genes or their product modulate cellular cycle or control normal cell division or apoptosis cell division [19,20,21,22,23,24]. On the contrary, tumor suppressor genes code proteins that repair damaged DNA or destroy damaged cells, and when these molecular switches become mutated, it leads to abnormal cell division and cellular growth. In this way, the abnormal cells continue to survive and may eventually develop into a cancer [25].
Cancer is mainly associated with loss of genome stability. Genome stability of cells is mostly altered through certain DNA damaging agents from carcinogens. Fortunately, our cells have proofreading machinery such as cell cycle checkpoints and a complex interconnected network of pathways to repair the damage [26]. However, mutation can occur in the regulatory genes and the cell will be unable to proofread such DNA breakages, and eventually the normal cellular cycle and proliferation rate will be disrupted [27,28]. For example, Rad54B is an important protein that exhibits a role in DNA repair and maintaining genome stability after DNA damage [27]. Various studies [29,30,31] have revealed that Rad54B mutation is involved in the development of some cancer’s cells, and such abnormal proteins are unable to terminate the cell cycle and will lead to the progression of cancer. Figure 1 shows regulation of cell cycle upon DNA damage and the role of Rad54B in the development of cancer.
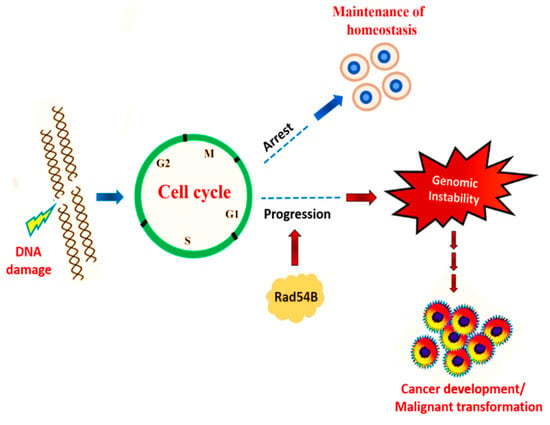
Figure 1.
Cell cycle regulation in response to DNA damage.
The development of cancer is preceded by the appearance of mutations in critical cellular genes involved in regulatory pathways of the cell cycle. This is the initial stage (initiation) of cancer development, an irreversible heritable alteration in DNA of normal cell referred to as initiated cell [32]. Initiation is associated with high efficacy of DNA repair, otherwise the initiated cell may ultimately die while progressing towards the development of the preneoplastic focal lesions. The initiated cells in preneoplastic focal lesions starts proliferating upon continual exposure to promoting agents, and further mutations during promotion leads to development of metastasis or neoplasm [33]. Neoplasia, an abnormal or uncontrolled growth of cells or tissues, can be benign (localized tumor) or malignant, which tend to proliferate rapidly, or metastasize (spread the tissues around them or other parts of the body) [34]. Figure 2 shows different stages of development of cancer; starting from a mutation in normal cells (initiation), proliferation of mutated cells (promotion), and uncontrolled growth of cells along with continued mutations in their genome, and their spread to other parts of the body (metastasis).
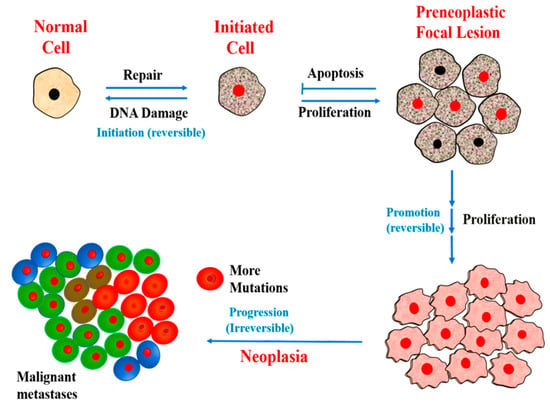
Figure 2.
Stages in the development of cancer.
3. Green Synthesized Metallic NPs: An Insight
Several metals and their oxides have been used for production of NPs, including silver (Ag), aluminum (Al), iron (Fe), gold (Au), silica (Si), copper (Cu), zinc (Zn), manganese (Mn), cerium (Ce), titanium (Ti), platinum (Pt) or thallium (TI) [35]. NPs are generally synthesized by via approaches, top-down approach and bottom-up approach, as shown in Figure 3. The top-down approach for NPs synthesis includes lithographic techniques, laser ablation, ball mining, sputtering, electro-explosion and etching. The bottom-up approach includes the most effective methods for NPs synthesis, where NPs are prepared using simpler molecules [36].
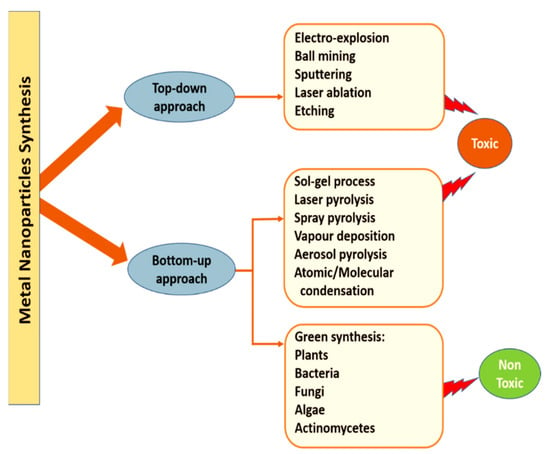
Figure 3.
Different approaches of synthesis of metal NPs.
From all the approaches of NPs synthesis, green synthesis approach is considered the most economic, sustainable, reliable and eco-friendly [37]. This approach of NPs synthesis does not require toxic chemicals, high temperature, high pressure and does not cause harm to human health and the environment [38]. At present, it is also considered a preferred method for NPs fabrication because of utilization of low-cost and non-hazardous raw material such as microorganisms fungi [39], algae [40], bacteria [41], plant extracts [42], natural polymers and proteins [43]. These resources contain biomolecules such as proteins including enzymes, polysaccharides, sugars, amides, ketones, aldehydes, and carboxylic acids, but also more importantly various phytochemicals such as terpenes, alkaloids or polyphenols including flavonoids that aid in immediate reduction (Figure 4).
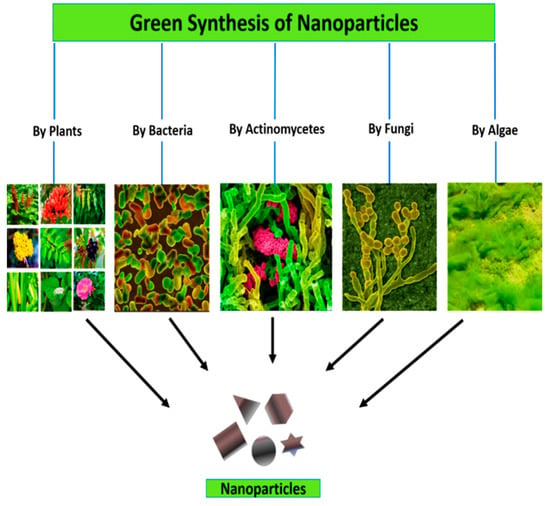
Figure 4.
Green synthesis of NPs.
For the reduction of metal ions, bacteria and fungi require a relatively extended incubation period compared to water-soluble phytochemicals that do it immediately in a much lesser time. Moreover, plants are considered better candidates for NPs synthesis as compared to microbes such as fungi and bacteria because, in case of plants, the intricate process of maintaining microbial cultures is eliminated. Another striking feature of biological synthesized NPs is their biocompatible nature. In contrast, the chemical route uses toxic reducing agents, thus limiting their biomedical potentials, and posing a threat to the ecosystem. Biological approach resolves this issue by using safe reducing agents and could be used in cancer therapeutics [44,45].
4. NPs for Cancer Therapy
At present, there are several treatment approaches are available for cancer, including radiation therapy, chemotherapy, immunotherapy, photodynamic therapy, cancer vaccinations, stem cell therapy and surgery, but these treatment options cause severe side effects and have pharmacokinetics issues [46,47]. NPs are progressing as an attractive tool of research to overcome these challenges [48]. NPs exhibit large surface to volume ratio, which is responsible for their interaction with the biological system because at the cell level, the atoms are freely available to commence various reactions [49,50]. These unique morphologies of NPs effect their insertion or entry into the cells. The charge present on the surface of NPs affects their circulation time in the blood stream and their rate of uptake and translocation. Cationic NPs apparently damage plasma-membrane integrity, hampers organelles architecture, and imbalance the normal cellular function compared to anionic NPs [51]. Hence, in this way, cationic NPs often show a higher rate of non-specific uptake as compared to neutral and negatively charged NPs. However, the neutral and negatively charged NPs exhibit shorter blood circulation time, which reduces their bioavailability [50]. It has been reported previously that positive groups like primary amine present at the surface of polystyrene microparticles helped in faster internalization in cells as compared to the microparticles, which contained hydroxyl, sulfate or carboxyl as surface groups [52]. Additionally, mesoporous silica NPs containing amine groups were used earlier in in vitro and in vivo studies as gene delivery tools and exhibited improved internalization owing to the positive groups on their surface [53].
NPs are attracting significant interest as carriers for diagnostic, hydrophobic medicine, hyperthermia, therapeutics and especially in delivery of antineoplastic drugs/agents to the cancerous tissues, where the delivered NPs can penetrate deep and deliver drug to a specific targeted site [54]. In cancerous cells, NPs have been reported to increase the intracellular concentration of drugs via either active targeting or passive targeting by minimizing toxicity to the normal cells [55]. Moreover, as a targeted drug delivery system, NPs have been developed as temperature- or pH-sensitive carriers. As a temperature-sensitive drug delivery system, these NPs can deliver and release drugs in the tumor area, by undergoing local changes in temperature via providing ultrasound waves or magnetic fields. The pH-sensitive system can carry and release drugs efficiently in the acidic environment of the cancerous cells [56]. These NPs can be further modified with specific targeting moieties, such as antibody fragments, antibodies, specific molecules, RNA aptamers and small peptides, which further enhance their ability to selectively bind to cancerous cells and tissues [57].
Angiogenesis (formation of new blood vessels) plays a key role in progression of a tumor towards metastasis. Cancer cells display abnormal membrane structure because of enhanced blood vasculature due to upregulated expression of angiogenic factors [58,59]. This dysregulated membrane architecture, can be of great interest to deliver anti-angiogenic nano-based targets into the tumor microenvironment to inhibit excess production of angiogenic stimulators [60]. Owing to effectiveness of this therapy, several studies have been reported to block signaling of VEGF, PDGF, EDGR, angiopoietin- key contributors of neovascularization [61]. Nano anti-angiogenic therapy can be a good delivery option for drugs that have a short half-life, poor oral availability, and distribution in tumor area [59]. Depending on their sizes, NPs can easily penetrate the tumor microenvironment and can efficiently deliver antiangiogenic drugs. Through enhanced permeability and retention effect (EPR), the NPs with optimum size can intrinsically approach the metastasized tumors and can efficiently release loaded drugs as shown in Figure 5 [60].
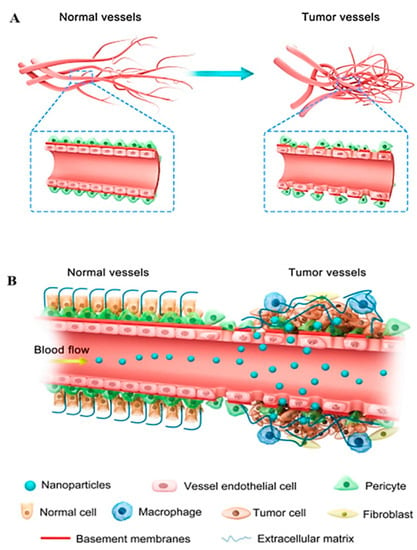
Figure 5.
(A) illustrates the vasculature of both normal and tumor cells and (B) shows accumulation and penetration of NPs in tumor tissues via EPR effect. Reproduced from [60].
5. The Fate of Cancer Cells Exposed to NPs
Metallic NPs offer more cytotoxicity to cancerous cell lines as compared to normal cells [62,63]. Various mechanisms have been proposed to explain the cytotoxicity mechanism of metallic NPs such as generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS), activation of caspase-3, permeabilization of mitochondrial outer membrane, and specific DNA cleavage, all of which lead to apoptotic, autophagic and necrotic death of the cancer cell [64]. Figure 6 demonstrates an overview of the proposed cytotoxicity mechanism of metallic NPs against cancerous cells.
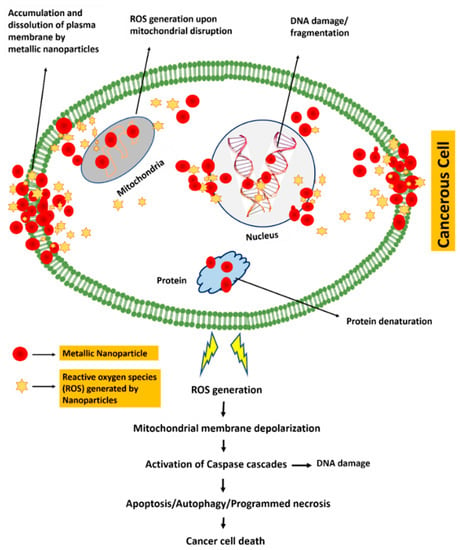
Figure 6.
Proposed mechanism of green synthesized metallic NPs mediated cytotoxicity in cancerous cells.
NPs of different sizes (either small or large) follow different mechanisms to enter the cells. Smaller NPs get into the cells via receptor-mediated uptake by developing interactions with the caveolin receptor present on the cell membrane. Larger NPs tend to enter the cells via clathrin-mediated endocytosis. Once they make entry to the cells NPs take different paths within the cell to perform their directed function, either they directly interact with the proteins in cytosol, or they undergo some surface modifications in the lysosome–endosome complex before release into the cytosol [64]. Inside the cell, NPs trigger a cascade of ROS and start releasing metal ions, which tend to bind with the SH groups of proteins and results in breakage of its S–S bridges. In this way, the physiology of the cell is affected, resulting in activation of several signaling pathways that leads to programmed cell death [65].
Apoptosis is often triggered either by intrinsic or by extrinsic pathways. Nanomaterials can activate apoptotic signaling by both intrinsic and extrinsic pathways. In case of apoptosis triggered via intrinsic pathway, ROS generation results in mitochondrial membrane depolarization, which leads to release of cytochrome c into the cytosol. This cytochrome c then leads to activation of caspase-9/3 apoptotic cascade by triggering pro-apoptotic proteases in apoptosis initiated by extrinsic pathway [66].
Autophagy is also a form of programmed cell death and is well controlled by autophagy-related genes (ATGs). Autophagy is stimulated by extracellular or intracellular stress, that is generally cytoprotective in nature and leads to cell survival, whereas an over-stimulation of autophagy causes cytotoxicity and may lead to autophagic cell death [66]. Nanomaterials can initiate autophagy through various pathways such as, aggregation of impaired proteins, which can cause organelle stress, oxidative stress, variation in gene expression, and inhibition of kinase-mediated regulatory pathways [67]. The elevated level of autophagic vacuoles in the cells as a response to nanomaterials could be a type of adaptive cellular response. Previous studies showed that nanomaterials can generate elevated levels of autophagic vacuoles as noticed in in vitro studies conducted on various animals and human cells and in in vivo models [68]. Before entering the cytoplasm, silver NPs undergo degradation within a double-membraned autophagosome compartment [69].
Programmed necrosis is also termed as programmed cell death, which involves binding of death ligands to their receptors. The ligation to death receptor leads to a complex formation, and this pro-necrotic complex further binds with metabolic enzymes and results in increased ROS production, which activates necrosis. Nanomaterials can induce ROS-mediated necrosis directly by affecting mitochondria or indirectly by elevating NADPH oxidase and cellular calcium levels, to generate more ROS and undergo programmed necrosis [65].
Subcellular location of NPs also plays an important role in death of cancer cells. NPs took 30–60 min for their release from the endosome, while NPs that are aggregated in multi-vesicular bodies are removed within a period of 6 days. Similarly, Golgi apparatuses also extruded the particles assembled in the microtubule [70].
6. Anti-Cancer Activities of Biosynthesized Metallic NPs
There are various advantages of using plants for NPs synthesis, because they are safe to handle, are easily available and contain a vast variety of biomolecules or metabolites that help in stabilization and reduction of NPs [71].
In modern medicine, plant-based nanotherapeutics drugs have become a potential weapon in cancer therapeutics. In recent years, optimal methods for metallic NPs preparations with anti-cancer properties are widely being examined both in vivo and in vitro [72]. Plant extract and bioactive compounds of several medicinal plants have been reported for their potential use as anticancer agents [73]. The mechanism of action of against cancer have been extensively studied by researchers and found that the functional groups capped on the NPs are involved directly or indirectly in improving the anticancer activity or reducing the toxicity or improving the bioavailability and uptake [74]. The anticancer properties of different NPs also exhibit variations because of differences in phytocontent of biological material used for their synthesis [75]. Figure 7 presents a schematic representation of synthesis of plant-based metallic NPs and their application as anti-cancer therapeutics. Here, it is worth mentioning that in order to keep this review article less verbose we have only discussed plant based green synthesis of silver (Ag), gold (Au), zinc (Zn) and copper (Co) metals and their inhibitory activities against several cancerous cell lines.
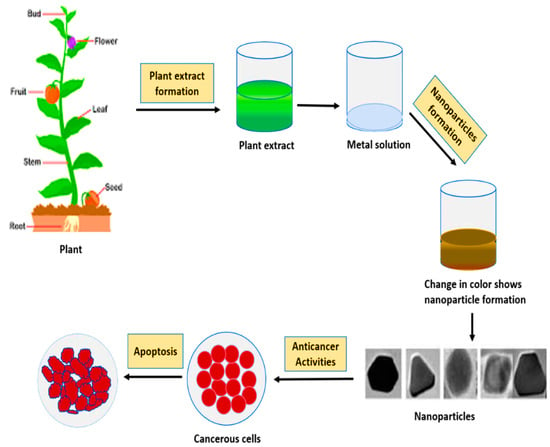
Figure 7.
Plant mediated metallic NPs synthesis and their anticancer activity.
6.1. Applications of Biosynthesized Silver NPs (AgNPs) as Anti-Cancer Therapeutics
Among all the noble metals, silver has received major attention from researchers due to its unique surface chemistry and morphologies [76].
According to the literature, biosynthesized AgNPs have displayed significant anticancer potential against the cervical cancer cell lines HeLa and Siha. Hexagonal and triangular shaped AgNPs sizes ranging from 2–18 nm have shown notable inhibitory actions against Siha cancer cell line with an ≤4.25 μg/mL IC50 value [77]. In contrast, growth of the HeLa cancer cell lines was successfully inhibited by AgNPs, which are spherical in shape with sizes ranging from 5–120 nm. NPs preparation from different plants exhibited a diverse range of IC50 values that depended on the method used for AgNPs synthesis and the type of plant extracts used [78,79,80,81,82,83,84,85,86]. The spherically shaped bio-synthesized AgNPs with sizes ranged between 7.39–80 nm have displayed inhibitory activities against colon cancer cell lines HCT 15, HT29 cells and HCT-116, and their IC50 values ranged between 5.5–100 μg/mL [87,88,89,90,91]. Inhibition by biosynthesized AgNPs have been successfully carried out against lung cancer cell line A549. The prepared NPs were spherical in shape with sizes ranging between 13–136 nm and showed a dose-dependent inhibitory activity with different values of IC50 and LD50, as mentioned in Table 1 [77,92,93,94,95,96,97,98,99]. Spherical biosynthesized AgNPs with sizes ranged between 5–50 nm inhibited the human gastric adenocarcinoma (AGS) cell line with 21.05 μg/mL IC50 value [100].

Table 1.
List of studies exhibiting biosynthesized silver NPs and their anticancer activity.
Inhibition by spherical biosynthesized AgNPs with sizes ranged between 6.4–27.2 nm was observed against the intestinal cancer cell line SMMC-7721 with above 27.75 μg/mL IC50 value [101]. Bio-extract-derived AgNPs, which are spherical and cuboidal in shape with sizes ranged between 59–94 nm, showed inhibitory actions against epidermoid carcinoma cell line A431, where IC50 values ranged between 78.58–83.57 μg/mL [102]. Many biosynthesized AgNPs were reported that inhibited the growth of the MCF-7 breast cancer cell lines or showed toxicity against them. The shapes of AgNPs reported in these anticancer studies varied such as cuboidal, hexagonal, spherical, and pentagonal with the sizes ranging between 5–80 nm and their IC50 values ranging between 3.04–250 μg/mL. Additionally, some studies outcomes suggested that the IC50 values of biosynthesized AgNPs varied in a dose dependent fashion and depended on the dose of the extract used [82,89,96,98,103,104,105,106,107,108,109,110,111,112]. Spherical AgNPs that ranged from 31–56 nm in size repressed the laryngeal carcinoma cell line Hep-2, with IC50 values ranged between 3.42–12.5 μg/mL [109,113,114]. The hepatic cancer cell lines Hep-G2 were inhibited by spherically shaped AgNPs [115,116]. Inhibition by biosynthesized spherical AgNPs that were 8–22 nm in sizes was observed against leukemia cell lines HL-60 and H1299 with 5.33 μg/mL IC50 value, and the inhibition depended on the dose of extract used for preparation [79,117]. The kidney cancer cell line Hek-293 was inhibited by 40 nm spherical AgNPs in a dose-dependent fashion [82]. Many studies have been conducted for biosynthesis of AgNPs and to ascertain their impact on various cancerous cell lines. AgNPs are known to possess anti-angiogenic properties. In one of the studies, performed on bovine retinal epithelial cells (BRECs), AgNPs of 40 nm size were shown to successfully reduce VEGF-induced angiogenesis by inhibiting the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway [3].
The available data related to biosynthesized AgNPs against cervical cancer, colon cancer, lung cancer, gastric carcinoma, intestinal cancer, epidermoid carcinoma, breast cancer, hepatic cancer, laryngeal carcinoma, leukemia, and kidney cancer are enumerated in Table 1.
6.2. Applications of Biosynthesized Gold NPs (AuNPs) as Anti-Cancer Therapeutics
Besides silver, gold is also considered a good candidate for NPs synthesis, showing high dispersion owing to their small size and large surface area. Moreover, due to its resistance to oxidation by moisture, air and acids and biocompatible nature, it has gained attention in the biomedical field, particularly in areas of cell targeting, tumors detection, drug-delivery and cancer therapy [118]. It was reported recently that AuNPs are more effective in drug delivery due to their self-assembled natural [119] and for hyperthermia because of their optical excitation properties [120].
A series of in vitro studies has been conducted on various cancer cell lines, to evaluate the anticancer potential of biosynthesized AuNPs. Biosynthesized AuNPs, which are spherical in shape with sizes ranged between 12–30 nm, showed inhibitory actions against MCF-7 breast cancer cell lines and their IC50 values depended on the method used for AuNPs synthesis and the type of plant extracts used for their preparation [121,122]. Spherical and triangular shaped AuNPs of sizes ranged between 13–28 nm showed cytotoxicity against MCF-7 breast cancer cells with a 257.8 µg/mL IC50 value [123].
In other studies, AuNPs which were spherical in shape with sizes ranged between 22–30 nm showed cytotoxicity against MDA- MB-231 breast cancer cell lines by activating apoptotic cell death pathways [124]. Bio-extract derived AuNPs with 14.6 nm size exhibited inhibitory actions against breast cancer cells through DNA damage and necrosis [125]. Spherically shaped biosynthesized AuNPs with average sizes of 95 nm repressed the growth of breast cancer cells MCF-7 by regulating the expression of anti-apoptotic (p53) and pro (Bcl-2) proteins with a 4.76 μg/mL IC50 value [126]. In another study, inhibition of breast cancer cell line HBL-100 was shown by spherically shaped AuNPs [127]. Inhibition by biosynthesized AuNPs that exhibited spherical and aggregated morphology was observed against A549 lung cancer cell lines. The size of these AuNPs ranged between 80–120 nm and offered cytotoxicity to cancerous cell lines by up-regulating many proinflammatory genes such as tumor necrotic factor-alpha (TNF-α) and interleukins IL-10 and IL-6 [128]. Inhibition of A549 lung cancer cell lines was shown by AuNPs, which are spherical in shape with 14 μg/mL IC50 value [129].
Biosynthesized AuNPs, which were hexagonal, triangular, and quasi-spherical in shape with sizes ranged between 6.03–150 nm repressed the A549 Lung cancer cell lines by offering low toxicity [130,131]. Pentagonal and triangular shaped biosynthesized AuNPs with sizes ranged between 10–50 nm showed substantial anticancer potential against cervical cancer cell lines HeLa by inhibiting their proliferation with an IC50 value of 100 µg/mL [132]. Other studies against cervical cancer using HeLa cell lines demonstrated the inhibitory activities of biosynthesized AuNPs derived from various plant extracts, their sizes and IC50 values varied and were dependent upon the type and dose of respective plant extracts used [133,134,135,136]. Moreover, cytotoxicity testing of biosynthesized AuNPs has been conducted on various other cell lines such as kidney [122,137,138], leukemia [139], and liver [140], as mentioned in Table 2.

Table 2.
List of studies exhibiting biosynthesized gold NPs and their anticancer activity.
Available data regarding anticancer activities of biosynthesized AuNPs against the cell lines mentioned above for cervical cancer, breast cancer, lung cancer, kidney cancer, leukemia and liver cancer are summarized in Table 2 with their citations.
6.3. Applications of Biosynthesized Zinc and Zinc Oxide NPs (Zn/ZnO-NPs) as Anti-Cancer Therapeutics
Biological synthesis of zinc and zinc oxide NPs are of great interest in recent years for the fabrication of eco-friendly NPs because of presence of phytochemical components like flavonoids, phenolics or alkaloids [141]. The specific physicochemical properties of ZnO NPs helps in their cellular uptake and their innate toxicity against cancerous cells can induce intracellular ROS generation, which ultimately leads to death via an apoptotic pathway, these characteristics make them an attractive candidate for biomedical applications [142].
Different parts of the plants have been extensively studied for the biosynthesis of ZnO NPs and their anticancer effects have been investigated in vitro using various cancerous cell lines. Spherical and hexagonal shaped bio-extract-derived Zn NPs have shown cytotoxicity in lung cancer cell lines A549 and Calu-6. These NPs exhibited various sizes and IC50 values depending on the types of plant extracts used for their preparation and their doses used [142,143,144,145,146]. Spherical and hexagonal biosynthesized ZnNPs with sizes ranging between 22.5–50 nm, prepared from different plant extracts, inhibited the WEHI-3 leukemia cancer cell lines, with IC50 values ranging between 2.25–12.4 μg/mL [147,148]. Spherical biosynthesized ZnNPs of cell lines and their IC50 values varied in a dose dependent manner and dependent upon the type of plant extracts used [106,149,150,151,152,153,154,155]. Biosynthesized hexagonal ZnNPs with sizes 10 ± 1.5 nm showed inhibitory actions against CaOV-3 ovarian cancer cell lines with IC50 value of 10.8 ± 0.3 μg/mL [156]. Inhibition by biosynthesized spherical ZnNPs that were 47 nm in sizes was observed against colon cancer cell lines HT-29 with 9.5 μg/mL IC50 value, respectively [157]. Similarly, biosynthesized ZnO-NPs showed potential inhibitory activities against epidermoid carcinoma cell lines A43 with an IC50 value of 16.5 ± 1.6 μg/mL [158], and against liver cancer cell lines Hep-G2 with an IC50 value of 14.1 ± 0.7 μg/mL [159]. Table 3 explains anticancer activities of ZnO NPs against lung cancer, breast cancer, ovarian cancer, colon cancer, epidermoid carcinoma, and liver cancer cell lines.

Table 3.
List of studies exhibiting biosynthesized zinc NPs and their anticancer activity.
6.4. Applications of Biosynthesized Copper/Copper Oxide NPs (Cu/CuO-NPs) as Anti-Cancer Therapeutics
Copper NPs have also gained significant attention as cytotoxic nano-entities because of their low cost, easy availability, and great similarity in properties with the noble metals [161]. Copper and copper oxide NPs are extensively used as a tool for cancer imaging owing to their highly effective light-to-heat transformation property under influence of near-infrared laser irradiation [162].
Different biologically synthesized Cu/CuO NP have been shown to be cytotoxic against multiple cancerous cell lines. Plant-mediated biosynthesized CuO NPs, which were spherical and hexagonal in shape with sizes of 26.6 nm exhibited inhibitory actions against cervical cancer cell lines HeLa by initiating ROS mediated apoptotic pathways [163]. Similarly, spherically shaped CuO NPs of 12 nm sizes, prepared from aqueous leaf extracts of different plants showed cytotoxicity against cervical cancer cell lines HeLa, breast cancer cell lines MCF-7 and lung cancer cell lines A549, and their IC50 values varied depending on the types of plants used [164]. Inhibition of MCF-7 breast cancer cell lines were carried out using biosynthesized spherically shaped CuO NPs of 26–30 nm sizes with a 56.16 μg/mL IC50 value [165].
In another study, aqueous leave extract derived CuO NPs, which are spherical in shape with sizes ranging between 20–50 nm, showed the highest anticancer activity against AMJ-13 breast cancer cell lines with an IC50 value of 1.47 μg/mL and against SKOV-3 ovarian cancer cell lines with a 2.27 μg/mL IC50 value [166]. Biosynthesized CuO NPs with 577 nm sizes displayed cytotoxicity against lung cancer cell lines A549 through apoptosis initiated via nuclear fragmentation and showed an IC50 value of 200 μg/mL [167]. Similarly, spherically shaped CuO NPs of different sizes were tested against cervical cancer cell lines HeLa and lung cancer cell lines A549 [168]. Cytotoxicity of spherically shaped biosynthesized CuO NPs with about 4.8 nm sizes were tested against prostate cancer cell lines PC-3 [169]. Table 4 shows anticancer activities of Cu/CuO NPs against cervical cancer, breast cancer, ovarian cancer, lung cancer, and prostate cancer cell lines.

Table 4.
List of studies exhibiting biosynthesized copper/copper oxide NPs and their anticancer activity.
7. Nano-Toxicity, the Concern/Bottleneck
Despite their promising potential in biomedical field. there are certain adverse health effects linked with their use [170]. For instance, agglomeration is one of the leading problems in translating this therapy into medicines as it poses toxicity in organ systems. Even if not agglomerated, it causes cellular injuries [171]. Toxicity offered by NPs is generally attributed to their morphology and surface reactivity. The toxicity associated with NPs can be controlled by including free groups at their surfaces such as –COOH groups, which are considered less toxic than –OH group and –NH2 groups [172]. Toxicity can also be minimized by controlling the size (30–100 nm) of metal NPs [173]. For specific and targeted use of nanomaterials, it is essential to understand the possible interactions between biological systems and the NPs, in this way the aggressive reactions can be minimized. To reduce toxicity, biological synthesis of NPs is preferred due to occurrence of biocompatible phytoconstituents [174,175]. Some studies also indicated that polyphenol compounds are nontoxic to healthy cells while exhibiting toxicity against cancerous cells [176].
8. Conclusions and Future Prospects
Despite all the recent advancements in cancer diagnosis and treatment, cancer remains one of the main causes of death globally. To date, no efficient treatment has been discovered to treat cancer, and all of the available anticancer drugs hold potential side effects. Thus, in a quest to find better diagnostics and treatment with maximal efficiency, specificity and lesser toxicity, scientists are looking to develop novel approaches. Recently, biological, or green, synthesis of NPs has gained significant attention in the biomedical field. Green synthesis is cost effective, less toxic and eco-friendly as compared to other methods of NPs formulation. The higher biocompatibility, lesser agglomeration rate, maximal clearance and lesser toxicity are the main aspects to be considered, this review article gives a compendious idea about the green synthesis of metallic NPs (Ag, Au, Zn/ZnO and Cu/CuO) and their mechanism of action and explored their therapeutic potential in vitro against various cancer cell lines. The effect of NPs varied from one type of cancer to the other, indicating that besides the specific properties of NPs, the cellular response is also important. ROS is an initiator molecule in autophagic, apoptotic and necroptotic death pathways and hence, it can be considered as the precursor component of cell death.
Metallic NPs showed remarkable promises in case of nano-based medical treatments, but their 3D tumor model studies and clinical trials remain unexplored. Therefore, their clinical trials are compulsory for leading the future direction regarding their applications. Currently, analysis into their dose, route of administration and biodegradability are the main hurdles that need to be tackled in the clinical trials.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, B.H.A., A.A. (Anisa Andleeb), C.H. and M.T.; writing—original draft preparation, A.A. (Anisa Andleeb), A.A. (Aneeta Andleeb), S.A., G.Z., A.M. and M.T.; writing—review and editing, A.A. (Anisa Andleeb), S.A., M.N., C.H. and J.M.L.; visualization, A.A. (Anisa Andleeb) and B.H.A.; supervision, B.H.A. and C.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sufyani, A.; Moslah, N.; Hussien, N.A.; Hawsawi, Y.M. Characterization and Anticancer Potential of Silver Nanoparticles Biosynthesized from Olea chrysophylla and Lavandula dentata Leaf Extracts on HCT116 Colon Cancer Cells. J. Nanomater. 2019, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratan, Z.A.; Haidere, M.F.; Nurunnabi, M.; Shahriar, S.M.; Ahammad, A.; Shim, Y.Y.; Reaney, M.J.; Cho, J.Y. Green chemistry synthesis of silver nanoparticles and their potential anticancer effects. Cancers 2020, 12, 855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jemal, A.; Bray, F.; Center, M.M.; Ferlay, J.; Ward, E.; Forman, D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2011, 61, 69–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patra, C.R.; Mukherjee, S.; Kotcherlakota, R. Biosynthesized silver nanoparticles: A step forward for cancer theranostics? Nanomedicine 2014, 9, 1445–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ovais, M.; Khalil, A.T.; Raza, A.; Khan, M.A.; Ahmad, I.; Islam, N.U.; Saravanan, M.; Ubaid, M.F.; Ali, M.; Shinwari, Z.K. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles via plant extracts: Beginning a new era in cancer theranostics. Nanomedicine 2016, 12, 3157–3177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macdonald, J.S. Toxicity of 5-fluorouracil. Oncology 1999, 13, 33–34. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Khan, S.; Parvez, S.; Chaudhari, B.; Ahmad, F.; Anjum, S.; Raisuddin, S. Ellagic acid attenuates bleomycin and cyclophosphamide-induced pulmonary toxicity in Wistar rats. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 58, 210–219. [Google Scholar]
- Adamson, I. Pulmonary toxicity of bleomycin. Environ. Health Perspect. 1976, 16, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avilés, A.; Arévila, N.; Díaz Maqueo, J.C.; Nambo, M.J. Late cardiac toxicity of doxorubicin, epirubicin, and mitoxantrone therapy for Hodgkin′s disease in adults. Leuk. Lymphoma 1993, 11, 275–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vickers, A. Alternative cancer cures:“unproven” or “disproven”? CA Cancer J. Clin. 2004, 54, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Thanou, M. Targeting nanoparticles to cancer. Pharmacol. Res. 2010, 62, 90–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zivyar, N.; Bagherzade, G.; Moudi, M.; Manzari Tavakoli, M. Evaluation of the green synthesis, characterization and antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles from corm extract of Crocus sativus var. Haussknechtii. J. Hortic. Postharvest Res. 2021, 19–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, K.T. Targeted nanoparticles for cancer therapy: Promises and challenge. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal-Esteban, L.C.; Fajas, L. Cell cycle regulators in cancer cell metabolism. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Mol. Basis Dis. 2020, 1866, 165715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otto, T.; Sicinski, P. Cell cycle proteins as promising targets in cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2017, 17, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontomanolis, E.N.; Koutras, A.; Syllaios, A.; Schizas, D.; Mastoraki, A.; Garmpis, N.; Diakosavvas, M.; Angelou, K.; Tsatsaris, G.; Pagkalos, A. Role of Oncogenes and Tumor-suppressor Genes in Carcinogenesis: A Review. Anticancer. Res. 2020, 40, 6009–6015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipsick, J. A history of cancer research: Tumor suppressor genes. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2020, 12, a035907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaptain, S.; Tan, L.K.; Chen, B. Her-2/neu and breast cancer. Diagn. Mol. Pathol. 2001, 10, 139–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Medarde, A.; Santos, E. Ras in cancer and developmental diseases. Genes Cancer 2011, 2, 344–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermeking, H. The MYC oncogene as a cancer drug target. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2003, 3, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finn, R. Targeting Src in breast cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2008, 19, 1379–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janknecht, R. On the road to immortality: hTERT upregulation in cancer cells. FEBS Lett. 2004, 564, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, J.M.; Cory, S. The Bcl-2 apoptotic switch in cancer development and therapy. Oncogene 2007, 26, 1324–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Liu, S.; Tao, Y. Regulating tumor suppressor genes: Post-translational modifications. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2020, 5, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pećina-Šlaus, N.; Kafka, A.; Salamon, I.; Bukovac, A. Mismatch repair pathway, genome stability and cancer. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2020, 7, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruggiano, A.; Ramadan, K. DNA–protein crosslink proteases in genome stability. Commun. Biol. 2021, 4, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ui, A.; Chiba, N.; Yasui, A. Relationship among DNA double-strand break (DSB), DSB repair, and transcription prevents genome instability and cancer. Cancer Sci. 2020, 111, 1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, X.; Han, Y.; Ji, T.; Huang, X.; Gao, Q.; Ma, D. RAD54B potentiates tumor growth and predicts poor prognosis of patients with luminal a breast cancer. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 118, 109341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAndrew, E.N.; McManus, K.J. The enigmatic oncogene and tumor suppressor-like properties of RAD54B: Insights into genome instability and cancer. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2017, 56, 513–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasuhara, T.; Suzuki, T.; Katsura, M.; Miyagawa, K. Rad54B serves as a scaffold in the DNA damage response that limits checkpoint strength. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitot, H.C. The molecular biology of carcinogenesis. Cancer 1993, 72, 962–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, G.; Sundaresan, V.; Hasleton, P.; Rudd, R.; Taylor, R.; Rabbitts, P. Sequential molecular genetic changes in lung cancer development. Oncogene 1995, 11, 2591–2598. [Google Scholar]
- Haggman, M.J.; Macoska, J.A.; Wojno, K.J.; Oesterling, J.E. The relationship between prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia and prostate cancer: Critical issues. J. Urol. 1997, 158, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.A. Metal nanoparticles toxicity: Role of physicochemical aspects. In Metal Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery and Diagnostic Applications; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, J.; Singh, T.; Rawat, M. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles via various plant extracts for anti-cancer applications. Nanomedicine 2017, 7, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Perveen, S.; Al-Taweel, A.M. Green Chemistry and Synthesis of Anticancer Molecule. Green Chem. 2018, 51–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cyril, N.; George, J.B.; Joseph, L.; Raghavamenon, A.; VP, S. Assessment of antioxidant, antibacterial and anti-proliferative (lung cancer cell line A549) activities of green synthesized silver nanoparticles from Derris trifoliata. Toxicol. Res. 2019, 8, 297–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.; Mukherjee, P.; Senapati, S.; Mandal, D.; Khan, M.I.; Kumar, R.; Sastry, M. Extracellular biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using the fungus Fusarium oxysporum. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2003, 28, 313–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, N.; Faraz, M.; Pandey, R.; Shakir, M.; Fatma, T.; Varma, A.; Barman, I.; Prasad, R. Facile algae-derived route to biogenic silver nanoparticles: Synthesis, antibacterial, and photocatalytic properties. Langmuir 2015, 31, 11605–11612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saifuddin, N.; Wong, C.; Yasumira, A. Rapid biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using culture supernatant of bacteria with microwave irradiation. E -J. Chem. 2009, 6, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandran, S.P.; Chaudhary, M.; Pasricha, R.; Ahmad, A.; Sastry, M. Synthesis of gold nanotriangles and silver nanoparticles using Aloevera plant extract. Biotechnol. Prog. 2006, 22, 577–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshimura, H. Protein-assisted nanoparticle synthesis. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2006, 282, 464–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, D.; Kanchi, S.; Bisetty, K. Biogenic synthesis of nanoparticles: A review. Arab. J. Chem. 2019, 12, 3576–3600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, P.V.; Nallappan, D.; Madhavi, K.; Rahman, S.; Jun Wei, L.; Gan, S.H. Phytochemicals and biogenic metallic nanoparticles as anticancer agents. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chahal, A.; SAINI, A.; Chhillar, A.K.; SAINI, R. Natural antioxidants as defense system against cancer. Asian J. Pharm. Clin. Res. 2018, 11, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, M.A.; Kanwal, Z.; Rauf, A.; Sabri, A.N.; Riaz, S.; Naseem, S. Size-and shape-dependent antibacterial studies of silver nanoparticles synthesized by wet chemical routes. Nanomaterials 2016, 6, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hira, I.; Kumar, A.; Kumari, R.; Saini, A.K.; Saini, R.V. Pectin-guar gum-zinc oxide nanocomposite enhances human lymphocytes cytotoxicity towards lung and breast carcinomas. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2018, 90, 494–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Likus, W.; Bajor, G.; Siemianowicz, K. Nanosilver-does it have only one face? Acta Biochim. Pol. 2013, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurj, A.; Braicu, C.; Pop, L.-A.; Tomuleasa, C.; Gherman, C.D.; Berindan-Neagoe, I. The new era of nanotechnology, an alternative to change cancer treatment. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2017, 11, 2871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fröhlich, E. The role of surface charge in cellular uptake and cytotoxicity of medical nanoparticles. Int. J. Nanomed. 2012, 7, 5577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexis, F.; Pridgen, E.; Molnar, L.K.; Farokhzad, O.C. Factors affecting the clearance and biodistribution of polymeric nanoparticles. Mol. Pharm. 2008, 5, 505–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, A.L.; Bernas, L.M.; Rutt, B.K.; Foster, P.J.; Gillies, E.R. Enhanced cell uptake of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles functionalized with dendritic guanidines. Bioconjugate Chem. 2008, 19, 2375–2384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Telrandhe, R. Anti-Cancer Potential of Green Synthesized Silver Nanoparticles-A Review. Asian J. Pharm. Technol. 2019, 9, 260–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, K.M. Key Receiver Circuits for Digital Beamforming in Millimeter-Wave Imaging. Mass. Inst. Technol. 2011. Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/1721.1/64587 (accessed on 10 March 2011).
- Saad, M.; Garbuzenko, O.B.; Ber, E.; Chandna, P.; Khandare, J.J.; Pozharov, V.P.; Minko, T. Receptor targeted polymers, dendrimers, liposomes: Which nanocarrier is the most efficient for tumor-specific treatment and imaging? J. Control. Release 2008, 130, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subbiah, R.; Veerapandian, M.; S Yun, K. Nanoparticles: Functionalization and multifunctional applications in biomedical sciences. Curr. Med. Chem. 2010, 17, 4559–4577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trédan, O.; Galmarini, C.M.; Patel, K.; Tannock, I.F. Drug resistance and the solid tumor microenvironment. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2007, 99, 1441–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, E.S.; Morton, J.G.; West, J.L. Nanoparticles for thermal cancer therapy. J. Biomech. Eng. 2009, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdalla, A.M.; Xiao, L.; Ullah, M.W.; Yu, M.; Ouyang, C.; Yang, G. Current challenges of cancer anti-angiogenic therapy and the promise of nanotherapeutics. Theranostics 2018, 8, 533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, R.K. Normalization of tumor vasculature: An emerging concept in antiangiogenic therapy. Science 2005, 307, 58–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barabadi, H.; Alizadeh, A.; Ovais, M.; Ahmadi, A.; Shinwari, Z.K.; Saravanan, M. Efficacy of green nanoparticles against cancerous and normal cell lines: A systematic review and meta-analysis. IET Nanobiotechnol. 2018, 12, 377–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, M.; Ingle, A.P.; Birla, S.; Yadav, A.; Santos, C.A.D. Strategic role of selected noble metal nanoparticles in medicine. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2016, 42, 696–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.K. Comparative therapeutic effects of plant-extract synthesized and traditionally synthesized gold nanoparticles on alcohol-induced inflammatory activity in SH-SY5Y cells in vitro. Biomedicines 2017, 5, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slavin, Y.N.; Asnis, J.; Häfeli, U.O.; Bach, H. Metal nanoparticles: Understanding the mechanisms behind antibacterial activity. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2017, 15, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouyang, L.; Shi, Z.; Zhao, S.; Wang, F.T.; Zhou, T.T.; Liu, B.; Bao, J.K. Programmed cell death pathways in cancer: A review of apoptosis, autophagy and programmed necrosis. Cell Prolif. 2012, 45, 487–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, T.; Yan, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Guo, F.; Jiang, C. Copper oxide nanoparticles induce autophagic cell death in A549 cells. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e43442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Stefano, D.; Carnuccio, R.; Maiuri, M.C. Nanomaterials toxicity and cell death modalities. J. Drug Deliv. 2012, 2012, 167896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halamoda Kenzaoui, B.; Chapuis Bernasconi, C.; Guney-Ayra, S.; Juillerat-Jeanneret, L. Induction of oxidative stress, lysosome activation and autophagy by nanoparticles in human brain-derived endothelial cells. Biochem. J. 2012, 441, 813–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akter, M.; Sikder, M.T.; Rahman, M.M.; Ullah, A.A.; Hossain, K.F.B.; Banik, S.; Hosokawa, T.; Saito, T.; Kurasaki, M. A systematic review on silver nanoparticles-induced cytotoxicity: Physicochemical properties and perspectives. J. Adv. Res. 2018, 9, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nath, D.; Banerjee, P. Green nanotechnology—A new hope for medical biology. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2013, 36, 997–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barabadi, H.; Ovais, M.; Shinwari, Z.K.; Saravanan, M. Anti-cancer green bionanomaterials: Present status and future prospects. Green Chem. Lett. Rev. 2017, 10, 285–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cragg, G.M.; Newman, D.J. Plants as a source of anti-cancer agents. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2005, 100, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaid, P.; Raizada, P.; Saini, A.K.; Saini, R.V. Biogenic silver, gold and copper nanoparticles-A sustainable green chemistry approach for cancer therapy. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2020, 16, 100247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, X.; Alvarez, P.J.; Li, Q. Applications of nanotechnology in water and wastewater treatment. Water Res. 2013, 47, 3931–3946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Schluesener, H.J. Nanosilver: A nanoproduct in medical application. Toxicol. Lett. 2008, 176, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, A.; Mehdi, S.J.; Irshad, M.; Ali, A.; Sardar, M.; Moshahid, M.; Rizvi, A. Effect of biologically synthesized silver nanoparticles on human cancer cells. Sci. Adv. Mater. 2012, 4, 1200–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasanth, K.; Ilango, K.; MohanKumar, R.; Agrawal, A.; Dubey, G.P. Anticancer activity of Moringa oleifera mediated silver nanoparticles on human cervical carcinoma cells by apoptosis induction. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2014, 117, 354–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Govindaraju, K.; Krishnamoorthy, K.; Alsagaby, S.A.; Singaravelu, G.; Premanathan, M. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles for selective toxicity towards cancer cells. IET Nanobiotechnol. 2015, 9, 325–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukirtha, R.; Priyanka, K.; Antony, J.; lakkannan, S.K.; Thangam, R.; Gunasekaran, P.; Krishnan, M.L.; Achiraman, S. Cytotoxic effect of Green synthesized silver nanoparticles using Melia azedarach against in vitro HeLa cell lines and lymphoma mice model. Process Biochemistry 2012, 47, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeyaraj, M.; Rajesh, M.; Arun, R.; MubarakAli, D.; Sathishkumar, G.; Sivanandhan, G.; Dev, G.K.; Manickavasagam, M.; Premkumar, K.; Thajuddin, N. An investigation on the cytotoxicity and caspase-mediated apoptotic effect of biologically synthesized silver nanoparticles using Podophyllum hexandrum on human cervical carcinoma cells. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2013, 102, 708–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mittal, A.K.; Thanki, K.; Jain, S.; Banerjee, U.C. Comparative studies of anticancer and antimicrobial potential of bioinspired silver and silver-selenium nanoparticles. J. Mater. Nanosci. 2016, 3, 22–27. [Google Scholar]
- Nakkala, J.R.; Mata, R.; Gupta, A.K.; Sadras, S.R. Biological activities of green silver nanoparticles synthesized with Acorous calamus rhizome extract. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 85, 784–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajkuberan, C.; Sudha, K.; Sathishkumar, G.; Sivaramakrishnan, S. Antibacterial and cytotoxic potential of silver nanoparticles synthesized using latex of Calotropis gigantea L. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2015, 136, 924–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijistella Bai, G. Green synthesis of silver nanostructures against human cancer cell lines and certain pathogens. Int. J. Pharm. Chem. Biol. Sci. 2014, 4, 101–111. [Google Scholar]
- Chanthini, A.B.; Balasubramani, G.; Ramkumar, R.; Sowmiya, R.; Balakumaran, M.D.; Kalaichelvan, P.T.; Perumal, P. Structural characterization, antioxidant and in vitro cytotoxic properties of seagrass, Cymodocea serrulata (R. Br.) Asch. & Magnus mediated silver nanoparticles. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2015, 153, 145–152. [Google Scholar]
- Devi, J.S.; Bhimba, B.V.; Ratnam, K. In vitro anticancer activity of silver nanoparticles synthesized using the extract of Gelidiella sp. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 4, 710–715. [Google Scholar]
- Kuppusamy, P.; Ichwan, S.J.; Al-Zikri, P.N.H.; Suriyah, W.H.; Soundharrajan, I.; Govindan, N.; Maniam, G.P.; Yusoff, M.M. In vitro anticancer activity of Au, Ag nanoparticles synthesized using Commelina nudiflora L. aqueous extract against HCT-116 colon cancer cells. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2016, 173, 297–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shawkey, A.M.; Rabeh, M.A.; Abdulall, A.K.; Abdellatif, A.O. Green nanotechnology: Anticancer activity of silver nanoparticles using Citrullus colocynthis aqueous extracts. Adv. Life Sci. Technol. 2013, 13, 60–70. [Google Scholar]
- Prabhu, D.; Arulvasu, C.; Babu, G.; Manikandan, R.; Srinivasan, P. Biologically synthesized green silver nanoparticles from leaf extract of Vitex negundo L. induce growth-inhibitory effect on human colon cancer cell line HCT15. Process. Biochem. 2013, 48, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manikandan, R.; Manikandan, B.; Raman, T.; Arunagirinathan, K.; Prabhu, N.M.; Basu, M.J.; Perumal, M.; Palanisamy, S.; Munusamy, A. Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using ethanolic petals extract of Rosa indica and characterization of its antibacterial, anticancer and anti-inflammatory activities. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2015, 138, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurunathan, S.; Jeong, J.-K.; Han, J.W.; Zhang, X.-F.; Park, J.H.; Kim, J.-H. Multidimensional effects of biologically synthesized silver nanoparticles in Helicobacter pylori, Helicobacter felis, and human lung (L132) and lung carcinoma A549 cells. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2015, 10, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanipandian, N.; Thirumurugan, R. A feasible approach to phyto-mediated synthesis of silver nanoparticles using industrial crop Gossypium hirsutum (cotton) extract as stabilizing agent and assessment of its in vitro biomedical potential. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2014, 55, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankar, R.; Karthik, A.; Prabu, A.; Karthik, S.; Shivashangari, K.S.; Ravikumar, V. Origanum vulgare mediated biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles for its antibacterial and anticancer activity. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2013, 108, 80–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venkatesan, B.; Subramanian, V.; Tumala, A.; Vellaichamy, E. Rapid synthesis of biocompatible silver nanoparticles using aqueous extract of Rosa damascena petals and evaluation of their anticancer activity. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Med. 2014, 7, S294–S300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venugopal, K.; Rather, H.; Rajagopal, K.; Shanthi, M.; Sheriff, K.; Illiyas, M.; Rather, R.; Manikandan, E.; Uvarajan, S.; Bhaskar, M. Synthesis of silver nanoparticles (Ag NPs) for anticancer activities (MCF 7 breast and A549 lung cell lines) of the crude extract of Syzygium aromaticum. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2017, 167, 282–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palaniappan, P.; Sathishkumar, G.; Sankar, R. Fabrication of nano-silver particles using Cymodocea serrulata and its cytotoxicity effect against human lung cancer A549 cells line. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2015, 138, 885–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sre, P.R.; Reka, M.; Poovazhagi, R.; Kumar, M.A.; Murugesan, K. Antibacterial and cytotoxic effect of biologically synthesized silver nanoparticles using aqueous root extract of Erythrina indica lam. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2015, 135, 1137–1144. [Google Scholar]
- Khanra, K.; Panja, S.; Choudhuri, I.; Chakraborty, A.; Bhattacharyya, N. Evaluation of antibacterial activity and cytotoxicity of green synthesized silver nanoparticles using Scoparia dulcis. Nano Biomed. Nano Biomed Eng. 2015, 7, 128–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi, S.; Shandiz, S.A.S.; Ghanbar, F.; Darvish, M.R.; Ardestani, M.S.; Mirzaie, A.; Jafari, M. Phytosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using Artemisia marschalliana Sprengel aerial part extract and assessment of their antioxidant, anticancer, and antibacterial properties. Int. J. Nanomed. 2016, 11, 1835. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, Q.H.; Ma, Y.J.; Wang, J.W. Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using Taxus yunnanensis callus and their antibacterial activity and cytotoxicity in human cancer cells. Nanomaterials 2016, 6, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, D.; Pradhan, S.; Ashe, S.; Rauta, P.R.; Nayak, B. Biologically synthesised silver nanoparticles from three diverse family of plant extracts and their anticancer activity against epidermoid A431 carcinoma. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 457, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firdhouse, J.; Lalitha, P. Apoptotic efficacy of biogenic silver nanoparticles on human breast cancer MCF-7 cell lines. Prog. Biomater. 2015, 4, 113–121. [Google Scholar]
- Elangovan, K.; Elumalai, S.; Anupriya, S.; Shenbhagaraman, R.; Kaleena, P.K.; Murugesan, K. Phyto mediated biogenic synthesis of silver nanoparticles using leaf extract of Andrographis echioides and its bio-efficacy on anticancer and antibacterial activities. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2015, 151, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sathishkumar, P.; Johnson, P.; Raji, V.; Abdull, R.M.Y.; Fuad, A.; Sadhasivam, S.; Ramasamy, B.; Thayumanavan, P. Anti-acne, anti-dandruff and anti-breast cancer efficacy of green synthesised silver nanoparticles using Coriandrum sativum leaf extract. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2016, 163, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukherjee, S.; Debabrata, C.; Rajesh, K.; Sujata, P. Potential theranostics application of bio-synthesized silver nanoparticles (4-in-1 system). Theranostics 2014, 4, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, N.; Jayachandra, D.; Nagoor, V.; Rani, M.; Sudha, S.R. Evaluation of antioxidant, antibacterial and cytotoxic effects of green synthesized silver nanoparticles by Piper longum fruit. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2014, 34, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, D.; Lalita, L.; Nitu, B. Antimicrobial and cytotoxic potential of silver nanoparticles synthesized using Rheum emodi roots extract. New Front. Chem. 2015, 24, 121. [Google Scholar]
- Devi, J.S.; Bhimba, B.V.; Ratnam, K. Anticancer activity of silver nanoparticles synthesized by the seaweed Ulva lactuca in vitro. Sci. Rep. 2012, 1, 242. [Google Scholar]
- Baharara, J.; Farideh, N.; Tayebe, R.; Marzieh, M.; Rosfarizan, M. Silver nanoparticles biosynthesized using Achillea biebersteinii flower extract: Apoptosis induction in MCF-7 cells via caspase activation and regulation of Bax and Bcl-2 gene expression. Molecules 2015, 20, 2693–2706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kathiravan, V.; Ravi, S.; Ashokkumar, S. Synthesis of silver nanoparticles from Melia dubia leaf extract and their in vitro anticancer activity. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2014, 130, 116–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeyaraj, M.; Sathishkumar, G.; Sivanandhan, G.; Mubarak, A.D.; Rajesh, M.; Arun, R.; Kapildev, G. Biogenic silver nanoparticles for cancer treatment: An experimental report. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2013, 106, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satyavani, K.; Gurudeeban, S.; Ramanathan, T.; Balasubramanian, T. Biomedical potential of silver nanoparticles synthesized from calli cells of Citrullus colocynthis (L.) Schrad. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2011, 9, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Satyavani, K.; Gurudeeban, S.; Ramanathan, T.; Balasubramanian, T. Toxicity Study of Silver Nanoparticles Synthesized from Suaeda monoica on Hep-2 Cell Line. Avicenna J. Med. Biotechnol. 2012, 4, 35. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kumar, B.; Kumari, S.; Rachid, S.; Karen, B.; Marcelo, G.; Luis, C. In vitro evaluation of silver nanoparticles cytotoxicity on Hepatic cancer (Hep-G2) cell line and their antioxidant activity: Green approach for fabrication and application. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2016, 159, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patra, S.; Sudip, M.; Ayan, K.B.; Anirban, G.; Bojja, S.; Chitta, R.P. Green synthesis, characterization of gold and silver nanoparticles and their potential application for cancer therapeutics. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2015, 53, 298–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Zhiyun, D.; Shijing, M.; Yue, L.; Dongli, L.; Huarong, H.; Sen, J. Effects of green-synthesized silver nanoparticles on lung cancer cells in vitro and grown as xenograft tumors in vivo. Int. J. Nanomed. 2016, 11, 1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, A.; Yogamoorthy, A.; Sundarapandian, S.M. Green synthesis of gold nanoparticles and evaluation of its cytotoxic property against colon cancer cell line. Res. J. Life Sci. Bioinform. Pharm. Chem. Sci. 2018, 4, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Jianwei, X.; Ye, Y.; Han, L.; Thiruventhan, K.; Feng, L. Green synthesis of gold nanoparticles from Scutellaria barbata and its anticancer activity in pancreatic cancer cell (PANC-1). Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2019, 47, 1617–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortie, M.B.; David, L.; Cortie Victoria, T. Heat transfer from nanoparticles for targeted destruction of infectious organisms. Int. J. Hyperth. 2018, 34, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uma Suganya, K.S.; Govindaraju, K.; Prabhu, D.; Arulvasu, C.; Karthick, V.; Niranjan, C. Anti-proliferative effect of biogenic gold nanoparticles against breast cancer cell lines (MDA-MB-231 & MCF-7). Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 371, 415–424. [Google Scholar]
- Arunkumar, P.; Hemamalini, V.; Kumpati, P. Rapid bioreduction of trivalent aurum using banana stem powder and its cytotoxicity against MCF-7 and HEK-293 cell lines. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2013, 15, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasubramani, G.; Rajendira, R.; Narayanaswamy, K.; Annamalai, P.; Thillainathan, N.; Rajamani, S.; Pachiappan, P. Structural characterization, antioxidant and anticancer properties of gold nanoparticles synthesized from leaf extract (decoction) of Antigonon leptopus Hook. & Arn. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2015, 30, 83–89. [Google Scholar]
- Krishnaraj, C.; Muthukumaran, P.; Ramachandran, R.; Balakumaran, M.D.; Kalaichelvan, P.T. Acalypha indica Linn: Biogenic synthesis of silver and gold nanoparticles and their cytotoxic effects against MDA-MB-231, human breast cancer cells. Biotechnol. Rep. 2014, 4, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Kassas, H.Y.; El-Sheekh, M.M. Cytotoxic activity of biosynthesized gold nanoparticles with an extract of the red seaweed Corallina officinalis on the MCF-7 human breast cancer cell line. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2014, 15, 4311–4317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banu, H.; Renuka, N.; Faheem, S.M.; Ismail, R.; Singh, V.; Saadatmand, Z.; Khan, S.S.; Narayanan, K.; Raheem, A.; Premkumar, K.; et al. Gold and silver nanoparticles biomimetically synthesized using date palm pollen extract-induce apoptosis and regulate p53 and Bcl-2 expression in human breast adenocarcinoma cells. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2018, 186, 122–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amarnath, K.; Mathew, N.L.; Nellore, J.; Siddarth, C.R.V.; Kumar, J. Facile synthesis of biocompatible gold nanoparticles from Vites vinefera and its cellular internalization against HBL-100 cells. Cancer Nanotechnol. 2011, 2, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagalingam, M.; Kalpana, V.N.; Panneerselvam, A. Biosynthesis, characterization, and evaluation of bioactivities of leaf extract-mediated biocompatible gold nanoparticles from Alternanthera bettzickiana. Biotechnol. Rep. 2018, 19, 268. [Google Scholar]
- Ramalingam, V.; Revathidevi, S.; Shanmuganayagam, T.; Muthulakshmi, L.; Rajaram, R. Biogenic gold nanoparticles induce cell cycle arrest through oxidative stress and sensitize mitochondrial membranes in A549 lung cancer cells. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 20598–20608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathishkumar, M.; Pavagadhi, S.; Mahadevan, A.; Balasubramanian, R. Biosynthesis of gold nanoparticles and related cytotoxicity evaluation using A549 cells. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2015, 114, 232–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, N.; WeiHong, L.; Hao, L. Biosynthesis of Au nanoparticles using agricultural waste mango peel extract and its in vitro cytotoxic effect on two normal cells. Mater. Lett. 2014, 134, 67–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baharara, J.; Ramezani, T.; Divsalar, A.; Mousavi, M.; Seyedarabi, A. Induction of apoptosis by green synthesized gold nanoparticles through activation of caspase-3 and 9 in human cervical cancer cells. Avicenna J. Med Biotechnol. 2016, 8, 75. [Google Scholar]
- Saikia, I.; Sonowal, S.; Pal, M.; Boruah, P.K.; Das, M.R.; Tamuly, C. Biosynthesis of gold decorated reduced graphene oxide and its biological activities. Mater. Lett. 2016, 178, 239–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, B.; Smita, K.; Cumbal, L.; Camacho, J.; Hernández-Gallegos, E.; de Guadalupe Chávez-López, M.; Grijalva, M.; Andrade, K. One pot phytosynthesis of gold nanoparticles using Genipa americana fruit extract and its biological applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 62, 725–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorosti, N.; Jamshidi, F. Plant-mediated gold nanoparticles by Dracocephalum kotschyi as anticholinesterase agent: Synthesis, characterization, and evaluation of anticancer and antibacterial activity. J. Appl. Biomed. 2016, 14, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajan, A.; Vilas, V.; Philip, D. Studies on catalytic, antioxidant, antibacterial and anticancer activities of biogenic gold nanoparticles. J. Mol. Liq. 2015, 212, 331–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, P.; Ray, S.; Sinha, S.; Das, B.; Khan, M.I.; Behera, S.K.; Yun, S.I.; Tripathy, S.K.; Mishra, A. Facile bio-synthesis of gold nanoparticles by using extract of Hibiscus sabdariffa and evaluation of its cytotoxicity against U87 glioblastoma cells under hyperglycemic condition. Biochem. Eng. J. 2016, 105, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wani, K.; Choudhari, A.; Chikate, R.; Kaul-Ghanekar, R. Synthesis and characterization of gold nanoparticles using Ficus religiosa extract. Carbon Sci. Technol. 2013, 5, 203–210. [Google Scholar]
- Geetha, R.; Ashokkumar, T.; Tamilselvan, S.; Govindaraju, K.; Sadiq, M.; Singaravelu, G. Green synthesis of gold nanoparticles and their anticancer activity. Cancer Nanotechnol. 2013, 4, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sathishkumar, G.; Bharti, R.; Jha, P.K.; Selvakumar, M.; Dey, G.; Jha, R.; Jeyaraj, M.; Mandal, M.; Sivaramakrishnan, S. Dietary flavone chrysin (5, 7-dihydroxyflavone ChR) functionalized highly-stable metal nanoformulations for improved anticancer applications. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 89869–89878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thema, F.T.; Manikandan, E.; Dhlamini, M.S.; Maaza, M. Green synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles via Agathosma betulina natural extract. Mater. Lett. 2015, 161, 124–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, J.W.; Martinez, E.; Louka, P.; Wingett, D.G. Zinc oxide nanoparticles for selective destruction of tumor cells and potential for drug delivery applications. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2010, 7, 1063–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firdhouse, M.J.; Lalitha, P. Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using the extract of Alternanthera sessilis—antiproliferative effect against prostate cancer cells. Cancer Nanotechnol. 2013, 4, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreau, J.W.; Weber, P.K.; Martin, M.C.; Gilbert, B.; Hutcheon, I.D.; Banfield, J.F. Extracellular proteins limit the dispersal of biogenic nanoparticles. Science 2007, 316, 1600–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bishop, G.M.; Dringen, R.; Robinson, S.R. Zinc stimulates the production of toxic reactive oxygen species (ROS) and inhibits glutathione reductase in astrocytes. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2007, 42, 1222–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gazaryan, I.G.; Krasnikov, B.F.; Ashby, G.A.; Thorneley, R.N.; Kristal, B.S.; Brown, A.M. Zinc is a potent inhibitor of thiol oxidoreductase activity and stimulates reactive oxygen species production by lipoamide dehydrogenase. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 10064–10072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Min, K.S. Physiological significance of metallothionein in oxidative stress. Yakugaku Zasshi J. Pharm. Soc. Jpn. 2007, 127, 695–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.J.; Park, Y.C.; Lee, S.W.; Jeong, M.S.; Yu, K.N.; Jung, H.; Lee, J.K.; Kim, J.S.; Cho, M.H. Comparing the toxic mechanism of synthesized zinc oxide nanomaterials by physicochemical characterization and reactive oxygen species properties. Toxicol. Lett. 2011, 207, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Liao, L.; Bian, X.; Kong, J.; Yang, P.; Liu, B. pH-Controlled delivery of doxorubicin to cancer cells, based on small mesoporous carbon nanospheres. Small 2012, 8, 2715–2720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Bowman, L.; Lu, Y.; Rojanasakul, Y.; Mercer, R.R.; Castranova, V.; Ding, M. Essential role of p53 in silica-induced apoptosis. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2005, 288, L488–L496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saud Alarifi, D.A.; Alkahtani, S.; Verma, A.; Ahamed, M.; Ahmed, M.; Alhadlaq, H.A. Induction of oxidative stress, DNA damage, and apoptosis in a malignant human skin melanoma cell line after exposure to zinc oxide nanoparticles. Int. J. Nanomed. 2013, 8, 983. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, K.W.; Zhao, W.; Li, N.; Barajas, B.; Kleinman, M.; Sioutas, C.; Horvath, S.; Lusis, A.J.; Nel, A.; Araujo, J.A. Air-pollutant chemicals and oxidized lipids exhibit genome-wide synergistic effects on endothelial cells. Genome Biol. 2007, 8, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Q.; Hein, S.; Misra, R.D.K. New generation of chitosan-encapsulated ZnO quantum dots loaded with drug: Synthesis, characterization and in vitro drug delivery response. Acta Biomater. 2010, 6, 2732–2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffitt, R.J.; Weil, R.; Hyndman, K.A.; Denslow, N.D.; Powers, K.; Taylor, D.; Barber, D.S. Exposure to copper nanoparticles causes gill injury and acute lethality in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 8178–8186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AshaRani, P.V.; Low Kah Mun, G.; Hande, M.P.; Valiyaveettil, S. Cytotoxicity and genotoxicity of silver nanoparticles in human cells. ACS Nano 2009, 3, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talalay, P.; Dinkova-Kostova, A.T.; Holtzclaw, W.D. Importance of phase 2 gene regulation in protection against electrophile and reactive oxygen toxicity and carcinogenesis. Adv. Enzym. Regul. 2003, 43, 121–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Xie, C. Zn2+ release from zinc and zinc oxide particles in simulated uterine solution. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2006, 47, 140–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Premanathan, M.; Karthikeyan, K.; Jeyasubramanian, K.; Manivannan, G. Selective toxicity of ZnO nanoparticles toward Gram-positive bacteria and cancer cells by apoptosis through lipid peroxidation. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2011, 7, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Wang, S.; Wu, Y.; You, H.; Lv, L. Acute ZnO nanoparticles exposure induces developmental toxicity, oxidative stress and DNA damage in embryo-larval zebrafish. Aquat. Toxicol. 2013, 136, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, N.; Manshian, B.; Jenkins, G.J.; Griffiths, S.M.; Williams, P.M.; Maffeis, T.G.; Wright, C.J.; Doak, S.H. NanoGenotoxicology: The DNA damaging potential of engineered nanomaterials. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 3891–3914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manke, A.; Wang, L.; Rojanasakul, Y. Mechanisms of nanoparticle-induced oxidative stress and toxicity. BioMed Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 942916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, M.; Tian, M.; Li, C. Copper-based nanomaterials for cancer imaging and therapy. Bioconjugate Chem. 2016, 27, 1188–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagajyothi, P.C.; Muthuraman, P.; Sreekanth, T.V.M.; Kim, D.H.; Shim, J. Green synthesis: In-vitro anticancer activity of copper oxide nanoparticles against human cervical carcinoma cells. Arab. J. Chem. 2017, 10, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehana, D.; Mahendiran, D.; Kumar, R.S.; Rahiman, A.K. Evaluation of antioxidant and anticancer activity of copper oxide nanoparticles synthesized using medicinally important plant extracts. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 89, 1067–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nisar, P.; Ali, N.; Rahman, L.; Ali, M.; Shinwari, Z.K. Antimicrobial activities of biologically synthesized metal nanoparticles: An insight into the mechanism of action. JBIC J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 2019, 24, 929–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulaiman, G.M.; Tawfeeq, A.T.; Jaaffer, M.D. Biogenic synthesis of copper oxide nanoparticles using olea europaea leaf extract and evaluation of their toxicity activities: An in vivo and in vitro study. Biotechnol. Prog. 2018, 34, 218–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sankar, R.; Maheswari, R.; Karthik, S.; Shivashangari, K.S.; Ravikumar, V. Anticancer activity of Ficus religiosa engineered copper oxide nanoparticles. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2014, 44, 234–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harne, S.; Sharma, A.; Dhaygude, M.; Joglekar, S.; Kodam, K.; Hudlikar, M. Novel route for rapid biosynthesis of copper nanoparticles using aqueous extract of Calotropis procera L. latex and their cytotoxicity on tumor cells. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2012, 95, 284–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasad, P.R.; Kanchi, S.; Naidoo, E.B. In-vitro evaluation of copper nanoparticles cytotoxicity on prostate cancer cell lines and their antioxidant, sensing and catalytic activity: One-pot green approach. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2016, 161, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Reece, S.P.; Brown, J.M. Immunotoxicological impact of engineered nanomaterial exposure: Mechanisms of immune cell modulation. Toxicol. Mech. Methods 2013, 23, 168–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, H.C.; Chan, W.C. Nanotoxicity: The growing need for in vivo study. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2007, 18, 565–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahab, R.; Kaushik, N.K.; Kaushik, N.; Choi, E.H.; Umar, A.; Dwivedi, S.; Musarrat, J.; Al-Khedhairy, A.A. ZnO nanoparticles induces cell death in malignant human T98G gliomas, KB and non-malignant HEK cells. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2013, 9, 1181–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Goyal, A.K.; Rath, G. Recent advances in metal nanoparticles in cancer therapy. J. Drug Target. 2018, 26, 617–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handy, R.D.; Von der Kammer, F.; Lead, J.R.; Hassellöv, M.; Owen, R.; Crane, M. The ecotoxicology and chemistry of manufactured nanoparticles. Ecotoxicology 2008, 17, 287–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nel, A.E.; Mädler, L.; Velegol, D.; Xia, T.; Hoek, E.M.; Somasundaran, P.; Klaessig, F.; Castranova, V.; Thompson, M. Understanding biophysicochemical interactions at the nano–bio interface. Nat. Mater. 2009, 8, 543–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khorrami, S.; Zarrabi, A.; Khaleghi, M.; Danaei, M.; Mozafari, M.R. Selective cytotoxicity of green synthesized silver nanoparticles against the MCF-7 tumor cell line and their enhanced antioxidant and antimicrobial properties. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 8013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).