Rapid Progress in Immunotherapies for Multiple Myeloma: An Updated Comprehensive Review
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
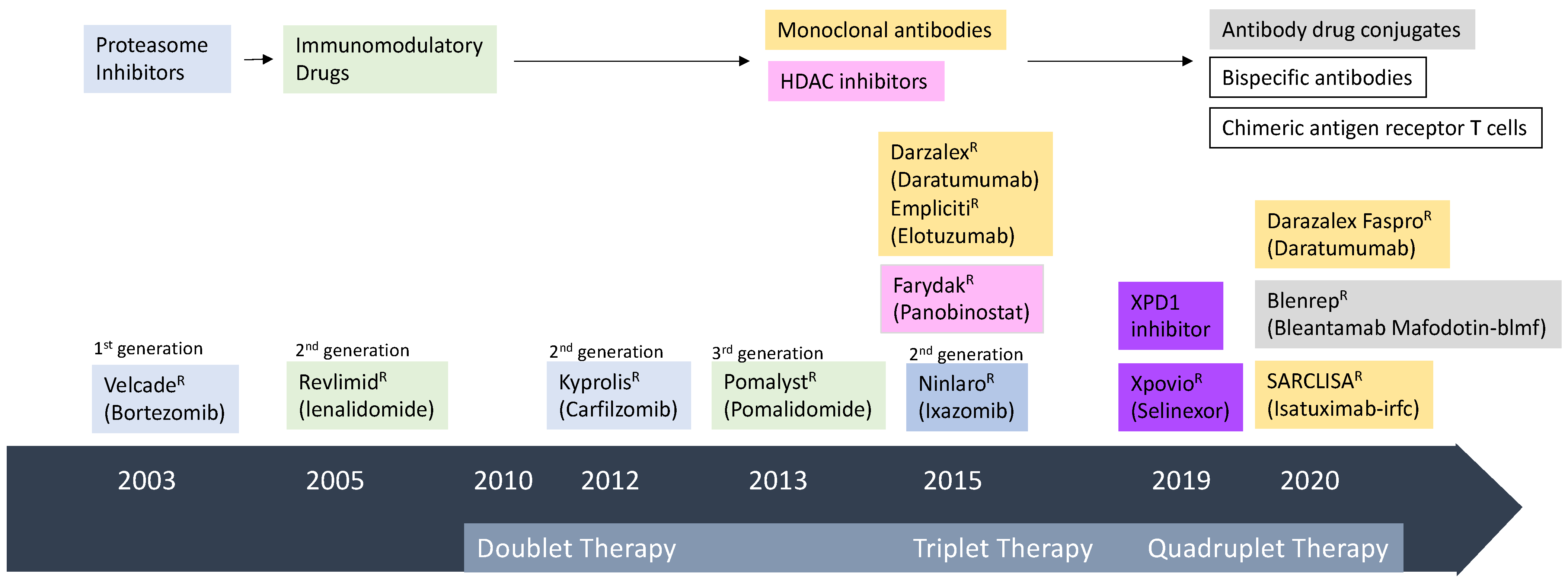
1. Introduction
2. Antibody Therapy
2.1. Monoclonal Antibodies (mAb) in MM
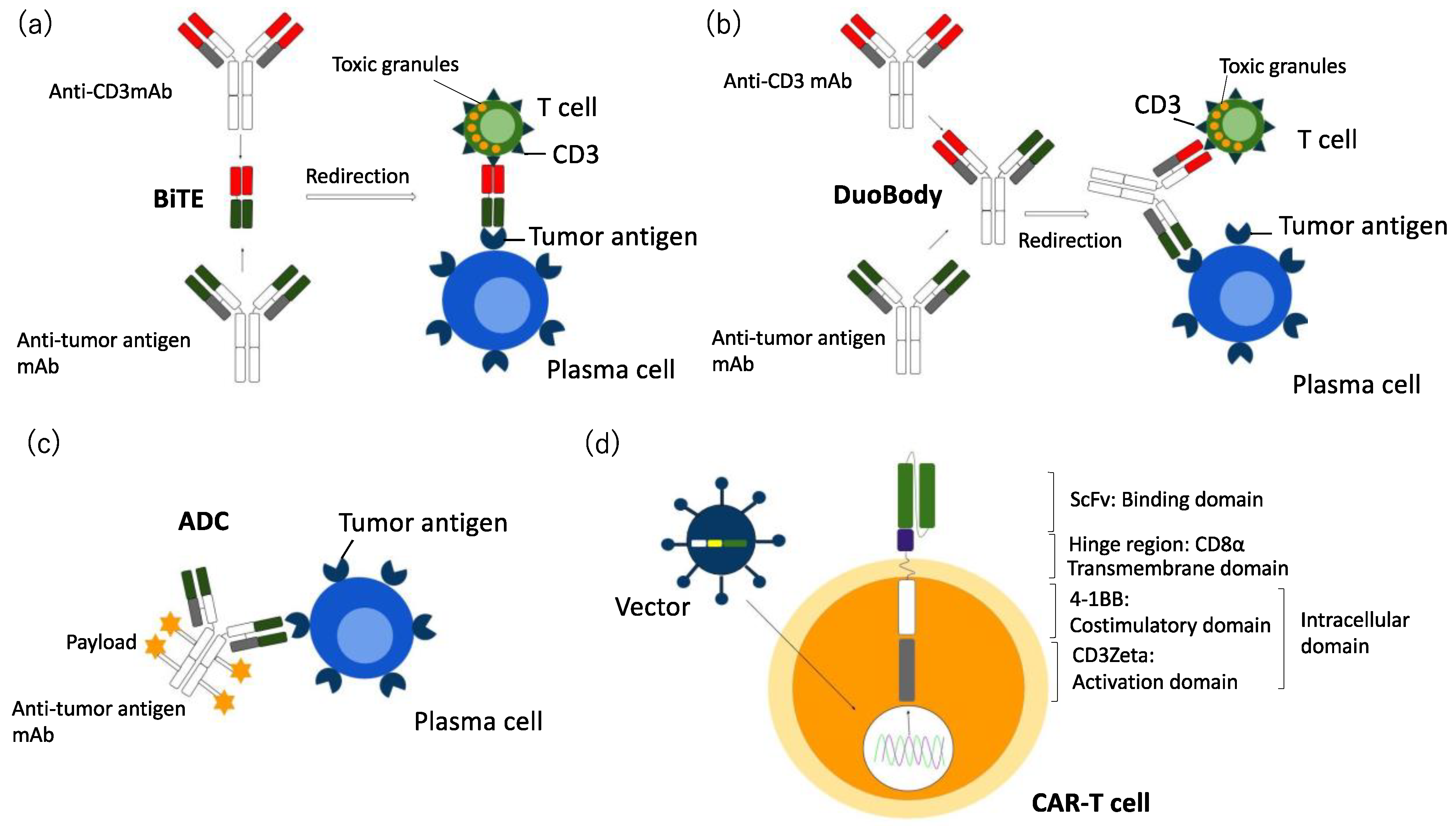
2.2. Bi-Specific Antibodies (BsAbs) and Tri-Specific Antibodies (TriAbs) in MM
2.3. Antibody Drug Conjugate (ADC) in MM
3. Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR) T Cell Therapy in MM
3.1. CAR-NK Cells
3.2. Dendritic Cells (DCs)
3.2.1. Idiotype (Id) Protein-Pulsed DCs
3.2.2. Whole MM Cell-Derived Antigen-Loaded DCs
3.2.3. MM Cell-Specific Antigen-Loaded DCs
4. Immune Check Point Inhibitors in MM
5. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Palumbo, A.; Anderson, K. Multiple myeloma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 1046–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajikumar, S.V.; Dimopoulos, M.A.; Palumbo, A.; Blade, J.; Merlini, G.; Mateos, M.V.; Kumar, S.; Hillenglass, J.; Kastritis, E.; Richarsoson, P.; et al. International Myeloma Working Group updated criteria for the diagnosis of multiple myeloma. Lancet Oncol. 2014, 15, e534–e548. [Google Scholar]
- Charlotte, P.; Davies, F. Toward personalized treatment in multiple myeloma based on molecular characteristic. Blood 2019, 133, 660–675. [Google Scholar]
- Moreau, P.; de Wit, E. Recent progress in relapsed multiple myeloma therapy implications for treatment decisions. Br. J. Haematol. 2017, 179, 98–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chim, C.S.; Kumad, S.K.; Orlowski, R.Z.; Cook, G.; Richardson, P.G.; Getz, M.A.; Giralt, S.; Maetos, M.V.; Leleu, C.; Anderson, K.C. Management of relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma: Novel agents, antibodies, immunotherapies and beyond. Leukemia 2018, 32, 252–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabwar, S.; Nabdakumar, B.; Kumar, S. Immune-based therapies in the management of multiple myeloma. Blood Cancer J. 2020, 10, 84. [Google Scholar]
- Varga, C.; Laubach, J.P.; Anderson, K.C.; Richardosn, P.G. Investigational agents in immunotherapy: A new horizon for the treatment of multiple myeloma. Br. J. Haematol. 2018, 181, 433–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Im, A.; Pavletic, S.Z. Immunotherapy in hematologic malignancies: Past, present, and future. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2017, 10, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardosn, P.G.; Lonial, S.; Jakubowiak, A.J.; Harousseau, J.L.; Anderson, K.C. Monoclonal antibodies in the treatment of multiple myeloma. Br. J. Haematol. 2011, 154, 745–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avet-Loiseau, H.; Fonseca, R.; Siegel, D.; Dimopoulos, M.A.; Spicka, I.; Masszi, T.; Hajek, R.; Rosinol, L.; Goranova-Marinova, V.; Mihaylov, G.; et al. Carfilzomib significantly improves the progression-free survival of high-risk patients in multiple myeloma. Blood 2016, 128, 1174–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, A.K.; Rajkumar, S.V.; Dimopoulos, M.A.; Masszi, T.; Spicka, I.; Oriol, A.; Hajek, R.; Rosinol, L.; Siegel, D.S.; Mihaylov, G.G.; et al. Carfilzomib, lenalidomide and dexamethasone for relapsed multiple myeloma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 142–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreau, P.; Mateos, M.V.; Berenson, J.R.; Weisel, K.; Lazzaro, A.; Song, K.; Dimopoulo, M.A.; Huang, M.; Zahlten-Kumeil, A.; Stewart, A.K. Once weekly versus twice weekly carfilzomib dosing in patients with relapsed and refractory multiple myeloma (A.R.R.O.W.): Interim analysis results of a randomised, phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol. 2018, 19, 953–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreau, P.; Masszi, T.; Grzasko, N.; Bahlis, N.J.; Hansson, M.; Pour, L.; Sandhu, J.; Ganly, P.; Baker, B.W.; Jackson, S.R.; et al. Oral ixazomib, lenalidomide, and dexamethasone for multiple myeloma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 374, 1621–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimopoulos, M.A.; Gay, F.; Schjesvold, F.; Beksac, M.; Hajek, R.; Weisel, K.C.; Gold Scmidt, H.; Maisnar, V.; Moreau, P.; Min, C.K.; et al. Oral ixazomib maintenance following autologous stem cell transplantation (TOURMALINE-MM3): A double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled phase 3 trial. Lancet 2019, 393, 253–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- San Miguel, J.; Weisel, K.; Moreau, P.; Lacy, M.; Song, K.; Delforge, M.; Karlin, L.; Goldschmid, H.; Banos, A.; Oriol, A.; et al. Pomalidomide plus low-dose dexamethasone versus high-dose dexamethasone alone for patients with relapsed and refractory multiple myeloma (MM-003): A randomized, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2013, 14, 1055–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ailawadhi, S.; Mikhael, J.R.; LaPlant, B.R.; Laumann, K.M.; Kumar, S.; Roy, V.; Dingli, D.; Bergsagel, P.L.; Buadi, F.K.; Rajikumar, S.V.; et al. Pomalidomide-dexamethasone in refractory multiple myeloma: Long-term follow-up of a multi-cohort phase II clinical trial. Leukemia 2017, 32, 719–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richardson, P.G.; Oriol, A.; Beksac, M.; Liberati, A.M.; Galli, M.; Schjesvold, F.; Lindsay, J.; Weisel, K.; White, D.; Facon, T.; et al. Pomalidomide, Bortezomib, and dexamethasone for patients with relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma previously treated with lenalidomide (OPTIMISMM): A randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, 781–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, S.; Safyan, R.A.; Lentxsch, S. Immunomodulatory Drugs (IMiDs) in multiple myeloma. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2017, 17, 846–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelhardt, M.; Wasch, R.; Reinhardt, H.; Kleber, M. Pomalidomide. Recent Results Cancer Res. 2018, 212, 169–185. [Google Scholar]
- Quail, D.F.; Joyce, J.A. Microenvironmental regulation of tumor progression and metastasis. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 1423–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swann, J.B.; Smyth, M.J. Immune surveillance of tumors. J. Clin. Investig. 2007, 117, 1137–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pratt, G.; Goodyear, O.; Moss, P. Immunodeficiency and immunotherapy in multiple myeloma. Br. J. Haematol. 2007, 138, 563–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lonial, S.; Dimopoulos, M.; Palumbo, A.; White, D.; Grosicki, S.; Spicka, I.; Walter-Croneck, A.; Moreau, P.; Maetos, M.V.; Magen, H.; et al. Elotuzumab therapy for relapsed multiple myeloma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 621–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laubach, J.P.; Richardon, P.G. CD38-targeted immunochemotherapy in refractory multiple myeloma: A new horizon. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 2660–2662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Weers, M.; Tai, Y.T.; Van Der Veer, M.S.; Bakker, J.M.; Vink, T.; Jacobs, D.C.; Oomen, L.A.; Peipp, M.; Valerius, T.; Slootstra, J.W.; et al. Daratumumab, a novel therapeutic human CD38 monoclonal antibody, induces killing of multiple myeloma and other hematological tumors. J. Immunol. 2011, 186, 1840–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overdijk, M.B.; Verploegen, S.; Bogels, M.; Van Egmond, M.; Van Bueren, J.L.J.; Mutis, T.; Groen, R.W.J.; Breij, J.; Martens, A.C.M.; Bleeker, W.K.; et al. Antibody-mediated phagocytosis contributes to the anti-tumor activity of the therapeutic antibody in lymphoma and multiple myeloma. mAbs 2015, 7, 311–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overdijk, M.B.; Jansen, J.H.; Nederend, M.; Van Bueren, J.J.L.; Groen, R.W.J.; Parren, P.W.H.I.; Lausen, J.H.W.; Borros, P. The therapeutic CD38 monoclonal antibody daratumumab induces programmed cell death via Fc gamma receptor-mediated cross-linking. J. Immunol. 2016, 197, 807–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krejcik, J.; Casneuf, T.; Nijhof, I.S.; Verbist, B.; Bald, J.; Plesner, T.; Syed, K.; Liu, K.; Van de Dank, N.W.C.J.; Weisss, B.M.; et al. Daratumumab depletes CD38+ immune-regulatory cells, promotes T-cell expansion, and skews T-cell repertoire in multiple myeloma. Blood 2016, 128, 384–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lokhorst, H.M.; Plesner, T.; Laubach, J.P.; Nahi, H.; Gimsing, P.; Hansson, M.; Minemma, M.C.; Lassen, U.; Krejcik, J.; Palumbo, A.; et al. Targeting CD38 with daratumumab monotherapy in multiple myeloma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 1207–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lonial, S.; Weiss, B.M.; Usmani, S.Z.; Singhal, S.; Chari, A.; Bahlis, N.J.; Belch, A.; Krishnan, A.; Vescio, R.A.; Maetos, M.V.; et al. Daratmumab monotherapy in patients with treatment-refratcory multiple myeloma (SIRIUS): An open-label, randomized, phase 2 trial. Lancet 2016, 387, 1551–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usmani, S.Z.; Weiss, B.M.; Plesner, T.; Bahlis, N.J.; Blech, A.; Lonial, S.; Lokhorst, H.M.; Voorhees, P.M.; Richardson, P.G.; Chiari, A.; et al. Clinical efficacy of daratumumab monotherapy in patients with heavily pretreated relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma. Blood 2016, 128, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimopoulos, M.A.; Orio, A.; Nahi, H.; San-Miguel, J.; Bahlis, N.J.; Usmani, S.Z.; Rabin, N.; Orlowski, W.Z.; Komarnicki, M.; Suzuki, K.; et al. Daratumumab, lenalidomide, and dexamethasone for multiple myeloma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 1319–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimopoulos, M.A.; San-Miguel, J.; Belch, A.; White, D.; Benboubker, L.; Cook, G.; Leiba, M.; Morton, J.; Ho, J.; Kim, K.; et al. Daratumumab plus lenalidomide and dexamethasone versus lenalidomide and dexamethasone in relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma: Updated analysis of POLLUX. Haematologica 2018, 103, 2088–2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chari, A.; Suvannasakha, A.; Fay, J.W.; Arnuff, B.; Kaufman, J.L.; Ifthikharuddin, J.J.; Weiss, B.M.; Krishnan, A.; Lentzsch, S.; Comenzo, R.; et al. Daratumumab plus pomalidomide and dexamethasone in relapsed and/or refractory myeloma. Blood 2018, 130, 974–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palumbo, A.; Chanan-khan, A.; Weisel, K.; Nooka, A.K.; Masszi, T.; Beksac, M.; Spicka, I.; Hungria, V.; Munder, M.; Maetos, M.V.; et al. Daratumumab, bortezomib, and dexamethasone for multiple myeloma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 54–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spencer, A.; Lentzsch, S.; Weisel, K.; Avet-Loiseau, H.; Mark, T.M.; Spicka, I.; Masszi, T.; Lauri, B.; Levin, M.D.; Bosi, A.; et al. Daratumumab plus bortezomib and dexamethasone versus bortezomib and dexamethasone in relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma: Updated analysis of CASTOR. Haematologica 2018, 103, 2079–2088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weisel, K.; Spencer, A.; Maetos, M.V. Daratumumab, bortezomib, and dexamethasone in relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma: Subgroup analysis of CASTOR based on cytogenetic risk. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2020, 13, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deckert, J.; Wetzel, M.C.; Bartle, L.M.; Skaletskaya, A.; Goldmacher, V.S.; Vallee, F.; Zhou-Liu, Q.; Ferrari, P.; Pouzieux, S.; Lahoute, C.; et al. SAR650984, a novel humanized CD38 targeting antibody, demonstrates potent antitumor activity in models of multiple myeloma and other CD38+ hematologic malignancies. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 4574–4583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, L.; Perez, C.; Zabaleta, A.; Manrique, I.; Alignani, D.; Ajona, D.; Blanco, L.; Lasa, M.; Masio, P.; Rozdigyez, I.; et al. The mechanism of action of the anti-CD38 monoclonal antibody isatuximab in multiple myeloma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 3176–3187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Acharya, C.; An, G.; Zhong, M.; Feng, X.; Wang, L.; Dasilva, N.; Song, Z.; Yang, G.; Adrian, F.; et al. SAR650984 directly induces multiple myeloma cell death via lysosomal-associated and apoptotic pathways, which is further enhanced by pomalidomide. Leukemia 2016, 30, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, T.; Strickland, S.; Glenn, M.; Charpentier, E.; Guillemin, H.; Hsu, K.; Mikhael, J. Phase I trial of isatuximab monotherapy in the treatment of refractory multiple myeloma. Blood Cancer J. 2019, 9, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, T.; Baz, R.; Benson, D.M.; Lendvai, M.; Wolf, J.; Munster, P.; Lesokhin, A.M.; Wack, C.; Charpentier, E.; Campana, F.; et al. A phase 1b study of isatuximab plus lenalidomide and dexamesasone for relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma. Blood 2017, 129, 3294–3303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikhael, J.; Richardson, P.; Usmani, S.Z.; Raje, N.; Bensinger, E.; Karanes, C.; Campana, F.; Kanagavel, D.; Dubin, F.; Liu, Q.; et al. A phase 1b study of isatuximab plus pomalidomide/dexamethasone in relapsed /refractory multiple myeloma. Blood 2019, 134, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attal, M.; Richardson, P.G.; Rajkumar, S.V.; San-Miguel, J.; Beksac, M.; Spicka, I.; Leleu, X.; Schjesvold, F.; Moreau, P.; Dimopoulos, M.A.; et al. Isatuximab plus pomalidomide and low-dose dexamethasone versus pomalidomide and low-dose dexamethasone in patients with relapsed and refractory multiple myeloma (ICARIA-MM): A randomized, multicenter, open-label, phase 3 study. Lancet 2019, 294, 2096–2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barou, R.; Leo, E.; Zugmaier, G.; Klinger, M.; Goebeler, M.; Knop, S.; Noppeney, R.; Viardot, A.; Hess, G.; Schuler, M.; et al. Tumor regression in cancer patients by very low doses of a T cell-engaging antibody. Science 2008, 321, 974–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baeuerle, P.A.; Reinhardt, C. Bispecific T-cell engaging antibodies for cancer therapy. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 4941–4944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caraccio, C.; Krishna, S.; Phillips, D.J.; Schurch, C.M. Bispecific antibodies for multiple myeloma. A review of target, drugs, clinical trials, and future directions. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, B.; Liu, D. Antibody-drug conjugates in clinical trials for lymphoid malignancies and multiple myeloma. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2019, 12, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikkilineni, L.; Kochenderfer, J.N. Chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapies for multiple myeloma. Blood 2017, 130, 2594–2602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grafall, A.L.; Marcela, V.; Hwang, W.T.; Lacey, S.F.; Mahnke, Y.D.; Melenhorst, J.J.; Zheng, Z.; Vogel, D.T.; Cohen, A.D.; Weiss, B.M.; et al. Chimeric antigen receptor T cells against CD19 for multiple myeloma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 1040–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paiva, B.; Azpilikueta, A.; Puig, N.; Ocio, E.M.; Sharma, R.; Oyaiobi, B.O.; Labiano, S.L.; San-Segundo, L.; Rodriguez, A.; Aires-Mejia, I.; et al. PD-L1/PD-1 presence in the tumor microenvironment and activity of PD-1 blockade in multiple myeloma. Leukemia 2015, 29, 2110–2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, Y.-T.; Mayes, P.A.; Acharya, C.; Ahong, M.Y.; Cea, M.; Cagnettta, A.; Craigen, J.; Yates, J.; Gliddon, L.; Fieles, W.; et al. Novel anti-B-cell maturation antigen antibody-drug conjugate (GSK2857916) selectively induces killing of myeloma. Blood 2014, 123, 3128–3138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trudel, S.; Lendvai, N.; Popat, R.; Voorhees, P.M.; Reeves, B.; Libby, E.N.; Richardson, P.G.; Anderson Jr, L.D.; Sutherland, H.J.; Yong, K.; et al. Targeting B-cell maturation antigen with GSK2857916 antibody-drug conjugate in relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma (BMA117159): A dose escalation and expansion phase 1 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2018, 19, 1641–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, A.D.; Popat, R.; Trudel, S.; Richardson, P.G.; Libby, E.N.; Lendvai, N.; Anderson Jr, L.D.; Sutherland, H.J.; DeWall, S.; Ellis, C.E.; et al. First in human study with GSK2857916, an antibody drug conjugated to microtubule-disrupting agent directed against B-cell maturation antigen (BCMA) in patients with relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma. Blood 2016, 128, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trudel, S.; Lendvai, N.; Popat, R.; Cohen, D. Antibocy-drug conjugate, GSK2857916, in relapsed/refractoy multiple myeloma: An update on safety and efficacy from dose expansion phase I study. Blood Cancer J. 2019, 9, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lonial, S.; Lee, H.C.; Badros, A.; Trudel, S.; Nooka, A.K.; Chari, A.; Abdalah, A.O.; Callande, N.; Lendvai, N.; Sorov, D.; et al. Belantamab mafodotin for relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma (DREAMM-2): A two-arm, randomized, open-label, phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol. 2020, 21, 207–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayes, P.A.; Hance, K.W.; Hoos, A. The promise and challenges of immune agonist antibody development in cancer. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2018, 17, 509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sehn, L.H.; Chua, N.; Mayer, J.; Dueck, G.; Trneny, M.; Bouabdallah, K.; Fowler, N.; Delwail, V.; Press, O.; Salles, G.; et al. Obinutuzumab plus bendamusutine versus bendamustine alone in patients with rituximab-refractory indolent non-Hodgkin lymphoma: Primary results of the GADOLIN study. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, 1081–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcus, R.; Davies, A.; Ando, K.; Klapper, W.; Opat, S.; Owen, C.; Phillips, E.; Sangha, R.; Schlag, R.; Seymour, J.F.; et al. Obinutuzumab for the first-line treatment of follicular lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 1331–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younes, A.; Gopal, A.K.; Smith, S.E.; Smith, S.E.; Ansell, A.M.; Rosenblatt, J.D.; Ramchandren, K.J.S.; Bartlett, N.L.; Chenson, B.D.; Vos, S.D.; et al. Results of a pivotal phase II study of brentuximab vedotin for patients with relapsed or refractory Hodgkin’s lymphoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 2183–2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prince, H.M.; Kim, Y.H.; Horwitz, S.M.; Dummer, R.; Scarisbrick, J.; Quaglino, P.; Zinzani, P.L.; Wolter, P.; Sanches, J.A.; Ortiz—Romero, P.L.; et al. Brentuximab vedotin physician’s choice in CD30 positive cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (ALCANZA): An international, open-label, randomizse, phase 3, multicenter trial. Lancet 2017, 390, 555–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barta, S.K.; Gong, J.Z.; Porcu, P. Brentuximab vedotin in the treatment of CD30+PTCL. Blood 2019, 26, 2339–2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goebeler, M.E.; Knop, S.; Viardot, A.; Kufer, P.; Topp, M.S.; Einsele, H.; Noppeney, R.; Hess, G.; Kallert, S.; Mackensen, A.; et al. Bispecific T-cell engager (BiTE) antibody construct blinatumomab for the treatment of patients with relapsed/refractory non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma: Final results from a phase I study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 1104–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kantarijian, H.; Stein, A.; Gokbuget, N.; Fielding, A.K.; Schuh, A.C.; Ribera, J.M.; Wei, A.; Dombert, H.; Foa, R.; Bassan, R.; et al. Blinatumomab versus chemotherapy for advanced acute lymphoblastic leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 836–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gokbuget, N.; Dombret, H.; Bonifacio, M.; Reichle, A.; Graux, C.; Fail, C.; Diedric, H.; Topp, M.S.; Bruggemann, M.; Horst, H.A.; et al. Blinatumomab for minimal residual disease in adults with B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood 2018, 131, 1522–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kantarjian, H.M.; DeAngelo, D.J.; Stelljes, M.; Martinelli, G.; Liedtke, M.; Stock, W.; Golbuget, N.; O’Brien, S.; Wang, K.; Wang, T.; et al. Inotuzumab ozogmaicin versus standard therapy for acute lymphoblastic leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 740–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jabbour, E.; Ravandi, F.; Kebriaei, P.; Huang, X.; Short, N.J.; Thomas, D.; Sasaki, K.; Rytting, M.; Jain, N.; Konopleva, M.; et al. Salvage chemoimminotherapy with inotuzumab ozogamicin combined with mini-hyper-CVD for patients with relapsed or refractory Philadelphia chromosome-negative acute lymphoblastic leukemia a phase 2 clinical trial. JAMA 2018, 4, 230–234. [Google Scholar]
- Kantarjian, H.; Ravandi, F.; Short, N.J.; Huang, X.; Jain, N.; Sasaki, K.; Daver, N.; Pemmaraju, N.; Khoury, J.D.; Jorgensen, J.; et al. Inotuzumab ozogamicin in combination with low-intensity chemotherapy for older patients with Philadelphia chromosome-negative acute lymphoblastic leukemia: A single-arm, phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol. 2018, 19, 240–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kantarijian, H.M.; DeAngleo, D.J.; Stelljes, M.; Liedtke, M.; Stock, W.; Gokbuget, N.; O’Brien, S.M.; Jabbour, E.; Wang, T.; White, J.L.; et al. Inotuzumab ozogamicin versus standard of care in relapsed or refractory acute lymphoblastic leukemia: Final report and long-term survival follow up from the randomised phase 3 INO-VATE study. Cancer 2019, 125, 2474–2487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dasanu, C.A. Immune alteration in untreated and treated multiple myeloma. J. Oncol. Pharm. Pract. 2012, 18, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feyler, S.; Selby, P.J.; Cook, G. Regulating the regulators in cancer immunosuppression in multiple myeloma (MM). Blood Rev. 2013, 27, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prabhala, R.H.; Neri, P.; Bae, J.E.; Tassone, P.; Shammas, M.A.; Allam, C.K.; Daley, J.F.; Chauhan, D.; Blanchard, E.; Thatte, H.S.; et al. Dysfunctional T regulatory cells in multiple myeloma. Blood 2006, 107, 301–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorgun, G.T.; Whitehill, G.; Anderson, J.L.; Hideshina, T.; Mahuire, C.; Laubach, J.; Raji, N.; Munshi, N.C.; Richardosn, P.G.; Anderson, K.C. Tumor-promoting immune-suppressive myeloid-derived suppressor cells in the multiple myeloma microenvironment in humans. Blood 2013, 121, 2975–2987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramachandran, I.R.; Martner, A.; Pisklakova, A.; Condamine, T.; Chase, T.; Vogl, T.; Roth, J.; Gabrilovich, D.; Nefedova, Y. Myeloid-derived suppressor cells regulate growth of multiple myeloma by inhibiting T cells in bone marrow. J. Immunol. 2013, 190, 3815–3823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Facon, T.; Mumar, S.; Plesner, T.; Orlowski, R.; Moreau, P.; Bahlis, N.; Hulin, C.; Quach, H.; Goldschmidt, H.; O’Dwyer, M.; et al. Daratumumab plus lenalidomide and dexamethasone for untreated myeloma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 2104–2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maeteos, M.V.; Dimopoulos, S.; Cavo, M.; Suzuji, K.; Jakubowiak, A.; Knop, S.; Douen, C.; Lucio, P.; Nagy, Z.; Kaplan, P.; et al. Daratumumab plus bortezomib, melphalan, and predonisone or untreated myeloma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 518–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeteos, M.V.; Cavo, M.; Blade, J.; Dimopoulos, M.A.; Suzuki, K.; Jakubowiak, A.; Knop, S.; Doyen, C.; Lusio, P.; Nagy, Z.; et al. Overall survival with daratumumab, bortezomib, melphalan, and predonisone in newly diagnosed multiple myeloma (ALCYONE): A randomized, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2020, 395, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chari, A.; Martinez-Lopez, J.; Maeteos, M.V.; Blade, J.; Benboubker, L.; Oriol, A.; Arnulf, B.; Rodriguez-Otero, P.; Pineiro, L.; Jakubowiak, A.; et al. Daratumumab plus carfilzomib and dexamethasone in patients with relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma. Blood 2019, 134, 421–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateos, M.V.; Nahi, H.; Legiec, W.; Grosicki, S.; Vorobyev, V.; Spicka, I.; Hungria, V.; Korenkova, S.; Bahlis, N.; Flogengard, M.; et al. Subcutaneous versus intraveneous daratumumab in patients with relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma (COLUMBA): A multicenter, open-label, non-inferiority, randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet Haematol. 2020, 7, e370–e380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chari, A.; Rodriguez-Otero, P.; McCarthy, H.; Suzuki, K.; Hungria, V.; Balari, A.S.; Perrot, A.; Chulin, C.; Magen, H.; Iida, S.; et al. Subcutaneous daratumumab plus standard treatment regimens in patients with multiple myeloma across lunes of therapy (PLEIADES): An open-label phase II study. Br. J. Haematol. 2020, 192, 869–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimopoulos, M.A.; Terpos, E.; Boccadoro, M.; Delimpasi, D.; Beksac, M.; Katodritou, E.; Moreau, P.; Baldini, L.; Symeonidis, A.; Bila, J.; et al. APOLLO: Phase 3 randomized study of subcutaneous daratumumab plus pomalidomide and dexameyhasone (D-Pd) versus pomalidomide anddexamethasone (Pd) alone in patients (Pts) with relapsed or refractory multiple multiple myeloma (RRMM). Blood 2020, 136 (Suppl. 1), 412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishida, H.; Suzuki, H.; Hayashi, M.; Morimoto, C.; Sakamoto, M.; Yamada, T. Blockade or CD26 signaling inhibits human osteoclast development. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2014, 29, 2439–2455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishida, H.; Hayashi, M.; Morimoto, C.; Sakamoto, M.; Yamada, T. CD26 is a potential therapeutic target by humanized anti-body for the treatment of multiple myeloma. Blood Cancer J. 2018, 9, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, B.; Jiang, T.; Liu, D. BCMA-targeted immunotherapy for multiple myeloma. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2020, 13, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, N.; Chari, A.; Scott, E.; Mezzi, K.; Usami, S.Z. B-cell maturation antigen (BCMA) in multiple myeloma: Rationale for targeting and current therapeutic approaches. Leukemia 2020, 34, 985–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, S.F.; Anderson, K.C.; Tai, Y.T. Targeting B cell maturation antigen (BCMA) in multiple myeloma: Potential uses of BCMA-based immunotherapy. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hipp, S.; Tai, Y.T.; Blanset, D.; Deegen, P.; Wahl, J.; Thomas, O.; Rattel, B.; Adam, P.J.; Anderson, K.C.; Friedrich, M. A novel BCMA/CD3 bispecific T-cell engager for the treatment of multiple myeloma induces selective lysis in vitro and in vivo. Leukemia 2016, 31, 1743–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topp, M.S.; Duell, J.; Zugmaier, G.; Attal, M.; Moreau, P.; Langer, C.; Kronke, J.; Facon, T.; Salnikov, A.V.; Lesley, R.; et al. Anti-B-cell maturation antigen BiTE molecule AMG420 induces responses in multiple myeloma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 775–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, S.J.; Minnema, M.C.; Lee, H.C.; Spencer, A.; Kapoor, P.; Maoouri, D.; Larsen, J.; Aiawadhi, S.; Kaufman, J.L.; Raab, M.S.; et al. A phase 1 first in human (FIH) study of AMG701, an anti-B-cell maturation antigen (BCMA) half-life extended (HLE) BiTE (bisecific T-cell engager) molecule in relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma. Blood 2020, 136 (Suppl. 1), 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labrijn, A.F.; Meesters, J.I.; de Goeij, B.E.C.G.; van den Bremer, E.T.J.; Neijssen, J.; van Kamern, M.D.; Strumane, K.; Verploegen, S.; Kundu, A.; Gramer, M.J.; et al. Efficient generation of stable bispecific IgG1 by cotrolled Fab-arm exchange. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 5145–5150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frerichs, K.A.; Broekmans, M.E.C.; Soto, J.A.M.; van Kessel, B.; Heymans, M.W.; Holthof, L.C.; Verkleij, C.P.M.; Boominathan, R.; Vaidya, B.; Sendecki, J.; et al. Preclinical activity of JNJ-7957, a nobvel BCMA × CD3 bispecific antibody for the treatment of multiple myeloma, is potentiated by daratumumab. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 2203–2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grafall, A.L.; Usmani, S.Z.; Maetos, M.V.; Nahi, H.; Van De Donk, N.W.C.J.; San-Miguel, J.F.; Rocafiguera, A.O.; Rosinol, L.; Chari, A.; Bhutani, M.; et al. Updated phase 1 results of teclistamab, a B-cell maturation antigen (BCMA)xCD3 bispecific antibody, in relapsed and/or refractory multiple myeloma. Blood 2020, 136 (Suppl. 1), 180. [Google Scholar]
- Madduri, D.; Rosko, A.; Brayer, J.; Zonder, J.; Bensinger, W.I.; Li, J.; Xu, L.; Adriaens, L.; Chokshi, D.; Whang, W.; et al. REGN5458, a BCMA × CD3 bispecific monoclonal angtibocy induces deep and durable responses in patients with relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma (RRMM). Blood 2020, 136 (Suppl. 1), 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, C.; D’Souza, A.; Shah, N.; Voorhees, P.M.; Buelow, B.; Vij, R.; Kumar, S.K. Initial results of a phase I study of TNB-383B, a BCMA × CD3 bispecific T-cell redirecting antibody, in relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma. Blood 2020, 136 (Suppl. 1), 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillarisetti, K.; Edavettal, S.; Mendinca, M.; Li, Y.; Tornetta, M.; Babich, A.; Majewski, N.; Husovsky, M.; Reeves, D.; Walsh, E.; et al. T-cell-redirecting bispecific G-protein-coupled receptor class 5 member D × CD3 antibody to treat multiple myeloma. Blood 2020, 134, 1232–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chari, A.; Berdeja, J.G.; Oriol, A.; Van De Donk, N.W.C.J.; Rodriguez, P.; Askari, E.; Maetos, M.-V.; Minnema, M.C.; Verona, R.; Girgis, S.; et al. A phase 1, first-in-human study of Talquetamab, a G protein-coupled receptor family C group 5 member (GPRC5D) × CD3 bispecific antibody, in patients with relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma (RRMM). Blood 2020, 136 (Suppl. 1), 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, A.; Harrison, S.J.; Krishnan, A.; Fonseca, R.; Forsber, P.A.; Spencer, A.; Berdeja, J.G.; Laubach, J.P.; Li, M.; Choeurng, V.; et al. Initial clinical activity and safety of BFCR4350A, a FcRH5/CD3 T-cell-engaging bispecific antibody in relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma. Blood 2020, 136 (Suppl. 1), 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, L.; Wong, S.; Bermudez, A.; De la Rubia, J.; Maetos, M.-V.; Ocio, E.M.; Rodriguez-Otero, P.; San-Miguel, J.; Li, S.; Sarmiento, R.; et al. First clinical study of the B-cell maturation antigen (BCMA)2+1 T cell engager (TCE) CC-93269 in patients with relapsed/refractory myeloma. Blood 2019, 134 (Suppl. 1), 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raje, N.; Jakubowiak, A.; Gasparetto, C.; Cornell, R.F.; Krupka, H.I.; Navarro, D.; Forgie, A.J.; Udata, C.; Basu, C.; Chou, J.; et al. Safety, clinical activity, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics from a phase 1 study of PF-06863135, a B-cell maturation antigen (BCMA)-CD3 bispecific antibody in patients with relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma (RRMM). Blood 2019, 134 (Suppl. 1), 1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, J.R.; Landgren, C.O.; Kauch, J.S.; Back, J.; Salhi, Y.; Reddy, V.; Bayever, E.; Berdeja, J.G. Phase 1, multicenter open-label study of single-agent bispecific antibody t-cell engager GBR1342 in relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36 (Suppl. 15), TPS3132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuch de Zafra, C.L.; Fajardo, F.; Zhong, W.; Bernett, M.J.; Muchhal, U.S.; Moore, G.L.; Stevens, J.; Case, R.; Pearson, J.T.; Liu, S.; et al. Targeting multiple myeloma with AMG424, 1 novel anti-CD38/CD3 bispecific T-cell recruiting antibody optimized for cytotoxicity and cytokine release. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 3921–3933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahao, H.; Atkinson, J.; Gulesserian, S.; Zeng, Z.; Nater, J.; Ou, J.; Yang, P.; Morrison, K.; Coleman, J.; Malik, F.; et al. Modulation of macropinocytosis-mediated internalization decreases ocular toxicity of antibody-drug conjugates. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 2115–2126. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.K.; Migkou, M.; Bhutani, M.; Spencer, A.; Ailawadhi, S.; Kalff, A.; Walcott, F.; Pore, N.; Gibson, D.; Wang, F.; et al. Phase 1, first-in-human study of MEDI2228, a BCMA-targeted ADC in patients with relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma. Blood 2020, 136 (Suppl. 1), 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.C.; Raje, N.S.; Landgren, O.; Upreti, V.V.; Wang, J.; Avilion, A.; Hu, X.; Rasmussen, E.; Ngarmchamnanrith, G.; Fujii, H.; et al. A phase 1 study of anti-BCMA antibody-drug conjugate AMG224 in patients with relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma. Leukemia 2020, 35, 255–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- A Study of CC-99712, A BCMA Antibody-Drug-Conjugate, in Subjects with Relapsed and Refractory Multiple Myeloma. ClinicalTrials. Gov Identifier: NCT04036461 (26 August 2019~27 May 2025). Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04036461 (accessed on 1 March 2021).
- Kelly, K.R.; Siegel, D.S.; Chanan-khan, A.A.; Somlo, G.; Heffner, L.T.; Jagabbath, S.; Zimmerman, T.; Munshi, N.C.; Madan, S.; Mohrbacher, A.; et al. Indatuximab ravtansine (BT062) in combination with low-dose dexamethasone and lenalidomide or pomalidomide: Clinical activity in patients with relapsed and/or refractory multiple myeloma. Blood 2016, 128, 4486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schonfeld, K.; Zuber, C.; Pinkas, J.; Hader, T.; Bernoster, K.; Uherek, C. Indatuximab ravtansine (BT062) combination treatment in multiple myeloma: Pre-clinical studies. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2017, 10, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ailawadhi, S.; Kelly, K.R.; Vescio, R.A.; Jagannath, S.; Wolf, J.; Gharibo, M.; Sher, T.; Bojanini, L.; Kriby, M.; Chanan-Khan, A. A phase 1 study to assess the safety and pharmacokinetics of single-agent lorotuzumab mertansine (IMGN901) in patients with relapsed/refractory CD56-positive multiple myeloma. Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2019, 19, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berdeja, J.G. Lorvotuzumab mertansine: Antibody-drug-conjugate for CD56+ multiple myeloma. Front. Biosci. 2014, 19, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govindan, S.V.; Cardillo, T.M.; Sharkey, R.M.; Tat, F.; Gold, D.V.; Goldenberg, D.M. Milatuzumab-SN-38 conjugates for the treatment of CD74 cancer. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2013, 6, 968–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufman, J.L.; Niesvizky, R.; Stadmauer, E.A.; Chanan-Khan, A.; Siegel, D.; Horne, H.; Wegener, W.A.; Goldenerg, D.M. Phase I multicenter, dose-escalation trial of monotherapy with milatuzumab (humanized anti-CD74 monoclonal antibody) in relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma. Br. J. Haematol. 2013, 163, 478–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafiq, S.; Hackett, C.S.; Brentjens, R.J. Engineering strategies to overcome the current road blocks in CAR T cell therapy. Nat. Rev. 2020, 17, 147–167. [Google Scholar]
- Holstein, S.A.; Lunning, M.A. CAR T-cell therapy in hematologic malignancies: A voyage in progress. Clin. Pharmacol. Therapeut. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- June, C.H.; Sadelain, M. Chimeric antigen receptor therapy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maude, S.L.; Frey, N.; Shaw, P.A.; Aplenc, R.; Barett, D.M.; Bunin, N.J.; Chew, A.; Gonzalez, W.E.; Zheng, A.; Lacey, S.F.; et al. Chimeric antigen receptor T cells for sustained remissions in leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 1507–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.W.; Kochenderfer, J.N.; Stetler-Stevenson, N.; Cui, Y.K.; Delbrook, C.; Feldman, S.A.; Fry, T.J.; Orenas, R.; Sabatino, M.; Sah, N.N.; et al. T cells expressing CD19 chimeric antigen receptors for acute lymphoblastic leukemia in children and young adults: A phase 1 dose-escalation trial. Lancet 2015, 385, 517–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maude, S.L.; Laetsch, T.W.; Buechner, J.; Rives, S.; Boyer, M.; Bittencourt, H.; Bader, P.; Verneris, M.R.; Stefanski, H.E.; Myers, G.D.; et al. Tisagenlecleucel in children and young adults in B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 439–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.H.; Riviere, I.; Gonen, M.; Wang, S.; Senechal, B.; Curran, K.J.; Sauter, C.; Wang, Y.; Santommasso, B.; Mead, E.; et al. Long-term follow-up of CD19 CAR therapy in acute lymphoblastic leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 449–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kochenderfer, J.N.; Dudley, M.E.; Kassim, S.H.; Somerville, R.P.T.; Carpenter, R.O.; Stetler-Stevenson, M.; Yang, J.C.; Phan, G.Q.; Hughes, M.S.; Sherry, R.M.; et al. Chemotherapy-refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and indolent B-cell malignancies can be effectively treated with autologous T cells expressing an anti-CD19 chimeric antigen receptor. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 540–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuster, S.J.; Bishop, M.R.; Tam, C.S.; Waller, E.K.; Borchmann, P.; MuGuirk, J.P.; Jager, U.; Jahlowski, S.; Andreadis, C.; Westin, J.R.; et al. Tisagenlecleucel in adult relapsed or refractory diffuse large B cell lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuster, S.J.; Svoboda, J.; Chong, E.A.; Nasta, S.D.; Mato, A.R.; Anak, O.; Brogdon, J.L.; Priteanu-Malinici, I.; Bhoj, V.; Landsburg, D.; et al. Chimeric antigen receptor T cells in refractory B-cell lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 2545–2554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neelapu, S.S.; Locke, F.L.; Bartlett, N.L.; Lekakis, L.; Miklos, D.B.; Jacobson, C.A.; Braunschweig, I.; Oluwole, O.O.; Siddiqi, T.; Lin, Y.; et al. Axicabtagene ciloleucel CAR T-cell therapy in refractory large B-cell lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 2531–2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raje, N.; Berdeja, J.; Lin, Y.; Siegel, D.; Jagannath, S.; Madduri, D.; Liedtke, M.; Rosenblatt, J.; Maus, M.V.; Turka, A.; et al. Anti- BCMA CAR T-cell therapy bb2121 in relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 1726–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grafall, A.L.; Stadtmauer, E.A.; Hwang, W.T.; Lacey, S.F.; Melenhorst, J.J.; Krevvata, M.; Carroll, M.P.; Matsui, W.H.; Wang, Q.; Dhodapkar, M.V.; et al. Anti-CD19 CAR T cells with high-dose melphalan and autologous stem cell transplantation for refractory myeloma. JCI Insight 2018, 4, e120505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, R.O.; Evbuomwan, M.O.; Pittaluga, S.; Rose, J.J.; Raffeld, M.; Yang, S.; Gress, R.R.; Hakim, F.T.; Kochenderfer, N.K. B-cell maturation antigen is a promising target for adoptive T-cell therapy of multiple myeloma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 2048–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Chen, L.J.; Yang, S.S.; Sun, Y.; Wu, W.; Liu, Y.F.; Xu, J.; Zhuang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Weng, X.Q.; et al. Explaratory trial of a biepitopic CAR T-targeting B cell maturation antigen in relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 9543–9551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, A.D.; Garfall, A.L.; Stadtmauer, E.A.; Melenhorst, J.J.; Lacey, S.F.; Lancaster, E.; Vogl, D.T.; Weiss, B.M.; Dengel, K.; Nelson, A.; et al. B cell maturation antigen-specific CAR T cells are clinically active in multiple myeloma. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 129, 2210–2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.A.; Shi, V.; Maric, I.; Wang, M.; Stroneck, D.F.; Rose, J.J.; Brudno, D.F.; Rose, J.J.; Brudno, J.N.; Stetler-Stevenson, M.; et al. T cells expressing an anti-B cell maturation antigen chimeric antigen receptor cause remissions of multiple myeloma. Blood 2016, 128, 1688–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brudno, J.N.; Kochenderfer, J.N. Recent advances in CAR-T cell toxicity: Mechanisms, manifestations and management. Blood Rev. 2019, 34, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, J.; Nagle, S.; Randall, J.; Hinson, H.E. Chimeric antigen receptor T cell-related neurotoxicity: Mechanism, clinical presentation and approach to treatment. Curr. Treat. Opin. Neurol. 2019, 21, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheth, V.S.; Gauthier, J. Taming the beast: CRS and ICANS after CAR T-cell therapy for ALL. Bone Marrow Transpant. 2021, 56, 552–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Q.; Han, G.; Puebla-Osorio, N.; Ma, M.C.J.; Strati, P.; Chasen, B.; Dai, E.; Dang, M.; Jain, N.; Yang, H.; et al. Characteristics of anti-CD19 CAR-T cell infusion products associated with efficacy and toxicity in patients with large B cell lymphoma. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 1878–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.K.; Yu, K.R.; Kenderian, S.S.; Ruella, M.; Chen, S.; Shin, T.-H.; Aljanahi, A.A.; Schreeder, D.; Klichinsky, M.; Shestova, O.; et al. Genetic inactivation of CD33 in hematopoietic stem cells to enable CAR T cell immunotherapy for acute myeloid leukemia. Cell 2018, 173, 1439–1453.e19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drent, E.; Groen, R.W.; Noort, W.A.; Themeli, M.; Lammerts van Bueren, J.J.; Parren, P.W.H.I.; Kuball, J.; Sebestyen, Z.; Yuan, H.; Joost de Bruijn, J.; et al. Pre-clinical evaluation of CD38 chimeric antigen receptor engineered T cells for the treatment of multiple myeloma. Haematologica 2016, 101, 616–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drent, E.; Poels, R.; Mulders, M.J.; van de Donk, N.W.C.J.; Themeli, M.; Lokhorst, H.M.; Mutis, T. Feasibility of controlling CD38-CAR T cell activity with a Tet-on inducible CAR design. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0197349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.; Chen, M.; Han, Q.; Hui, F.; Dai, H.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, H.; Gan, W. CD138-directed adoptive immunotherapy of chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-modified T cells for multiple myeloma. J. Cell Immunother. 2016, 2, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Mahendravada, A.; Ballard, B.; Kale, B.; Ramos, C.; West, J.; Maguire, T.; Mckay, K.; Lichtman, E.; Tuchman, S. Safety and efficacy of targeting CD138 with a chimeric antigen receptor for the treatment of multiple myeloma. Oncotarget 2019, 10, 2369–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, J.; He, S.; Deng, Y.; Zhang, J.; Peny, Y.; Hughes, T.; Yi, L.; Kwon, C.-H.; Wang, Q.-E.; Devine, S.M.; et al. Genetic modofication of T cells redirected toward CS1 engages eradication of myeloma cells. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 3989–4000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gogishvili, T.; Danhof, S.; Prommersberger, S.; Rydwek, J.; Schreder, M.; Brede, C.; Einsele, H. Hudecek, M/ SLAMF7-CAR T cells eliminate myeloma and confer selective fratricide of SLAMF7+ normal lymphocytes. Blood 2017, 130, 2838–2847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, C.A.; Savoldo, B.; Torrano, V.; Ballard, B.; Zhang, H.; Dakhova, O.; Liu, E.; Carrum, G.; Kamble, R.T.; Gee, A.P.; et al. Clinical responses with T lymphocytes targeting malignancy-associated kappa light chains. J. Clin. Investig. 2016, 126, 2588–2596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjiamin, R.; Condomines, M.; Gunset, G.; Sadelain, M. CD56 targeted chimeric antigen receptors for immunotherapy of multiple myeloma. Cancer Res. 2012, 72 (Suppl. 8), 3499. [Google Scholar]
- Casucci, M.; Nicolis di Robilant, B.; Falcone, L.; Camisa, B.; Norelli, M.; Genovese, P.; Gentner, B.; Gullotta, F.; Ponzoni, M.; Bernardi, M.; et al. CD44v6-targeted T cells mediate potent antitumor effects against acute myeloid leukemia and multiple myeloma. Blood 2013, 122, 3461–3472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaffer, D.R.; Savoldo, B.; Yi, Z.; Chow, K.K.H.; Kakarla, S.; Spencer, D.M.; Dotti, G.; Wu, M.-F.; Liu, H.; Kenney, S.; et al. T cells redirected against CD70 for immunotherapy of CD70-positive malignancies. Blood 2011, 117, 4304–4314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hengeveld, P.J.; Kersten, M.J. B-cell activating factor in the pathophysiology of multiple myeloma: A target for therapy? Blood Cancer J. 2015, 5, e282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosen, N.; Matsunaga, Y.; Hasgawa, K.; Matsuno, H.; Nakamura, Y.; Makita, M.; Watanabe, K.; Yoshida, M.; Satoh, K.; Morimoto, S.; et al. The activated confirmation of integrin β7 is a novel multiple myeloma-specific target for CAR T cell therapy. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 1436–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.; Raji, N.S.; Berdeja, J.G.; Siegel, D.S.; Jagannath, S.; Madduri, D.; Liedtke, M.; Rosenblatt, J.; Maus, M.V.; Massaro, M.; et al. Idecabtagene Vicleucel (ide-cel, bb2121), a BCMA-directed CAR T cell therapy, in patients with relapsed and refractory multiple myeloma: Updated results from phase 1 CRB-401 study. Blood 2020, 136 (Suppl. 1), 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsina, M.; Shah, N.; Raji, N.S.; Jagannath, S.; Madduri, D.; Kaufman, J.L.; Siegel, D.S.; Munshi, N.C.; Rosenblatt, J.; Lin, Y.; et al. Updated results from the phase 1 CRB-402 study of anti-BCMA CAR-T cell therapy bb2127 in patients with relapsed and refractory multiple myeloma: Correction and expansion and duration of response with T cell phenotypes. Blood 2020, 136 (Suppl. 1), 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, S.; Jie, J.; Jiang, S.; Zonghai, L.; Zhang, W.; Yang, M.; Yu, K.; Wang, W.; Chen, L.; Meng, H.; et al. Two-year follow-up of investigator-initiated phase 1 trials of the safety and efficacy of fully human anti-Bcma CRA-T cell (CT53) in relapsed /refractory multiple myeloma. Blood 2020, 136 (Suppl. 1), 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Baz, R.C.; Orlowski, R.Z.; Anderson Jr, L.D.; Ma, H.; Shrewsbury, A.; Croghan, K.A.; Bilhi, M.; Kansagra, A.; Kapoor, P.; et al. Results from Lummicar-2: A phase 1b/2 study of fully human B-cell maturation antigen-specific CAR T cells (CT053) in patients with relapsed and /or refractory multiple myeloma. Blood 2020, 136 (Suppl. 1), 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costello, C.L.; Cohen, A.; Patel, K.K.; Ali, S.; Berdeja, J.G.; Shah, N.; Ganguly, S.; Kocoglu, M.H.; Abedi, M.; Ostertag, E.M.; et al. Phase1/2 study of the safety and response of P-BCMA-101 CAR-T cells in patients with relapsed/refractory (r/r) multiple myeloma (MM)(PRIM) with novel therapeutic strategies. Blood 2020, 136 (Suppl. 1), 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.-Y.; Zhao, W.-H.; Liu, J.; Chen, Y.-X. Long term follow up of a phase 1 first-in-human open-label study of LCAR-B38M, a structurally differentiated chimeric antigen receptor T (CAR-T) cell therapy targeting B-cell maturation antigen (BCMA) in patients (pts) with relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma (RRMM). Blood 2019, 134 (Suppl. 1), 579. [Google Scholar]
- Madduri, D.; Berdeja, J.G.; Usmani, S.Z.; Jakubowiak, A.; Agha, M.; Cohen, A.D.; Stewart, A.K.; Hari, P.; Htut, M.; O’Donnell, E.; et al. CARTITUDE-1: Phase 1b/2 study of ciltacabtagene autoleucel, a B-cell maturation antigen-directed chimeric antigen receptor T cell therapy, in relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma. Blood 2020, 136 (Suppl. 1), 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, G.; Sui, W.; Wang, T.; Qu, X.; Zhang, X.; Yang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, J.; Zheng, C.; et al. An anti-Bcma CAR-T cell therapy (C-CAR088) shows promising safety and efficacy profile in relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma. Blood 2020, 136 (Suppl. 1), 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mailankody, S.; Jakubowiak, A.J.; Htut, M.; Costa, L.J.; Lee, K.; Ganguly, S.; Kaufman, J.L.; Siegel, D.S.D.; Bensigner, A.; Costa, M.; et al. Orvacabtagene autoleucel (orva-cel), a B-cell maturation antigen (BCMA)-directed CAR T cell therapy for patients (Pts) with relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma (RRMM): Update of the phase 1/2ELOVEbstudy. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38 (Suppl. 15), 8504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maude, S.L.; Teachey, D.T.; Rheingold, S.R.; Shaw, P.A.; Aplenc, R.; Barrett, D.M.; Barker, C.S.; Callahan, C.; Frey, N.V.; Nazimuddin, F.; et al. Sustained remissions with CD19-specific chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-modified T cells in children with relapsed/refractory ALL. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 3011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sotillo, E.; Barrett, D.M.; Black, K.L.; Bagashev, A.; Black, K.L.; Bagashev, A.; Oldridge, A.; Wu, G.; Sussman, R.; Lanauze, C.; et al. Convergence of aquired mutations and alternative splicing of CD19 enables resistance to CART-19 immunotherapy. Cancer Discov. 2015, 5, 1282–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braig, F.; Brandt, A.; Goebeler, M.; Tony, H.-P.; Kurze, A.-K.; Nollau, P.; Bumm, T.; Bottcher, S.; Bagou, R.C.; Binder, M. Resistance to anti-CD19/CD3 BiTE in acute lymphoblastic leukemia may be mediated by disrupted CD19 membrane trafficking. Blood 2017, 129, 100–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majzner, R.G.; Mackall, C.L. Tumor Antigen escape from CAR T-cell therapy. Cancer Discov. 2018, 8, 1219–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Z.; Cao, J.; Chenh, H.; Qiao, J.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.; Shi, M.; Lan, J.; Fei, X.; Jin, L.; et al. A combination of humanized anti-CD19 and anti-BCMA CAR-T cells in patients with relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma: A single-arm, phase 2 trial. Lancet Haematol. 2019, 6, e521–e529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nerreter, T.; Letschert, S.; Gotz, R.; Doose, S.; Danhod, S.; Einsele, H.; Sauer, M.; Hudecek, M. Super-resolution microscopy reveals ultra-low CD19 expression on myeloma cells target triggers elimination by CD19 CAR-T. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Dong, B.; Gao, L.; Liu, L.; Ge, J.; He, A.; Du Jr, J.; Li, L.; Lu, J.; Chen, X.; et al. Clinical results of a multicenter study of the first-in-human dual BCMA and CD19 targeted novel platform fast CAR-T cell therapy for patients with relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma. Blood 2020, 136 (Suppl. 1), 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kochenderfer, J.N.; Dudley, M.E.; Carpenter, R.O.; Kassim, S.H.; Rose, J.J.; Telfore, W.G.; Hakim, F.T.; Halverson, D.C.; Fowler, D.H.; Hardy, N.M.; et al. Donor-derived CD19-targeted T cells cause regression of malignancy persisting after allogenic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Blood. 2013, 122, 4129–4139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Georgiadis, C.; Preece, R.; Nickolay, L.; Etyj, A.; Petrova, A.; Ladon, D.; Danyi, A.; Humphryes-Kirilov, N.; Ajetunmobi, A.; Kim, D.; et al. Long terminal repeat CRSPER-CAR-coupled universal T cells mediate anti-potent anti-leukemic effects. Mol. Ther. 2018, 26, 1215–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busch, D.; Fraβle, S.P.; Sommermeyer, D.; Buchholz, V.R.; Riddell, S.R. Role of memory T cells subset for adoptive immunotherapy. Semin. Immunol. 2016, 28, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sermer, D.; Brentjens, R. CAR-T cell therapy: Full speed ahead. Hematol. Oncol. 2019, 37, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carbone, E.; Neri, P.; Mesuraca, M.; Fulciniti, T.; Otsuki, T.; Pendem, D.; Groh, V.; Spies, T.; Pollio, G.; Cosman, D.; et al. HLA class I, NKG2D, and natural cytotoxicity receptors regulate multiple myeloma cell recognition by natural killer cells. Blood 2005, 105, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, G.; Dong, H.; Liang, Y.; Ham, J.D.; Rizwan, R.; Chen, J. CAR-NK cells: A promising cellular immunotherapy for cancer. EBioMedicine 2020, 59, 102975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, U.A.; Mailankody, S. CAR T and CAR NK cels in multiple myeloma: Expanding the targtes. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Haematol. 2020, 33, 101141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bari, R.; Granzin, M.; Tsang, K.S.; Roy, A.; Krueger, W.; Orentas, R.; Schineider, D.; Pfeifer, R.; Moeker, N.; Verhoeyen, E.; et al. A distinct subset of highly proliferative and lentiviral vector transducible NK cells define a readily engineered subset for adoptive cellular therapy. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guven, H.; Konstantinidis, K.V.; Alici, E.; Aints, A.; Abedi-Valugerdi, A.; Christensson, B.; Ljunggren, H.-G.; Dilber, M.S. Efficient gene transfer into primary human natural killer cells by retroviral transduction. Exp. Hematol. 2005, 33, 1320–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlsten, M.; Childs, R.W. Genetic manipulation of NK cells for cancer immunotherapy: Techniques and clinical implications. Front. Immunol. 2015, 6, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papayannakos, C.; Daniel, R. Understanding lentiviral vector chromatin targeting: Working to reduce insertional mutagenic potential for gene therapy. Gene Ther. 2013, 20, 581–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, E.; Marin, D.; Banerjee, P.; Macapinlac, H.A.; Thompson, P.; Basar, R.; Kerbauy, L.N.; Overman, B.; Thall, P.; Kaplam, M.; et al. Use of CAR-transduced Natural killer cells in CD19 positive lymphoid tumors. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 545–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Liu, Q.; Zhong, M.; Wang, Z.; Chen, A.; Zhang, Y.; Xing, H.; Tian, Z.; Tang, K.; Liao, X.; et al. 2B4 costimulatory domain enhancing cytotoxic ability of anti-CD5 chimeric antigen receptor engineered natural killer cells against T cell malignancies. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2019, 12, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romee, R.; Schneider, S.E.; Leong, J.W.; Leong, J.W.; Chase, J.M.; Kappel, C.R.; Sullivan, R.P.; Cooper, M.A.; Fehniger, T.A. Cytokine activation induces human memory-like NK cells. Blood 2012, 120, 4751–4760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kloss, S.; Oberschmidt, O.; Morgan, M.; Dahlke, J.; Arseniev, L.; Huppert, V.; Graniz, M.; Gardlowski, T.; Matthie, N.; Soltenborn, S.; et al. Optimization of human NK cell manufacturing fully automated separation improved Ex vivo expansion using IL-21 with autologous feeder cells and generation of anti-CD123 CAR expressing effector cells. Hum. Gene Ther. 2017, 28, 897–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, J.H.; Lanier, L.L. A model for the differentiation of human natural killer cells. Studies on the in vitro activation of Leu11+ granular lymphocytes with a natural killer sensitive tumor cell, K 562. J. Exp. Med. 1985, 161, 1464–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, S.R.; Manus, M.V. Gene editing for immune cell therapies. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 1425–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Zhang, W.; Shang, P.; Zhang, H.; Fu, W.; Ye, F.; Zeng, T.; Huang, H.; Zhang, X.; Sun, W.; et al. Transfection of chimeric anti-CD138 gene enhances natural killer cell activation and killing of multiple myeloma cells. Mol. Oncol. 2014, 8, 297–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, J.; Deng, Y.; Benson, D.M.; He, S.; Hughes, T.; Zhang, J.; Peng, Y.; Mao, H.; Yi, L.; Ghoshal, K.; et al. CS-1 specific chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-engineered natural killer cells enhance in vitro and in vivo anti-tumor activity against human multiple myeloma. Leukemia 2014, 28, 917–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanuza, P.M.; Pesini, C.; Arias, M.A.; Calvo, C.; Ramirez-Labrada, A.; Pardo, J. Recalling the biological significance of immune checkpoints on NK cells: A chance to overcome LAG3, PD1 and CTCL4 inhibitory pathways by adoptive NK cell transfer? Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 3010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rupp, L.J.; Schumann, K.; Roybal, K.T.; Gate, R.E.; Ye, C.J.; Lim, W.A.; Marson, A. CRISPER/CAS9-mediated PD-1 disruption enhances anti-tumor efficacy of human chimeric antigen receptor T cells. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, S.H.; Lee, H.J.; Vo, M.-C.; Kim, H.-J.; Lee, J.-J. Immunotherapy for the treatment of multiple myeloma. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2017, 111, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, M.-D.; Jung, S.-H.; Lee, H.-J.; Lee, Y.-K.; Nguyen-Pham, T.-N.; Choi, N.-R.; Vo, M.-C.; Lee, S.-S.; Ahe, J.-S.; Yang, D.H.; et al. Dendritic cell-based cancer immunotherapy against multiple myeloma. Chon. Med. J. 2015, 51, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen-Pharm, T.-N.; Jung, S.H.; Vo, M.-C.; Thanh-Tran, H.-T.; Lee, Y.-K.; Lee, H.-J.; Choi, N.-R.; Hpang, M.-R.; Hoang, M.D.; Kim, H.J.; et al. Lenalidomide synergistically enhances the effect of dendritic cell vaccination in a model of murine multiple myeloma. J. Immunother. 2015, 38, 330–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, Y.J.; Ling, M.; Bailey-Wood, R.; Lim, S.H. Idiotypic protein-pulsed adherent peripheral blood mononuclear cell-derived dendritic cells prime immune system in multiple myeloma. Clin. Cancer Res. 1998, 4, 957–962. [Google Scholar]
- Liso, A.; Stockerl-Goldstein, K.E.; Auffermann-Gretzinger, S.; Benike, C.; Reichardt, V.; Van Beckhoven, A.; Rajapaksa, R.; Engleman, E.G.; Blume, K.G.; Levy, R. Idiotype vaccination using dendritic cells after autologous peripheral blood progenitor cell transplantation for multiple myeloma. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2000, 6, 621–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-J.; Choi, B.-H.; Kang, H.-K.; Park, M.-S.; Park, J.-S.; Kim, S.-K.; Nguyen Pham, T.-N.; Cho, D.; Nam, L.-J.; Kim, Y.-J.; et al. Induction of multiple myeloma-specific cytotoxic T lymphocyte stimulation by dendritic cell pulsing with purified and optimized myeloma lysate. Leuk. Lymphoma. 2007, 48, 2022–2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenblatt, J.; Vasir, B.; Uhl, L.; Blotta, S.; Macnamara, C.; Somaiya, S.; Wu, Z.; Joyce, R.; Levine, J.D.; Dombagoda, D.; et al. Vaccination with dendritic cell/tumor fusion cells results in cellular and humoral antitumor immune responses in patients with multiple myeloma. Blood 2011, 117, 342–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, S.-H.; Lee, H.-J.; Lee, Y.-K.; Yang, D.-H.; Kim, Y.H.-J.; Rhee, J.H.; Emmrich, F.; Lee, J.-J. A phase I clinical study of autologous dendritic cell therapy in patients with relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 41538–41548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, J.; Smith, R.; Daley, J.; Mimura, N.; Tai, Y.-T.; Anderson, K.C.; Munshi, N.C. Myeloma-specific multiple peptides able to generate cytotoxic T lymphocytes: A potential therapeutic application in multiple myeloma and other plasma cell disorders. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 4850–4860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellat-Deceunynck, C.; Mellerin, M.P.; Labrriere, N.; Jego, G.; Moreau-Aubry, A.; Harousseau, J.L.; Jotereau, F.; Bataille, R. The cancer germ-line genes MAGE-1, MAGE-3 and PRAME are commonly expressed by human myeloma cells. Eur. J. Immunol. 2000, 30, 803–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, J.; Xie, J.; Hong, S.; Yang, J.; Zhang, L.; Han, X.; Wang, M.; Zhan, F.; Shaughnessy Jr, J.D.; Epstein, J.; et al. Dickkopf-1 (DKK1) is a widely expressed and potent tumor-associated antigen in multiple myeloma. Blood 2007, 110, 1587–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, J.; Tai, Y.-T.; Anderson, K.C.; Munshi, N.C. Novel epitope evoking CD138 antigen-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes targeting multiple myeloma and other plasma cell disorders. Br. J. Haematol. 2011, 155, 349–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, J.; Song, W.; Smith, R.; Daley, J.; Tai, Y.-T.; Anderson, K.C.; Munshi, N.C. A novel immunogenic CS1-specific peptide inducing antigen-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes targeting multiple myeloma. Br. J. Haematol. 2012, 157, 687–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, S.M.; Schang, K.; Muller, M.R.; Weck, M.M.; Appel, S.; Kanz, L.; Grunebach, F.; Brossart, p. Survivin is a sharped tumor-associated antigen expressed in a broad variety of malignancies and recognized by specific cytotoxic T cells. Blood 2003, 102, 571–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jelinek, T.; Mihalyova, J.; Kascak, R.; Duras, J.; Hajek, R. PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors in haematological malignancies: Update 2017. Immunology 2017, 152, 357–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansell, S.M.; Lesokhin, A.M.; Borrello, I.; Halwani, A.; Scott, E.C.; Gutierrez, M.; Schuster, S.J.; Nukkenson, M.M.; Cattry, D.; Freeman, G.J.; et al. PD-1 blockade with nivolumab in relapsed or refractory Hodgkin’s lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benson Jr, D.M.; Bakan, C.E.; Mishra, A.; Hofmeister, C.C.; Efebera, Y.; Becknell, B.; Baiocchi, R.A.; Zhang, J.; Yu, J.; Smith, M.K.; et al. The PD-1/PD-L1 axis modulates the natural killer cell versus multiple myeloma effect: A therapeutic target for CT-011, a novel monoclonal anti-PD-1 antibody. Blood 2010, 116, 2286–2294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suen, H.; Brown, R.; Yang, S.; Ho, P.J.; Gibson, J.; Joshua, D. The failure of immune checkpoint blockade in multiple myeloma with PD-1 inhibiters in a phase 1 study. Leukemia 2015, 29, 1621–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesokhin, A.M.; Ansell, S.M.; Armand, P.; Scott, E.C.; Halwani, A.; Gutierrez, M.; Millenson, M.M.; Cohem, A.D.; Schuster, S.J.; Lebovic, D.; et al. Nivolumab in patients with relapsed or refractory hematologic malignancy: Preliminary results of a phase Ib study. J Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 2698–2704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribrag, V.; Avigan, D.E.; Green, D.J.; Wise-Draper, T.; Posada, J.G.; Vij, R.; Zhu, Y.; Farooqui, M.Z.H.; Marinello, P.; Siegel, D.S. Phase 1b trial of pembrolizumab monotherapy for relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma: KEYNOTE-013. Br. J. Haematol. 2019, 186, e41–e44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorgun, G.; Samur, M.K.; Cowens, K.B.; Paila, S.; Bianchi, G.; Anderson, J.E.; White, R.E.; Singh, A.; Ohguchi, H.; Suzuki, E.; et al. Lenalidomide Enhances immune checkpoint blockade-induced immune response in multiple myeloma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 4607–4618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mateos, M.V.; Hernandez, M.T.; Giraldo, P.; de la Rubia, J.; de Arriba, F.; Corral, L.L.; Rosinol, L.; Pavia, B.; Palomera, L.; Bargay, J.; et al. Phase2 study Pembrolizumab plus lenalidomide plus dexamethasone versus observation in high-risk smouldering multiple myeloma (QuiRedex): Long-term follow-up of ransomised, controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, 1127–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badros, A.; Hyjek, E.; Ma, N.; Lesokhin, A.; Dogan, A.; Rapoport, A.P.; Kocoglu, M.; Lederer, E.; Philip, S.; Milliron, T.; et al. Pembrolizumab, pomalidomide, and low-dose dexamethasone for relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma. Blood 2017, 130, 1189–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usami, S.Z.; Schjesvold, F.; Oriol, A.; Karlin, L.; Cavo, M.; Rifkin, R.M.; Yomer, H.A.; LeBlanc, R.; Takezako, N.; McCroskey, R.D.; et al. Pembrolizumab plus lenalidomide and dexamethasone for patients with treatment-naïve multiple myeloma (KEYNOTE-185) randomized, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Haematol. 2019, 6, e448–e458. [Google Scholar]
- Maetos, M.V.; Blacklock, H.; Schjesvold, F.; Oriol, A.; Simpson, D.; George, A.; Goldschmidt, H.; Laroccoa, A.; Chanan-Khan, A.; Sherbenpi, S.; et al. Pembrolizumab plus pomalidomide and dexamethasone for patients with relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma KEYNOTE-183): A ramdomized, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Haematol. 2019, 6, e459–e469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| mAb | Daratumumab | Isatuximab |
|---|---|---|
| Isotype | IgG1λ | IgG1κ |
| Origin | human | chimeric |
| Administration route | IV, SC | IV |
| ADDC | + | ++ |
| CDC | ++ | + |
| ADCP | + | + |
| Programmed direct cell death | − | ++ |
| Cross linking | + | − |
| Ectoenzymic activity | + | ++ |
| Agent | Target | Phase | Response | Adverse Effects-Grade 1, 2 (>3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AMG420 | BCMA × CD3 | I | ORR * 70%/31%, DOR 9 | CRS 38(2)%, Infections 33(24)% |
| CC-93269 | BCMA × CD3 | I | ORR ″ 89%/36% | CRS 77(3)%, Infections (26)%, 0% |
| PF-06863135 | BCMA × CD3 | I | ORR 75% | CRS 61(0)%, IRS 33(0)% |
| REGN5458 | BCMA × CD3 | I/II | ORR # 62%/35.6%, DOR 6.0 m | CRS 39(0)%, Infection 47(18)%, NTX 12(0)% |
| AMG701 | BCMA × CD3 | I/II | ORR 36%, DOR 3.8 m | CRS 61(7)%, Infections (17)%, NTX 8(0)% |
| TNB-383B | BCMA × CD3 | I | ORR $ 80%, DOR 4.5 m | CRS 45(0)%, Infections 21% |
| Teclistamab/JNJ-64007957 | BCMA × CD3 | I | ORR 69%, DOR NR | CRS 55(0)%, Infections 52(15)%, NTX 5(2)% |
| GBR1342 | CD38 × CD3 | I | On going until 2021 | - |
| AMG424 | CD38 × CD3 | I | On going until 2022 | - |
| Talquetamab/JNJ-64407564 | GPRC5D × CD3 | I | ORR & 69%/63%, DOR NR | CRS 68(10)%, Infections 38(8)%, Skin 45%, NTX 6(2)% |
| Cevostamab/BFCR4350A | FcRH5 × CD3 | I | ORR | 53%, DOR 6 m | CRS 76(2)%, NTX > 2% |
| Agents | Target | Toxin | Phase | Response |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Belanatmab mafadotin/GSK2857916 | BCMA | MMAF | I(DREAMM-1) | ORR 60%, PFS 12 m, DOR 14.3 m |
| BCMA | MMAF | II(DREAMM-2) | ORR 34%/31%, PFS 4.9 m/2.9 m | |
| BCMA | MMAF | I/II(DREAMM-4) | ORR 67%, PFS NR | |
| BCMA | MMMAF | I/II(DREAMM-6) | ORR 78%, PFS NR | |
| MEDI2228 | BCMA | PBD | I | ORR 61%, PFS NR |
| AMG224 | BCMA | Mertansine | I | ORR 23% |
| CC99712 | BCMA | MMAE | I | Not results yet |
| TAK-169 | CD38 | Shiga like toxin | I | Not results yet |
| TAK-573 | CD38 | IFNα2b | I | ORR 7% |
| Indatuximab ravtansine/BT062 | CD138 | Ravtansine | I/II | ORR 78% (with Rd) |
| Lorvotuzumab mertanisine/IMGN901 | CD56 | Mertansine | I/IIa, I/IIb | ORR 5.7%, SD 42.9%, DOR 15.8 m |
| Milatuzumab doxorubicin/STRO-001 | CD74 | Doxorubicin | I | No ORR, SD 26% (1/14 Pts) |
| FOR46 | CD46 | MMAE | I | Not results yet |
| Target | CAR Construct | Costimulatory Molecule | MM Cells | Normal Cells | Clinical Trials |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CD19 | murine scFv | 4-1BB | +/− or − | B cell | Done; NR or MR |
| CD38 | murine scFv | CD28 | ++ | B, T, NK, plasma cell, osteoclast | Not yet reported |
| CD44v6 | human | CD28 | + or − | T cell, monocyte | Not ret reported |
| CD70 | human | CD28, 4-1BB | + or − | B, T cell | Done |
| CD138 | murine scFv | CD28 | ++ | Plasma cell | Not yet reported |
| Igκ | murine scFv | CD28 | + or − | B cell | Done; SD |
| SLAMF7/CS1 | CD28, 4-1BB | ++ | B, T, NK, plasma cell, monocyte | Not yet reported | |
| BCMA/ | murine scFv | CD28, 4-1BB | ++ | B cell, plasma cell | Reported (Table 5) |
| CD269 | human scFv | ||||
| Integrinβ7 | human scFv | CD28 | + | B, T cell | Not yet reported |
| Trial | Target | Activation Domain | Binding Domain | Phase | Responses | Outcome | CRS Gr > 3 | NTX Gr > 3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CRB401/ KarMMa | Ide-cel/ bb2121 | 4-1BB | Murine scFv | 1/2 | ORR 85%, CR 9%, sCR 36% | PFS 11.8 m | 76% 6% | 42% 3% |
| CRB-401 | Ide-cel/bb2121 | 4-1BB | Murine scFv | 1 | ORR 76%, DOR 10.3 m | PFS 8.8 m OS 34.2 m | 76% 6% | 44% 3% |
| CT053 | CT053 | 4-1BB | Human scFv | 1 | ORR 87.5%,CR 12.5%, sCR 66.7% | PFS 18.8 m DOR 21.8 m | 62.5% 0% | 4% 4% |
| LUMMICAR-2 | CT053 | 4-1BB | Human scFv | 1b/2 | ORR 100%, sCR 20% CR 20% | - | 86% 0% | 7% 7% |
| PRIME | P-BCMA-101/Poseida | 4-1BB | Centyrin human | 1/2 | ORR 57% | PFS NR | 17% 2% | 9% - |
| C-CAR088 | C-CAR088 | 4-1BB | Human scFv | 1/2 | ORR 95.2%, sCR + CR 28.6%, VGPR 10% | DOR NR | 95% 4% | 4% - |
| CRB-402 | Ide-cel bb21217 | 4-1BB PI3Ki | Murine scFv | 1 | ORR 55%, CR 18%, VGPR 30% | DOR 11.9 m | 67% 4% | 22% 6% |
| LEGEND-2 | CAR-B38M | 4-1BB | Human scFv | 1 | ORR 88% | PFS 19.9 m | - - | - - |
| CARTITUD | Cilta-cel/JNJ-68284528 | 4-1BB | IIama-dual VHH | 1b/2 | ORR 96.9%, sCR 67.0%, VGPR 25.8%, MRDneg at 10-5 93% | PFS NR, DOR NR | 94% 4% | 20% 10% |
| EVOLVE | Orva-cel CARH125 | 4-1BB | Human scFv | 1/2 | ORR 92%, CR 36% | PFS NR | 80% 2% | 25% 7% |
| ChiCTR | CD19CAR/BCMA CAR | 4-1BB | Human scFv | 1 | ORR 95%, CR 43% MRD neg 81% | - | 90% 4% | - - |
| GC012F | BCMA-CD19dual FasT CAR-T | 4-1BB | Human scFv | 1 | ORR 93.8%, sCR + CR 56.3%, VGPR 23.8% MRDneg at 10-4s | DOR NR | 87.5% 12.5% | - - |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nishida, H. Rapid Progress in Immunotherapies for Multiple Myeloma: An Updated Comprehensive Review. Cancers 2021, 13, 2712. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13112712
Nishida H. Rapid Progress in Immunotherapies for Multiple Myeloma: An Updated Comprehensive Review. Cancers. 2021; 13(11):2712. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13112712
Chicago/Turabian StyleNishida, Hiroko. 2021. "Rapid Progress in Immunotherapies for Multiple Myeloma: An Updated Comprehensive Review" Cancers 13, no. 11: 2712. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13112712
APA StyleNishida, H. (2021). Rapid Progress in Immunotherapies for Multiple Myeloma: An Updated Comprehensive Review. Cancers, 13(11), 2712. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13112712





