The Real-World Data in Japanese Patients with Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma Treated with Lenvatinib from a Nationwide Multicenter Study
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Design and Patients
2.1.1. Study Design
2.1.2. Patients
2.2. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Overall Efficacy and Safety Data
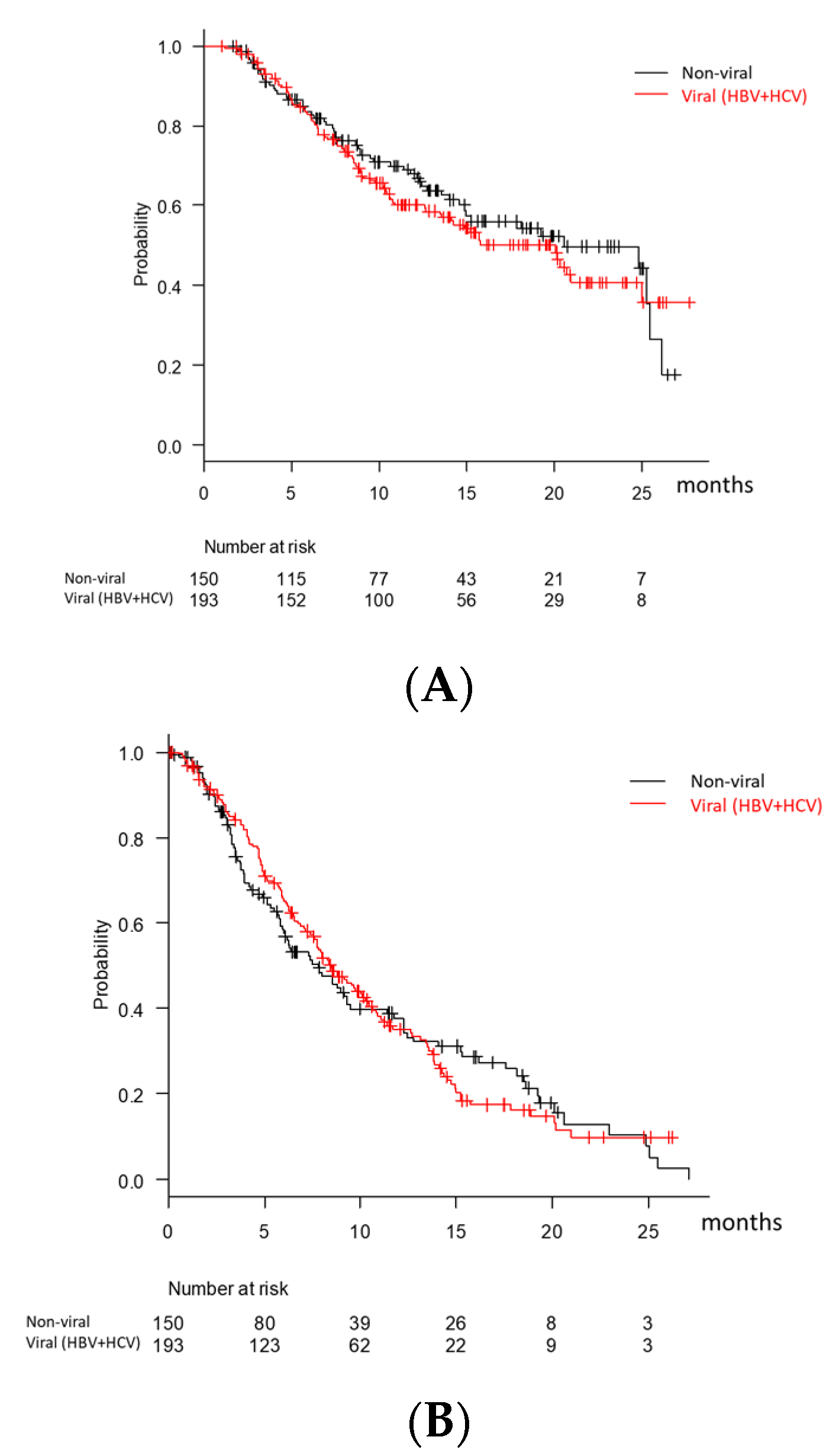
3.2. Overall Survival and Progression-Free Survival According to BCLC Stage, MTT Experience, and Modified ALBI Grade in Child-Pugh A Patients Treated with Lenvatinib
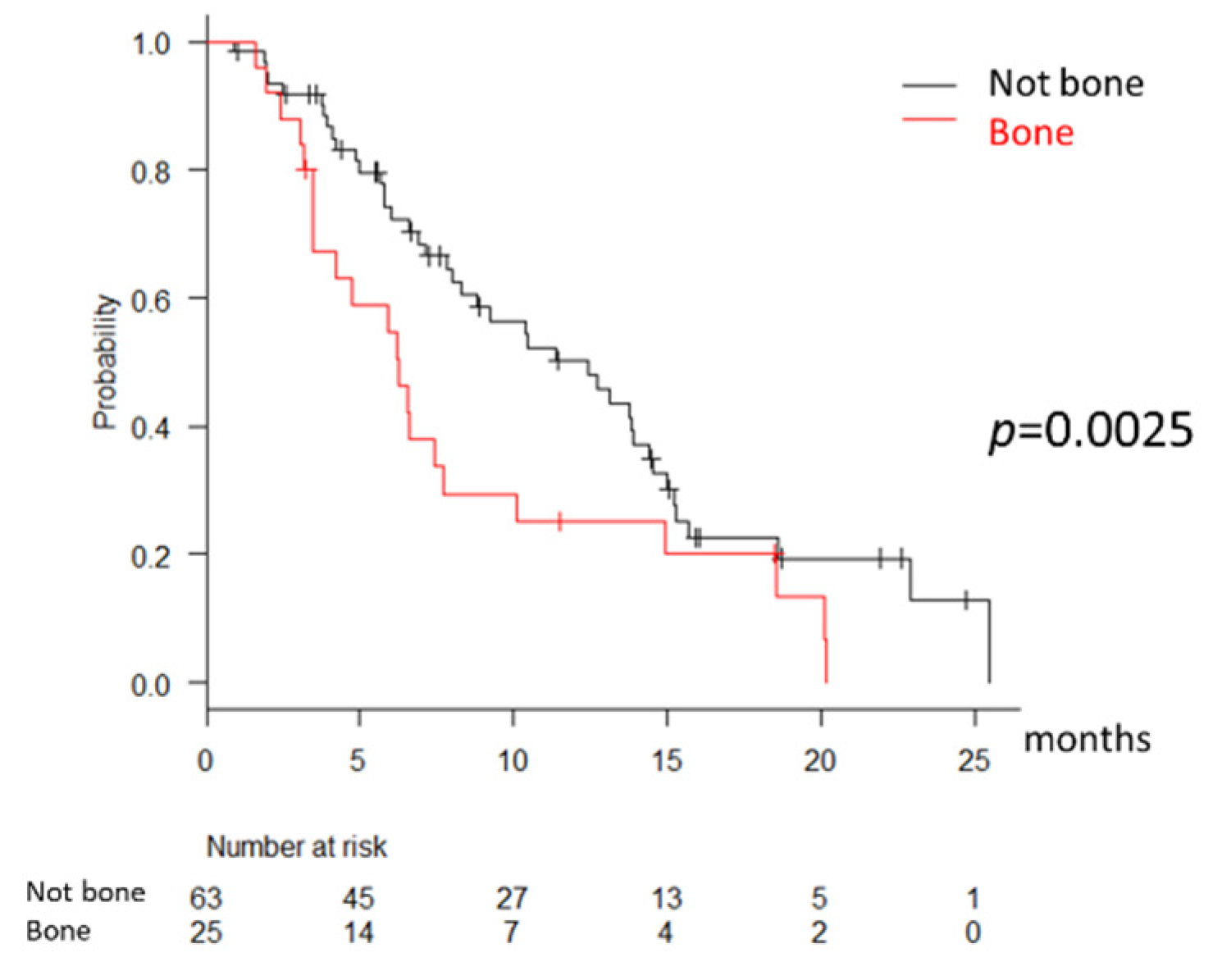
3.3. Overall Survival in Child-Pugh A Patients with Extrahepatic Metastasis and No Major Vascular Invasion
3.4. Adverse Events (AEs) Associated with Lenvatinib Therapy
3.5. Factors Associated with Mortality in Lenvatinib Therapy
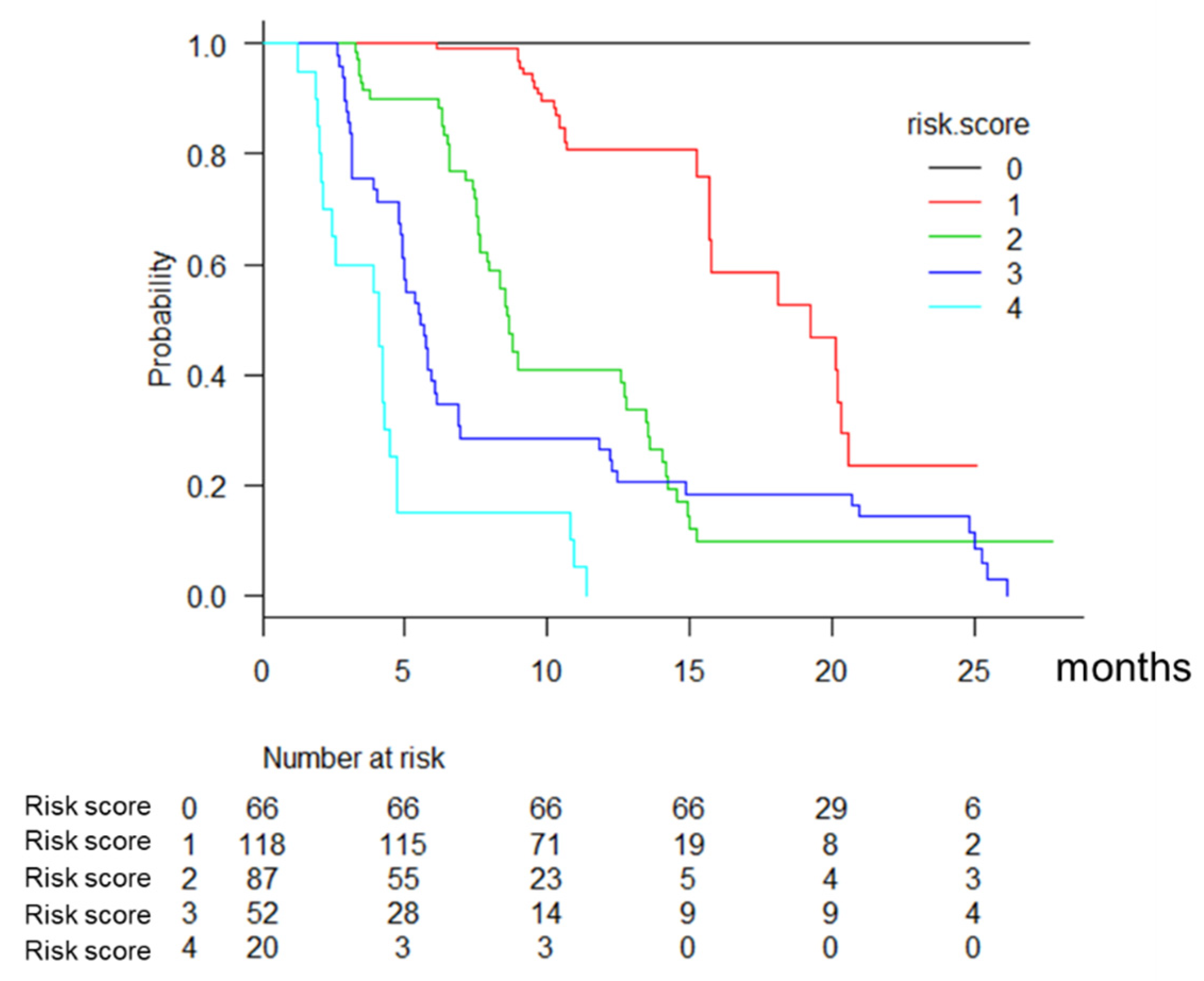
3.6. Prognostic Model in Lenvatinib Therapy
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llovet, J.M.; Ricci, S.; Mazzaferro, V.; Hilgard, P.; Gane, E.; Blanc, J.F.; De Oliveira, A.C.; Santoro, A.; Raoul, J.L.; Forner, A.; et al. Sorafenib in Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 378–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, A.-L.; Kang, Y.-K.; Chen, Z.; Tsao, C.-J.; Qin, S.; Kim, J.S.; Luo, R.; Feng, J.; Ye, S.; Yang, T.-S.; et al. Efficacy and safety of sorafenib in patients in the Asia-Pacific region with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: A phase III randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2009, 10, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruix, J.; Qin, S.; Merle, P.; Granito, A.; Huang, Y.-H.; Bodoky, G.; Pracht, M.; Yokosuka, O.; Rosmorduc, O.; Breder, V.; et al. Regorafenib for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma who progressed on sorafenib treatment (RESORCE): A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2017, 389, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudo, M.; Finn, R.S.; Qin, S.; Han, K.-H.; Ikeda, K.; Piscaglia, F.; Baron, A.; Park, J.-W.; Han, G.; Jassem, J.; et al. Lenvatinib versus sorafenib in first-line treatment of patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: A randomised phase 3 non-inferiority trial. Lancet 2018, 391, 1163–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou-Alfa, G.K.; Meyer, T.; Cheng, A.-L.; El-Khoueiry, A.B.; Rimassa, L.; Ryoo, B.-Y.; Cicin, I.; Merle, P.; Chen, Y.; Park, J.-W.; et al. Cabozantinib in Patients with Advanced and Progressing Hepatocellular Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Khoueiry, A.B.; Sangro, B.; Yau, T.; Crocenzi, T.S.; Kudo, M.; Hsu, C.; Kim, T.-Y.; Choo, S.-P.; Trojan, J.; Welling, T.H.; et al. Nivolumab in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (CheckMate 040): An open-label, non-comparative, phase 1/2 dose escalation and expansion trial. Lancet 2017, 389, 2492–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, A.X.; Kang, Y.K.; Yen, C.J.; Finn, R.S.; Galle, P.R.; Llovet, J.M.; Assenat, E.; Brandi, G.; Pracht, M.; Lim, H.Y.; et al. Ramucirumab in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma and elevated alpha-fetoprotein following sorafenib (REACH-2): A randomised, double-blind, pla-cebocontrolled phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, 282–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finn, R.S.; Ryoo, B.-Y.; Merle, P.; Kudo, M.; Bouattour, M.; Lim, H.Y.; Breder, V.; Edeline, J.; Chao, Y.; Ogasawara, S.; et al. Pembrolizumab As Second-Line Therapy in Patients With Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma in KEYNOTE-240: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Phase III Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finn, R.S.; Qin, S.; Ikeda, M.; Galle, P.R.; Ducreux, M.; Kim, T.-Y.; Kudo, M.; Breder, V.; Merle, P.; Kaseb, A.O. Atezolizumab plus Bevacizumab in Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1894–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pugh, R.N.H.; Murray-Lyon, I.M.; Dawson, J.L.; Pietroni, M.C.; Williams, R. Transection of the oesophagus for bleeding oesophageal varices. BJS 2005, 60, 646–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, P.J.; Berhane, S.; Kagebayashi, C.; Satomura, S.; Teng, M.; Reeves, H.L.; O’Beirne, J.; Fox, R.; Skowronska, A.; Palmer, D.; et al. As-sessment of liver function in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: A new evidence-based approach-the ALBI grade. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 550–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiraoka, A.; Michitaka, K.; Kumada, T.; Izumi, N.; Kadoya, M.; Kokudo, N.; Kubo, S.; Matsuyama, Y.; Nakashima, O.; Sakamoto, M.; et al. Validation and Potential of Albumin-Bilirubin Grade and Prognostication in a Nationwide Survey of 46,681 Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients in Japan: The Need for a More Detailed Evaluation of Hepatic Function. Liver Cancer 2017, 6, 325–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lencioni, R.; Llovet, J. Modified RECIST (mRECIST) Assessment for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Semin. Liver Dis. 2010, 30, 052–060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanda, Y. Investigation of the freely available easy-to-use software ‘EZR’ for medical statistics. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2012, 48, 452–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karachristos, A.; Liloglou, T.; Field, J.K.; Deligiorgi, E.; Kouskouni, E.; Spandidos, D.A. Microsatellite Instability and p53 Mutations in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Mol. Cell Biol. Res. Commun. 1999, 2, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, D.T.; Durham, J.N.; Smith, K.N.; Wang, H.; Bartlett, B.R.; Aulakh, L.K.; Lu, S.; Kemberling, H.; Wilt, C.; Luber, B.S.; et al. Mismatch repair deficiency predicts response of solid tumors to PD-1 blockade. Science 2017, 357, 409–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ang, C.; Klempner, S.J.; Ali, S.M.; Madison, R.; Ross, J.S.; Severson, E.A.; Fabrizio, D.; Goodman, A.; Kurzrock, R.; Suh, J.; et al. Prevalence of established and emerging biomarkers of immune checkpoint inhibitor response in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget 2019, 10, 4018–4025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, S.; Subudhi, S.K.; Aparicio, A.; Ge, Z.; Guan, B.; Miura, Y.; Sharma, P. Differences in Tumor Microenvironment Dictate T Helper Lineage Polarization and Response to Immune Checkpoint Therapy. Cell 2019, 179, 1177–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bollig, C.A.; Newberry, C.I.; Galloway, T.L.I.; Zitsch, R.P.; Hanly, E.K.; Zhu, V.L.; Pagedar, N.; Nallani, R.; Bur, A.M.; Spanos, W.C.; et al. Prognostic Impact of Metastatic Site and Pattern in Patients with Metastatic Head and Neck Cancer. Laryngoscope 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haaker, L.; Tryssesoone, L.; Renders, I.; Verbiest, A.; Lerut, E.; Baldewijns, M.; Bourgain, C.; Roussel, E.; Bulck, H.V.D.; Wynendaele, W.; et al. Bone metastasis is associated with poor prognosis in metastatic papillary renal cell carcinoma patients treated with first agent angiogenesis inhibitors. Urol. Oncol. Semin. Orig. Investig. 2020, 38, 686.e1–686.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harding, J.J.; Abu-Zeinah, G.; Chou, J.F.; Owen, D.H.; Ly, M.; Lowery, M.A.; Capanu, M.; Do, R.; Kemeny, N.E.; O’Reilly, E.M.; et al. Frequency, Morbidity, and Mortality of Bone Metastases in Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2018, 16, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueshima, K.; Nishida, N.; Hagiwara, S.; Aoki, T.; Minami, T.; Chishina, H.; Takita, M.; Minami, Y.; Ida, H.; Takenaka, M.; et al. Impact of Baseline ALBI Grade on the Outcomes of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients Treated with Lenvatinib: A Multicenter Study. Cancers 2019, 11, 952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiraoka, A.; Kumada, T.; Atsukawa, M.; Hirooka, M.; Tsuji, K.; Ishikawa, T.; Takaguchi, K.; Kariyama, K.; Itobayashi, E.; Tajiri, K.; et al. Prognostic factor of lenvatinib for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma in real-world conditions—Multicenter analysis. Cancer Med. 2019, 8, 3719–3728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuchigami, A.; Imai, Y.; Uchida, Y.; Uchiya, H.; Fujii, Y.; Nakazawa, M.; Ando, S.; Sugawara, K.; Nakayama, N.; Tomiya, T.; et al. Therapeutic efficacy of lenvatinib for patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma based on the middle-term outcome. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0231427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirino, S.; Tsuchiya, K.; Kurosaki, M.; Kaneko, S.; Inada, K.; Yamashita, K.; Osawa, L.; Hayakawa, Y.; Sekiguchi, S.; Okada, M.; et al. Relative dose intensity over the first four weeks of lenvatinib therapy is a factor of favorable response and overall survival in patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0231828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwamoto, H.; Suzuki, H.; Shimose, S.; Niizeki, T.; Nakano, M.; Shirono, T.; Okamura, S.; Noda, Y.; Kamachi, N.; Nakamura, T.; et al. Weekends-Off Lenvatinib for Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma Improves Therapeutic Response and Tolerability Toward Adverse Events. Cancers 2020, 12, 1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| n = 343 | |
|---|---|
| Age (years), median (range) | 73 (44–93) |
| Sex: Male/Female (%) | 277 (81)/66 (19) |
| MTT naïve/experienced | 246 (72)/97(28) |
| Body weight (kg): median (range) | 60.0 (30.3–101) |
| Etiology HBV/HCV/Alcohol/Others (%) | 49 (14)/144 (42)/41 (12)/109 (32) |
| Child–Pugh A/B (%) | 276 (80)/67 (20) |
| Pretreatment ALBI score: median (range) | −2.34 (−0.60 to −3.52) |
| Modified ALBI grade 1/2a/2b/3 (%) | 95 (28)/98 (29)/136 (39)/14 (4) |
| ECOG PS 0/1/2 (%) | 226 (66)/110 (32)/7 (2) |
| BCLC stage A/B/C (%) | 9 (3)/152 (44)/182 (53) |
| Major vascular invasion Yes/No (%) | 60 (17)/283 (83) |
| Extrahepatic metastasis Yes/No (%) | 118 (34)/225 (66) |
| Baseline AFP concentration (ng/mL), median (range) | 75.1 (1.2–458151) |
| Baseline AFP < 400 ng/mL Yes/No/unknown (%) | 224 (65)/104 (30)/15 (5) |
| MTT Naïve (n = 246) | MTT Experienced (n = 97) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (median) | 74 | 70 | 0.0016 |
| Gender (male, %) | 194 (79) | 83 (86) | 0.17 |
| BW (median, kg) | 60.5 | 60.0 | 0.17 |
| Alb (median, g/dL) | 3.7 | 3.4 | 0.0028 |
| T-Bil (median, mg/dL) | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.37 |
| ALBI score (median) | −2.36 | −2.22 | 0.017 |
| pretreatment AFP (median, ng/mL) | 56 | 170 | 0.13 |
| Extrahepatic metastasis (yes, %) | 75 (30) | 43 (44) | 0.023 |
| Major vascular invasion (yes, %) | 50 (20) | 10 (10) | 0.028 |
| Treatment duration of lenvatinib (median, day) | 125 | 172 | 0.6 |
| Median OS (Months) | Median PFS (Months) | |
|---|---|---|
| BCLC stage B, MTT naïve, ALBI 1 or mALBI 2a (n = 68) | 25.3 | 12.3 |
| BCLC stage B, MTT naïve, mALBI 2b (n = 29) | 13.5 | 7.7 |
| BCLC stage B, MTT experienced, ALBI 1 or mALBI 2a (n = 14) | 15.2 | 11.8 |
| BCLC stage B, MTT experienced, mALBI 2b (n = 21) | 14.0 | 5.5 |
| BCLC stage C, MTT naïve, ALBI 1 or mALBI 2a (n = 64) | 20.9 | 12.7 |
| BCLC stage C, MTT naïve, mALBI 2b (n = 32) | 15.2 | 6.6 |
| BCLC stage C, MTT experienced, ALBI 1 or mALBI 2a (n = 30) | 9.7 | 7.1 |
| BCLC stage C, MTT experienced, mALBI 2b (n = 9) | * | 6.8 |
| p-Value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OS | PFS | |||
| MTT naïve | BCLC stage B | ALBI 1 or mALBI 2a vs. mALBI 2b | 0.009 | 0.002 |
| MTT naïve | BCLC stage C | ALBI 1 or mALBI 2a vs. mALBI 2b | 0.136 | 0.036 |
| MTT experienced | BCLC stage B | ALBI 1 or mALBI 2a vs. mALBI 2b | 0.31 | 0.034 |
| MTT experienced | BCLC stage C | ALBI 1 or mALBI 2a vs. mALBI 2b | 0.13 | 0.96 |
| ALBI 1 or mALBI 2a | MTT naïve | BCLC stage B vs. BCLC stage C | 0.014 | 0.1 |
| ALBI 1 or mALBI 2a | MTT experienced | BCLC stage B vs. BCLC stage C | 0.22 | 0.12 |
| mALBI 2b | MTT naïve | BCLC stage B vs. BCLC stage C | 0.76 | 0.91 |
| mALBI 2b | MTT experienced | BCLC stage B vs. BCLC stage C | 0.14 | 0.4 |
| Univariate | Multivariate | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Factor | p Value | HR | 95% CI | p Value |
| Age (years) | 0.16 | |||
| Body weight (kg) | 0.62 | |||
| Performance Status > 0 | 0.015 | 1.50 | 1.09–2.08 | 0.014 |
| Pretreatment modified ALBI grade 2b or grade 3 | 0.00027 | 1.56 | 1.09–2.17 | 0.012 |
| Pretreatment AFP ≥ 400 ng/mL | <0.0001 | 2.00 | 1.42–2.80 | <0.0001 |
| Extrahepatic metastasis | 0.52 | |||
| Major vascular invasion | 0.00089 | 1.91 | 1.26–2.89 | 0.0022 |
| MTT experience | 0.00043 | 2.22 | 1.56–3.13 | 0.00038 |
| Univariate | Multivariate | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Factor | p Value | HR | 95% CI | p Value |
| Age (years) | 0.044 | 0.27 | ||
| Body weight (kg) | 0.41 | |||
| Performance Status > 0 | 0.45 | |||
| Pretreatment modified ALBI grade 2b or grade 3 | 0.0005 | 1.92 | 1.25–2.96 | 0.0032 |
| Pretreatment AFP ≥ 400 ng/mL | 0.0001 | 2.05 | 1.32–3.18 | 0.0014 |
| Extrahepatic metastasis | 0.80 | |||
| Major vascular invasion | 0.0001 | 1.89 | 1.15–3.08 | 0.012 |
| Univariate | Multivariate | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Factor | p Value | HR | 95% CI | p Value |
| Age (years) | 0.12 | 0.056 | ||
| Body weight (kg) | 0.042 | |||
| Performance Status > 0 | 0.00078 | 2.36 | 1.41–3.92 | 0.0009 |
| Pretreatment modified ALBI grade 2b or grade 3 | 0.29 | |||
| Pretreatment AFP ≥ 400 ng/mL | 0.0056 | 2.39 | 1.37–4.16 | 0.0020 |
| Extrahepatic metastasis | 0.99 | |||
| Major vascular invasion | 0.42 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tsuchiya, K.; Kurosaki, M.; Sakamoto, A.; Marusawa, H.; Kojima, Y.; Hasebe, C.; Arai, H.; Joko, K.; Kondo, M.; Tsuji, K.; et al. The Real-World Data in Japanese Patients with Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma Treated with Lenvatinib from a Nationwide Multicenter Study. Cancers 2021, 13, 2608. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13112608
Tsuchiya K, Kurosaki M, Sakamoto A, Marusawa H, Kojima Y, Hasebe C, Arai H, Joko K, Kondo M, Tsuji K, et al. The Real-World Data in Japanese Patients with Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma Treated with Lenvatinib from a Nationwide Multicenter Study. Cancers. 2021; 13(11):2608. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13112608
Chicago/Turabian StyleTsuchiya, Kaoru, Masayuki Kurosaki, Azusa Sakamoto, Hiroyuki Marusawa, Yuji Kojima, Chitomi Hasebe, Hirotaka Arai, Kouji Joko, Masahiko Kondo, Keiji Tsuji, and et al. 2021. "The Real-World Data in Japanese Patients with Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma Treated with Lenvatinib from a Nationwide Multicenter Study" Cancers 13, no. 11: 2608. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13112608
APA StyleTsuchiya, K., Kurosaki, M., Sakamoto, A., Marusawa, H., Kojima, Y., Hasebe, C., Arai, H., Joko, K., Kondo, M., Tsuji, K., Sohda, T., Kimura, H., Ogawa, C., Uchida, Y., Wada, S., Kobashi, H., Furuta, K., Shigeno, M., Kusakabe, A., ... on behalf of Japanese Red Cross Liver Study Group. (2021). The Real-World Data in Japanese Patients with Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma Treated with Lenvatinib from a Nationwide Multicenter Study. Cancers, 13(11), 2608. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13112608






