The Association between Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs) Use and the Risk of Bladder Cancer: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Characteristics of Subjects with or without SSRIs Use
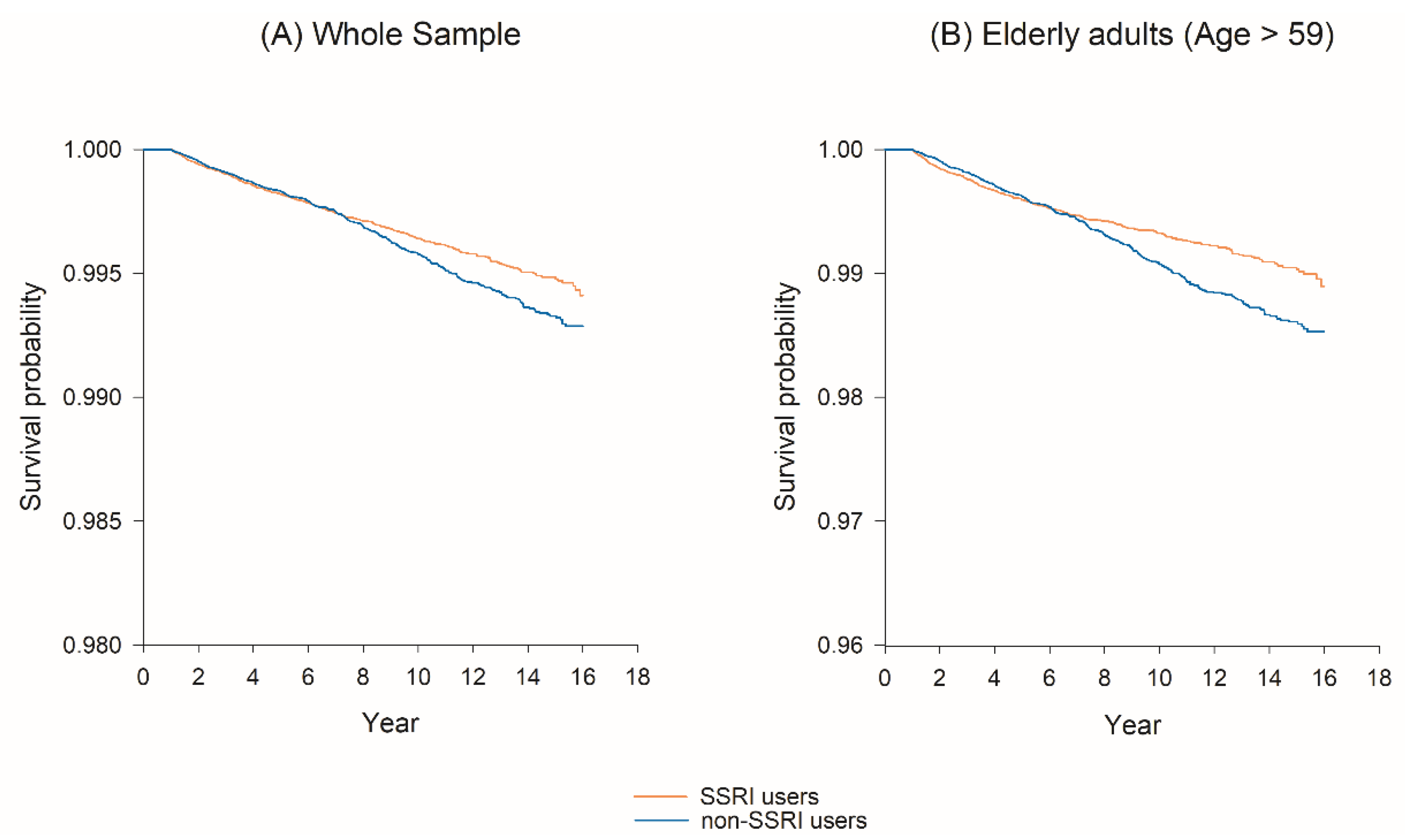
2.2. SSRI Use and the Risk of Bladder Cancer
2.3. Specific SSRI Use and the Risk of Bladder Cancer
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Source Population
4.2. Study and Control Cohorts
4.3. SSRI Exposure
4.4. Data Analyses
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sanchez, A.; Wszolek, M.F.; Niemierko, A.; Clayman, R.H.; Drumm, M.; Rodriguez, D.; Feldman, A.S.; Dahl, D.M.; Heney, N.M.; Shipley, W.U.; et al. Incidence, clinicopathological risk factors, management and outcomes of nonmuscle invasive recurrence after complete response to trimodality therapy for muscle invasive bladder cancer. J. Urol. 2018, 199, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, A.B.; Jaeger, B.; Pinheiro, L.C.; Edwards, L.J.; Tan, H.J.; Nielsen, M.E.; Reeve, B.B. Impact of bladder cancer on health-related quality of life. BJU Int. 2018, 121, 549–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moorman, P.G.; Grubber, J.M.; Millikan, R.C.; Newman, B. Antidepressant medications and their association with invasive breast cancer and carcinoma in situ of the breast. Epidemiology 2003, 14, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cotterchio, M.; Kreiger, N.; Darlington, G.; Steingart, A. Antidepressant medication use and breast cancer risk. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2000, 151, 951–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalton, S.O.; Johansen, C.; Mellemkjaer, L.; Sorensen, H.T.; McLaughlin, J.K.; Olsen, J.; Olsen, J.H. Antidepressant medications and risk for cancer. Epidemiology 2000, 11, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azmitia, E.C. Modern views on an ancient chemical: Serotonin effects on cell proliferation, maturation, and apoptosis. Brain Res. Bull. 2001, 56, 413–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haukka, J.; Sankila, R.; Klaukka, T.; Lonnqvist, J.; Niskanen, L.; Tanskanen, A.; Wahlbeck, K.; Tiihonen, J. Incidence of cancer and antidepressant medication: Record linkage study. Int. J. Cancer 2010, 126, 285–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.F.; Chan, H.L.; Hsieh, Y.H.; Liang, H.Y.; Chiu, W.C.; Huang, K.Y.; Lee, Y.; McIntyre, R.S.; Chen, V.C. Endometrial cancer and antidepressants: A nationwide population-based study. Medicine 2016, 95, e4178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, Y.H.; Chiu, W.C.; Lin, C.F.; Chan, H.L.; Liang, H.Y.; Lee, Y.; McIntyre, R.S.; Chen, V.C. Antidepressants and gastric cancer: A nationwide population-based nested case-control study. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0143668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morch, L.S.; Dehlendorff, C.; Baandrup, L.; Friis, S.; Kjaer, S.K. Use of antidepressants and risk of epithelial ovarian cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2017, 141, 2197–2203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, H.L.; Chiu, W.C.; Chen, V.C.; Huang, K.Y.; Wang, T.N.; Lee, Y.; McIntyre, R.S.; Hsu, T.C.; Lee, C.T.; Tzang, B.S. SSRIs associated with decreased risk of hepatocellular carcinoma: A population-based case-control study. Psychooncology 2018, 27, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, W.; Tamim, H.; Shapiro, S.; Stang, M.R.; Collet, J.P. Use of antidepressants and risk of colorectal cancer: A nested case-control study. Lancet Oncol. 2006, 7, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steffensen, E.H.; Cary, C.; Jensen, J.B.; Larsson, H.; Weiner, M.; Norgaard, M. Preadmission antidepressant use and bladder cancer: A population-based cohort study of stage at diagnosis, time to surgery, and surgical outcomes. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, K.Y.; Lu, T.; Chang, C.H.; Lo, Y.K.; Cheng, J.S.; Wang, J.L.; Chang, H.T.; Jan, C.R. Effect of fluoxetine on intracellular Ca2+ levels in bladder female transitional carcinoma (BFTC) cells. Pharm. Res. 2001, 43, 503–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, K.Y.; Cheng, J.S.; Lee, K.C.; Chou, K.J.; Huang, J.K.; Chen, W.C.; Jan, C.R. Fluoxetine-induced Ca2+ signals in Madin-Darby canine kidney cells. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 2001, 363, 16–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.C.; Chou, C.T.; Pan, C.C.; Hsieh, Y.D.; Liang, W.Z.; Chao, D.; Tsai, J.Y.; Liao, W.C.; Kuo, D.H.; Shieh, P.; et al. Paroxetine-induced Ca2+ movement and death in OC2 human oral cancer cells. Chin. J. Physiol. 2011, 54, 310–317. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.K.; Chang, H.T.; Chou, C.T.; Shu, S.S.; Kuo, C.C.; Tsai, J.Y.; Liao, W.C.; Wang, J.L.; Lin, K.L.; Lu, Y.C.; et al. The mechanism of sertraline-induced [Ca(2+)](i) rise in human PC3 prostate cancer cells. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2011, 109, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.H.; Yang, S.T.; Lin, Y.K.; Lin, J.W.; Lee, Y.H.; Wang, J.Y.; Hu, C.J.; Lin, E.Y.; Chen, S.M.; Then, C.K.; et al. Fluoxetine, an antidepressant, suppresses glioblastoma by evoking AMPAR-mediated calcium-dependent apoptosis. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 5088–5101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, W.J.; Jung, S.K.; Vo, T.T.L.; Jeong, C.H. Anticancer activity of paroxetine in human colon cancer cells: Involvement of MET and ERBB3. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2019, 23, 1106–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, C.A.; Benarroch-Gampel, J.; Sheffield, K.M.; Han, Y.; Kuo, Y.F.; Riall, T.S. The effect of depression on stage at diagnosis, treatment, and survival in pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Surgery 2012, 152, 403–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.H.; Li, J.Q.; Shi, J.F.; Que, J.Y.; Liu, J.J.; Lappin, J.M.; Leung, J.; Ravindran, A.V.; Chen, W.Q.; Qiao, Y.L.; et al. Depression and anxiety in relation to cancer incidence and mortality: A systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies. Mol. Psychiatry 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gross, A.L.; Gallo, J.J.; Eaton, W.W. Depression and cancer risk: 24 years of follow-up of the Baltimore Epidemiologic Catchment Area sample. Cancer Causes Control 2010, 21, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, S.M.; Eggener, S.E.; Lipsitz, S.R.; Irwin, M.R.; Ganz, P.A.; Hu, J.C. Effect of depression on diagnosis, treatment, and mortality of men with clinically localized prostate cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 32, 2471–2478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kisely, S.; Crowe, E.; Lawrence, D. Cancer-related mortality in people with mental illness. JAMA Psychiatry 2013, 70, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadian, E.; Eftekhari, A.; Babaei, H.; Nayebi, A.M.; Eghbal, M.A. Anti-cancer effects of citalopram on hepatocellular carcinoma cells occur via cytochrome C release and the activation of NF-kB. Anticancer Agents Med. Chem. 2017, 17, 1570–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boehning, D.; Patterson, R.L.; Sedaghat, L.; Glebova, N.O.; Kurosaki, T.; Snyder, S.H. Cytochrome c binds to inositol (1,4,5) trisphosphate receptors, amplifying calcium-dependent apoptosis. Nat. Cell Biol. 2003, 5, 1051–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.M.; Yu, B.C.; Chiu, W.T.; Sun, H.Y.; Chien, Y.C.; Su, H.C.; Yen, S.Y.; Lai, H.W.; Bai, C.H.; Young, K.C.; et al. Fluoxetine regulates cell growth inhibition of interferon-alpha. Int. J. Oncol. 2016, 49, 1746–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannen, V.; Hintzsche, H.; Zanette, D.L.; Silva, W.A., Jr.; Garcia, S.B.; Waaga-Gasser, A.M.; Stopper, H. Antiproliferative effects of fluoxetine on colon cancer cells and in a colonic carcinogen mouse model. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e50043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sim, W.J.; Iyengar, P.V.; Lama, D.; Lui, S.K.L.; Ng, H.C.; Haviv-Shapira, L.; Domany, E.; Kappei, D.; Tan, T.Z.; Saei, A.; et al. c-Met activation leads to the establishment of a TGFbeta-receptor regulatory network in bladder cancer progression. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.L.; Trink, B.; Tzai, T.S.; Liu, H.S.; Chan, S.H.; Ho, C.L.; Sidransky, D.; Chow, N.H. Overexpression of c-met as a prognostic indicator for transitional cell carcinoma of the urinary bladder: A comparison with p53 nuclear accumulation. J. Clin. Oncol. 2002, 20, 1544–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kao, W.H.; Hong, J.H.; See, L.C.; Yu, H.P.; Hsu, J.T.; Chou, I.J.; Chou, W.C.; Chiou, M.J.; Wang, C.C.; Kuo, C.F. Validity of cancer diagnosis in the national health insurance database compared with the linked national cancer registry in Taiwan. Pharm. Drug Saf. 2018, 27, 1060–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Letasiova, S.; Medve’ova, A.; Sovcikova, A.; Dusinska, M.; Volkovova, K.; Mosoiu, C.; Bartonova, A. Bladder cancer, a review of the environmental risk factors. Environ. Health 2012, 11 (Suppl. 1), S11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Zalabani, A.H.; Stewart, K.F.; Wesselius, A.; Schols, A.M.; Zeegers, M.P. Modifiable risk factors for the prevention of bladder cancer: A systematic review of meta-analyses. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2016, 31, 811–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nhr, I. National Health Insurance Research Database. Available online: https://nhird.nhri.org.tw/en/Data_Subsets.Html (accessed on 12 January 2020).
- Jacquez, G.M.; Meliker, J.; Kaufmann, A. In search of induction and latency periods: Space-time interaction accounting for residential mobility, risk factors and covariates. Int. J. Health Geogr. 2007, 6, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, B.H.; Chen, P.C.; Yang, Y.H.; Lee, C.P.; Huang, K.E.; Chen, V.C. Effects of depression and antidepressant medications on hip fracture: A population-based cohort study in Taiwan. Medicine 2016, 95, e4655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanza, S.T.; Moore, J.E.; Butera, N.M. Drawing causal inferences using propensity scores: A practical guide for community psychologists. Am. J. Community Psychol. 2013, 52, 380–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richters, A.; Aben, K.K.H.; Kiemeney, L. The global burden of urinary bladder cancer: An update. World J. Urol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Variable | Users of SSRIs | Non-Users of SSRIs | Standardized Mean Difference |
|---|---|---|---|
| N = 192,392 | N = 191,786 | ||
| Sex | |||
| Men | 92,863 (48.3%) | 91,032 (47.5%) | −0.0075 |
| Women | 99,529 (51.7%) | 100,754 (52.5%) | |
| Age (years) | |||
| ≤50 | 88,914 (46.2%) | 75,981 (39.6%) | −a |
| 51–60 | 31,781 (16.5%) | 33,197 (17.3%) | |
| 61–70 | 21,356 (11.1%) | 24,239 (12.6%) | |
| >70 | 50,341 (26.2%) | 58,369 (30.4%) | |
| Urbanization | |||
| Urban | 158,421 (82.3%) | 156,864 (81.8%) | −0.006 |
| Rural | 33,971 (17.7%) | 34,922 (18.2%) | |
| Associated disease | |||
| Anxiety disorder | 76,704 (39.9%) | 83,066 (43.3%) | 0.035 |
| Depressive disorder | 18,812 (9.8%) | 14,701 (7.7%) | −0.021 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 35,256 (18.3%) | 40,644 (21.2%) | 0.029 |
| Hypertension | 67,205 (34.9%) | 77,025 (40.2%) | 0.053 |
| Hyperlipidemia | 15,486 (8.0%) | 18,259 (9.5%) | 0.015 |
| Alcohol use disorder | 726 (0.4%) | 693 (0.4%) | <0.001 |
| Tobacco use disorder | 2791 (1.5%) | 2698 (1.4%) | <0.001 |
| Obesity | 1221 (0.6%) | 1225 (0.6%) | <0.001 |
| COPD | 32,328 (16.8%) | 36,134 (18.8%) | 0.021 |
| Chronic cystitis | 1184 (0.6%) | 1188 (0.6%) | <0.001 |
| Polycystic kidney | 172 (0.1%) 180 (0.1%) 172 (0.1%) | 180 (0.1%) | <0.001 |
| Calculus of kidney and ureter | 67,975 (35.3%) | 6873 (3.6%) | 0.003 |
| Medication use | |||
| Aspirin | 67,975 (35.3%) | 72,363 (37.7%) | −0.016 |
| NSAIDs | 93,151 (48.4%) | 89,883 (46.9%) | 0.005 |
| Statins | 19,735 (10.3%) | 20,544 (10.7%) | 0.024 |
| Cyclophosphamide | 1069 (0.6%) | 1237 (0.6%) | 0.001 |
| Pioglitazone | 5542 (2.9%) | 5887 (3.1%) | 0.002 |
| Outcome | |||
| Bladder cancer | 518 (0.3%) | 559 (0.3%) | - |
| Age of diagnosis, Median (IQR) | 73 (44–89) | 75 (51–87) |
| Induction Period | Adjusted HR (95% CI) a | |
|---|---|---|
| Whole Sample | Elderly Adults (Age > 59) | |
| N = 384178 | N = 154305 | |
| 6 months | 0.86 (0.76–0.98) * | 0.86 (0.74–1.01) |
| 1 year | 0.85 (0.75–0.97) * | 0.83 (0.71–0.98) * |
| 2 years | 0.77 (0.66–0.89) ** | 0.70 (0.58–0.85) *** |
| Specific SSRIs | N (%) | 6 Months | 1 Year Induction Period | 2 Year Induction Period |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adjusted HR (95%CI) | Adjusted HR (95%CI) | Adjusted HR (95%CI) | ||
| Fluoxetine | 77,769 (40.4) | 0.78 (0.65–0.93) * | 0.78 (0.65–0.94) * | 0.73 (0.60–0.89) * |
| Paroxetine | 47,018 (24.4) | 0.78 (0.61–0.99) * | 0.79 (0.61–1.01) | 0.72 (0.54–0.95) * |
| Sertraline | 81,326 (42.3) | 1.03 (0.74–1.43) | 1.00 (0.70–1.43) | 1.00 (0.66–1.51) |
| Escitalopram | 40,740 (21.2) | 1.03 (0.74–1.43) | 1.00 (0.70–1.43) | 1.00 (0.66–1.51) |
| Citalopram | 25,971 (13.5) | 0.74 (0.53–1.03) | 0.70 (0.50–0.99) * | 0.60 (0.41–0.88) ** |
| Fluvoxamine | 16,403 (8.5) | 0.94 (0.65–1.37) | 1.04 (0.70–1.55) | 1.06 (0.68–1.65) |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Y.-C.; Chen, V.C.-H.; Lu, M.-L.; Lee, M.-J.; McIntyre, R.S.; Majeed, A.; Lee, Y.; Chen, Y.-L. The Association between Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs) Use and the Risk of Bladder Cancer: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study. Cancers 2020, 12, 1184. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12051184
Liu Y-C, Chen VC-H, Lu M-L, Lee M-J, McIntyre RS, Majeed A, Lee Y, Chen Y-L. The Association between Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs) Use and the Risk of Bladder Cancer: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study. Cancers. 2020; 12(5):1184. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12051184
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Yi-Chun, Vincent Chin-Hung Chen, Mong-Liang Lu, Min-Jing Lee, Roger S. McIntyre, Amna Majeed, Yena Lee, and Yi-Lung Chen. 2020. "The Association between Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs) Use and the Risk of Bladder Cancer: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study" Cancers 12, no. 5: 1184. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12051184
APA StyleLiu, Y.-C., Chen, V. C.-H., Lu, M.-L., Lee, M.-J., McIntyre, R. S., Majeed, A., Lee, Y., & Chen, Y.-L. (2020). The Association between Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs) Use and the Risk of Bladder Cancer: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study. Cancers, 12(5), 1184. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12051184





