HNC0014, a Multi-Targeted Small-Molecule, Inhibits Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma by Suppressing c-Met/STAT3/CD44/PD-L1 Oncoimmune Signature and Eliciting Antitumor Immune Responses
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture and Reagents
2.2. Molecular Docking
2.3. Generation of HNSCC Tumorspheres (Sp)
2.4. Isolation of Tumorsphere-Derived Exosomes (Exosp)
2.5. Exosome-Induced Transformation of Fibroblasts
2.6. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
2.7. Cell Viability Assay
2.8. Colony Formation Assay
2.9. Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) and Western Blotting
2.10. Animal Experiments
2.11. Data Analysis
3. Results
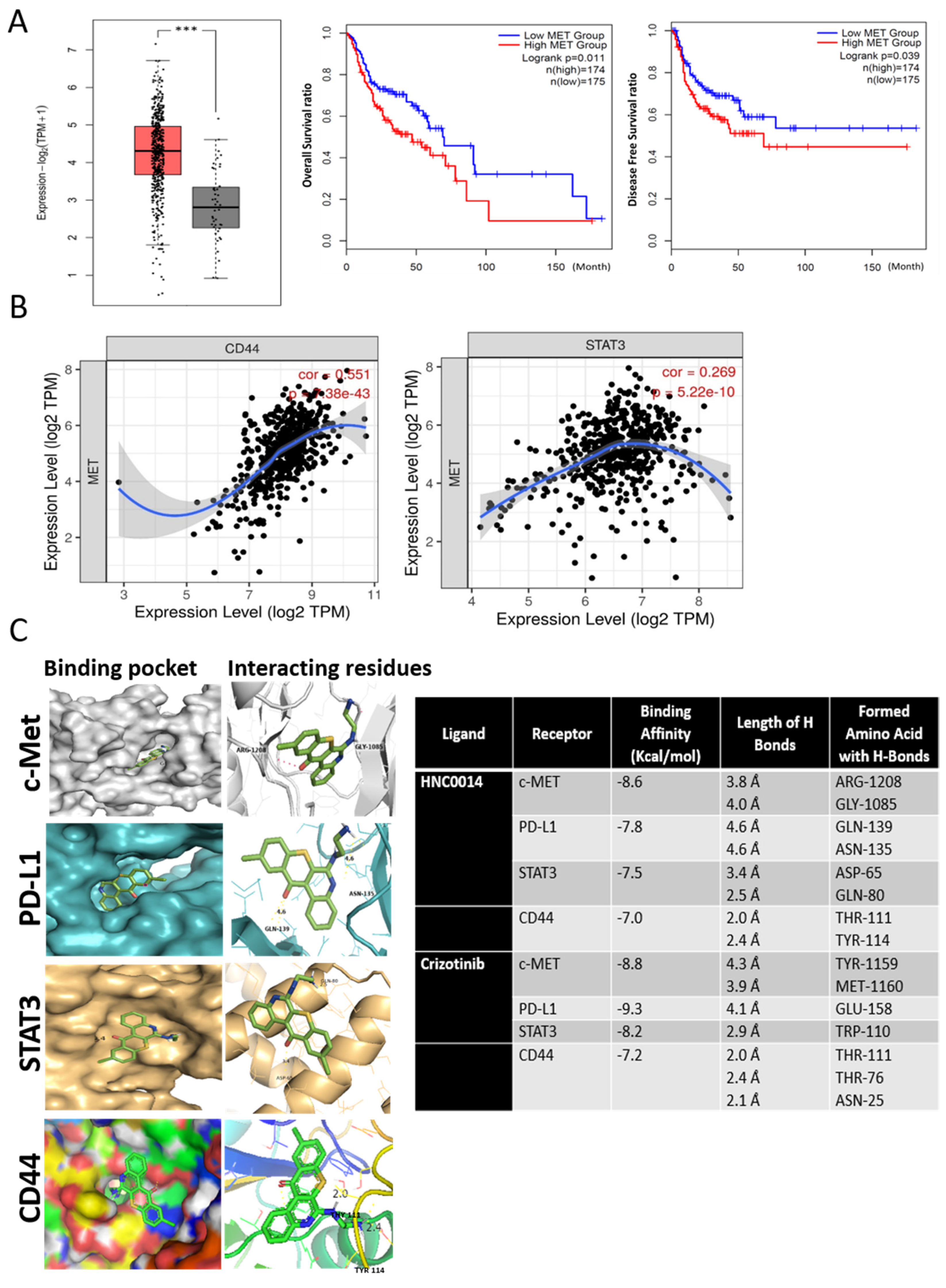
3.1. An Increased c-Met-Associated Signaling Network in HNSCC Patients Is Associated with Poor Prognosis and Cancer Stemness
3.2. In Silico Molecular Docking Simulations Predicted Strong Interactions between HNC0014 with c-Met/STAT3/CD44/PD-L1
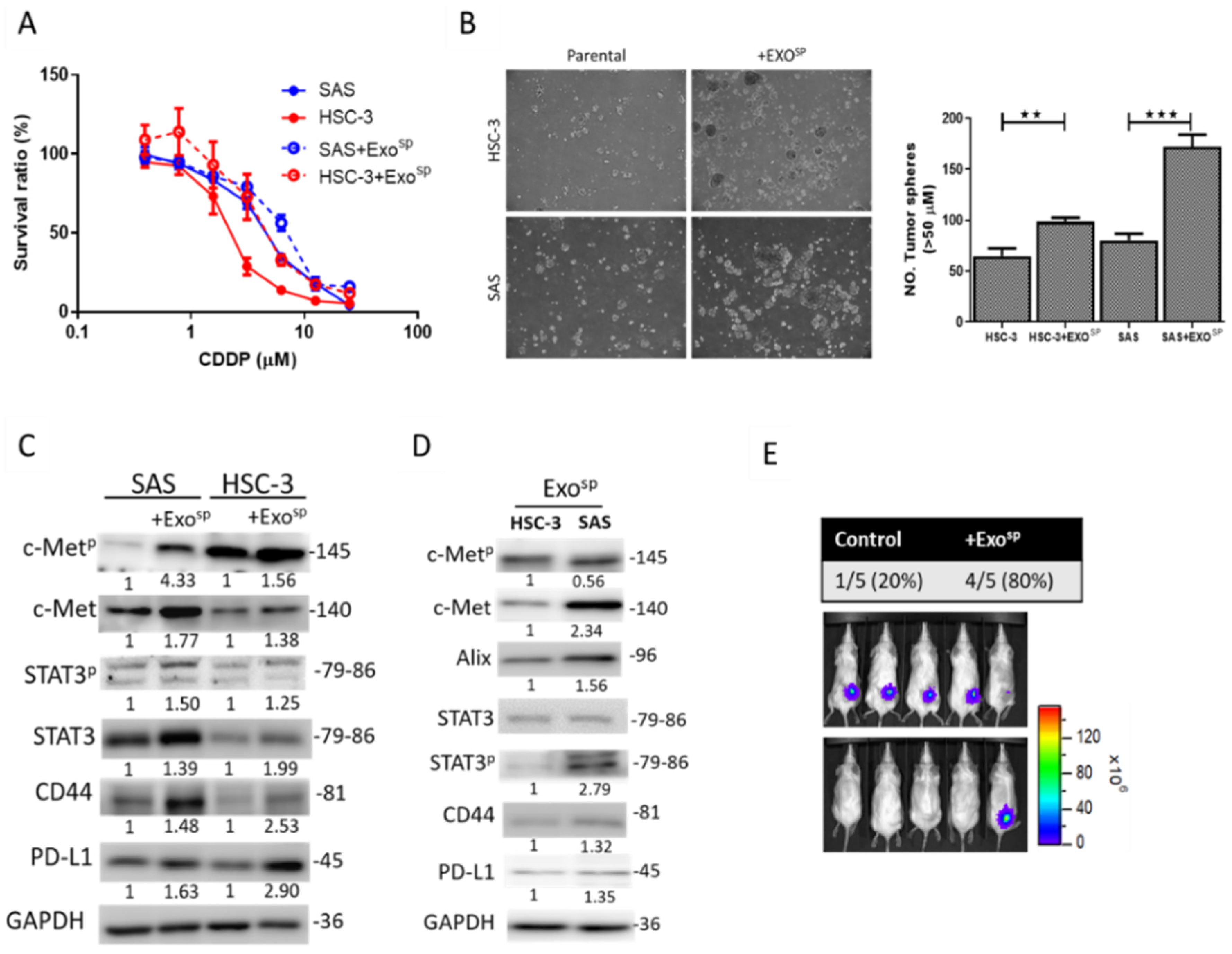
3.3. Tumorsphere-Derived Exosomes (Exosp) Promoted c-Met/STAT3/CD44/PD-L1 Expressions, Cisplatin Resistance, and Tumor-Initiating Ability
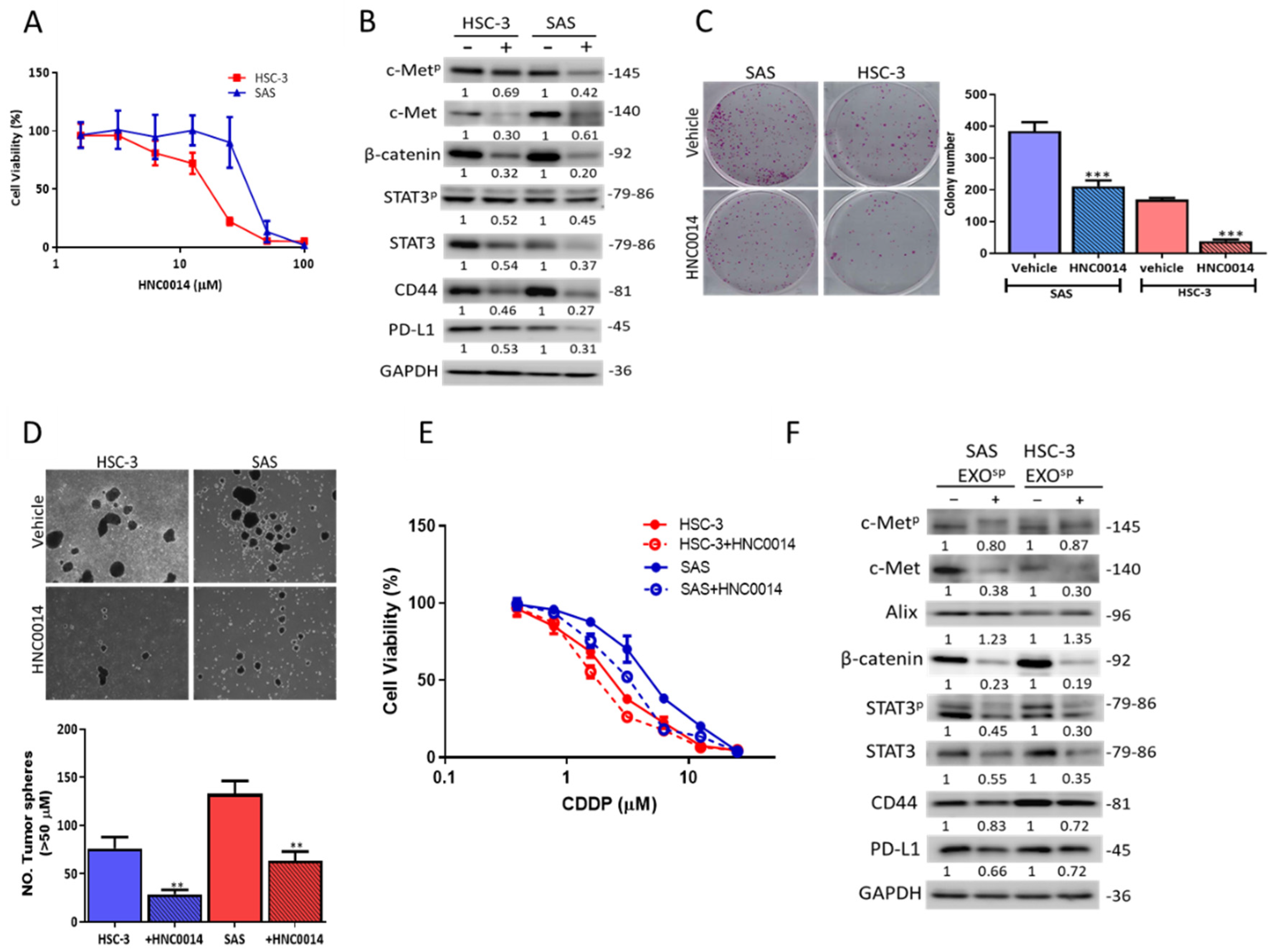
3.4. HNC0014 Treatment Inhibits Tumorigenic and Stemness Properties via Downregulating c-Met/STAT3/PD-L1 Expressions
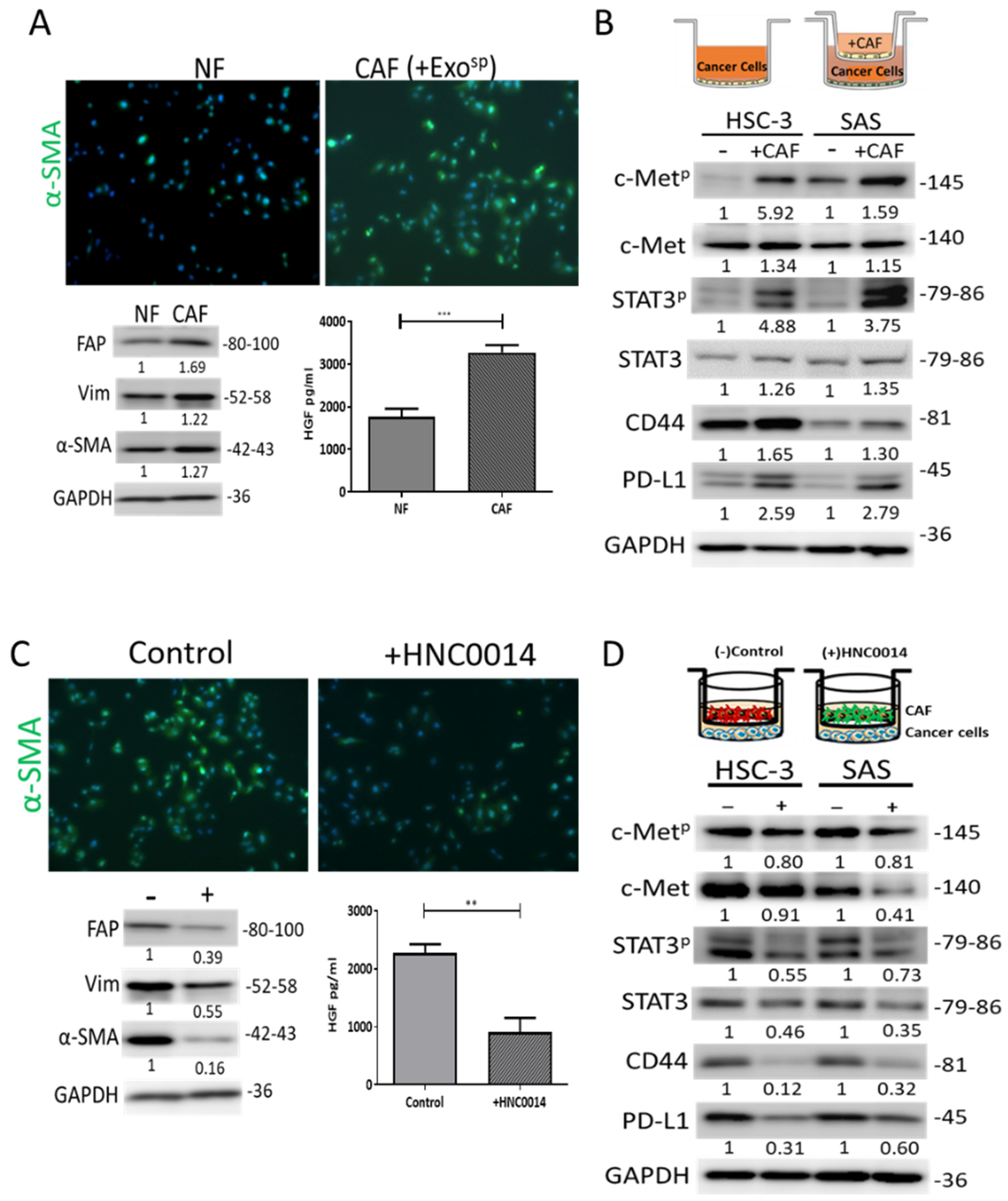
3.5. HNC0014 Reduced HNSCC-Induced CAF Transformation and Its Protumorigenic Properties In Vitro
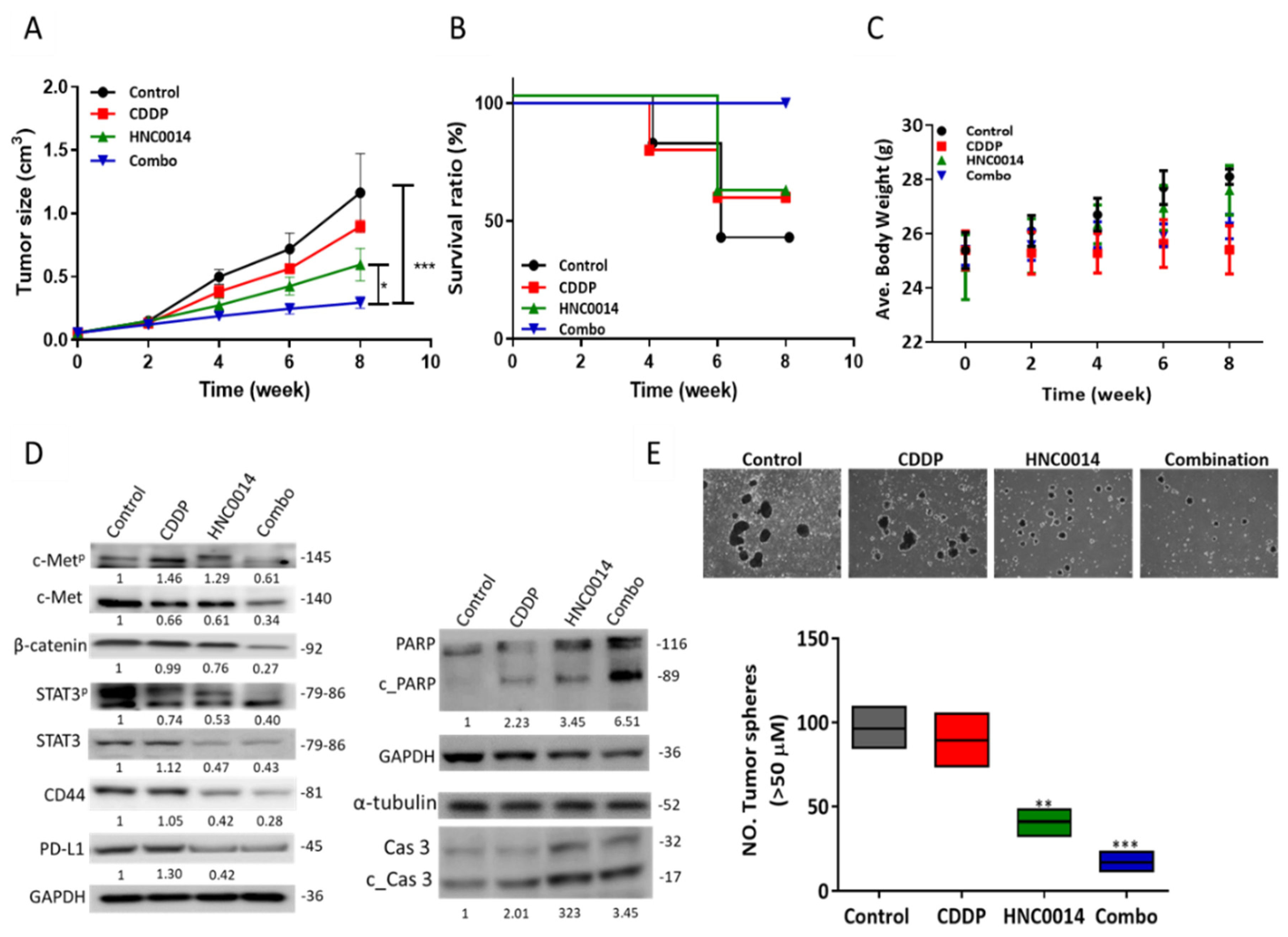
3.6. HNC0014 Treatment Improved Cisplatin Sensitivity and Suppressed Tumorsphere-Initiated Tumor Growth In Vivo
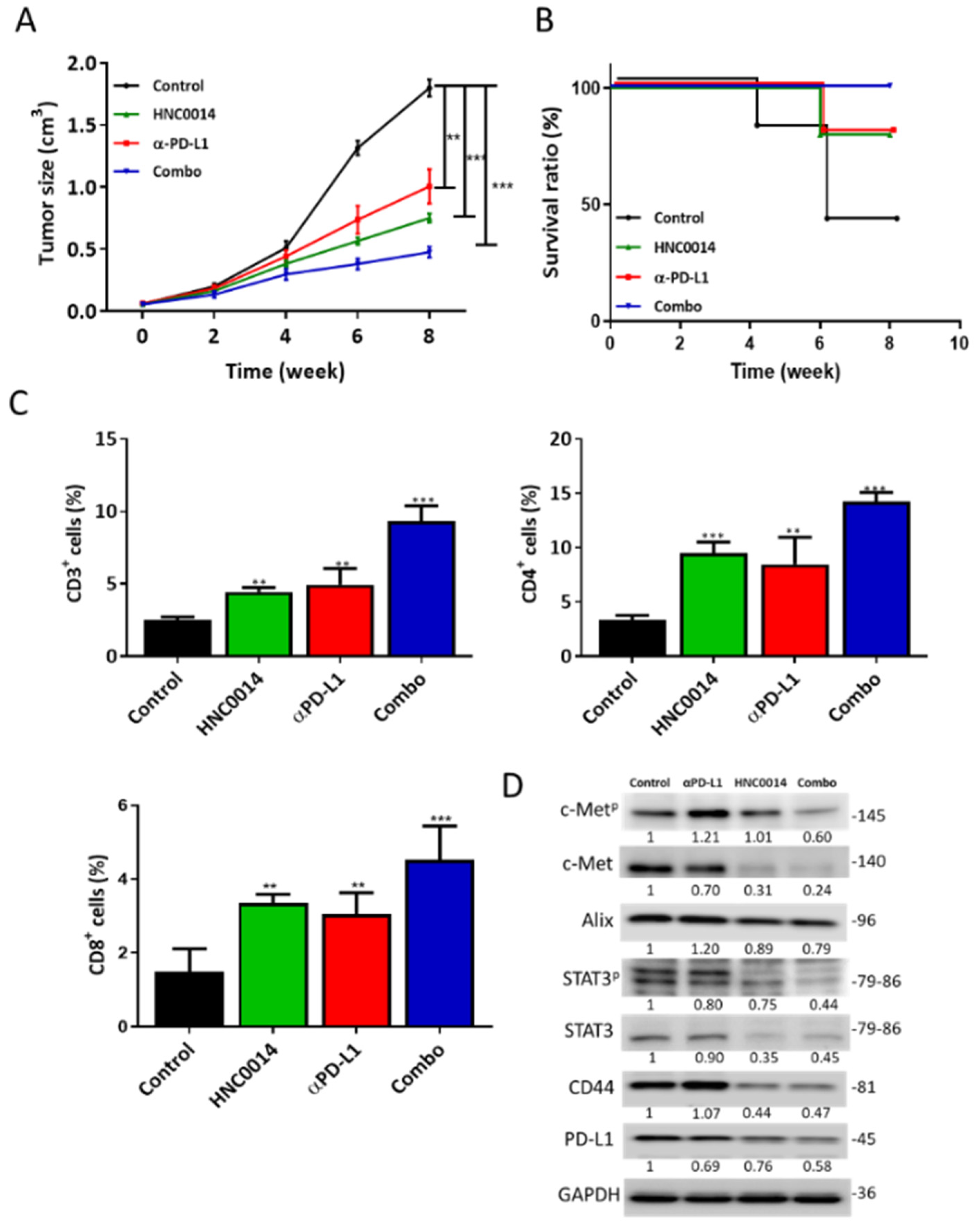
3.7. HNC0014 Treatment Suppressed Tumor Growth in a Syngeneic Mouse Model and Exhibited an Antitumor Immune Profile
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO. WHO Report on Cancer: Setting Priorities, Investing Wisely and Providing Care for All; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Wellington, K.W. Understanding cancer and the anticancer activities of naphthoquinones—A review. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 20309–20338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byeon, H.K.; Ku, M.; Yang, J. Beyond EGFR inhibition: Multilateral combat strategies to stop the progression of head and neck cancer. Exp. Mol. Med. 2019, 51, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO Report on Cancer. Available online: http://apps.who.int/bookorders/anglais/detart1.jsp?codlan=1&codcol=76&codcch=31 (accessed on 20 September 2020).
- Huang, G.; Pan, S.-T. ROS-Mediated Therapeutic Strategy in Chemo-/Radiotherapy of Head and Neck Cancer. Oxidat. Med. Cell. Longev. 2020, 2020, 5047987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. A Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vigneswaran, N.; Williams, M.D. Epidemiologic trends in head and neck cancer and aids in diagnosis. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. Clin. N. Am. 2014, 26, 123–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boscolo-Rizzo, P.; Zorzi, M.; Del Mistro, A.; Da Mosto, M.C.; Tirelli, G.; Buzzoni, C.; Rugge, M.; Polesel, J.; Guzzinati, S.; AIRTUM Working Group. The evolution of the epidemiological landscape of head and neck cancer in Italy: Is there evidence for an increase in the incidence of potentially HPV-related carcinomas? PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0192621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dixit, R.; Weissfeld, J.L.; Wilson, D.O.; Balogh, P.; Sufka, P.; Siegfried, J.M.; Grandis, J.R.; Diergaarde, B. Incidence of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma among subjects at high risk of lung cancer: Results from the Pittsburgh Lung Screening Study. Cancer 2015, 121, 1431–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harari, P.M. Epidermal growth factor receptor inhibition strategies in oncology. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2004, 11, 689–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.B.; Harris, R.C. Autocrine, paracrine and juxtacrine signaling by EGFR ligands. Cell. Signal. 2005, 17, 1183–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, L.; Enders, J.; Thomas, S.M. Activated HGF-c-Met Axis in Head and Neck Cancer. Cancers 2017, 9, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cramer, J.D.; Burtness, B.; Le, Q.T.; Ferris, R.L. The changing therapeutic landscape of head and neck cancer. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 16, 669–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nekhlyudov, L.; Lacchetti, C.; Davis, N.B.; Garvey, T.Q.; Goldstein, D.P.; Nunnink, J.C.; Ninfea, J.I.R.; Salner, A.L.; Salz, T.; Siu, L.L. Head and Neck Cancer Survivorship Care Guideline: American Society of Clinical Oncology Clinical Practice Guideline Endorsement of the American Cancer Society Guideline. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 1606–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leemans, C.R.; Braakhuis, B.J.; Brakenhoff, R.H. The molecular biology of head and neck cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2011, 11, 9–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chow, L.Q.M. Head and Neck Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, E.E.W.; LaMonte, S.J.; Erb, N.L.; Beckman, K.L.; Sadeghi, N.; Hutcheson, K.A.; Stubblefield, M.D.; Abbott, D.M.; Fisher, P.S.; Stein, K.D.; et al. American Cancer Society Head and Neck Cancer Survivorship Care Guideline. A Cancer J. Clin. 2016, 66, 203–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egloff, A.M.; Grandis, J.R. Targeting epidermal growth factor receptor and SRC pathways in head and neck cancer. Semin. Oncol. 2008, 35, 286–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madoz-Gúrpide, J.; Zazo, S.; Chamizo, C.; Casado, V.; Caramés, C.; Gavín, E.; Cristóbal, I.; García-Foncillas, J.; Rojo, F. Activation of MET pathway predicts poor outcome to cetuximab in patients with recurrent or metastatic head and neck cancer. J. Transl. Med. 2015, 13, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martens-de Kemp, S.R.; Dalm, S.U.; Wijnolts, F.M.J.; Brink, A.; Honeywell, R.J.; Peters, G.J.; Braakhuis, B.J.M.; Brakenhoff, R.H. DNA-Bound Platinum Is the Major Determinant of Cisplatin Sensitivity in Head and Neck Squamous Carcinoma Cells. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matta, A.; Ralhan, R. Overview of current and future biologically based targeted therapies in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Head Neck Oncol. 2009, 1, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.W.; Chen, T.C.; Huang, H.S.; Lee, H. TC-N19, a novel dual inhibitor of EGFR and cMET, efficiently overcomes EGFR-TKI resistance in non-small-cell lung cancer cells. Cell Death Dis. 2016, 7, e2290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Chen, T.C.; Wu, C.L.; Lee, C.C.; Chen, C.L.; Yu, D.S.; Huang, H.S. Structure-based hybridization, synthesis and biological evaluation of novel tetracyclic heterocyclic azathioxanthone analogues as potential anti-tumor agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 103, 615–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vichai, V.; Kirtikara, K. Sulforhodamine B colorimetric assay for cytotoxicity screening. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 1112–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishida, K.; Tomita, H.; Nakashima, T.; Hirata, A.; Tanaka, T.; Shibata, T.; Hara, A. Current mouse models of oral squamous cell carcinoma: Genetic and chemically induced models. Oral Oncol. 2017, 73, 16–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, L.; Allen, C.T.; Xiao, R.; Moore, E.; Davis, R.; Park, S.J.; Spielbauer, K.; Van Waes, C.; Schmitt, N.C. Cisplatin Alters Antitumor Immunity and Synergizes with PD-1/PD-L1 Inhibition in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2017, 5, 1141–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzahrani, F.A.; El-Magd, M.A.; Abdelfattah-Hassan, A.; Saleh, A.A.; Saadeldin, I.M.; El-Shetry, E.S.; Badawy, A.A.; Alkarim, S. Potential Effect of Exosomes Derived from Cancer Stem Cells and MSCs on Progression of DEN-Induced HCC in Rats. Stem Cells Int. 2018, 2018, 8058979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Vega, V.; Venegas Rojas, B.; Donoso Torres, W. Immunohistochemical analysis of cancer-associated fibroblasts and podoplanin in head and neck cancer. Med. Oral Patol. Oral Cir. Bucal 2020, 25, e268–e276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, I.; Sato, H.; Tsukahara, K. Overall survival and PD-L1 expression in patients with recurrent or metastatic head and neck cancer treated with nivolumab. Auris Nasus Larynx 2020, 47, 676–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Sun, Z.; Huang, X.; Li, X.; Sun, L.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, X.; Ye, L.; Yuan, J.; Mao, L.; et al. Role of c-Met expression on prognosis of head and neck cancer: A literature review and meta-analysis. Head Neck 2019, 41, 1999–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, Y.C.; Kang, H.J.; Moon, J.H. C-Met pathway promotes self-renewal and tumorigenecity of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma stem-like cell. Oral Oncol. 2014, 50, 633–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theodoraki, M.-N.; Yerneni, S.S.; Hoffmann, T.K.; Gooding, W.E.; Whiteside, T.L. Clinical Significance of PD-L1(+) Exosomes in Plasma of Head and Neck Cancer Patients. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 896–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.-H.; Wu, A.T.H.; Bamodu, O.A.; Yadav, V.K.; Chao, T.-Y.; Tzeng, Y.-M.; Mukhopadhyay, D.; Hsiao, M.; Lee, J.-C. Ovatodiolide Suppresses Oral Cancer Malignancy by Down-Regulating Exosomal Mir-21/STAT3/β-Catenin Cargo and Preventing Oncogenic Transformation of Normal Gingival Fibroblasts. Cancers 2019, 12, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Zhao, K.; Hackert, T.; Zöller, M. CD44/CD44v6 a Reliable Companion in Cancer-Initiating Cell Maintenance and Tumor Progression. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2018, 6, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Li, C.-W.; Chan, L.-C.; Wei, Y.; Hsu, J.-M.; Xia, W.; Cha, J.-H.; Hou, J.; Hsu, J.L.; Sun, L.; et al. Exosomal PD-L1 harbors active defense function to suppress T cell killing of breast cancer cells and promote tumor growth. Cell Res. 2018, 28, 862–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.; Huang, A.C.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, G.; Wu, M.; Xu, W.; Yu, Z.; Yang, J.; Wang, B.; Sun, H.; et al. Exosomal PD-L1 contributes to immunosuppression and is associated with anti-PD-1 response. Nature 2018, 560, 382–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuo, Z.; Zong, Y.; Li, J.; Xiao, G.; Zhang, F.; Li, G.; Wang, S.; Lv, Y.; Xia, J.; Liu, J. PD-L1 regulation by SDH5 via β-catenin/ZEB1 signaling. Oncoimmunology 2019, 8, 1655361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, H.K.; Kim, S.; Kwon, D.; Koh, J.; Kim, Y.A.; Kim, K.; Chung, D.H.; Jeon, Y.K. MET Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Regulates the Expression of Co-Stimulatory and Co-Inhibitory Molecules in Tumor Cells and Contributes to PD-L1-Mediated Suppression of Immune Cell Function. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Wang, R.; Zhang, X.; Ma, Y.; Zhong, L.; Li, K.; Nishiyama, A.; Arai, S.; Yano, S.; Wang, W. EGFR-TKI resistance promotes immune escape in lung cancer via increased PD-L1 expression. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brennen, W.N.; Rosen, D.M.; Wang, H.; Isaacs, J.T.; Denmeade, S.R. Targeting Carcinoma-Associated Fibroblasts Within the Tumor Stroma With a Fibroblast Activation Protein-Activated Prodrug. J. Nat.Cancer Inst. 2012, 104, 1320–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonda, T.A.; Varro, A.; Wang, T.C.; Tycko, B. Molecular biology of cancer-associated fibroblasts: Can these cells be targeted in anti-cancer therapy? Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2010, 21, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvorak, H.F. Tumors: Wounds that do not heal. Similarities between tumor stroma generation and wound healing. N. Engl. J. Med. 1986, 315, 1650–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barker, H.E.; Paget, J.T.E.; Khan, A.A.; Harrington, K.J. The tumour microenvironment after radiotherapy: Mechanisms of resistance and recurrence. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2015, 15, 409–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, N.-N.; Wang, P.; Zhao, D.; Zhang, F.-J.; Yang, K.; Chen, R. Significance of oral cancer-associated fibroblasts in angiogenesis, lymphangiogenesis, and tumor invasion in oral squamous cell carcinoma. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2017, 46, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, X.; Guo, H.; Wang, X.; Zhu, X.; Yan, M.; Wang, X.; Xu, Q.; Shi, J.; Lu, E.; Chen, W.; et al. Exosomal miR-196a derived from cancer-associated fibroblasts confers cisplatin resistance in head and neck cancer through targeting CDKN1B and ING5. Genome Biol. 2019, 20, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, T.; Ahn, R.; Yang, K.; Zhu, X.; Fu, Z.; Morin, G.; Bramley, R.; Cliffe, N.C.; Xue, Y.; Kuasne, H.; et al. CD44 Promotes PD-L1 Expression and Its Tumor-Intrinsic Function in Breast and Lung Cancers. Cancer Res. 2020, 80, 444–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Q.; Wu, J.; Wang, W.J.; Chen, S.; Zheng, Y.; Yu, X.; Meeth, K.; Sahraei, M.; Bothwell, A.L.M.; Chen, L.; et al. DKK2 imparts tumor immunity evasion through β-catenin-independent suppression of cytotoxic immune-cell activation. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 262–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spolski, R.; Li, P.; Leonard, W.J. Biology and regulation of IL-2: From molecular mechanisms to human therapy. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2018, 18, 648–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, J.-C.; Wu, A.T.H.; Chen, J.-H.; Huang, W.-Y.; Lawal, B.; Mokgautsi, N.; Huang, H.-S.; Ho, C.-L. HNC0014, a Multi-Targeted Small-Molecule, Inhibits Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma by Suppressing c-Met/STAT3/CD44/PD-L1 Oncoimmune Signature and Eliciting Antitumor Immune Responses. Cancers 2020, 12, 3759. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12123759
Lee J-C, Wu ATH, Chen J-H, Huang W-Y, Lawal B, Mokgautsi N, Huang H-S, Ho C-L. HNC0014, a Multi-Targeted Small-Molecule, Inhibits Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma by Suppressing c-Met/STAT3/CD44/PD-L1 Oncoimmune Signature and Eliciting Antitumor Immune Responses. Cancers. 2020; 12(12):3759. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12123759
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Jih-Chin, Alexander T. H. Wu, Jia-Hong Chen, Wen-Yen Huang, Bashir Lawal, Ntlotlang Mokgautsi, Hsu-Shan Huang, and Ching-Liang Ho. 2020. "HNC0014, a Multi-Targeted Small-Molecule, Inhibits Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma by Suppressing c-Met/STAT3/CD44/PD-L1 Oncoimmune Signature and Eliciting Antitumor Immune Responses" Cancers 12, no. 12: 3759. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12123759
APA StyleLee, J.-C., Wu, A. T. H., Chen, J.-H., Huang, W.-Y., Lawal, B., Mokgautsi, N., Huang, H.-S., & Ho, C.-L. (2020). HNC0014, a Multi-Targeted Small-Molecule, Inhibits Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma by Suppressing c-Met/STAT3/CD44/PD-L1 Oncoimmune Signature and Eliciting Antitumor Immune Responses. Cancers, 12(12), 3759. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12123759







