Enhanced Malignant Phenotypes of Glioblastoma Cells Surviving NPe6-Mediated Photodynamic Therapy are Regulated via ERK1/2 Activation
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Antibodies
2.2. Cell Culture
2.3. Small Interfering RNA (siRNA)-Mediated Gene Knockdown
2.4. In Vitro NPe6-Mediated PDT Model of GBM Cells
2.5. Cell Toxicity Assay
2.6. Quantitation of Caspase-Dependent Apoptosis-To-Caspase-Independent Apoptosis Ratio
2.7. 5-FU Treatment of GBM Cells
2.8. Immunoblotting, In Vitro Protein Crosslinking Assay, and Cell Fractionation
2.9. Measurement of Poly ADP-Ribose (PARP) Activity
2.10. Wound Healing Assay
2.11. Transwell Migration and Invasion Assay
2.12. Invadopodia Assay
2.13. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
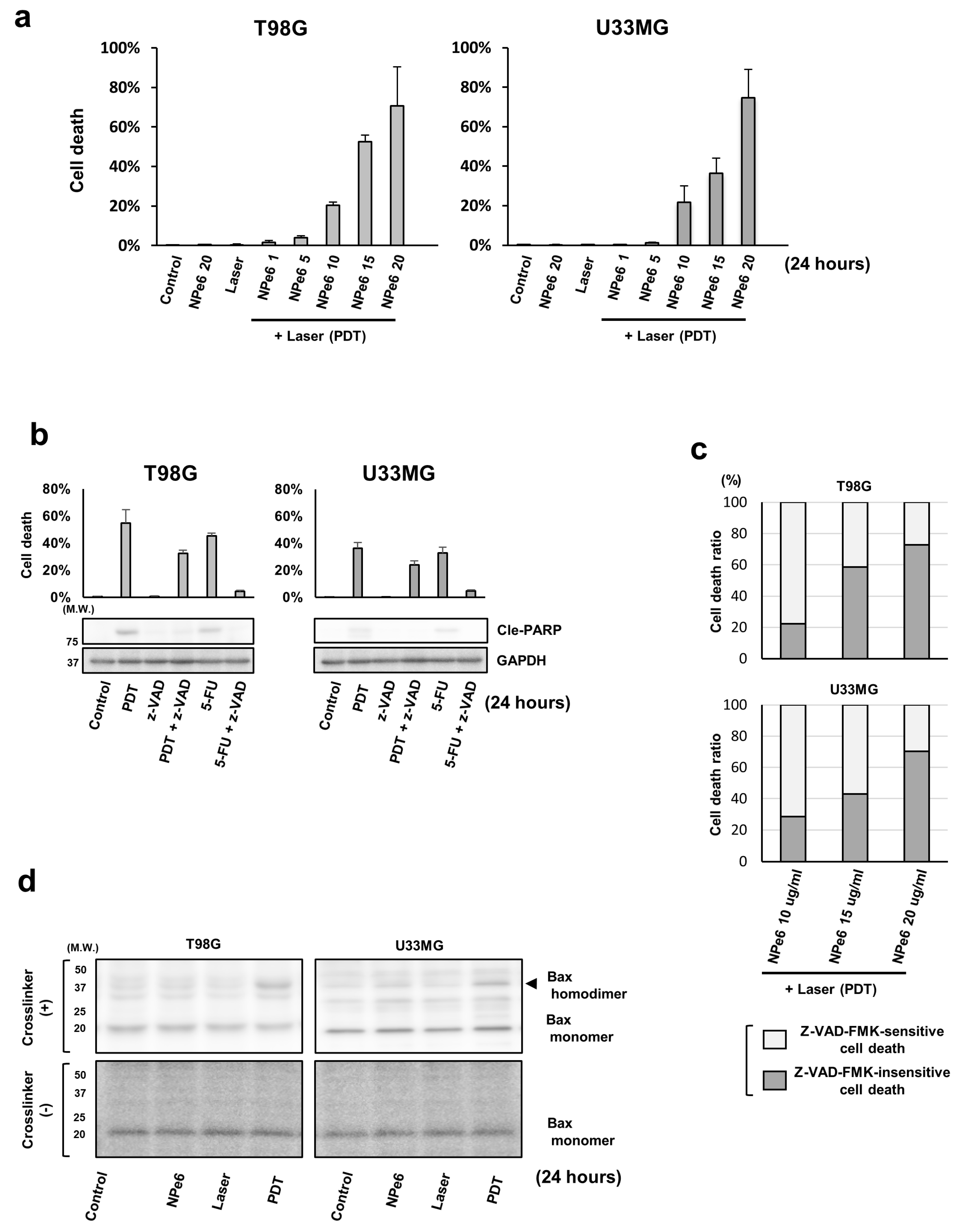
3.1. NPe6-PDT Induced Caspase-Dependent/Independent GBM Cell Death In Vitro through the Mitochondrial Pathway
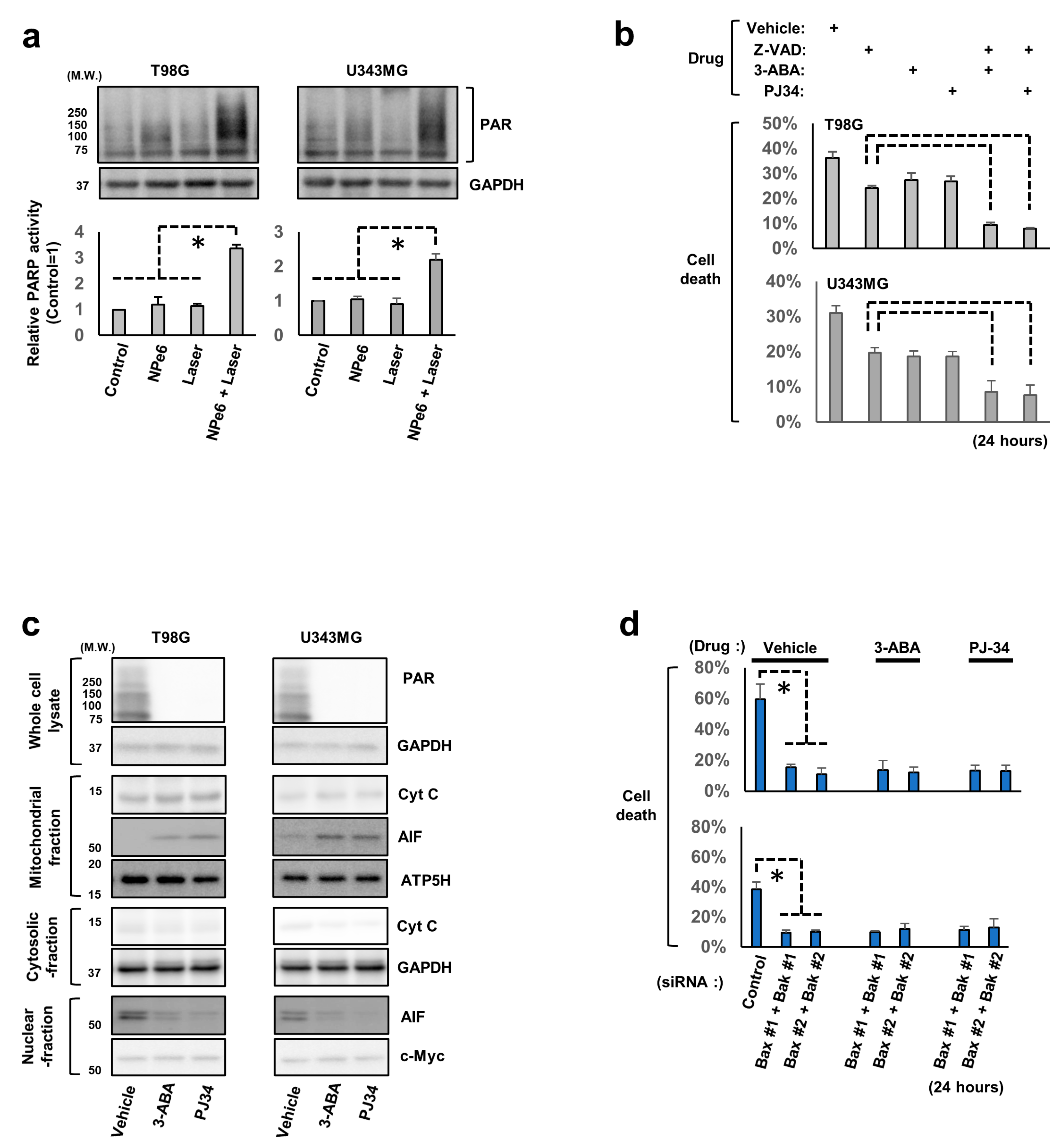
3.2. AIF and Poly (ADP-Ribose) Polymerase 1 (PARP1) Are Involved in NPe6-PDT-Induced Caspase-Independent GBM Cell Death
3.3. The Established In Vitro GBM Cell Model Survived NPe6-PDT
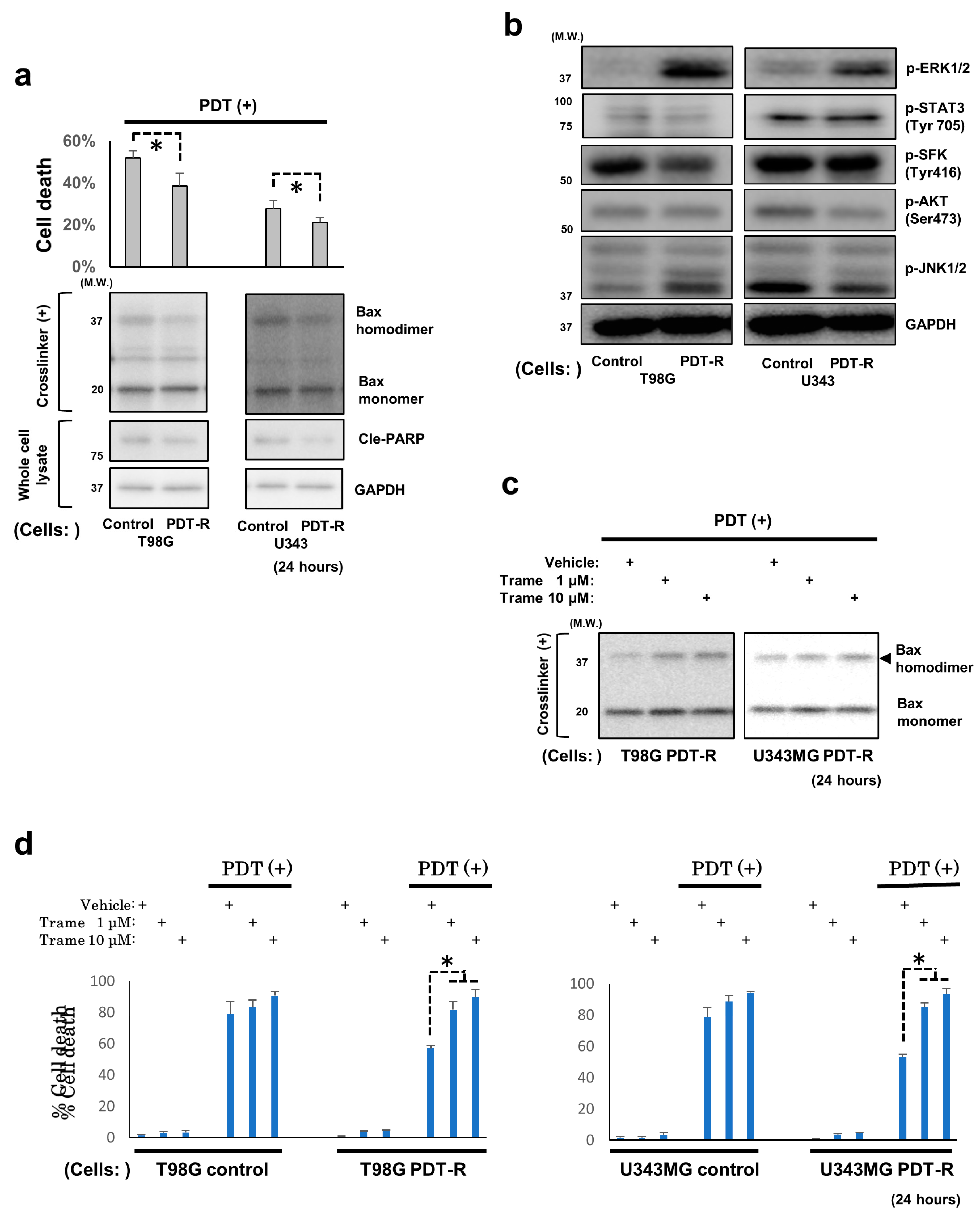
3.4. Upregulated ERK1/2 Activation Is Essential for the Resistance of Surviving GBM Cells and GBM Stem Cells to NPe6-PDT-Induced Cell Death
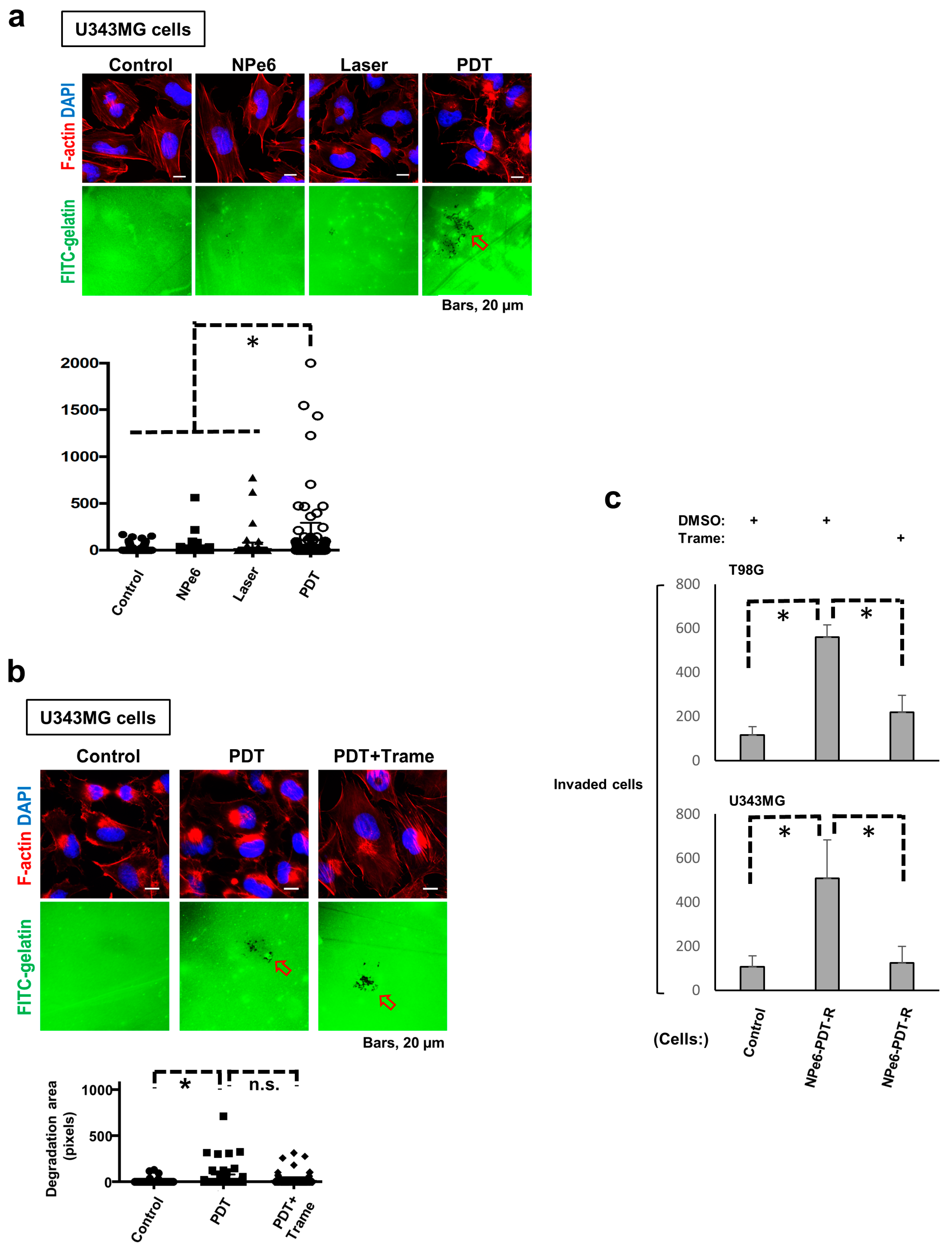
3.5. NPe6-PDT-R Cell Migration Is Enhanced via ERK1/2 Activation-Dependent Machinery
3.6. Degradation of Extracellular Matrix (ECM) Is Promoted in NPe6-PDT-R Cells Independent of ERK Activation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stupp, R.; Hegi, M.E.; Mason, W.P.; van den Bent, M.J.; Taphoorn, M.J.; Janzer, R.C.; Ludwin, S.K.; Allgeier, A.; Fisher, B.; Belanger, K.; et al. Effects of radiotherapy with concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide versus radiotherapy alone on survival in glioblastoma in a randomised phase III study: 5-year analysis of the EORTC-NCIC trial. Lancet Oncol. 2009, 10, 459–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dougherty, T.J. Photosensitization of malignant tumors. Semin. Surg. Oncol. 1986, 2, 24–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Briffa, D.V.; Warin, A.P. Photochemotherapy in psoriasis: A review. J. R. Soc. Med. 1979, 72, 440–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Straten, D.; Mashayekhi, V.; de Bruijn, H.S.; Oliveira, S.; Robinson, D.J. Oncologic Photodynamic Therapy: Basic Principles, Current Clinical Status and Future Directions. Cancers 2017, 9, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanovsky, R.L.; Bartenstein, D.W.; Rogers, G.S.; Isakoff, S.J.; Chen, S.T. Photodynamic therapy for solid tumors: A review of the literature. Photodermatol. Photoimmunol. Photomed. 2019, 35, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muragaki, Y.; Akimoto, J.; Maruyama, T.; Iseki, H.; Ikuta, S.; Nitta, M.; Maebayashi, K.; Saito, T.; Okada, Y.; Kaneko, S.; et al. Phase II clinical study on intraoperative photodynamic therapy with talaporfin sodium and semiconductor laser in patients with malignant brain tumors. J. Neurosurg. 2013, 119, 845–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nitta, M.; Muragaki, Y.; Maruyama, T.; Iseki, H.; Komori, T.; Ikuta, S.; Saito, T.; Yasuda, T.; Hosono, J.; Okamoto, S.; et al. Role of photodynamic therapy using talaporfin sodium and a semiconductor laser in patients with newly diagnosed glioblastoma. J. Neurosurg. 2018, 131, 1361–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomiyama, A.; Ichimura, K. Signal transduction pathways and resistance to targeted therapies in glioma. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2019, 58, 118–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Downward, J. Targeting RAS signalling pathways in cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2003, 3, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pylayeva-Gupta, Y.; Grabocka, E.; Bar-Sagi, D. RAS oncogenes: Weaving a tumorigenic web. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2011, 11, 761–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brennan, C.W.; Verhaak, R.G.; McKenna, A.; Campos, B.; Noushmehr, H.; Salama, S.R.; Zheng, S.; Chakravarty, D.; Sanborn, J.Z.; Berman, S.H.; et al. The somatic genomic landscape of glioblastoma. Cell 2013, 155, 462–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cancer Genome Atlas Research, N. Comprehensive genomic characterization defines human glioblastoma genes and core pathways. Nature 2008, 455, 1061–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicolaides, T.P.; Li, H.; Solomon, D.A.; Hariono, S.; Hashizume, R.; Barkovich, K.; Baker, S.J.; Paugh, B.S.; Jones, C.; Forshew, T.; et al. Targeted therapy for BRAFV600E malignant astrocytoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 7595–7604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schiffman, J.D.; Hodgson, J.G.; VandenBerg, S.R.; Flaherty, P.; Polley, M.Y.; Yu, M.; Fisher, P.G.; Rowitch, D.H.; Ford, J.M.; Berger, M.S.; et al. Oncogenic BRAF mutation with CDKN2A inactivation is characteristic of a subset of pediatric malignant astrocytomas. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 512–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomiyama, A.; Uekita, T.; Kamata, R.; Sasaki, K.; Takita, J.; Ohira, M.; Nakagawara, A.; Kitanaka, C.; Mori, K.; Yamaguchi, H.; et al. Flotillin-1 regulates oncogenic signaling in neuroblastoma cells by regulating ALK membrane association. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 3790–3801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichimura, K.; Fukushima, S.; Totoki, Y.; Matsushita, Y.; Otsuka, A.; Tomiyama, A.; Niwa, T.; Takami, H.; Nakamura, T.; Suzuki, T.; et al. Recurrent neomorphic mutations of MTOR in central nervous system and testicular germ cell tumors may be targeted for therapy. Acta Neuropathol. 2016, 131, 889–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomiyama, A.; Tachibana, K.; Suzuki, K.; Seino, S.; Sunayama, J.; Matsuda, K.I.; Sato, A.; Matsumoto, Y.; Nomiya, T.; Nemoto, K.; et al. MEK-ERK-dependent multiple caspase activation by mitochondrial proapoptotic Bcl-2 family proteins is essential for heavy ion irradiation-induced glioma cell death. Cell Death Dis. 2010, 1, e60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, H.; Yoshida, S.; Muroi, E.; Yoshida, N.; Kawamura, M.; Kouchi, Z.; Nakamura, Y.; Sakai, R.; Fukami, K. Phosphoinositide 3-kinase signaling pathway mediated by p110alpha regulates invadopodia formation. J. Cell Biol. 2011, 193, 1275–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Kang, C.S.; Yuan, X.B.; Zhou, X.; Xu, P.; Han, L.; Wang, G.X.; Jia, Z.; Zhong, Y.; Yu, S.; et al. Co-delivery of as-miR-21 and 5-FU by poly(amidoamine) dendrimer attenuates human glioma cell growth in vitro. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2010, 21, 303–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luna-Vargas, M.P.A.; Chipuk, J.E. Physiological and Pharmacological Control of BAK, BAX, and Beyond. Trends Cell Biol. 2016, 26, 906–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.C.; Zong, W.X.; Cheng, E.H.; Lindsten, T.; Panoutsakopoulou, V.; Ross, A.J.; Roth, K.A.; MacGregor, G.R.; Thompson, C.B.; Korsmeyer, S.J. Proapoptotic BAX and BAK: A requisite gateway to mitochondrial dysfunction and death. Science 2001, 292, 727–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westphal, D.; Kluck, R.M.; Dewson, G. Building blocks of the apoptotic pore: How Bax and Bak are activated and oligomerize during apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 2014, 21, 196–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabon, L.; Galan-Malo, P.; Bouharrour, A.; Delavallee, L.; Brunelle-Navas, M.N.; Lorenzo, H.K.; Gross, A.; Susin, S.A. BID regulates AIF-mediated caspase-independent necroptosis by promoting BAX activation. Cell Death Differ. 2012, 19, 245–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, S.W.; Wang, H.; Poitras, M.F.; Coombs, C.; Bowers, W.J.; Federoff, H.J.; Poirier, G.G.; Dawson, T.M.; Dawson, V.L. Mediation of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1-dependent cell death by apoptosis-inducing factor. Science 2002, 297, 259–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.J.; Dawson, T.M.; Dawson, V.L. Nuclear and mitochondrial conversations in cell death: PARP-1 and AIF signaling. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2004, 25, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Zhang, Z.; Xing, D. Cell death via mitochondrial apoptotic pathway due to activation of Bax by lysosomal photodamage. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2011, 51, 53–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Usuda, J.; Hirata, T.; Ichinose, S.; Ishizumi, T.; Inoue, T.; Ohtani, K.; Maehara, S.; Yamada, M.; Tsutsui, H.; Okunaka, T.; et al. Tailor-made approach to photodynamic therapy in the treatment of cancer based on Bcl-2 photodamage. Int. J. Oncol. 2008, 33, 689–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrario, A.; Rucker, N.; Wong, S.; Luna, M.; Gomer, C.J. Survivin, a member of the inhibitor of apoptosis family, is induced by photodynamic therapy and is a target for improving treatment response. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 4989–4995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mroz, P.; Yaroslavsky, A.; Kharkwal, G.B.; Hamblin, M.R. Cell death pathways in photodynamic therapy of cancer. Cancers 2011, 3, 2516–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panzarini, E.; Inguscio, V.; Dini, L. Timing the multiple cell death pathways initiated by Rose Bengal acetate photodynamic therapy. Cell Death Dis. 2011, 2, e169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tait, S.W.; Green, D.R. Caspase-independent cell death: Leaving the set without the final cut. Oncogene 2008, 27, 6452–6461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Constantinou, C.; Papas, K.A.; Constantinou, A.I. Caspase-independent pathways of programmed cell death: The unraveling of new targets of cancer therapy? Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2009, 9, 717–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kessel, D.H.; Ito, A.; Matsuo, H.; Suenari, T.; Miyoshi, S.; Takatsuki, S.; Ogawa, S.; Arai, T. The mechanism of PDT-induced electrical blockade: The dependence of time-lapse localization of talaporfin sodium on the cell death phenotypes in rat cardiac myocytes. In Proceedings of the Optical Methods for Tumor Treatment and Detection: Mechanisms and Techniques in Photodynamic Therapy XVIII, San Jose, CA, USA, 24–29 January 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Tong, Z.; Singh, G.; Rainbow, A.J. Sustained activation of the extracellular signal-regulated kinase pathway protects cells from photofrin-mediated photodynamic therapy. Cancer Res. 2002, 62, 5528–5535. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lamberti, M.J.; Pansa, M.F.; Vera, R.E.; Fernandez-Zapico, M.E.; Rumie Vittar, N.B.; Rivarola, V.A. Transcriptional activation of HIF-1 by a ROS-ERK axis underlies the resistance to photodynamic therapy. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0177801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, T.; Suzuki, S.; Misawa, S.; Akimoto, J.; Shinoda, Y.; Fujiwara, Y. Photodynamic therapy using talaporfin sodium induces heme oxygenase-1 expression in rat malignant meningioma KMY-J cells. J. Toxicol. Sci. 2018, 43, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhowmick, R.; Girotti, A.W. Cytoprotective signaling associated with nitric oxide upregulation in tumor cells subjected to photodynamic therapy-like oxidative stress. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2013, 57, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lake, D.; Correa, S.A.; Muller, J. Negative feedback regulation of the ERK1/2 MAPK pathway. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2016, 73, 4397–4413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemmon, M.A.; Freed, D.M.; Schlessinger, J.; Kiyatkin, A. The Dark Side of Cell Signaling: Positive Roles for Negative Regulators. Cell 2016, 164, 1172–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neben, C.L.; Lo, M.; Jura, N.; Klein, O.D. Feedback regulation of RTK signaling in development. Dev. Biol. 2019, 447, 71–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.K.; Abdollah, N.A.; Shafie, N.H.; Yusof, N.M.; Razak, S.R.A. Dual-specificity phosphatase 6 (DUSP6): A review of its molecular characteristics and clinical relevance in cancer. Cancer Biol. Med. 2018, 15, 14–28. [Google Scholar]
- Mathe, C.; Garda, T.; Freytag, C.; M, M.H. The Role of Serine-Threonine Protein Phosphatase PP2A in Plant Oxidative Stress Signaling-Facts and Hypotheses. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomiyama, A.; Kobayashi, T.; Mori, K.; Ichimura, K. Protein Phosphatases-A Touchy Enemy in the Battle against Glioblastomas: A Review. Cancers 2019, 11, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, K.M.; Collins, J.W.; Cruz Walma, D.A.; Doyle, A.D.; Morales, S.G.; Lu, J.; Matsumoto, K.; Nazari, S.S.; Sekiguchi, R.; Shinsato, Y.; et al. Extracellular matrix dynamics in cell migration, invasion and tissue morphogenesis. Int. J. Exp. Pathol. 2019, 100, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kai, F.; Drain, A.P.; Weaver, V.M. The Extracellular Matrix Modulates the Metastatic Journey. Dev. Cell 2019, 49, 332–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kobayashi, T.; Miyazaki, M.; Sasaki, N.; Yamamuro, S.; Uchida, E.; Kawauchi, D.; Takahashi, M.; Otsuka, Y.; Kumagai, K.; Takeuchi, S.; et al. Enhanced Malignant Phenotypes of Glioblastoma Cells Surviving NPe6-Mediated Photodynamic Therapy are Regulated via ERK1/2 Activation. Cancers 2020, 12, 3641. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12123641
Kobayashi T, Miyazaki M, Sasaki N, Yamamuro S, Uchida E, Kawauchi D, Takahashi M, Otsuka Y, Kumagai K, Takeuchi S, et al. Enhanced Malignant Phenotypes of Glioblastoma Cells Surviving NPe6-Mediated Photodynamic Therapy are Regulated via ERK1/2 Activation. Cancers. 2020; 12(12):3641. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12123641
Chicago/Turabian StyleKobayashi, Tatsuya, Makoto Miyazaki, Nobuyoshi Sasaki, Shun Yamamuro, Eita Uchida, Daisuke Kawauchi, Masamichi Takahashi, Yohei Otsuka, Kosuke Kumagai, Satoru Takeuchi, and et al. 2020. "Enhanced Malignant Phenotypes of Glioblastoma Cells Surviving NPe6-Mediated Photodynamic Therapy are Regulated via ERK1/2 Activation" Cancers 12, no. 12: 3641. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12123641
APA StyleKobayashi, T., Miyazaki, M., Sasaki, N., Yamamuro, S., Uchida, E., Kawauchi, D., Takahashi, M., Otsuka, Y., Kumagai, K., Takeuchi, S., Toyooka, T., Otani, N., Wada, K., Narita, Y., Yamaguchi, H., Muragaki, Y., Kawamata, T., Mori, K., Ichimura, K., & Tomiyama, A. (2020). Enhanced Malignant Phenotypes of Glioblastoma Cells Surviving NPe6-Mediated Photodynamic Therapy are Regulated via ERK1/2 Activation. Cancers, 12(12), 3641. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12123641







