Accuracy of Magnetometer-Guided Sentinel Lymphadenectomy after Intraprostatic Injection of Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles in Prostate Cancer: The SentiMag Pro II Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
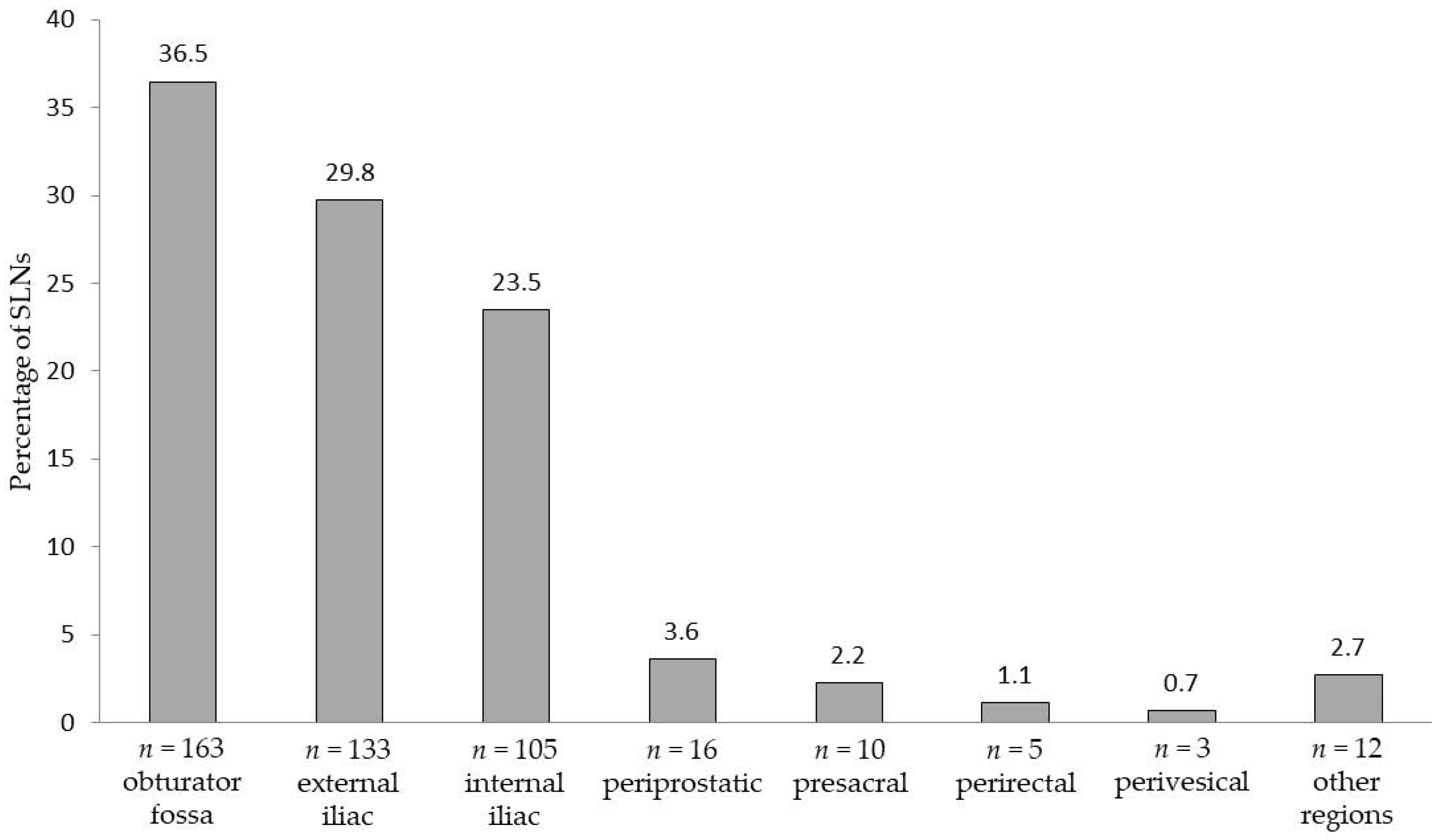
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Design and Patients
4.2. Magnetic Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticle (SPION) Tracer
4.3. Tracer Injection
4.4. Magnetometer-Guided sLND, eLND, and Histopathological Examination
4.5. Outcome Measures of Magnetometer-Guided sLND
4.6. Ethical Approval
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Heidenreich, A.; Ohlmann, C.H.; Polyakov, S. Anatomical extent of pelvic lymphadenectomy in patients undergoing radical prostatectomy. Eur. Urol. 2007, 52, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Briganti, A.; Chun, F.K.; Salonia, A.; Suardi, N.; Gallina, A.; Da Pozzo, L.F.; Roscigno, M.; Zanni, G.; Valiquette, L.; Rigatti, P.; et al. Complications and other surgical outcomes associated with extended pelvic lymphadenectomy in men with localized prostate cancer. Eur. Urol. 2006, 50, 1006–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wawroschek, F.; Vogt, H.; Weckermann, D.; Wagner, T.; Harzmann, R. The sentinel lymph node concept in prostate cancer—first results of gamma probe-guided sentinel lymph node identification. Eur. Urol. 1999, 36, 595–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wit, E.M.K.; Acar, C.; Grivas, N.; Yuan, C.; Horenblas, S.; Liedberg, F.; Valdes Olmos, R.A.; van Leeuwen, F.W.B.; van den Berg, N.S.; Winter, A.; et al. Sentinel node procedure in prostate cancer: A systematic review to assess diagnostic accuracy. Eur. Urol. 2017, 71, 596–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winter, A.; Kneib, T.; Henke, R.P.; Wawroschek, F. Sentinel lymph node dissection in more than 1200 prostate cancer cases: Rate and prediction of lymph node involvement depending on preoperative tumor characteristics. Int. J. Urol. 2014, 21, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winter, A.; Kneib, T.; Wasylow, C.; Reinhardt, L.; Henke, R.P.; Engels, S.; Gerullis, H.; Wawroschek, F. Updated nomogram incorporating percentage of positive cores to predict probability of lymph node invasion in prostate cancer patients undergoing sentinel lymph node dissection. J. Cancer 2017, 8, 2692–2698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grivas, N.; Wit, E.; Tillier, C.; van Muilekom, E.; Pos, F.; Winter, A.; van der Poel, H. Validation and head-to-head comparison of three nomograms predicting probability of lymph node invasion of prostate cancer in patients undergoing extended and/or sentinel lymph node dissection. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2017, 44, 2213–2226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wáng, Y.X.; Idée, J.M. A comprehensive literatures update of clinical researches of superparamagnetic resonance iron oxide nanoparticles for magnetic resonance imaging. Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 2017, 7, 88–122. [Google Scholar]
- Stark, D.D.; Weissleder, R.; Elizondo, G.; Hahn, P.F.; Saini, S.; Todd, L.E.; Wittenberg, J.; Ferrucci, J.T. Superparamagnetic iron oxide: Clinical application as a contrast agent for MR imaging of the liver. Radiology 1988, 168, 297–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, A.; Chavan, A.; Wawroschek, F. Magnetic resonance imaging of sentinel lymph nodes using intraprostatic injection of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles in prostate cancer patients: First-in-human results. Eur. Urol. 2018, 73, 813–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pouw, J.J.; Grootendorst, M.R.; Bezooijen, R.; Klazen, C.A.; De Bruin, W.I.; Klaase, J.M.; Hall-Craggs, M.A.; Douek, M.; Ten Haken, B. Pre-operative sentinel lymph node localization in breast cancer with superparamagnetic iron oxide MRI: The SentiMAG Multicentre Trial imaging subprotocol. Br. J. Radiol. 2015, 88, 20150634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douek, M.; Klaase, J.; Monypenny, I.; Kothari, A.; Zechmeister, K.; Brown, D.; Wyld, L.; Drew, P.; Garmo, H.; Agbaje, O.; et al. Sentinel node biopsy using a magnetic tracer versus standard technique: The SentiMAG Multicentre Trial. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2014, 21, 1237–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winter, A.; Woenkhaus, J.; Wawroschek, F. A novel method for intraoperative sentinel lymph node detection in prostate cancer patients using superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles and a handheld magnetometer: The initial clinical experience. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2014, 21, 4390–4396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winter, A.; Kowald, T.; Engels, S.; Wawroschek, F. Magnetic resonance sentinel lymph node imaging and magnetometer-guided intraoperative detection in penile cancer, using superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: First results. Urol. Int. 2019, 29, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karakatsanis, A.; Daskalakis, K.; Stålberg, P.; Olofsson, H.; Andersson, Y.; Eriksson, S.; Bergkvist, L.; Wärnberg, F. Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles as the sole method for sentinel node biopsy detection in patients with breast cancer. Br. J. Surg. 2017, 104, 1675–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holl, G.; Dorn, R.; Wengenmair, H.; Weckermann, D.; Sciuk, J. Validation of sentinel lymph node dissection in prostate cancer: Experience in more than 2000 patients. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2009, 36, 1377–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadeghi, R.; Tabasi, K.T.; Bazaz, S.M.; Kakhki, V.R.; Massoom, A.F.; Gholami, H.; Zakavi, S.R. Sentinel node mapping in the prostate cancer. Meta-analysis. Nuklearmedizin 2011, 50, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zada, A.; Peek, M.C.; Ahmed, M.; Anninga, B.; Baker, R.; Kusakabe, M.; Sekino, M.; Klaase, J.M.; Ten Haken, B.; Douek, M. Meta-analysis of sentinel lymph node biopsy in breast cancer using the magnetic technique. Br. J. Surg. 2016, 103, 1409–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, A.; Kowald, T.; Paulo, T.S.; Goos, P.; Engels, S.; Gerullis, H.; Schiffmann, J.; Chavan, A.; Wawroschek, F. Magnetic resonance sentinel lymph node imaging and magnetometer-guided intraoperative detection in prostate cancer using superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 6689–6698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cousins, A.; Balalis, G.L.; Thompson, S.K.; Morales, D.F.; Mohtar, A.; Wedding, A.B.; Thierry, B. Novel handheld magnetometer probe based on magnetic tunnelling junction sensors for intraoperative sentinel lymph node identification. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 10842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van de Loosdrecht, M.M.; Waanders, S.; Krooshoop, H.J.G.; ten Haken, B. Separation of excitation and detection coils for in vivo detection of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2019, 475, 563–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taruno, K.; Kurita, T.; Kuwahata, A.; Yanagihara, K.; Enokido, K.; Katayose, Y.; Nakamura, S.; Takei, H.; Sekino, M.; Kusakabe, M. Multicenter clinical trial on sentinel lymph node biopsy using superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles and a novel handheld magnetic probe. J. Surg. Oncol. 2019, 120, 1391–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anninga, B.; White, S.H.; Moncrieff, M.; Dziewulski, P.; LC Geh, J.; Klaase, J.; Garmo, H.; Castro, F.; Pinder, S.; Pankhurst, Q.A.; et al. Magnetic technique for sentinel lymph node biopsy in melanoma: The MELAMAG trial. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2016, 23, 2070–2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weckermann, D.; Dorn, R.; Holl, G.; Wagner, T.; Harzmann, R. Limitations of radioguided surgery in high-risk prostate cancer. Eur. Urol. 2007, 51, 1549–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan-Parkes, J.H. Metastases: Mechanisms, pathways, and cascades. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 1995, 164, 1075–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joniau, S.; Van den Bergh, L.; Lerut, E.; Deroose, C.M.; Haustermans, K.; Oyen, R.; Budiharto, T.; Ameye, F.; Bogaerts, K.; Van Poppel, H. Mapping of pelvic lymph node metastases in prostate cancer. Eur. Urol. 2013, 63, 450–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thill, M.; Kurylcio, A.; Welter, R.; van Haasteren, V.; Grosse, B.; Berclaz, G.; Polkowski, W.; Hauser, N. The Central-European SentiMag study: Sentinel lymph node biopsy with superparamagnetic iron oxide (SPIO) vs. radioisotope. Breast 2014, 23, 175–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleaveland, P.; Lau, M.; Parnham, A.; Murby, B.; Ashworth, D.; Manohoran, P.; Taylor, B.; Bell, J.; Najran, P.; Oliveira, P.; et al. Testing the feasibility of sentimag/sienna+ for detecting inguinal sentinel nodes in penile cancer (SentiPen): An eUROGEN and national cancer research institute trial. Eur. Urol. 2019, 76, 874–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimczak, P.; Kalus, M.; Kryszpin, M.; Manowiec, M.; Hirowska-Tracz, M.; Jedryka, M. A novel and promising technique of sentinel lymph nodes detection in vulvar cancer patients. EJSO 2019, 45, e151–e152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pouw, J.J.; Grootendorst, M.R.; Klaase, J.M.; van Baarlen, J.; Ten Haken, B. Ex vivo sentinel lymph node mapping in colorectal cancer using a magnetic nanoparticle tracer to improve staging accuracy: A pilot study. Colorectal Dis. 2016, 18, 1147–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imai, K.; Kawaharada, Y.; Ogawa, J.; Saito, H.; Kudo, S.; Takashima, S.; Saito, Y.; Atari, M.; Ito, A.; Terata, K.; et al. Development of a new magnetometer for sentinel lymph node mapping designed for video-assisted thoracic surgery in non-small cell lung cancer. Surg. Innov. 2015, 22, 401–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.; Forbes, M.E.; Bitting, R.L.; O’Neill, S.S.; Chou, P.C.; Topaloglu, U.; Miller, L.D.; Hawkins, G.A.; Grant, S.C.; DeYoung, B.R.; et al. Incorporating blood-based liquid biopsy information into cancer staging: Time for a TNMB system? Ann. Oncol. 2018, 29, 311–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Jeong, H.; Choi, J.W.; Oh, H.E.; Kim, Y.S. Liquid biopsy prediction of axillary lymph node metastasis, cancer recurrence, and patient survival in breast cancer: A meta-analysis. Medicine 2018, 97, e12862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loeian, M.S.; Mehdi Aghaei, S.; Farhadi, F.; Rai, V.; Yang, H.W.; Johnson, M.D.; Aqil, F.; Mandadi, M.; Rai, S.N.; Panchapakesan, B. Liquid biopsy using the nanotube-CTC-chip: Capture of invasive CTCs with high purity using preferential adherence in breast cancer patients. Lab. Chip. 2019, 19, 1899–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mottet, N.; Bellmunt, J.; Bolla, M.; Briers, E.; Cumberbatch, M.G.; De Santis, M.; Fossati, N.; Gross, T.; Henry, A.M.; Joniau, S.; et al. EAU-ESTRO-SIOG guidelines on prostate cancer. Part 1: Screening, diagnosis, and local treatment with curative intent. Eur. Urol. 2017, 71, 618–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weingärtner, K.; Ramaswamy, A.; Bittinger, A.; Gerharz, E.W.; Vöge, D.; Riedmiller, H. Anatomical basis for pelvic lymphadenectomy in prostate cancer: Results of an autopsy study and implications for the clinic. J. Urol. 1996, 156, 1969–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Poel, H.G.; Wit, E.M.; Acar, C.; van den Berg, N.S.; van Leeuwen, F.W.B.; Valdes Olmos, R.A.; Winter, A.; Wawroschek, F.; Liedberg, F.; Maclennan, S.; et al. Sentinel node biopsy for prostate cancer: Report from a consensus panel meeting. BJU Int. 2017, 120, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Characteristics | Overall | Patients with Negative LNs | Patients with Positive LNs |
|---|---|---|---|
| n = 50 | n = 32 (64%) | n = 18 (36%) | |
| Age, years (median) | 69.5 | 68.5 | 71.5 |
| IQR | 64–73 | 64–73 | 64.5–73 |
| Total PSA, ng/mL (median) | 10.8 | 9.8 | 12.0 |
| IQR | 7.4–19.2 | 6.9–14.7 | 8.3–30.1 |
| Number of LNs removed (median) | 18 | 19 | 17.5 |
| IQR | 15–23 | 15–23 | 16–22 |
| Number of SLNs removed (median) | 9 | 9 | 10 |
| IQR | 6–12 | 5–11 | 7–12 |
| Number of positive LNs (median) | 2 | ||
| IQR | 1–3 | ||
| Tumor stage (%) | |||
| T1c | 28 (56) | 22 (68.8) | 6 (33.3) |
| T2a | 2 (4) | 1 (3.1) | 1 (5.6) |
| T2b | 6 (12) | 4 (12.5) | 2 (11.1) |
| T2c | 12 (24) | 5 (15.6) | 7 (38.9) |
| T3 | 2 (4) | 0 (0) | 2 (11.1) |
| Biopsy Gleason score (%) | |||
| 6 (3 + 3) | 8 (16) | 8 (25.0) | 0 (0) |
| 7 (3 + 4) | 26 (52) | 18 (56.3) | 8 (44.4) |
| 7 (4 + 3) | 6 (12) | 5 (15.6) | 1 (5.6) |
| ≥8 | 10 (20) | 1 (3.1) | 9 (50.0) |
| Postoperative Gleason score (%) | |||
| 6 (3 + 3) | 2 (4) | 2 (6.3) | 0 (0) |
| 7 (3 + 4) | 23 (46) | 19 (59.4) | 4 (22.2) |
| 7 (4 + 3) | 14 (28) | 8 (25.0) | 6 (33.3) |
| ≥8 | 11 (22) | 3 (9.4) | 8 (44.4) |
| Pathologic stage (%) | |||
| pT2 | 24 (48) | 22 (68.8) | 2 (11.1) |
| pT3a | 12 (24) | 7 (21.9) | 5 (27.8) |
| pT3b | 12 (24) | 3 (9.4) | 9 (50.0) |
| pT4 | 2 (4) | 0 (0) | 2 (11.1) |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Winter, A.; Engels, S.; Goos, P.; Süykers, M.-C.; Gudenkauf, S.; Henke, R.-P.; Wawroschek, F. Accuracy of Magnetometer-Guided Sentinel Lymphadenectomy after Intraprostatic Injection of Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles in Prostate Cancer: The SentiMag Pro II Study. Cancers 2020, 12, 32. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12010032
Winter A, Engels S, Goos P, Süykers M-C, Gudenkauf S, Henke R-P, Wawroschek F. Accuracy of Magnetometer-Guided Sentinel Lymphadenectomy after Intraprostatic Injection of Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles in Prostate Cancer: The SentiMag Pro II Study. Cancers. 2020; 12(1):32. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12010032
Chicago/Turabian StyleWinter, Alexander, Svenja Engels, Philipp Goos, Marie-Christin Süykers, Stefan Gudenkauf, Rolf-Peter Henke, and Friedhelm Wawroschek. 2020. "Accuracy of Magnetometer-Guided Sentinel Lymphadenectomy after Intraprostatic Injection of Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles in Prostate Cancer: The SentiMag Pro II Study" Cancers 12, no. 1: 32. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12010032
APA StyleWinter, A., Engels, S., Goos, P., Süykers, M.-C., Gudenkauf, S., Henke, R.-P., & Wawroschek, F. (2020). Accuracy of Magnetometer-Guided Sentinel Lymphadenectomy after Intraprostatic Injection of Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles in Prostate Cancer: The SentiMag Pro II Study. Cancers, 12(1), 32. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12010032




