Molecular Complexity of Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma: Can It Be a Roadmap for Precision Medicine?
Abstract
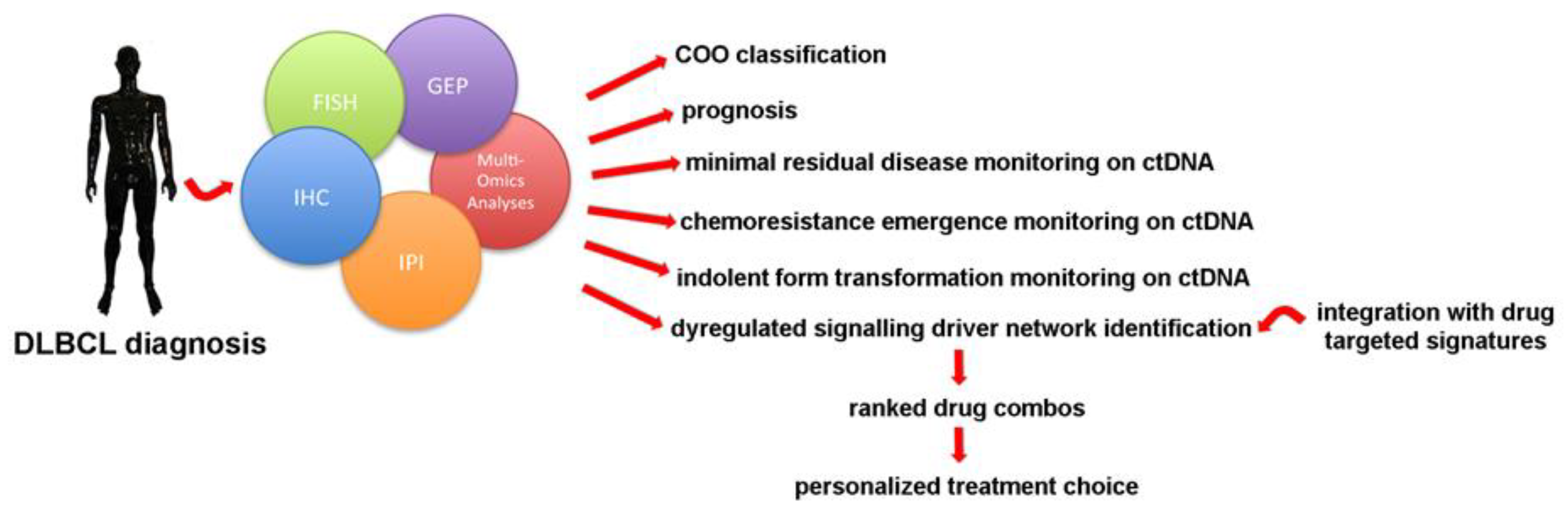
1. Introduction
1.1. Standard Prognosticators for DLBCL
1.2. Discovering New Prognostic Biomarkers and Models
1.3. Discovering Causes of Transformation and Chemoresistence
1.4. Double Hit or Triple Hit B-Cell Lymphomas
1.5. NGS Application in Clinical Practice: Liquid Biopsy
1.6. Discovering Personalized Treatment Approaches
2. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Swerdlow, S.H.; Campo, E.; Pileri, S.A.; Lee-Harris, N.; Stein, H.; Siebert, R.; Advani, R.; Ghielmini, M.; Salles, G.A.; Zelenetz, A.D.; et al. The 2016 revision of the World Health Organization classification of lymphoid neoplasms. Blood 2016, 127, 2375–2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poeschel, V.; Held, G.; Ziepert, M.; Altmann, B.; Witzens-Harig, M.; Holte, H.; Thurner, L.; Viardot, A.; Borchmann, P.; Kanz, L.; et al. Excellent Outcome of Young Patients (18–60 years) with Favourable-Prognosis Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma (DLBCL) Treated with 4 Cycles CHOP Plus 6 Applications of Rituximab: Results of the 592 Patients of the Flyer Trial of the Dshnhl/GLA. Blood 2018, 132, 781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sehn, L.H.; Donaldson, J.; Chhanabhai, M.; Fitzgerald, C.; Gill, K.; Klasa, R.; MacPherson, N.; O’Reilly, S.; Spinelli, J.J.; Sutherland, J.; et al. Introduction of combined CHOP plus rituximab therapy dramatically improved outcome of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma in British Columbia. J. Clin. Oncol. 2005, 23, 5027–5033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Philip, T.; Guglielmi, C.; Hagenbeek, A.; Somers, R.; Van Der Lelie, H.; Bron, D.; Sonneveld, P.; Gisselbrecht, C.; Cahn, J.Y.; Harousseau, J.L.; et al. Autologous bone marrow transplantation as compared with salvage chemotherapy in relapses of chemotherapy-sensitive non-hodgkin’s lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 1995, 333, 1540–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Imhoff, G.W.; McMillan, A.; Matasar, M.J.; Radford, J.; Ardeshna, K.M.; Kuliczkowski, K.; Kim, W.; Hong, X.; Soenderskov Goerloev, J.; Davies, A.; et al. Ofatumumab Versus Rituximab Salvage Chemoimmunotherapy in Relapsed or Refractory Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma: The Orcharrd Study (OMB110928). Blood 2014, 124, 630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crump, M.; Neelapu, S.S.; Farooq, U.; Van Den Neste, E.; Kuruvilla, J.; Westin, J.; Link, B.K.; Hay, A.; Cerhan, J.R.; Zhu, L.; et al. Outcomes in refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: Results from the international SCHOLAR-1 study. Blood 2017, 130, 1800–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Den Neste, E.; Schmitz, N.; Mounier, N.; Gill, D.; Linch, D.; Trneny, M.; Milpied, N.; Radford, J.; Ketterer, N.; Shpilberg, O.; et al. Outcome of patients with relapsed diffuse large B-cell lymphoma who fail second-line salvage regimens in the International CORAL study. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2016, 51, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, H.J.; Rafiq, S.; Brentjens, R.J. Driving CAR T-cells forward. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 13, 370–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, V.A.; Shadman, M.; Gopal, A.K. Translating anti-CD19 CAR T-cell therapy into clinical practice for relapsed/refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Blood 2018, 132, 777–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachanova, V.; Perales, M.-A.; Abramson, J.S. Modern management of relapsed and refractory aggressive B-cell lymphoma: A perspective on the current treatment landscape and patient selection for CAR T-cell therapy. Blood Rev. 2019, 100640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neelapu, S.S.; Locke, F.L.; Bartlett, N.L.; Lekakis, L.J.; Miklos, D.B.; Jacobson, C.A.; Braunschweig, I.; Oluwole, O.O.; Siddiqi, T.; Lin, Y.; et al. Axicabtagene ciloleucel CAR T-cell therapy in refractory large B-Cell lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 2531–2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shipp, M.A. A predictive model for aggressive non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. The International Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma Prognostic Factors Project. N. Engl. J. Med. 1993, 329, 987–994. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Z.; Sehn, L.H.; Rademaker, A.W.; Gordon, L.I.; LaCasce, A.S.; Crosby-Thompson, A.; Vanderplas, A.; Zelenetz, A.D.; Abel, G.A.; Rodriguez, M.A.; et al. An enhanced International Prognostic Index (NCCN-IPI) for patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma treated in the rituximab era. Blood 2014, 123, 837–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alizadeh, A.A.; Elsen, M.B.; Davis, R.E.; Ma, C.L.; Lossos, I.S.; Rosenwald, A.; Boldrick, J.C.; Sabet, H.; Tran, T.; Yu, X.; et al. Distinct types of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma identified by gene expression profiling. Nature 2000, 403, 503–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, R.I.; Gaynor, E.R.; Dahlberg, S.; Oken, M.M.; Grogan, T.M.; Mize, E.M.; Glick, J.H.; Coltman, C.A.; Miller, T.P. Comparison of a Standard Regimen (CHOP) with Three Intensive Chemotherapy Regimens for Advanced Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 1993, 328, 1002–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenwald, A.; Wright, G.; Chan, W.C.; Connors, J.M.; Campo, E.; Fisher, R.I.; Gascoyne, R.D.; Konrad Muller-Hermelink, H.; Smeland, E.B.; Giltnane, J.M.; et al. The use of molecular profiling to predict survival after chemotherapy for diffuse large-B-cell lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 346, 1937–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hans, C.P.; Weisenburger, D.D.; Greiner, T.C.; Gascoyne, R.D.; Delabie, J.; Ott, G.; Müller-Hermelink, H.K.; Campo, E.; Braziel, R.M.; Jaffe, E.S.; et al. Confirmation of the molecular classification of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma by immunohistochemistry using a tissue microarray. Blood 2004, 103, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, W.W.L.; Weisenburger, D.D.; Greiner, T.C.; Piris, M.A.; Banham, A.H.; Delabie, J.; Braziel, R.M.; Geng, H.; Iqbal, J.; Lenz, G.; et al. A new immunostain algorithm classifies diffuse large B-cell lymphoma into molecular subtypes with high accuracy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 5494–5502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colomo, L.; López-Guillermo, A.; Perales, M.; Rives, S.; Martínez, A.; Bosch, F.; Colomer, D.; Falini, B.; Montserrat, E.; Campo, E. Clinical impact of the differentiation profile assessed by immunophenotyping in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Blood 2003, 101, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muris, J.J.F.; Meijer, C.J.L.M.; Vos, W.; van Krieken, J.H.J.M.; Jiwa, N.M.; Ossenkoppele, G.J.; Oudejans, J.J. Immunohistochemical profiling based on Bcl-2, CD10 and MUMI expression improves risk stratification in patients with primary nodal diffuse large B cell lymphoma. J. Pathol. 2006, 208, 714–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, P.N.; Fu, K.; Greiner, T.C.; Smith, L.M.; Delabie, J.; Gascoyne, R.D.; Ott, G.; Rosenwald, A.; Braziel, R.M.; Campo, E.; et al. Immunohistochemical methods for predicting cell of origin and survival in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma treated with rituximab. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visco, C.; Li, Y.; Xu-Monette, Z.Y.; Miranda, R.N.; Green, T.M.; Li, Y.; Tzankov, A.; Wen, W.; Liu, W.M.; Kahl, B.S.; et al. Comprehensive gene expression profiling and immunohistochemical studies support application of immunophenotypic algorithm for molecular subtype classification in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: A report from the International DLBCL Rituximab-CHOP Consortiu. Leukemia 2012, 26, 2103–2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perfecto-Avalos, Y.; Garcia-Gonzalez, A.; Hernandez-Reynoso, A.; Sánchez-Ante, G.; Ortiz-Hidalgo, C.; Scott, S.P.; Fuentes-Aguilar, R.Q.; DIaz-Dominguez, R.; León-Martínez, G.; Velasco-Vales, V.; et al. Discriminant analysis and machine learning approach for evaluating and improving the performance of immunohistochemical algorithms for COO classification of DLBCL. J. Transl. Med. 2019, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, D.W.; Wright, G.W.; Williams, P.M.; Lih, C.J.; Walsh, W.; Jaffe, E.S.; Rosenwald, A.; Campo, E.; Chan, W.C.; Connors, J.M.; et al. Determining cell-of-origin subtypes of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma using gene expression in formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissue. Blood 2014, 123, 1214–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jais, J.P.; Molina, T.J.; Ruminy, P.; Gentien, D.; Reyes, C.; Scott, D.W.; Rimsza, L.M.; Wright, G.; Gascoyne, R.D.; Staudt, L.M.; et al. Reliable subtype classification of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma samples from GELA LNH2003 trials using the Lymph2Cx gene expression assay. Haematologica 2017, 102, e404–e406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vitolo, U.; Trneny, M.; Belada, D.; Burke, J.M.; Carella, A.M.; Chua, N.; Abrisqueta, P.; Demeter, J.; Flinn, I.; Hong, X.; et al. Obinutuzumab or rituximab plus cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone in previously untreated diffuse large b-cell lymphoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 3529–3537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, D.W.; Mottok, A.; Ennishi, D.; Wright, G.W.; Farinha, P.; Ben-Neriah, S.; Kridel, R.; Barry, G.S.; Hother, C.; Abrisqueta, P.; et al. Prognostic significance of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma cell of origin determined by digital gene expression in formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissue biopsies. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 2848–2856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loeffler-Wirth, H.; Kreuz, M.; Hopp, L.; Arakelyan, A.; Haake, A.; Cogliatti, S.B.; Feller, A.C.; Hansmann, M.L.; Lenze, D.; Möller, P.; et al. A modular transcriptome map of mature B cell lymphomas. Genome Med. 2019, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monti, S.; Savage, K.J.; Kutok, J.L.; Feuerhake, F.; Kurtin, P.; Mihm, M.; Wu, B.; Pasqualucci, L.; Neuberg, D.; Aguiar, R.C.T.; et al. Molecular profiling of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma identifies robust subtypes including one characterized by host inflammatory response. Blood 2005, 105, 1851–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dybkær, K.; Bøgsted, M.; Falgreen, S.; Bødker, J.S.; Kjeldsen, M.K.; Schmitz, A.; Bilgrau, A.E.; Xu-Monette, Z.Y.; Li, L.; Bergkvist, K.S.; et al. Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma classification system that associates normal B-cell subset phenotypes with prognosis. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 1379–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenz, G.; Wright, G.; Dave, S.S.; Xiao, W.; Powell, J.; Zhao, H.; Xu, W.; Tan, B.; Goldschmidt, N.; Iqbal, J.; et al. Stromal gene signatures in large-B-cell lymphomas. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 2313–2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciavarella, S.; Vegliante, M.C.; Fabbri, M.; De Summa, S.; Melle, F.; Motta, G.; De Iuliis, V.; Opinto, G.; Enjuanes, A.; Rega, S.; et al. Dissection of DLBCL microenvironment provides a gene expression-based predictor of survival applicable to formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissue. Ann. Oncol. 2018, 29, 2363–2370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keane, C.; Vari, F.; Hertzberg, M.; Cao, K.A.L.; Green, M.R.; Han, E.; Seymour, J.F.; Hicks, R.J.; Gill, D.; Crooks, P.; et al. Ratios of T-cell immune effectors and checkpoint molecules as prognostic biomarkers in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: A population-based study. Lancet Haematol. 2015, 2, e445–e455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaelsen, T.Y.; Richter, J.; Brøndum, R.F.; Klapper, W.; Johnsen, H.E.; Albertsen, M.; Dybkær, K.; Bøgsted, M. A B-cell-associated gene signature classification of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma by NanoString technology. Blood Adv. 2018, 2, 1542–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, L.; Lin, P.; Xiong, H.; Tu, S.; Chen, G. Molecular heterogeneity in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and its implications in clinical diagnosis and treatment. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Rev. Cancer 2018, 1869, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Copie-Bergman, C.; Cuillière-Dartigues, P.; Baia, M.; Briere, J.; Delarue, R.; Canioni, D.; Salles, G.; Parrens, M.; Belhadj, K.; Fabiani, B.; et al. MYC-IG rearrangements are negative predictors of survival in DLBCL patients treated with immunochemotherapy: A GELA/LYSA study. Blood 2015, 126, 2466–2474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savage, K.J.; Johnson, N.A.; Ben-Neriah, S.; Connors, J.M.; Sehn, L.H.; Farinha, P.; Horsman, D.E.; Gascoyne, R.D. MYC gene rearrangements are associated with a poor prognosis in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma patients treated with R-CHOP chemotherapy. Blood 2009, 114, 3533–3537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, J.; Neppalli, V.T.; Wright, G.; Dave, B.J.; Horsman, D.E.; Rosenwald, A.; Lynch, J.; Hans, C.P.; Weisenburger, D.D.; Greiner, T.C.; et al. BCL2 expression is a prognostic marker for the activated B-cell-like type of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2006, 24, 961–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, K.H.; Weisenburger, D.D.; Dave, B.J.; Smith, L.; Sanger, W.; Iqbal, J.; Campo, E.; Delabie, J.; Gascoyne, R.D.; Ott, G.; et al. Mutations in the DNA-binding codons of TP53, which are associated with decreased expression of TRAIL receptor-2, predict for poor survival in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Blood 2007, 110, 4396–4405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu-Monette, Z.Y.; Wu, L.; Visco, C.; Tai, Y.C.; Tzankov, A.; Liu, W.M.; Montes-Moreno, S.; Dybkær, K.; Chiu, A.; Orazi, A.; et al. Mutational profile and prognostic significance of TP53 in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma patients treated with R-CHOP: Report from an International DLBCL Rituximab-CHOP Consortium Program Study. Blood 2012, 120, 3986–3996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Xu-Monette, Z.Y.; Balasubramanyam, A.; Manyam, G.C.; Visco, C.; Tzankov, A.; Liu, W.M.; Miranda, R.N.; Zhang, L.; Montes-Moreno, S.; et al. CD30 expression defines a novel subgroup of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma with favorable prognosis and distinct gene expression signature: A report from the International DLBCL Rituximab-CHOP Consortium Program Study. Blood 2013, 121, 2715–2724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ok, C.Y.; Li, L.; Xu-Monette, Z.Y.; Visco, C.; Tzankov, A.; Manyam, G.C.; Montes-Moreno, S.; Dybaer, K.; Chiu, A.; Orazi, A.; et al. Prevalence and clinical implications of Epstein-Barr virus infection in de Novo diffuse large B-cell lymphoma in western countries. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 2338–2349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rimsza, L.M.; Roberts, R.A.; Miller, T.P.; Unger, J.M.; LeBlanc, M.; Braziel, R.M.; Weisenberger, D.D.; Chan, W.C.; Muller-Hermelink, H.K.; Jaffe, E.S.; et al. Loss of MHC class II gene and protein expression in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma is related to decreased tumor immunosurveillance and poor patient survival regardless of other prognostic factors: A follow-up study from the Leukemia and Lymphoma Molecular. Blood 2004, 103, 4251–4258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.J.; Medeiros, L.J.; Bueso-Ramos, C.E.; Tang, G.; Wang, S.; Oki, Y.; Desai, P.; Khoury, J.D.; Miranda, R.N.; Tang, Z.; et al. P53 expression correlates with poorer survival and augments the negative prognostic effect of MYC rearrangement, expression or concurrent MYC/BCL2 expression in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Mod. Pathol. 2017, 30, 194–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godfrey, J.; Tumuluru, S.; Bao, R.; Leukam, M.; Venkataraman, G.; Phillip, J.; Fitzpatrick, C.; McElherne, J.; MacNabb, B.W.; Orlowski, R.; et al. PD-L1 gene alterations identify a subset of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma harboring a T-cell–inflamed phenotype. Blood 2019, 133, 2279–2290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, L.; Cheng, L. Aberrant ERG expression associates with downregulation of miR-4638-5p and selected genomic alterations in a subset of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Mol. Carcinog. 2019, 58, 1846–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolen, C.R.; Klanova, M.; Trneny, M.; Sehn, L.H.; He, J.; Tong, J.; Paulson, J.N.; Kim, E.; Vitolo, U.; Di Rocco, A.; et al. Prognostic impact of somatic mutations in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and relationship to cell-of-origin: Data from the phase III GOYA study. Haematologica 2019, 329, 987–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storlazzi, C.T.; Albano, F.; Lo Cunsolo, C.; Doglioni, C.; Guastadisegni, M.C.; Impera, L.; Lonoce, A.; Funes, S.; Macrí, E.; Iuzzolino, P.; et al. Upregulation of the SOX5 by promoter swapping with the P2RY8 gene in primary splenic follicular lymphoma. Leukemia 2007, 21, 2221–2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Reddy, A.; Zhang, J.; Davis, N.S.; Moffitt, A.B.; Love, C.L.; Waldrop, A.; Leppa, S.; Pasanen, A.; Meriranta, L.; Karjalainen-Lindsberg, M.L.; et al. Genetic and Functional Drivers of Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma. Cell 2017, 171, 481–494.e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz, R.; Wright, G.W.; Huang, D.W.; Johnson, C.A.; Phelan, J.D.; Wang, J.Q.; Roulland, S.; Kasbekar, M.; Young, R.M.; Shaffer, A.L.; et al. Genetics and pathogenesis of diffuse large B-Cell lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 1396–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapuy, B.; Stewart, C.; Dunford, A.J.; Kim, J.; Kamburov, A.; Redd, R.A.; Lawrence, M.S.; Roemer, M.G.M.; Li, A.J.; Ziepert, M.; et al. Molecular subtypes of diffuse large B cell lymphoma are associated with distinct pathogenic mechanisms and outcomes. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 679–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vermaat, J.S.; Somers, S.F.; de Wreede, L.C.; Kraan, W.; de Groen, R.A.L.; Schrader, A.M.R.; Kerver, E.D.; Scheepstra, C.G.; Beerenschot, H.; Deenik, W.; et al. MYD88 mutations identify a molecular subgroup of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma with an unfavourable prognosis. Haematologica 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, N.; Hartert, K.; Tadros, S.; Fiskus, W.; Havranek, O.; Ma, M.C.J.; Bouska, A.; Heavican, T.; Kumar, D.; Deng, Q.; et al. Targetable genetic alterations of TCF4 (E2-2) drive immunoglobulin expression in diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Sci. Transl. Med. 2019, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Intlekofer, A.M.; Joffe, E.; Batlevi, C.L.; Hilden, P.; He, J.; Seshan, V.E.; Zelenetz, A.D.; Palomba, M.L.; Moskowitz, C.H.; Portlock, C.; et al. Integrated DNA/RNA targeted genomic profiling of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma using a clinical assay. Blood Cancer J. 2018, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkodsi, A.; Cervera, A.; Zhang, K.; Louhimo, R.; Meriranta, L.; Pasanen, A.; Leivonen, S.K.; Holte, H.; Leppä, S.; Lehtonen, R.; et al. Distinct subtypes of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma defined by hypermutated genes. Leukemia 2019, 33, 2662–2672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arthur, S.E.; Jiang, A.; Grande, B.M.; Alcaide, M.; Cojocaru, R.; Rushton, C.K.; Mottok, A.; Hilton, L.K.; Lat, P.K.; Zhao, E.Y.; et al. Genome-wide discovery of somatic regulatory variants in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Feng, W.; Liu, P. Genomic pattern of intratumor heterogeneity predicts the risk of progression in early stage diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Carcinogenesis 2019, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasqualucci, L.; Khiabanian, H.; Fangazio, M.; Vasishtha, M.; Messina, M.; Holmes, A.B.; Ouillette, P.; Trifonov, V.; Rossi, D.; Tabbò, F.; et al. Genetics of Follicular Lymphoma Transformation. Cell Rep. 2014, 6, 130–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Rincón, J.; Méndez, M.; Gómez, S.; García, J.F.; Martín, P.; Bellas, C.; Pedrosa, L.; Rodríguez-Pinilla, S.M.; Camacho, F.I.; Quero, C.; et al. Unraveling transformation of follicular lymphoma to diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0212813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Redmond, D.; Nie, K.; Eng, K.W.; Clozel, T.; Martin, P.; Tan, L.; Melnick, A.M.; Tam, W.; Elemento, O. Deep-sequencing reveals clonal evolution patterns and mutation events associated with relapse in B-cell lymphomas. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morin, R.D.; Assouline, S.; Alcaide, M.; Mohajeri, A.; Johnston, R.L.; Chong, L.; Grewal, J.; Yu, S.; Fornika, D.; Bushell, K.; et al. Genetic Landscapes of Relapsed and Refractory Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphomas. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 2290–2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nijland, M.; Seitz, A.; Terpstra, M.; van Imhoff, G.W.; Kluin, P.M.; van Meerten, T.; Atayar, Ç.; van Kempen, L.C.; Diepstra, A.; Kok, K.; et al. Mutational evolution in relapsed diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Cancers (Basel). 2018, 10, 459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fornecker, L.M.; Muller, L.; Bertrand, F.; Paul, N.; Pichot, A.; Herbrecht, R.; Chenard, M.P.; Mauvieux, L.; Vallat, L.; Bahram, S.; et al. Multi-omics dataset to decipher the complexity of drug resistance in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rushton, C.; Alcaide, M.; Cheung, M.; Thomas, N.; Arthur, S.; Michaud, N.; Daigle, S.; Davidson, J.; Bushell, K.; Yu, S.; et al. Identifying Mutations Enriched in Relapsed-Refractory Dlbcl to Derive Genetic Factors Underlying Treatment Resistance. Hematol. Oncol. 2019, 37, 35–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, R.E.; Ngo, V.N.; Lenz, G.; Tolar, P.; Young, R.M.; Romesser, P.B.; Kohlhammer, H.; Lamy, L.; Zhao, H.; Yang, Y.; et al. Chronic active B-cell-receptor signalling in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Nature 2010, 463, 88–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenz, G.; Davis, R.E.; Ngo, V.N.; Lam, L.; George, T.C.; Wright, G.W.; Dave, S.S.; Zhao, H.; Xu, W.; Rosenwald, A.; et al. Oncogenic CARD11 mutations in human diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Science 2008, 319, 1676–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngo, V.N.; Young, R.M.; Schmitz, R.; Jhavar, S.; Xiao, W.; Lim, K.H.; Kohlhammer, H.; Xu, W.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, H.; et al. Oncogenically active MYD88 mutations in human lymphoma. Nature 2011, 470, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morin, R.D.; Mendez-Lago, M.; Mungall, A.J.; Goya, R.; Mungall, K.L.; Corbett, R.D.; Johnson, N.A.; Severson, T.M.; Chiu, R.; Field, M.; et al. Frequent mutation of histone-modifying genes in non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Nature 2011, 476, 298–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruminy, P.; Etancelin, P.; Couronné, L.; Parmentier, F.; Rainville, V.; Mareschal, S.; Bohers, E.; Burgot, C.; Cornic, M.; Bertrand, P.; et al. The isotype of the BCR as a surrogate for the GCB and ABC molecular subtypes in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Leukemia 2011, 25, 681–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasqualucci, L.; Neumeister, P.; Goossens, T.; Nanjangud, G.; Chaganti, R.S.K.; Küppers, R.; Dalla-Favera, R. Hypermutation of multiple proto-oncogenes in B-cell diffuse large-cell lymphomas. Nature 2001, 412, 341–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodabakhshi, A.H.; Morin, R.D.; Fejes, A.P.; Mungall, A.J.; Mungall, K.L.; Bolger-Munro, M.; Johnson, N.A.; Connors, J.M.; Gascoyne, R.D.; Marra, M.A.; et al. Recurrent targets of aberrant somatic hypermutation in lymphoma. Oncotarget 2012, 3, 1308–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasqualucci, L.; Bhagat, G.; Jankovic, M.; Compagno, M.; Smith, P.; Muramatsu, M.; Honjo, T.; Morse, H.C.; Nussenzweig, M.C.; Dalla-Favera, R. AID is required for germinal center-derived lymphomagenesis. Nat. Genet. 2008, 40, 108–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puente, X.S.; Beà, S.; Valdés-Mas, R.; Villamor, N.; Gutiérrez-Abril, J.; Martín-Subero, J.I.; Munar, M.; Rubio-Pérez, C.; Jares, P.; Aymerich, M.; et al. Non-coding recurrent mutations in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Nature 2015, 526, 519–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morin, R.D.; Mungall, K.; Pleasance, E.; Mungall, A.J.; Goya, R.; Huff, R.D.; Scott, D.W.; Ding, J.; Roth, A.; Chiu, R.; et al. Mutational and structural analysis of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma using whole-genome sequencing. Blood 2013, 122, 1256–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aukema, S.M.; van Pel, R.; Nagel, I.; Bens, S.; Siebert, R.; Rosati, S.; van den Berg, E.; Bosga-Bouwer, A.G.; Kibbelaar, R.E.; Hoogendoorn, M.; et al. MYC expression and translocation analyses in low-grade and transformed follicular lymphoma. Histopathology 2017, 71, 960–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swerdlow, S.H.; Campo, E.; Harris, N.L.; Jaffe, E.S.; Pileri, S.A.; Stein, H.T.J. WHO Classification of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017; ISBN 9789283244943. [Google Scholar]
- Sha, C.; Barrans, S.; Cucco, F.; Bentley, M.A.; Care, M.A.; Cummin, T.; Kennedy, H.; Thompson, J.S.; Uddin, R.; Worrillow, L.; et al. Molecular high-grade B-cell lymphoma: Defining a poor-risk group that requires different approaches to therapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 202–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ennishi, D.; Jiang, A.; Boyle, M.; Collinge, B.; Grande, B.M.; Ben-Neriah, S.; Rushton, C.; Tang, J.; Thomas, N.; Slack, G.W.; et al. Double-hit gene expression signature defines a distinct subgroup of germinal center B-cell-like diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 190–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilton, L.K.; Tang, J.; Ben-Neriah, S.; Alcaide, M.; Jiang, A.; Grande, B.M.; Rushton, C.K.; Boyle, M.; Meissner, B.; Scott, D.W.; et al. The double-hit signature identifies double-hit diffuse large B-cell lymphoma with genetic events cryptic to FISH. Blood 2019, 134, 1528–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dave, K.; Sur, I.; Yan, J.; Zhang, J.; Kaasinen, E.; Zhong, F.; Blaas, L.; Li, X.; Kharazi, S.; Gustafsson, C.; et al. Mice deficient of Myc super-enhancer region reveal differential control mechanism between normal and pathological growth. Elife 2017, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahr, C.; Von Paleske, L.; Uslu, V.V.; Remeseiro, S.; Takayama, N.; Ng, S.W.; Murison, A.; Langenfeld, K.; Petretich, M.; Scognamiglio, R.; et al. A Myc enhancer cluster regulates normal and leukaemic haematopoietic stem cell hierarchies. Nature 2018, 553, 515–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yada, M.; Hatakeyama, S.; Kamura, T.; Nishiyama, M.; Tsunematsu, R.; Imaki, H.; Ishida, N.; Okumura, F.; Nakayama, K.; Nakayama, K.I. Phosphorylation-dependent degradation of c-Myc is mediated by the F-box protein Fbw7. EMBO J. 2004, 23, 2116–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallardo, M.; Malaney, P.; Aitken, M.J.L.; Zhang, X.; Link, T.M.; Shah, V.; Alybayev, S.; Wu, M.-H.; Pageon, L.R.; Ma, H.; et al. Uncovering the Role of RNA-Binding Protein hnRNP K in B-Cell Lymphomas. JNCI J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2019, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sesques, P.; Johnson, N.A. Approach to the diagnosis and treatment of high-grade B-cell lymphomas with MYC and BCL2 and/or BCL6 rearrangements. Blood 2017, 129, 280–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, D.W.; King, R.L.; Staiger, A.M.; Ben-Neriah, S.; Jiang, A.; Horn, H.; Mottok, A.; Farinha, P.; Slack, G.W.; Ennishi, D.; et al. High-grade B-cell lymphoma with MYC and BCL2 and/or BCL6 rearrangements with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma morphology. Blood 2018, 131, 2060–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pillai, R.K.; Sathanoori, M.; Van Oss, S.B.; Swerdlow, S.H. Double-hit B-cell lymphomas with BCL6 and MYC translocations are aggressive, frequently extranodal lymphomas distinct from BCL2 double-hit B-cell lymphomas. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2013, 37, 323–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chong, L.C.; Ben-Neriah, S.; Slack, G.W.; Freeman, C.; Ennishi, D.; Mottok, A.; Collinge, B.; Abrisqueta, P.; Farinha, P.; Boyle, M.; et al. High-resolution architecture and partner genes of MYC rearrangements in lymphoma with DLBCL morphology. Blood Adv. 2018, 2, 2755–2765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenwald, A.; Bens, S.; Advani, R.; Barrans, S.; Copie-Bergman, C.; Elsensohn, M.-H.; Natkunam, Y.; Calaminici, M.; Sander, B.; Baia, M.; et al. Prognostic Significance of MYC Rearrangement and Translocation Partner in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma: A Study by the Lunenburg Lymphoma Biomarker Consortium. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunleavy, K. Double-hit lymphomas: Current paradigms and novel treatment approaches. Hematology 2014, 2014, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, N.A.; Slack, G.W.; Savage, K.J.; Connors, J.M.; Ben-Neriah, S.; Rogic, S.; Scott, D.W.; Tan, K.L.; Steidl, C.; Sehn, L.H.; et al. Concurrent expression of MYC and BCL2 in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma treated with rituximab plus cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 3452–3459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, T.M.; Young, K.H.; Visco, C.; Xu-Monette, Z.Y.; Orazi, A.; Go, R.S.; Nielsen, O.; Gadeberg, O.V.; Mourits-Andersen, T.; Frederiksen, M.; et al. Immunohistochemical double-hit score is a strong predictor of outcome in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma treated with rituximab plus cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 3460–3467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchida, A.; Isobe, Y.; Asano, J.; Uemura, Y.; Hoshikawa, M.; Takagi, M.; Miura, I. Targeting BCL2 with venetoclax is a promising therapeutic strategy for “double-proteinexpression” lymphoma with MYC and BCL2 rearrangements. Haematologica 2019, 104, 1417–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Jonge, M.J.A.; Carneiro, B.A.; Devriese, L.; Doi, T.; Penugonda, S.; Petrich, A.M.; Nuthalapati, S.; Motwani, M.; Modi, D.A.; Chang, Y.-W.; et al. First-in-Human Study of Abbv-621, a TRAIL Receptor Agonist Fusion Protein, in Patients (Pts) with Relapsed/Refractory (RR) Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) and Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma (DLBCL). Blood 2019, 134, 3924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, D.; Diop, F.; Spaccarotella, E.; Monti, S.; Zanni, M.; Rasi, S.; Deambrogi, C.; Spina, V.; Bruscaggin, A.; Favini, C.; et al. Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma genotyping on the liquid biopsy. Blood 2017, 129, 1947–1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roschewski, M.; Dunleavy, K.; Pittaluga, S.; Moorhead, M.; Pepin, F.; Kong, K.; Shovlin, M.; Jaffe, E.S.; Staudt, L.M.; Lai, C.; et al. Circulating tumour DNA and CT monitoring in patients with untreated diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: A correlative biomarker study. Lancet Oncol. 2015, 16, 541–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherer, F.; Kurtz, D.M.; Newman, A.M.; Stehr, H.; Craig, A.F.M.; Esfahani, M.S.; Lovejoy, A.F.; Chabon, J.J.; Klass, D.M.; Liu, C.L.; et al. Distinct biological subtypes and patterns of genome evolution in lymphoma revealed by circulating tumor DNA. Sci. Transl. Med. 2016, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camus, V.; Stamatoullas, A.; Mareschal, S.; Viailly, P.J.; Sarafan-Vasseur, N.; Bohers, E.; Dubois, S.; Picquenot, J.M.; Ruminy, P.; Maingonnat, C.; et al. Detection and prognostic value of recurrent exportin 1 mutations in tumor and cell-free circulating DNA of patients with classical Hodgkin lymphoma. Haematologica 2016, 101, 1094–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camus, V.; Sarafan-Vasseur, N.; Bohers, E.; Dubois, S.; Mareschal, S.; Bertrand, P.; Viailly, P.J.; Ruminy, P.; Maingonnat, C.; Lemasle, E.; et al. Digital PCR for quantification of recurrent and potentially actionable somatic mutations in circulating free DNA from patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Leuk. Lymphoma 2016, 57, 2171–2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, A.F.; Kim, H.T.; Kong, K.A.; Faham, M.; Sun, H.; Sohani, A.R.; Alyea, E.P.; Carlton, V.E.; Chen, Y.B.; Cutler, C.S.; et al. Next-generation sequencing-based detection of circulating tumour DNA After allogeneic stem cell transplantation for lymphoma. Br. J. Haematol. 2016, 175, 841–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurtz, D.M.; Scherer, F.; Jin, M.C.; Soo, J.; Craig, A.F.M.; Esfahani, M.S.; Chabon, J.J.; Stehr, H.; Liu, C.L.; Tibshirani, R.; et al. Circulating tumor DNA measurements as early outcome predictors in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 2845–2853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.; Chen, C.; Xia, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, P.P.; Bi, X.W.; Shao, Y.W.; Ou, Q.X.; Wu, X.; Yang, H.; et al. Mutation profiling of malignant lymphoma by next-generation sequencing of circulating cell-free DNA. J. Cancer 2019, 10, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurtz, D.M.; Esfahani, M.S.; Scherer, F.; Soo, J.; Jin, M.C.; Liu, C.L.; Newman, A.M.; Dührsen, U.; Hüttmann, A.; Casasnovas, O.; et al. Dynamic Risk Profiling Using Serial Tumor Biomarkers for Personalized Outcome Prediction. Cell 2019, 178, 699–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mondello, P.; Mian, M. Frontline treatment of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: Beyond R-CHOP. Hematol. Oncol. 2019, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Barta, S.K. Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: 2019 update on diagnosis, risk stratification, and treatment. Am. J. Hematol. 2019, 94, 604–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narkhede, M.; Yazdy, M.S.; Cheson, B.D. Targeting Biology in Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma. Hematol. Oncol. Clin. North Am. 2019, 33, 727–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Chen, J.; Tamayo, A.T.; Ruan, C.; Li, L.; Zhou, S.; Shen, C.; Young, K.H.; Westin, J.; Davis, R.E.; et al. Preclinical efficacy and biological effects of the oral proteasome inhibitor ixazomib in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 346–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horn, H.; Staiger, A.M.; Ott, G. New targeted therapies for malignant lymphoma based on molecular heterogeneity. Expert Rev. Hematol. 2017, 10, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Jong, M.R.W.; Visser, L.; Huls, G.; Diepstra, A.; Van Vugt, M.; Ammatuna, E.; van Rijn, R.S.; Vellenga, E.; Van Den Berg, A.; Fehrmann, R.S.N.; et al. Identification of relevant drugable targets in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma using a genome-wide unbiased CD20 guilt-by association approach. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0193098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younes, A.; Thieblemont, C.; Morschhauser, F.; Flinn, I.; Friedberg, J.W.; Amorim, S.; Hivert, B.; Westin, J.; Vermeulen, J.; Bandyopadhyay, N.; et al. Combination of ibrutinib with rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone (R-CHOP) for treatment-naive patients with CD20-positive B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma: A non-randomised, phase 1b study. Lancet Oncol. 2014, 15, 1019–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowakowski, G.S.; Chiappella, A.; Witzig, T.E.; Spina, M.; Gascoyne, R.D.; Zhang, L.; Flament, J.; Repici, J.; Vitolo, U. ROBUST: Lenalidomide-R-CHOP versus placebo-R-CHOP in previously untreated ABC-type diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Futur. Oncol. 2016, 12, 1553–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonard, J.P.; Kolibaba, K.S.; Reeves, J.A.; Tulpule, A.; Flinn, I.W.; Kolevska, T.; Robles, R.; Flowers, C.R.; Collins, R.; DiBella, N.J.; et al. Randomized Phase II study of R-CHOP with or without bortezomib in previously untreated patients with non-germinal center B-cell-like diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 3538–3546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, A.; Cummin, T.E.; Barrans, S.; Maishman, T.; Mamot, C.; Novak, U.; Caddy, J.; Stanton, L.; Kazmi-Stokes, S.; McMillan, A.; et al. Gene-expression profiling of bortezomib added to standard chemoimmunotherapy for diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (REMoDL-B): An open-label, randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, 649–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdy, M.S.; Mato, A.R.; Cheson, B.D. Combinations or sequences of targeted agents in CLL: Is the whole greater than the sum of its parts (Aristotle, 360 BC)? Blood 2019, 133, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernards, R. A missing link in genotype-directed cancer therapy. Cell 2012, 151, 465–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaguchi, H.; Chang, S.S.; Hsu, J.L.; Hung, M.C. Signaling cross-talk in the resistance to HER family receptor targeted therapy. Oncogene 2014, 33, 1073–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmer, A.C.; Chidley, C.; Sorger, P. Drugs in a Curative Combination Therapy for Lymphoma Exhibit Low Cross-Resistance But Not Pharmacological Synergy. SSRN Electron. J. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preuer, K.; Lewis, R.P.I.; Hochreiter, S.; Bender, A.; Bulusu, K.C.; Klambauer, G. DeepSynergy: Predicting anti-cancer drug synergy with Deep Learning. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 1538–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Kim, D.G.; Bae, T.J.; Rho, K.; Kim, J.T.; Lee, J.J.; Jang, Y.; Kim, B.C.; Park, K.M.; Kim, S. CDA: Combinatorial drug discovery using transcriptional response modules. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e42573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Karhinen, L.; Xu, T.; Szwajda, A.; Yadav, B.; Wennerberg, K.; Aittokallio, T. Target Inhibition Networks: Predicting Selective Combinations of Druggable Targets to Block Cancer Survival Pathways. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2013, 9, e1003226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Brunell, D.; Stephan, C.; Mancuso, J.; Yu, X.; He, B.; Thompson, T.C.; Zinner, R.; Kim, J.; Davies, P.; et al. Driver network as a biomarker: Systematic integration and network modeling of multi-omics data to derive driver signaling pathways for drug combination prediction. Bioinformatics 2019, 35, 3709–3717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Reference | Kind of Study | Main Molecular Findings | Clinical Implications |
|---|---|---|---|
| New Prognostic Biomarkers and Models | |||
| Reddy et al., Cell 2017 [49] | Exome and transcriptome sequencing of 1001 DLBCL cases | Identification of 150 driver genes set, definition of a prognostic model better than current ones |
|
| Schmitz et al., NEJM 2018 [50] | WES, RNA-seq, gene copy number analysis and targeted sequencing of 372 genes in 574 DLBCL cases | Development of a specific algorithm identifying four genetic subtypes:
|
|
| Chapuy et al., Nat Med 2018 [51] | WES and targeted sequencing on 304 DLBCL patients | Identification of five DLBCL subsets:
|
|
| Vermaat et al., Haematologica 2019 [52] | NGS, allele-specific PCR and FISH on 250 DLBCL cases | Identification of:
| MYD88 mutations: adverse prognostic impact |
| Jain et al., Sci. Transl. Med 2019 [53] | DNA copy number analysis of 1000 DLBCL cases | Identification of 18q21.2 gains as the most frequent genetic alteration in the ABC-like group, with involvement of TCF4 (E2-2) transcription factor gene | The inhibition of TCF4 activity through BET inhibitors could be employed in the treatment of this patient subset |
| Intlekofer et al., Blood Cancer 2018 [54] | Targeted NGS on 198 DLBCL cases | Identification of a median number of six genetic aberrations per case, with 97% of patients presenting at least one alteration and 54% of cases more than one (e.g., MYD88, CREBBP, CD79B, EZH2) |
|
| Alkodsi et al., Leukemia 2019 [55] | WGS, RNA-seq, and gene expression from literature DLBCL cohorts | The expression of 36 SHM target genes identifies four SHM subtypes:
|
|
| Arthur et al., Nat. Commun. 2018 [56] | Integrative analysis of whole genomes, exomes, and transcriptomes on thousands of DLBCL cases | Identification of:
| These results revealed new driver DLBCL mutations, improving diagnostic assays and offering new possibilities for the development of targeted therapeutics |
| Wang et al., Carcinogenesis 2019 [57] | WES on 22 early stage DLBCL and validation on 35 primary DLBCL cases | Identification of two MATH score classes: low and high MATH score groups according to the median expression level |
|
| Causes of Transformation and Chemoresistance | |||
| Pasqualucci et al., Cell Rep. 2014 [58] | WES and SNP array analysis on 12 FL samples at diagnosis and on 39 transformed FL | Identification of CDKN2A/B, MYC and TP53 as major drivers of transformation of FL to an aggressive malignancy, typically DLBCL | The genomic profile of transformed FL shares similarities with de novo DLBCL-GCB but also displays unique gene mutations with diagnostic and therapeutic implications |
| González-Rincón et al., PLoS One 2019 [59] | Targeted NGS on 22 pre-transformed /transformed and on 20 non-transformed FL cases | Transformed FL are characterized by several recurrently mutated genes with roles in B-cell differentiation, GC architecture and migration (LRP1B, GNA13 and POU2AF1) |
|
| Jiang et al., Genome Biol. 2014 [60] | High-throughput sequencing of rearranged VDJ junctions in 14 pairs of matched diagnosis-relapse DLBCL | Two proposed mechanisms of clonal evolution:
| Although DLBCL relapse may result from multiple tumour evolutionary mechanisms, each mechanism could provide rationale for therapies |
| Morin et al., Clin. Cancer Res. 2016 [61] | WES on 38 R/R DLBCL biopsies and on an unrelated cohort of 138 diagnostic DLBCLs | Identification of TP53, FOXO1, MLL3 (KMT2C), CCND3, NFKBIZ, and STAT6 as top candidate genes implicated in therapeutic resistance | Detection of mutations (MYD88 and CD79B) that may affect sensitivity to novel therapeutics |
| Nijland et al., Cancers (Basel). 2018 [62] | WES on 14 matched primary/relapse samples from six DLBCL patients | Identification of 264 genes possibly related to therapy resistance, including tyrosine kinases, transmembrane glycoproteins, and genes involved in the JAK-STAT pathway | Identification of resistance-related genes such as PIM1, SOCS1, and MYC, that confer a risk for treatment failure |
| Fornecker et al., Sci. Rep. 2019 [63] | Integrated quantitative proteomics and targeted RNA-sequencing in 8 R/R DLBCL cases versus 12 chemosensitive DLBCL patients | Identification of a set of 22 transcripts/proteins pairs, whose expression levels significantly differed between the two analysed groups | Identification of new biomarkers related to chemoresistance, new potential drug targets: Hexokinase 3, IDO1, CXCL13, S100 proteins, CD79B |
| Rushton et al., Hematol. Oncol. 2019 [64] | WES and targeted NGS on plasma samples and tissue biopsies from 134 R/R patients | R/R patients were enriched for mutations in five genes: TP53, IL4R, HVCN1, RB1 and MS4A1 | DLBCL patients with mutations in these five genes present a higher risk of treatment failure |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Coccaro, N.; Anelli, L.; Zagaria, A.; Perrone, T.; Specchia, G.; Albano, F. Molecular Complexity of Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma: Can It Be a Roadmap for Precision Medicine? Cancers 2020, 12, 185. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12010185
Coccaro N, Anelli L, Zagaria A, Perrone T, Specchia G, Albano F. Molecular Complexity of Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma: Can It Be a Roadmap for Precision Medicine? Cancers. 2020; 12(1):185. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12010185
Chicago/Turabian StyleCoccaro, Nicoletta, Luisa Anelli, Antonella Zagaria, Tommasina Perrone, Giorgina Specchia, and Francesco Albano. 2020. "Molecular Complexity of Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma: Can It Be a Roadmap for Precision Medicine?" Cancers 12, no. 1: 185. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12010185
APA StyleCoccaro, N., Anelli, L., Zagaria, A., Perrone, T., Specchia, G., & Albano, F. (2020). Molecular Complexity of Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma: Can It Be a Roadmap for Precision Medicine? Cancers, 12(1), 185. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12010185








