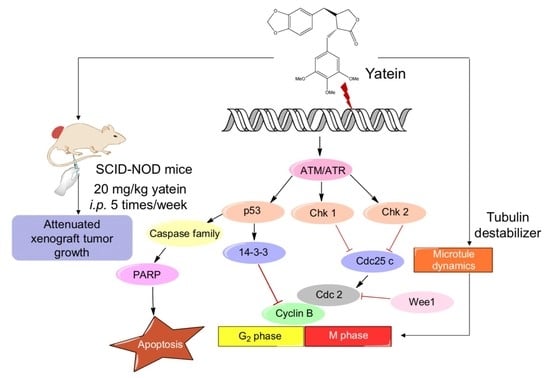
Molecular Mechanisms Underlying Yatein-Induced Cell-Cycle Arrest and Microtubule Destabilization in Human Lung Adenocarcinoma Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
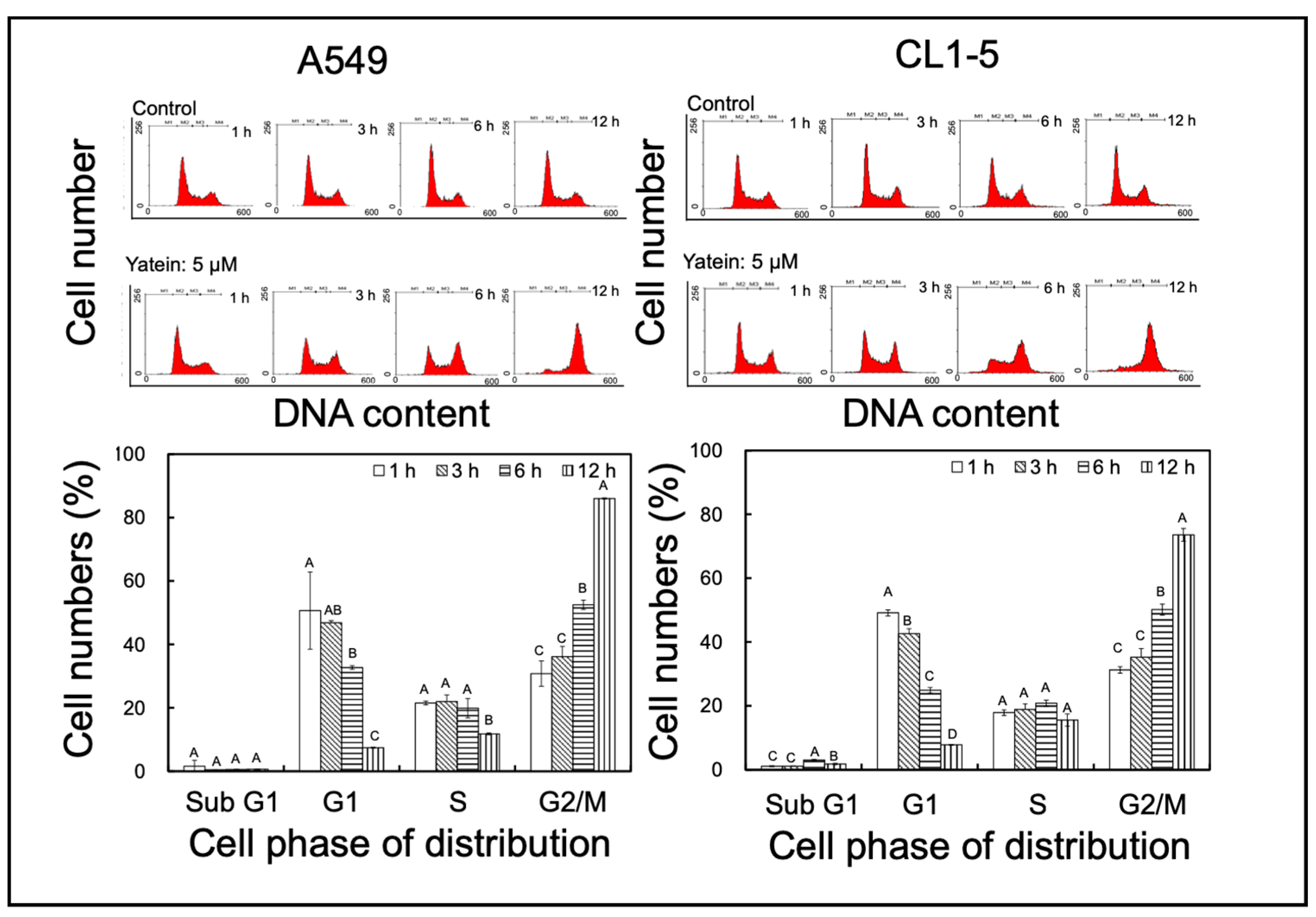
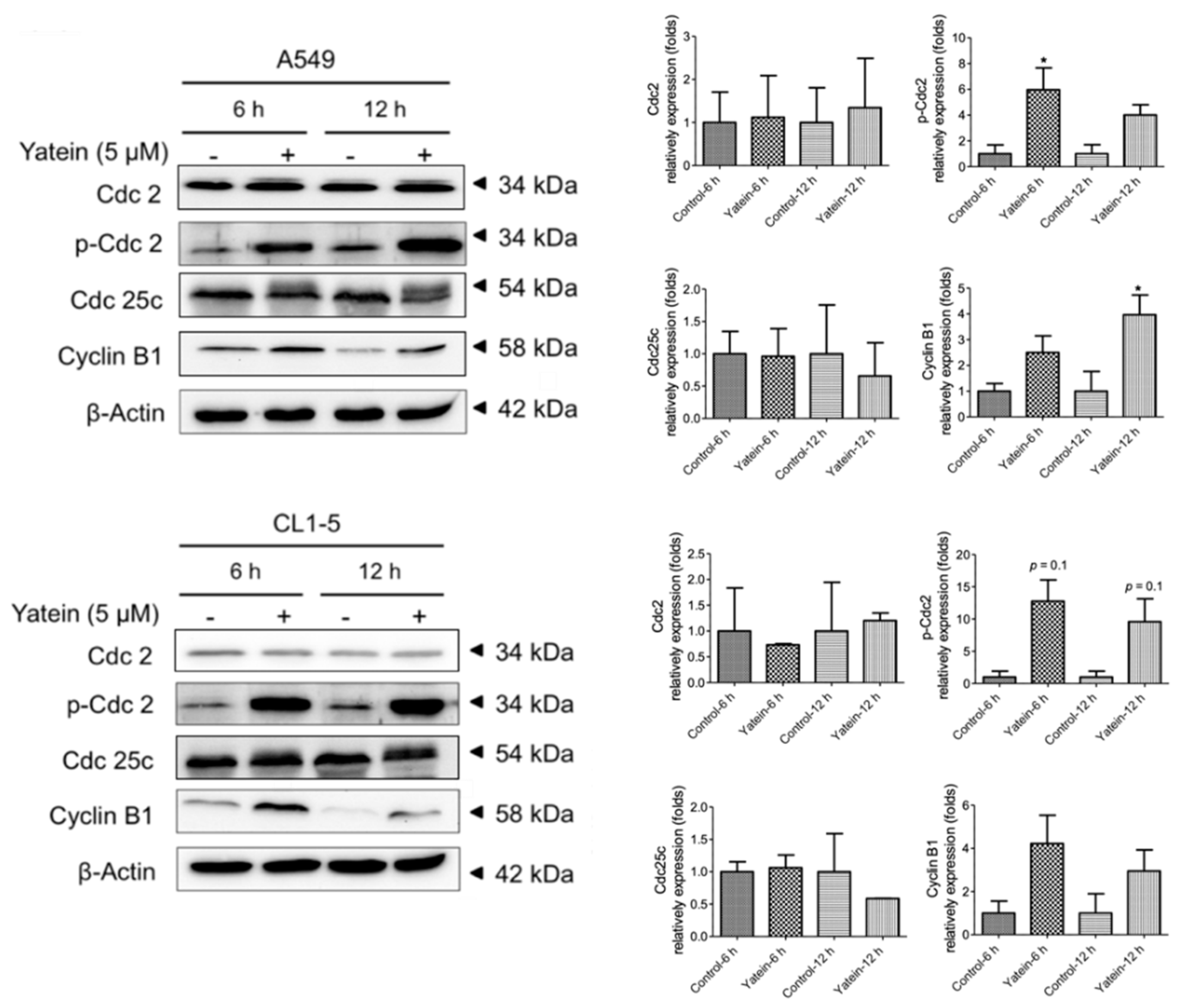
2.1. Yatein Induces Cell-Cycle Arrest at G2/M Phase and Enhances G2/M Phase-Related Protein Expression in Human A549 and CL1-5 Cells
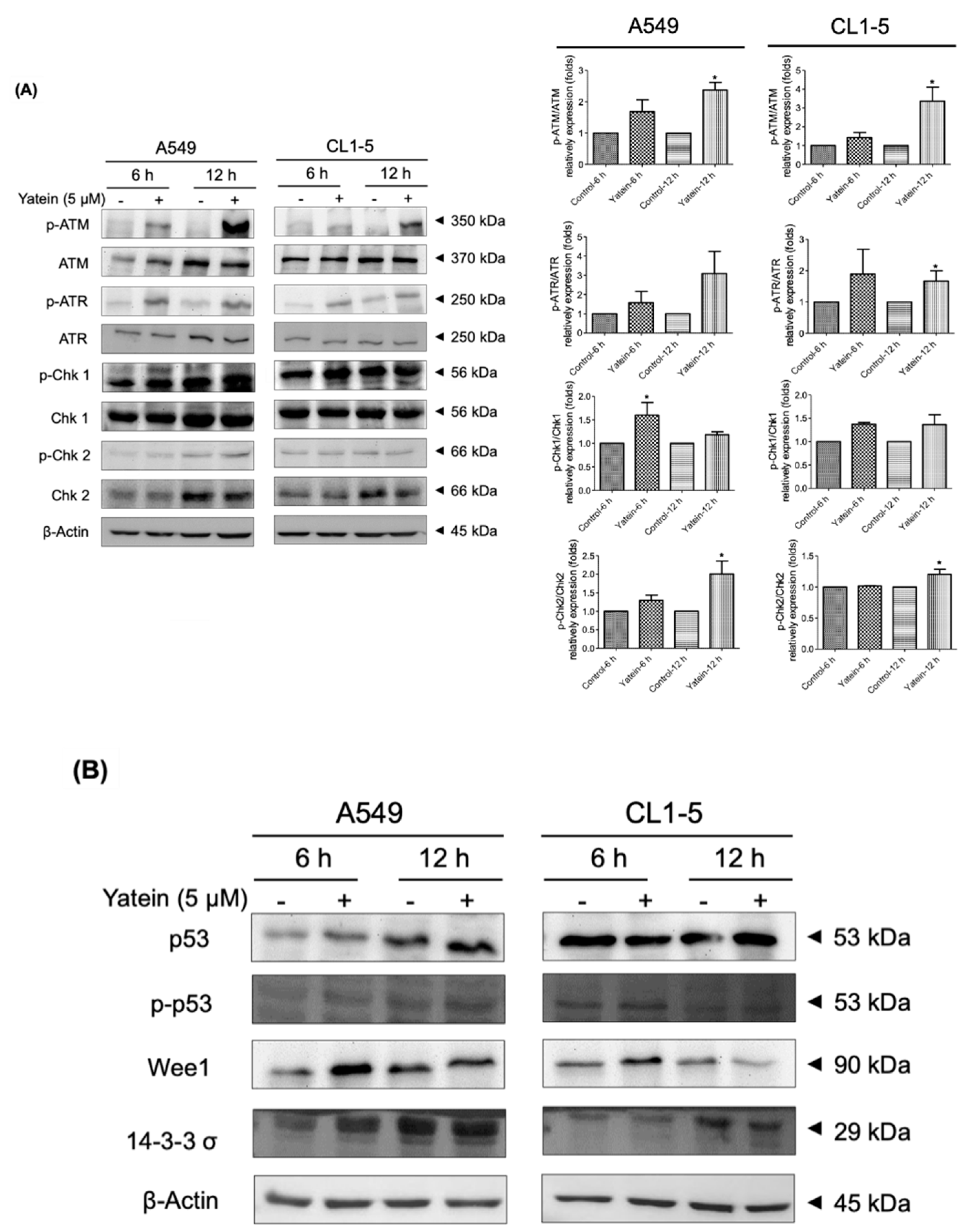
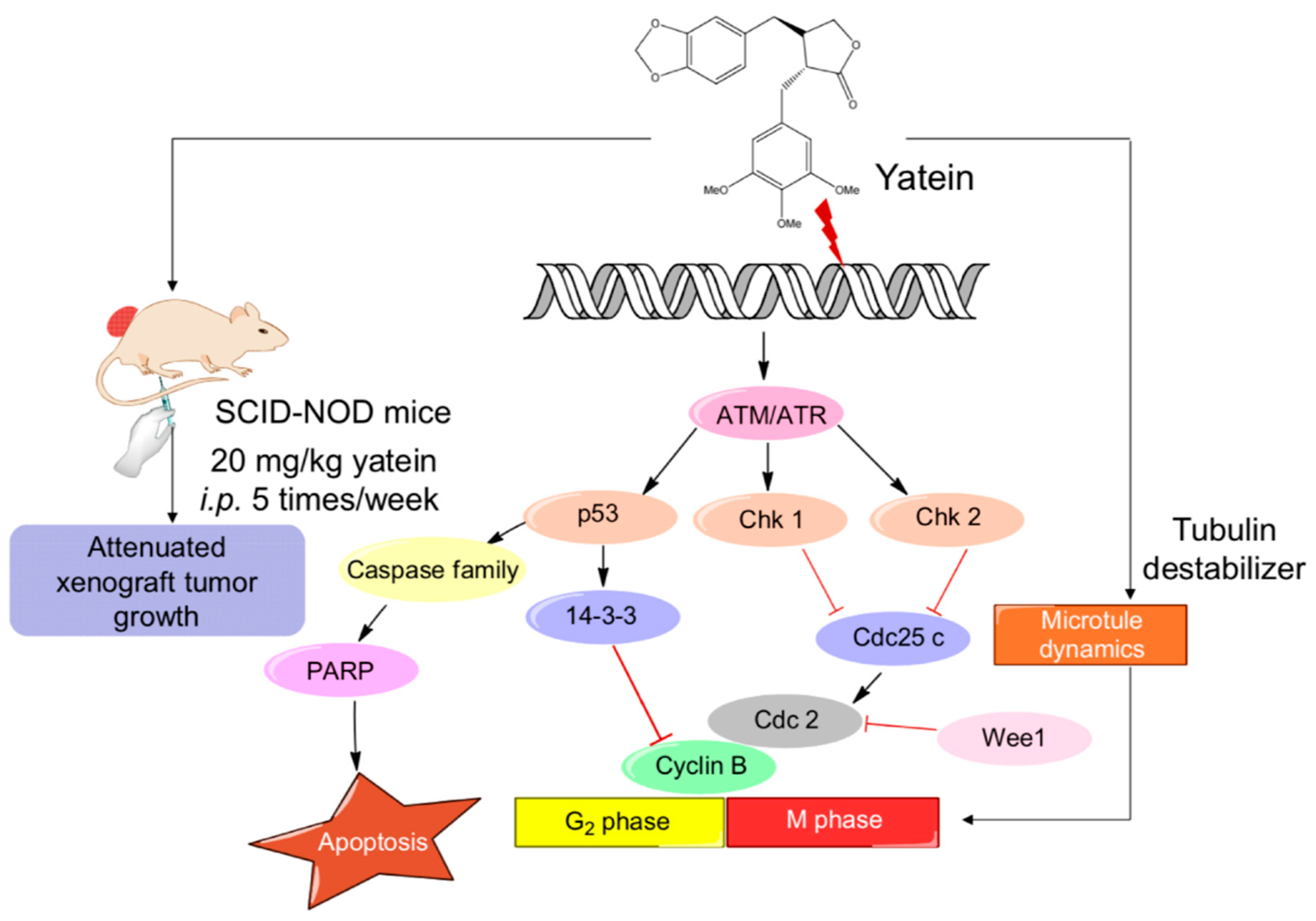
2.2. Yatein Induces DNA Damage through Activation of the ATM/ATR Pathway in Human A549 and CL1-5 Cells
2.3. Yatein Influences Microtubule Dynamics in Human A549 and CL1-5 Cells
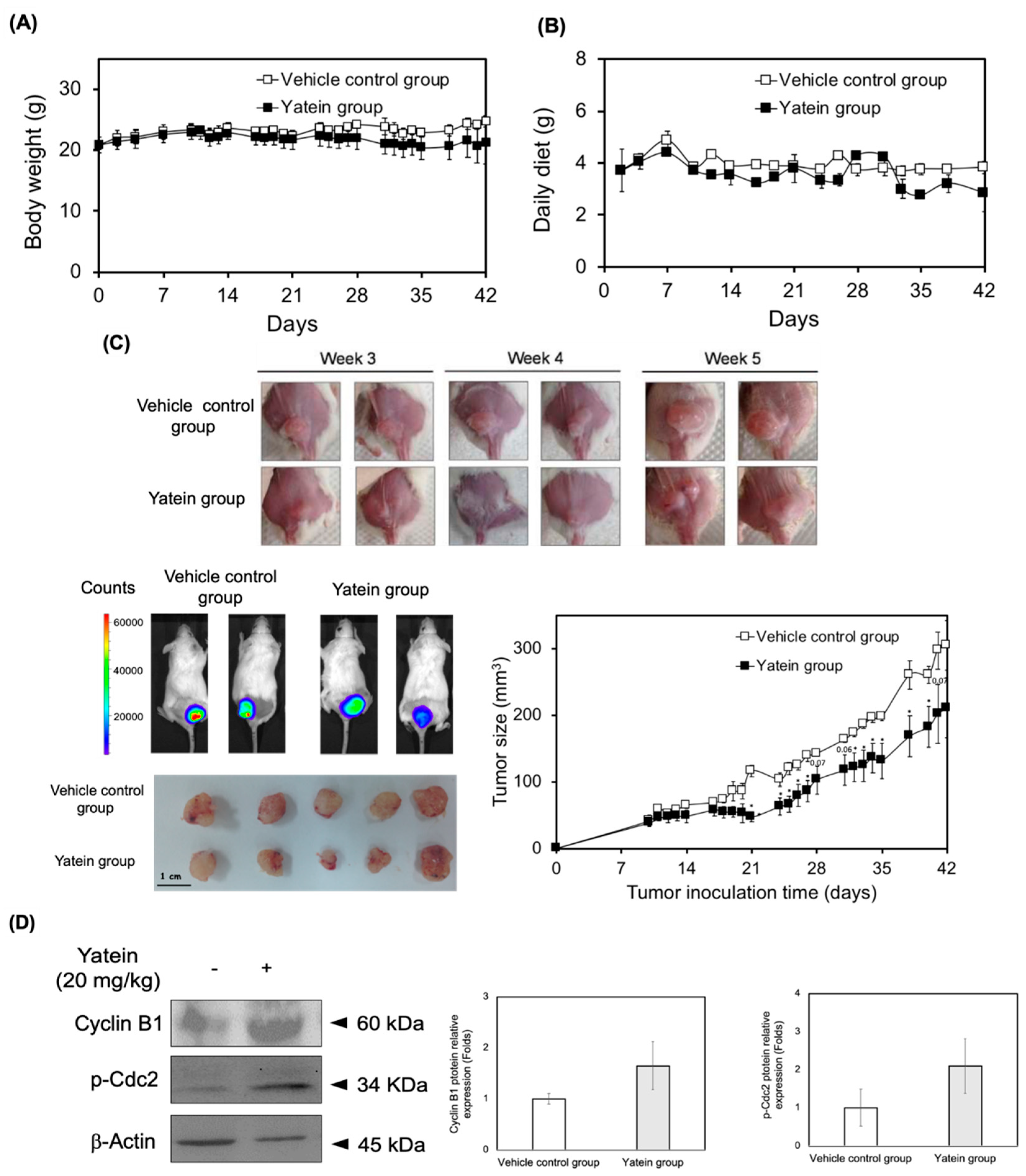
2.4. Yatein Exhibits In Vivo Antitumor Effects in a Xenograft Mouse Model
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Preparation of Yatein
4.2. Cell Culture
4.3. Cell-Cycle Distribution Analysis
4.4. Isolation of Microtubule Proteins
4.5. Western Blot Analysis
4.6. Immunofluorescence
4.7. In Vivo Antitumor Activity
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Newman, D.J.; Cragg, G.M. Natural products as sources of new drugs from 1981 to 2014. J. Nat. Prod. 2016, 79, 629–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visconti, R.; Della Monica, R.; Grieco, D. Cell cycle checkpoint in cancer: a therapeutically targetable double-edged sword. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 35, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otto, T.; Sicinski, P. Cell cycle proteins as promising targets in cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2017, 17, 93–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailon-Moscoso, N.; Cevallos-Solorzano, G.; Romero-Benavides, J.C.; Orellana, M.I. Natural compounds as modulators of cell cycle arrest: application for anticancer chemotherapies. Curr. Genom. 2017, 18, 106–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, H.T.; Cheng, Y.H.; Wu, C.L.; Chang, S.T.; Chang, T.T.; Su, Y.C. Antifungal activity of essential oil and its constituents from Calocedrus macrolepis var. formosana Florin leaf against plant pathogenic fungi. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 6266–6270. [Google Scholar]
- Yen, T.B.; Chang, H.T.; Hsieh, C.C.; Chang, S.T. Antifungal properties of ethanolic extract and its active compounds from Calocedrus macrolepis var. formosana (Florin) heartwood. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 4871–4877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, C.L.; Tseng, Y.H.; Wang, E.I.; Liao, P.C.; Chou, J.C.; Lin, C.N.; Su, Y.C. Composition, antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of the seed essential oil of Calocedrus formosana from Taiwan. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2011, 6, 133–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.Y.; Wu, J.H.; Cheng, S.S.; Lo, C.P.; Chang, H.N.; Shyur, L.F.; Chang, S.T. Antioxidant activity of extracts from Calocedrus formosana leaf, bark, and heartwood. J. Wood Sci. 2004, 50, 422–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yen, P.L.; Wu, C.L.; Chang, S.T.; Huang, S.L.; Chang, H.T. Antioxidative lignans from phytochemical extract of Calocedrus formosana Florin. BioResources 2012, 7, 4122–4131. [Google Scholar]
- Chiang, Y.M.; Liu, H.K.; Lo, J.M.; Chien, S.C.; Chan, Y.F.; Lee, T.H.; Su, J.K.; Kuo, Y.H. Cytotoxic constituents of the leaves of Calocedrus formosana. J. Chin. Chem. Soc. 2013, 50, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.Y.; Lin, C.C.; Hsu, S.L.; Cheng, Y.W.; Wu, J.H.; Cheng, C.L.; Yang, C.R. Leaf extracts of Calocedrus formosana (Florin) induce G2/M cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in human bladder cancer cells. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2011, 2011, 380923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, C.C.; Chen, C.J.; Tseng, H.W.; Hua, K.F.; Tsai, R.Y.; Lai, M.H.; Chao, L.K.; Chen, S.T. Cytomic screening of immuno-modulating activity compounds from Calocedrus formosana. Comb. Chem. High Throughput Screen. 2008, 11, 834–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, K.P.; Hua, K.F.; Hsu, H.Y.; Su, Y.C.; Chang, S.T. Anti-Inflammatory activity of sugiol, a diterpene isolated from Calocedrus formosana bark. Planta Med. 2005, 71, 300–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayakumar, T.; Liu, C.H.; Wu, G.Y.; Lee, T.Y.; Manubolu, M.; Hsieh, C.Y.; Yang, C.H.; Sheu, J.R. Hinokitiol inhibits migration of A549 lung cancer cells via suppression of MMPs and induction of antioxidant enzymes and apoptosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, S.T.; Lin, C.C.; Wu, T.L.; Tung, Y.T.; Wu, J.H. Antitumor agent yatein from Calocedrus formosana Florin leaf induces apoptosis in non-small-cell lung cancer cells. J. Wood Sci. under review.
- Sancar, A.; Lindsey-Boltz, L.A.; Ünsal-Kaçmaz, K.; Linn, S. Molecular mechanisms of mammalian DNA repair and the DNA damage checkpoints. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2004, 73, 39–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacus, S.S.; Gudkov, A.V.; Lowe, M.; Lyass, L.; Yung, Y.; Komarov, A.P.; Keyomarsi, K.; Yarden, Y.; Seger, R. Taxol-Induced apoptosis depends on MAP kinase pathways (ERK and p38) and is independent of p53. Oncogene 2001, 20, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, H.; Kong, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Li, D.; Tan, W. Lignans extracted from Vitex negundo possess cytotoxic activity by G2/M phase cell cycle arrest and apoptosis induction. Phytomedicine 2013, 20, 640–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manna, S.K.; Bose, J.S.; Gangan, V.; Raviprakash, N.; Navaneetha, T.; Raghavendra, P.B.; Babajan, B.; Kumar, C.S.; Jain, S.K. Novel derivative of benzofuran induces cell death mostly by G2/M cell cycle arrest through p53-dependent pathway but partially by inhibition of NF-Kappab. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 22318–22327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satyanarayana, A.; Kaldis, P. Mammalian cell-cycle regulation: several Cdks, numerous cyclins and diverse compensatory mechanisms. Oncogene 2009, 28, 2925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vakifahmetoglu, H.; Olsson, M.; Zhivotovsky, B. Death through a tragedy: mitotic catastrophe. Cell Death Differ. 2008, 15, 1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.T.; Chen, C.; Lu, I.C.; Kuo, S.C.; Lee, K.H.; Chen, T.L.; Song, T.S.; Lu, Y.L.; Gean, P.W.; Hour, M.J. MJ-66 induces malignant glioma cells G2/M phase arrest and mitotic catastrophe through regulation of cyclin B1/Cdk1 complex. Neuropharmacology 2014, 86, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subramaniam, D.; Ramalingam, S.; Linehan, D.C.; Dieckgraefe, B.K.; Postier, R.G.; Houchen, C.W.; Jensen, R.A.; Anant, S. RNA binding protein CUGBP2/CELF2 mediates curcumin-induced mitotic catastrophe of pancreatic cancer cells. PLoS ONE 2011, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maréchal, A.; Zou, L. DNA damage sensing by the ATM and ATR kinases. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2013, 5, 012716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, J.; Tho, L.M.; Xu, N.; Gillespie, D.A. The ATM-Chk2 and ATR-Chk1 pathways in DNA damage signaling and cancer. Adv. Cancer Res. 2010, 108, 73–112. [Google Scholar]
- Sahu, R.P.; Batra, S.; Srivastava, S.K. Activation of ATM/Chk1 by curcumin causes cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in human pancreatic cancer cells. Br. J. Cancer 2009, 100, 1425–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Liu, Z.; Li, B.; Sun, Z.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, X.; Gong, Y.; Shao, C. Berberine, a genotoxic alkaloid, induces ATM-Chk1 mediated G2 arrest in prostate cancer cells. Mutat. Res. 2012, 734, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, T.W.; Lin, S.C.; Su, J.H.; Chen, Y.K.; Lin, C.C.; Chan, H.L. Sinularin induces DNA damage, G2/M phase arrest, and apoptosis in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. BMC Complement Altern. Med. 2017, 17, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiloh, Y. ATM and related protein kinases: Safeguarding genome integrity. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2003, 3, 155–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, M.; Rohe, A.; Platzer, C.; Najjar, A.; Erdmann, F.; Sippl, W. Regulation of G2/M transition by inhibition of WEE1 and PKMYT1 kinases. Molecules 2017, 22, 2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashwell, S. Chapter 10—Checkpoint Kinase and Wee1 inhibitors as anticancer therapeutics. In DNA Repair in Cancer Therapy; Kelley, M.R., Ed.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2012; pp. 211–234. [Google Scholar]
- Cotugno, R.; Fortunato, R.; Santoro, A.; Gallotta, D.; Braca, A.; De Tommasi, N.; Belisario, M.A. Effect of sesquiterpene lactone coronopilin on leukaemia cell population growth, cell type-specific induction of apoptosis and mitotic catastrophe. Cell Prolif. 2011, 45, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dumontet, C.; Jordan, M.A. Microtubule-Binding agents: a dynamic field of cancer therapeutics. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2010, 9, 790–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikeda, R.; Nagao, T.; Okabe, H.; Nakano, Y.; Matsunaga, H.; Katano, M.; Mori, M. Antiproliferative constituents in umbelliferae plants. III. Constituents in the root and the ground part of Anthriscus sylvestris Hoffm. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1998, 46, 871–887. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]


© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ho, S.-T.; Lin, C.-C.; Tung, Y.-T.; Wu, J.-H. Molecular Mechanisms Underlying Yatein-Induced Cell-Cycle Arrest and Microtubule Destabilization in Human Lung Adenocarcinoma Cells. Cancers 2019, 11, 1384. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11091384
Ho S-T, Lin C-C, Tung Y-T, Wu J-H. Molecular Mechanisms Underlying Yatein-Induced Cell-Cycle Arrest and Microtubule Destabilization in Human Lung Adenocarcinoma Cells. Cancers. 2019; 11(9):1384. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11091384
Chicago/Turabian StyleHo, Shang-Tse, Chi-Chen Lin, Yu-Tang Tung, and Jyh-Horng Wu. 2019. "Molecular Mechanisms Underlying Yatein-Induced Cell-Cycle Arrest and Microtubule Destabilization in Human Lung Adenocarcinoma Cells" Cancers 11, no. 9: 1384. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11091384
APA StyleHo, S.-T., Lin, C.-C., Tung, Y.-T., & Wu, J.-H. (2019). Molecular Mechanisms Underlying Yatein-Induced Cell-Cycle Arrest and Microtubule Destabilization in Human Lung Adenocarcinoma Cells. Cancers, 11(9), 1384. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11091384