1. Introduction
Lung cancer is one of the deadliest diseases. This is primarily due to the late diagnosis, which results from a lack of symptoms in the early stages, and which evidently promotes high mortality rates [
1,
2,
3]. Even among patients diagnosed at an early stage, metastases frequently develop, and therapeutic options are, unfortunately, rather limited [
4,
5]. Therefore, in addition to the ongoing efforts for early lung cancer diagnosis, metastasis prevention is of great importance.
Despite the increasing number of personalized targeted therapies for specific genetic profiles, and the availability of over 60 FDA-approved drugs for treating lung cancer [
6], prophylactic therapy for lung metastases is not yet available. Patients diagnosed with early-stage lung cancer, or those with primary tumors that are known to be susceptible to developing lung metastases could potentially benefit from such therapy, which could prevent further progression of the disease.
In our recently published work, we demonstrated that carbenoxolone, a derivate of a natural compound, can significantly diminish the metastatic burden in the lungs of mice [
7,
8]. Carbenoxolone is a water-soluble-small-molecule that is chemically derived from glycyrrhizin, an anti-inflammatory active compound found in the licorice root extract. Carbenoxolone is a licensed drug in the UK, prescribed for inflammation and esophageal ulcers [
9]. It was found to be an antagonist of endotoxin-induced secretion of high mobility group box 1 (HMGB1) [
10], a known pro-inflammatory protein. One of the receptors of HMGB1 is the receptor for advanced glycation end-products (RAGE), which is highly abundant in the lung tissue. As demonstrated here, applying both in-vitro and in-vivo models, carbenoxolone has the capacity to antagonize HMGB1 and to inhibit lung cancer colonization. Interference of carbenoxolone in cancer colonization was found to be mediated by impairment of cell adhesion via reduction of intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM1) expression levels, thus diminishing cell-cell interactions and cellular adherence to the extracellular matrix (ECM) [
8].
Although prescribed for gastrointestinal inflammation, carbenoxolone carries potential adverse side effects under systemic exposure to high dosage. The common dosage is 100 mg for one week, three times a week, followed by a reduction to 50 mg every other day, to prevent potential side effects [
11] such as sodium retention, hypokalemia [
12], increased blood pressure, and edema [
13]. Localizing the effect of the drug to the organ-of-interest would decrease the required dosage, thus provide more effective treatment, with fewer side effects and increased patient compliance.
Here we show our development of a pulmonary slow-release system containing carbenoxolone. Carbenoxolone-loaded biodegradable poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA) particles were fabricated, optimized, and characterized. The drug carrier was designed to localize drug activity in the lung, and enable the steady and continuous release of the drug. Repurposing and reformulating carbenoxolone to prevent lung metastases, offer a promising direction for clinical use. In a recently published study [
7], we showed that combined treatment of carbenoxolone with Bevacizumab (Avastin), an anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) drug, prolonged the efficacy of the drug and resulted in a significantly lower tumor volume. The method of drug delivery, as presented in the current study may be extended to include different drug combinations and to serve as a platform for simultaneously treating and preventing cancer progression.
3. Discussion
Metastases are responsible for over 90% of cancer-related deaths, therefore is an important target for cancer therapy [
15]. There is currently no available standard preventative treatment, and first-line therapy is commonly non-selective broad cytotoxic chemotherapy. Optimal prophylactic therapy would require a high safety profile and targeted non-invasive administration, to provide low systematic exposure over time that would maintain drug efficacy with minimal toxicity.
In a recently published study, we showed that carbenoxolone possesses anti-cancer properties mediated by its antagonistic effect on HMGB1, as demonstrated in mice that were pre-treated with the drug [
8]. This activity is highly relevant to the lungs, as this tissue expresses exceptionally high basal levels of RAGE, the receptor for HMGB1 [
10]. The rationale of using pre-treatment is based on our former observation of carbenoxolone to reduce tumor colonization in the lung via the reduction of ICAM1 [
8]. This finding suggests a possible clinical scenario in which carbenoxolone treatment can be prescribed as a prophylactic treatment to reduce the metastatic burden immediately after a diagnosis of a primary tumor with susceptibility to spreading into the lungs.
Carbenoxolone is known to provoke fluid retention, one of its dose-related side-effects and the main reason for its limited prescription [
16,
17]. To achieve the maximal therapeutic effect, together with minimal side-effects, carbenoxolone is usually given at a dose of 100 mg three times daily for one week, followed by 50 mg three times daily for up to 12 weeks. The lower dose provokes fewer side-effects but also provides a lesser effect [
11].
In addition to sodium retention and hypokalemia [
12], increased levels of carbenoxolone in the serum have been shown to be correlated with a drop in the levels of potassium in the blood, which could increase blood pressure and promote edema [
13]. As expected, patient age was found to be associated with side-effects. This was attributed to the decreased rates of plasma clearance in elderly patients [
18]. Therefore, elderly patients and patients with renal or liver diseases are prescribed lower than usual dosages [
11].
The equivalent dose of 40 mg/kg was selected in our study based on previous experiments which identified 60 mg/kg dose in mice as the maximum tolerated dose, leading to a >10% weight loss in nude mice [
8]. A dose of 50 mg/kg for 8 days with the free drug was less toxic, showing 6% of weight loss compared with 3% weight gain in the control mice (
Table S3). Further in-depth toxicity studies should be performed in the future.
To provide locally targeted treatment, rather than a systemic treatment, we propose introducing carbenoxolone in a pulmonary targeting formulation, as this easier application could increase patient compliance [
19]. In mice, biodegradable poly(sebacic anhydride) (poly(SA)) particles [
20] and siRNA particles (siNS1) [
21] were shown to penetrate the lung after intranasal delivery. In humans, the design can be further optimized to target the lungs, since both particle size and density affect the deposition of particles in this tissue [
22,
23]. Previous publications demonstrated that to reach the smaller airways in the lung, small (micron range) particles should be used [
24]. The mechanism of these small particles is diffusion, as opposed to gravitation which is the mechanism of large particles [
19].
A common means of drug encapsulation in PLGA spheres is the solvent evaporation method, by which water-soluble or insoluble drugs can be encapsulated using water-in-oil-in-water (W/O/W) double emulsion [
25,
26]. PLGA is a biodegradable biocompatible copolymer of lactic and glycolic acids that can be fabricated into various shapes and sizes [
25,
27,
28] and is used in several FDA approved products [
27]. PLGA has been widely studied in controlled-release systems for small molecules, and also with peptides and hormones [
29,
30,
31]. First, we determined the stability of carbenoxolone in its free-form (
Figure 1), to further compare it with the presence of the drug post encapsulation.
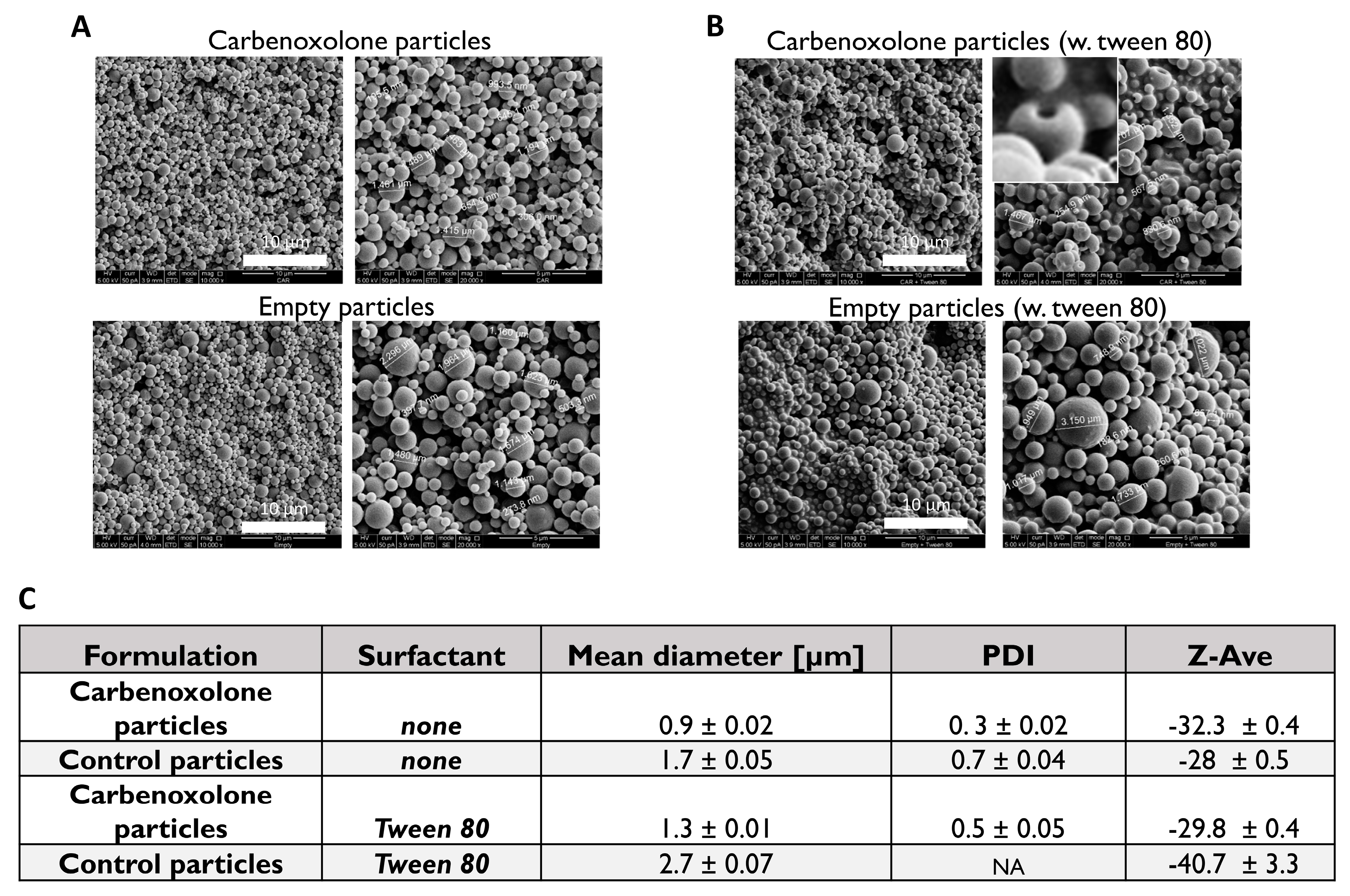
Characterization of carbenoxolone particles showed that Tween 80, which is usually added to stabilize the oil drops that disperse in the water, increased the size of the particles (
Figure 2C,
Figure S1); In the case of empty particles (no drug) with Tween 80, a diverse size distribution with no valid particle diameter (PDI) was obtained by DLS (
Figure S1). SEM images revealed a spherical shape with a ‘hollow-like’ core only in the presence of the drug. Interestingly, this morphological defect was not observed when fabricating the drug-free particles with Tween 80 (polyoxyethylene sorbitan monooleate 80), nor was it detected in our Tween 80-free formulations. A similar phenomenon was reported in PLGA particles fabricated with various surfactants encapsulated with insulin [
32], but in that case, the cause was the addition of Span 80 (sorbitan monooleate 80), which is of a low hydrophilic-lipophilic balance (HLB) and is usually added to stabilize the water-in-oil (W/O) emulsion. There the phenomenon was attributed to the migration of the drug aqueous solution droplets towards the outer aqueous phase in the process of emulsification, which was immediately stopped by the hardening of particles [
32,
33].
In our case, it is possible that the drug migrated from the non-stabilized water drops, through the polymer matrix, and to the outer water continuous phase, followed by rapid hardening of the matrix by evaporation. The relatively high loading capacity (~60%) is typical for PLGA microspheres. The cumulative release kinetic profile showed a burst release in the first 5 h, followed by a zero-order release up to day 4, and subsequently by a plateau resulting from complete depletion of the drug (
Figure 1C). (For calculations see
Appendix A).
To validate the efficacy of the encapsulated drug in-vitro, we performed a bioassay of anoikis, which is increased upon carbenoxolone treatment, as we previously demonstrated in LLC cells [
8]. In another study, human thyroid cancer cells that were exposed to a high dose of carbenoxolone (up to 50 µM) were also shown to increase susceptibility to anoikis, which was attributed to the loss of gap junctions [
34]. Moreover, patient-derived glioblastoma cells showed increased sensitivity to anoikis when treated with carbenoxolone [
35]. In the encapsulated form, carbenoxolone maintains its activity suggesting that at a low dosage, as in our slow-release particles, the drug provides sufficient efficacy (
Figure 3). The effect we detected with 100 μg/mL particles (~0.5 μM) of the encapsulated drug was similar to that of 0.1 μM with the free drug as previously shown (22% (
Figure 3) and 37% [
8] respectively). This could be attributed to the slow release of the drug in the encapsulated form and the lower availability of loaded drug after 72 h in this assay (only ~80% is released after 72 h in complete hydration). Moreover, it is common for encapsulated drugs to require higher dosage in-vitro, compared with the free form, to be more efficient in-vivo as was previously shown [
26]. Since cell death in circulation is one of the pivotal stages in the metastatic multi-step process, the ability of the drug to reduce floating cell survival is of great clinical relevance.
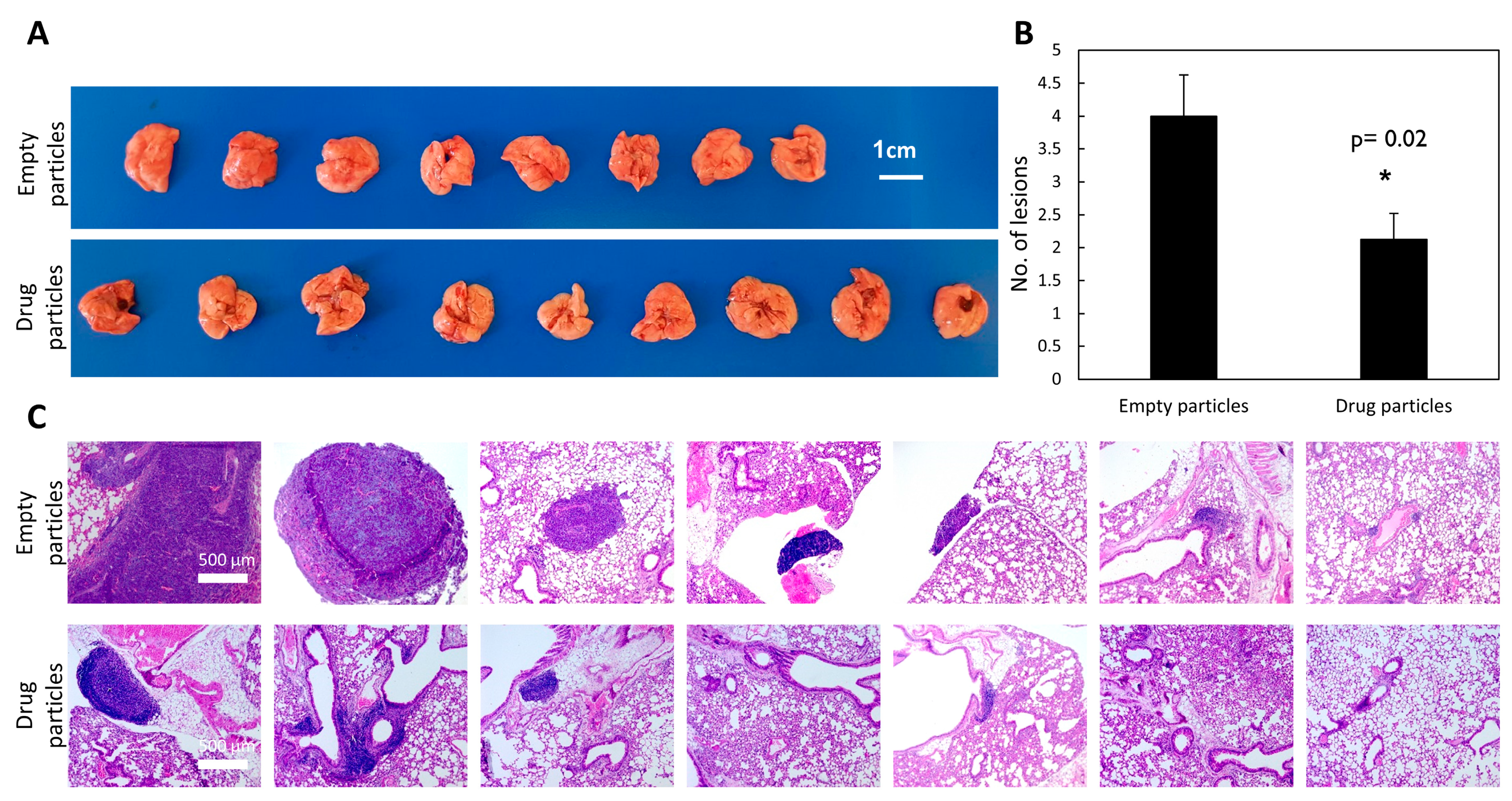
To evaluate the efficacy of carbenoxolone particles in preventing lung metastases, we utilized the tail-vein injection model, which is commonly used in studies of metastatic formation [
36,
37]. This model monitors the ability of cancer cells to circulate and colonize in the lungs, as the cells are injected directly into the circular system. We previously showed that pre-treating mice with carbenoxolone 5 days prior to LLC injections, followed by intraperitoneal (IP) administration of the encapsulated drug, 40 mg/kg every other day over 25 days, resulted in 48% less metastatic formation in the lungs compared with the control group [
8]. Moreover, the lesions formed were smaller than those found in the untreated group. These studies showed that the drug has impaired the cells’ adherence to the lung tissue, thereby reducing the formation of metastatic lesions. Here, we recapitulated this experiment, but instead of using free carbenoxolone, we introduced a single systemic administration of slow-release drug-loaded particles of 40 mg/kg carbenoxolone. The drug-loaded particles maintain drug efficacy in-vivo, as demonstrated by thereduction in the number and size of metastatic lung lesions (
Figure 4).
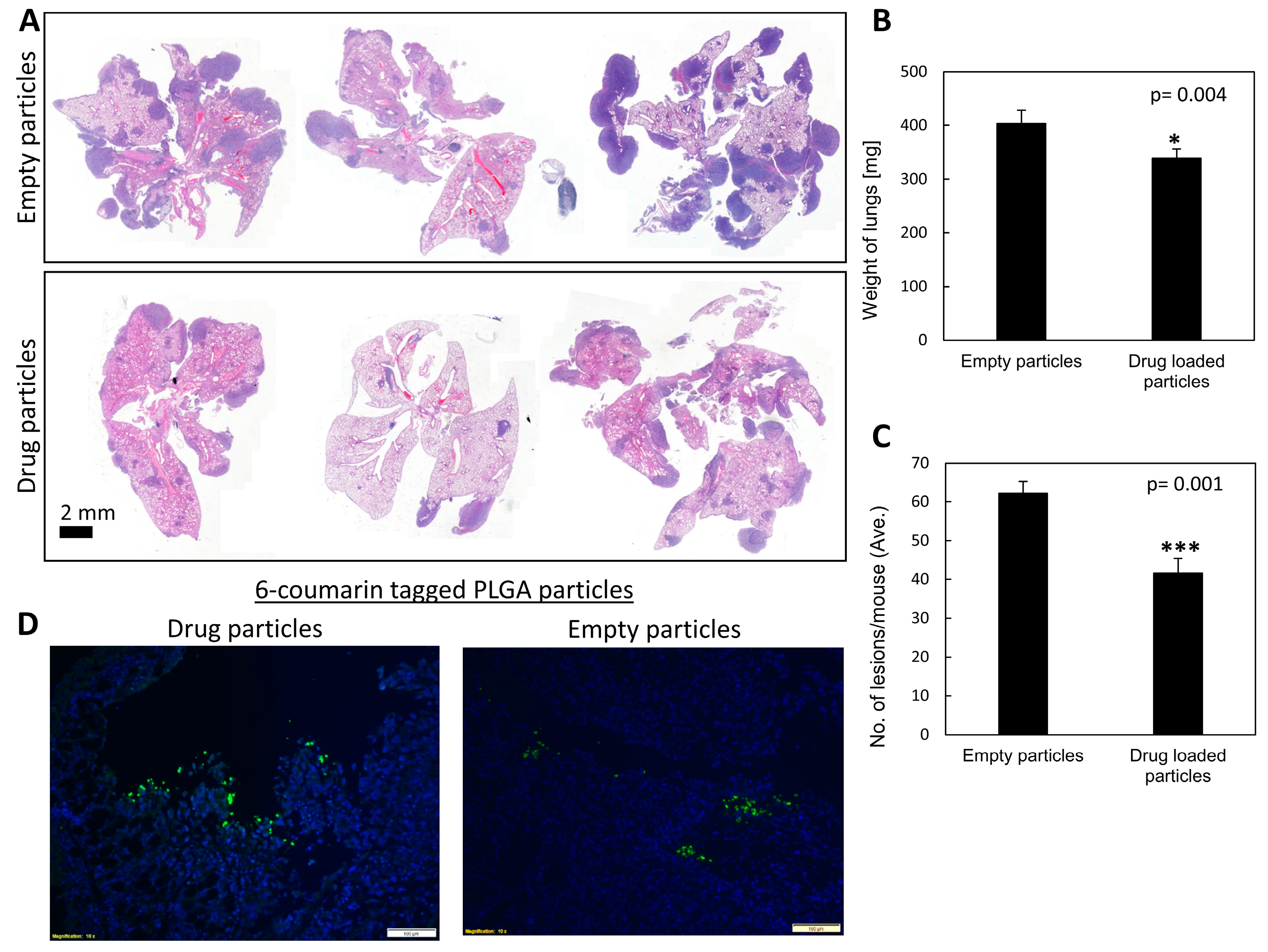
To provide a proof of concept of targeting carbenoxolone treatment to the pulmonary tissue, we delivered the particles also via intranasal administration. A single intranasal treatment of a fixed dose of 1 mg/mouse encapsulated carbenoxolone was administered 5 days prior to IV injections of LLC cells. We found this concentration safe in intranasal administration, as higher concentrations were more viscous and posed a risk for accidental suffocation of the mice. While all treated mice were alive on day 20, two of the controlled mice died at day 19. Gross pathology of these mice revealed detectable metastatic lesions in the lungs, which could explain their death. Images show that 6-coumarin tagged particles were detected clearly in the lungs of the mice as long as 20 days post drug-encapsulated particle administration (
Figure 5D). These findings are in agreement with other studies showing the respiratory tract to be successfully used to deliver particles to the lungs [
20,
21,
38]. The efficacy of the slowly released particles was high, as indicated by the lower number and smaller size of metastatic lesions in the lungs of mice compared with both control groups (
Figure 5A,
Tables S1 and S2).
In our previous study, the free drug was administered using different LLC in-vivo models; subcutaneous, orthotropic, tail vein and resection, where a repeated administration of the drug was required [
8]. Interestingly, we can determine that the encapsulated drug, whether administered IV or intranasally, required a considerably lower dose (<×10) using a single pre-treatment, and resulted with a similar effect to that of repeated dosage of the free drug in our previous study [
8].
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Stability of Carbenoxolone in Water
The stability of free carbenoxolone in double distilled water was assessed using the calibration of HPLC (System Gold Microbore, Beckman Coulter). Carbenoxolone released fractions were analyzed with Kinetex 5u EVO Column C18, 150 × 3.9 mm. The mobile phase was acetone: PBS 40:60, and the flow rate was 1 mL per minute. The temperature was set to 20 °C and detection was at 254 nm. Elution time was 1.5–1.6 s (
Figure 1A).
4.2. Preparation of Drug-Loaded Particles
To fabricate drug encapsulated particles with a mean diameter of ~1 micron, which would be compatible for inhalation, we used two distinct W/O/W formulations of PLGA (50:50, capped, Mw 24,000–38,000), either with or without Tween 80 (HLB = 15) [
39] as a stabilizer. Carbenoxolone drug-loaded particles were prepared as previously described [
26,
40,
41]. In short, 100 mg PLGA (Sigma-Aldrich, Cat. No. 739952) with 50:50 lactic-to-glycolic acid ratio were dissolved in 2 mL dichloromethane. A solution of carbenoxolone in PBS (140 mg/mL) was added (200 μL) to the dissolved polymer, and the mixture was homogenized using WiseTis Homogenize (type HG-15D, Witeg, Germany) for 1 min on ice, leading to the formation of the primary emulsion W/O. PVA (Poly-vinyl alcohol) 5%
w/v of ~67 kDa (Sigma-Aldrich, Cat. No. 81383), saturated in dichloromethane (4 mL), was rapidly added to the emulsion, and the solution was again homogenized. The primary emulsion was then emulsified into 50 mL of 2.5%
w/v aqueous solution of PVA. The resulting multiple W/O/W was mixed for 5 min, and 2.5 mL of cold isopropanol was added to the W/O/W double emulsion. After 60 min of extensive stirring, the particles were centrifuged and washed three times. After the final wash, the particles were lyophilized (Freezone 6 plus, Labconco, Kansas City, MO, USA) for 48 h, resulting in a fine powder of dry PLGA particles loaded with carbenoxolone. For the preparation of the particles with the surfactant, 4%
v/v Tween 80 (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Cat. No. BP338-500) was added after the addition of the drug. Empty particles were prepared in the same way, without carbenoxolone. (A more detailed protocol can be found in the
Supplementary section). The average yield of particle batch was ~86%
w/w.
4.3. Particle Characterization
The particle samples were imaged and examined SEM (FEI Quanta 200 microscope). A small amount of the sample was spread onto a conductive adhesive carbon tape attached to an SEM grid. A thin film of Pd/Au coating was sputtered onto the sample (SC7620 Sputter coater, UK). The mean diameter of the particles was calculated based on measurements of 30 randomly chosen particles. Size and charge of particles were analyzed using DLS/Zeta sizer nano series (Malvern Instruments, Malvern, UK) at 25 °C in DTS1070 disposable capillary cells. One mL of each sample in 100 µg/mL was injected to measure the size and the zeta potential.
4.4. Drug Loading and Release Kinetics
To study the kinetic release of carbenoxolone, we performed dissolution tests as follows: drug-loaded particles (10 mg) were incubated with 1 mL PBS pH = 7.4. The release assay was performed in PBS containing 0.1% solutol-HS15, for particle dispersity. The solution was sampled every 24 h, over the course of 120 h, and analyzed for carbenoxolone concentration using HPLC, after which a cumulative release graph was plotted. Carbenoxolone was detected as a peak at 1.5 min, with 40% acetonitrile in PBS at the mobile phase. The flow rate was 1 mL per minute and the detection monitored at 254 nm wavelength (
Figure 1B,C).
4.5. Anoikis Assay
Carbenoxolone was previously shown to increase the susceptibility of cells through the induction of apoptosis under non-adherent conditions, i.e., anoikis using poly(2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate) (p-HEMA) coated plates (Sigma-Aldrich, Cat. No. P3932). To evaluate the activity of drug-loaded particles, the same bioassay was applied. Briefly, a solution containing 20 mg/mL p-HEMA in 95% ethanol was prepared and left at room temperature to dissolve for 48 h. Once dissolved, the solution was pipetted into 6-well culture plates. The plates were left half covered in a sterile environment on a rocking plate until the ethanol evaporated and the p-HEMA solidified, coating the plates evenly. The plates were then washed twice with PBS to remove any possible traces of ethanol. Each plate was incubated with growth media containing either empty or carbenoxolone-loaded particles at a concentration of 100 µg/mL. All the plates were seeded with 50,000 LLC cells/well and incubated for 72 h at 37 °C. Cell viability was measured using WST-8 (Sigma-Aldrich, Cat. No. 96992) according to the manufacturer’s protocol, and the cells were incubated at 37 °C for 90 min. Absorbance was measured at 450 nm using a plate reader (Wallac 1420 VICTOR plate-reader, Perkin-Elmer Life Sciences, Waltham, MA, USA) and bright-field images were obtained using an Olympus IX-73 microscope.
4.6. Tail Vein In-Vivo Model
Eight-week-old C57BL/6J mice (Harlan, Rehovot, Israel) were pretreated IV with either carbenoxolone loaded particles or control particles of the non-surfactant preparation, 8 mice per group. On the 5th day, all mice have been injected IV with 1 × 10
6 LLC-GFP cells in 100 μL PBS. The endpoint was set as 21 days after treatment initiation, and all mice were then sacrificed, as in our previously published work [
8]. Lung tissue was harvested, weighed, and left in 4% formalin overnight for fixation. Lungs were then transferred to 80% ethanol and a histological serial section was performed. H&E staining of histological sections enabled lesion counting. Images of lungs were taken using a light microscope (Zeiss), and the total number of lesions per slide was counted.
4.7. Intranasal In-Vivo Model
To direct the particles to the lungs of the mice, we used an intranasal delivery of suspended particles. Eight-week-old C57BL/6J mice (Harlan, Israel) were pretreated with carbenoxolone loaded particles, empty particles as a control treatment, or PBS as an additional control. Treatment was administered intranasally by applying 50 µL of a 20 mg/mL solution (equivalent to 25 mg/kg). On the 5th day, all mice have been injected IV with 1 × 10
6 LLC cells in 100 µL PBS. On day 19, two mice of the two untreated control groups died at which point all the mice were sacrificed. The lungs were harvested, weighed, and fixed in 4% formalin overnight, followed by histological analysis, as detailed in the tail vein experiment (For more details please see
Appendix B).
4.8. Lung Biodistribution Study Using Fluorescently Labeled PLGA Particles
To detect pulmonary localization of carbenoxolone PLGA particles following intranasal administration, particles were co-loaded with 6-coumarin, enabling fluorescent imaging. For detection of 6-coumarin particles in the lungs, paraffin-fixed lung sections (as detailed above) were stained with DAPI and imaged using an inverted fluorescent microscope. Non-labeled PLGA particles served as a control to set a fluorescence baseline (Olympus IX73).
4.9. Statistical Analysis
In-vitro data are presented as means ± SD, whereas in-vivo data are presented as means ± SE. Differences in cell viability, the number of lesions, and lung weight were assessed using the unpaired two-tailed Student’s t-test, and p < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
4.10. Ethical Approval
All institutional and national guidelines for the care and use of laboratory animals were followed and protocols were approved by the Hebrew University Ein Kerem Medical School IACUC (protocol MD-16-14648-5).
4.11. Cell Culture
All cell lines were characterized and purchased from ATCC. Cells were used for experiments up to p20 and were Mycoplasma free, using EZ-PCR Mycoplasma Test Kit (Biological Industries, catalog number 2070020).