Dual Targeting of Y-Box Binding Protein-1 and Akt Inhibits Proliferation and Enhances the Chemosensitivity of Colorectal Cancer Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Mutation in KRAS Gene Diminishes the Antiproliferative Effect of Cetuximab in CRC Cells
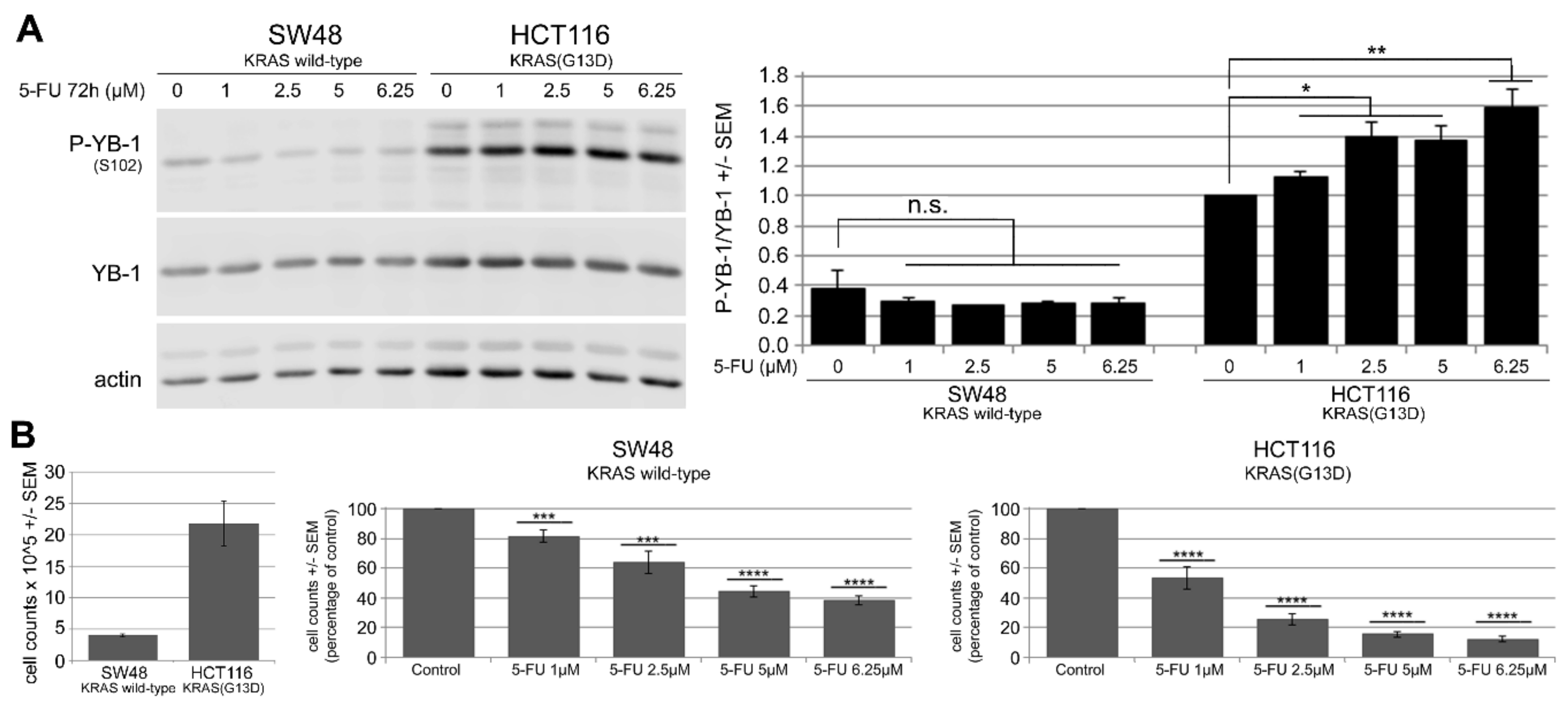
2.2. 5-FU Induces YB-1 Phosphorylation at S102 in KRAS(G13D)-Mutated HCT116 Cells but Not in KRAS Wild-Type SW48 Cells
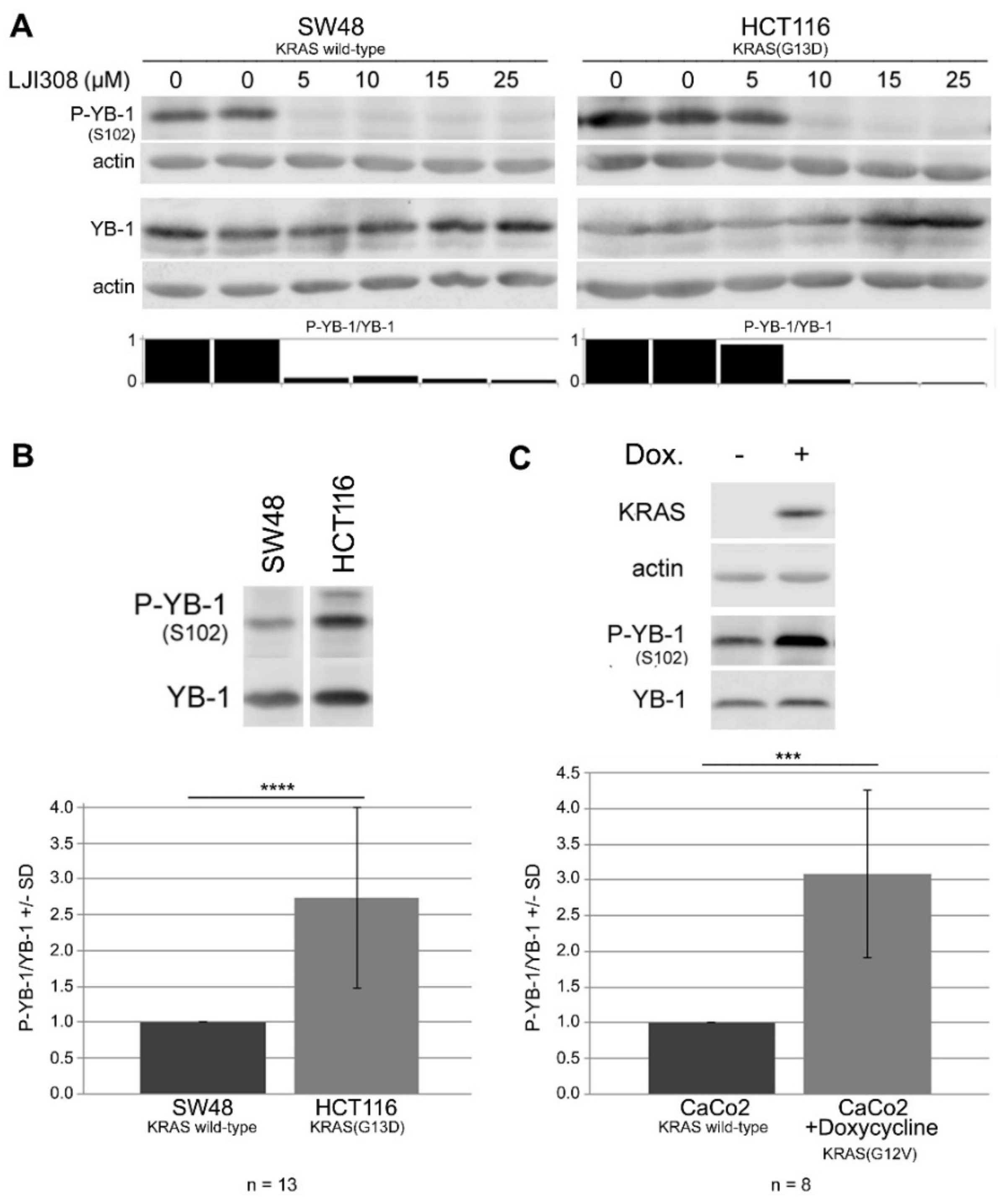
2.3. Targeting RSK by LJI308 Inhibits Phosphorylation of YB-1 at S102 in CRC Cells
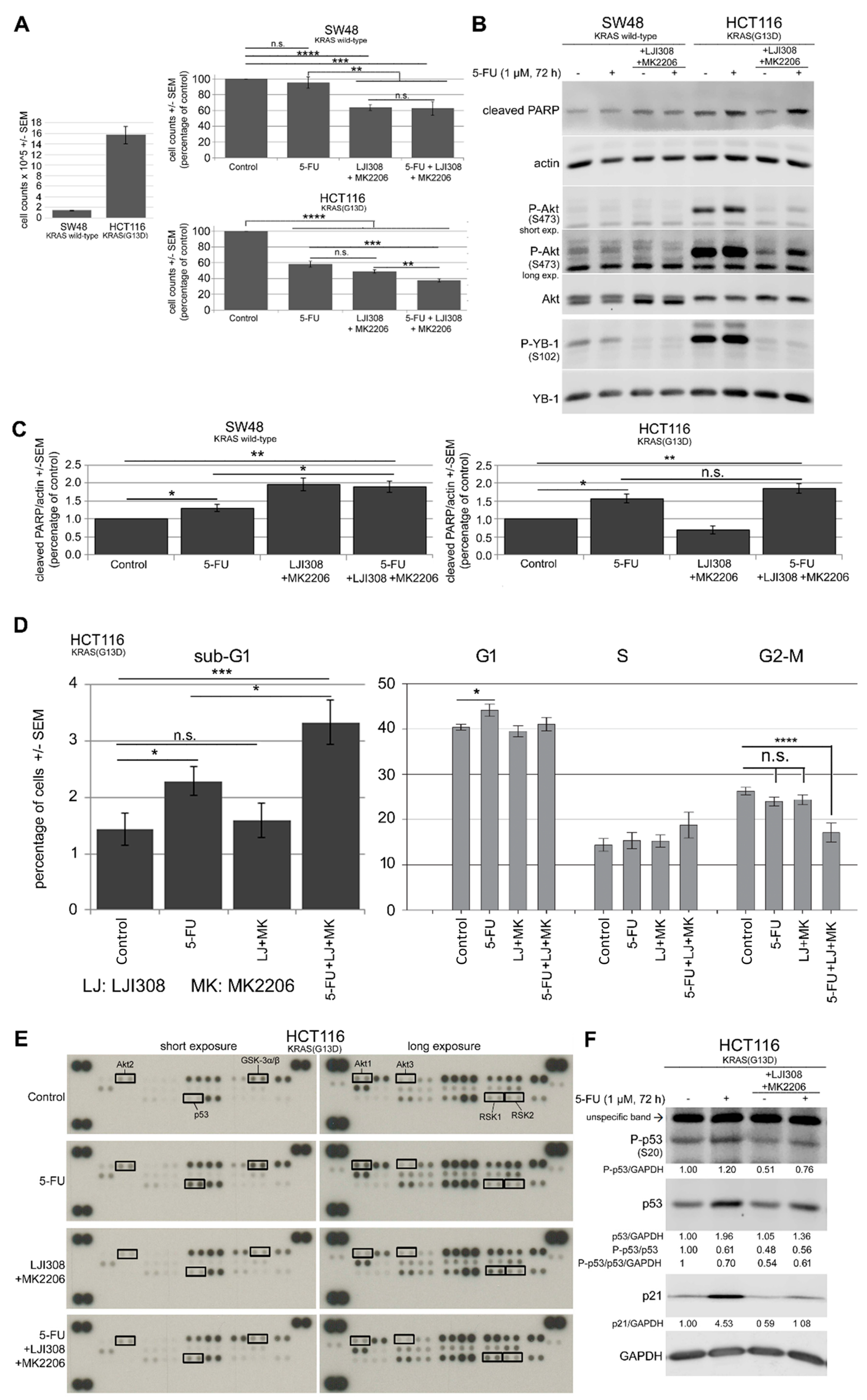
2.4. Upregulation of Akt after RSK Targeting Interferes with the Antiproliferative Effect of the LJI308 RSK Inhibitor
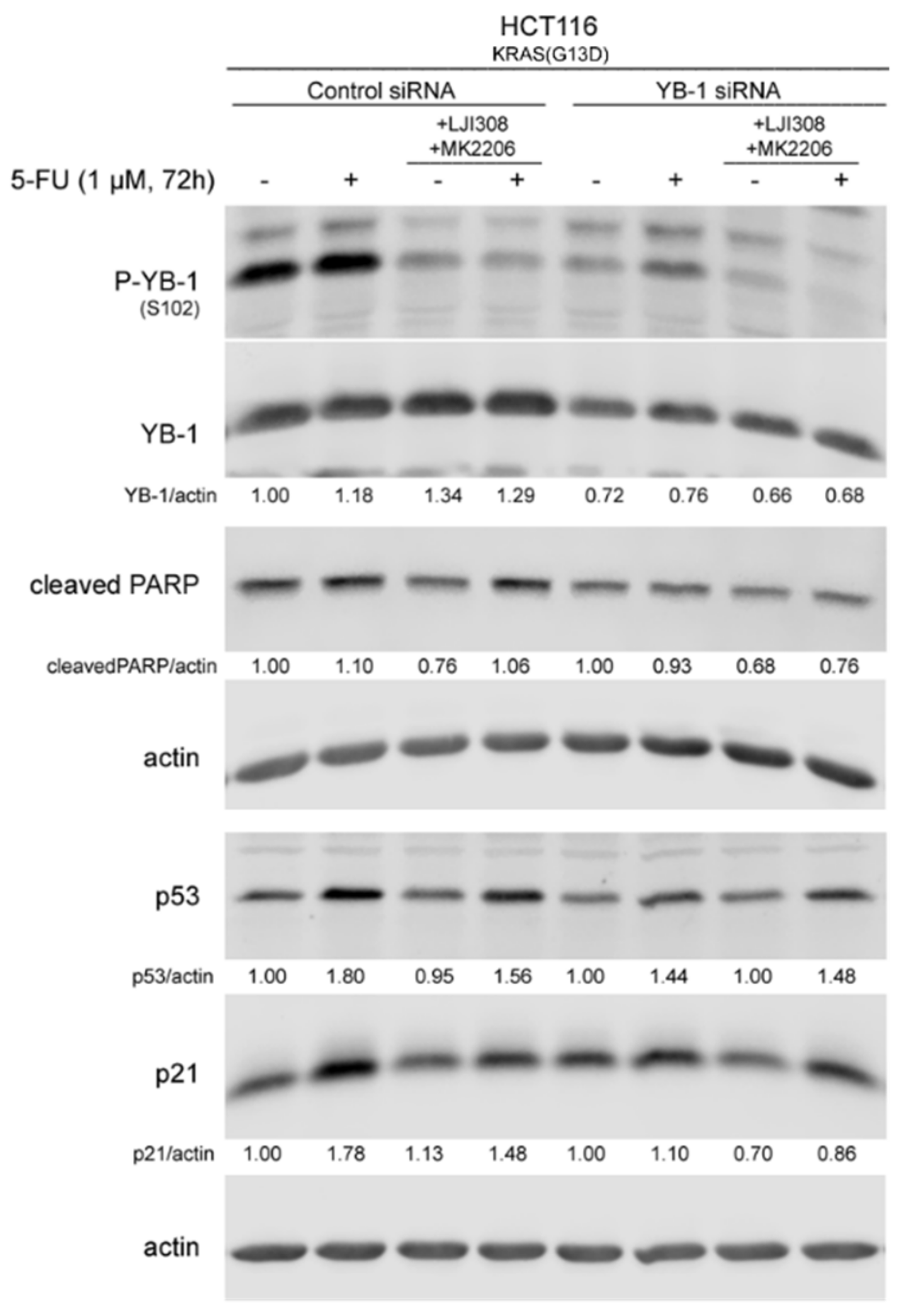
2.5. Dual Targeting of the RSK/YB-1 Pathway and Akt Enhances the Antiproliferative Effect of 5-FU in KRAS(G13D)-Mutated HCT116 Cells but Not in KRAS Wild-Type SW48 Cells by Stimulating Apoptosis
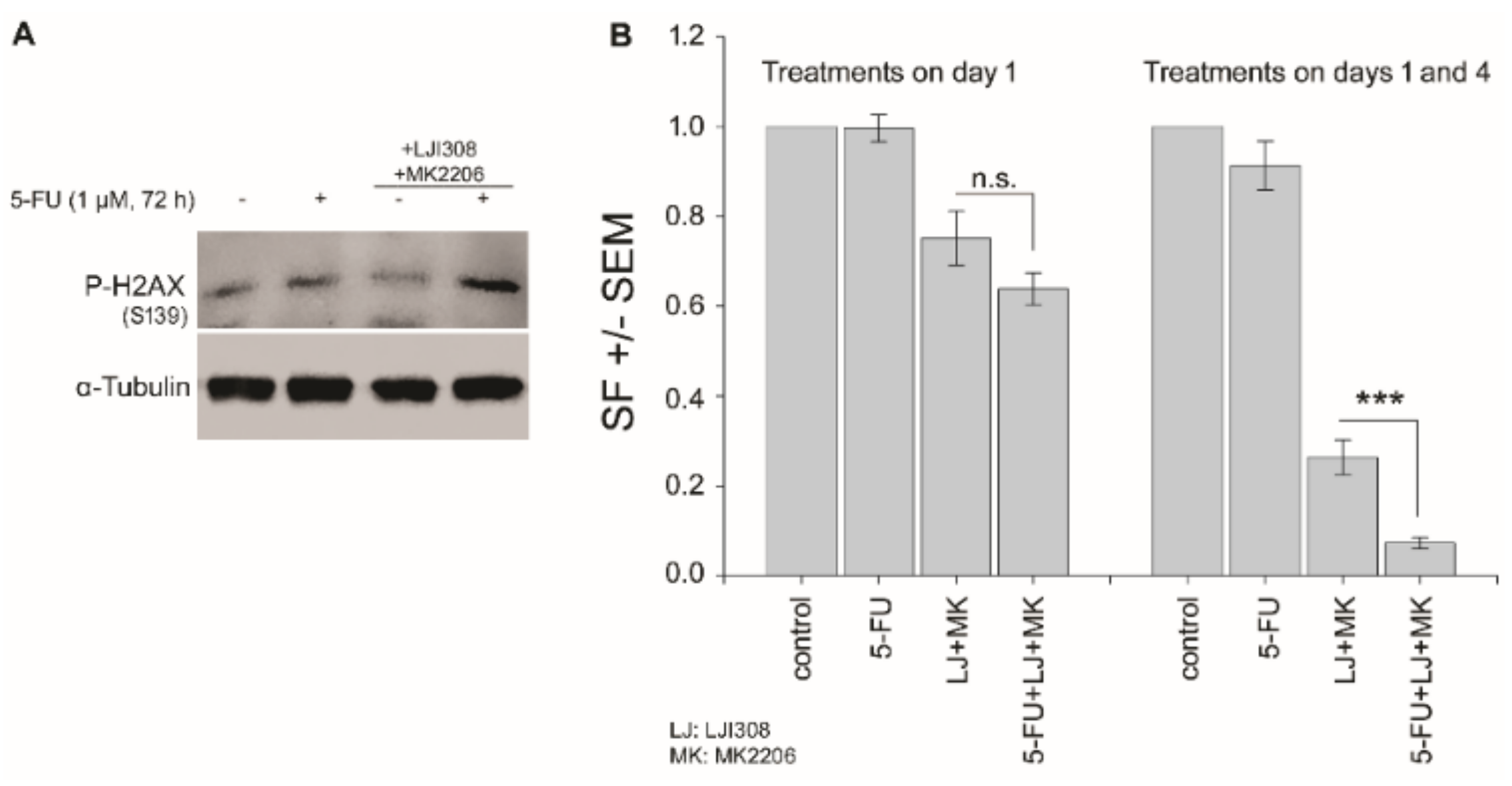
2.6. Dual Targeting of the RSK/YB-1 Pathway and Akt Enhances the Clonogenic Inactivation by 5-FU in KRAS(G13D)-Mutated HCT116 Cells
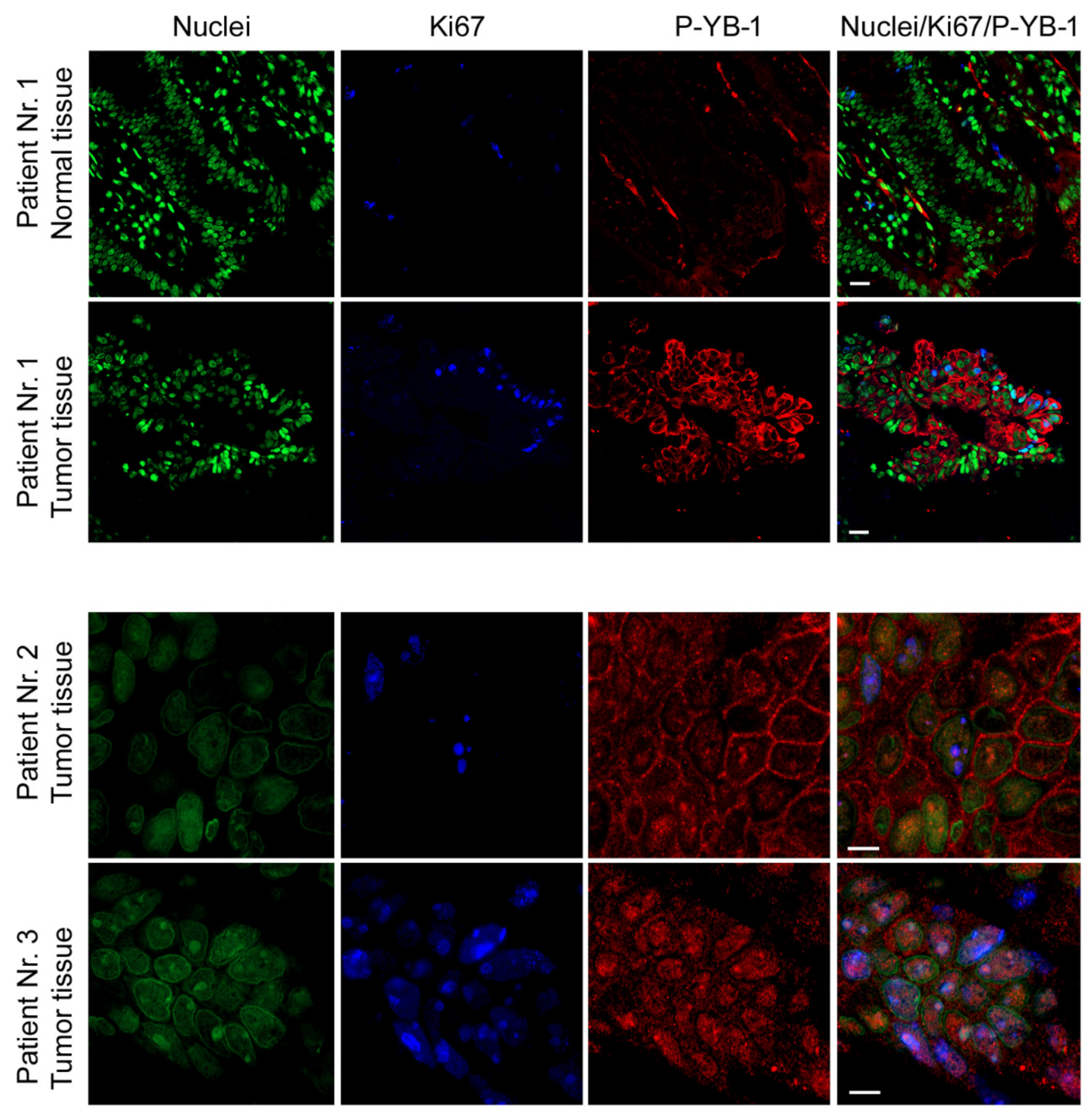
2.7. YB-1 Is Highly Phosphorylated in CRC Patient Tumor Tissues
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Lines
4.2. Antibodies and Reagents
4.3. Western Blotting
4.4. Proliferation Assay
4.5. Cell Cycle Analysis
4.6. Human Phospho-MAPK Array
4.7. Clonogenic Assay
4.8. Transfection with siRNA
4.9. Immunofluorescence Analysis
4.10. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Torre, L.A.; Bray, F.; Siegel, R.L.; Ferlay, J.; Lortet-Tieulent, J.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2015, 65, 87–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuipers, E.J.; Grady, W.M.; Lieberman, D.; Seufferlein, T.; Sung, J.J.; Boelens, P.G.; van de Velde, C.J.; Watanabe, T. Colorectal cancer. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2015, 1, 15065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fakih, M.G. Metastatic colorectal cancer: Current state and future directions. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 1809–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Fiore, F.; Blanchard, F.; Charbonnier, F.; Le Pessot, F.; Lamy, A.; Galais, M.P.; Bastit, L.; Killian, A.; Sesboue, R.; Tuech, J.J.; et al. Clinical relevance of KRAS mutation detection in metastatic colorectal cancer treated by Cetuximab plus chemotherapy. Br. J. Cancer 2007, 96, 1166–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lievre, A.; Bachet, J.B.; Boige, V.; Cayre, A.; Le Corre, D.; Buc, E.; Ychou, M.; Bouche, O.; Landi, B.; Louvet, C.; et al. KRAS mutations as an independent prognostic factor in patients with advanced colorectal cancer treated with cetuximab. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 26, 374–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karapetis, C.S.; Khambata-Ford, S.; Jonker, D.J.; O’Callaghan, C.J.; Tu, D.; Tebbutt, N.C.; Simes, R.J.; Chalchal, H.; Shapiro, J.D.; Robitaille, S.; et al. K-ras mutations and benefit from cetuximab in advanced colorectal cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 1757–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vecchione, L.; Jacobs, B.; Normanno, N.; Ciardiello, F.; Tejpar, S. EGFR-targeted therapy. Exp. Cell Res. 2011, 317, 2765–2771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allegra, C.J.; Jessup, J.M.; Somerfield, M.R.; Hamilton, S.R.; Hammond, E.H.; Hayes, D.F.; McAllister, P.K.; Morton, R.F.; Schilsky, R.L. American Society of Clinical Oncology provisional clinical opinion: Testing for KRAS gene mutations in patients with metastatic colorectal carcinoma to predict response to anti-epidermal growth factor receptor monoclonal antibody therapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 2091–2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Roock, W.; Claes, B.; Bernasconi, D.; De Schutter, J.; Biesmans, B.; Fountzilas, G.; Kalogeras, K.T.; Kotoula, V.; Papamichael, D.; Laurent-Puig, P.; et al. Effects of KRAS, BRAF, NRAS, and PIK3CA mutations on the efficacy of cetuximab plus chemotherapy in chemotherapy-refractory metastatic colorectal cancer: A retrospective consortium analysis. Lancet Oncol. 2010, 11, 753–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallagher, D.J.; Kemeny, N. Metastatic colorectal cancer: From improved survival to potential cure. Oncology 2010, 78, 237–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldberg, R.M.; Sargent, D.J.; Morton, R.F.; Fuchs, C.S.; Ramanathan, R.K.; Williamson, S.K.; Findlay, B.P.; Pitot, H.C.; Alberts, S.R. A randomized controlled trial of fluorouracil plus leucovorin, irinotecan, and oxaliplatin combinations in patients with previously untreated metastatic colorectal cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2004, 22, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasham, A.; Woolley, A.G.; Dunn, S.E.; Braithwaite, A.W. YB-1: Oncoprotein, prognostic marker and therapeutic target? Biochem. J. 2013, 449, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyabin, D.N.; Eliseeva, I.A.; Ovchinnikov, L.P. YB-1 protein: Functions and regulation. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. RNA 2014, 5, 95–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosnopfel, C.; Sinnberg, T.; Schittek, B. Y-box binding protein 1--a prognostic marker and target in tumour therapy. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 2014, 93, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, E.R.; Selyutina, A.A.; Buldakov, I.A.; Evdokimova, V.; Ovchinnikov, L.P.; Sorokin, A.V. The proteolytic YB-1 fragment interacts with DNA repair machinery and enhances survival during DNA damaging stress. Cell Cycle 2013, 12, 3791–3803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alemasova, E.E.; Moor, N.A.; Naumenko, K.N.; Kutuzov, M.M.; Sukhanova, M.V.; Pestryakov, P.E.; Lavrik, O.I. Y-box-binding protein 1 as a non-canonical factor of base excision repair. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2016, 1864, 1631–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.W.; Mai, R.T.; Fang, W.H.; Lin, C.C.; Chiu, C.C.; Lee, Y.W. YB-1 disrupts mismatch repair complex formation, interferes with MutSalpha recruitment on mismatch and inhibits mismatch repair through interacting with PCNA. Oncogene 2014, 33, 5065–5077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhao, P.W.; Feng, G.; Xie, G.; Wang, A.Q.; Yang, Y.H.; Wang, D.; Du, X.B. The expression level and prognostic value of Y-box binding protein-1 in rectal cancer. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0119385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Yan, L.; Zhou, J.; Liu, S.; Shan, Z.; Jiang, C.; Tian, Y.; Jin, Z. High expression of Y-box-binding protein 1 is associated with local recurrence and predicts poor outcome in patients with colorectal cancer. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2014, 7, 8715–8723. [Google Scholar]
- Shiraiwa, S.; Kinugasa, T.; Kawahara, A.; Mizobe, T.; Ohchi, T.; Yuge, K.; Fujino, S.; Katagiri, M.; Shimomura, S.; Tajiri, K.; et al. Nuclear Y-Box-binding Protein-1 Expression Predicts Poor Clinical Outcome in Stage III Colorectal Cancer. Anticancer Res. 2016, 36, 3781–3788. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, C.; Ma, Y.; Yong, L.; Yang, C.; Wang, P.; Liu, X.; Zhu, B.; Zhou, H.; Liu, X.; Liu, Z. Y-box binding protein-1 promotes tumorigenesis and progression via the epidermal growth factor receptor/AKT pathway in spinal chordoma. Cancer Sci. 2019, 110, 166–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosnopfel, C.; Sinnberg, T.; Sauer, B.; Busch, C.; Niessner, H.; Schmitt, A.; Forchhammer, S.; Grimmel, C.; Mertens, P.R.; Hailfinger, S.; et al. YB-1 Expression and Phosphorylation Regulate Tumorigenicity and Invasiveness in Melanoma by Influencing EMT. Mol. Cancer Res. 2018, 16, 1149–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, T.; Zhao, S.; Wang, P.; Xue, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, M.; Li, N.; Li, Z.; Xu, L.; Jiang, L.; et al. YB-1 regulates tumor growth by promoting MACC1/c-Met pathway in human lung adenocarcinoma. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 48110–48125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurya, P.K.; Mishra, A.; Yadav, B.S.; Singh, S.; Kumar, P.; Chaudhary, A.; Srivastava, S.; Murugesan, S.N.; Mani, A. Role of Y Box Protein-1 in cancer: As potential biomarker and novel therapeutic target. J. Cancer 2017, 8, 1900–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Sun, R.; Chi, Z.; Li, S.; Hao, L. Silencing of Y-box binding protein-1 by RNA interference inhibits proliferation, invasion, and metastasis, and enhances sensitivity to cisplatin through NF-kappaB signaling pathway in human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2017, 433, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamashita, T.; Higashi, M.; Momose, S.; Morozumi, M.; Tamaru, J.I. Nuclear expression of Y box binding-1 is important for resistance to chemotherapy including gemcitabine in TP53-mutated bladder cancer. Int. J. Oncol. 2017, 51, 579–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, U.; Bergmann, S.; Scheffer, G.L.; Scheper, R.J.; Royer, H.D.; Schlag, P.M.; Walther, W. YB-1 facilitates basal and 5-fluorouracil-inducible expression of the human major vault protein (MVP) gene. Oncogene 2005, 24, 3606–3618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Stratford, A.L.; Fry, C.J.; Desilets, C.; Davies, A.H.; Cho, Y.Y.; Li, Y.; Dong, Z.; Berquin, I.M.; Roux, P.P.; Dunn, S.E. Y-box binding protein-1 serine 102 is a downstream target of p90 ribosomal S6 kinase in basal-like breast cancer cells. Breast Cancer Res. 2008, 10, R99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, A.; Rebholz, S.; Maier, E.; Dehghan Harati, M.; Zips, D.; Sers, C.; Rodemann, H.P.; Toulany, M. Stress-Induced Phosphorylation of Nuclear YB-1 Depends on Nuclear Trafficking of p90 Ribosomal S6 Kinase. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toulany, M.; Schickfluss, T.A.; Eicheler, W.; Kehlbach, R.; Schittek, B.; Rodemann, H.P. Impact of oncogenic K-RAS on YB-1 phosphorylation induced by ionizing radiation. Breast Cancer Res. 2011, 13, R28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aronchik, I.; Appleton, B.A.; Basham, S.E.; Crawford, K.; Del Rosario, M.; Doyle, L.V.; Estacio, W.F.; Lan, J.; Lindvall, M.K.; Luu, C.A.; et al. Novel potent and selective inhibitors of p90 ribosomal S6 kinase reveal the heterogeneity of RSK function in MAPK-driven cancers. Mol. Cancer Res. 2014, 12, 803–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, A.H.; Reipas, K.; Hu, K.; Berns, R.; Firmino, N.; Stratford, A.L.; Dunn, S.E. Inhibition of RSK with the novel small-molecule inhibitor LJI308 overcomes chemoresistance by eliminating cancer stem cells. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 20570–20577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossner, F.; Gieseler, C.; Morkel, M.; Royer, H.D.; Rivera, M.; Blaker, H.; Dietel, M.; Schafer, R.; Sers, C. Uncoupling of EGFR-RAS signaling and nuclear localization of YBX1 in colorectal cancer. Oncogenesis 2016, 5, e187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutherland, B.W.; Kucab, J.; Wu, J.; Lee, C.; Cheang, M.C.; Yorida, E.; Turbin, D.; Dedhar, S.; Nelson, C.; Pollak, M.; et al. Akt phosphorylates the Y-box binding protein 1 at Ser102 located in the cold shock domain and affects the anchorage-independent growth of breast cancer cells. Oncogene 2005, 24, 4281–4292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendoza, M.C.; Er, E.E.; Blenis, J. The Ras-ERK and PI3K-mTOR pathways: Cross-talk and compensation. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2011, 36, 320–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turke, A.B.; Song, Y.; Costa, C.; Cook, R.; Arteaga, C.L.; Asara, J.M.; Engelman, J.A. MEK inhibition leads to PI3K/AKT activation by relieving a negative feedback on ERBB receptors. Cancer Res. 2012, 72, 3228–3237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Won, J.K.; Yang, H.W.; Shin, S.Y.; Lee, J.H.; Heo, W.D.; Cho, K.H. The crossregulation between ERK and PI3K signaling pathways determines the tumoricidal efficacy of MEK inhibitor. J. Mol. Cell Biol. 2012, 4, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, R.; Oren, M. p53; from inductive signal to cellular effect. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 1997, 7, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, K.M.; Phillips, A.C.; Vousden, K.H. Regulation and function of the p53 tumor suppressor protein. Curr. Opin. Cell. Biol. 2001, 13, 332–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napolitano, S.; Martini, G.; Rinaldi, B.; Martinelli, E.; Donniacuo, M.; Berrino, L.; Vitagliano, D.; Morgillo, F.; Barra, G.; De Palma, R.; et al. Primary and Acquired Resistance of Colorectal Cancer to Anti-EGFR Monoclonal Antibody Can Be Overcome by Combined Treatment of Regorafenib with Cetuximab. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 2975–2983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alamo, P.; Gallardo, A.; Di Nicolantonio, F.; Pavon, M.A.; Casanova, I.; Trias, M.; Mangues, M.A.; Lopez-Pousa, A.; Villaverde, A.; Vazquez, E.; et al. Higher metastatic efficiency of KRas G12V than KRas G13D in a colorectal cancer model. FASEB J. 2015, 29, 464–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cisowski, J.; Sayin, V.I.; Liu, M.; Karlsson, C.; Bergo, M.O. Oncogene-induced senescence underlies the mutual exclusive nature of oncogenic KRAS and BRAF. Oncogene 2016, 35, 1328–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, P.C.; Lin, P.C.; Wu, H.Y.; Lin, K.T.; Wu, C.; Bekaii-Saab, T.; Lin, Y.J.; Lee, C.T.; Lee, J.C.; Chen, C.S. Mutant KRAS promotes liver metastasis of colorectal cancer, in part, by upregulating the MEK-Sp1-DNMT1-miR-137-YB-1-IGF-IR signaling pathway. Oncogene 2018, 37, 3440–3455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stratford, A.L.; Reipas, K.; Hu, K.; Fotovati, A.; Brough, R.; Frankum, J.; Takhar, M.; Watson, P.; Ashworth, A.; Lord, C.J.; et al. Targeting p90 ribosomal S6 kinase eliminates tumor-initiating cells by inactivating Y-box binding protein-1 in triple-negative breast cancers. Stem Cells 2012, 30, 1338–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toulany, M. Targeting DNA Double-Strand Break Repair Pathways to Improve Radiotherapy Response. Genes (Basel) 2019, 10, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toulany, M.; Rodemann, H.P. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt signaling as a key mediator of tumor cell responsiveness to radiation. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2015, 35, 180–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moritz, A.; Li, Y.; Guo, A.; Villen, J.; Wang, Y.; MacNeill, J.; Kornhauser, J.; Sprott, K.; Zhou, J.; Possemato, A.; et al. Akt-RSK-S6 kinase signaling networks activated by oncogenic receptor tyrosine kinases. Sci. Signal. 2010, 3, ra64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotake, Y.; Arikawa, N.; Tahara, K.; Maru, H.; Naemura, M. Y-box Binding Protein 1 Is Involved in Regulating the G2/M Phase of the Cell Cycle. Anticancer Res. 2017, 37, 1603–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Longley, D.B.; Harkin, D.P.; Johnston, P.G. 5-fluorouracil: Mechanisms of action and clinical strategies. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2003, 3, 330–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wyatt, M.D.; Wilson, D.M., 3rd. Participation of DNA repair in the response to 5-fluorouracil. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2009, 66, 788–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaudreault, I.; Guay, D.; Lebel, M. YB-1 promotes strand separation in vitro of duplex DNA containing either mispaired bases or cisplatin modifications, exhibits endonucleolytic activities and binds several DNA repair proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, 316–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, E.J.; Kang, G.J.; Kang, J.I.; Boo, H.J.; Hyun, J.W.; Koh, Y.S.; Chang, W.Y.; Kim, Y.R.; Kwon, J.M.; Maeng, Y.H.; et al. Over-activation of AKT signaling leading to 5-Fluorouracil resistance in SNU-C5/5-FU cells. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 19911–19928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Zhang, B.; Chen, X.; Bae, S.; Singh, K.; Washington, M.K.; Datta, P.K. Loss of Smad4 in colorectal cancer induces resistance to 5-fluorouracil through activating Akt pathway. Br. J. Cancer 2014, 110, 946–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, H.; Zhao, K.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, J.; Xiao, J. YB-1 modulates the drug resistance of glioma cells by activation of MDM2/p53 pathway. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2019, 13, 317–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heumann, A.; Kaya, O.; Burdelski, C.; Hube-Magg, C.; Kluth, M.; Lang, D.S.; Simon, R.; Beyer, B.; Thederan, I.; Sauter, G.; et al. Up regulation and nuclear translocation of Y-box binding protein 1 (YB-1) is linked to poor prognosis in ERG-negative prostate cancer. Sci Rep. 2017, 7, 2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toulany, M.; Dittmann, K.; Baumann, M.; Rodemann, H.P. Radiosensitization of Ras-mutated human tumor cells in vitro by the specific EGF receptor antagonist BIBX1382BS. Radiother. Oncol. 2005, 74, 117–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toulany, M.; Kasten-Pisula, U.; Brammer, I.; Wang, S.; Chen, J.; Dittmann, K.; Baumann, M.; Dikomey, E.; Rodemann, H.P. Blockage of epidermal growth factor receptor-phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-AKT signaling increases radiosensitivity of K-RAS mutated human tumor cells in vitro by affecting DNA repair. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006, 12, 4119–4126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Maier, E.; Attenberger, F.; Tiwari, A.; Lettau, K.; Rebholz, S.; Fehrenbacher, B.; Schaller, M.; Gani, C.; Toulany, M. Dual Targeting of Y-Box Binding Protein-1 and Akt Inhibits Proliferation and Enhances the Chemosensitivity of Colorectal Cancer Cells. Cancers 2019, 11, 562. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11040562
Maier E, Attenberger F, Tiwari A, Lettau K, Rebholz S, Fehrenbacher B, Schaller M, Gani C, Toulany M. Dual Targeting of Y-Box Binding Protein-1 and Akt Inhibits Proliferation and Enhances the Chemosensitivity of Colorectal Cancer Cells. Cancers. 2019; 11(4):562. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11040562
Chicago/Turabian StyleMaier, Eva, Felix Attenberger, Aadhya Tiwari, Konstanze Lettau, Simone Rebholz, Birgit Fehrenbacher, Martin Schaller, Cihan Gani, and Mahmoud Toulany. 2019. "Dual Targeting of Y-Box Binding Protein-1 and Akt Inhibits Proliferation and Enhances the Chemosensitivity of Colorectal Cancer Cells" Cancers 11, no. 4: 562. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11040562
APA StyleMaier, E., Attenberger, F., Tiwari, A., Lettau, K., Rebholz, S., Fehrenbacher, B., Schaller, M., Gani, C., & Toulany, M. (2019). Dual Targeting of Y-Box Binding Protein-1 and Akt Inhibits Proliferation and Enhances the Chemosensitivity of Colorectal Cancer Cells. Cancers, 11(4), 562. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11040562





