Tumour-Secreted Protein S (ProS1) Activates a Tyro3-Erk Signalling Axis and Protects Cancer Cells from Apoptosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Expression of TAM Receptors and TAM Ligands in Human Cancer Cell Lines
2.2. ProS1 Is a Preferential Ligand for Tyro3 than Gas6
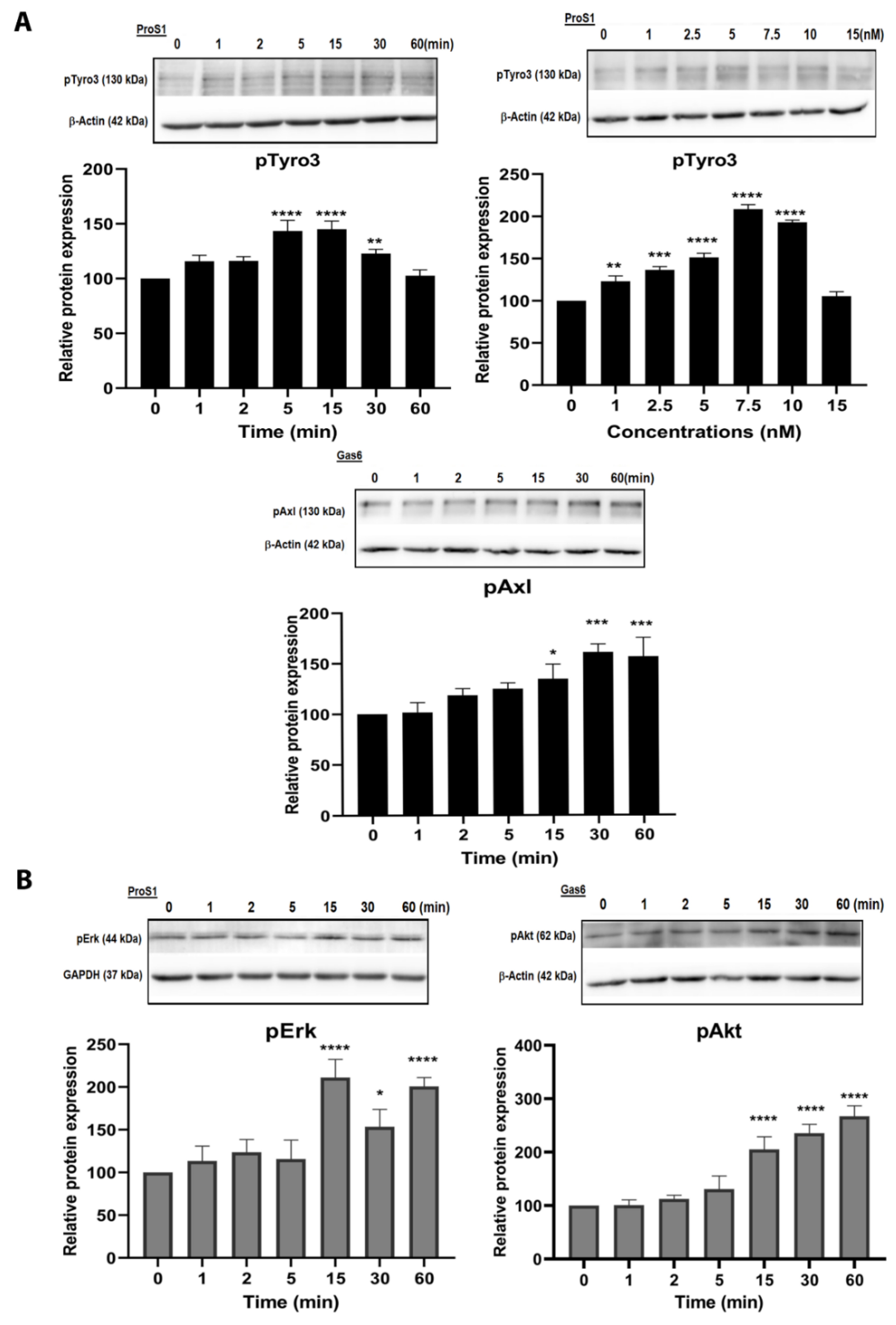
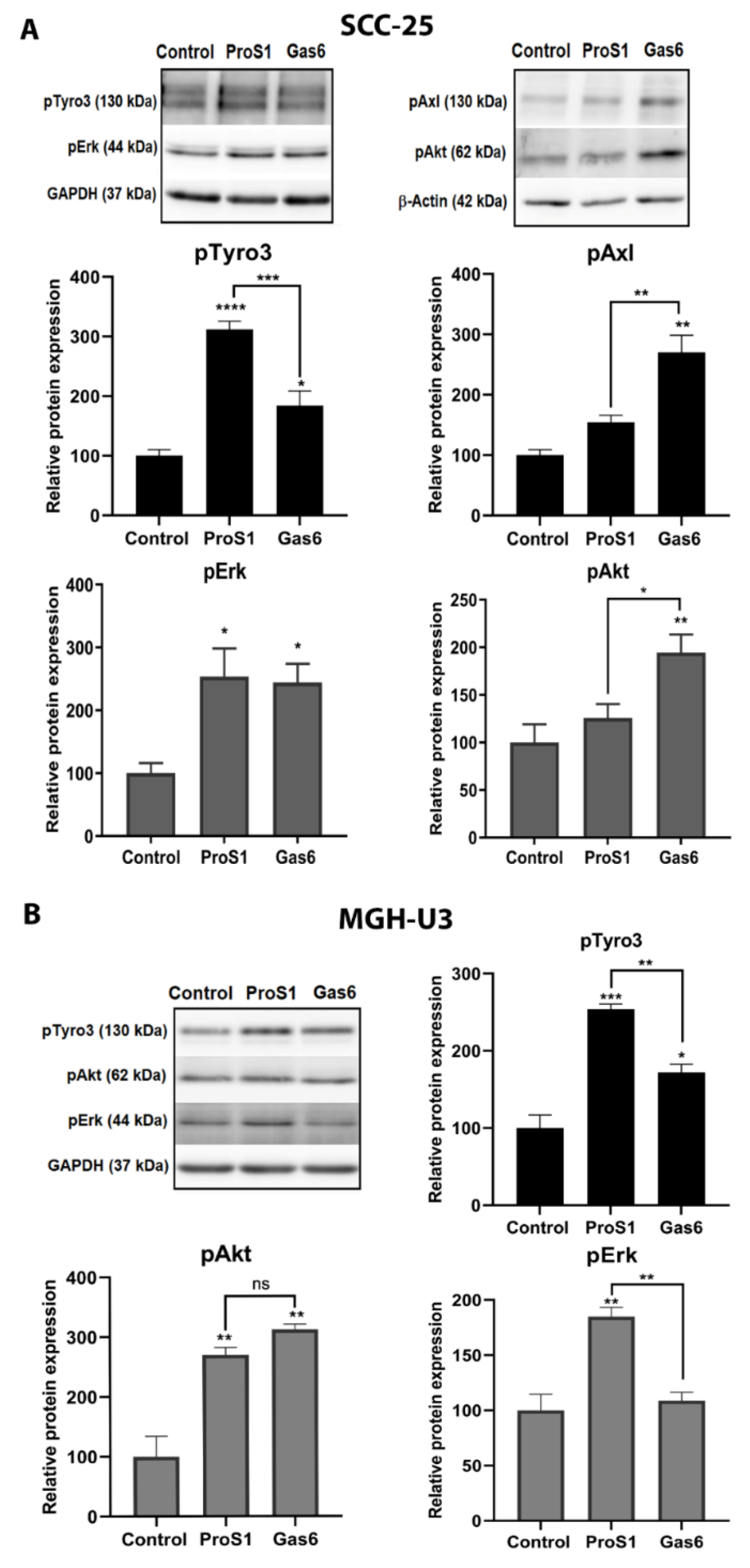
2.3. In Cells Expressing Tyro3 as Sole TAM Receptor, the ProS1-Tyro3-Erk Signalling Axis Prevails but Is Diversified
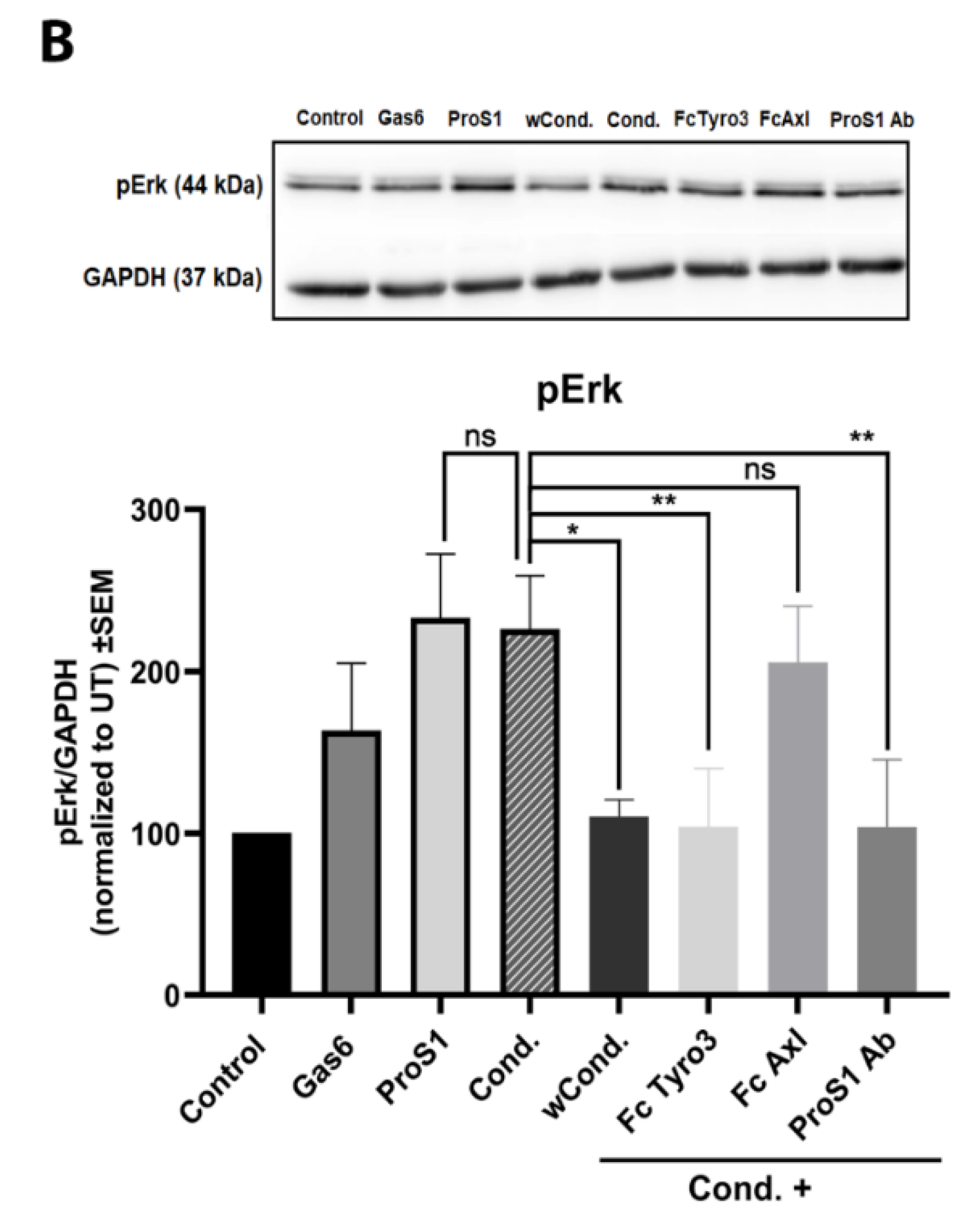
2.4. ProS1 Is Secreted from Cancer Cells as a Functionally Active Vitamin K-Dependent Ligand for Tyro3
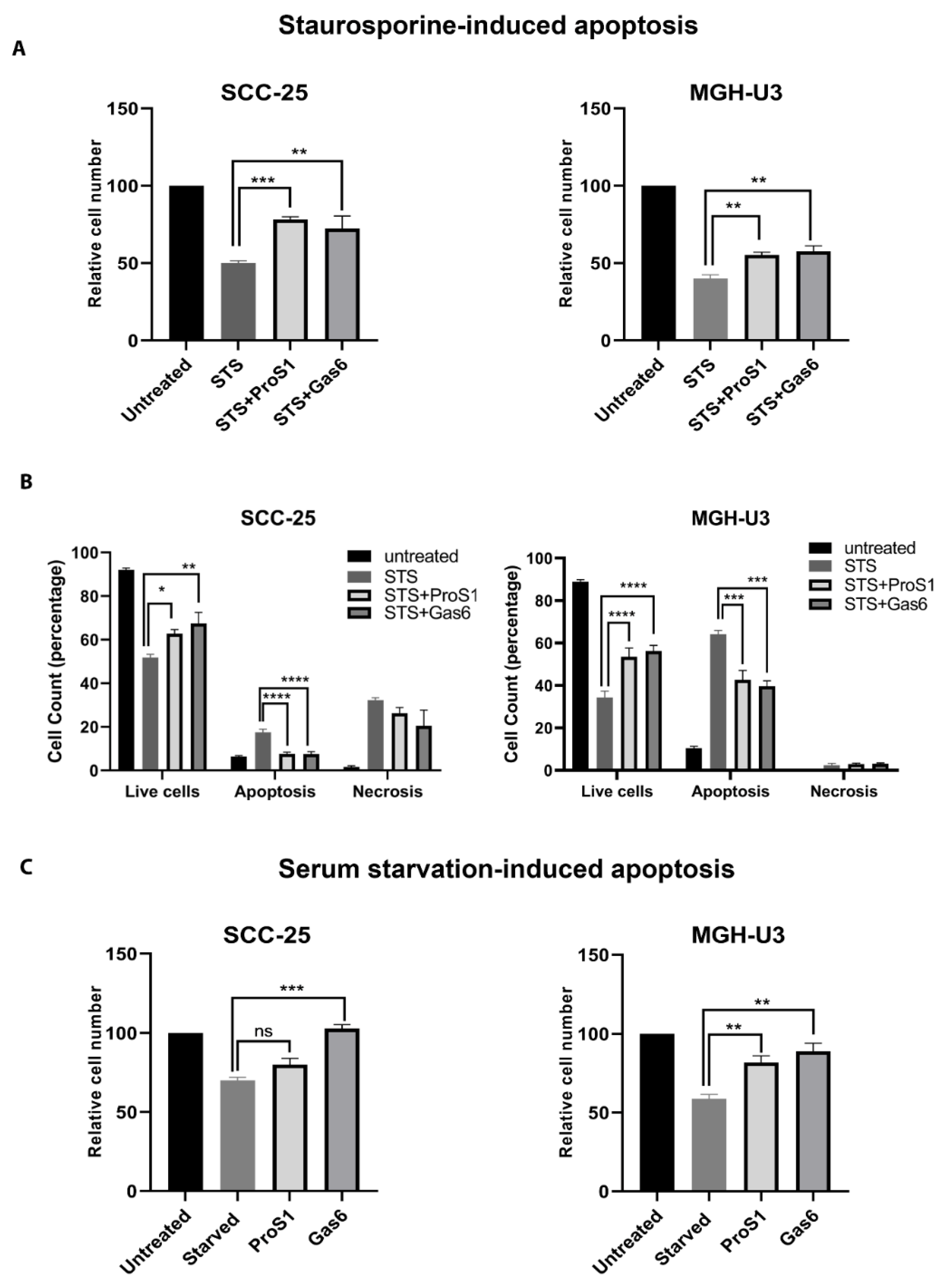
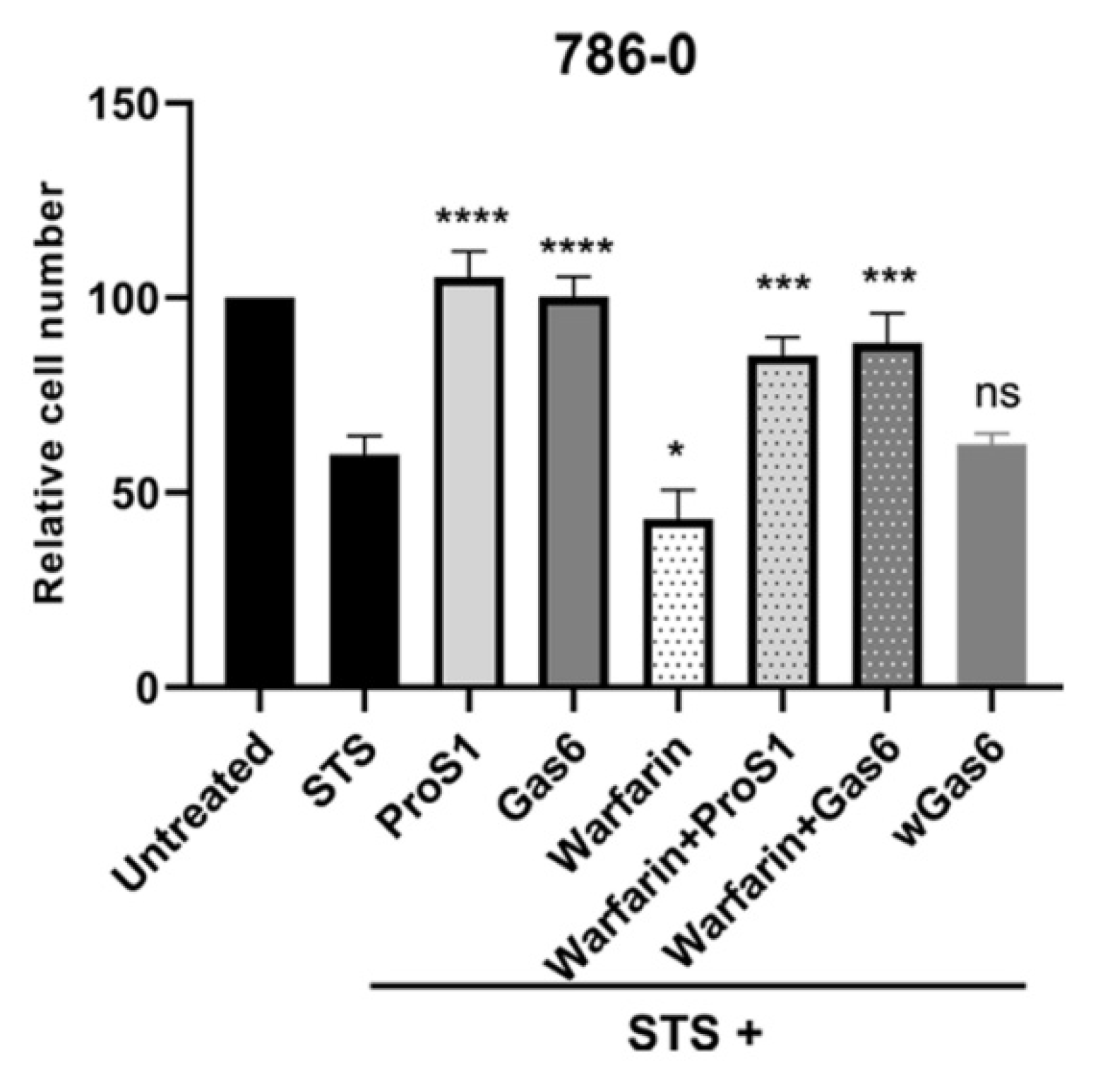
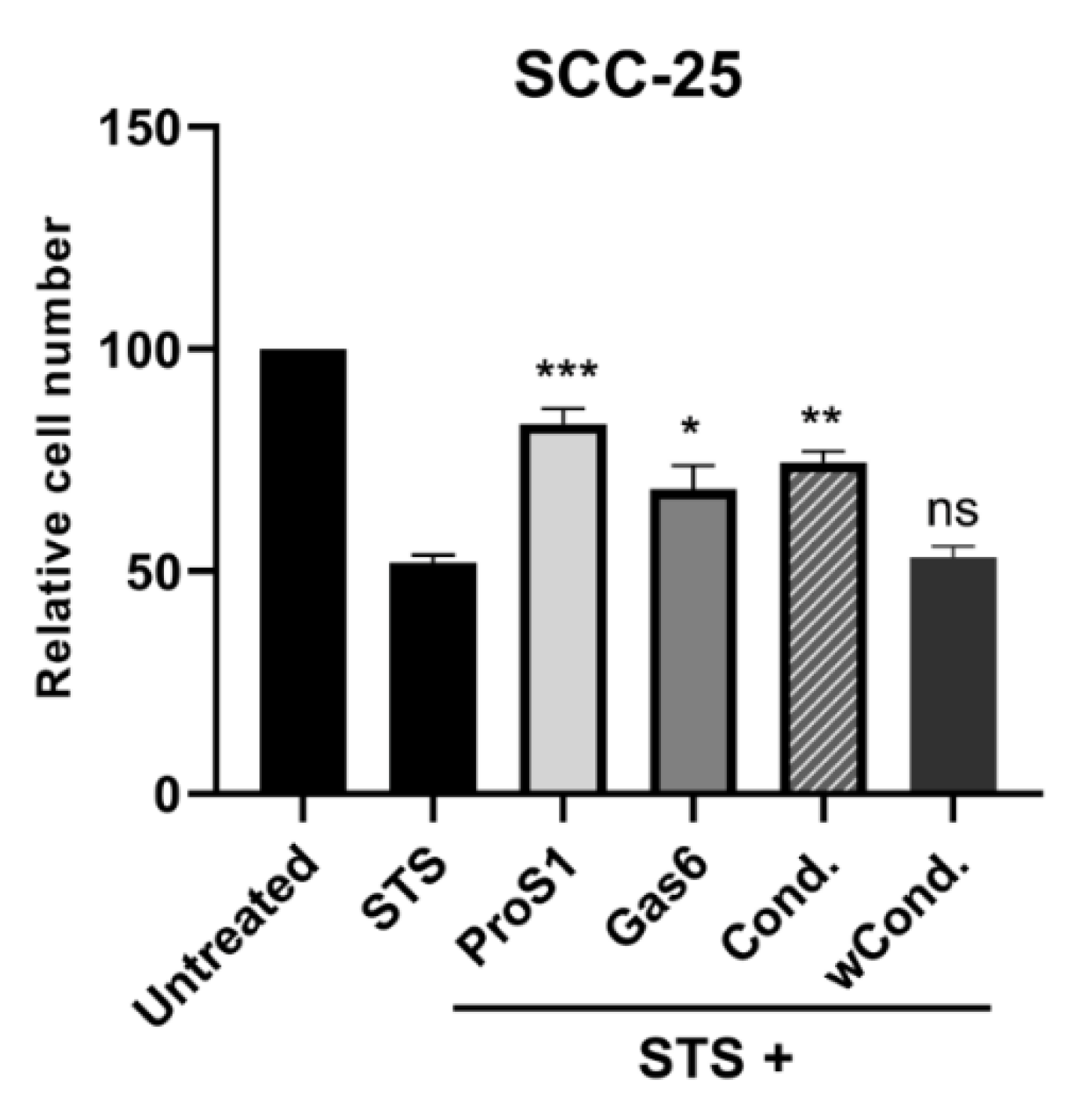
2.5. ProS1-Tyro3 Protects Cancer Cells from Apoptosis
3. Discussion
4. Material and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture
4.2. Cell Treatments
4.3. RNA Extraction and Quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction
4.4. SDS–PAGE and Western Blotting
4.5. Cell Survival/Growth Assay
4.6. Flow Cytometry and Apoptosis Assay
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Linger, R.; Keating, A.; Earp, H.; Graham, D. TAM receptor tyrosine kinase: biological functions, signaling, and potential theraputics targeting in human cancer. Adv. Cancer Res. 2008, 100, 35–83. [Google Scholar]
- Tsou, W.I.; Nguyen, K.Q.N.; Calarese, D.A.; Garforth, S.J.; Antes, A.L.; Smirnov, S.V.; Almo, S.C.; Birge, R.B.; Kotenko, S.V. Receptor tyrosine kinases, TYRO3, AXL, and MER, demonstrate distinct patterns and complex regulation of ligand-induced activatione. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 25750–25763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paolino, M.; Penninger, J.M. The role of TAM family receptors in immune cell function: Implications for cancer therapy. Cancers 2016, 8, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafit-Zagardo, B.; Gruber, R.C.; DuBois, J.C. The role of TAM family receptors and ligands in the nervous system: From development to pathobiology. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 188, 97–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vouri, M.; An, Q.; Birt, M.; Pilkington, G.J.; Hafizi, S. Small molecule inhibition of Axl receptor tyrosine kinase potently suppresses multiple malignant properties of glioma cells. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 16183–16197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vouri, M.; Hafizi, S. TAM receptor tyrosine kinases in cancer drug resistance. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 2775–2778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davra, V.; Kimani, S.G.; Calianese, D.; Birge, R.B. Ligand activation of TAM family receptors-implications for tumor biology and therapeutic response. Cancers 2016, 8, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chien, C.W.; Hou, P.C.; Wu, H.C.; Chang, Y.L.; Lin, S.C.; Lin, S.C.; Lin, B.W.; Lee, J.C.; Chang, Y.J.; Sun, H.S.; et al. Targeting TYRO3 inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition and increases drug sensitivity in colon cancer. Oncogene 2016, 35, 5872–5881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, H.; Lauffenburger, D.; Wells, A. Tyro3 carboxyl terminal region confers stability and contains the autophosphorylation sites. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 490, 1074–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, D.K.; Deryckere, D.; Davies, K.D.; Earp, H.S. The TAM family: Phosphatidylserine-sensing receptor tyrosine kinases gone awry in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2014, 14, 769–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafizi, S.; Dahlbäck, B. Gas6 and protein S: Vitamin K-dependent ligands for the Axl receptor tyrosine kinase subfamily. FEBS J. 2006, 273, 5231–5244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hafizi, S.; Dahlbäck, B. Signalling and functional diversity within the Axl subfamily of receptor tyrosine kinases. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2006, 17, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemke, G. Biology of the TAM receptors. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2013, 5, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suleiman, L.; Négrier, C.; Boukerche, H. Protein S: A multifunctional anticoagulant vitamin K-dependent protein at the crossroads of coagulation, inflammation, angiogenesis, and cancer. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2013, 88, 637–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemke, G. Phosphatidylserine is the signal for TAM receptors and their ligands. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2017, 42, 738–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stenhoff, J.; Dahlbäck, B.; Hafizi, S. Vitamin K-dependent Gas6 activates ERK kinase and stimulates growth of cardiac fibroblasts. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2004, 319, 871–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafizi, S.; Gustafsson, A.; Stenhoff, J.; Dahlbäck, B. The Ran binding protein RanBPM interacts with Axl and Sky receptor tyrosine kinases. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2005, 37, 2344–2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abboud-jarrous, G.; Priya, S.; Maimon, A.; Fischman, S. Protein S drives oral squamous cell carcinoma tumorigenicity through regulation of AXL. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 13986–14002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vouri, M.; Croucher, D.R.; Kennedy, S.P.; An, Q.; Pilkington, G.J.; Hafizi, S. Axl-EGFR receptor tyrosine kinase hetero-interaction provides EGFR with access to pro-invasive signalling in cancer cells. Oncogenesis 2016, 5, e266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goudarzi, S.; Rivera, A.; Butt, A.M.; Hafizi, S. Gas6 Promotes Oligodendrogenesis and Myelination in the Adult Central Nervous System and After Lysolecithin-Induced Demyelination. ASN Neuro. 2016, 8, 1759091416668430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelillo-Scherrer, A.; Burnier, L.; Flores, N.; Savi, P.; DeMol, M.; Schaeffer, P.; Herbert, J.M.; Lemke, G.; Goff, S.P.; Matsushima, G.K.; et al. Role of Gas6 receptors in platelet signaling during thrombus stabilization and implications for antithrombotic therapy Find the latest version: Role of Gas6 receptors in platelet signaling during thrombus stabilization and implications for antithrombotic therapy. J. Clin. Investig. 2005, 115, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Katagiri, M.; Hakeda, Y.; Chikazu, D.; Ogasawara, T.; Takato, T.; Kumegawa, M.; Nakamura, K.; Kawaguchi, H. Mechanism of stimulation of osteoclastic bone resorption through Gas6/Tyro 3, a receptor tyrosine kinase signaling, in mouse osteoclasts. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 7376–7382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pierce, A.; Xu, M.; Bliesner, B.; Liu, Z.; Richards, J.; Tobet, S.; Wierman, M.E. Hypothalamic but not pituitary or ovarian defects underlie the reproductive abnormalities in Axl/Tyro3 null mice. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2011, 339, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smart, S.K.; Vasileidadi, E.; Wang, X.; DeRychere, D.; Graham, D.K. The emerging role of TYRO3 as a therapeutic target in cancer. Cancers 2018, 10, 474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabir, T.D.; Ganda, C.; Brown, R.M.; Beveridge, D.J.; Richardson, K.L.; Chaturvedi, V.; Candy, P.; Epis, M.; Wintle, L.; Kalinowski, F.; et al. A microRNA-7/growth arrest specific 6/TYRO3 axis regulates the growth and invasiveness of sorafenib-resistant cells in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2018, 67, 216–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Wong, W.; Chua, S.C.; Wee, H.L.; Lim, S.G.; Chua, B.T.; Ho, H.K. Overexpression of Tyro3 and its implications on hepatocellular carcinoma progression. Int. J. Oncol. 2016, 48, 358–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekyalongo, R.; Mukohara, T.; Funakoshi, Y.; Tomioka, H.; Kataoka, Y.; Shimono, Y.; Chayahara, N.; Toyoda, M.; Kiyota, N.; Minami, H. TYRO3 as a potential therapeutic target in breast cancer. Antiancer Res. 2014, 34, 3337–3345. [Google Scholar]
- Dufour, F.; Silina, L.; Neyret-Kahn, H.; Moreno-Vega, A.; Krucker, C.; Karboul, N.; Dorland-Galliot, M.; Maillé, P.; Chapeaublanc, E.; Allory, Y.; et al. TYRO3 as a molecular target for growth inhibition and apoptosis induction in bladder cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2019, 120, 555–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J.; Jeng, Y.M.; Chen, Y.L.; Chung, L.; Yuan, R.H. Gas6/Axl pathway promotes tumor invasion through the transcriptional activation of slug in hepatocellular carcinoma. Carcinogenesis 2014, 35, 769–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Meer, J.H.M.; Van Der Poll, T.; Van’t Veer, C. TAM receptors, Gas6, and protein S: Roles in inflammation and hemostasis. Blood 2014, 123, 2460–2469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lew, E.D.; Oh, J.; Burrola, P.G.; Lax, I.; Zagórska, A.; Través, P.G.; Schlessinger, J.; Lemke, G. Differential TAM receptor-ligand-phospholipid interactions delimit differential TAM bioactivities. Elife 2014, 3, e03385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heiring, C.; Dahlbäck, B.; Muller, Y.A. Ligand recognition and homophilic interactions in Tyro3: Structural insights into the Axl/Tyro3 receptor tyrosine kinase family. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 6952–6958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraineau, S.; Monvoisin, A.; Clarhaut, J.; Talbot, J.; Simonneau, C.; Kanthou, C.; Kanse, S.M.; Philippe, M.; Benzakour, O. The vitamin K-dependent anticoagulant factor, protein S, inhibits multiple VEGF-A-induced angiogenesis events in a Mer- and SHP2-dependent manner. Blood 2012, 120, 5073–5083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Png, K.J.; Halberg, N.; Yoshida, M.; Tavazoie, S.F. A microRNA regulon that mediates endothelial recruitment and metastasis by cancer cells. Nature 2012, 481, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furukawa, M.; Ohkawara, H.; Ogawa, K.; Ikeda, K.; Ueda, K.; Shichishima-Nakamura, A.; Ito, E.; Imai, J.I.; Yanagisawa, Y.; Honma, R.; et al. Autocrine and Paracrine Interactions between Multiple Myeloma Cells and Bone Marrow Stromal Cells by Growth Arrest-specific Gene 6 Cross-talk with Interleukin-6. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 4280–4292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, P.; Jou, J.; Tsai, S.J. Minireview TYRO3: A potential therapeutic target in cancer. Exp. Biol. Med. 2019, 244, 83–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Wurdak, H.; Wang, Y.; Galkin, A.; Tao, H.; Li, J.; Lyssiotis, C.A.; Yan, F.; Tu, B.P.; Miraglia, L.; et al. A genomic screen identifies TYRO3 as a MITF regulator in melanoma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 17025–17030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Liu, X.; Koul, S.; Lee, C.Y.; Zhang, Z.; Halmos, B. AXL kinase as a novel target for cancer therapy. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 9546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kariolis, M.S.; Miao, Y.R.; Diep, A.; Nash, S.E.; Olcina, M.M.; Jiang, D.; Ii, D.S.J.; Kapur, S.; Mathews, I.I.; Koong, A.C.; et al. Inhibition of the GAS6/AXL pathway augments the efficacy of chemotherapies. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 183–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, C.; Rasband, W.; Eliceiri, K. NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Axelrod, H.; Pienta, K.J. Axl as a mediator of cellular growth and survival. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 8818–8852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Al Kafri, N.; Hafizi, S. Tumour-Secreted Protein S (ProS1) Activates a Tyro3-Erk Signalling Axis and Protects Cancer Cells from Apoptosis. Cancers 2019, 11, 1843. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11121843
Al Kafri N, Hafizi S. Tumour-Secreted Protein S (ProS1) Activates a Tyro3-Erk Signalling Axis and Protects Cancer Cells from Apoptosis. Cancers. 2019; 11(12):1843. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11121843
Chicago/Turabian StyleAl Kafri, Nour, and Sassan Hafizi. 2019. "Tumour-Secreted Protein S (ProS1) Activates a Tyro3-Erk Signalling Axis and Protects Cancer Cells from Apoptosis" Cancers 11, no. 12: 1843. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11121843
APA StyleAl Kafri, N., & Hafizi, S. (2019). Tumour-Secreted Protein S (ProS1) Activates a Tyro3-Erk Signalling Axis and Protects Cancer Cells from Apoptosis. Cancers, 11(12), 1843. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11121843





