Cell-Free DNA Methylation Profiling Analysis—Technologies and Bioinformatics
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Technologies for DNA Methylation Detection
2.1. Restriction Enzyme-Based Methods
2.2. Bisulfite Conversion-Based Methods
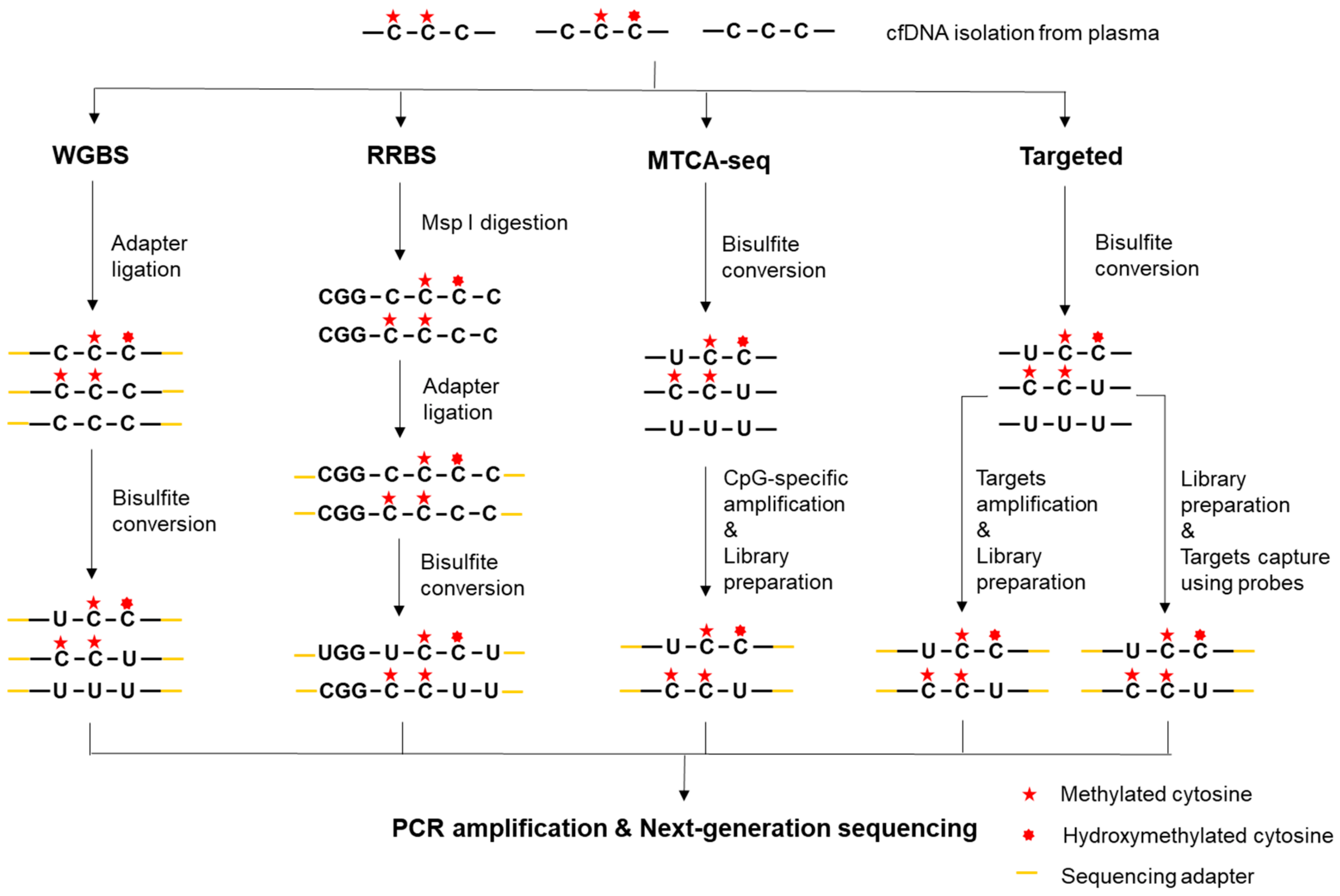
2.2.1. Whole-Genome Bisulfite Sequencing (WGBS)
2.2.2. Reduced-Representation Bisulfite Sequencing (RRBS)
2.2.3. Methylated CpG Tandems Amplification and Sequencing (MCTA-seq)
2.2.4. Targeted Bisulfite Sequencing
2.2.5. Methylation Array
2.2.6. Methylation-specific PCR (MSP)
2.3. Enrichment-based methods
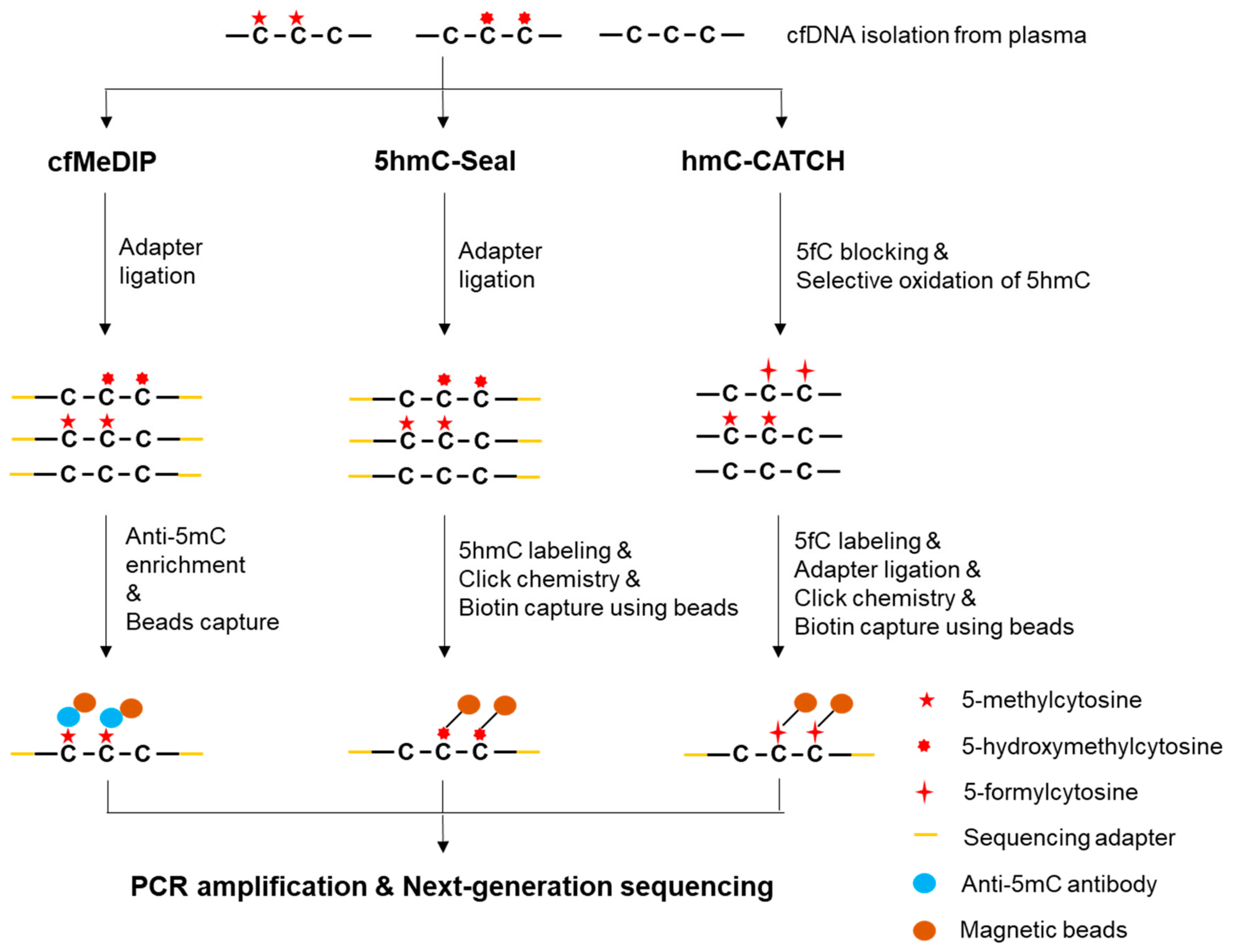
2.3.1. Methylated DNA Immunoprecipitation Sequencing (MeDIP-seq)
2.3.2. Methyl-CpG Binding Domain Protein Capture Sequencing (MBD-seq)
2.4. 5-hydroxymethylation profiling
2.4.1. 5hmC-Seal (aka hMe-Seal)
2.4.2. hmC-CATCH
2.4.3. Hydroxymethylated DNA Immunoprecipitation Sequencing (hMeDIP-seq)
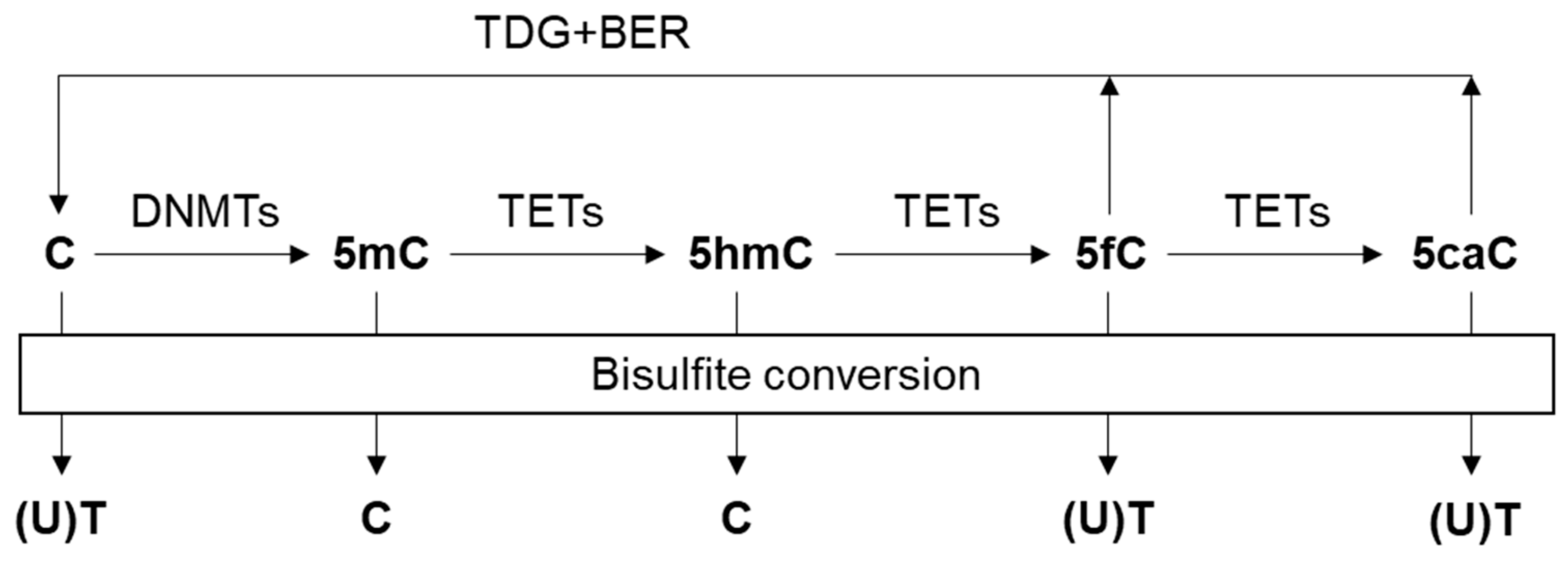
2.4.4. Oxidative Bisulfite Conversion
3. Bioinformatics Analysis of Sequencing-Based DNA Methylation Data
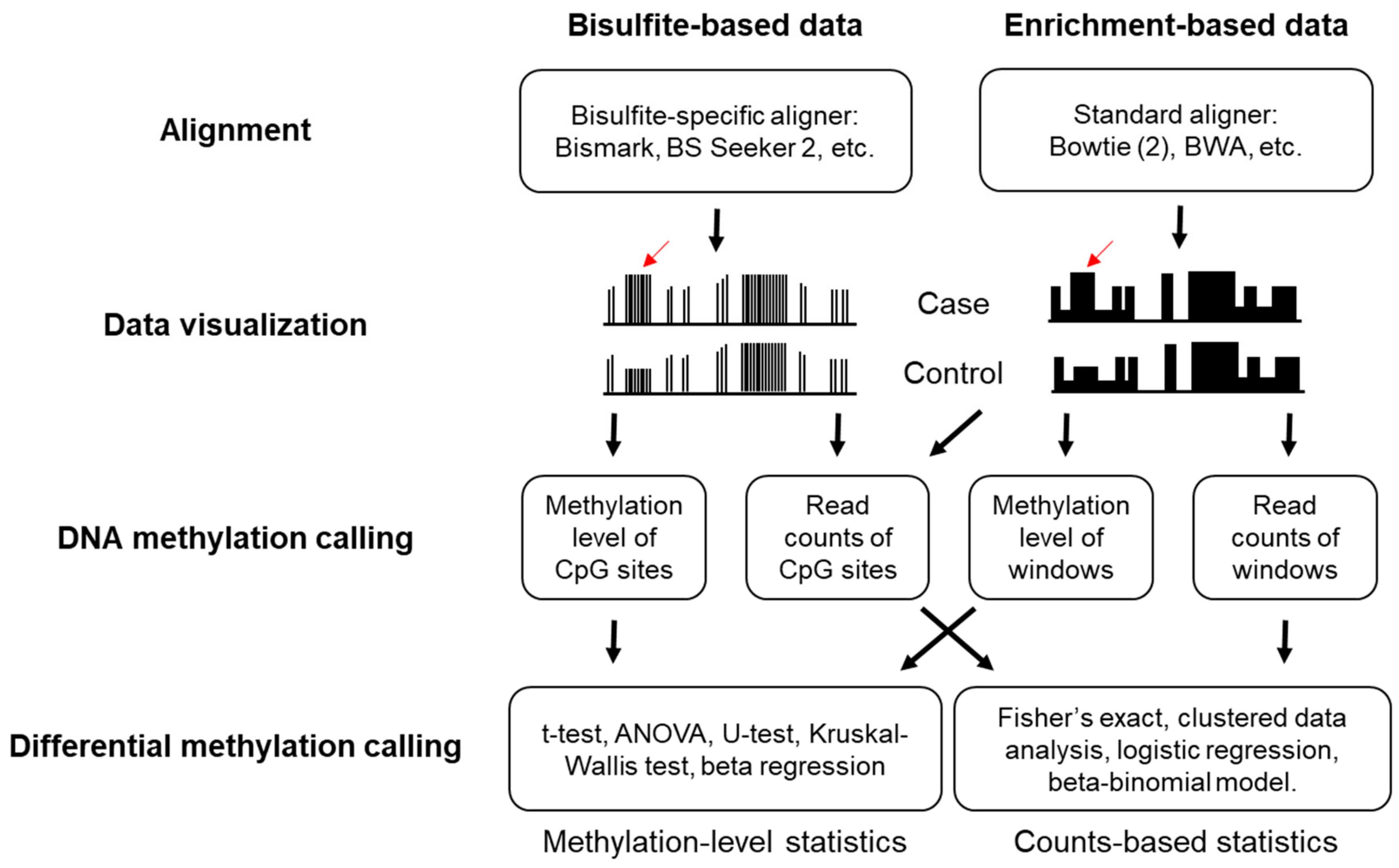
3.1. Alignment and Quality Controls
3.2. DNA Methylation Calling
3.3. Determination of Differential Methylation
3.4. Identification of Tumor-Specific Methylation Profile
4. Current Challenges and Future Directions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wan, J.C.M.; Massie, C.; Garcia-Corbacho, J.; Mouliere, F.; Brenton, J.D.; Caldas, C.; Pacey, S.; Baird, R.; Rosenfeld, N. Liquid biopsies come of age: Towards implementation of circulating tumour DNA. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2017, 17, 223–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diehl, F.; Schmidt, K.; Choti, M.A.; Romans, K.; Goodman, S.; Li, M.; Thornton, K.; Agrawal, N.; Sokoll, L.; Szabo, S.A.; et al. Circulating mutant DNA to assess tumor dynamics. Nat. Med. 2008, 14, 985–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamal-Hanjani, M.; Wilson, G.A.; Horswell, S.; Mitter, R.; Sakarya, O.; Constantin, T.; Salari, R.; Kirkizlar, E.; Sigurjonsson, S.; Pelham, R.; et al. Detection of ubiquitous and heterogeneous mutations in cell-free DNA from patients with early-stage non-small-cell lung cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2016, 27, 862–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattos-Arruda, L.; Weigelt, B.; Cortes, J.; Won, H.H.; Ng, C.K.Y.; Nuciforo, P.; Bidard, F.C.; Aura, C.; Saura, C.; Peg, V.; et al. Capturing intra-tumor genetic heterogeneity by de novo mutation profiling of circulating cell-free tumor DNA: A proof-of-principle. Ann. Oncol. 2018, 29, 2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, K.C.; Jiang, P.; Zheng, Y.W.; Liao, G.J.; Sun, H.; Wong, J.; Siu, S.S.; Chan, W.C.; Chan, S.L.; Chan, A.T.; et al. Cancer genome scanning in plasma: Detection of tumor-associated copy number aberrations, single-nucleotide variants, and tumoral heterogeneity by massively parallel sequencing. Clin. Chem. 2013, 59, 211–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowley, E.; Di Nicolantonio, F.; Loupakis, F.; Bardelli, A. Liquid biopsy: Monitoring cancer-genetics in the blood. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 10, 472–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siravegna, G.; Marsoni, S.; Siena, S.; Bardelli, A. Integrating liquid biopsies into the management of cancer. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 14, 531–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thierry, A.R.; El Messaoudi, S.; Gahan, P.B.; Anker, P.; Stroun, M. Origins, structures, and functions of circulating DNA in oncology. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2016, 35, 347–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chandrananda, D.; Thorne, N.P.; Bahlo, M. High-resolution characterization of sequence signatures due to non-random cleavage of cell-free DNA. BMC Med. Genom. 2015, 8, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, Y.M.; Chan, K.C.; Sun, H.; Chen, E.Z.; Jiang, P.; Lun, F.M.; Zheng, Y.W.; Leung, T.Y.; Lau, T.K.; Cantor, C.R.; et al. Maternal plasma DNA sequencing reveals the genome-wide genetic and mutational profile of the fetus. Sci. Transl. Med. 2010, 2, 61ra91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarzenbach, H.; Hoon, D.S.; Pantel, K. Cell-free nucleic acids as biomarkers in cancer patients. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2011, 11, 426–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catarino, R.; Ferreira, M.M.; Rodrigues, H.; Coelho, A.; Nogal, A.; Sousa, A.; Medeiros, R. Quantification of free circulating tumor DNA as a diagnostic marker for breast cancer. DNA Cell Biol. 2008, 27, 415–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Messaoudi, S.; Rolet, F.; Mouliere, F.; Thierry, A.R. Circulating cell free DNA: Preanalytical considerations. Clin. Chim. Acta 2013, 424, 222–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaz, L.A., Jr.; Bardelli, A. Liquid biopsies: Genotyping circulating tumor DNA. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 32, 579–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janku, F.; Huang, H.J.; Claes, B.; Falchook, G.S.; Fu, S.; Hong, D.; Ramzanali, N.M.; Nitti, G.; Cabrilo, G.; Tsimberidou, A.M.; et al. BRAF Mutation Testing in Cell-Free DNA from the Plasma of Patients with Advanced Cancers Using a Rapid, Automated Molecular Diagnostics System. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2016, 15, 1397–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janku, F.; Huang, H.J.; Fujii, T.; Shelton, D.N.; Madwani, K.; Fu, S.; Tsimberidou, A.M.; Piha-Paul, S.A.; Wheler, J.J.; Zinner, R.G.; et al. Multiplex KRASG12/G13 mutation testing of unamplified cell-free DNA from the plasma of patients with advanced cancers using droplet digital polymerase chain reaction. Ann. Oncol. 2017, 28, 642–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baylin, S.B.; Esteller, M.; Rountree, M.R.; Bachman, K.E.; Schuebel, K.; Herman, J.G. Aberrant patterns of DNA methylation, chromatin formation and gene expression in cancer. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2001, 10, 687–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vrba, L.; Futscher, B.W. A suite of DNA methylation markers that can detect most common human cancers. Epigenetics 2018, 13, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jones, P.A. Functions of DNA methylation: Islands, start sites, gene bodies and beyond. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2012, 13, 484–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, Z.D.; Meissner, A. DNA methylation: Roles in mammalian development. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2013, 14, 204–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, M.M.; Bird, A. DNA methylation landscapes: Provocative insights from epigenomics. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2008, 9, 465–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esteller, M. Epigenetics in cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 358, 1148–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baylin, S.B.; Jones, P.A. A decade of exploring the cancer epigenome - biological and translational implications. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2011, 11, 726–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koch, A.; Joosten, S.C.; Feng, Z.; de Ruijter, T.C.; Draht, M.X.; Melotte, V.; Smits, K.M.; Veeck, J.; Herman, J.G.; Van Neste, L.; et al. Analysis of DNA methylation in cancer: Location revisited. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 15, 459–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laird, P.W. The power and the promise of DNA methylation markers. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2003, 3, 253–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeshima, H.; Ushijima, T. Accumulation of genetic and epigenetic alterations in normal cells and cancer risk. NPJ Precis Oncol. 2019, 3, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widschwendter, M.; Jones, A.; Evans, I.; Reisel, D.; Dillner, J.; Sundstrom, K.; Steyerberg, E.W.; Vergouwe, Y.; Wegwarth, O.; Rebitschek, F.G.; et al. Epigenome-based cancer risk prediction: Rationale, opportunities and challenges. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 15, 292–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moss, J.; Magenheim, J.; Neiman, D.; Zemmour, H.; Loyfer, N.; Korach, A.; Samet, Y.; Maoz, M.; Druid, H.; Arner, P.; et al. Comprehensive human cell-type methylation atlas reveals origins of circulating cell-free DNA in health and disease. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 5068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Board, R.E.; Knight, L.; Greystoke, A.; Blackhall, F.H.; Hughes, A.; Dive, C.; Ranson, M. DNA methylation in circulating tumour DNA as a biomarker for cancer. Biomark. Insights 2008, 2, 307–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, H.; Jin, P.; Wu, H. Disease prediction by cell-free DNA methylation. Brief. Bioinform. 2019, 20, 585–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dam-Dcm and CpG Methylation. Available online: https://www.neb.com/tools-and-resources/selection-charts/dam-dcm-and-cpg-methylation (accessed on 6 November 2019).
- Oda, M.; Glass, J.L.; Thompson, R.F.; Mo, Y.; Olivier, E.N.; Figueroa, M.E.; Selzer, R.R.; Richmond, T.A.; Zhang, X.; Dannenberg, L.; et al. High-resolution genome-wide cytosine methylation profiling with simultaneous copy number analysis and optimization for limited cell numbers. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, 3829–3839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ball, M.P.; Li, J.B.; Gao, Y.; Lee, J.H.; LeProust, E.M.; Park, I.H.; Xie, B.; Daley, G.Q.; Church, G.M. Targeted and genome-scale strategies reveal gene-body methylation signatures in human cells. Nat. Biotechnol. 2009, 27, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maunakea, A.K.; Nagarajan, R.P.; Bilenky, M.; Ballinger, T.J.; D'Souza, C.; Fouse, S.D.; Johnson, B.E.; Hong, C.; Nielsen, C.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Conserved role of intragenic DNA methylation in regulating alternative promoters. Nature 2010, 466, 253–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunner, A.L.; Johnson, D.S.; Kim, S.W.; Valouev, A.; Reddy, T.E.; Neff, N.F.; Anton, E.; Medina, C.; Nguyen, L.; Chiao, E.; et al. Distinct DNA methylation patterns characterize differentiated human embryonic stem cells and developing human fetal liver. Genome Res. 2009, 19, 1044–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, Z.; Bai, Y.; Cheng, Z.; Liu, F.; Wang, P.; Yang, D.; Li, G.; Jin, Q.; Mao, H.; Zhao, J. Absolute quantification of DNA methylation using microfluidic chip-based digital PCR. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 96, 339–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frommer, M.; McDonald, L.E.; Millar, D.S.; Collis, C.M.; Watt, F.; Grigg, G.W.; Molloy, P.L.; Paul, C.L. A genomic sequencing protocol that yields a positive display of 5-methylcytosine residues in individual DNA strands. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 1827–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, K.; Okamoto, A. Degradation of DNA by bisulfite treatment. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2007, 17, 1912–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, S.; Rakyan, V.K. The methylome: Approaches for global DNA methylation profiling. Trends Genet. 2008, 24, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lister, R.; Pelizzola, M.; Dowen, R.H.; Hawkins, R.D.; Hon, G.; Tonti-Filippini, J.; Nery, J.R.; Lee, L.; Ye, Z.; Ngo, Q.M.; et al. Human DNA methylomes at base resolution show widespread epigenomic differences. Nature 2009, 462, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Clark, S.J.; Smallwood, S.A.; Lee, H.J.; Krueger, F.; Reik, W.; Kelsey, G. Genome-wide base-resolution mapping of DNA methylation in single cells using single-cell bisulfite sequencing (scBS-seq). Nat. Protoc. 2017, 12, 534–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smallwood, S.A.; Lee, H.J.; Angermueller, C.; Krueger, F.; Saadeh, H.; Peat, J.; Andrews, S.R.; Stegle, O.; Reik, W.; Kelsey, G. Single-cell genome-wide bisulfite sequencing for assessing epigenetic heterogeneity. Nat. Methods 2014, 11, 817–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farlik, M.; Sheffield, N.C.; Nuzzo, A.; Datlinger, P.; Schonegger, A.; Klughammer, J.; Bock, C. Single-cell DNA methylome sequencing and bioinformatic inference of epigenomic cell-state dynamics. Cell Rep. 2015, 10, 1386–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, F.; Enomoto, Y.; Dairiki, R.; Ito, T. Amplification-free whole-genome bisulfite sequencing by post-bisulfite adaptor tagging. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, e136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Legendre, C.; Gooden, G.C.; Johnson, K.; Martinez, R.A.; Liang, W.S.; Salhia, B. Whole-genome bisulfite sequencing of cell-free DNA identifies signature associated with metastatic breast cancer. Clin. Epigenet. 2015, 7, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meissner, A.; Mikkelsen, T.S.; Gu, H.; Wernig, M.; Hanna, J.; Sivachenko, A.; Zhang, X.; Bernstein, B.E.; Nusbaum, C.; Jaffe, D.B.; et al. Genome-scale DNA methylation maps of pluripotent and differentiated cells. Nature 2008, 454, 766–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gu, H.; Smith, Z.D.; Bock, C.; Boyle, P.; Gnirke, A.; Meissner, A. Preparation of reduced representation bisulfite sequencing libraries for genome-scale DNA methylation profiling. Nat. Protoc. 2011, 6, 468–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, Z.D.; Gu, H.; Bock, C.; Gnirke, A.; Meissner, A. High-throughput bisulfite sequencing in mammalian genomes. Methods 2009, 48, 226–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, H.; Zhu, P.; Wu, X.; Li, X.; Wen, L.; Tang, F. Single-cell methylome landscapes of mouse embryonic stem cells and early embryos analyzed using reduced representation bisulfite sequencing. Genome Res. 2013, 23, 2126–2135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, H.; Zhu, P.; Guo, F.; Li, X.; Wu, X.; Fan, X.; Wen, L.; Tang, F. Profiling DNA methylome landscapes of mammalian cells with single-cell reduced-representation bisulfite sequencing. Nat. Protoc. 2015, 10, 645–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Diep, D.; Plongthongkum, N.; Fung, H.L.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, K. Identification of methylation haplotype blocks aids in deconvolution of heterogeneous tissue samples and tumor tissue-of-origin mapping from plasma DNA. Nat. Genet. 2017, 49, 635–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, L.; Li, J.; Guo, H.; Liu, X.; Zheng, S.; Zhang, D.; Zhu, W.; Qu, J.; Guo, L.; Du, D.; et al. Genome-scale detection of hypermethylated CpG islands in circulating cell-free DNA of hepatocellular carcinoma patients. Cell Res. 2015, 25, 1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Zhou, X.; Liu, X.; Ren, J.; Wang, J.; Wang, W.; Zheng, Y.; Shi, X.; Sun, T.; Li, Z.; et al. Detection of Colorectal Cancer in Circulating Cell-Free DNA by Methylated CpG Tandem Amplification and Sequencing. Clin. Chem. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samorodnitsky, E.; Datta, J.; Jewell, B.M.; Hagopian, R.; Miya, J.; Wing, M.R.; Damodaran, S.; Lippus, J.M.; Reeser, J.W.; Bhatt, D.; et al. Comparison of custom capture for targeted next-generation DNA sequencing. J. Mol. Diagn. 2015, 17, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widschwendter, M.; Evans, I.; Jones, A.; Ghazali, S.; Reisel, D.; Ryan, A.; Gentry-Maharaj, A.; Zikan, M.; Cibula, D.; Eichner, J.; et al. Methylation patterns in serum DNA for early identification of disseminated breast cancer. Genome Med. 2017, 9, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmila, R.; Sklias, A.; Muller, D.C.; Degli Esposti, D.; Guilloreau, P.; McKay, J.; Sangrajrang, S.; Srivatanakul, P.; Hainaut, P.; Merle, P.; et al. Targeted deep sequencing of plasma circulating cell-free DNA reveals Vimentin and Fibulin 1 as potential epigenetic biomarkers for hepatocellular carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0174265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Toung, J.M.; Jassowicz, A.F.; Vijayaraghavan, R.; Kang, H.; Zhang, R.; Kruglyak, K.M.; Huang, H.J.; Hinoue, T.; Shen, H.; et al. Targeted methylation sequencing of plasma cell-free DNA for cancer detection and classification. Ann. Oncol. 2018, 29, 1445–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bibikova, M.; Barnes, B.; Tsan, C.; Ho, V.; Klotzle, B.; Le, J.M.; Delano, D.; Zhang, L.; Schroth, G.P.; Gunderson, K.L.; et al. High density DNA methylation array with single CpG site resolution. Genomics 2011, 98, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stirzaker, C.; Taberlay, P.C.; Statham, A.L.; Clark, S.J. Mining cancer methylomes: Prospects and challenges. Trends Genet. 2014, 30, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, S.; Arribas, C.; Esteller, M. Validation of a DNA methylation microarray for 850,000 CpG sites of the human genome enriched in enhancer sequences. Epigenomics 2016, 8, 389–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Barrett, T.; Wilhite, S.E.; Ledoux, P.; Evangelista, C.; Kim, I.F.; Tomashevsky, M.; Marshall, K.A.; Phillippy, K.H.; Sherman, P.M.; Holko, M.; et al. NCBI GEO: Archive for functional genomics data sets--update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D991–D995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Cancer Genome Atlas. Available online: https://www.cancer.gov/tcga (accessed on 6 November 2019).
- Hao, X.K.; Luo, H.Y.; Krawczyk, M.; Wei, W.; Wang, W.Q.; Wang, J.; Flagg, K.; Hou, J.Y.; Zhang, H.; Yi, S.H.; et al. DNA methylation markers for diagnosis and prognosis of common cancers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 7414–7419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gallardo-Gomez, M.; Moran, S.; Paez de la Cadena, M.; Martinez-Zorzano, V.S.; Rodriguez-Berrocal, F.J.; Rodriguez-Girondo, M.; Esteller, M.; Cubiella, J.; Bujanda, L.; Castells, A.; et al. A new approach to epigenome-wide discovery of non-invasive methylation biomarkers for colorectal cancer screening in circulating cell-free DNA using pooled samples. Clin. Epigenet. 2018, 10, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herman, J.G.; Graff, J.R.; Myohanen, S.; Nelkin, B.D.; Baylin, S.B. Methylation-specific PCR: A novel PCR assay for methylation status of CpG islands. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 9821–9826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eads, C.A.; Danenberg, K.D.; Kawakami, K.; Saltz, L.B.; Blake, C.; Shibata, D.; Danenberg, P.V.; Laird, P.W. MethyLight: A high-throughput assay to measure DNA methylation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, E32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, P.K.; Watanabe, H.; Cheng, P.C.; Teo, W.W.; Liang, X.; Argani, P.; Lee, J.S.; Sukumar, S. MethySYBR, a novel quantitative PCR assay for the dual analysis of DNA methylation and CpG methylation density. J. Mol. Diagn. 2009, 11, 400–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dugast-Darzacq, C.; Grange, T. MethylQuant: A real-time PCR-based method to quantify DNA methylation at single specific cytosines. Methods Mol. Biol. 2009, 507, 281–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojdacz, T.K.; Dobrovic, A. Methylation-sensitive high resolution melting (MS-HRM): A new approach for sensitive and high-throughput assessment of methylation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, e41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Li, P.; Wu, J.; Yi, J.; Dou, Y.; Guo, X.; Yin, Y.; Wang, D.; Ma, C.; Qiu, L. Methylation of NBPF1 as a novel marker for the detection of plasma cell-free DNA of breast cancer patients. Clin. Chim. Acta 2018, 484, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eissa, M.A.L.; Lerner, L.; Abdelfatah, E.; Shankar, N.; Canner, J.K.; Hasan, N.M.; Yaghoobi, V.; Huang, B.; Kerner, Z.; Takaesu, F.; et al. Promoter methylation of ADAMTS1 and BNC1 as potential biomarkers for early detection of pancreatic cancer in blood. Clin. Epigenet. 2019, 11, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannopoulou, L.; Mastoraki, S.; Buderath, P.; Strati, A.; Pavlakis, K.; Kasimir-Bauer, S.; Lianidou, E.S. ESR1 methylation in primary tumors and paired circulating tumor DNA of patients with high-grade serous ovarian cancer. Gynecol. Oncol. 2018, 150, 355–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wasenang, W.; Chaiyarit, P.; Proungvitaya, S.; Limpaiboon, T. Serum cell-free DNA methylation of OPCML and HOXD9 as a biomarker that may aid in differential diagnosis between cholangiocarcinoma and other biliary diseases. Clin. Epigenet. 2019, 11, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nunes, S.P.; Moreira-Barbosa, C.; Salta, S.; Palma de Sousa, S.; Pousa, I.; Oliveira, J.; Soares, M.; Rego, L.; Dias, T.; Rodrigues, J.; et al. Cell-Free DNA Methylation of Selected Genes Allows for Early Detection of the Major Cancers in Women. Cancers (Basel) 2018, 10, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, B.; Yan, P.; Zhang, S.; Lu, Y.; Pan, L.; Tang, W.; Chen, S.; Chen, S.; Zhang, A.; Liu, W. Cell-Free Circulating Methylated SEPT9 for Noninvasive Diagnosis and Monitoring of Colorectal Cancer. Dis. Markers 2018, 2018, 6437104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oussalah, A.; Rischer, S.; Bensenane, M.; Conroy, G.; Filhine-Tresarrieu, P.; Debard, R.; Forest-Tramoy, D.; Josse, T.; Reinicke, D.; Garcia, M.; et al. Plasma mSEPT9: A Novel Circulating Cell-free DNA-Based Epigenetic Biomarker to Diagnose Hepatocellular Carcinoma. EBioMedicine 2018, 30, 138–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Uehiro, N.; Sato, F.; Pu, F.; Tanaka, S.; Kawashima, M.; Kawaguchi, K.; Sugimoto, M.; Saji, S.; Toi, M. Circulating cell-free DNA-based epigenetic assay can detect early breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2016, 18, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boeckx, N.; Op de Beeck, K.; Beyens, M.; Deschoolmeester, V.; Hermans, C.; De Clercq, P.; Garrigou, S.; Normand, C.; Monsaert, E.; Papadimitriou, K.; et al. Mutation and Methylation Analysis of Circulating Tumor DNA Can Be Used for Follow-up of Metastatic Colorectal Cancer Patients. Clin. Colorectal Cancer 2018, 17, e369–e379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barault, L.; Amatu, A.; Siravegna, G.; Ponzetti, A.; Moran, S.; Cassingena, A.; Mussolin, B.; Falcomata, C.; Binder, A.M.; Cristiano, C.; et al. Discovery of methylated circulating DNA biomarkers for comprehensive non-invasive monitoring of treatment response in metastatic colorectal cancer. Gut 2018, 67, 1995–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, R.F.; Shabalin, A.A.; Xie, L.Y.; Adkins, D.E.; Zhao, M.; Turecki, G.; Clark, S.L.; Aberg, K.A.; van den Oord, E. Enrichment methods provide a feasible approach to comprehensive and adequately powered investigations of the brain methylome. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, e97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, M.; Davies, J.J.; Wittig, D.; Oakeley, E.J.; Haase, M.; Lam, W.L.; Schubeler, D. Chromosome-wide and promoter-specific analyses identify sites of differential DNA methylation in normal and transformed human cells. Nat. Genet. 2005, 37, 853–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taiwo, O.; Wilson, G.A.; Morris, T.; Seisenberger, S.; Reik, W.; Pearce, D.; Beck, S.; Butcher, L.M. Methylome analysis using MeDIP-seq with low DNA concentrations. Nat. Protoc. 2012, 7, 617–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, S.Y.; Singhania, R.; Fehringer, G.; Chakravarthy, A.; Roehrl, M.H.A.; Chadwick, D.; Zuzarte, P.C.; Borgida, A.; Wang, T.T.; Li, T.T.; et al. Sensitive tumour detection and classification using plasma cell-free DNA methylomes. Nature 2018, 563, 579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, S.Y.; Burgener, J.M.; Bratman, S.V.; De Carvalho, D.D. Preparation of cfMeDIP-seq libraries for methylome profiling of plasma cell-free DNA. Nat. Protoc. 2019, 14, 2749–2780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, W.; Lu, J.; Zhao, Q.; Wu, J.; Sun, J.; Han, B.; Zhao, X.; Kang, Y. Genome-Wide Plasma Cell-Free DNA Methylation Profiling Identifies Potential Biomarkers for Lung Cancer. Dis. Markers 2019, 2019, 4108474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brinkman, A.B.; Simmer, F.; Ma, K.; Kaan, A.; Zhu, J.; Stunnenberg, H.G. Whole-genome DNA methylation profiling using MethylCap-seq. Methods 2010, 52, 232–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, S.S.; Coolen, M.W.; Stirzaker, C.; Song, J.Z.; Statham, A.L.; Strbenac, D.; Robinson, M.D.; Clark, S.J. Comparison of methyl-DNA immunoprecipitation (MeDIP) and methyl-CpG binding domain (MBD) protein capture for genome-wide DNA methylation analysis reveal CpG sequence coverage bias. Epigenetics 2011, 6, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aberg, K.A.; Chan, R.F.; Shabalin, A.A.; Zhao, M.; Turecki, G.; Staunstrup, N.H.; Starnawska, A.; Mors, O.; Xie, L.Y.; van den Oord, E.J. A MBD-seq protocol for large-scale methylome-wide studies with (very) low amounts of DNA. Epigenetics 2017, 12, 743–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tahiliani, M.; Koh, K.P.; Shen, Y.; Pastor, W.A.; Bandukwala, H.; Brudno, Y.; Agarwal, S.; Iyer, L.M.; Liu, D.R.; Aravind, L.; et al. Conversion of 5-methylcytosine to 5-hydroxymethylcytosine in mammalian DNA by MLL partner TET1. Science 2009, 324, 930–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.F.; Li, B.Z.; Li, Z.; Liu, P.; Wang, Y.; Tang, Q.; Ding, J.; Jia, Y.; Chen, Z.; Li, L.; et al. Tet-mediated formation of 5-carboxylcytosine and its excision by TDG in mammalian DNA. Science 2011, 333, 1303–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachman, M.; Uribe-Lewis, S.; Yang, X.; Williams, M.; Murrell, A.; Balasubramanian, S. 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine is a predominantly stable DNA modification. Nat. Chem. 2014, 6, 1049–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vasanthakumar, A.; Godley, L.A. 5-hydroxymethylcytosine in cancer: Significance in diagnosis and therapy. Cancer Genet. 2015, 208, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, D.; Lu, X.; Shih, A.H.; Nie, J.; You, Q.; Xu, M.M.; Melnick, A.M.; Levine, R.L.; He, C. A Highly Sensitive and Robust Method for Genome-wide 5hmC Profiling of Rare Cell Populations. Mol. Cell 2016, 63, 711–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, Y.; Pastor, W.A.; Shen, Y.; Tahiliani, M.; Liu, D.R.; Rao, A. The behaviour of 5-hydroxymethylcytosine in bisulfite sequencing. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e8888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, C.X.; Szulwach, K.E.; Fu, Y.; Dai, Q.; Yi, C.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Chen, C.H.; Zhang, W.; Jian, X.; et al. Selective chemical labeling reveals the genome-wide distribution of 5-hydroxymethylcytosine. Nat. Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Song, C.X.; Yin, S.; Ma, L.; Wheeler, A.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, B.; Xiong, J.; Zhang, W.; Hu, J.; et al. 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine signatures in cell-free DNA provide information about tumor types and stages. Cell Res. 2017, 27, 1231–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, W.; Zhang, X.; Lu, X.; You, L.; Song, Y.; Luo, Z.; Zhang, J.; Nie, J.; Zheng, W.; Xu, D.; et al. 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine signatures in circulating cell-free DNA as diagnostic biomarkers for human cancers. Cell Res. 2017, 27, 1243–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Han, X.; Gao, C.; Xing, Y.; Qi, Z.; Liu, R.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yang, Y.G.; Li, X.; et al. 5-Hydroxymethylome in Circulating Cell-free DNA as A Potential Biomarker for Non-small-cell Lung Cancer. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2018, 16, 187–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.; Lin, S.; Cai, M.; Zhu, Y.; Song, Y.; Sui, Y.; Lin, J.; Liu, J.; Lu, X.; Zhong, Y.; et al. 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine profiling from genomic and cell-free DNA for colorectal cancers patients. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2019, 23, 3530–3537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Chen, L.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Lu, X.; Liu, W.; Shi, G.; Ge, Y.; Gao, P.; Yang, Y.; et al. Genome-wide mapping of 5-hydroxymethylcytosines in circulating cell-free DNA as a non-invasive approach for early detection of hepatocellular carcinoma. Gut 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Sun, B.; Chen, C.; Gao, C.; Zhang, J.; Lu, X.; Wang, L.; Li, X.; Xing, Y.; Liu, R.; et al. Circulating tumor DNA 5-hydroxymethylcytosine as a novel diagnostic biomarker for esophageal cancer. Cell Res. 2018, 28, 597–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zeng, H.; He, B.; Xia, B.; Bai, D.; Lu, X.; Cai, J.; Chen, L.; Zhou, A.; Zhu, C.; Meng, H.; et al. Bisulfite-Free, Nanoscale Analysis of 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine at Single Base Resolution. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 13190–13194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nestor, C.E.; Meehan, R.R. Hydroxymethylated DNA immunoprecipitation (hmeDIP). Methods Mol. Biol. 2014, 1094, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Booth, M.J.; Ost, T.W.; Beraldi, D.; Bell, N.M.; Branco, M.R.; Reik, W.; Balasubramanian, S. Oxidative bisulfite sequencing of 5-methylcytosine and 5-hydroxymethylcytosine. Nat. Protoc. 2013, 8, 1841–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yu, M.; Hon, G.C.; Szulwach, K.E.; Song, C.X.; Jin, P.; Ren, B.; He, C. Tet-assisted bisulfite sequencing of 5-hydroxymethylcytosine. Nat. Protoc. 2012, 7, 2159–2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barros-Silva, D.; Marques, C.J.; Henrique, R.; Jeronimo, C. Profiling DNA Methylation Based on Next-Generation Sequencing Approaches: New Insights and Clinical Applications. Genes (Basel) 2018, 9, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FastQC. Available online: https://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc/ (accessed on 6 November 2019).
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trim Galore. Available online: https://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/trim_galore/ (accessed on 6 November 2019).
- Haeussler, M.; Zweig, A.S.; Tyner, C.; Speir, M.L.; Rosenbloom, K.R.; Raney, B.J.; Lee, C.M.; Lee, B.T.; Hinrichs, A.S.; Gonzalez, J.N.; et al. The UCSC Genome Browser database: 2019 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D853–D858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorvaldsdottir, H.; Robinson, J.T.; Mesirov, J.P. Integrative Genomics Viewer (IGV): High-performance genomics data visualization and exploration. Brief. Bioinform. 2013, 14, 178–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallona, I.; Diez-Villanueva, A.; Peinado, M.A. Methylation plotter: A web tool for dynamic visualization of DNA methylation data. Source Code Biol. Med. 2014, 9, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, F.; Tang, B.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Yu, C.; Chen, X.; Zhu, J.; Yan, J.; Zhao, W.; Li, R. WBSA: Web service for bisulfite sequencing data analysis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e86707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bock, C. Analysing and interpreting DNA methylation data. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2012, 13, 705–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bock, C.; Tomazou, E.M.; Brinkman, A.B.; Muller, F.; Simmer, F.; Gu, H.; Jager, N.; Gnirke, A.; Stunnenberg, H.G.; Meissner, A. Quantitative comparison of genome-wide DNA methylation mapping technologies. Nat. Biotechnol. 2010, 28, 1106–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, T.D.; Reeder, J.; Lawrence, M.; Becker, G.; Brauer, M.J. GMAP and GSNAP for Genomic Sequence Alignment: Enhancements to Speed, Accuracy, and Functionality. Methods Mol. Biol. 2016, 1418, 283–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krueger, F.; Andrews, S.R. Bismark: A flexible aligner and methylation caller for Bisulfite-Seq applications. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 1571–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, W.; Fiziev, P.; Yan, W.; Cokus, S.; Sun, X.; Zhang, M.Q.; Chen, P.Y.; Pellegrini, M. BS-Seeker2: A versatile aligning pipeline for bisulfite sequencing data. BMC Genom. 2013, 14, 774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, P.Y.; Cokus, S.J.; Pellegrini, M. BS Seeker: Precise mapping for bisulfite sequencing. BMC Bioinform. 2010, 11, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunde-Ramamoorthy, G.; Coarfa, C.; Laritsky, E.; Kessler, N.J.; Harris, R.A.; Xu, M.; Chen, R.; Shen, L.; Milosavljevic, A.; Waterland, R.A. Comparison and quantitative verification of mapping algorithms for whole-genome bisulfite sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, e43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daca-Roszak, P.; Pfeifer, A.; Zebracka-Gala, J.; Rusinek, D.; Szybinska, A.; Jarzab, B.; Witt, M.; Zietkiewicz, E. Impact of SNPs on methylation readouts by Illumina Infinium HumanMethylation450 BeadChip Array: Implications for comparative population studies. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. Fast gapped-read alignment with Bowtie 2. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 357–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, H.; Durbin, R. Fast and accurate short read alignment with Burrows-Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1754–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lienhard, M.; Grimm, C.; Morkel, M.; Herwig, R.; Chavez, L. MEDIPS: Genome-wide differential coverage analysis of sequencing data derived from DNA enrichment experiments. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 284–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Baheti, S.; Sun, Z. Statistical method evaluation for differentially methylated CpGs in base resolution next-generation DNA sequencing data. Brief. Bioinform. 2018, 19, 374–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mortazavi, A.; Williams, B.A.; McCue, K.; Schaeffer, L.; Wold, B. Mapping and quantifying mammalian transcriptomes by RNA-Seq. Nat. Methods 2008, 5, 621–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, M.D.; Oshlack, A. A scaling normalization method for differential expression analysis of RNA-seq data. Genome Biol. 2010, 11, R25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anders, S.; Huber, W. Differential expression analysis for sequence count data. Genome Biol. 2010, 11, R106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Down, T.A.; Rakyan, V.K.; Turner, D.J.; Flicek, P.; Li, H.; Kulesha, E.; Graf, S.; Johnson, N.; Herrero, J.; Tomazou, E.M.; et al. A Bayesian deconvolution strategy for immunoprecipitation-based DNA methylome analysis. Nat. Biotechnol. 2008, 26, 779–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lienhard, M.; Grasse, S.; Rolff, J.; Frese, S.; Schirmer, U.; Becker, M.; Borno, S.; Timmermann, B.; Chavez, L.; Sultmann, H.; et al. QSEA-modelling of genome-wide DNA methylation from sequencing enrichment experiments. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, e44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Oord, E.J.; Bukszar, J.; Rudolf, G.; Nerella, S.; McClay, J.L.; Xie, L.Y.; Aberg, K.A. Estimation of CpG coverage in whole methylome next-generation sequencing studies. BMC Bioinform. 2013, 14, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabalin, A.A.; Hattab, M.W.; Clark, S.L.; Chan, R.F.; Kumar, G.; Aberg, K.A.; van den Oord, E. RaMWAS: Fast methylome-wide association study pipeline for enrichment platforms. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 2283–2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, K.D.; Langmead, B.; Irizarry, R.A. BSmooth: From whole genome bisulfite sequencing reads to differentially methylated regions. Genome Biol. 2012, 13, R83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smyth, G.K. Linear models and empirical bayes methods for assessing differential expression in microarray experiments. Stat. Appl. Genet. Mol. Biol. 2004, 3. Article3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aryee, M.J.; Jaffe, A.E.; Corrada-Bravo, H.; Ladd-Acosta, C.; Feinberg, A.P.; Hansen, K.D.; Irizarry, R.A. Minfi: A flexible and comprehensive Bioconductor package for the analysis of Infinium DNA methylation microarrays. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 1363–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Podolsky, R.H.; Ryu, D.; Wang, X.; Su, S.; Shi, H.; George, V. A method to detect differentially methylated loci with next-generation sequencing. Genet. Epidemiol. 2013, 37, 377–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akalin, A.; Kormaksson, M.; Li, S.; Garrett-Bakelman, F.E.; Figueroa, M.E.; Melnick, A.; Mason, C.E. methylKit: A comprehensive R package for the analysis of genome-wide DNA methylation profiles. Genome Biol. 2012, 13, R87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, H.; Conneely, K.N.; Wu, H. A Bayesian hierarchical model to detect differentially methylated loci from single nucleotide resolution sequencing data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, e69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, Y.; Figueroa, M.E.; Rozek, L.S.; Sartor, M.A. MethylSig: A whole genome DNA methylation analysis pipeline. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2414–2422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dolzhenko, E.; Smith, A.D. Using beta-binomial regression for high-precision differential methylation analysis in multifactor whole-genome bisulfite sequencing experiments. BMC Bioinform. 2014, 15, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Day, K.; Waite, L.L.; Thalacker-Mercer, A.; West, A.; Bamman, M.M.; Brooks, J.D.; Myers, R.M.; Absher, D. Differential DNA methylation with age displays both common and dynamic features across human tissues that are influenced by CpG landscape. Genome Biol. 2013, 14, R102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wreczycka, K.; Gosdschan, A.; Yusuf, D.; Gruning, B.; Assenov, Y.; Akalin, A. Strategies for analyzing bisulfite sequencing data. J. Biotechnol. 2017, 261, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakyan, V.K.; Down, T.A.; Balding, D.J.; Beck, S. Epigenome-wide association studies for common human diseases. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2011, 12, 529–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ayyala, D.N.; Frankhouser, D.E.; Ganbat, J.O.; Marcucci, G.; Bundschuh, R.; Yan, P.; Lin, S. Statistical methods for detecting differentially methylated regions based on MethylCap-seq data. Brief. Bioinform. 2016, 17, 926–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.P.; Lin, Y.C.; Fann, C.S. Methods for identifying differentially methylated regions for sequence- and array-based data. Brief. Funct. Genom. 2016, 15, 485–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuji, J.; Weng, Z. Evaluation of preprocessing, mapping and postprocessing algorithms for analyzing whole genome bisulfite sequencing data. Brief. Bioinform. 2016, 17, 938–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Han, Y.; Zhou, L.; Chen, E.; Lu, B.; Liu, Y.; Pan, X.; Cowley, A.W., Jr.; Liang, M.; Wu, Q.; et al. A comprehensive evaluation of alignment software for reduced representation bisulfite sequencing data. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 2715–2723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yong, W.S.; Hsu, F.M.; Chen, P.Y. Profiling genome-wide DNA methylation. Epigenet. Chromatin 2016, 9, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akalin, A.; Franke, V.; Vlahovicek, K.; Mason, C.E.; Schubeler, D. Genomation: A toolkit to summarize, annotate and visualize genomic intervals. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 1127–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.J.; Gazin, C.; Lawson, N.D.; Pages, H.; Lin, S.M.; Lapointe, D.S.; Green, M.R. ChIPpeakAnno: A Bioconductor package to annotate ChIP-seq and ChIP-chip data. BMC Bioinform. 2010, 11, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teschendorff, A.E.; Breeze, C.E.; Zheng, S.C.; Beck, S. A comparison of reference-based algorithms for correcting cell-type heterogeneity in Epigenome-Wide Association Studies. BMC Bioinform. 2017, 18, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.; Li, Q.; Chen, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Park, S.; Lee, G.; Grimes, B.; Krysan, K.; Yu, M.; Wang, W.; et al. CancerLocator: Non-invasive cancer diagnosis and tissue-of-origin prediction using methylation profiles of cell-free DNA. Genome Biol. 2017, 18, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Li, Q.; Kang, S.; Same, M.; Zhou, Y.; Sun, C.; Liu, C.C.; Matsuoka, L.; Sher, L.; Wong, W.H.; et al. CancerDetector: Ultrasensitive and non-invasive cancer detection at the resolution of individual reads using cell-free DNA methylation sequencing data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, e89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, M.; Klotzek, S.; Lewandowski, M.; Fleischhacker, M.; Jung, K. Changes in concentration of DNA in serum and plasma during storage of blood samples. Clin. Chem. 2003, 49, 1028–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panagopoulou, M.; Karaglani, M.; Balgkouranidou, I.; Biziota, E.; Koukaki, T.; Karamitrousis, E.; Nena, E.; Tsamardinos, I.; Kolios, G.; Lianidou, E.; et al. Circulating cell-free DNA in breast cancer: Size profiling, levels, and methylation patterns lead to prognostic and predictive classifiers. Oncogene 2019, 38, 3387–3401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Q.; Zou, J.; Tang, J.; Fang, Y.; Yu, Z.; Fan, S. MRCNN: A deep learning model for regression of genome-wide DNA methylation. BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pantel, K.; Alix-Panabieres, C. Liquid biopsy and minimal residual disease - latest advances and implications for cure. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gkountela, S.; Castro-Giner, F.; Szczerba, B.M.; Vetter, M.; Landin, J.; Scherrer, R.; Krol, I.; Scheidmann, M.C.; Beisel, C.; Stirnimann, C.U.; et al. Circulating Tumor Cell Clustering Shapes DNA Methylation to Enable Metastasis Seeding. Cell 2019, 176, 98–112.e114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cristiano, S.; Leal, A.; Phallen, J.; Fiksel, J.; Adleff, V.; Bruhm, D.C.; Jensen, S.O.; Medina, J.E.; Hruban, C.; White, J.R.; et al. Genome-wide cell-free DNA fragmentation in patients with cancer. Nature 2019, 570, 385–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ovcharenko, A.; Rentmeister, A. Emerging approaches for detection of methylation sites in RNA. Open Biol. 2018, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
| Class | Technology | Strength | Weakness | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Restriction enzyme-based | -High CGI coverage | -Low resolution -Limited to regions in proximity to restriction enzyme sites | ||
| qPCR or ddPCR | -Allows ultra-low DNA input -Easy primer design | -Loci-specific studies only | Low | |
| Bisulfite-based | -Single-based resolution | -Substantial DNA degradation during bisulfite treatment -Cannot discriminate between 5mC and 5hmC | ||
| WGBS | -The most comprehensive profiling of the whole methylome | -Relatively low sequencing depth | High | |
| RRBS | -High CGIs coverage | -Limited to regions in proximity to restriction enzyme sites | Moderate | |
| MTCA-seq | -High CGIs coverage | -Limited to CGIs and might decrease other methylation backgrounds | Moderate | |
| Targeted | -Detect target CpG sites at high coverage | -Complicated primer or probe design | Low | |
| Microarray | -Pre-designed panel covering hotspot methylation | -Low genome-wide coverage of CpGs | Low | |
| qMSP or ddMSP | -Allows ultra-low DNA input | -Loci-specific studies only -Complicated primer or probe design | Low | |
| Enrichment-based | -No mutation introduced | -Low resolution -Biased toward hypermethylated regions | ||
| MeDIP-seq | -Antibody is specific to 5mC | -Less sensitive in regions with high CpG density than MBD-seq | Moderate | |
| 5hmC profiling | -Specific to 5hmC | -High sequencing depth is required as 5hmC has a low abundance | ||
| 5hmC-Seal | -Ensures accurate capture of DNA containing 5hmC | -Low resolution | Moderate | |
| hmC-CATCH | -Single-based resolution | -Oxidative environment would cause DNA damage | Moderate |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, J.; Wang, L. Cell-Free DNA Methylation Profiling Analysis—Technologies and Bioinformatics. Cancers 2019, 11, 1741. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11111741
Huang J, Wang L. Cell-Free DNA Methylation Profiling Analysis—Technologies and Bioinformatics. Cancers. 2019; 11(11):1741. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11111741
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Jinyong, and Liang Wang. 2019. "Cell-Free DNA Methylation Profiling Analysis—Technologies and Bioinformatics" Cancers 11, no. 11: 1741. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11111741
APA StyleHuang, J., & Wang, L. (2019). Cell-Free DNA Methylation Profiling Analysis—Technologies and Bioinformatics. Cancers, 11(11), 1741. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11111741





