The Role and Function of microRNA in the Pathogenesis of Multiple Myeloma
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. What Is miRNA?
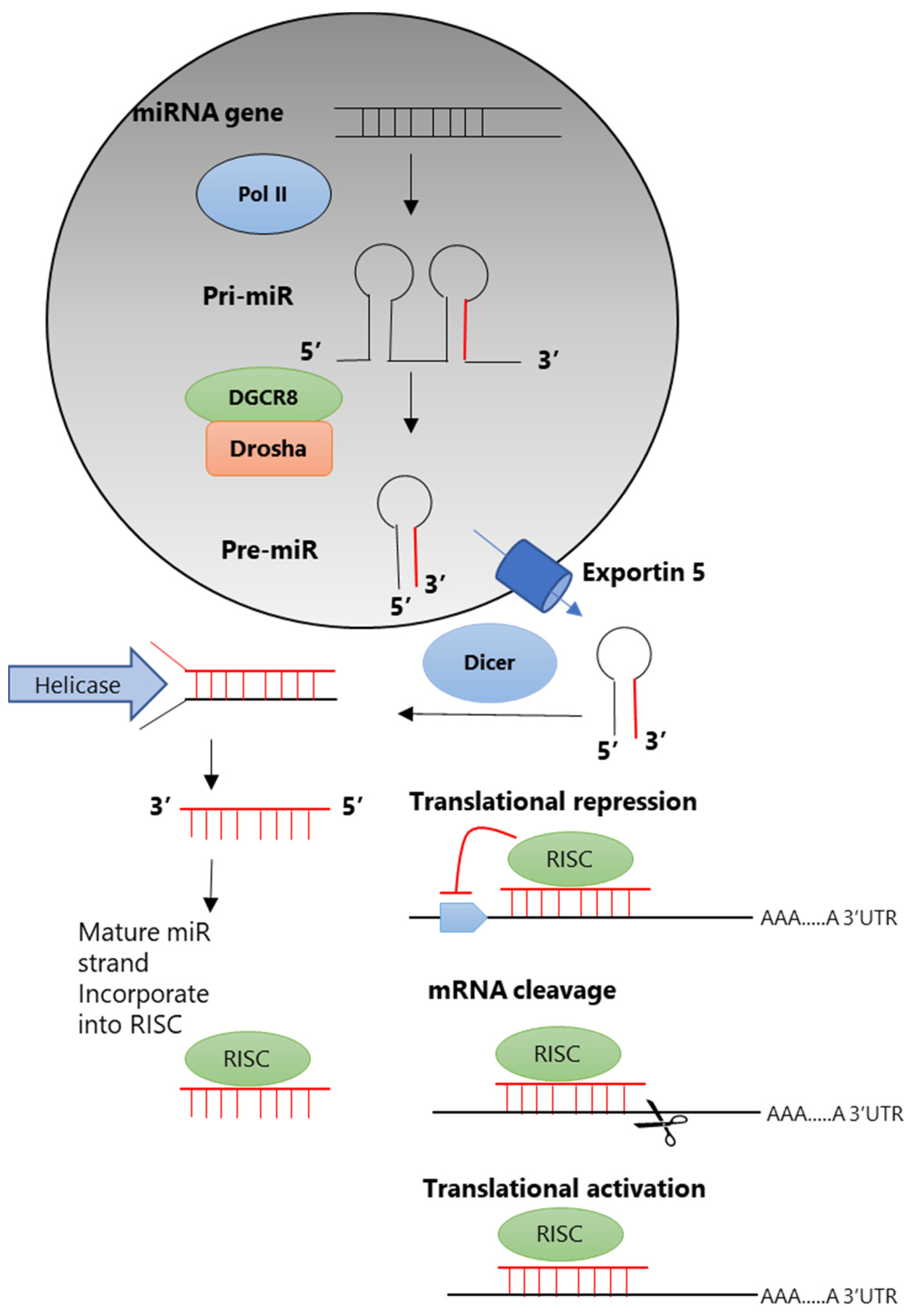
3. Mechanisms of miRNA Production and Action
4. Cancer and miRNAs
5. miRNA Abnormalities in MM
6. Chromosomal Abnormalities and miRNA Expression in MM
7. miRNA and the p53 Pathway
8. Epigenetic Regulation and miRNA in MM
9. Other miRNA Regulatory Mechanisms in MM
10. Drug Resistance and miRNA
11. Possible Classification of MM by miRNA Expression Profiling
12. Circulating miRNA in the Bloodstream
13. miRNA and the Microenvironment
14. Potential Therapies Using miRNA
15. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lee, R.C.; Feinbaum, R.L.; Ambros, V. The C. elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense complementarity to lin-14. Cell 1993, 75, 843–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinhart, B.J.; Slack, F.J.; Basson, M.; Pasquinelli, A.E.; Bettinger, J.C.; Rougvie, A.E.; Horvitz, H.R.; Ruvkun, G. The 21-nucleotide let-7 RNA regulates developmental timing in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature 2000, 403, 901–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berezikov, E. Evolution of microRNA diversity and regulation in animals. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2011, 12, 846–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deline, B.; Greenwood, J.M.; Clark, J.W.; Puttick, M.N.; Peterson, K.J.; Donoghue, P.C.J. Evolution of metazoan morphological disparity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E8909–E8918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarver, J.E.; Donoghue, P.C.; Peterson, K.J. Do miRNAs have a deep evolutionary history? Bioessays 2012, 34, 857–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Cordoba, S.L.; Salido-Guadarrama, I.; Rodriguez-Dorantes, M.; Hidalgo-Miranda, A. miRNA biogenesis: Biological impact in the development of cancer. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2014, 15, 1444–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iorio, M.V.; Croce, C.M. MicroRNA dysregulation in cancer: Diagnostics, monitoring and therapeutics. A comprehensive review. EMBO Mol. Med. 2012, 4, 143–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iorio, M.V.; Croce, C.M. microRNA involvement in human cancer. Carcinogenesis 2012, 33, 1126–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aqeilan, R.I.; Calin, G.A.; Croce, C.M. miR-15a and miR-16-1 in cancer: Discovery, function, and future perspectives. Cell Death Differ. 2010, 17, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calin, G.A.; Dumitru, C.D.; Shimizu, M.; Bichi, R.; Zupo, S.; Noch, E.; Aldler, H.; Rattan, S.; Keating, M.; Rai, K.; et al. Frequent deletions and down-regulation of micro-RNA genes miR15 and miR16 at 13q14 in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 15524–15529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cimmino, A.; Calin, G.A.; Fabbri, M.; Iorio, M.V.; Ferracin, M.; Shimizu, M.; Wojcik, S.E.; Aqeilan, R.I.; Zupo, S.; Dono, M.; et al. miR-15 and miR-16 induce apoptosis by targeting BCL2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 13944–13949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svoronos, A.A.; Engelman, D.M.; Slack, F.J. OncomiR or Tumor Suppressor? The Duplicity of MicroRNAs in Cancer. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 3666–3670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Masri, A.; Price-Troska, T.; Chesi, M.; Chung, T.H.; Kim, S.; Carpten, J.; Bergsagel, P.L.; Fonseca, R. MicroRNA Expression Analysis in Multiple Myeloma. Blood 2005, 106, 1554. [Google Scholar]
- Pichiorri, F.; Suh, S.S.; Ladetto, M.; Kuehl, M.; Palumbo, T.; Drandi, D.; Taccioli, C.; Zanesi, N.; Alder, H.; Hagan, J.P.; et al. MicroRNAs regulate critical genes associated with multiple myeloma pathogenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 12885–12890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerner, M.; Harada, M.; Lovén, J.; Castro, J.; Davis, Z.; Oscier, D.; Henriksson, M.; Sangfelt, O.; Grandér, D.; Corcoran, M.M. DLEU2, frequently deleted in malignancy, functions as a critical host gene of the cell cycle inhibitory microRNAs miR-15a and miR-16-1. Exp. Cell Res. 2009, 315, 2941–2952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roccaro, A.M.; Sacco, A.; Thompson, B.; Leleu, X.; Azab, A.K.; Azab, F.; Runnels, J.; Jia, X.; Ngo, H.T.; Melhem, M.R.; et al. MicroRNAs 15a and 16 regulate tumor proliferation in multiple myeloma. Blood 2009, 113, 6669–6680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handa, H.; Hattori, H.; Takahashi, N.; Sasaki, Y.; Saitoh, T.; Osaki, Y.; Tahara, K.; Koiso, H.; Mitsui, T.; Shimizu, H.; et al. Association between micro-RNA and epigenetic modifiers DNA methyltransferases (DNMTs), histone deacetylases (HDACs) in multiple myeloma (MM) and monoclonal gammopathy with undetermined significance (MGUS). Blood 2012, 120, 3942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löffler, D.; Brocke-Heidrich, K.; Pfeifer, G.; Stocsits, C.; Hackermüller, J.; Kretzschmar, A.K.; Burger, R.; Gramatzki, M.; Blumert, C.; Bauer, K.; et al. Interleukin-6 dependent survival of multiple myeloma cells involves the Stat3-mediated induction of microRNA-21 through a highly conserved enhancer. Blood 2007, 110, 1330–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leone, E.; Morelli, E.; Di Martino, M.T.; Amodio, N.; Foresta, U.; Gullà, A.; Rossi, M.; Neri, A.; Giordano, A.; Munshi, N.C.; et al. Targeting miR-21 inhibits in vitro and in vivo multiple myeloma cell growth. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 2096–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Martino, M.T.; Gullà, A.; Cantafio, M.E.; Lionetti, M.; Leone, E.; Amodio, N.; Guzzi, P.H.; Foresta, U.; Conforti, F.; Cannataro, M.; et al. In vitro and in vivo anti-tumor activity of miR-221/222 inhibitors in multiple myeloma. Oncotarget 2013, 4, 242–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gullà, A.; Di Martino, M.T.; Gallo Cantafio, M.E.; Morelli, E.; Amodio, N.; Botta, C.; Pitari, M.R.; Lio, S.G.; Britti, D.; Stamato, M.A.; et al. A 13 mer LNA-i-miR-221 inhibitor restores drug sensitivity in melphalan-refractory multiple myeloma cells. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 1222–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.J.; Chu, Z.B.; Hu, Y.; Lin, J.; Wang, Z.; Jiang, M.; Chen, M.; Wang, X.; Kang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; et al. Targeting the miR-221/222/PUMA/BAK/BAX pathway abrogates dexamethasone resistance in multiple myeloma. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 4384–4397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, X.Y.; Zhang, S.S.; Wu, S.; Hong, M.; Li, J.Y.; Chen, L.J.; Xu, J.R. Expression level of microRNA-92a and its clinical significance in multiple myeloma patients. Chin. J. Hematol. 2013, 34, 332–336. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.K.; Wang, H.; Leng, Y.; Li, Z.L.; Yang, Y.F.; Xiao, F.J.; Li, Q.F.; Chen, X.Q.; Wang, L.S. Overexpression of microRNA-29b induces apoptosis of multiple myeloma cells through down regulating Mcl-1. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2011, 414, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lionetti, M.; Biasiolo, M.; Agnelli, L.; Todoerti, K.; Mosca, L.; Fabris, S.; Sales, G.; Deliliers, G.L.; Bicciato, S.; Lombardi, L.; et al. Identification of microRNA expression patterns and definition of a microRNA/mRNA regulatory network in distinct molecular groups of multiple myeloma. Blood 2009, 114, e20–e26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corthals, S.L.; Jongen-Lavrencic, M.; de Knegt, Y.; Peeters, J.K.; Beverloo, H.B.; Lokhorst, H.M.; Sonneveld, P. Micro-RNA-15a and micro-RNA-16 expression and chromosome 13 deletions in multiple myeloma. Leuk. Res. 2010, 34, 677–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corthals, S.L.; Sun, S.M.; Kuiper, R.; de Knegt, Y.; Broyl, A.; van der Holt, B.; Beverloo, H.B.; Peeters, J.K.; el Jarari, L.; Lokhorst, H.M.; et al. MicroRNA signatures characterize multiple myeloma patients. Leukemia 2011, 25, 1784–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lionetti, M.; Agnelli, L.; Mosca, L.; Fabris, S.; Andronache, A.; Todoerti, K.; Ronchetti, D.; Deliliers, G.L.; Neri, A. Integrative high-resolution microarray analysis of human myeloma cell lines reveals deregulated miRNA expression associated with allelic imbalances and gene expression profiles. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2009, 48, 521–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez, N.C.; Sarasquete, M.E.; Misiewicz-Krzeminska, I.; Delgado, M.; De Las Rivas, J.; Ticona, F.V.; Fermiñán, E.; Martín-Jiménez, P.; Chillón, C.; Risueño, A.; et al. Deregulation of microRNA expression in the different genetic subtypes of multiple myeloma and correlation with gene expression profiling. Leukemia 2010, 24, 629–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, J.; Ballabio, E.; Chen, X.H.; Kušec, R.; Taylor, S.; Hay, D.; Tramonti, D.; Saunders, N.J.; Littlewood, T.; Pezzella, F.; et al. MicroRNA expression in multiple myeloma is associated with genetic subtype, isotype and survival. Biol. Direct 2011, 6, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, B.; Xu, A.; Xu, J.; Huang, H.; Chen, L.; Su, Y.; Zhang, L.; Li, J.; Fan, F.; Deng, J.; et al. MicroRNA-324-5p regulates stemness, pathogenesis and sensitivity to bortezomib in multiple myeloma cells by targeting hedgehog signaling. Int. J. Cancer 2018, 142, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyd, K.D.; Ross, F.M.; Tapper, W.J.; Chiecchio, L.; Dagrada, G.; Konn, Z.J.; Gonzalez, D.; Walker, B.A.; Hockley, S.L.; Wardell, C.P.; et al. NCRI Haematology Oncology Studies Group. The clinical impact and molecular biology of del(17p) in multiple myeloma treated with conventional or thalidomide-based therapy. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2011, 50, 765–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avet-Loiseau, H.; Attal, M.; Campion, L.; Caillot, D.; Hulin, C.; Marit, G.; Stoppa, A.M.; Voillat, L.; Wetterwald, M.; Pegourie, B.; et al. Long-term analysis of the IFM 99 trials for myeloma: Cytogenetic abnormalities [t(4;14), del(17p), 1q gains] play a major role in defining long-term survival. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 1949–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avet-Loiseau, H.; Durie, B.G.; Cavo, M.; Attal, M.; Gutierrez, N.; Haessler, J.; Goldschmidt, H.; Hajek, R.; Lee, J.H.; Sezer, O.; et al. International Myeloma Working Group. Combining fluorescent in situ hybridization data with ISS staging improves risk assessment in myeloma: An International Myeloma Working Group collaborative project. Leukemia 2013, 27, 711–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nag, S.; Zhang, X.; Srivenugopal, K.S.; Wang, M.H.; Wang, W.; Zhang, R. Targeting MDM2-p53 interaction for cancer therapy: Are we there yet? Curr. Med. Chem. 2014, 21, 553–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elnenaei, M.O.; Gruszka-Westwood, A.M.; A’Hernt, R.; Matutes, E.; Sirohi, B.; Powles, R.; Catovsky, D. Gene abnormalities in multiple myeloma; the relevance of TP53, MDM2, and CDKN2A. Haematologica 2003, 88, 529–537. [Google Scholar]
- Pichiorri, F.; Suh, S.S.; Rocci, A.; De Luca, L.; Taccioli, C.; Santhanam, R.; Zhou, W.; Benson, D.M., Jr.; Hofmainster, C.; Alder, H.; et al. Downregulation of p53-inducible microRNAs 192, 194, and 215 impairs the p53/MDM2 autoregulatory loop in multiple myeloma development. Cancer Cell 2010, 18, 367–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hünten, S.; Siemens, H.; Kaller, M.; Hermeking, H. The p53/microRNA network in cancer: Experimental and bioinformatics approaches. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2013, 774, 77–101. [Google Scholar]
- Leotta, M.; Biamonte, L.; Raimondi, L.; Ronchetti, D.; Di Martino, M.T.; Botta, C.; Leone, E.; Pitari, M.R.; Neri, A.; Giordano, A.; et al. A p53-dependent tumor suppressor network is induced by selective miR-125a-5p inhibition in multiple myeloma cells. J. Cell. Physiol. 2014, 229, 2106–2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, M.T.; Teh, C.; Shyh-Chang, N.; Xie, H.; Zhou, B.; Korzh, V.; Lodish, H.F.; Lim, B. MicroRNA-125b is a novel negative regulator of p53. Genes Dev. 2009, 23, 862–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Chan, C.S.; Wu, R.; Zhang, C.; Sun, Y.; Song, J.S.; Tang, L.H.; Levine, A.J.; Feng, Z. Negative regulation of tumor suppressor p53 by microRNA miR-504. Mol. Cell 2010, 38, 689–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, M.Y.; Rushworth, S.A.; Zaitseva, L.; Bowles, K.M.; Macewan, D.J. Attenuation of dexamethasone-induced cell death in multiple myeloma is mediated by miR-125b expression. Cell Cycle 2013, 12, 2144–2153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misso, G.; Zarone, M.R.; Lombardi, A.; Grimaldi, A.; Cossu, A.M.; Ferri, C.; Russo, M.; Vuoso, D.C.; Luce, A.; Kawasaki, H.; et al. miR-125b Upregulates miR-34a and Sequentially Activates Stress Adaption and Cell Death Mechanisms in Multiple Myeloma. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2019, 16, 391–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hermeking, H. The miR-3a family in cancer and apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 2010, 17, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okada, N.; Lin, C.P.; Ribeiro, M.C.; Biton, A.; Lai, G.; He, X.; Bu, P.; Vogel, H.; Jablons, D.M.; Keller, A.C.; et al. A positive feedback between p53 and miR-34 miRNAs mediates tumor suppression. Genes Dev. 2014, 28, 438–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chim, C.S.; Wong, K.Y.; Qi, Y.; Loong, F.; Lam, W.L.; Wong, L.G.; Jin, D.Y.; Costello, J.F.; Liang, R. Epigenetic inactivation of the miR-34a in hematological malignancies. Carcinogenesis 2010, 31, 745–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, K.; Kuroda, Y.; Masuda, Y.; Yamane, A.; Hattori, H.; Tahara, K.; Kaneko, A.; Suda, I.; Takahashi, N.; Gotoh, N.; et al. Loop regulation between microRNAs and epigenetics underlie microRNA dysregulation in multiple myeloma and is associated with the disease progression. Blood 2015, 126, 3013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handa, H. Aberrant micro RNA and epigenetic network are associated with progression from MGUS to multiple myeloma. Rinsho Ketsueki 2015, 56, 981–988. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, K.Y.; Yim, R.L.; So, C.C.; Jin, D.Y.; Liang, R.; Chim, C.S. Epigenetic inactivation of the MIR34B/C in multiple myeloma. Blood 2011, 118, 5901–5904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, K.Y.; Huang, X.; Chim, C.S. DNA methylation of microRNA genes in multiple myeloma. Carcinogenesis 2012, 33, 1629–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Wang, Y.E.; Zhang, Y.; Leleu, X.; Reagan, M.; Zhang, Y.; Mishima, Y.; Glavey, S.; Manier, S.; Sacco, A.; et al. Global epigenetic regulation of microRNAs in multiple myeloma. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e110973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misiewicz-Krzeminska, I.; Krzeminski, P.; Corchete, L.A.; Quwaider, D.; Rojas, E.A.; Herrero, A.B.; Gutiérrez, N.C. Factors regulating microRNA expression and function in multiple myeloma. Noncoding RNA 2019, 5, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tatekawa, S.; Chinen, Y.; Ri, M.; Narita, T.; Shimura, Y.; Matsumura-Kimoto, Y.; Tsukamoto, T.; Kobayashi, T.; Kawata, E.; Uoshima, N.; et al. Epigenetic repression of miR-375 is the dominant mechanism for constitutive activation of the PDPK1/RPS6KA3 signalling axis in multiple myeloma. Br. J. Haematol. 2017, 178, 534–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amodio, N.; Stamato, M.A.; Gullà, A.M.; Morelli, E.; Romeo, E.; Raimondi, L.; Pitari, M.R.; Ferrandino, I.; Misso, G.; Caraglia, M.; et al. Therapeutic Targeting of miR-29b/HDAC4 Epigenetic Loop in Multiple Myeloma. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2016, 15, 1364–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamato, M.A.; Juli, G.; Romeo, E.; Ronchetti, D.; Arbitrio, M.; Caracciolo, D.; Neri, A.; Tagliaferri, P.; Tassone, P.; Amodio, N. Inhibition of EZH2 triggers the tumor suppressive miR-29b network in multiple myeloma. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 106527–106537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, D.J.; Ezponda, T.; Kim, M.K.; Will, C.M.; Martinez-Garcia, E.; Popovic, R.; Basrur, V.; Elenitoba-Johnson, K.S.; Licht, J.D. MMSET stimulates myeloma cell growth through microRNA-mediated modulation of c-MYC. Leukemia 2013, 27, 686–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandoval, J.; Esteller, M. Cancer epigenomics: Beyond genomics. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2012, 22, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amodio, N.; Leotta, M.; Bellizzi, D.; Di Martino, M.T.; D’Aquila, P.; Lionetti, M.; Fabiani, F.; Leone, E.; Gullà, A.M.; Passarino, G.; et al. DNA-demethylating and anti-tumor activity of synthetic miR-29b mimics in multiple myeloma. Oncotarget 2012, 3, 1246–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garzon, R.; Liu, S.; Fabbri, M.; Liu, Z.; Heaphy, C.E.; Callegari, E.; Schwind, S.; Pang, J.; Yu, J.; Muthusamy, N.; et al. MicroRNA-29b induces global DNA hypomethylation and tumor suppressor gene reexpression in acute myeloid leukemia by targeting directly DNMT3A and 3B and indirectly DNMT1. Blood 2009, 113, 6411–6418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Wu, L.C.; Pang, J.; Santhanam, R.; Schwind, S.; Wu, Y.Z.; Hickey, C.J.; Yu, J.; Becker, H.; Maharry, K.; et al. Sp1/NFkappaB/HDAC/miR-29b regulatory network in KIT-driven myeloid leukemia. Cancer Cell 2010, 17, 333–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabbri, M.; Garzon, R.; Cimmino, A.; Liu, Z.; Zanesi, N.; Callegari, E.; Liu, S.; Alder, H.; Costinean, S.; Fernandez-Cymering, C.; et al. MicroRNA-29 family reverts aberrant methylation in lung cancer by targeting DNA methyltransferases 3A and 3B. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 15805–15810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amodio, N.; Bellizzi, D.; Leotta, M.; Raimondi, L.; Biamonte, L.; D’Aquila, P.; Di Martino, M.T.; Calimeri, T.; Rossi, M.; Lionetti, M.; et al. miR-29b induces SOCS-1 epression by promoter demethylation and negatively regulates migration of multiple myeloma and endothelial cells. Cell Cycle 2013, 12, 3650–3662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mott, J.L.; Kurita, S.; Cazanave, S.C.; Bronk, S.F.; Werneburg, N.W.; Fernandez-Zapico, M.E. Transcriptional suppression of mir-29b-1/mir-29a promoter by c-Myc, hedgehog, and NF-kappaB. J. Cell. Biochem. 2010, 110, 1155–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amodio, N.; Di Martino, M.T.; Foresta, U.; Leone, E.; Lionetti, M.; Leotta, M.; Gullà, A.M.; Pitari, M.R.; Conforti, F.; Rossi, M.; et al. miR-29b sensitizes multiple myeloma cells to bortezomib-induced apoptosis through the activation of a feedback loop with the transcription factor Sp1. Cell Death Dis. 2012, 3, e436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fulciniti, M.; Amodio, N.; Bandi, R.L.; Cagnetta, A.; Samur, M.K.; Acharya, C.; Prabhala, R.; D’Aquila, P.; Bellizzi, D.; Passarino, G.; et al. miR-23b/SP1/c-myc forms a feed-forward loop supporting multiple myeloma cell growth. Blood Cancer J. 2016, 6, e380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarasquete, M.E.; Gutiérrez, N.C.; Misiewicz-Krzeminska, I.; Paiva, B.; Chillón, M.C.; Alcoceba, M.; García-Sanz, R.; Hernández, J.M.; González, M.; San-Miguel, J.F. Upregulation of Dicer is more frequent in monoclonal gammopathies of undetermined significance than in multiple myeloma patients and is associated with longer survival in symptomatic myeloma patients. Haematologica 2011, 96, 468–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cesana, M.; Cacchiarelli, D.; Legnini, I.; Santini, T.; Sthandier, O.; Chinappi, M.; Tramontano, A.; Bozzoni, I. A long noncoding RNA controls muscle differentiation by functioning as a competing endogenous RNA. Cell 2011, 147, 358–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmena, L.; Poliseno, L.; Tay, Y.; Kats, L.; Pandolfi, P.P. A ceRNA hypothesis: The Rosetta Stone of a hidden RNA language? Cell 2011, 146, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomson, D.W.; Dinger, M.E. Endogenous microRNA sponges: Evidence and controversy. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2016, 17, 272–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Yao, W.; Gumireddy, K.; Li, A.; Wang, J.; Xiao, W.; Chen, K.; Xiao, H.; Li, H.; Tang, K.; et al. Pseudogene PTENP1 functions as a competing endogenous RNA to suppress clear-cell renal cell carcinoma progression. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2014, 13, 3086–3097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdi, J.; Jian, H.; Chang, H. Role of micro-RNAs in drug resistance of multiple myeloma. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 60723–60735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, M.; Zhang, L.; An, G.; Sui, W.; Yu, Z.; Zou, D.; Xu, Y.; Chang, H.; Qiu, L. Suppressing miRNA-15a/-16 expression by interleukin-6 enhances drug-resistance in myeloma cells. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2011, 4, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Li, F.; Saha, M.N.; Abdi, J.; Qiu, L.; Chang, H. miR-137 and miR-197 induce apoptosis and suppress tumorigenicity by targeting MCL-1 in multiple myeloma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 2399–2411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Ma, L.; Wei, J.; Hu, J.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, F. miR-137 suppresses the phosphorylation of AKT and improves the dexamethasone sensitivity in multiple myeloma cells via targeting MITF. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2016, 16, 807–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, Y.; Zhang, S.; Deng, S.; An, G.; Qin, X.; Li, F.; Xu, Y.; Hao, M.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, W.; et al. Epigenetic silencing of miR-137 induces drug resistance and chromosomal instability by targeting AURKA in multiple myeloma. Leukemia 2017, 31, 1123–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballabio, E.; Armesto, M.; Breeze, C.E.; Manterola, L.; Arestin, M.; Tramonti, D.; Hatton, C.S.; Lawrie, C.H. Bortezomib action in multiple myeloma: microRNA-mediated synergy (and miR-27a/CDK5 driven sensitivity)? Blood Cancer J. 2012, 2, e83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xi, H.; Li, L.; Du, J.; An, R.; Fan, R.; Lu, J.; Wu, Y.X.; Wu, S.X.; Hou, J.; Zhao, L.M. hsa-miR-631 resensitizes bortezomib-resistant multiple myeloma cell lines by inhibiting UbcH10. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 37, 961–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amodio, N.; Gallo Cantafio, M.E.; Botta, C.; Agosti, V.; Federico, C.; Caracciolo, D.; Ronchetti, D.; Rossi, M.; Driessen, C.; Neri, A.; et al. Replacement of miR-155 Elicits Tumor Suppressive Activity and Antagonizes Bortezomib Resistance in Multiple Myeloma. Cancers 2019, 11, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, F.; Zhan, Y.; Zhu, W.; Li, J.; Tang, M.; Chen, X.; Jiang, J. MicroRNA-497 inhibits multiple myeloma growth and increases susceptibility to bortezomib by targeting Bcl-2. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2019, 43, 1058–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Ma, R.; Yang, S.; Jiang, L.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, Z.; Li, H. miR-520g and miR-520h overcome bortezomib resistance in multiple myeloma via suppressing APE1. Cell Cycle 2019, 18, 1660–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, C.; Ju, S.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhong, R. Myeloma cell adhesion to bone marrow stromal cells confers drug resistance by microRNA-21 up-regulation. Leuk. Lymphoma 2011, 52, 1991–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Su, Y.; Xu, A.; Fan, F.; Mu, S.; Chen, L.; Chu, Z.; Zhang, B.; Huang, H.; Zhang, J.; et al. miR-221/222-Mediated Inhibition of Autophagy Promotes Dexamethasone Resistance in Multiple Myeloma. Mol. Ther. 2019, 27, 559–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Xu, Y.; Deng, S.; Li, Z.; Zou, D.; Yi, S.; Sui, W.; Hao, M.; Qiu, L. MicroRNA-15a/16-1 cluster located at chromosome 13q14 is down-regulated but displays different expression pattern and prognostic significance in multiple myeloma. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 38270–38282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Zhang, R.; Qu, X.; Zhao, M.; Zhang, S.; Wu, H.; Jianyong, L.; Chen, L. MiR-15a, miR-16-1 and miR-17-92 cluster expression are linked to poor prognosis in multiple myeloma. Leuk. Res. 2012, 36, 1505–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, P.; Agnelli, L.; Walker, B.A.; Todoerti, K.; Lionetti, M.; Johnson, D.C.; Kaiser, M.; Mirabella, F.; Wardell, C.; Gregory, W.M.; et al. Improved risk stratification in myeloma using a microRNA-based classifier. Br. J. Haematol. 2013, 162, 348–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, P.; Xia, T.; Ling, Y.; Chen, B. MiRNAs with prognostic significance in multiple myeloma: A systemic review and meta-analysis. Medicine 2019, 98, e16711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Hao, M.; Feng, X.; Zang, M.; Qin, Y.; Yi, S.; Li, Z.; Xu, Y.; Zhou, L.; Sui, W.; et al. Downregulated miR-33b is a novel predictor associated with disease progression and poor prognosis in multiple myeloma. Leuk. Res. 2015, 39, 793–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Leva, G.; Croce, C.M. miRNA profiling of cancer. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2013, 23, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannafon, B.N.; Ding, W.Q. Intercellular Communication by Exosome-Derived microRNAs in Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 14240–14269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, M.A.; Ludwig, R.G.; Garcia-Martin, R.; Brandão, B.B.; Kahn, C.R. Extracellular miRNAs: From Biomarkers to Mediators of Physiology and Disease. Cell Metab. 2019, 30, 656–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moloudizargari, M.; Abdollahi, M.; Asghari, M.H.; Zimta, A.A.; Neagoe, I.B.; Nabavi, S.M. The emerging role of exosomes in multiple myeloma. Blood Rev. 2019, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grimaldi, A.; Zarone, M.R.; Irace, C.; Zappavigna, S.; Lombardi, A.; Kawasaki, H.; Caraglia, M.; Misso, G. Non-coding RNAs as a new dawn in tumor diagnosis. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2018, 78, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vickers, K.C.; Palmisano, B.T.; Shoucri, B.M.; Shamburek, R.D.; Remaley, A.T. MicroRNAs are transported in plasma and delivered to recipient cells by high-density lipoproteins. Nat. Cell Biol. 2011, 13, 423–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arroyo, J.D.; Chevillet, J.R.; Kroh, E.M.; Ruf, I.K.; Pritchard, C.C.; Gibson, D.F.; Mitchell, P.S.; Bennett, C.F.; Pogosova-Agadjanyan, E.L.; Stirewalt, D.L.; et al. Argonaute2 complexes carry a population of circulating microRNAs independent of vesicles in human plasma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 5003–5008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roccaro, A.M.; Sacco, A.; Maiso, P.; Azab, A.K.; Tai, Y.T.; Reagan, M.; Azab, F.; Flores, L.M.; Campigotto, F.; Weller, E.; et al. BM mesenchymal stromal cell-derived exosomes facilitate multiple myeloma progression. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 1542–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manier, S.; Liu, C.J.; Avet-Loiseau, H.; Park, J.; Shi, J.; Campigotto, F.; Salem, K.Z.; Huynh, D.; Glavey, S.V.; Rivotto, B.; et al. Prognostic role of circulating exosomal miRNAs in multiple myeloma. Blood 2017, 129, 2429–2436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.Y.; Li, Y.C.; Geng, C.Y.; Zhou, H.X.; Gao, W.; Chen, W.M. Serum exosomal microRNAs as novel biomarkers for multiple myeloma. Hematol. Oncol. 2019, 37, 409–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Pan, L.; Xiang, B.; Zhu, H.; Wu, Y.; Chen, M.; Guan, P.; Zou, X.; Valencia, C.A.; Dong, B.; et al. Potential role of exosome-associated microRNA panels and in vivo environment to predict drug resistance for patients with multiple myeloma. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 30876–30891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frassanito, M.A.; Desantis, V.; Di Marzo, L.; Craparotta, I.; Beltrame, L.; Marchini, S.; Annese, T.; Visino, F.; Arciuli, M.; Saltarella, I.; et al. Bone marrow fibroblasts overexpress miR-27b and miR-214 in step with multiple myeloma progression, dependent on tumour cell-derived exosomes. J. Pathol. 2019, 247, 241–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Veirman, K.; Wang, J.; Xu, S.; Leleu, X.; Himpe, E.; Maes, K.; De Bruyne, E.; Van Valckenborgh, E.; Vanderkerken, K.; Menu, E.; et al. Induction of miR-146a by multiple myeloma cells in mesenchymal stromal cells stimulates their pro-tumoral activity. Cancer Lett. 2016, 377, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botta, C.; Cucè, M.; Pitari, M.R.; Caracciolo, D.; Gullà, A.; Morelli, E.; Riillo, C.; Biamonte, L.; Gallo Cantafio, M.E.; Prabhala, R.; et al. MiR-29b antagonizes the pro-inflammatory tumor-promoting activity of multiple myeloma-educated dendritic cells. Leukemia 2018, 32, 1003–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossi, M.; Pitari, M.R.; Amodio, N.; Di Martino, M.T.; Conforti, F.; Leone, E.; Botta, C.; Paolino, F.M.; Del Giudice, T.; Iuliano, E.; et al. miR-29b negatively regulates human osteoclastic cell differentiation and function: Implications for the treatment of multiple myeloma-related bone disease. J. Cell. Physiol. 2013, 228, 1506–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsukamoto, S.; Løvendorf, M.B.; Park, J.; Salem, K.Z.; Reagan, M.R.; Manier, S.; Zavidij, O.; Rahmat, M.; Huynh, D.; Takagi, S.; et al. Inhibition of microRNA-138 enhances bone formation in multiple myeloma bone marrow niche. Leukemia 2018, 32, 1739–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garzon, R.; Marcucci, G.; Croce, C.M. Targeting microRNAs in cancer: Rationale, strategies and challenges. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2010, 9, 775–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.Y.; She, X.M.; Qin, Y.; Chu, Z.B.; Chen, L.; Ai, L.S.; Zhang, L.; Hu, Y. miR-15a and miR-16 affect the angiogenesis of multiple myeloma by targeting VEGF. Carcinogenesis 2013, 34, 426–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Martino, M.T.; Leone, E.; Amodio, N.; Foresta, U.; Lionetti, M.; Pitari, M.R.; Cantafio, M.E.; Gullà, A.; Conforti, F.; Morelli, E.; et al. Synthetic miR-34a mimics as a novel therapeutic agent for multiple myeloma: In vitro and in vivo evidence. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 6260–6270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarone, M.R.; Misso, G.; Grimaldi, A.; Zappavigna, S.; Russo, M.; Amler, E.; Di Martino, M.T.; Amodio, N.; Tagliaferri, P.; Tassone, P.; et al. Evidence of novel miR-34a-based therapeutic approaches for multiple myeloma treatment. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 17949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Martino, M.T.; Gullà, A.; Gallo Cantafio, M.E.; Altomare, E.; Amodio, N.; Leone, E.; Morelli, E.; Lio, S.G.; Caracciolo, D.; Rossi, M.; et al. In vitro and in vivo activity of a novel locked nucleic acid (LNA)-inhibitor-miR-221 against multiple myeloma cells. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e89659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagannathan, S.; Vad, N.; Vallabhapurapu, S.; Vallabhapurapu, S.; Anderson, K.C.; Driscoll, J.J. MiR-29b replacement inhibits proteasomes and disrupts aggresome+autophagosome formation to enhance the antimyeloma benefit of bortezomib. Leukemia 2015, 29, 727–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaham, L.; Binder, V.; Gefen, N.; Borkhardt, A.; Izraeli, S. MiR-125 in normal and malignant hematopoiesis. Leukemia 2012, 26, 2011–2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.M.; Lin, K.Y.; Chen, Y.Q. Diverse functions of miR-125 family in different cell contexts. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2013, 6, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Cytogenetic Group | Deregulated miRNA | Chromosomal Location | miRNA Target | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| t(4;14) | miR-133b | 6p12.2 | FSCN1 | [29] |
| miR-135b | 1q32.1 | |||
| miR-146a | 5q34 | IRAK1, Fas, SMAD4, TBP, CCL8/MCP2 | ||
| miR-155 | 21q21.3 | KPC1, IL-13Rα1, CYR61, SMAD1, SMAD2, SMAD5, HIVEP2, CEBPB, RUNX2, MYO10, JARID2, AGTR1 | ||
| miR-193a | 17q11.2 | |||
| miR-196b | 7p15.2 | |||
| miR-203 | 14q32.33 | P63, SOCS-3 | ||
| miR-215 | 1q41 | DHFR, TS | ||
| miR-342 | 14q32.2 | |||
| miR-375 | 2q35 | YAP, RASD1, PDK1, 14-3-3Zeta | ||
| miR-650 | 22q11.22 | NDRG2, ING4 | ||
| t(11;14) | miR-95 | 4p16.1 | SNX1 | [29] |
| miR-125a | 19q13.41 | PDPN, BAK1, KLF13, preproET1, ARID3B, HuR, ERBB2, ERBB3 | ||
| miR-184 | 15q25.1 | AKT2 | ||
| miR-199a | 19p13.2/1q24.3 | CD44, mTOR, c-MET, HIF1-α | ||
| miR-215 | 1q41 | DHFR, TS | ||
| miR-375 | 2q35 | YAP, RASD1, PDK1, 14-3-3Zeta | ||
| miR-650 | 22q13.41 | NDRG2, ING4 | ||
| t(14;16) | miR-1 | 20q13.33 | TAGLN2, KLF4, c-MET | [25,29] |
| miR-99b | 19q13.41 | |||
| miR-125a-5p | 19q13.42 | PDPN, BAK1, KLF13, preproET1, ARID3B, HuR, ERBB2, ERBB3 | ||
| miR-133a | 18q11.2/20q13.33 | |||
| miR-135b | 1q32.1 | |||
| miR-196b | 7p15.2 | |||
| miR-214 | 1q24.3 | PTEN | ||
| miR-375 | 2p35 | YAP, RASD1, PDK1, 14-3-3Zeta | ||
| miR-642 | 19q13.32 | |||
| Deletion 13q14 | miR-15a-16 | 13q14.3 | E2F, CCND1, WNT3A, BCL-2 | [16,27] |
| miR-181a/b | 1q32.1/9q33.3 | RASSF1A, TIMP3, NLK, Prox1, HOXA11 | ||
| miR-221 | Xp11.3 | p27, ETS1, PUMA, p57, TIMP3, PTEN | ||
| miR-222 | Xp11.3 | p27, PUMA, p57, TIMP3, PETN | ||
| miR-382 | 14q32.31 | SOD2, NPM1, PSPC1, HSPD1, ECH1 | ||
| 1q gain | miR-205 | 1q32.2 | [25] | |
| miR-215 | 1q41 | MDM2, RUNX1 | ||
| miR-488 | 1q25.2 | |||
| miR-1231 | 1q32.1 | |||
| Deletion 17p | miR-22 | 17p13.3 | [25,29] | |
| miR-324-5p | 17p13.1 | MDR, MRP, BCRP, BCL-2 family | [31] |
| miRNA | Observed Alteration | Target | Functional Response | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15a/16 | Downregulated | NA | IL-6 downregulates miR-15a/16 and enhances drug resistance | [72] |
| 221/222 | Upregulated in melphalan-resistant HMCLs | PUMA/BBC3 | miR-221/222 inhibitor upregulates PUMA, increasing apoptosis in drug-resistant HMCLs | [20,21] |
| 221/222 | Upregulated in DEX-resistant HMCL (MM.1R) | PUMA/BBC3 | Inhibition of miR-221/222 in MM.1R cells partially restores their DEX sensitivity, whereas enforced expression in MM.1S cells downregulates PUMA and renders them resistant to DEX | [22] |
| 125a | Upregulated in MM cells following adhesion to BMSCs | p53 | NA | [39] |
| 125b | Upregulated in DEX-responsive MM cells | p53, interacts with miR-34a targeting SIRT1 | Anti-miR-125b increases p53, miR-34a, decreased SIRT1, and increases DEX-induced apoptosis | [42] |
| 137 | Downregulated in MM cells harboring 1p12-21 deletion | MCL-1, AKT, AURKA | Targets MCL1, AURKA, and AKT; Ectopic expression of miR-137 sensitizes cells to bortezomib via upregulating p53 and downregulating ATM/Chk2 | [73,74,75] |
| 27a | Downregulated in BTZ-resistant HMCLs | CDK5 | Ectopic expression of miR-27a in MM cells increases their sensitivity to BTZ | [76] |
| 631 | Downregulated in BTZ-resistant HMCL | UbcH10/MDR1 | Modulates UbcH10/MDR1 pathway, which is associated with BTZ resistance in HMCL | [77] |
| 324-5p | Located on 17p and downregulated in MM cells harboring 17p deletion | BCL2 family gene and MDR1, BCRP, MRP | Regulates sensitivity to bortezomib in MM cells by targeting hedgehog signaling | [31] |
| 155 | Downregulated in MM cells | PSMβ5 | miR-155 elicits anti-MM activity likely via proteasome inhibition | [78] |
| 497 | Downregulated in MM cells | BCL-2 | miR-497 suppresses MM cell proliferation and promotes apoptosis by directly targeting BCL-2 and increases the sensitivity of MM cells to bortezomib | [79] |
| 520g/520h | Downregulated in BTZ-resistant HMCL | APE1 | Combined overexpression of miR-520g and miR-520h overcomes bortezomib resistance in MM through inhibition of DNA repair | [80] |
| 21 | Upregulated in MM cells following adhesion to BMSCs | RhoB | Enforced expression of miR-21 leads to reduced apoptosis induced by DEX, DOX, and BTZ; inhibition of this miRNA induces the opposite effects | [81] |
| 21 | Upregulated in melphalan-resistant HMCLs | NA | NA | [19] |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Handa, H.; Murakami, Y.; Ishihara, R.; Kimura-Masuda, K.; Masuda, Y. The Role and Function of microRNA in the Pathogenesis of Multiple Myeloma. Cancers 2019, 11, 1738. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11111738
Handa H, Murakami Y, Ishihara R, Kimura-Masuda K, Masuda Y. The Role and Function of microRNA in the Pathogenesis of Multiple Myeloma. Cancers. 2019; 11(11):1738. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11111738
Chicago/Turabian StyleHanda, Hiroshi, Yuki Murakami, Rei Ishihara, Kei Kimura-Masuda, and Yuta Masuda. 2019. "The Role and Function of microRNA in the Pathogenesis of Multiple Myeloma" Cancers 11, no. 11: 1738. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11111738
APA StyleHanda, H., Murakami, Y., Ishihara, R., Kimura-Masuda, K., & Masuda, Y. (2019). The Role and Function of microRNA in the Pathogenesis of Multiple Myeloma. Cancers, 11(11), 1738. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11111738





