Targeting STAT3 in Cancer with Nucleotide Therapeutics
Abstract
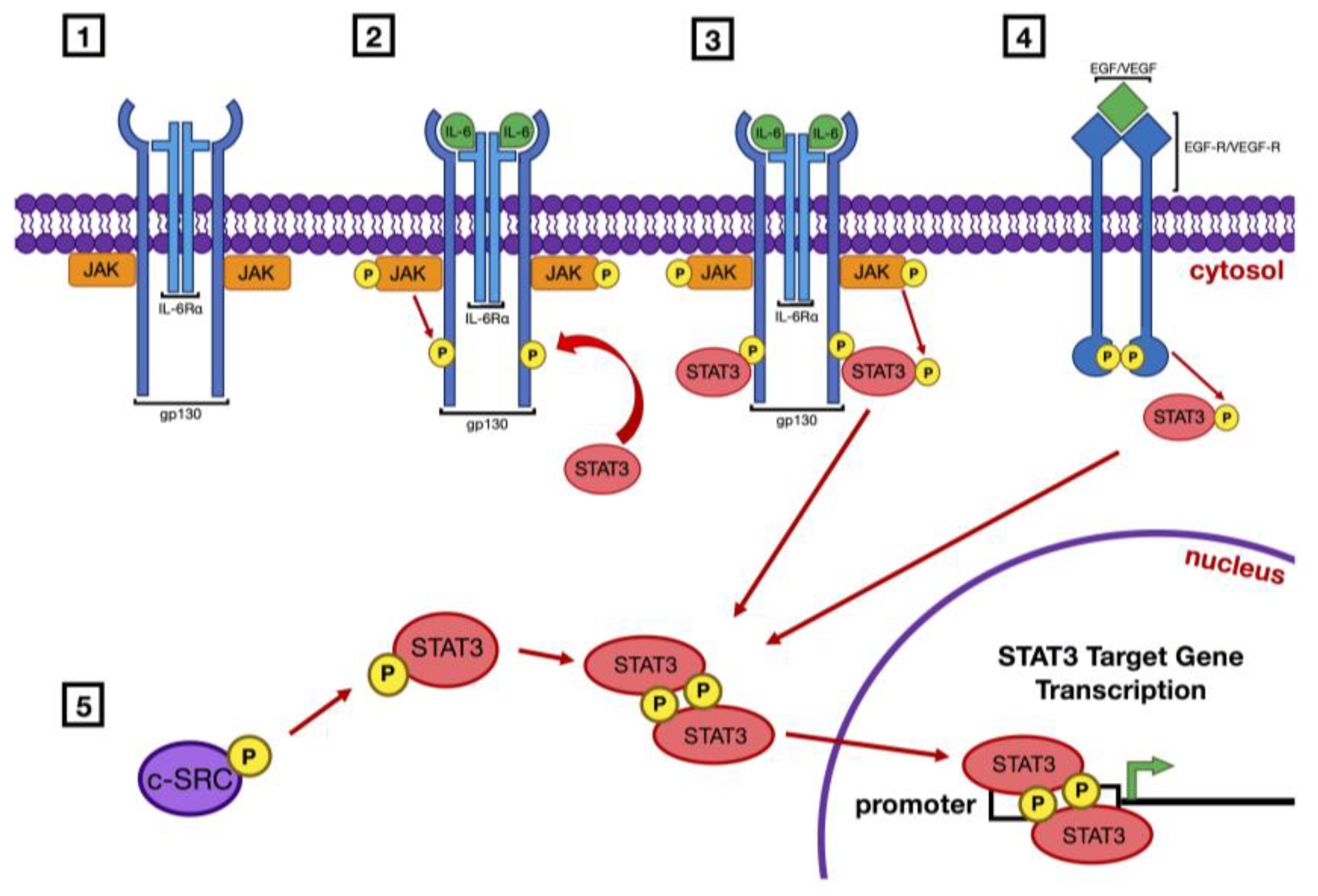
1. Introduction
1.1. Peptide and Small Molecule Inhibitors of STAT3
1.2. Peptide Inhibitors
1.3. Small Molecule Inhibitors
1.4. Future Directions for Small Molecule STAT3 Inhibitors
1.5. Natural Inhibitors
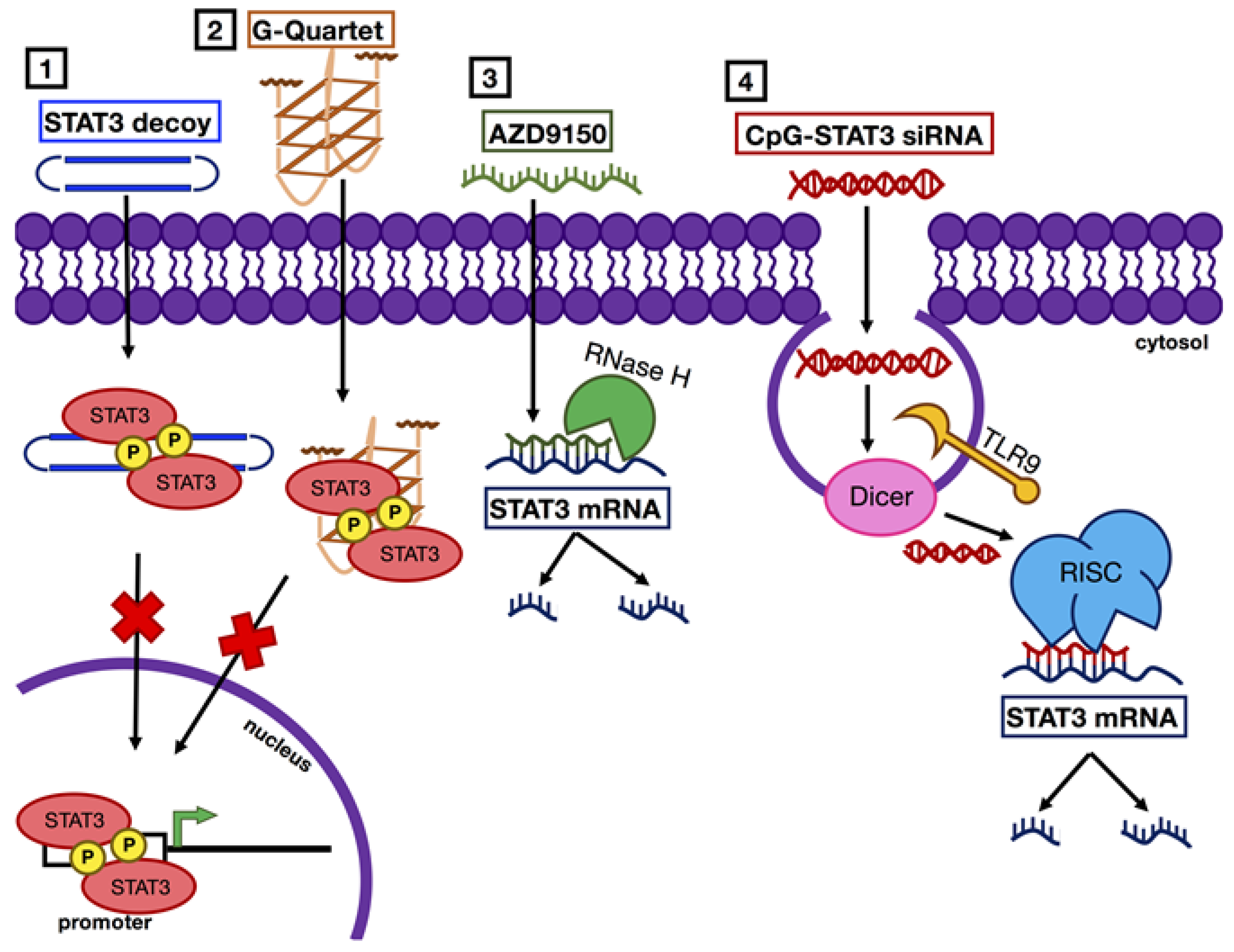
1.6. Nucleic Acid-Based Agents to Inhibit Expression of STAT3
1.6.1. AZD9150
1.6.2. CpG-coupled STAT3 siRNA
1.7. Nucleic Acid-Based Agents that Act as Competitive Inhibitors of STAT3
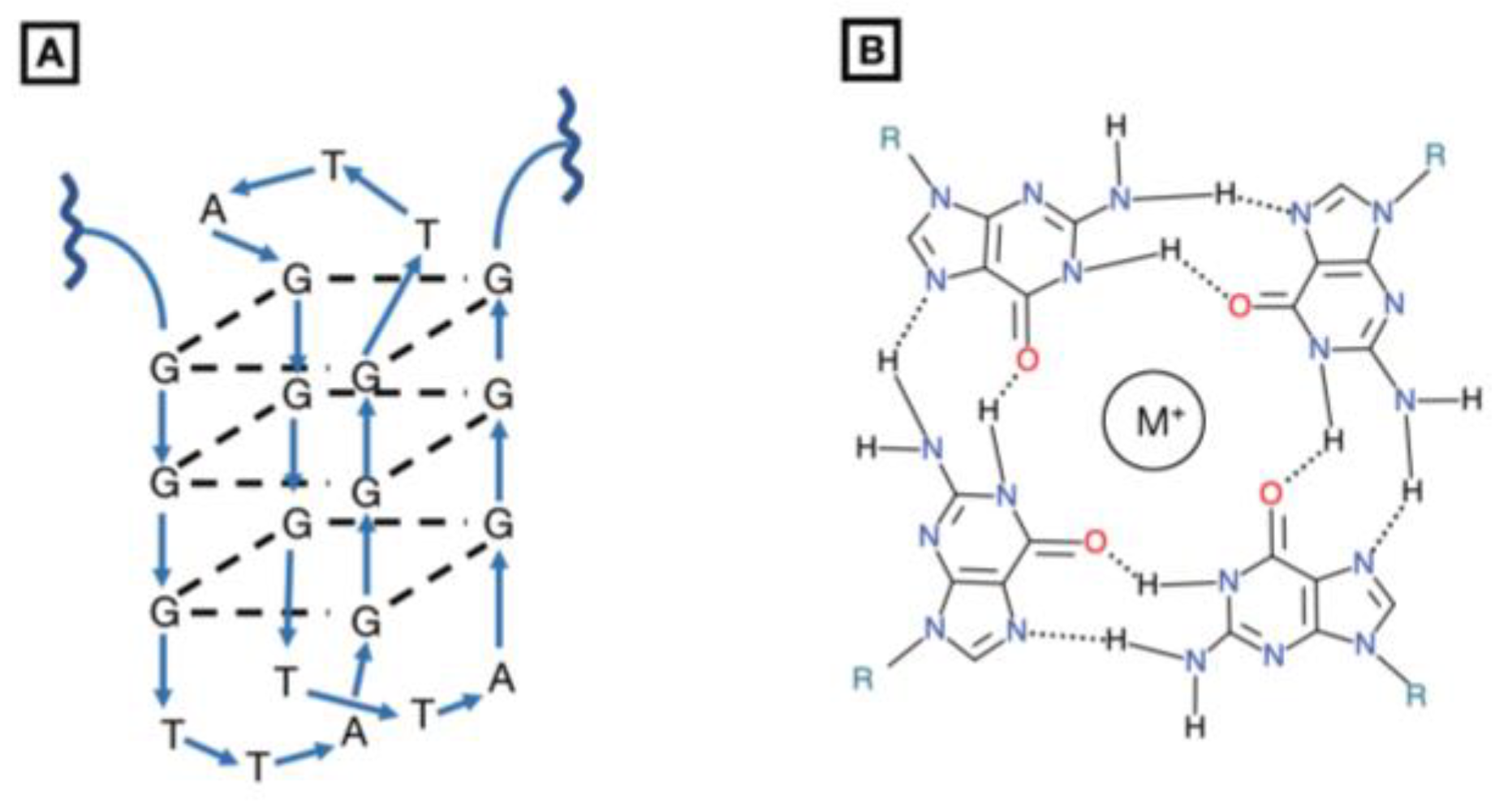
1.7.1. G-Quartet Oligodeoxynucleotides (GQ-ODNs)
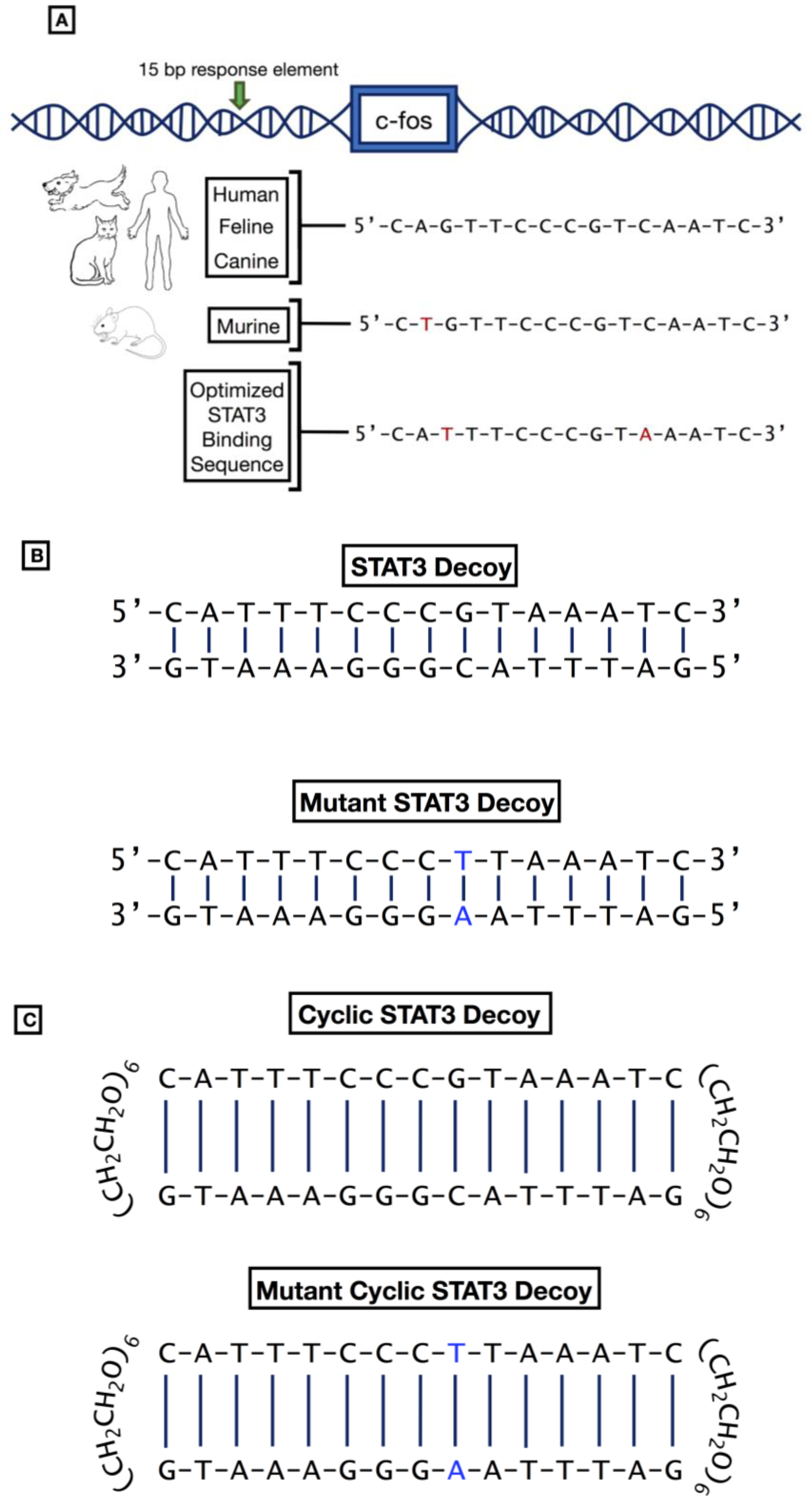
1.7.2. STAT3 Decoys
2. Conclusion
3. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huynh, J.; Chand, A.; Gough, D.; Ernst, M. Therapeutically Exploiting STAT3 Activity in Cancer—Using Tissue Repair as a Road Map. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2019, 19, 82–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gough, D.J.; Corlett, A.; Schlessinger, K.; Wegrzyn, J.; Larner, A.C.; Levy, D.E. Mitochondrial STAT3 Supports Ras-Dependent Oncogenic Transformation. Science 2009, 324, 1713–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gough, D.J.; Koetz, L.; Levy, D.E. The MEK-ERK Pathway is Necessary for Serine Phosphorylation of Mitochondrial STAT3 and Ras-Mediated Transformation. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e83395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, W.; Hong, J.; Wang, Y.-C.; Zhang, Y.-J.; Wang, P.; Su, W.-Y.; Lin, Y.-W.; Lu, R.; Zou, W.-P.; Xiong, H.; et al. Inhibition of JAK2/STAT3 Signalling Induces Colorectal Cancer Cell Apoptosis via Mitochondrial Pathway. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2012, 16, 1878–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Lee, H.; Herrmann, A.; Buettner, R.; Jove, R. Revisiting STAT3 Signalling in Cancer: New and Unexpected Biological Functions. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2014, 14, 736–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Rincon, M. Mitochondrial Stat3, the Need for Design Thinking. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2016, 12, 532–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Wu, D.; Zhao, L.; Huang, L.; Shen, G.; Huang, J.; Chai, Y. Prognostic role of STAT3 in Solid Tumors: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 19863–19883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakaguchi, M.; Oka, M.; Iwasaki, T.; Fukami, Y.; Nishigori, C. Role and Regulation of STAT3 Phosphorylation at Ser727 in Melanocytes and Melanoma Cells. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2012, 132, 1877–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuringa, J.-J.; Wierenga, A.T.J.; Kruijer, W.; Vellenga, E. Constitutive Stat3, Tyr705, and Ser727 Phosphorylation in Acute Myeloid Leukemia Cells Caused by the Autocrine Secretion of Interleukin-6. Blood 2000, 95, 3765–3770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lui, V.W.Y.; Peyser, N.D.; Ng, P.K.-S.; Hritz, J.; Zeng, Y.; Lu, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, L.; Gilbert, B.R.; General, I.J.; et al. Frequent Mutation of Receptor Protein Tyrosine Phosphatases Provides a Mechanism for STAT3 Hyperactivation in Head and Neck Cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 1114–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geiger, J.L.; Grandis, J.R.; Bauman, J.E. The STAT3 Pathway as a Therapeutic Target in Head and Neck Cancer: Barriers and Innovations. Oral Oncol. 2016, 56, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spitzner, M.; Ebner, R.; Wolff, H.A.; Michael Ghadimi, B.; Wienands, J.; Grade, M. STAT3: A Novel Molecular Mediator of Resistance to Chemoradiotherapy. Cancers 2014, 6, 1986–2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Pal, S.K.; Reckamp, K.; Figlin, R.A.; Yu, H. STAT3: A Target to Enhance Antitumor Immune Response. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2011, 344, 41–59. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, M.-F.; Chen, P.-T.; Lu, M.S.; Lin, P.Y.; Chen, W.-C.; Lee, K.-D. IL-6 Expression Predicts Treatment Response and Outcome in Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Esophagus. Mol. Cancer 2013, 12, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.-T.; Chen, M.-F.; Chen, W.-C.; Hsieh, C.-C. The Role of IL-6 in the Radiation Response of Prostate Cancer. Radiat. Oncol. 2013, 8, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, B.C.; Kim, S.M.; Solca, F.; Kim, J.-H. Abstract 1886: Activation of IL-6R/JAK1/STAT3 Signaling Induces de Novo Resistance to Irreversible EGFR Inhibitors in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer with T790M Resistance Mutation. Exp. Mol. Ther. 2012, 11, 2254–2264. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, H.; Kortylewski, M.; Pardoll, D. Crosstalk between Cancer and Immune Cells: Role of STAT3 in the Tumour Microenvironment. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2007, 7, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, S.D.; Srinivasan, V.M.; Heimberger, A.B. The Role of STAT3 in Tumor-Mediated Immune Suppression. J. Neurooncol. 2015, 123, 385–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rébé, C.; Végran, F.; Berger, H.; Ghiringhelli, F. STAT3 Activation: A Key Factor in Tumor Immunoescape. JAKSTAT 2013, 2, e23010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Z.; Zhong, Z.; Darnell, J.E., Jr. Maximal Activation of Transcription by Stat1 and Stat3 Requires both Tyrosine and Serine Phosphorylation. Cell 1995, 82, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Z.; Wen, Z.; Darnell, J.E., Jr. Stat3: A STAT Family Member Activated by Tyrosine Phosphorylation in Response to Epidermal Growth Factor and Interleukin-6. Science 1994, 264, 95–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgoffe, G.M.; Vignali, D.A.A. STAT Heterodimers in Immunity: A Mixed Message or a Unique Signal? JAKSTAT 2013, 2, e23060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegrzyn, J.; Potla, R.-J.; Chwae, Y.; Sepuri, N.B.V.; Zhang, Q.; Koeck, T.; Derecka, M.; Szczepanek, K.; Szelag, M.; Gornicka, A.; et al. Function of Mitochondrial Stat3 in Cellular Respiration. Science 2009, 323, 793–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbognin, E.; Betto, R.M.; Soriano, M.E.; Smith, A.G.; Martello, G. Stat3 Promotes Mitochondrial Transcription and Oxidative Respiration during Maintenance and Induction of Naive Pluripotency. EMBO J. 2016, 35, 618–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Jia, L.; Farren, T.; Gribben, J.; Agrawal, S. 2.21 Autocrine Interleukin-6 Production Correlated with Survival of Chronic Lymphocytic Leukaemia Cells. Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2011, 11, S172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wake, M.S.; Watson, C.J. STAT3 the oncogene - still eluding therapy? FEBS J. 2015, 282, 2600–2611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turkson, J.; Ryan, D.; Kim, J.S.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Haura, E.; Laudano, A.; Sebti, S.; Hamilton, A.D.; Jove, R. Phosphotyrosyl Peptides Block Stat3-mediated DNA Binding Activity, Gene Regulation, and Cell Transformation. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 45443–45455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turkson, J.; Kim, J.S.; Zhang, S.; Yuan, J.; Huang, M.; Glenn, M.; Haura, E.; Sebti, S.; Hamilton, A.D.; Jove, R. Novel Peptidomimetic Inhibitors of Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3 Dimerization and Biological Activity. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2004, 3, 261–269. [Google Scholar]
- Mandal, P.K.; Gao, F.; Lu, Z.; Ren, Z.; Ramesh, R.; Birtwistle, J.S.; Kaluarachchi, K.K.; Chen, X.; Bast, R.C., Jr.; Liao, W.S.; et al. Potent and Selective Phosphopeptide Mimetic Prodrugs Targeted to the Src Homology 2 (SH2) Domain of Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 54, 3549–3563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schust, J.; Berg, T. A High-Throughput Fluorescence Polarization Assay for Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3. Anal. Biochem. 2004, 330, 114–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schust, J.; Sperl, B.; Hollis, A.; Mayer, T.U.; Berg, T. Stattic: A Small-Molecule Inhibitor of STAT3 Activation and Dimerization. Chem. Biol. 2006, 13, 1235–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auzenne, E.J.; Klostergaard, J.; Mandal, P.K.; Liao, W.S.; Lu, Z.; Gao, F.; Bast, R.C., Jr.; Robertson, F.M.; McMurray, J.S. A Phosphopeptide Mimetic Prodrug Targeting the SH2 Domain of Stat3 Inhibits Tumor Growth and Angiogenesis. J. Exp. Ther. Oncol. 2012, 10, 155–162. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, Y.; Zhou, F.; Zhang, R.; Claret, F.X. Stat3 inhibitor Stattic Exhibits Potent Antitumor Activity and Induces Chemo- and Radio-Sensitivity in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e54565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brambilla, L.; Genini, D.; Laurini, E.; Merulla, J.; Perez, L.; Fermeglia, M.; Carbone, G.M.; Pricl, S.; Catapano, C.V. Hitting the right spot: Mechanism of action of OPB-31121, a novel and potent inhibitor of the Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3 (STAT3). Mol. Oncol. 2015, 9, 1194–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayakawa, F.; Sugimoto, K.; Harada, Y.; Hashimoto, N.; Ohi, N.; Kurahashi, S.; Naoe, T. A novel STAT inhibitor, OPB-31121, has a Significant Antitumor Effect on Leukemia with STAT-Addictive Oncokinases. Blood Cancer J. 2013, 3, e166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.-J.; Nam, H.-J.; Kim, H.-P.; Han, S.-W.; Im, S.-A.; Kim, T.-Y.; Oh, D.-Y.; Bang, Y.-J. OPB-31121, a Novel Small Molecular Inhibitor, Disrupts the JAK2/STAT3 Pathway and Exhibits an Antitumor Activity in Gastric Cancer Cells. Cancer Lett. 2013, 335, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendell, J.C.; Hong, D.S.; Burris, H.A., 3rd; Naing, A.; Jones, S.F.; Falchook, G.; Bricmont, P.; Elekes, A.; Rock, E.P.; Kurzrock, R. Phase 1, Open-Label, Dose-Escalation, and Pharmacokinetic Study of STAT3 Inhibitor OPB-31121 in Subjects with Advanced Solid Tumors. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2014, 74, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogura, M.; Uchida, T.; Terui, Y.; Hayakawa, F.; Kobayashi, Y.; Taniwaki, M.; Takamatsu, Y.; Naoe, T.; Tobinai, K.; Munakata, W.; et al. Phase I Study of OPB-51602, an Oral Inhibitor of Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3, in Patients with Relapsed/Refractory Hematological Malignancies. Cancer Sci. 2015, 106, 896–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, A.L.; Soo, R.A.; Tan, D.S.; Lee, S.C.; Lim, J.S.; Marban, P.C.; Kong, L.R.; Lee, Y.J.; Wang, L.Z.; Thuya, W.L.; et al. Phase I and Biomarker Study of OPB-51602, a Novel Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription (STAT) 3 Inhibitor, in Patients with Refractory Solid Malignancies. Ann. Oncol. 2015, 26, 998–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Kasembeli, M.M.; Jiang, X.; Tweardy, B.J.; Tweardy, D.J. Chemical Probes that Competitively and Selectively Inhibit Stat3 Activation. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e4783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharadwaj, U.; Eckols, T.K.; Xu, X.; Kasembeli, M.M.; Chen, Y.; Adachi, M.; Song, Y.; Mo, Q.; Lai, S.Y.; Tweardy, D.J. Small-Molecule Inhibition of STAT3 in Radioresistant Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 26307–26330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, K.M.; Bharadwaj, U.; Eckols, T.K.; Kolosov, M.; Kasembeli, M.M.; Fridley, C.; Siller, R.; Tweardy, D.J. Small-Molecule Targeting of Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription (STAT) 3 to Treat Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Lung Cancer 2015, 90, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, K.H.; Yoo, W.; Stevenson, H.L.; Deshpande, D.; Shen, H.; Gagea, M.; Yoo, S.-Y.; Wang, J.; Kris Eckols, T.; Bharadwaj, U.; et al. Multifunctional Effects of a Small-Molecule STAT3 Inhibitor on NASH and Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Mice. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 5537–5546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kettner, N.M.; Vijayaraghavan, S.; Durak, M.G.; Bui, T.; Kohansal, M.; Ha, M.J.; Liu, B.; Rao, X.; Wang, J.; Yi, M.; et al. Combined Inhibition of STAT3 and DNA Repair in Palbociclib-Resistant ER-Positive Breast Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 3996–4013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackenzie, G.G.; Huang, L.; Alston, N.; Ouyang, N.; Vrankova, K.; Mattheolabakis, G.; Constantinides, P.P.; Rigas, B. Targeting Mitochondrial STAT3 with the Novel Phospho-Valproic Acid (MDC-1112) Inhibits Pancreatic Cancer Growth in Mice. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, D.; Fraga-Lauhirat, M.; Millings, J.; Ho, C.; Villarreal, E.M.; Fletchinger, T.C.; Bonfiglio, J.V.; Mata, L.; Nemesure, M.D.; Bartels, L.E.; et al. Phospho-Valproic Acid (MDC-1112) Suppresses Glioblastoma Growth in Preclinical Models Through the Inhibition of STAT3 Phosphorylation. Carcinogenesis 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shitara, K.; Yodo, Y.; Iino, S. A Phase I Study of Napabucasin Plus Paclitaxel for Japanese Patients with Advanced/Recurrent Gastric Cancer. In Vivo 2019, 33, 933–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonbol, M.B.; Ahn, D.H.; Goldstein, D.; Okusaka, T.; Tabernero, J.; Macarulla, T.; Reni, M.; Li, C.-P.; O’Neil, B.; Van Cutsem, E.; et al. CanStem111P trial: A Phase III Study of Napabucasin Plus Nab-Paclitaxel with Gemcitabine. Future Oncol. 2019, 15, 1295–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettersson, M.; Crews, C.M. PROteolysis TArgeting Chimeras (PROTACs)—Past, Present and Future. Drug Discov. Today Technol. 2019, 31, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paiva, S.-L.; Crews, C.M. Targeted Protein Degradation: Elements of PROTAC Design. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2019, 50, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demain, A.L.; Vaishnav, P. Natural Products for Cancer Chemotherapy. Microb. Biotechnol. 2011, 4, 687–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lis, C.; Rubner, S.; Roatsch, M.; Berg, A.; Gilcrest, T.; Fu, D.; Nguyen, E.; Schmidt, A.-M.; Krautscheid, H.; Meiler, J.; et al. Development of Erasin: A Chromone-Based STAT3 Inhibitor which Induces Apoptosis in Erlotinib-Resistant Lung Cancer Cells. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 17390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, N.; Li, J.; Fang, C.; Chang, J.; Xirou, V.; Syrigos, N.K.; Marks, B.J.; Chu, E.; Schmitz, J.C. Targeting Colon Cancer with the Novel STAT3 Inhibitor Bruceantinol. Oncogene 2019, 38, 1676–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glienke, W.; Maute, L.; Wicht, J.; Bergmann, L. Curcumin Inhibits Constitutive STAT3 Phosphorylation in Human Pancreatic Cancer Cell Lines and Downregulation of Survivin/BIRC5 Gene Expression. Cancer Investig. 2010, 28, 166–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dean, N.M.; Bennett, C.F. Antisense Oligonucleotide-Based Therapeutics for Cancer. Oncogene 2003, 22, 9087–9096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelhard, H.H. Antisense Oligodeoxynucleotide Technology: Potential Use for the Treatment of Malignant Brain Tumors. Cancer Control 1998, 5, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khvorova, A.; Watts, J.K. The Chemical Evolution of Oligonucleotide Therapies of Clinical Utility. Nat. Biotechnol. 2017, 35, 238–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Corey, D.R. Chemistry, Mechanism and Clinical Status of Antisense Oligonucleotides and Duplex RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, 1584–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barton, B.E.; Karras, J.G.; Murphy, T.F.; Barton, A.; Huang, H.F.-S. Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3 (STAT3) Activation in Prostate Cancer: Direct STAT3 Inhibition Induces Apoptosis in Prostate Cancer Lines. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2004, 3, 11–20. [Google Scholar]
- Mora, L.B.; Buettner, R.; Seigne, J.; Diaz, J.; Ahmad, N.; Garcia, R.; Bowman, T.; Falcone, R.; Fairclough, R.; Cantor, A.; et al. Constitutive Activation of Stat3 in Human Prostate Tumors and Cell Lines: Direct Inhibition of Stat3 Signaling Induces Apoptosis of Prostate Cancer Cells. Cancer Res. 2002, 62, 6659–6666. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, G.; Wright, K.L.; Huang, M.; Song, L.; Haura, E.; Turkson, J.; Zhang, S.; Wang, T.; Sinibaldi, D.; Coppola, D.; et al. Constitutive Stat3 Activity Up-Regulates VEGF Expression and Tumor Angiogenesis. Oncogene 2002, 21, 2000–2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.-C.; Ye, S.-L.; Sun, R.-X.; Liu, Y.-K.; Tang, Z.-Y.; Kim, Y.; Karras, J.G.; Zhang, H. Inhibition of Growth and Metastasis of Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Antisense Oligonucleotide Targeting Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006, 12, 7140–7148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, D.; Kurzrock, R.; Kim, Y.; Woessner, R.; Younes, A.; Nemunaitis, J.; Fowler, N.; Zhou, T.; Schmidt, J.; Jo, M.; et al. AZD9150, a Next-Generation Antisense Oligonucleotide Inhibitor of STAT3 with Early Evidence of Clinical Activity in Lymphoma and Lung Cancer. Sci. Transl. Med. 2015, 7, 314ra185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odate, S.; Veschi, V.; Yan, S.; Lam, N.; Woessner, R.; Thiele, C.J. Inhibition of STAT3 with the Generation 2.5 Antisense Oligonucleotide, AZD9150, Decreases Neuroblastoma Tumorigenicity and Increases Chemosensitivity. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 1771–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shastri, A.; Choudhary, G.; Teixeira, M.; Gordon-Mitchell, S.; Ramachandra, N.; Bernard, L.; Bhattacharyya, S.; Lopez, R.; Pradhan, K.; Giricz, O.; et al. Antisense STAT3 Inhibitor Decreases Viability of Myelodysplastic and Leukemic Stem Cells. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 128, 5479–5488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barton, B.E.; Murphy, T.F.; Shu, P.; Huang, H.F.; Meyenhofer, M.; Barton, A. Novel Single-Stranded Oligonucleotides that Inhibit Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3 Induce Apoptosis in Vitro and in Vivo in Prostate Cancer Cell Lines. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2004, 3, 1183–1191. [Google Scholar]
- Burel, S.A.; Han, S.-R.; Lee, H.-S.; Norris, D.A.; Lee, B.-S.; Machemer, T.; Park, S.-Y.; Zhou, T.; He, G.; Kim, Y.; et al. Preclinical Evaluation of the Toxicological Effects of a Novel Constrained Ethyl Modified Antisense Compound Targeting Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3 in Mice and Cynomolgus Monkeys. Nucleic Acid Ther. 2013, 23, 213–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phase 1/2, Open-Label, Dose-Escalation Study of IONIS-STAT3Rx, Administered to Patients with Advanced Cancers—Full Text View—ClinicalTrials.gov. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01563302 (accessed on 10 July 2019).
- Reilley, M.J.; McCoon, P.; Cook, C.; Lyne, P.; Kurzrock, R.; Kim, Y.; Woessner, R.; Younes, A.; Nemunaitis, J.; Fowler, N.; et al. STAT3 Antisense Oligonucleotide AZD9150 in a Subset of Patients with Heavily Pretreated Lymphoma: Results of a Phase 1b Trial. J. Immunother. Cancer 2018, 6, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroemer, G.; Galluzzi, L.; Zitvogel, L. STAT3 Inhibition for Cancer Therapy: Cell-Autonomous Effects Only? Oncoimmunology 2016, 5, e1126063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kortylewski, M.; Moreira, D. Myeloid Cells as a Target for Oligonucleotide Therapeutics: Turning Obstacles into Opportunities. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2017, 66, 979–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, D.M.S.; Pal, S.K.; Moreira, D.; Duttagupta, P.; Zhang, Q.; Won, H.; Jones, J.; D’Apuzzo, M.; Forman, S.; Kortylewski, M. TLR9-Targeted STAT3 Silencing Abrogates Immunosuppressive Activity of Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells from Prostate Cancer Patients. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 3771–3782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kortylewski, M.; Swiderski, P.; Herrmann, A.; Wang, L.; Kowolik, C.; Kujawski, M.; Lee, H.; Scuto, A.; Liu, Y.; Yang, C.; et al. In Vivo Delivery of siRNA to Immune Cells by Conjugation to a TLR9 Agonist Enhances Antitumor Immune Responses. Nat. Biotechnol. 2009, 27, 925–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kortylewski, M.; Kuo, Y.-H. Push and Release: TLR9 activation plus STAT3 Blockade for Systemic Antitumor Immunity. Oncoimmunology 2014, 3, e27441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Zhang, Q.; Hossain, D.M.S.; Nechaev, S.; Kozlowska, A.; Zhang, W.; Liu, Y.; Kowolik, C.M.; Swiderski, P.; Rossi, J.J.; Forman, S.; et al. TLR9-Mediated siRNA Delivery for Targeting of Normal and Malignant Human Hematopoietic Cells in Vivo. Blood 2013, 121, 1304–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, G.; Mei, L.; Vishwasrao, H.D.; Jacobson, O.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Yung, B.C.; Fu, X.; Jin, A.; Niu, G.; et al. Intertwining DNA-RNA Nanocapsules Loaded with Tumor Neoantigens as Synergistic Nanovaccines for Cancer Immunotherapy. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kortylewski, M.; Kujawski, M.; Herrmann, A.; Yang, C.; Wang, L.; Liu, Y.; Salcedo, R.; Yu, H. Toll-like Receptor 9 Activation of Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3 Constrains Its Agonist-Based Immunotherapy. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 2497–2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Setten, R.L.; Rossi, J.J.; Han, S.-P. The Current State and Future Directions of RNAi-Based Therapeutics. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2019, 18, 421–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nechaev, S.; Gao, C.; Moreira, D.; Swiderski, P.; Jozwiak, A.; Kowolik, C.M.; Zhou, J.; Armstrong, B.; Raubitschek, A.; Rossi, J.J.; et al. Intracellular Processing of Immunostimulatory CpG-siRNA: Toll-like Receptor 9 Facilitates siRNA Dicing and Endosomal Escape. J. Control. Release 2013, 170, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrmann, A.; Kortylewski, M.; Kujawski, M.; Zhang, C.; Reckamp, K.; Armstrong, B.; Wang, L.; Kowolik, C.; Deng, J.; Figlin, R.; et al. Targeting Stat3 in the Myeloid Compartment Drastically Improves the in vivo Antitumor Functions of Adoptively Transferred T cells. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 7455–7464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, D.M.S.; Dos Santos, C.; Zhang, Q.; Kozlowska, A.; Liu, H.; Gao, C.; Moreira, D.; Swiderski, P.; Jozwiak, A.; Kline, J.; et al. Leukemia Cell-Targeted STAT3 Silencing and TLR9 Triggering Generate Systemic Antitumor Immunity. Blood 2014, 123, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, D.; Zhang, Q.; Hossain, D.M.S.; Nechaev, S.; Li, H.; Kowolik, C.M.; D’Apuzzo, M.; Forman, S.; Jones, J.; Pal, S.K.; et al. TLR9 Signaling Through NF-κB/RELA and STAT3 Promotes Tumor-Propagating Potential of Prostate Cancer Cells. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 17302–17313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, J.T. G-quartets 40 years later: From 5′-GMP to Molecular Biology and Supramolecular Chemistry. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2004, 43, 668–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, N.; Gao, X.; Rando, R.F.; Hogan, M.E. Potassium-Induced Loop Conformational Transition of a Potent anti-HIV Oligonucleotide. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 1997, 15, 573–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMicken, H.W.; Bates, P.J.; Chen, Y. Antiproliferative activity of G-Quartet-Containing Oligonucleotides Generated by a Novel Single-Stranded DNA Expression System. Cancer Gene Ther. 2003, 10, 867–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Jing, N.; Marchand, C.; Guan, Y.; Liu, J.; Pallansch, L.; Lackman-Smith, C.; De Clercq, E.; Pommier, Y. Structure–Activity of Inhibition of HIV-1 Integrase and Virus Replication by G-quartet Oligonucleotides. DNA Cell Biol. 2001, 20, 499–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazumder, A.; Neamati, N.; Ojwang, J.O.; Sunder, S.; Rando, R.F.; Pommier, Y. Inhibition of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 integrase by guanosine quartet structures. Biochemistry 1996, 35, 13762–13771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rando, R.F.; Ojwang, J.; Elbaggari, A.; Reyes, G.R.; Tinder, R.; McGrath, M.S.; Hogan, M.E. Suppression of Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 Activity in Vitro by Oligonucleotides which Form Intramolecular Tetrads. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 1754–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, N.; Tweardy, D.J. Targeting Stat3 in Cancer Therapy. Anticancer Drugs 2005, 16, 601–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, M.; Grandis, J.R. Nucleic Acid-Based Approaches to STAT Inhibition. JAKSTAT 2012, 1, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Jing, N. Computational Study on Mechanism of G-Quartet Oligonucleotide T40214 Selectively Targeting Stat3. J. Comput.-Aided Mol. Des. 2007, 21, 641–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, J.S.; Guy-Caffey, J.K.; Ojwang, J.O.; Smith, S.R.; Hogan, M.E.; Cossum, P.A.; Rando, R.F.; Chaudhary, N. Intramolecular G-quartet Motifs Confer Nuclease Resistance to a Potent anti-HIV Oligonucleotide. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 5698–5703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weerasinghe, P.; Li, Y.; Guan, Y.; Zhang, R.; Tweardy, D.J.; Jing, N. T40214/PEI complex: A Potent Therapeutics for Prostate Cancer that Targets STAT3 Signaling. Prostate 2008, 68, 1430–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, N.; Zhu, Q.; Yuan, P.; Li, Y.; Mao, L.; Tweardy, D.J. Targeting Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3 with G-quartet Oligonucleotides: A Potential Novel Therapy for Head and Neck Cancer. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2006, 5, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weerasinghe, P.; Garcia, G.E.; Zhu, Q.; Yuan, P.; Feng, L.; Mao, L.; Jing, N. Inhibition of Stat3 Activation and Tumor Growth Suppression of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer by G-Quartet Oligonucleotides. Int. J. Oncol. 2007, 31, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fagard, R.; Metelev, V.; Souissi, I.; Baran-Marszak, F. STAT3 Inhibitors for Cancer Therapy: Have All Roads Been Explored? JAKSTAT 2013, 2, e22882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, B.J.; Hayes, T.E.; Hoban, C.J.; Cochran, B.H. The SIF Binding Element Confers sis/PDGF Inducibility onto the c-fos Promoter. EMBO J. 1990, 9, 4477–4484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leong, P.L.; Andrews, G.A.; Johnson, D.E.; Dyer, K.F.; Xi, S.; Mai, J.C.; Robbins, P.D.; Gadiparthi, S.; Burke, N.A.; Watkins, S.F.; et al. Targeted Inhibition of Stat3 with a Decoy Oligonucleotide Abrogates Head and Neck Cancer Cell Growth. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 4138–4143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lui, V.W.Y.; Boehm, A.L.; Koppikar, P.; Leeman, R.J.; Johnson, D.; Ogagan, M.; Childs, E.; Freilino, M.; Grandis, J.R. Antiproliferative Mechanisms of a Transcription Factor Decoy Targeting Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription (STAT) 3: The Role of STAT1. Mol. Pharmacol. 2007, 71, 1435–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Li, R.; Li, G. Inhibitory Effects of Decoy-ODN Targeting Activated STAT3 on Human Glioma Growth in Vivo. In Vivo 2009, 23, 237–243. [Google Scholar]
- Xi, S.; Gooding, W.E.; Grandis, J.R. In Vivo Antitumor Efficacy of STAT3 Blockade Using a Transcription Factor Decoy Approach: Implications for Cancer Therapy. Oncogene 2005, 24, 970–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, P.; Zhang, B.; Mao, H.; Shen, L.; Ma, Y. Inhibitory Effects of STAT3 Decoy Oligodeoxynucleotides on Human Epithelial Ovarian Cancer Cell Growth in Vivo. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2013, 32, 623–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, J.; Wang, L.; Wei, H.; Tian, Z. Therapeutic Effects of STAT3 Decoy Oligodeoxynucleotide on Human Lung Cancer in Xenograft Mice. BMC Cancer 2007, 7, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sen, M.; Joyce, S.; Panahandeh, M.; Li, C.; Thomas, S.M.; Maxwell, J.; Wang, L.; Gooding, W.E.; Johnson, D.E.; Grandis, J.R. Targeting Stat3 Abrogates EGFR Inhibitor Resistance in Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 4986–4996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sen, M.; Thomas, S.M.; Kim, S.; Yeh, J.I.; Ferris, R.L.; Johnson, J.T.; Duvvuri, U.; Lee, J.; Sahu, N.; Joyce, S.; et al. First-in-Human Trial of a STAT3 Decoy Oligonucleotide in Head and Neck Tumors: Implications for Cancer Therapy. Cancer Discov. 2012, 2, 694–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Hossain, D.M.S.; Duttagupta, P.; Moreira, D.; Zhao, X.; Won, H.; Buettner, R.; Nechaev, S.; Majka, M.; Zhang, B.; et al. Serum-Resistant CpG-STAT3 Decoy for Targeting Survival and Immune Checkpoint Signaling in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Blood 2016, 127, 1687–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Zhang, Z.; Moreira, D.; Su, Y.-L.; Won, H.; Adamus, T.; Dong, Z.; Liang, Y.; Yin, H.H.; Swiderski, P.; et al. B Cell Lymphoma Immunotherapy Using TLR9-Targeted Oligonucleotide STAT3 Inhibitors. Mol. Ther. 2018, 26, 695–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.S.; O’Keefe, R.A.; Ha, P.K.; Grandis, J.R.; Johnson, D.E. Biochemical Properties of a Decoy Oligodeoxynucleotide Inhibitor of STAT3 Transcription Factor. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Njatcha, C.; Farooqui, M.; Kornberg, A.; Johnson, D.E.; Grandis, J.R.; Siegfried, J.M. STAT3 Cyclic Decoy Demonstrates Robust Antitumor Effects in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2018, 17, 1917–1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, M.; Paul, K.; Freilino, M.L.; Li, H.; Li, C.; Johnson, D.E.; Wang, L.; Eiseman, J.; Grandis, J.R. Systemic Administration of a Cyclic Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3 (STAT3) Decoy Oligonucleotide Inhibits Tumor Growth without Inducing Toxicological Effects. Mol. Med. 2014, 20, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zang, Y.; Sen, M.; Leeman-Neill, R.J.; Man, D.S.K.; Grandis, J.R.; Johnson, D.E. Bortezomib up-Regulates Activated Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription-3 and Synergizes with Inhibitors of Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription-3 to Promote Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cell Death. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2009, 8, 2211–2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, P.; Zhang, B.; Wang, A.; Yang, M. Role of STAT3 Decoy Oligodeoxynucleotides on Cell Invasion and chemosensitivity in Human Epithelial Ovarian Cancer Cells. Cancer Genet. Cytogenet. 2010, 197, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Xiao, W.; Wang, L.; Tian, Z.; Zhang, J. Deactivation of Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3 Reverses Chemotherapeutics Resistance of Leukemia Cells via Down-Regulating P-gp. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e20965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bharadwaj, U.; Kasembeli, M.M.; Tweardy, D.J. STAT3 Inhibitors in Cancer: A Comprehensive Update. In Cancer Drug Discovery and Development; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 95–161. [Google Scholar]
- Hodge, J.A.; Kawabata, T.T.; Krishnaswami, S.; Clark, J.D.; Telliez, J.-B.; Dowty, M.E.; Menon, S.; Lamba, M.; Zwillich, S. The Mechanism of Action of Tofacitinib—An Oral Janus Kinase Inhibitor for the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2016, 34, 318–328. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhou, T.; Georgeon, S.; Moser, R.; Moore, D.J.; Caflisch, A.; Hantschel, O. Specificity and Mechanism-of-Action of the JAK2 Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors Ruxolitinib and SAR302503 (TG101348). Leukemia 2014, 28, 404–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eiring, A.M.; Page, B.D.G.; Kraft, I.L.; Mason, C.C.; Vellore, N.A.; Resetca, D.; Zabriskie, M.S.; Zhang, T.Y.; Khorashad, J.S.; Engar, A.J.; et al. Combined STAT3 and BCR-ABL1 Inhibition Induces Synthetic Lethality in Therapy-Resistant Chronic Myeloid Leukemia. Leukemia 2017, 31, 1253–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, W.; Wu, J.; Liu, L.; Tian, Y.; Buettner, R.; Hsieh, M.-Y.; Horne, D.; Dellinger, T.H.; Han, E.S.; Jove, R.; et al. Synergistic Anti-Tumor Effect of Combined Inhibition of EGFR and JAK/STAT3 Pathways in Human Ovarian Cancer. Mol. Cancer 2015, 14, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woessner, R.; McCoon, P.; Bell, K.; DuPont, R.; Collins, M.; Lawson, D.; Nadella, P.; Pablo, L.; Reimer, C.; Sah, V.; et al. Abstract A93: STAT3 Inhibition Enhances the Activity of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in Murine Syngeneic Tumor Models by Creating a More Immunogenic Tumor Microenvironment. Tumor Microenviron. 2015, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Li, Y.; Hsu, E.; Wang, Y.; Huang, J.; Brooks, E.; Li, C.J. Abstract LB-140: Inhibition of Cancer Stemness Sensitizes Colorectal Cancer to Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors. Tumor Biol. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, R.; Fleming, V.; Hu, X.; Nagibin, V.; Groth, C.; Altevogt, P.; Utikal, J.; Umansky, V. Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells Hinder the Anti-Cancer Activity of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, D.E.; O’Keefe, R.A.; Grandis, J.R. Targeting the IL-6/JAK/STAT3 signalling axis in cancer. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 15, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Yamazaki, T.; Pietrocola, F.; Zhou, H.; Zitvogel, L.; Ma, Y.; Kroemer, G. STAT3 Inhibition Enhances the Therapeutic Efficacy of Immunogenic Chemotherapy by Stimulating Type 1 Interferon Production by Cancer Cells. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 3812–3822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
K. Lau, Y.-T.; Ramaiyer, M.; E. Johnson, D.; R. Grandis, J. Targeting STAT3 in Cancer with Nucleotide Therapeutics. Cancers 2019, 11, 1681. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11111681
K. Lau Y-T, Ramaiyer M, E. Johnson D, R. Grandis J. Targeting STAT3 in Cancer with Nucleotide Therapeutics. Cancers. 2019; 11(11):1681. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11111681
Chicago/Turabian StyleK. Lau, Yue-Ting, Malini Ramaiyer, Daniel E. Johnson, and Jennifer R. Grandis. 2019. "Targeting STAT3 in Cancer with Nucleotide Therapeutics" Cancers 11, no. 11: 1681. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11111681
APA StyleK. Lau, Y.-T., Ramaiyer, M., E. Johnson, D., & R. Grandis, J. (2019). Targeting STAT3 in Cancer with Nucleotide Therapeutics. Cancers, 11(11), 1681. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11111681



