Immune Response against ALK in Children with ALK-Positive Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma
Abstract
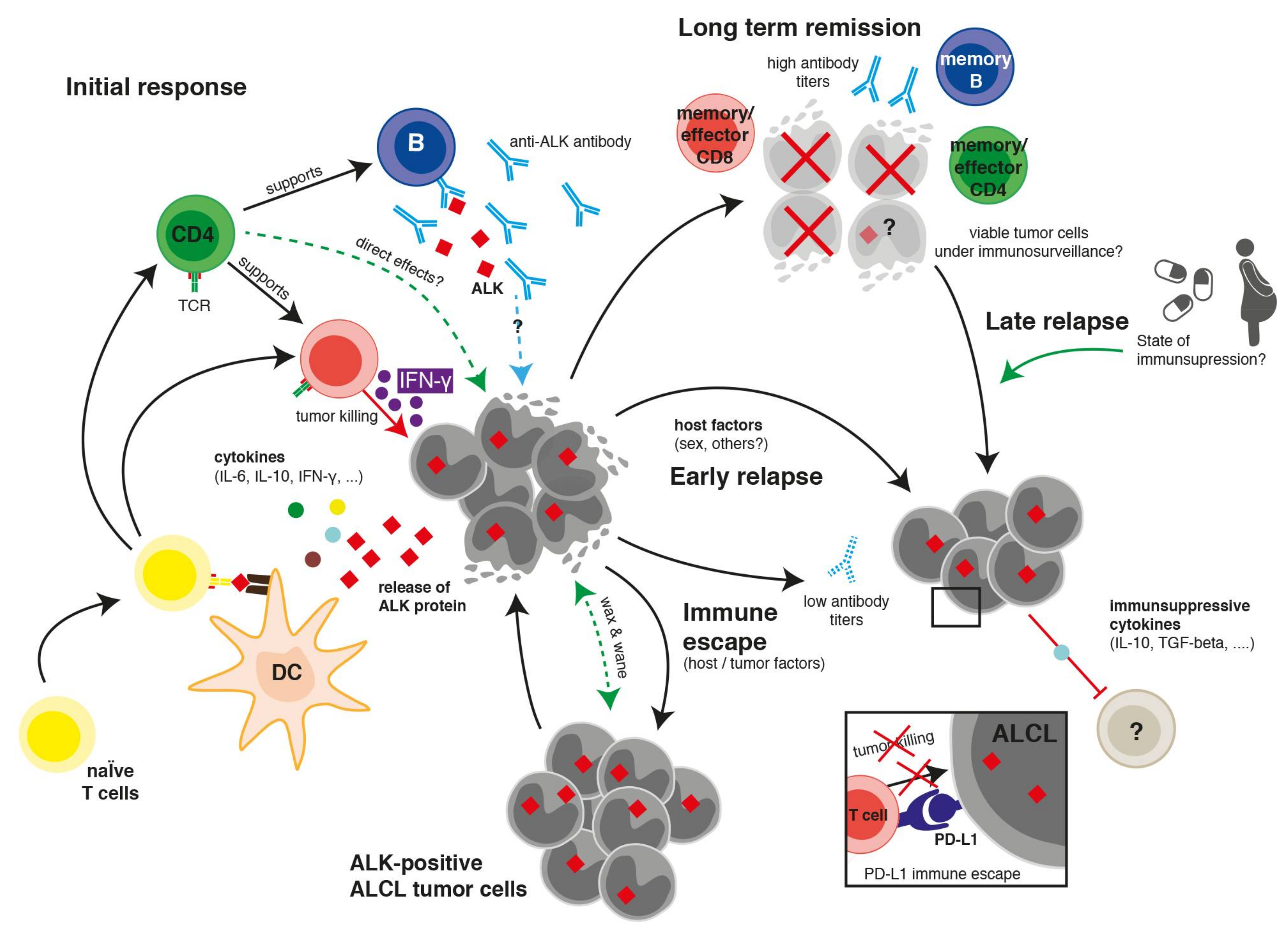
1. Introduction
2. Clinical, Laboratory, and Pathological Hints towards an Immune Reaction against ALCL
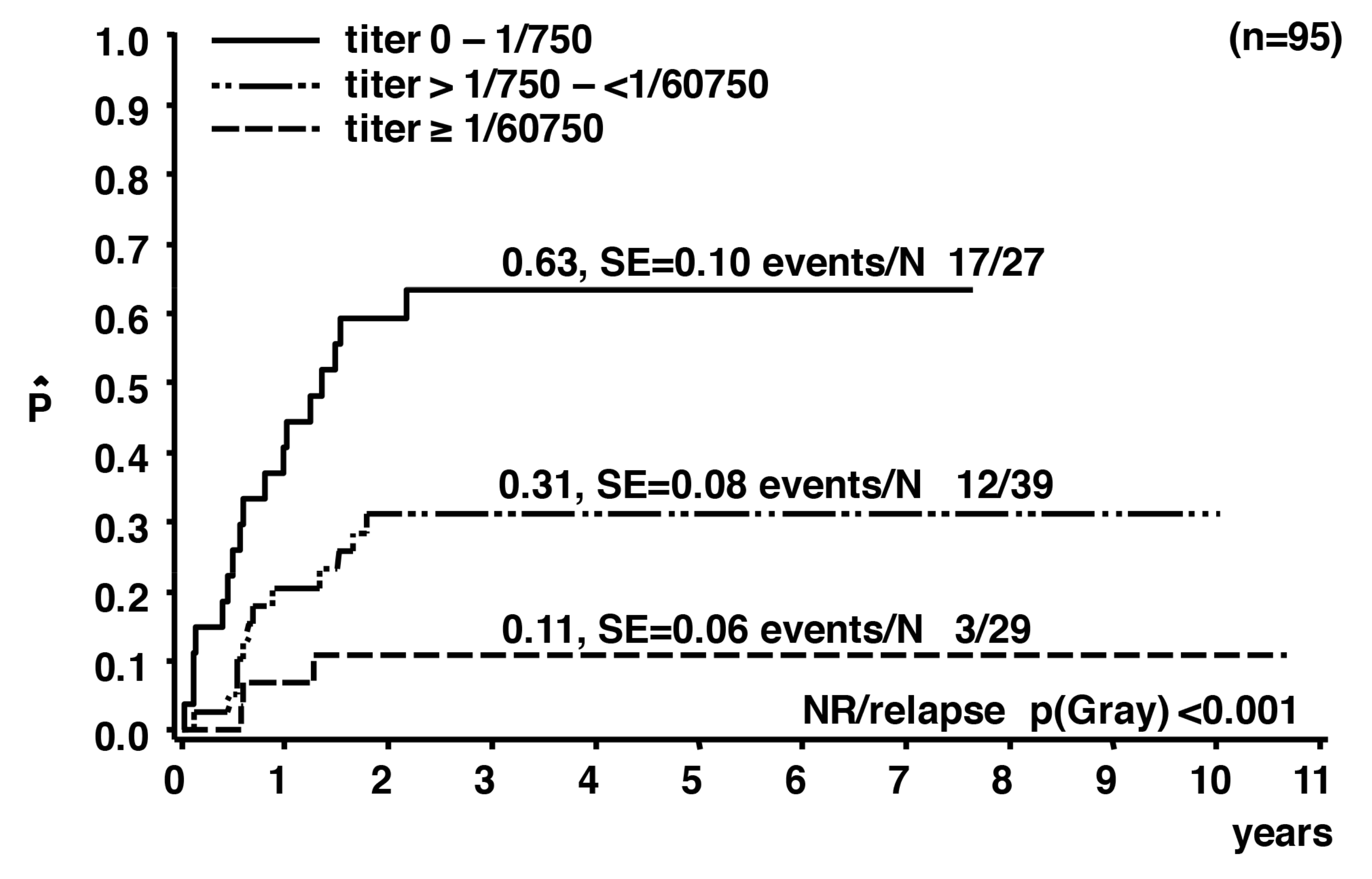
3. Humoral Immune Response against ALK
4. Cellular Immune Response against ALK
4.1. CD8 T Cell Response against ALK
4.2. CD4 T Cell Response against ALK
5. Immune Escape Mechanisms
6. Therapeutic Implications
7. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Falini, B.; Pileri, S.; Zinzani, P.L.; Carbone, A.; Zagonel, V.; Wolf-Peeters, C.; Verhoef, G.; Menestrina, F.; Todeschini, G.; Paulli, M.; et al. ALK+ lymphoma: Clinico-pathological findings and outcome. Blood 1999, 93, 2697–2706. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Burkhardt, B.; Zimmermann, M.; Oschlies, I.; Niggli, F.; Mann, G.; Parwaresch, R.; Riehm, H.; Schrappe, M.; Reiter, A.; Group, B.F.M. The impact of age and gender on biology, clinical features and treatment outcome of non-Hodgkin lymphoma in childhood and adolescence. Br. J. Haematol. 2005, 131, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, S.W.; Kirstein, M.N.; Valentine, M.B.; Dittmer, K.G.; Shapiro, D.N.; Saltman, D.L.; Look, A.T. Fusion of a kinase gene, ALK, to a nucleolar protein gene, npm, in non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Science 1994, 263, 1281–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perkins, S.L.; Pickering, D.; Lowe, E.J.; Zwick, D.; Abromowitch, M.; Davenport, G.; Cairo, M.S.; Sanger, W.G. Childhood anaplastic large cell lymphoma has a high incidence of ALK gene rearrangement as determined by immunohistochemical staining and fluorescent in situ hybridisation: A genetic and pathological correlation. Br. J. Haematol. 2005, 131, 624–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damm-Welk, C.; Klapper, W.; Oschlies, I.; Gesk, S.; Rottgers, S.; Bradtke, J.; Siebert, R.; Reiter, A.; Woessmann, W. Distribution of NPM1-ALK and x-ALK fusion transcripts in paediatric anaplastic large cell lymphoma: A molecular-histological correlation. Br. J. Haematol. 2009, 146, 306–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pulford, K.; Morris, S.W.; Turturro, F. Anaplastic lymphoma kinase proteins in growth control and cancer. J. Cell. Physiol. 2004, 199, 330–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiarle, R.; Voena, C.; Ambrogio, C.; Piva, R.; Inghirami, G. The anaplastic lymphoma kinase in the pathogenesis of cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2008, 8, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Werner, M.T.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, Q.; Wasik, M.A. Nucleophosmin-anaplastic lymphoma kinase: The ultimate oncogene and therapeutic target. Blood 2017, 129, 823–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reiter, A.; Schrappe, M.; Tiemann, M.; Parwaresch, R.; Zimmermann, M.; Yakisan, E.; Dopfer, R.; Bucsky, P.; Mann, G.; Gadner, H.; et al. Successful treatment strategy for ki-1 anaplastic large-cell lymphoma of childhood: A prospective analysis of 62 patients enrolled in three consecutive berlin-frankfurt-munster group studies. J. Clin. Oncol. 1994, 12, 899–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brugieres, L.; Deley, M.C.; Pacquement, H.; Meguerian-Bedoyan, Z.; Terrier-Lacombe, M.J.; Robert, A.; Pondarre, C.; Leverger, G.; Devalck, C.; Rodary, C.; et al. Cd30(+) anaplastic large-cell lymphoma in children: Analysis of 82 patients enrolled in two consecutive studies of the French society of pediatric oncology. Blood 1998, 92, 3591–3598. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Seidemann, K.; Tiemann, M.; Schrappe, M.; Yakisan, E.; Simonitsch, I.; Janka-Schaub, G.; Dorffel, W.; Zimmermann, M.; Mann, G.; Gadner, H.; et al. Short-pulse B-non-Hodgkin lymphoma-type chemotherapy is efficacious treatment for pediatric anaplastic large cell lymphoma: A report of the Berlin-Frankfurt-Munster group trial NHL-BFM 90. Blood 2001, 97, 3699–3706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, D.M.; Hobson, R.; Imeson, J.; Gerrard, M.; McCarthy, K.; Pinkerton, C.R.; United Kingdom Children’s Cancer Study Group. Anaplastic large cell lymphoma in childhood: Analysis of 72 patients treated on the United Kingdom children’s cancer study group chemotherapy regimens. Br. J. Haematol. 2002, 117, 812–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mori, T.; Kiyokawa, N.; Shimada, H.; Miyauchi, J.; Fujimoto, J. Anaplastic large cell lymphoma in Japanese children: Retrospective analysis of 34 patients diagnosed at the national research institute for child health and development. Br. J. Haematol. 2003, 121, 94–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosolen, A.; Pillon, M.; Garaventa, A.; Burnelli, R.; d’Amore, E.S.; Giuliano, M.; Comis, M.; Cesaro, S.; Tettoni, K.; Moleti, M.L.; et al. Anaplastic large cell lymphoma treated with a leukemia-like therapy: Report of the Italian association of pediatric hematology and oncology (aieop) LNH-92 protocol. Cancer 2005, 104, 2133–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowe, E.J.; Sposto, R.; Perkins, S.L.; Gross, T.G.; Finlay, J.; Zwick, D.; Abromowitch, M.; Children’s Cancer Group Study. Intensive chemotherapy for systemic anaplastic large cell lymphoma in children and adolescents: Final results of children’s cancer group study 5941. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2009, 52, 335–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brugieres, L.; Le Deley, M.C.; Rosolen, A.; Williams, D.; Horibe, K.; Wrobel, G.; Mann, G.; Zsiros, J.; Uyttebroeck, A.; Marky, I.; et al. Impact of the methotrexate administration dose on the need for intrathecal treatment in children and adolescents with anaplastic large-cell lymphoma: Results of a randomized trial of the eicnhl group. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 897–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexander, S.; Kraveka, J.M.; Weitzman, S.; Lowe, E.; Smith, L.; Lynch, J.C.; Chang, M.; Kinney, M.C.; Perkins, S.L.; Laver, J.; et al. Advanced stage anaplastic large cell lymphoma in children and adolescents: Results of ANHL0131, a randomized phase III trial of apo versus a modified regimen with vinblastine: A report from the children’s oncology group. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2014, 61, 2236–2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Deley, M.C.; Rosolen, A.; Williams, D.M.; Horibe, K.; Wrobel, G.; Attarbaschi, A.; Zsiros, J.; Uyttebroeck, A.; Marky, I.M.; Lamant, L.; et al. Vinblastine in children and adolescents with high-risk anaplastic large-cell lymphoma: Results of the randomized ALCL99-vinblastine trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 3987–3993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pro, B.; Advani, R.; Brice, P.; Bartlett, N.L.; Rosenblatt, J.D.; Illidge, T.; Matous, J.; Ramchandren, R.; Fanale, M.; Connors, J.M.; et al. Brentuximab vedotin (SGN-35) in patients with relapsed or refractory systemic anaplastic large-cell lymphoma: Results of a phase ii study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 2190–2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pro, B.; Advani, R.; Brice, P.; Bartlett, N.L.; Rosenblatt, J.D.; Illidge, T.; Matous, J.; Ramchandren, R.; Fanale, M.; Connors, J.M.; et al. Five-year results of brentuximab vedotin in patients with relapsed or refractory systemic anaplastic large cell lymphoma. Blood 2017, 130, 2709–2717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosse, Y.P.; Lim, M.S.; Voss, S.D.; Wilner, K.; Ruffner, K.; Laliberte, J.; Rolland, D.; Balis, F.M.; Maris, J.M.; Weigel, B.J.; et al. Safety and activity of crizotinib for paediatric patients with refractory solid tumours or anaplastic large-cell lymphoma: A children’s oncology group phase 1 consortium study. Lancet Oncol. 2013, 14, 472–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosse, Y.P.; Voss, S.D.; Lim, M.S.; Rolland, D.; Minard, C.G.; Fox, E.; Adamson, P.; Wilner, K.; Blaney, S.M.; Weigel, B.J. Targeting ALK with crizotinib in pediatric anaplastic large cell lymphoma and inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor: A children’s oncology group study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 3215–3221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gambacorti Passerini, C.; Farina, F.; Stasia, A.; Redaelli, S.; Ceccon, M.; Mologni, L.; Messa, C.; Guerra, L.; Giudici, G.; Sala, E.; et al. Crizotinib in advanced, chemoresistant anaplastic lymphoma kinase-positive lymphoma patients. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2014, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brugieres, L.; Quartier, P.; Le Deley, M.C.; Pacquement, H.; Perel, Y.; Bergeron, C.; Schmitt, C.; Landmann, J.; Patte, C.; Terrier-Lacombe, M.J.; et al. Relapses of childhood anaplastic large-cell lymphoma: Treatment results in a series of 41 children—A report from the french society of pediatric oncology. Ann. Oncol. 2000, 11, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mori, T.; Takimoto, T.; Katano, N.; Kikuchi, A.; Tabuchi, K.; Kobayashi, R.; Ayukawa, H.; Kumagai, M.A.; Horibe, K.; Tsurusawa, M. Recurrent childhood anaplastic large cell lymphoma: A retrospective analysis of registered cases in Japan. Br. J. Haematol. 2006, 132, 594–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woessmann, W.; Zimmermann, M.; Lenhard, M.; Burkhardt, B.; Rossig, C.; Kremens, B.; Lang, P.; Attarbaschi, A.; Mann, G.; Oschlies, I.; et al. Relapsed or refractory anaplastic large-cell lymphoma in children and adolescents after berlin-frankfurt-muenster (BFM)-type first-line therapy: A bfm-group study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 3065–3071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruf, S.; Brugieres, L.; Pillon, M.; Zimmermann, M.; Attarbaschi, A.; Mellgren, K.; Williams, D.; Uyttebroeck, A.; Wrobel, G.; Reiter, A.; et al. Risk-adapted therapy for patients with relapsed or refractory ALCL—final report of the prospective ALCL-relapse trial of the eicnhl. Br. J. Haematol. 2015, 171, 45. [Google Scholar]
- Iwahara, T.; Fujimoto, J.; Wen, D.; Cupples, R.; Bucay, N.; Arakawa, T.; Mori, S.; Ratzkin, B.; Yamamoto, T. Molecular characterization of ALK, a receptor tyrosine kinase expressed specifically in the nervous system. Oncogene 1997, 14, 439–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woessmann, W.; Department of Pediatric Hematology and Oncology, Justus-Liebig University, D-35392 Giessen, Germany. Unpublished work. 2018.
- Woessmann, W.; Peters, C.; Lenhard, M.; Burkhardt, B.; Sykora, K.W.; Dilloo, D.; Kremens, B.; Lang, P.; Fuhrer, M.; Kuhne, T.; et al. Allogeneic haematopoietic stem cell transplantation in relapsed or refractory anaplastic large cell lymphoma of children and adolescents—A Berlin-Frankfurt-Munster group report. Br. J. Haematol. 2006, 133, 176–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gross, T.G.; Hale, G.A.; He, W.; Camitta, B.M.; Sanders, J.E.; Cairo, M.S.; Hayashi, R.J.; Termuhlen, A.M.; Zhang, M.J.; Davies, S.M.; et al. Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for refractory or recurrent non-Hodgkin lymphoma in children and adolescents. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2010, 16, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strullu, M.; Thomas, C.; Le Deley, M.C.; Chevance, A.; Kanold, J.; Bertrand, Y.; Jubert, C.; Dalle, J.H.; Paillard, C.; Baruchel, A.; et al. Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in relapsed ALK+ anaplastic large cell lymphoma in children and adolescents: A study on behalf of the sfce and SFGM-TC. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2015, 50, 795–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukano, R.; Mori, T.; Kobayashi, R.; Mitsui, T.; Fujita, N.; Iwasaki, F.; Suzumiya, J.; Chin, M.; Goto, H.; Takahashi, Y.; et al. Haematopoietic stem cell transplantation for relapsed or refractory anaplastic large cell lymphoma: A study of children and adolescents in Japan. Br. J. Haematol. 2015, 168, 557–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamant, L.; McCarthy, K.; d’Amore, E.; Klapper, W.; Nakagawa, A.; Fraga, M.; Maldyk, J.; Simonitsch-Klupp, I.; Oschlies, I.; Delsol, G.; et al. Prognostic impact of morphologic and phenotypic features of childhood ALK-positive anaplastic large-cell lymphoma: Results of the ALCL99 study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 4669–4676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abramov, D.; Oschlies, I.; Zimmermann, M.; Konovalov, D.; Damm-Welk, C.; Wossmann, W.; Klapper, W. Expression of CD8 is associated with non-common type morphology and outcome in pediatric anaplastic lymphoma kinase-positive anaplastic large cell lymphoma. Haematologica 2013, 98, 1547–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damm-Welk, C.; Busch, K.; Burkhardt, B.; Schieferstein, J.; Viehmann, S.; Oschlies, I.; Klapper, W.; Zimmermann, M.; Harbott, J.; Reiter, A.; et al. Prognostic significance of circulating tumor cells in bone marrow or peripheral blood as detected by qualitative and quantitative pcr in pediatric NPM-ALK-positive anaplastic large-cell lymphoma. Blood 2007, 110, 670–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savan, R.; McFarland, A.P.; Reynolds, D.A.; Feigenbaum, L.; Ramakrishnan, K.; Karwan, M.; Shirota, H.; Klinman, D.M.; Dunleavy, K.; Pittaluga, S.; et al. A novel role for IL-22R1 as a driver of inflammation. Blood 2011, 117, 575–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mellgren, K.; Hedegaard, C.J.; Schmiegelow, K.; Muller, K. Plasma cytokine profiles at diagnosis in pediatric patients with non-Hodgkin lymphoma. J. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 2012, 34, 271–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knorr, F.; Damm-Welk, C.; Ruf, S.; Singh, V.K.; Zimmermann, M.; Reiter, A.; Woessmann, W. Blood cytokine concentrations of pediatric anaplastic lymphoma kinase-positive anaplastic large cell lymphoma patients. Haematologica 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasqualini, C.; Minard-Colin, V.; Saada, V.; Lamant, L.; Delsol, G.; Patte, C.; Le Deley, M.C.; Valteau-Couanet, D.; Brugieres, L. Clinical analysis and prognostic significance of haemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis-associated anaplastic large cell lymphoma in children. Br. J. Haematol. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Li, X.; Song, W.; Fang, Y.; Yu, L.; Liu, S.; Churilov, L.P.; Zhang, F. The roles and applications of autoantibodies in progression, diagnosis, treatment and prognosis of human malignant tumours. Autoimmun. Rev. 2017, 16, 1270–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaenker, P.; Gray, E.S.; Ziman, M.R. Autoantibody production in cancer—The humoral immune response toward autologous antigens in cancer patients. Autoimmun. Rev. 2016, 15, 477–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsou, P.; Katayama, H.; Ostrin, E.J.; Hanash, S.M. The emerging role of b cells in tumor immunity. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 5597–5601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pulford, K.; Falini, B.; Banham, A.H.; Codrington, D.; Roberton, H.; Hatton, C.; Mason, D.Y. Immune response to the ALK oncogenic tyrosine kinase in patients with anaplastic large-cell lymphoma. Blood 2000, 96, 1605–1607. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ait-Tahar, K.; Cerundolo, V.; Banham, A.H.; Hatton, C.; Blanchard, T.; Kusec, R.; Becker, M.; Smith, G.L.; Pulford, K. B and CTL responses to the ALK protein in patients with ALK-positive ALCL. Int. J. Cancer 2006, 118, 688–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mussolin, L.; Bonvini, P.; Ait-Tahar, K.; Pillon, M.; Tridello, G.; Buffardi, S.; Lombardi, A.; Pulford, K.; Rosolen, A. Kinetics of humoral response to ALK and its relationship with minimal residual disease in pediatric ALCL. Leukemia 2009, 23, 400–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Ait-Tahar, K.; Damm-Welk, C.; Burkhardt, B.; Zimmermann, M.; Klapper, W.; Reiter, A.; Pulford, K.; Woessmann, W. Correlation of the autoantibody response to the ALK oncoantigen in pediatric anaplastic lymphoma kinase-positive anaplastic large cell lymphoma with tumor dissemination and relapse risk. Blood 2010, 115, 3314–3319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mussolin, L.; Pillon, M.; Zimmermann, M.; Carraro, E.; Basso, G.; Knoerr, F.; Woessmann, W.; Damm-Welk, C. Course of anti-ALK antibody titres during chemotherapy in children with anaplastic large cell lymphoma. Br. J. Haematol. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mussolin, L.; Damm-Welk, C.; Pillon, M.; Zimmermann, M.; Franceschetto, G.; Pulford, K.; Reiter, A.; Rosolen, A.; Woessmann, W. Use of minimal disseminated disease and immunity to NPM-ALK antigen to stratify ALK-positive ALCL patients with different prognosis. Leukemia 2013, 27, 416–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damm-Welk, C.; Siddiqi, F.; Fischer, M.; Hero, B.; Narayanan, V.; Camidge, D.R.; Harris, M.; Burke, A.; Lehrnbecher, T.; Pulford, K.; et al. Anti-ALK antibodies in patients with ALK-positive malignancies not expressing NPM-ALK. J. Cancer 2016, 7, 1383–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Awad, M.M.; Mastini, C.; Blasco, R.B.; Mologni, L.; Voena, C.; Mussolin, L.; Mach, S.L.; Adeni, A.E.; Lydon, C.A.; Sholl, L.M.; et al. Epitope mapping of spontaneous autoantibodies to anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) in non-small cell lung cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 92265–92274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montgomery, R.B.; Makary, E.; Schiffman, K.; Goodell, V.; Disis, M.L. Endogenous anti-HER2 antibodies block HER2 phosphorylation and signaling through extracellular signal-regulated kinase. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 650–656. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chiarle, R.; Martinengo, C.; Mastini, C.; Ambrogio, C.; D’Escamard, V.; Forni, G.; Inghirami, G. The anaplastic lymphoma kinase is an effective oncoantigen for lymphoma vaccination. Nat. Med. 2008, 14, 676–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Passoni, L.; Scardino, A.; Bertazzoli, C.; Gallo, B.; Coluccia, A.M.; Lemonnier, F.A.; Kosmatopoulos, K.; Gambacorti-Passerini, C. ALK as a novel lymphoma-associated tumor antigen: Identification of 2 HLA-A2.1-restricted CD8+ T-cell epitopes. Blood 2002, 99, 2100–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Passoni, L.; Gallo, B.; Biganzoli, E.; Stefanoni, R.; Massimino, M.; Di Nicola, M.; Gianni, A.M.; Gambacorti-Passerini, C. In vivo t-cell immune response against anaplastic lymphoma kinase in patients with anaplastic large cell lymphomas. Haematologica 2006, 91, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Beckhove, P.; Feuerer, M.; Dolenc, M.; Schuetz, F.; Choi, C.; Sommerfeldt, N.; Schwendemann, J.; Ehlert, K.; Altevogt, P.; Bastert, G.; et al. Specifically activated memory T cell subsets from cancer patients recognize and reject xenotransplanted autologous tumors. J. Clin. Investig. 2004, 114, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enamorado, M.; Iborra, S.; Priego, E.; Cueto, F.J.; Quintana, J.A.; Martinez-Cano, S.; Mejias-Perez, E.; Esteban, M.; Melero, I.; Hidalgo, A.; et al. Enhanced anti-tumour immunity requires the interplay between resident and circulating memory CD8(+) t cells. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 16073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nizard, M.; Roussel, H.; Diniz, M.O.; Karaki, S.; Tran, T.; Voron, T.; Dransart, E.; Sandoval, F.; Riquet, M.; Rance, B.; et al. Induction of resident memory T cells enhances the efficacy of cancer vaccine. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voena, C.; Menotti, M.; Mastini, C.; Di Giacomo, F.; Longo, D.L.; Castella, B.; Merlo, M.E.B.; Ambrogio, C.; Wang, Q.; Minero, V.G.; et al. Efficacy of a cancer vaccine against ALK-rearranged lung tumors. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2015, 3, 1333–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, K.V.; Werner, S.; Hackstein, H.; Lennerz, V.; Reiter, A.; Wolfel, T.; Damm-Welk, C.; Woessmann, W. Analysis of nucleophosmin-anaplastic lymphoma kinase (NPM-ALK)-reactive CD8(+) t cell responses in children with NPM-ALK(+) anaplastic large cell lymphoma. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2016, 186, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janssen, E.M.; Lemmens, E.E.; Wolfe, T.; Christen, U.; von Herrath, M.G.; Schoenberger, S.P. Cd4+ t cells are required for secondary expansion and memory in CD8+ T lymphocytes. Nature 2003, 421, 852–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crotty, S. A brief history of t cell help to b cells. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 15, 185–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ait-Tahar, K.; Barnardo, M.C.; Pulford, K. CD4 T-helper responses to the anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) protein in patients with ALK-positive anaplastic large-cell lymphoma. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 1898–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.S.; Mellman, I. Oncology meets immunology: The cancer-immunity cycle. Immunity 2013, 39, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motz, G.T.; Coukos, G. Deciphering and reversing tumor immune suppression. Immunity 2013, 39, 61–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marzec, M.; Zhang, Q.; Goradia, A.; Raghunath, P.N.; Liu, X.; Paessler, M.; Wang, H.Y.; Wysocka, M.; Cheng, M.; Ruggeri, B.A.; et al. Oncogenic kinase NPM/ALK induces through STAT3 expression of immunosuppressive protein CD274 (PD-L1, B7-H1). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 20852–20857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andorsky, D.J.; Yamada, R.E.; Said, J.; Pinkus, G.S.; Betting, D.J.; Timmerman, J.M. Programmed death ligand 1 is expressed by non-Hodgkin lymphomas and inhibits the activity of tumor-associated T cells. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 4232–4244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasprzycka, M.; Marzec, M.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Q.; Wasik, M.A. Nucleophosmin/anaplastic lymphoma kinase (NPM/ALK) oncoprotein induces the t regulatory cell phenotype by activating stat3. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 9964–9969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thibodeau, J.; Bourgeois-Daigneault, M.C.; Huppe, G.; Tremblay, J.; Aumont, A.; Houde, M.; Bartee, E.; Brunet, A.; Gauvreau, M.E.; de Gassart, A.; et al. Interleukin-10-induced march1 mediates intracellular sequestration of mhc class ii in monocytes. Eur. J. Immunol. 2008, 38, 1225–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chattopadhyay, G.; Shevach, E.M. Antigen-specific induced t regulatory cells impair dendritic cell function via an IL-10/march1-dependent mechanism. J. Immunol. 2013, 191, 5875–5884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tze, L.E.; Horikawa, K.; Domaschenz, H.; Howard, D.R.; Roots, C.M.; Rigby, R.J.; Way, D.A.; Ohmura-Hoshino, M.; Ishido, S.; Andoniou, C.E.; et al. CD83 increases mhc ii and CD86 on dendritic cells by opposing IL-10-driven march1-mediated ubiquitination and degradation. J. Exp. Med. 2011, 208, 149–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, V.K.; Department of Pediatric Hematology and Oncology, Justus-Liebig University, D-35392 Giessen, Germany. Unpublished work. 2018.
- Zitvogel, L.; Kepp, O.; Kroemer, G. Immune parameters affecting the efficacy of chemotherapeutic regimens. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 8, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, H.; Matsushima, H.; Mizumoto, N.; Takashima, A. Classification of chemotherapeutic agents based on their differential in vitro effects on dendritic cells. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 6978–6986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, H.; Matsushima, H.; Nishibu, A.; Clausen, B.E.; Takashima, A. Dual therapeutic efficacy of vinblastine as a unique chemotherapeutic agent capable of inducing dendritic cell maturation. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 6987–6994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brugieres, L.; Pacquement, H.; Le Deley, M.C.; Leverger, G.; Lutz, P.; Paillard, C.; Baruchel, A.; Frappaz, D.; Nelken, B.; Lamant, L.; et al. Single-drug vinblastine as salvage treatment for refractory or relapsed anaplastic large-cell lymphoma: A report from the french society of pediatric oncology. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 5056–5061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hebart, H.; Lang, P.; Woessmann, W. Nivolumab for refractory anaplastic large cell lymphoma: A case report. Ann. Intern Med. 2016, 165, 607–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rigaud, C.; Abbou, S.; Minard-Colin, V.; Geoerger, B.; Scoazec, J.Y.; Vassal, G.; Jaff, N.; Heuberger, L.; Valteau-Couanet, D.; Brugieres, L. Efficacy of nivolumab in a patient with systemic refractory ALK+ anaplastic large cell lymphoma. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hombach, A.A.; Gorgens, A.; Chmielewski, M.; Murke, F.; Kimpel, J.; Giebel, B.; Abken, H. Superior therapeutic index in lymphoma therapy: CD30(+) CD34(+) hematopoietic stem cells resist a chimeric antigen receptor T-cell attack. Mol. Ther. 2016, 24, 1423–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos, C.A.; Ballard, B.; Zhang, H.; Dakhova, O.; Gee, A.P.; Mei, Z.; Bilgi, M.; Wu, M.F.; Liu, H.; Grilley, B.; et al. Clinical and immunological responses after CD30-specific chimeric antigen receptor-redirected lymphocytes. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 3462–3471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, A.J.; Majzner, R.G.; Zhang, L.; Wanhainen, K.; Long, A.H.; Nguyen, S.M.; Lopomo, P.; Vigny, M.; Fry, T.J.; Orentas, R.J.; et al. Tumor antigen and receptor densities regulate efficacy of a chimeric antigen receptor targeting anaplastic lymphoma kinase. Mol. Ther. 2017, 25, 2189–2201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maus, M.V.; Fraietta, J.A.; Levine, B.L.; Kalos, M.; Zhao, Y.; June, C.H. Adoptive immunotherapy for cancer or viruses. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 32, 189–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stadler, S.; Singh, V.K.; Knörr, F.; Damm-Welk, C.; Woessmann, W. Immune Response against ALK in Children with ALK-Positive Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma. Cancers 2018, 10, 114. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers10040114
Stadler S, Singh VK, Knörr F, Damm-Welk C, Woessmann W. Immune Response against ALK in Children with ALK-Positive Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma. Cancers. 2018; 10(4):114. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers10040114
Chicago/Turabian StyleStadler, Serena, Vijay Kumar Singh, Fabian Knörr, Christine Damm-Welk, and Wilhelm Woessmann. 2018. "Immune Response against ALK in Children with ALK-Positive Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma" Cancers 10, no. 4: 114. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers10040114
APA StyleStadler, S., Singh, V. K., Knörr, F., Damm-Welk, C., & Woessmann, W. (2018). Immune Response against ALK in Children with ALK-Positive Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma. Cancers, 10(4), 114. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers10040114



