Human Bocavirus Infection of Permanent Cells Differentiated to Air-Liquid Interface Cultures Activates Transcription of Pathways Involved in Tumorigenesis
Abstract
1. Introduction
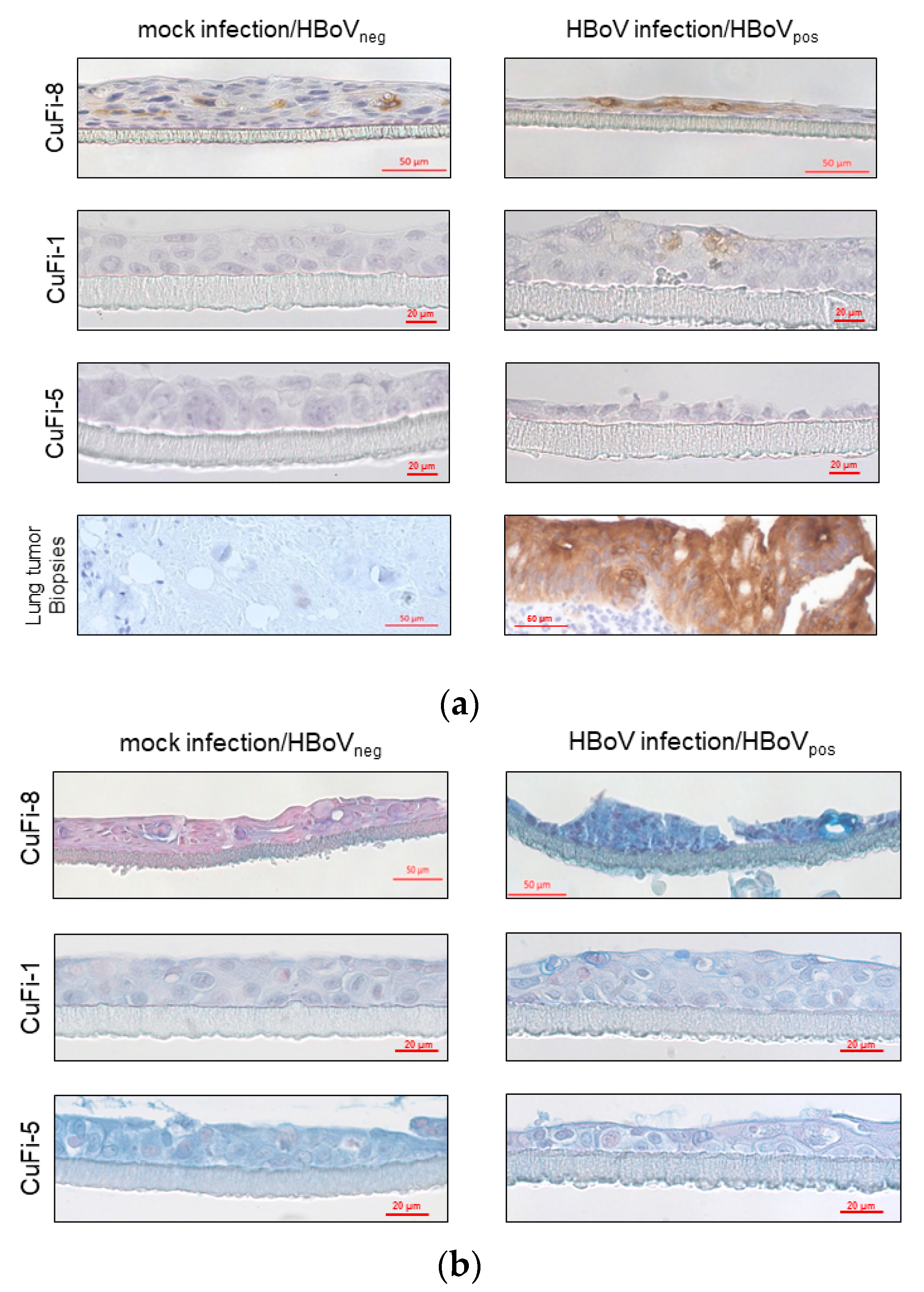
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cells and Infections
4.2. RNA Extractions and Whole Transcriptome Analyses
4.3. Immunohistochemical Analyses of CuFi air–Liquid-Interface Cultures
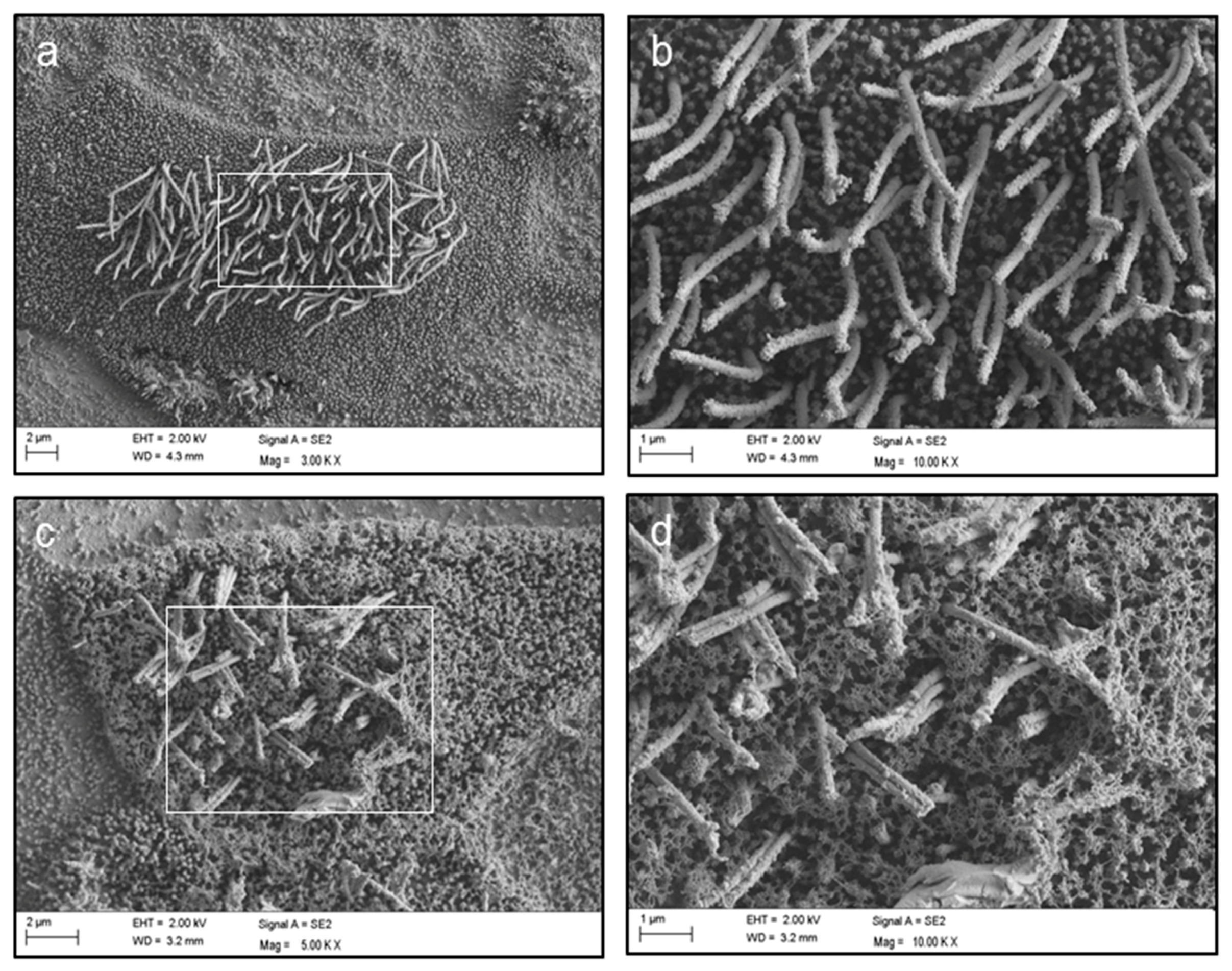
4.4. Scanning Electron Microscopy
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schildgen, V.; Malecki, M.; Tillmann, R.L.; Brockmann, M.; Schildgen, O. The human bocavirus is associated with some lung and colorectal cancers and persists in solid tumors. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e68020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Moneim, A.S.; El-Fol, H.A.; Kamel, M.M.; Soliman, A.S.; Mahdi, E.A.; El-Gammal, A.S.; Mahran, T.Z. Screening of human bocavirus in surgically excised cancer specimens. Arch. Virol. 2016, 161, 2095–2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Chen, X.Z.; Waterboer, T.; Castro, F.A.; Brenner, H. Viral infections and colorectal cancer: A systematic review of epidemiological studies. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 137, 12–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Dong, Y.; Jiang, J.; Yang, Y.; Liu, K. High prevelance of human parvovirus infection in patients with malignant tumors. Oncol. Lett. 2012, 3, 635–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guido, M.; Tumolo, M.R.; Verri, T.; Romano, A.; Serio, F.; De Giorgi, M.; De Donno, A.; Bagordo, F.; Zizza, A. Human bocavirus: Current knowledge and future challenges. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 8684–8697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broccolo, F.; Falcone, V.; Esposito, S.; Toniolo, A. Human bocaviruses: Possible etiologic role in respiratory infection. J. Clin. Virol. 2015, 72, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lusebrink, J.; Schildgen, V.; Tillmann, R.L.; Wittleben, F.; Bohmer, A.; Muller, A.; Schildgen, O. Detection of head-to-tail DNA sequences of human bocavirus in clinical samples. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e19457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, J.C.; Pyles, R.B.; Miller, A.L.; Nokso-Koivisto, J.; Loeffelholz, M.J.; Chonmaitree, T. Determining persistence of bocavirus DNA in the respiratory tract of children by pyrosequencing. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2016, 35, 471–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Garcia, M.L.; Calvo, C.; Pozo, F.; Perez-Brena, P.; Quevedo, S.; Bracamonte, T.; Casas, I. Human bocavirus detection in nasopharyngeal aspirates of children without clinical symptoms of respiratory infection. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2008, 27, 358–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, J.; Schildgen, V.; Tillmann, R.; Hardt, A.-L.; Lüsebrink, J.; Windisch, W.; Schildgen, O. Low copy number detection of hbov DNA in bal of asymptomatic adult patients. Future Virol. 2014, 9, 715–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chonmaitree, T.; Alvarez-Fernandez, P.; Jennings, K.; Trujillo, R.; Marom, T.; Loeffelholz, M.J.; Miller, A.L.; McCormick, D.P.; Patel, J.A.; Pyles, R.B. Symptomatic and asymptomatic respiratory viral infections in the first year of life: Association with acute otitis media development. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2015, 60, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Windisch, W.; Pieper, M.; Ziemele, I.; Rockstroh, J.; Brockmann, M.; Schildgen, O.; Schildgen, V. Latent infection of human bocavirus accompanied by flare of chronic cough, fatigue and episodes of viral replication in an immunocompetent adult patient, cologne, germany. JMM Case Rep. 2016, 3, e005052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapoor, A.; Hornig, M.; Asokan, A.; Williams, B.; Henriquez, J.A.; Lipkin, W.I. Bocavirus episome in infected human tissue contains non-identical termini. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e21362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Pesavento, P.A.; Leutenegger, C.M.; Estrada, M.; Coffey, L.L.; Naccache, S.N.; Samayoa, E.; Chiu, C.; Qiu, J.; Wang, C.; et al. A novel bocavirus in canine liver. Virol. J. 2013, 10, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Zhao, L.; Sun, Y.; Qian, Y.; Liu, L.; Jia, L.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, H. Detection of a bocavirus circular genome in fecal specimens from children with acute diarrhea in beijing, china. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e48980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schildgen, V.; Khalfaoui, S.; Schildgen, O. Human bocavirus: From common cold to cancer? Speculations on the importance of an episomal genomic form of human bocavirus. Rev. Med. Microbiol. 2014, 25, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalfaoui, S.; Eichhorn, V.; Karagiannidis, C.; Bayh, I.; Brockmann, M.; Pieper, M.; Windisch, W.; Schildgen, O.; Schildgen, V. Lung infection by human bocavirus induces the release of profibrotic mediator cytokines in vivo and in vitro. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0147010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Q.; Deng, X.; Yan, Z.; Cheng, F.; Luo, Y.; Shen, W.; Lei-Butters, D.C.; Chen, A.Y.; Li, Y.; Tang, L.; et al. Establishment of a reverse genetics system for studying human bocavirus in human airway epithelia. PLoS Pathog. 2012, 8, e1002899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, X.; Yan, Z.; Cheng, F.; Engelhardt, J.F.; Qiu, J. Replication of an autonomous human parvovirus in non-dividing human airway epithelium is facilitated through the DNA damage and repair pathways. PLoS Pathog. 2016, 12, e1005399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, X.; Xu, P.; Zou, W.; Shen, W.; Peng, J.; Liu, K.; Engelhardt, J.F.; Yan, Z.; Qiu, J. DNA damage signaling is required for replication of human bocavirus 1 DNA in dividing hek293 cells. J. Virol. 2017, 91, e01831-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schildgen, V.; Mai, S.; Khalfaoui, S.; Lusebrink, J.; Pieper, M.; Tillmann, R.L.; Brockmann, M.; Schildgen, O. Pneumocystis jirovecii can be productively cultured in differentiated cufi-8 airway cells. mBio 2014, 5, e01186-14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kramer, A.; Green, J.; Pollard, J., Jr.; Tugendreich, S. Causal analysis approaches in ingenuity pathway analysis. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 523–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Errington, T.M.; Macara, I.G. Depletion of the adaptor protein nck increases uv-induced p53 phosphorylation and promotes apoptosis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e76204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kremer, B.E.; Adang, L.A.; Macara, I.G. Septins regulate actin organization and cell-cycle arrest through nuclear accumulation of nck mediated by socs7. Cell 2007, 130, 837–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalan, S.; Matveyenko, A.; Loayza, D. Lim protein ajuba participates in the repression of the atr-mediated DNA damage response. Front. Genet. 2013, 4, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, X.; Zou, W.; Xiong, M.; Wang, Z.; Engelhardt, J.F.; Ye, S.Q.; Yan, Z.; Qiu, J. Human parvovirus infection of human airway epithelia induces pyroptotic cell death by inhibiting apoptosis. J. Virol. 2017, 91, e01533-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarrett, S.G.; Wolf Horrell, E.M.; D’Orazio, J.A. Akap12 mediates pka-induced phosphorylation of atr to enhance nucleotide excision repair. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, 10711–10726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garber, M.E.; Troyanskaya, O.G.; Schluens, K.; Petersen, S.; Thaesler, Z.; Pacyna-Gengelbach, M.; van de Rijn, M.; Rosen, G.D.; Perou, C.M.; Whyte, R.I.; et al. Diversity of gene expression in adenocarcinoma of the lung. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 13784–13789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tessema, M.; Willink, R.; Do, K.; Yu, Y.Y.; Yu, W.; Machida, E.O.; Brock, M.; Van Neste, L.; Stidley, C.A.; Baylin, S.B.; et al. Promoter methylation of genes in and around the candidate lung cancer susceptibility locus 6q23-25. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 1707–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morchikh, M.; Cribier, A.; Raffel, R.; Amraoui, S.; Cau, J.; Severac, D.; Dubois, E.; Schwartz, O.; Bennasser, Y.; Benkirane, M. Hexim1 and neat1 long non-coding rna form a multi-subunit complex that regulates DNA-mediated innate immune response. Mol. Cell 2017, 67, 387–399.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajesh, C.; Baker, D.K.; Pierce, A.J.; Pittman, D.L. The splicing-factor related protein sfpq/psf interacts with rad51d and is necessary for homology-directed repair and sister chromatid cohesion. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, 132–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salton, M.; Lerenthal, Y.; Wang, S.Y.; Chen, D.J.; Shiloh, Y. Involvement of matrin 3 and sfpq/nono in the DNA damage response. Cell Cycle 2010, 9, 1568–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.L.; Carmichael, G.G. Altered nuclear retention of mrnas containing inverted repeats in human embryonic stem cells: Functional role of a nuclear noncoding rna. Mol. Cell 2009, 35, 467–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reinertsen, T.; Halgunset, J.; Viset, T.; Flatberg, A.; Haugsmoen, L.L.; Skogseth, H. Gene expressional changes in prostate fibroblasts from cancerous tissue. Apmis 2012, 120, 558–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Midwood, K.S.; Orend, G. The role of tenascin-c in tissue injury and tumorigenesis. J. Cell Commun. Signal. 2009, 3, 287–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Midwood, K.; Sacre, S.; Piccinini, A.M.; Inglis, J.; Trebaul, A.; Chan, E.; Drexler, S.; Sofat, N.; Kashiwagi, M.; Orend, G.; et al. Tenascin-c is an endogenous activator of toll-like receptor 4 that is essential for maintaining inflammation in arthritic joint disease. Nat. Med. 2009, 15, 774–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattacharyya, S.; Wang, W.; Morales-Nebreda, L.; Feng, G.; Wu, M.; Zhou, X.; Lafyatis, R.; Lee, J.; Hinchcliff, M.; Feghali-Bostwick, C.; et al. Tenascin-c drives persistence of organ fibrosis. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tavazoie, S.F.; Alarcon, C.; Oskarsson, T.; Padua, D.; Wang, Q.; Bos, P.D.; Gerald, W.L.; Massague, J. Endogenous human micrornas that suppress breast cancer metastasis. Nature 2008, 451, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos, J.M.; Ruiz, A.; Colen, R.; Lopez, I.D.; Grossman, L.; Matta, J.L. DNA repair and breast carcinoma susceptibility in women. Cancer 2004, 100, 1352–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pugacheva, E.N.; Jablonski, S.A.; Hartman, T.R.; Henske, E.P.; Golemis, E.A. Hef1-dependent aurora a activation induces disassembly of the primary cilium. Cell 2007, 129, 1351–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pugacheva, E.N.; Golemis, E.A. The focal adhesion scaffolding protein hef1 regulates activation of the aurora-a and nek2 kinases at the centrosome. Nat. Cell Biol. 2005, 7, 937–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pugacheva, E.N.; Golemis, E.A. Hef1-aurora a interactions: Points of dialog between the cell cycle and cell attachment signaling networks. Cell Cycle 2006, 5, 384–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefanovic, L.; Longo, L.; Zhang, Y.; Stefanovic, B. Characterization of binding of larp6 to the 5’ stem-loop of collagen mrnas: Implications for synthesis of type i collagen. RNA Biol. 2014, 11, 1386–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fahim, A.; Crooks, M.G.; Wilmot, R.; Campbell, A.P.; Morice, A.H.; Hart, S.P. Serum carcinoembryonic antigen correlates with severity of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Respirology 2012, 17, 1247–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carmichael, L. Neonatal Viral Infections of Pups: Canine Herpesvirus and Minute Virus of Canines (Canine Parvovirus-1); International Veterinary Information Service, Ithaca: New York, NY, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Storz, J.; Young, S.; Carroll, E.J.; Bates, R.C.; Bowen, R.A.; Keney, D.A. Parvovirus infection of the bovine fetus: Distribution of infection, antibody response, and age-related susceptibility. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1978, 39, 1099–1102. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Windisch, W.; Schildgen, V.; Malecki, M.; Lenz, J.; Brockmann, M.; Karagiannidis, C.; Schildgen, O. Detection of hbov DNA in idiopathic lung fibrosis, cologne, germany. J. Clin. Virol. 2013, 58, 325–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakrabarty, S.; Tobon, A.; Varani, J.; Brattain, M.G. Induction of carcinoembryonic antigen secretion and modulation of protein secretion/expression and fibronectin/laminin expression in human colon carcinoma cells by transforming growth factor-beta. Cancer Res. 1988, 48, 4059–4064. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jain, P.; Mondal, S.K.; Sinha, S.K.; Mukhopadhyay, M.; Chakraborty, I. Diagnostic and prognostic significance of different mucin expression, preoperative cea, and ca-125 in colorectal carcinoma: A clinicopathological study. J. Nat. Sci. Biol. Med. 2014, 5, 404–408. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pai, P.; Rachagani, S.; Dhawan, P.; Batra, S.K. Mucins and wnt/beta-catenin signaling in gastrointestinal cancers: An unholy nexus. Carcinogenesis 2016, 37, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
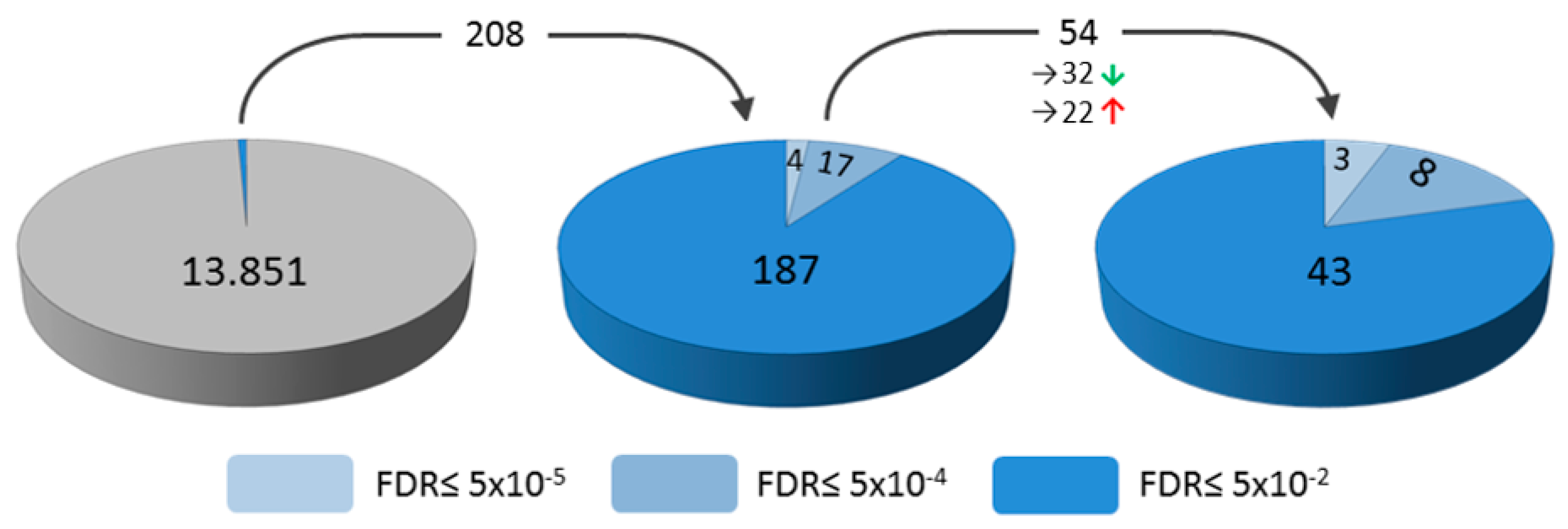
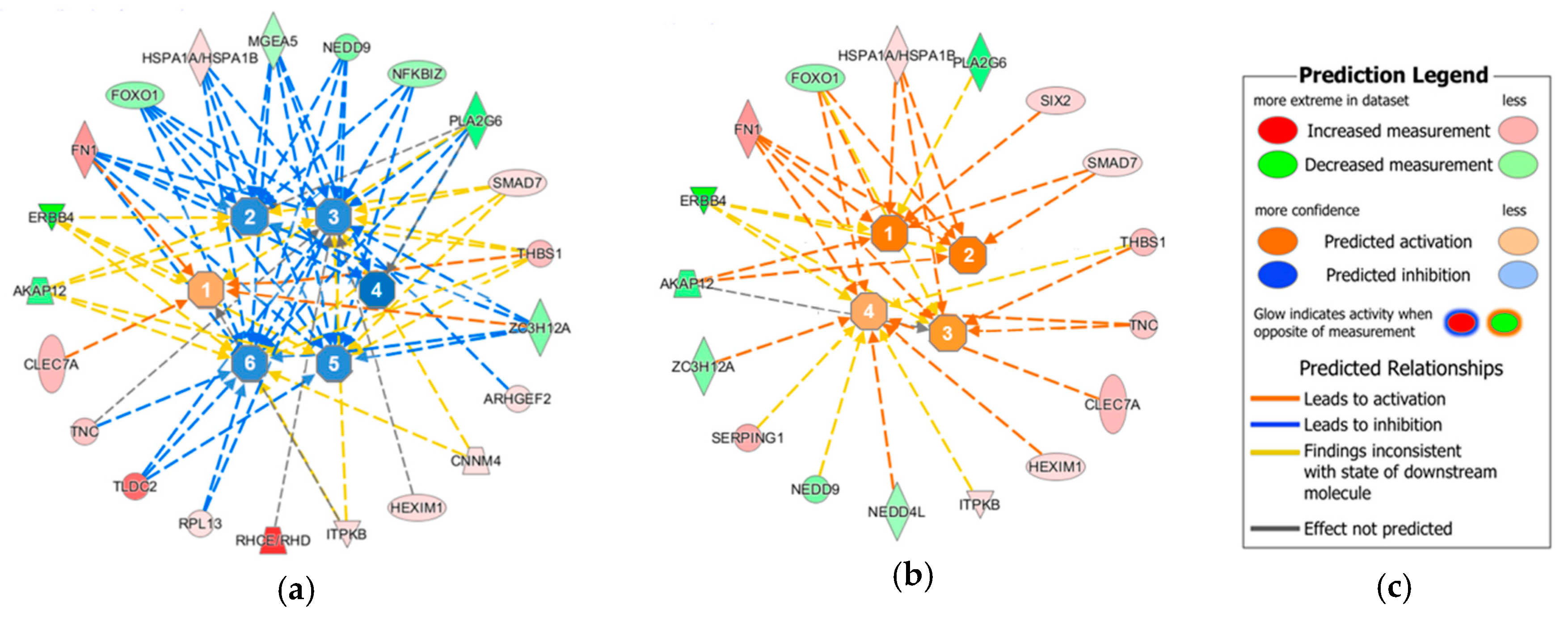
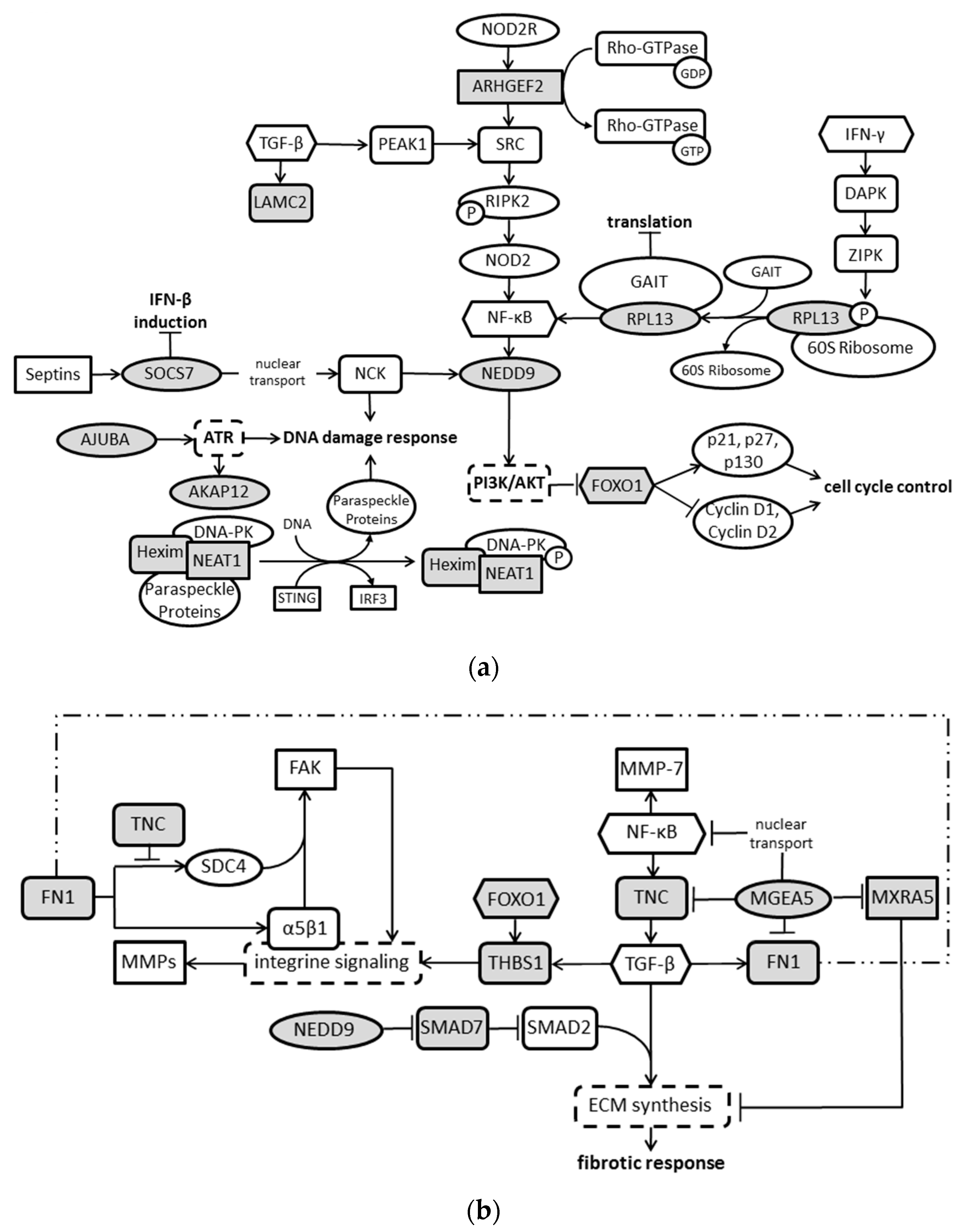
| Upregulated | Downregulated | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target RNA | Characterization | Target RNA | Characterization | Target RNA | Characterization | Target RNA | Characterization | Target RNA | Characterization |
| HEXIM1 (I) | transcription regulator | TAGLN (XII) | calcium binding protein | SRSF5 (1) | splicing factor | PHLDB2 (12) | microtubule-anchoring factor | ADGRF4 (23) | G protein-coupled receptor |
| FN1 (II) | ECM glycoprotein | IFITM1 (XIII) | transmembrane protein | NEAT1 (2) | lnc RNA | PLA2G4F (13) | Phospholipase A | LINC0113 8 (24) | lncRNA |
| RHCE/RHD (III) | membrane protein | SOCS7 (XIV) | SSI protein nucleocytoplasmic shuttling protein | ERBB4 (3) | receptor tyrosine kinase | NEDD4L (14) | ubiquitin ligase | SNORD80 (25) | C/D box snoRNA |
| AJUBA (IV) | transcription regulator | ITPKB (XV) | kinase | AKAP12 (4) | scaffold protein | ZNF587B (15) | transcriptional inhibitor | LINC00365 (26) | lncRNA |
| THBS1 (V) | ECM glycoprotein | CNNM4 (XVI) | metal cation transport mediator | SNHG3 (5) | lncRNA | LINC01451 (16) | lncRNA | ANO9 (27) | membrane channel |
| HSPA1A/HSPA1B (VI) | chaperon | LAMC2 (XVII) | ECM glycoprotein | S100A3 (6) | Calcium binding protein | TNNI2 (17) | inhibitory subunit of the troponin complex | NFKBIZ (28) | transcription regulator |
| ARHGEF2 (VII) | guanine nucleotide exchange factor | CLEC7A (XVIII) | membrane receptor | NEDD9 (7) | scaffold protein | PLA2G6 (18) | phospholipase A | MIR5047 (29) | miRNA |
| ANKLE1 (VIII) | endonuclease | LARP6 (XIX) | translational regulator | LOC105374476 (8) | uncharacterized, affiliated with ncRNA class | THUMPD3-AS1 (19) | lncRNA | MXRA5 (30) | matrix-remodelling associated protein |
| SERPING1 (IX) | protease inhibitor | SIX2 (XX) | transcription regulator | ZC3H12A (9) | transcriptional activator | MGEA5 (20) | O-GlcNAcase & Acetyltransferase | CAPN8 (31) | cysteine peptidase |
| TNC (X) | ECM glycoprotein | RPL13 (XXI) | translational regulator | RIMKLB (10) | N-Acetylaspartyl-Glutamate Synthetase | PSG8 (21) | glycoprotein | LENG8 (32) | Member of leukocyte receptor cluster |
| TLDC2 (XI) | OXR1 protein | SMAD7 (XXII) | transcription regulator | FOXO1 (11) | transcription regulator | SH3D21 (22) | nuclear protein | ||
| Disease Pattern (Σ Involved Molecules) | Involved Molecules |
|---|---|
| Cancer in general (Σ 43) | I, II, III, IV, V, VI, VII, VIII, IX, X, XI, XII, XIII, XV, XVI, XVII, XVIII, XIX, XX, XXI, XXII, 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 7, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 17, 18, 20, 21, 22, 27, 28, 30, 31, 32 |
| Lung cancer (Σ 9) | II, IV, V, X, XVIII, 3, 4, 7, 30 |
| Gastrointestinal cancer (Σ 40) | I, II, III, IV, V, VI, VII, VIII, IX, X, XI, XII, XIII, XV, XVI, XVII, XIX, XX, XXII, 1, 2, 3, 4, 7, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 17, 18, 20, 21, 22, 27, 28, 30, 31, 32 |
| Head and neck cancer (Σ 19) | IV, 4, 27, VII, 3, II, 11, XV, XVII, 30, 18, 21, IX, XX, XXII, XII, V, X, 9 |
| Neoplasia of epithelial tissue (Σ 41) | I, II, III, IV, V, VI, VII, VIII, IX, X, XI, XII, XIII, XV, XVI, XVII, XVIII, XIX, XX, XXII, 1, 3, 4, 6, 7, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 17, 18, 20, 21, 22, 27, 28, 30, 31, 32 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schildgen, V.; Pieper, M.; Khalfaoui, S.; Arnold, W.H.; Schildgen, O. Human Bocavirus Infection of Permanent Cells Differentiated to Air-Liquid Interface Cultures Activates Transcription of Pathways Involved in Tumorigenesis. Cancers 2018, 10, 410. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers10110410
Schildgen V, Pieper M, Khalfaoui S, Arnold WH, Schildgen O. Human Bocavirus Infection of Permanent Cells Differentiated to Air-Liquid Interface Cultures Activates Transcription of Pathways Involved in Tumorigenesis. Cancers. 2018; 10(11):410. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers10110410
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchildgen, Verena, Monika Pieper, Soumaya Khalfaoui, Wolfgang H. Arnold, and Oliver Schildgen. 2018. "Human Bocavirus Infection of Permanent Cells Differentiated to Air-Liquid Interface Cultures Activates Transcription of Pathways Involved in Tumorigenesis" Cancers 10, no. 11: 410. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers10110410
APA StyleSchildgen, V., Pieper, M., Khalfaoui, S., Arnold, W. H., & Schildgen, O. (2018). Human Bocavirus Infection of Permanent Cells Differentiated to Air-Liquid Interface Cultures Activates Transcription of Pathways Involved in Tumorigenesis. Cancers, 10(11), 410. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers10110410






