Measurement of Carcinoembryonic Antigen in Clinical Serum Samples Using a Centrifugal Microfluidic Device
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
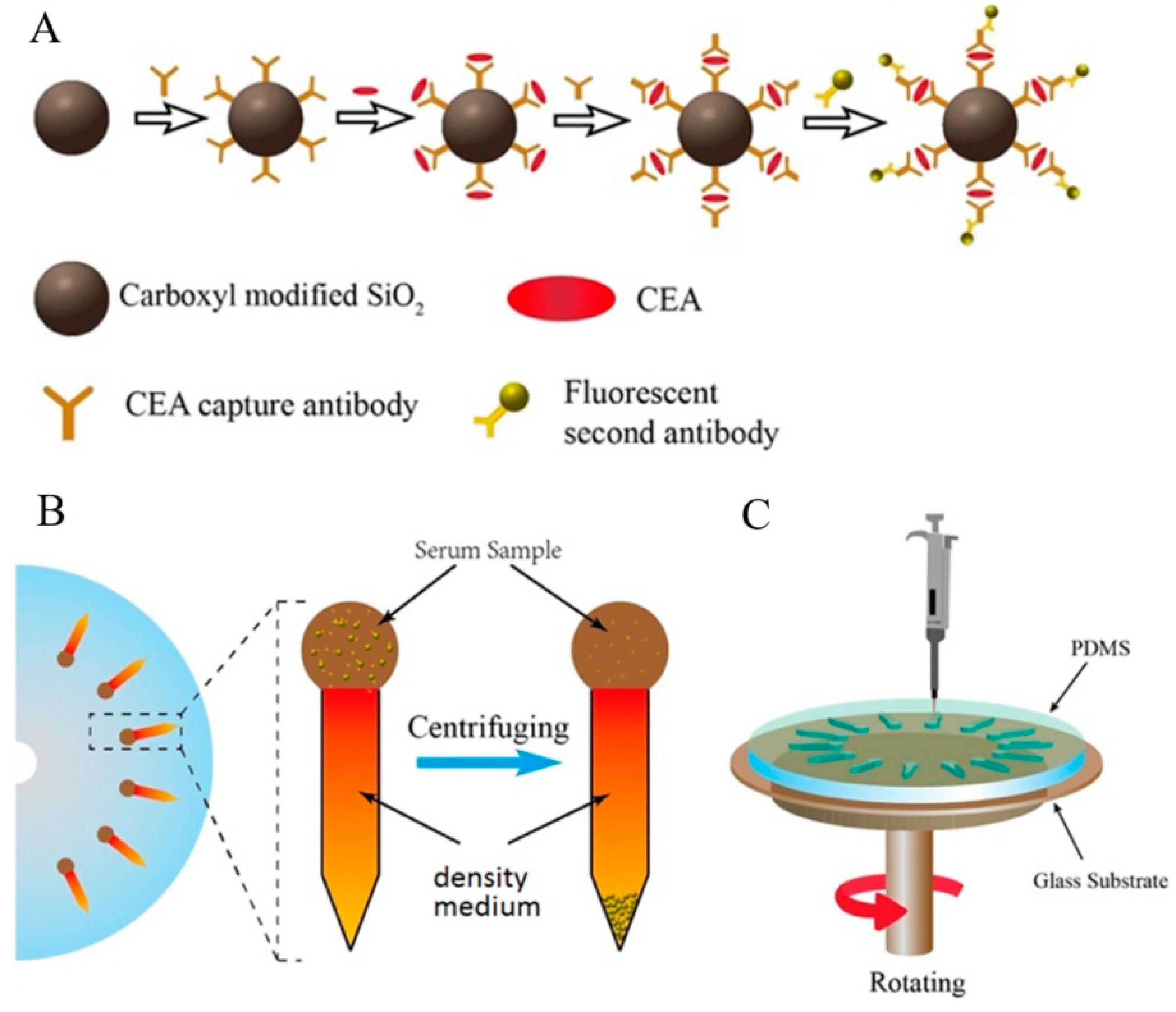
2.1. Design and Manufacture of the Centrifugal Microfluidic Device
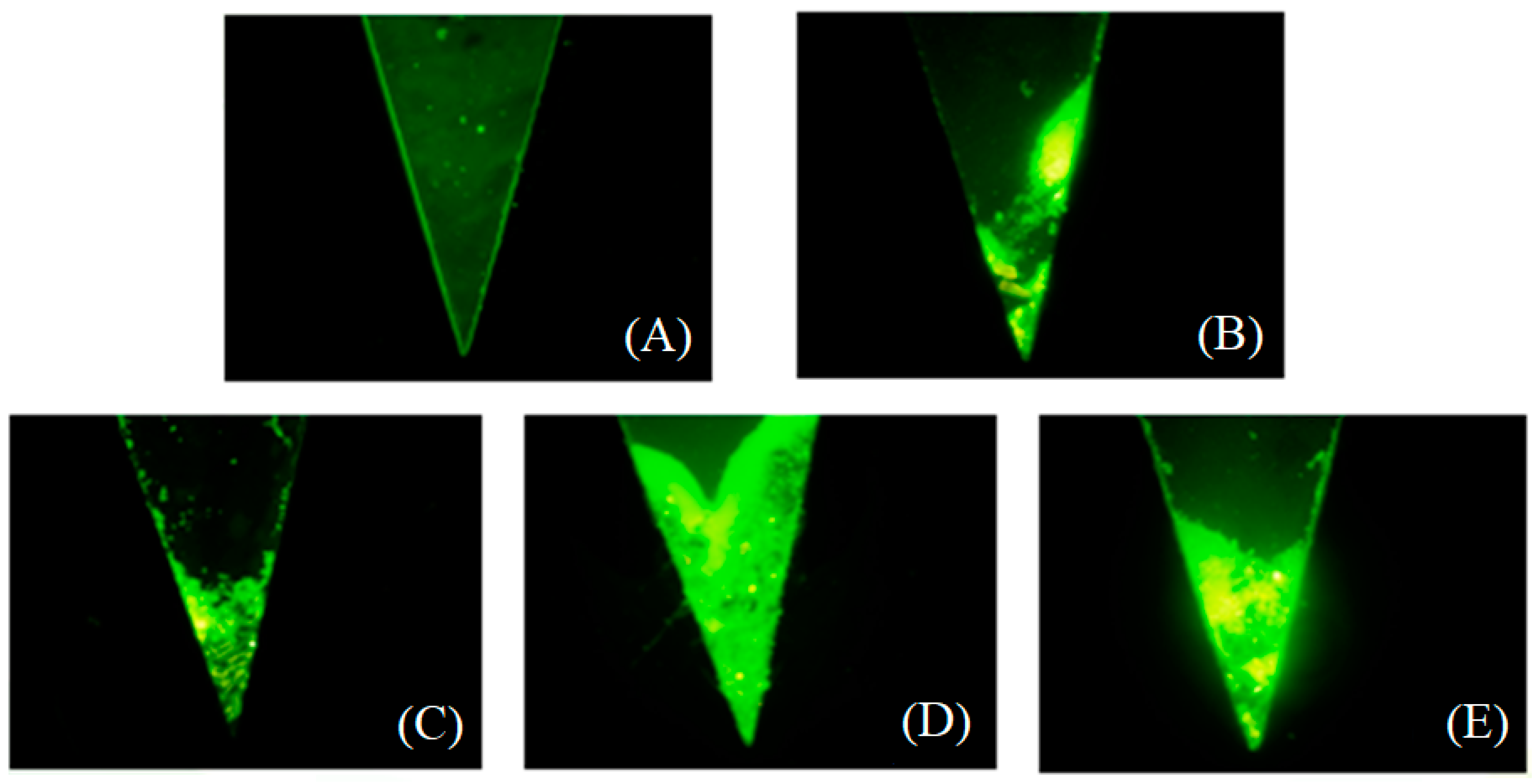
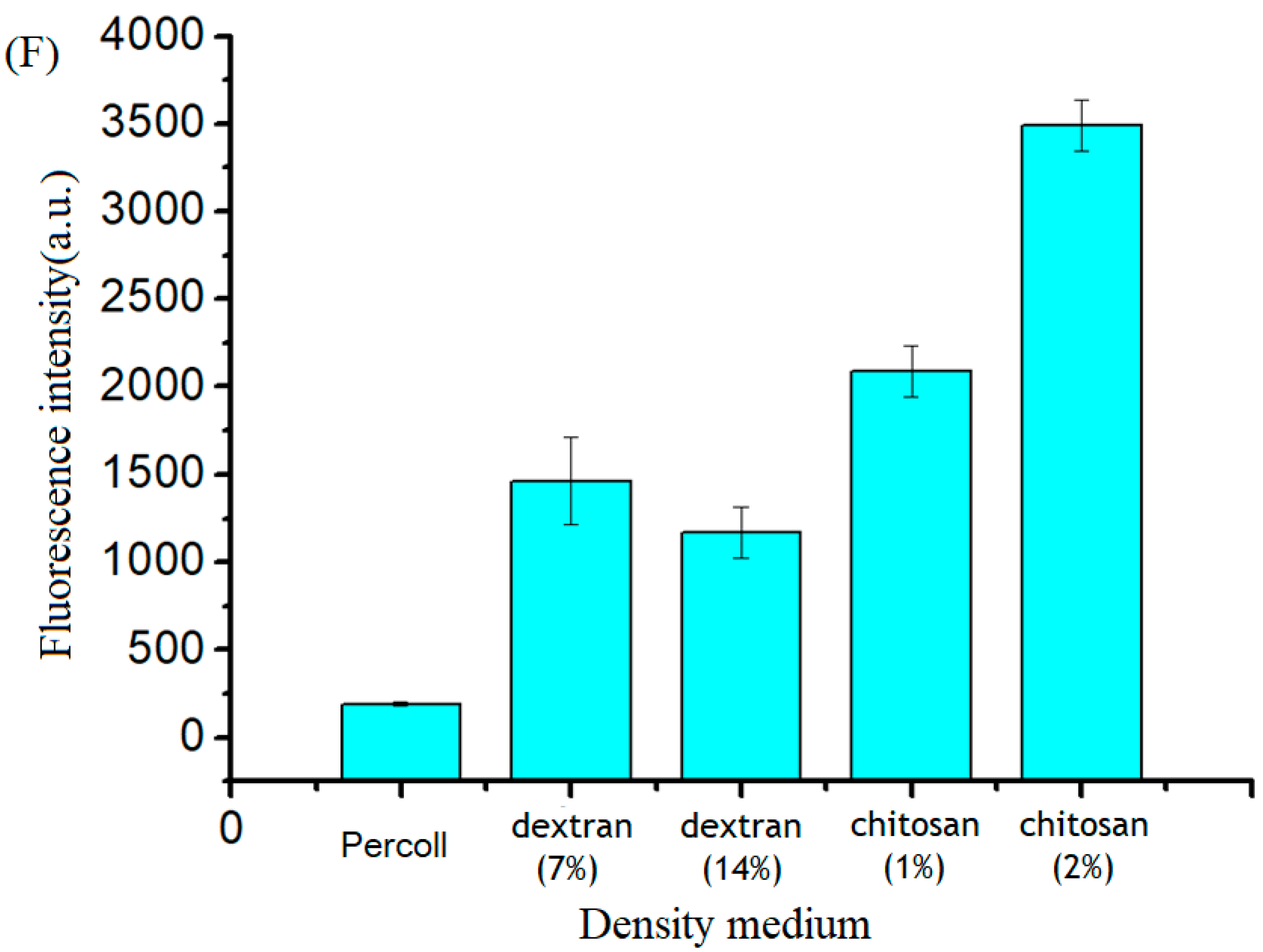
2.2. Medium Density Screening
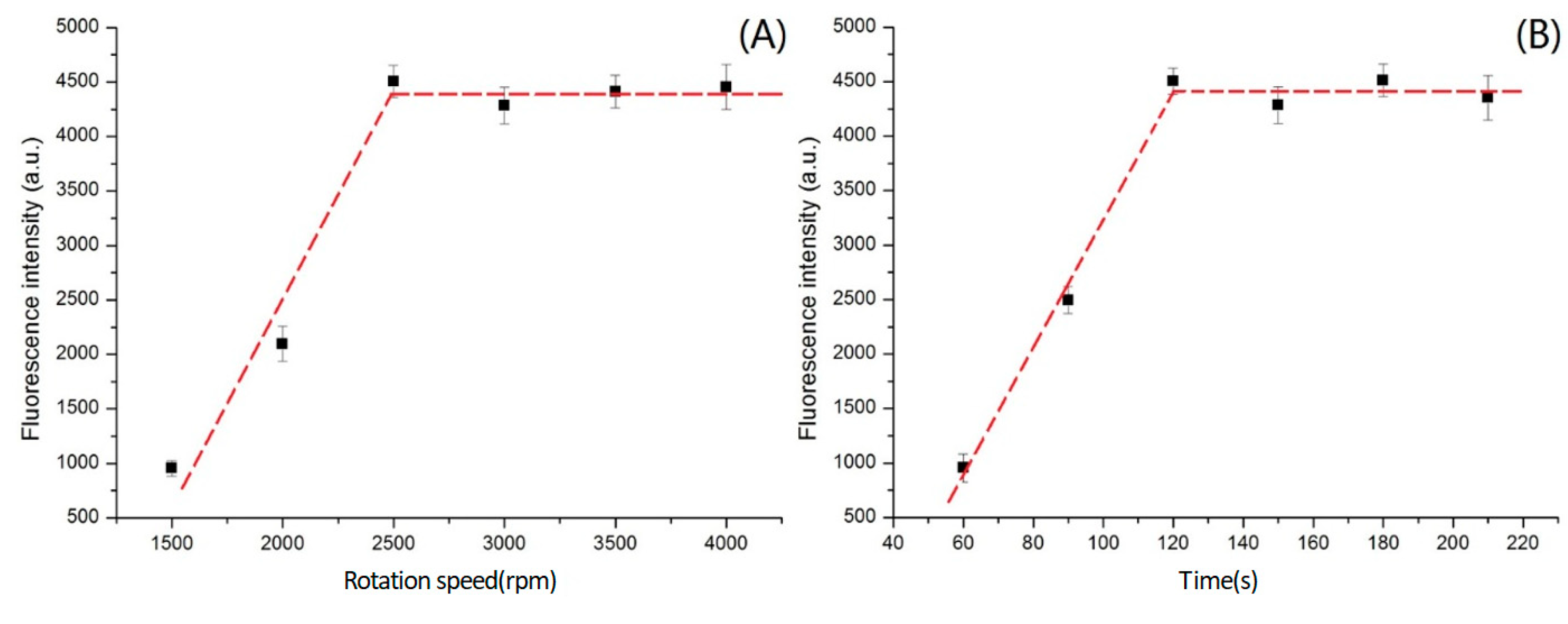
2.3. Optimization of the Rotation Speed and Spin Time
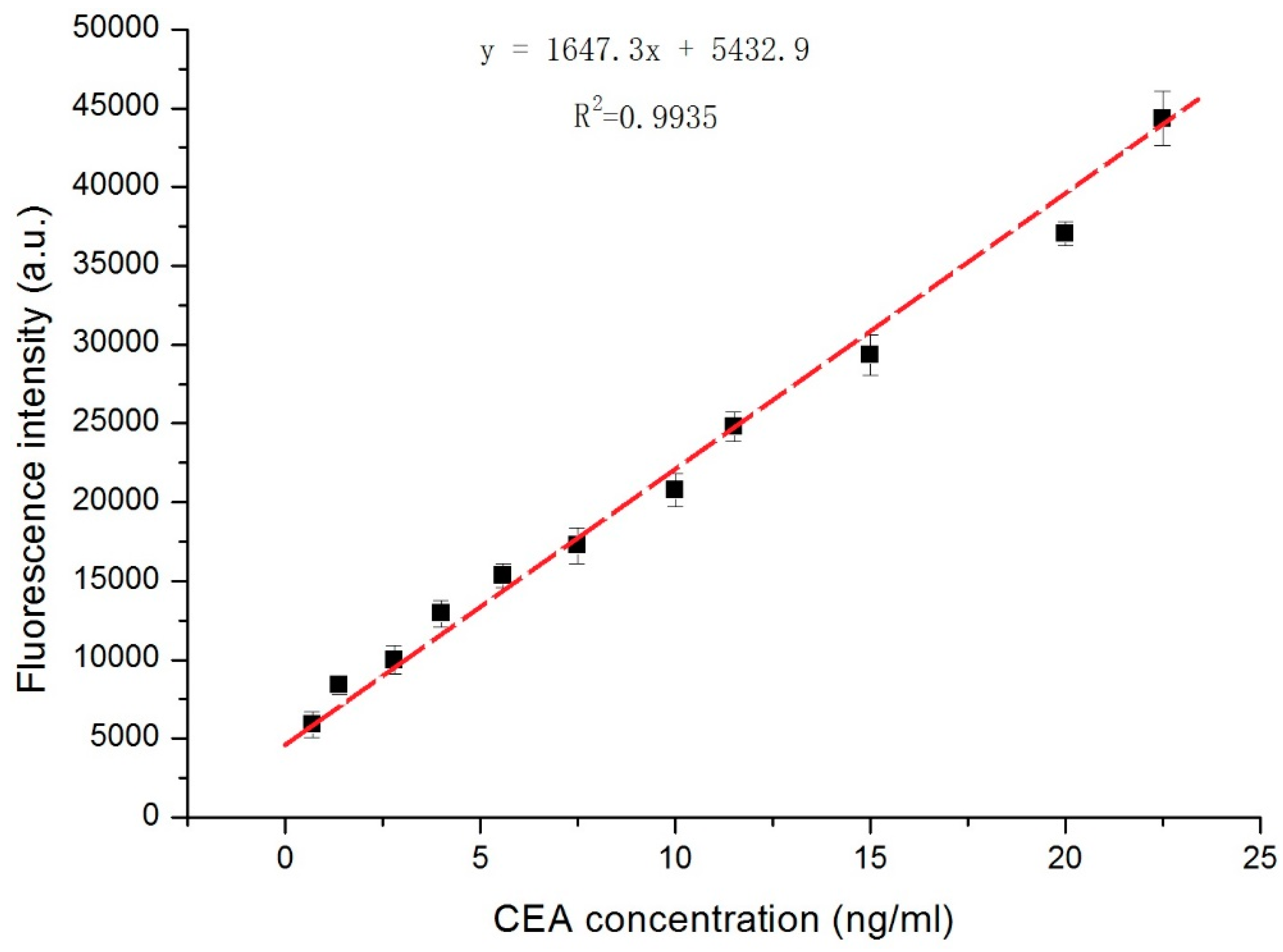
2.4. Establishing a CEA Standard Curve
2.5. Detection of CEA in Human Serum
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Design, Fabrication, and Verification of the Centrifugal Microfluidic Device
3.2. Medium Screening and Structure Optimization of the Microfluidic Device
3.3. Effects of Rotation Speed and Spin Duration on the Detection of CEA
3.4. CEA Detection in Human Serum Samples
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Braik, T.; Gupta, S.; Poola, H.; Jain, P.; Beiranvand, A.; Lad, T.E.; Hussein, L. Carcino embryonic antigen (CEA) elevation as a predictor of better response to first line pemetrexed in advanced lung adenocarcinoma. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2012, 7, S310. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, D.H.; Li, J.H.; Wang, Y.C.; Xu, J.G.; Pan, P.T.; Wang, L. Serum anti-p53 antibody detection in carcinomas and the predictive values of serum p53 antibodies, carcino-embryonic antigen and carbohydrate antigen 12–5 in the neoadjuvant chemotherapy treatment for III stage non-small cell lung cancer patients. Clin. Chim. Acta 2011, 412, 930–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, H.; Yu, D.; Wang, J.; Qiu, T.; Yang, J.; Wang, L. Predictive value of serum anti-p53 antibodies, carcino-embryonic antigen, carbohydrate antigen 15-3, estrogen receptor, progesterone receptor and human epidermal growth factor receptor-2 in taxane-based and anthracycline-based neoadjuvant chemotherapy in locally advanced breast cancer patients. Anti-Cancer Drug 2008, 19, 317–323. [Google Scholar]
- Thriveni, K.; Krishnamoorthy, L.; Ramaswamy, G. Correlation study of carcino embryonic antigen & cancer antigen 15.3 in pretreated female breast cancer patients. India J. Clin. Biochem. 2007, 22, 57–60. [Google Scholar]
- Cierpinski, A.; Stein, A.; Ruessel, J.; Ettrich, T.; Schmoll, H.J.; Arnold, D. Prognostic impact of carcino embryonic antigen (CEA), carbohydrate antigen (CA 19–9), and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) decrease in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC) receiving a bevacizumab- or cetuximab-chemotherapy combination. Onkologie 2011, 34, 250. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.R.; Yan, J.X.; Wang, L.N. The diagnostic value of serum carcino-embryonic antigen, alpha fetoprotein and carbohydrate antigen 19-9 for colorectal cancer. J. Cancer Res. Ther. 2014, 10, 307–309. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lai, H.; Jin, Q.; Lin, Y.; Mo, X.; Li, B.; He, K.; Chen, J. Combined use of lysyl oxidase, carcino-embryonic antigen, and carbohydrate antigens improves the sensitivity of biomarkers in predicting lymph node metastasis and peritoneal metastasis in gastric cancer. Tumor Biol. 2014, 35, 10547–10554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Szajda, S.D.; Snarska, J.; Jankowska, A.; Roszkowska-Jakimiec, W.; Puchalski, Z.; Zwierz, K. Cathepsin D and carcino-embryonic antigen in serum, urine and tissues of colon adenocarcinoma patients. Hepatogastroenterology 2008, 55, 388–393. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Xu, S.; Fjaertoft, G.; Pauksen, K.; Hakansson, L.; Venge, P. An enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for human carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 8, a biological marker of granulocyte activities in vivo. J. Immunol. Methods 2004, 293, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chester, S.J.; Maimonis, P.; Vanzuiden, P.; Finklestein, M.; Bookout, J.; Vezeridis, M.P. A new radioimmunoassay detecting early stages of colon cancer: a comparison with CEA, AFP, and Ca 19-9. Dis. Markers 1991, 9, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yan, F.; Zhou, J.; Lin, J.; Ju, H.; Hu, X. Flow injection immunoassay for carcinoembryonic antigen combined with time-resolved fluorometric detection. J. Immunol. Methods 2005, 305, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.; Yan, F.; Hu, X.; Ju, H. Chemiluminescent immunosensor for CA19-9 based on antigen immobilization on a cross-linked chitosan membrane. J. Immunol. Methods 2004, 291, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Yang, J.; Lin, J. 3,3′-diaminobenzidine (DAB)-H2O2-HRP voltammetric enzyme-linked immunoassay for the detection of carcionembryonic antigen. Bioelectrochemistry 2008, 72, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaff, U.Y.; Sommer, G.J. Whole blood immunoassay based on centrifugal bead sedimentation. Clin. Chem. 2011, 57, 753–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koh, C.-Y.; Schaff, U.Y.; Piccini, M.E.; Stanker, L.H.; Cheng, L.W.; Ravichandran, E.; Singh, B.-R.; Sommer, G.J.; Singh, A.K. Centrifugal microfluidic platform for ultrasensitive detection of botulinum toxin. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 922–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strohmeier, O.; Keller, M.; Schwemmer, F.; Zehnle, S.; Mark, D.; Von Stetten, F.; Zengerle, R.; Paust, N. Centrifugal microfluidic platforms: advanced unit operations and applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 6187–6229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
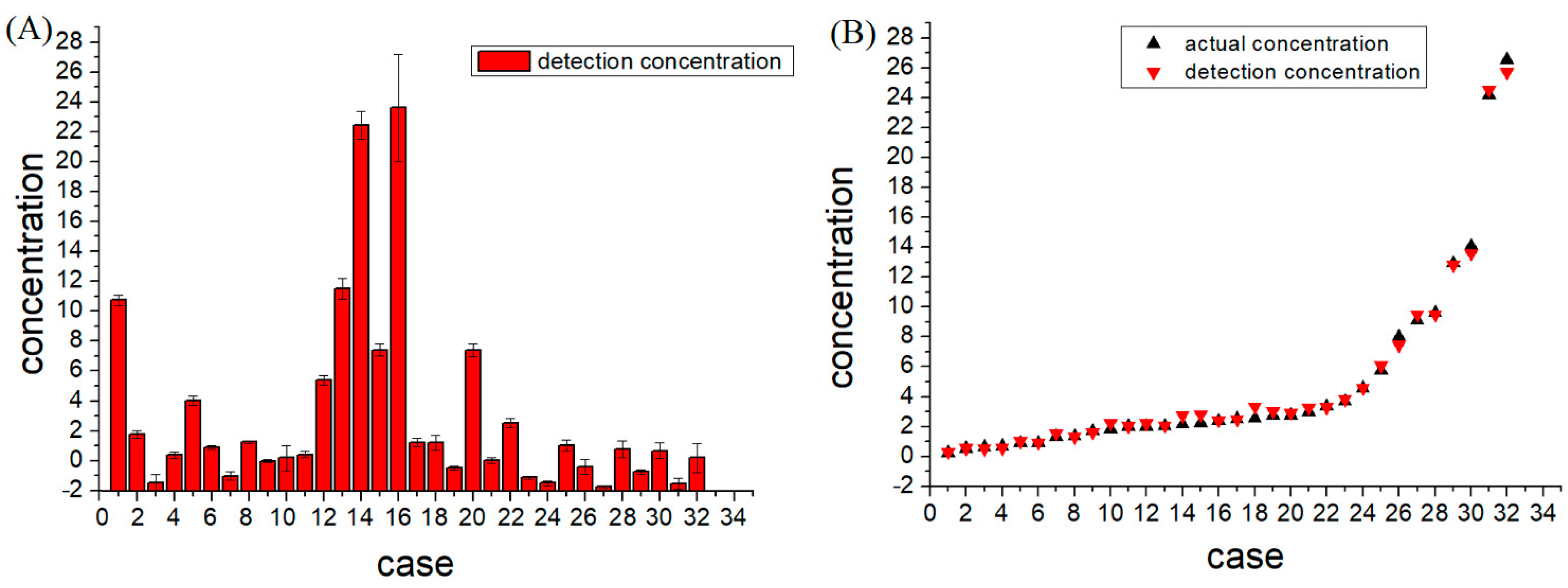
| No. | Known Value (ng/mL) | Measured Value (ng/mL), n = 3 | Relative Error |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 12.94 | 12.82 ± 0.33 | 0.96% |
| 2 | 3.69 | 3.82 ± 0.26 | 3.52% |
| 3 | 0.71 | 0.58 ± 0.52 | 18.59% |
| 4 | 2.4 | 2.43 ± 0.21 | 1.45% |
| 5 | 5.76 | 6.10 ± 0.30 | 5.87% |
| 6 | 2.75 | 2.94 ± 0.15 | 7% |
| 7 | 0.91 | 1.03 ± 0.29 | 13.14% |
| 8 | 2.55 | 3.31 ± 0.10 | 29.96% |
| 9 | 2.01 | 2.04 ± 0.07 | 1.55% |
| 10 | 2.02 | 2.23 ± 0.85 | 10.50% |
| 11 | 2.52 | 2.47 ± 0.22 | 1.99% |
| 12 | 8.01 | 7.46 ± 0.29 | 6.86% |
| 13 | 14.07 | 13.59 ± 0.69 | 3.43% |
| 14 | 24.16 | 24.54 ± 0.93 | 1.59% |
| 15 | 9.12 | 9.48 ± 0.39 | 3.99% |
| 16 | 26.54 | 25.69 ± 3.57 | 3.19% |
| 17 | 3.35 | 3.29 ± 0.28 | 1.66% |
| 18 | 2.98 | 3.27 ± 0.48 | 9.61% |
| 19 | 1.34 | 1.57 ± 0.10 | 17.39% |
| 20 | 9.63 | 9.48 ± 0.44 | 1.59% |
| 21 | 2.04 | 2.08 ± 0.19 | 1.94% |
| 22 | 4.58 | 4.60 ± 0.31 | 0.36% |
| 23 | 0.91 | 0.93 ± 0.11 | 1.91% |
| 24 | 0.53 | 0.55±0.15 | 4.67% |
| 25 | 2.72 | 3.05 ± 0.37 | 12.31% |
| 26 | 1.71 | 1.63 ± 0.46 | 4.48% |
| 27 | 0.25 | 0.30 ± 0.08 | 21.68% |
| 28 | 2.24 | 2.83 ± 0.57 | 26.23% |
| 29 | 1.38 | 1.29 ± 0.18 | 6.55% |
| 30 | 2.17 | 2.73 ± 0.51 | 25.8% |
| 31 | 0.66 | 0.52 ± 0.36 | 21.22% |
| 32 | 1.81 | 2.24 ± 0.97 | 24.02% |
| Samples | p-Value | Samples | p-Value | Samples | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.299 | 12 | 0.655 | 23 | 0.514 |
| 2 | 0.752 | 13 | 0.728 | 24 | 0.953 |
| 3 | 0.497 | 14 | 0.114 | 25 | 0.112 |
| 4 | 0.655 | 15 | 0.13 | 26 | 0.032 |
| 5 | 0.474 | 16 | 0.761 | 27 | 0.162 |
| 6 | 0.748 | 17 | 0.662 | 28 | 0.545 |
| 7 | 0.016 | 18 | 0.001 | 29 | 0.394 |
| 8 | 0.389 | 19 | 0.164 | 30 | 0.255 |
| 9 | 0.762 | 20 | 0.084 | 31 | 0.471 |
| 10 | 0.437 | 21 | 0.32 | 32 | 0.668 |
| 11 | 0.453 | 22 | 0.71 | -- | -- |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, Z.; Chen, Z.; Deng, J.; Li, X.; Qu, Y.; Xu, L.; Luo, Y.; Lu, Y.; Liu, T.; Zhao, W.; et al. Measurement of Carcinoembryonic Antigen in Clinical Serum Samples Using a Centrifugal Microfluidic Device. Micromachines 2018, 9, 470. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi9090470
Gao Z, Chen Z, Deng J, Li X, Qu Y, Xu L, Luo Y, Lu Y, Liu T, Zhao W, et al. Measurement of Carcinoembryonic Antigen in Clinical Serum Samples Using a Centrifugal Microfluidic Device. Micromachines. 2018; 9(9):470. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi9090470
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Zhigang, Zongzheng Chen, Jiu Deng, Xiaorui Li, Yueyang Qu, Lingling Xu, Yong Luo, Yao Lu, Tingjiao Liu, Weijie Zhao, and et al. 2018. "Measurement of Carcinoembryonic Antigen in Clinical Serum Samples Using a Centrifugal Microfluidic Device" Micromachines 9, no. 9: 470. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi9090470
APA StyleGao, Z., Chen, Z., Deng, J., Li, X., Qu, Y., Xu, L., Luo, Y., Lu, Y., Liu, T., Zhao, W., & Lin, B. (2018). Measurement of Carcinoembryonic Antigen in Clinical Serum Samples Using a Centrifugal Microfluidic Device. Micromachines, 9(9), 470. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi9090470






