Respiratory Motion Sensor Measuring Capacitance Constructed across Skin in Daily Activities
Abstract
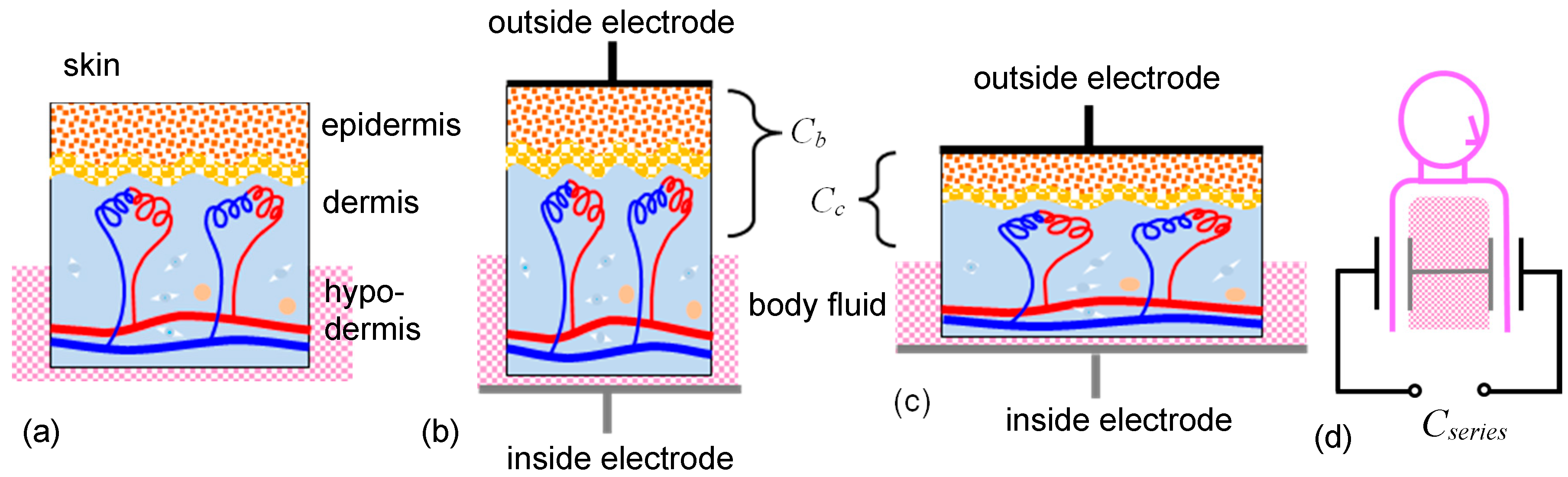
1. Introduction
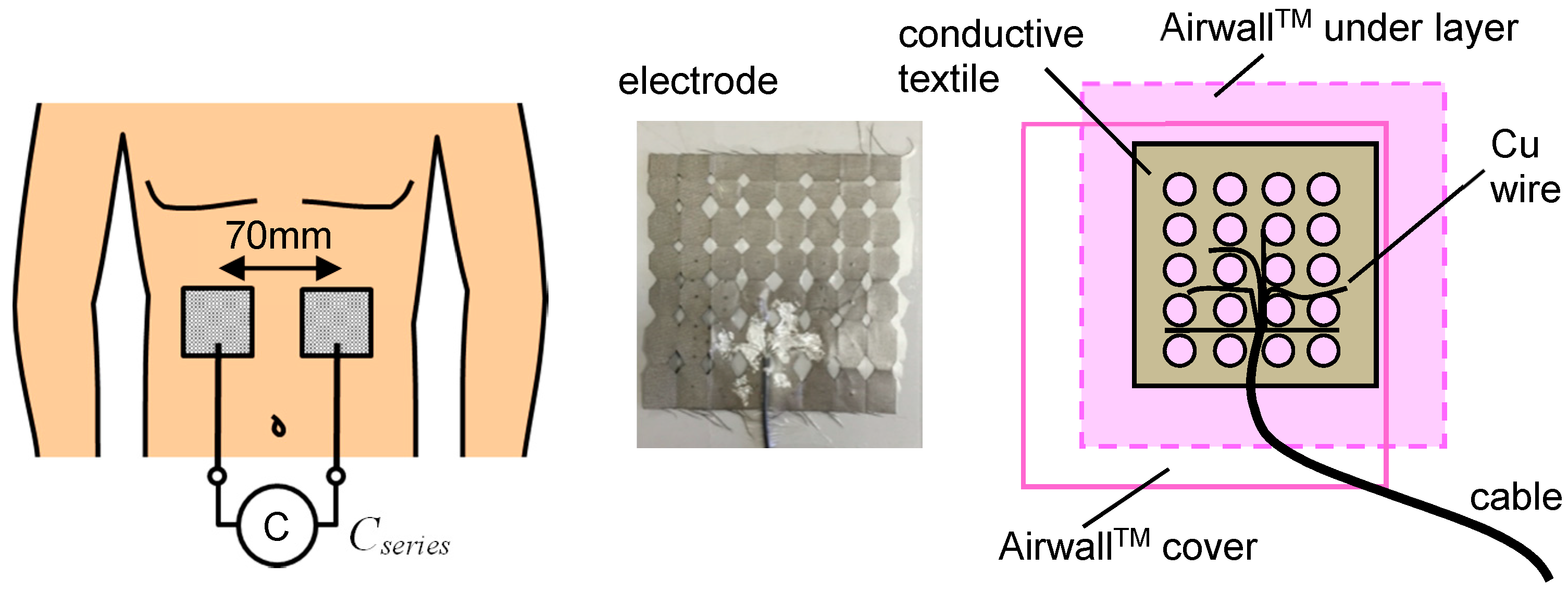
2. Method for Fitting Electrodes on the Skin
3. Results
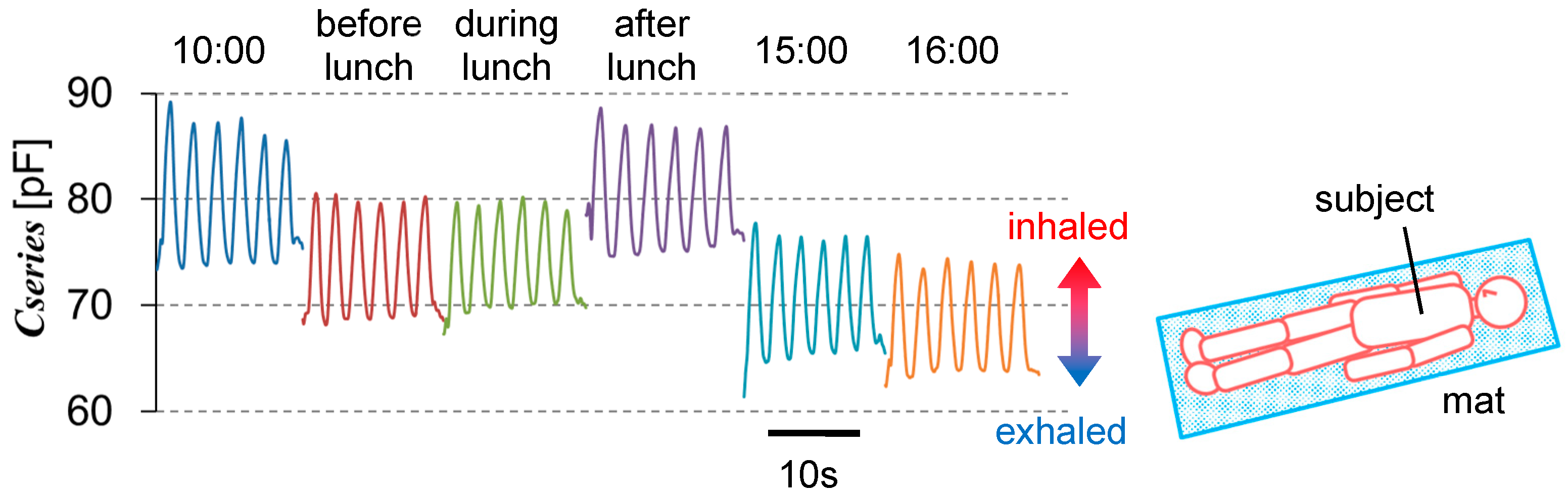
3.1. Signal under Gentle Conditions in Daytime
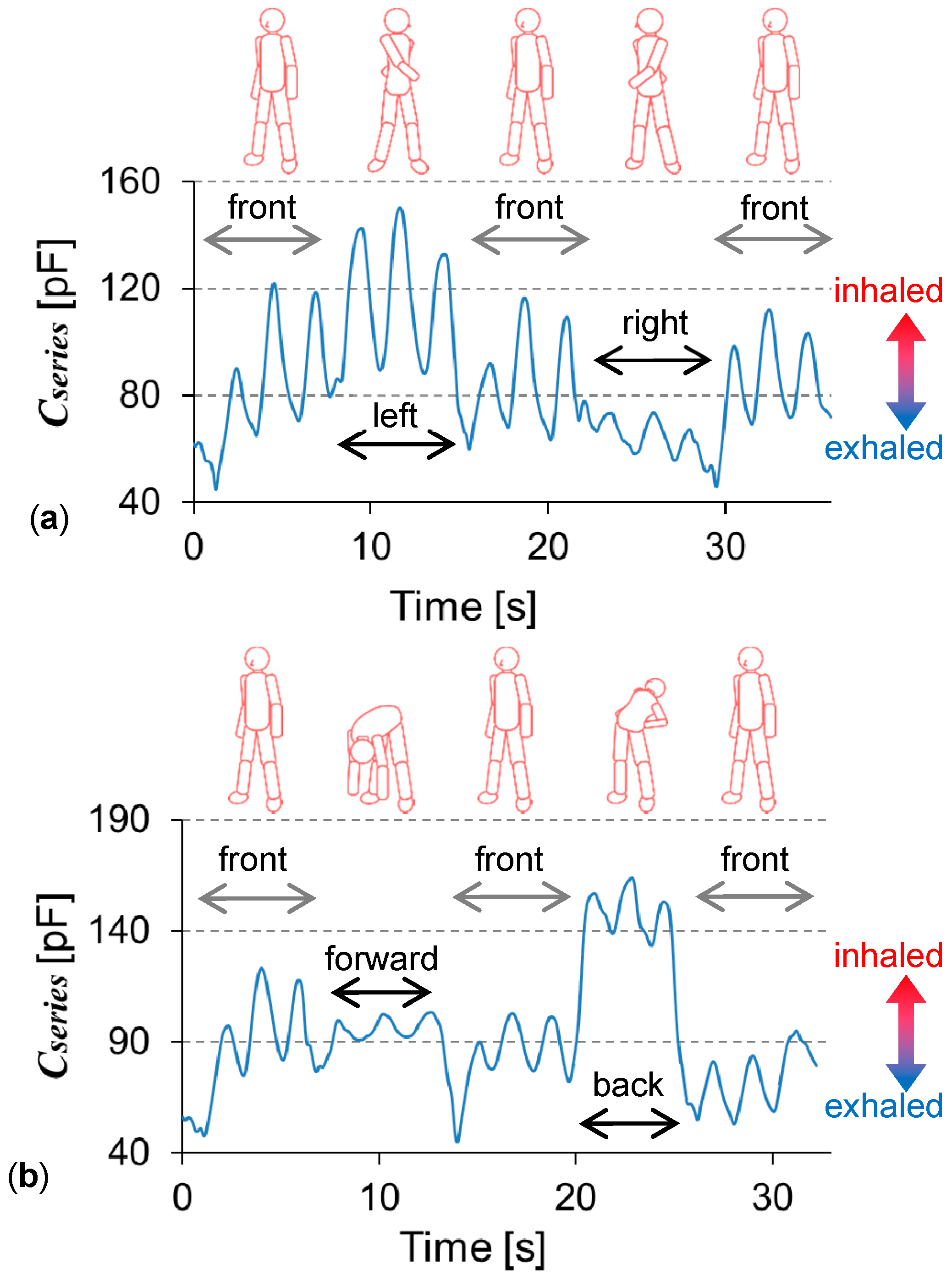
3.2. Singals during Twisting/Bending of the Upper Body
3.3. Signals during Walking for Six Minutes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chu, M.-X.; Shirai, T.; Takahashi, D.; Arakawa, T.; Kudo, H.; Sano, K.; Sawada, S.; Yano, K.; Iwasaki, Y.; Akiyoshi, K.; et al. Biomedical soft contact-lens sensor for in situ ocular biomonitoring of tear contents. Biomed. Microdevices 2011, 13, 603–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Company Examples are VX Sport. Available online: https://www.vxsport.com/ (accessed on 23 October 2018).
- GPSports, STATSports. Available online: https://statsports.com/ (accessed on 23 October 2018).
- Zephyr Technology. Available online: https://www.zephyranywhere.com/ (accessed on 23 October 2018).
- Product Examples Are Silmee™ from TDK and Toshiba Corporations. Available online: https://product.tdk.com/info/ja/products/biosensor/biosensor/silmee_btl/index.html (accessed on 23 October 2018).
- Hitoe™ from NTT Corporation. Available online: http://www.ntt.co.jp/journal/1807/files/JN20180710.pdf (accessed on 23 October 2018).
- Cretikos, M.A.; Bellomo, R.; Hillman, K.; Chen, J.; Finfer, S.; Flabouris, A. Respiratory rate: The neglected vital sign. Med. J. Aust. 2008, 188, 657–659. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Folke, M.; Cernerud, L.; Ekstrum, M.; Hok, B. Critical review of non-invasive respiratory monitoring in medical care. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2003, 41, 377–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scilingo, E.P.; Gemignani, A.; Paradiso, R.; Taccini, N.; Ghelarducci, B.; Rossi, D.D. Performance evaluation of sensing fabrics for monitoring physiological and biomechanical variables. IEEE Trans. Inf. Technol. Biomed. 2005, 9, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guay, P.; Gorgutsa, S.; LaRochelle, S.; Messaddeq, Y. Wearable Contactless Respiration Sensor Based on Multi-Material Fibers Integrated into Textile. Sensors 2017, 17, 1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Güder, F.; Ainla, A.; Redston, J.; Mosadegh, B.; Glavan, A.; Martin, T.J.; Whitesides, G.M. Paper-Based Electrical Respiration Sensor. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 5727–5732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.-H.; Lin, B.-S.; Tsai, C.-H.; Yang, C.-T.; Lin, B.-S. Design of Wearable Breathing Sound Monitoring System for Real-Time Wheeze Detection. Sensors 2017, 17, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pimentel, M.A.F.; Charlton, P.H.; Clifton, D.A. Wearable Electronics Sensors, Probabilistic Estimation of Respiratory Rate from Wearable Sensors; Springer International Publishing: Basel, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 241–262. ISBN 978-3-319-18191-2. [Google Scholar]
- Elfaramawy, T.; Fall, C.L.; Gosselin, B. Wireless respiratory monitoring and coughing detection using a wearable patch sensor network. In Proceedings of the 15th IEEE International New Circuits and Systems Conference, Strasbourg, France, 25–28 June 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Company Examples Are Spire. Available online: https://spire.io/ (accessed on 23 October 2018).
- Vitali Smart Bra & GEM. Available online: https://vitaliwear.com/ (accessed on 23 October 2018).
- Aliverti, A. Wearable technology: Role in respiratory health and disease. Breathe 2017, 13, e27–e36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baxter, L.K. Capacitive Sensors; IEEE Press: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 1997; pp. 1–5. ISBN 0-7803-535L-X. [Google Scholar]
- Kundu, S.K.; Kumagai, S.; Sasaki, M. A Wearable Capacitive Sensor to Monitor Human Respiratory Rate. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2013, 52, 04CL05. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karita, M.; Terasawa, M.; Kumagai, S.; Sasaki, M. Respiratory Sensor Measuring Capacitance Constructed Across Skin Allowing Exercise. In Proceedings of the Asia-Pacific Conference of Transducers and Micro-Nano Technology, Kanazawa, Japan, 26–29 June 2016; pp. 249–250. [Google Scholar]
- Terasawa, M.; Karita, M.; Kumagai, S.; Sasaki, M. Respiratory Sensor Continuously Attached on the Abdomen. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Solid State Devices and Materials, Tsukuba, Japan, 19–22 September 2017; pp. 265–266. [Google Scholar]
- Terasawa, M.; Kumagai, S.; Sasaki, M. Frequency Response Based Analysis of Respiratory Sensor Measuring Capacitance Constructed Across Skin. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2016, 55, 04EM13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| - | Sports Tape | Silicone Gel | Dressing Film |
|---|---|---|---|
| Original use | For taping in sports | For artificial scabs | For fixing the needle of a drip infusion |
| Specification | 0.4-mm-thick tape used for under-layer and cover. | 2-mm-thick plate used for under-layer. Cover is sports tape. | 7-μm -thick films used for under-layer and cover. |
| Setup for fixing electrode |  |  |  |
| Signal evaluation | Drift is large for long time measurement. | Signal is stable but its magnitude decreases. | Signal is stable and large. |
| Judgement | bad | bad | good |
| - | Peak | Valley | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Timing | Average (pF) | Standard Deviation (pF) | Ratio | Average (pF) | Standard Deviation (pF) | Ratio |
| 10:00 a.m. | 87.15 | 1.170 | 0.0134 | 73.83 | 0.201 | 0.0027 |
| Before lunch | 80.08 | 0.372 | 0.0046 | 68.67 | 0.282 | 0.0041 |
| During lunch | 79.66 | 0.394 | 0.0049 | 69.81 | 0.319 | 0.0046 |
| After lunch | 87.16 | 0.669 | 0.0077 | 75.02 | 0.321 | 0.0043 |
| 3:00 p.m. | 76.65 | 0.523 | 0.0068 | 65.25 | 0.422 | 0.0065 |
| 4:00 p.m. | 74.10 | 0.439 | 0.0059 | 63.67 | 0.255 | 0.0040 |
| Posture | Front | Left | Front | Right | Front |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Period in Figure 4a (s) | 2.43–6.89 | 9.49–14.15 | 16.76–21.06 | 23.57–27.98 | 30.51–34.64 |
| Respiratory rate (cycle/min) | 26.9 | 25.7 | 27.9 | 27.2 | 29.1 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Terazawa, M.; Karita, M.; Kumagai, S.; Sasaki, M. Respiratory Motion Sensor Measuring Capacitance Constructed across Skin in Daily Activities. Micromachines 2018, 9, 543. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi9110543
Terazawa M, Karita M, Kumagai S, Sasaki M. Respiratory Motion Sensor Measuring Capacitance Constructed across Skin in Daily Activities. Micromachines. 2018; 9(11):543. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi9110543
Chicago/Turabian StyleTerazawa, Makie, Momoko Karita, Shinya Kumagai, and Minoru Sasaki. 2018. "Respiratory Motion Sensor Measuring Capacitance Constructed across Skin in Daily Activities" Micromachines 9, no. 11: 543. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi9110543
APA StyleTerazawa, M., Karita, M., Kumagai, S., & Sasaki, M. (2018). Respiratory Motion Sensor Measuring Capacitance Constructed across Skin in Daily Activities. Micromachines, 9(11), 543. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi9110543




