AlN-Based Ceramic Patch Antenna-Type Wireless Passive High-Temperature Sensor
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Measurement Principle
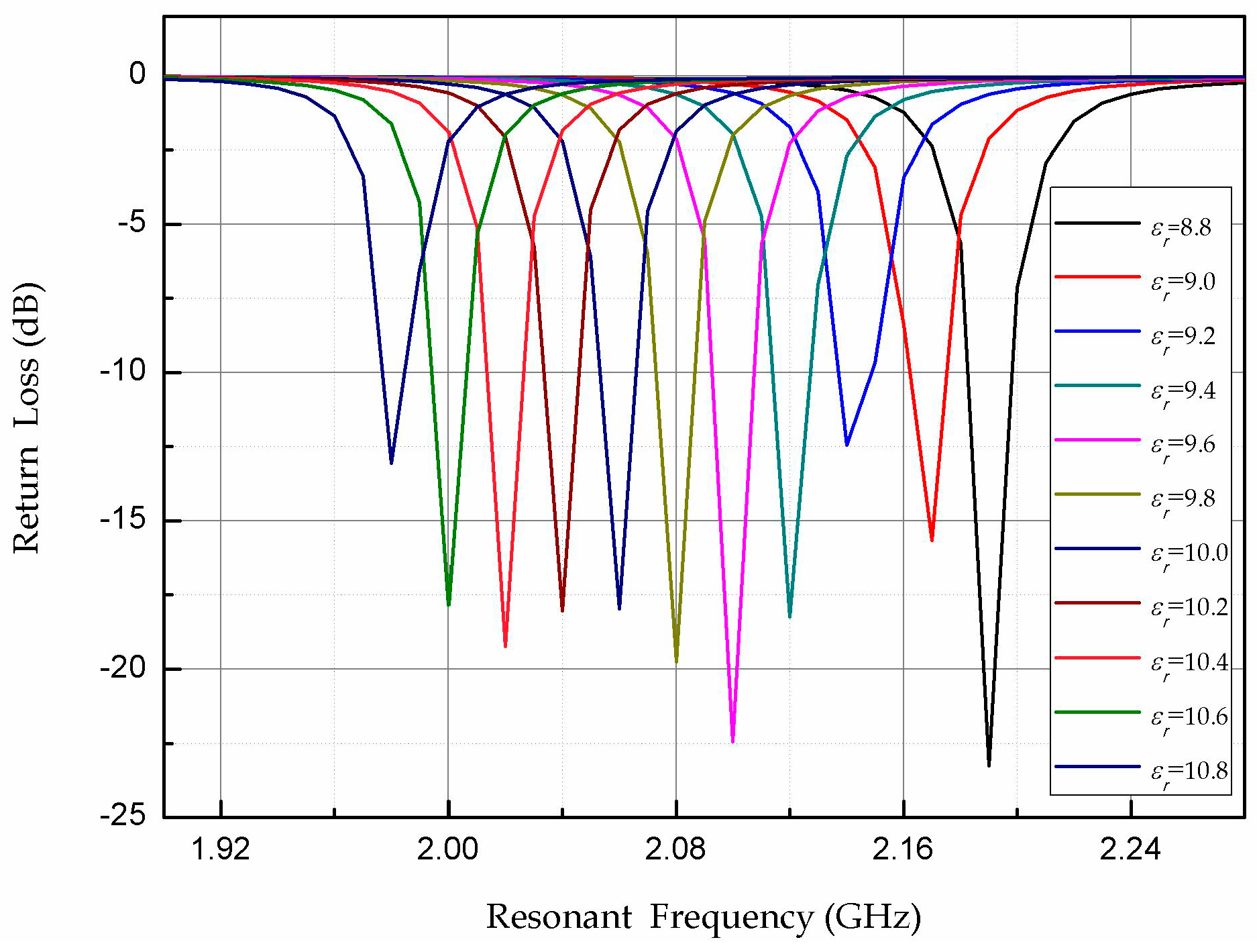
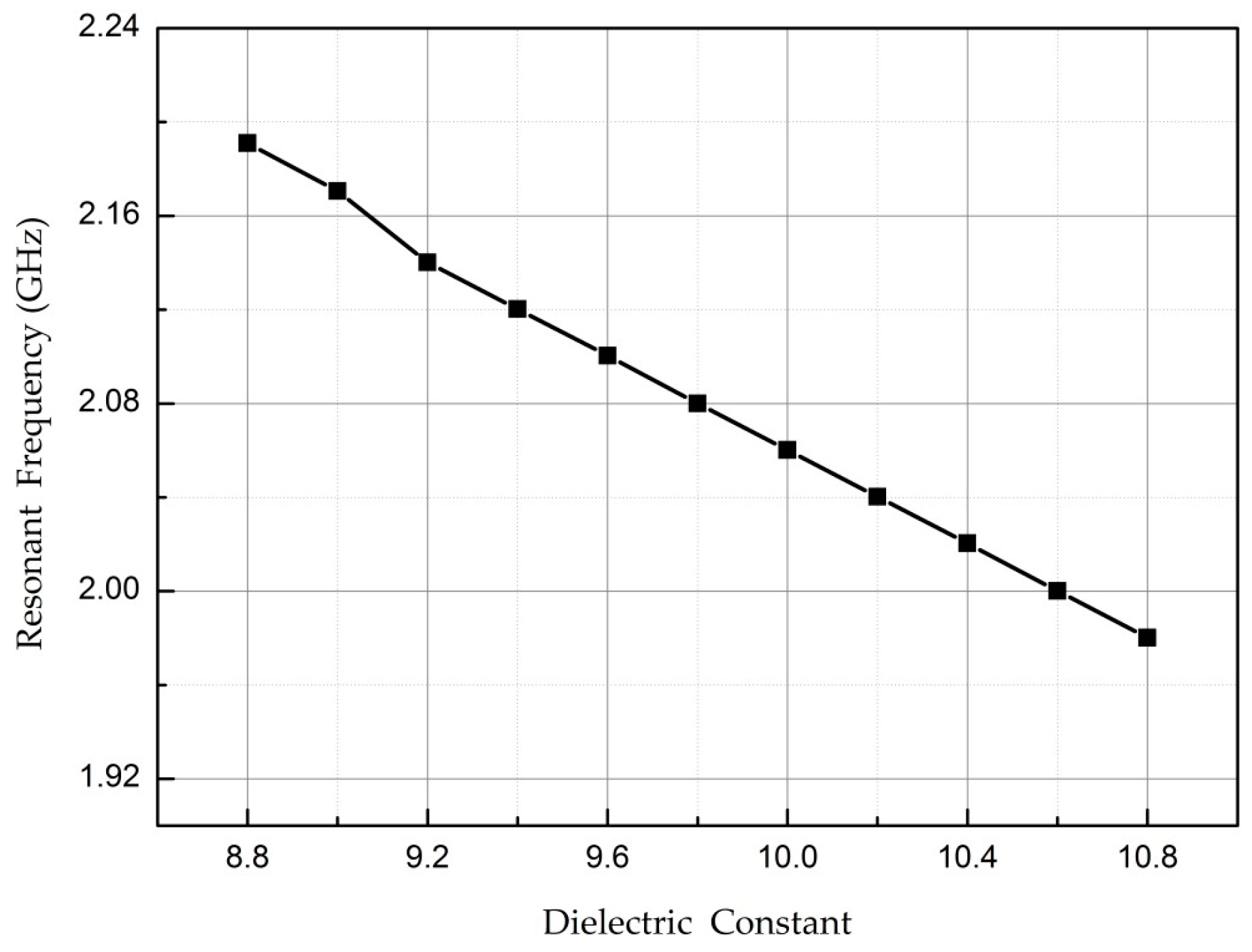
3. Temperature Sensor Design
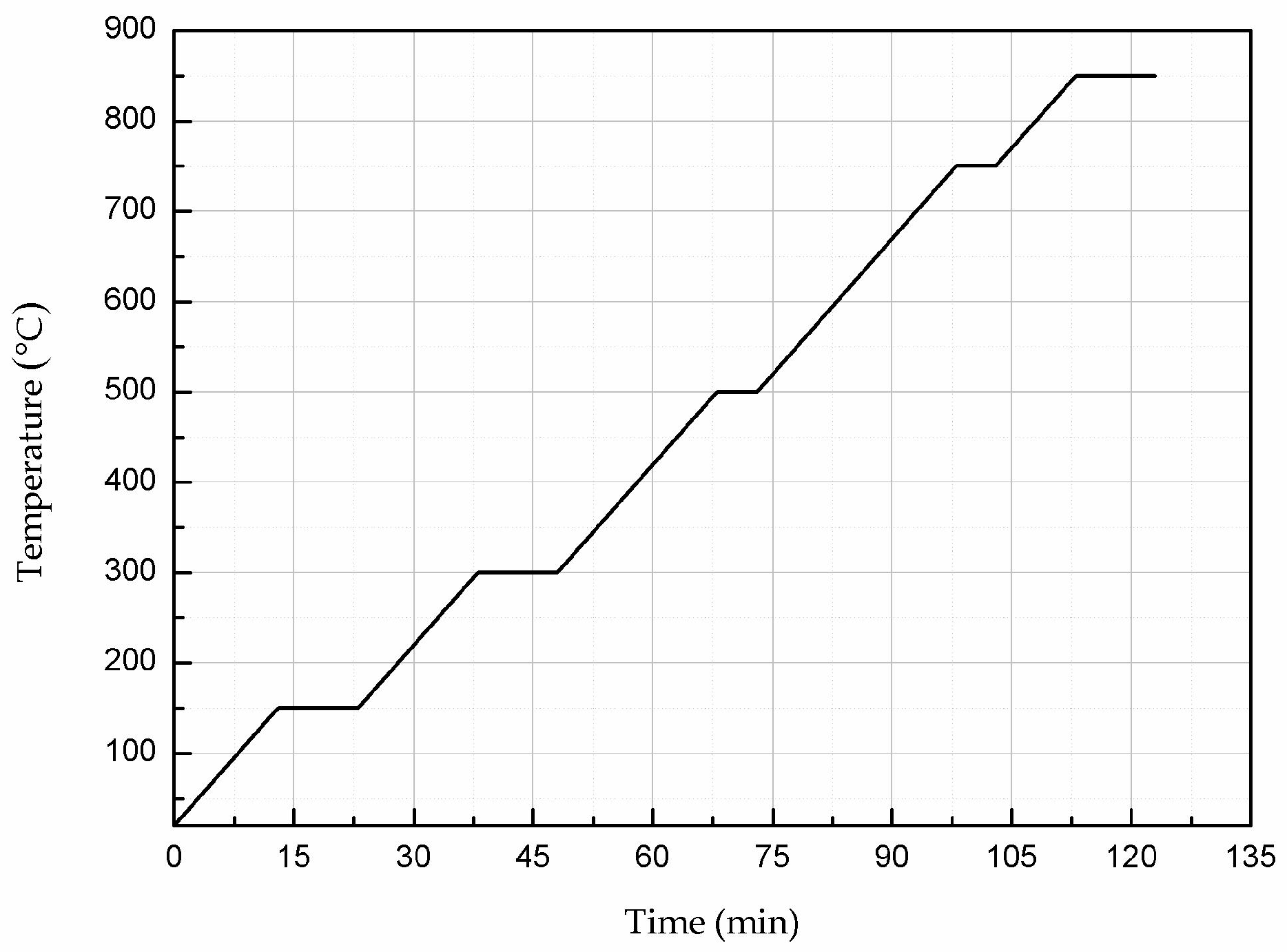
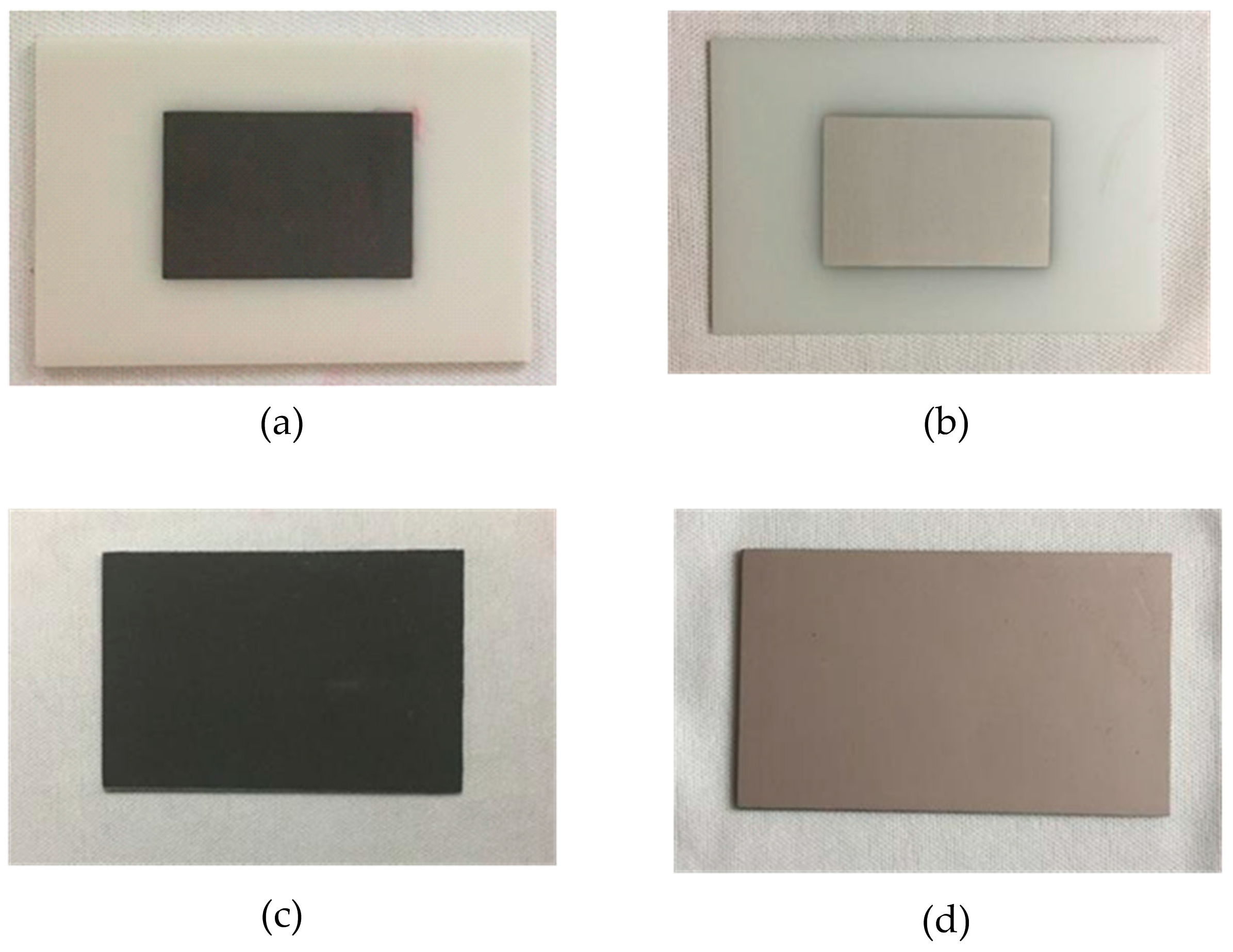
4. Temperature Sensor Fabrication
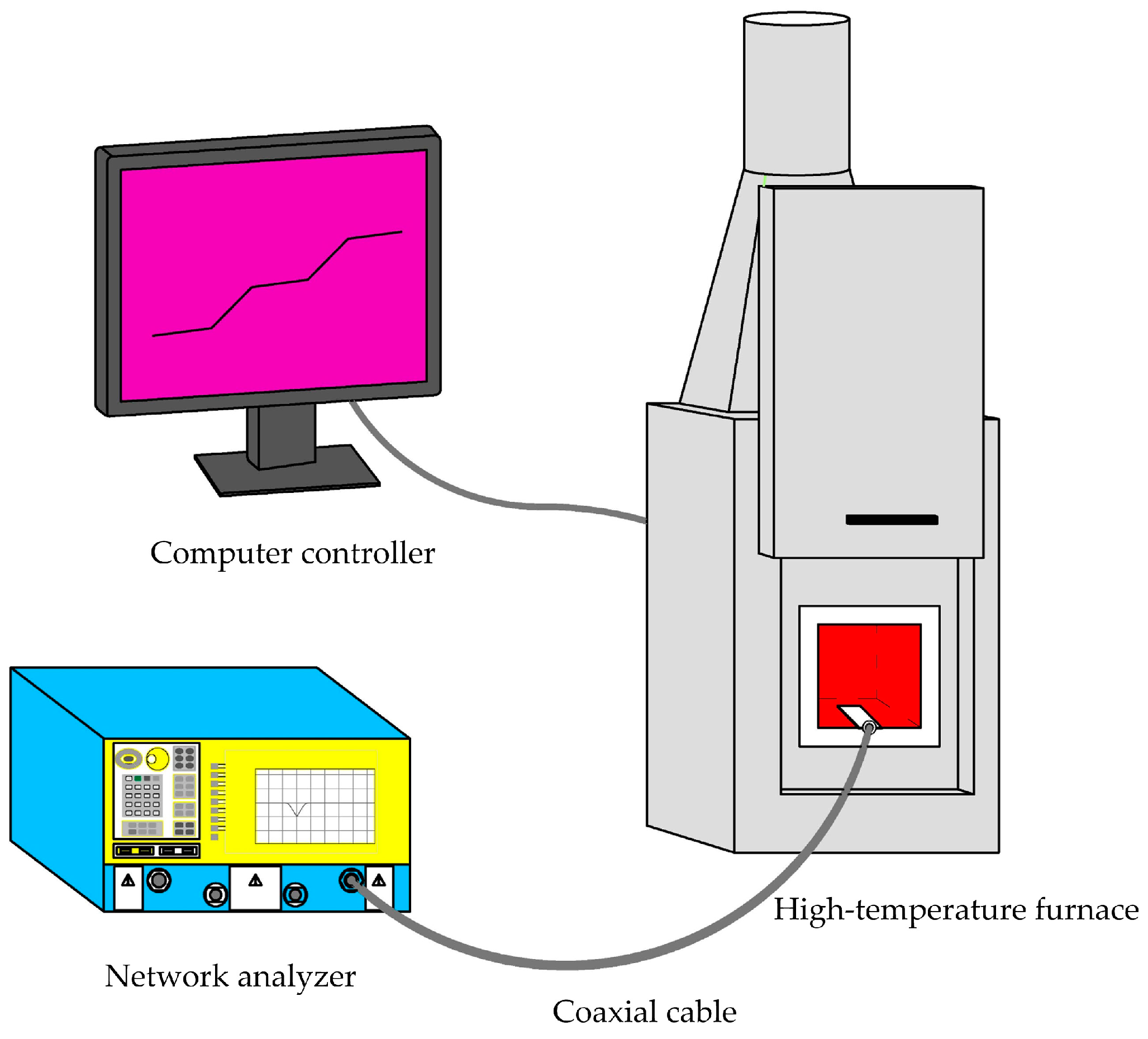
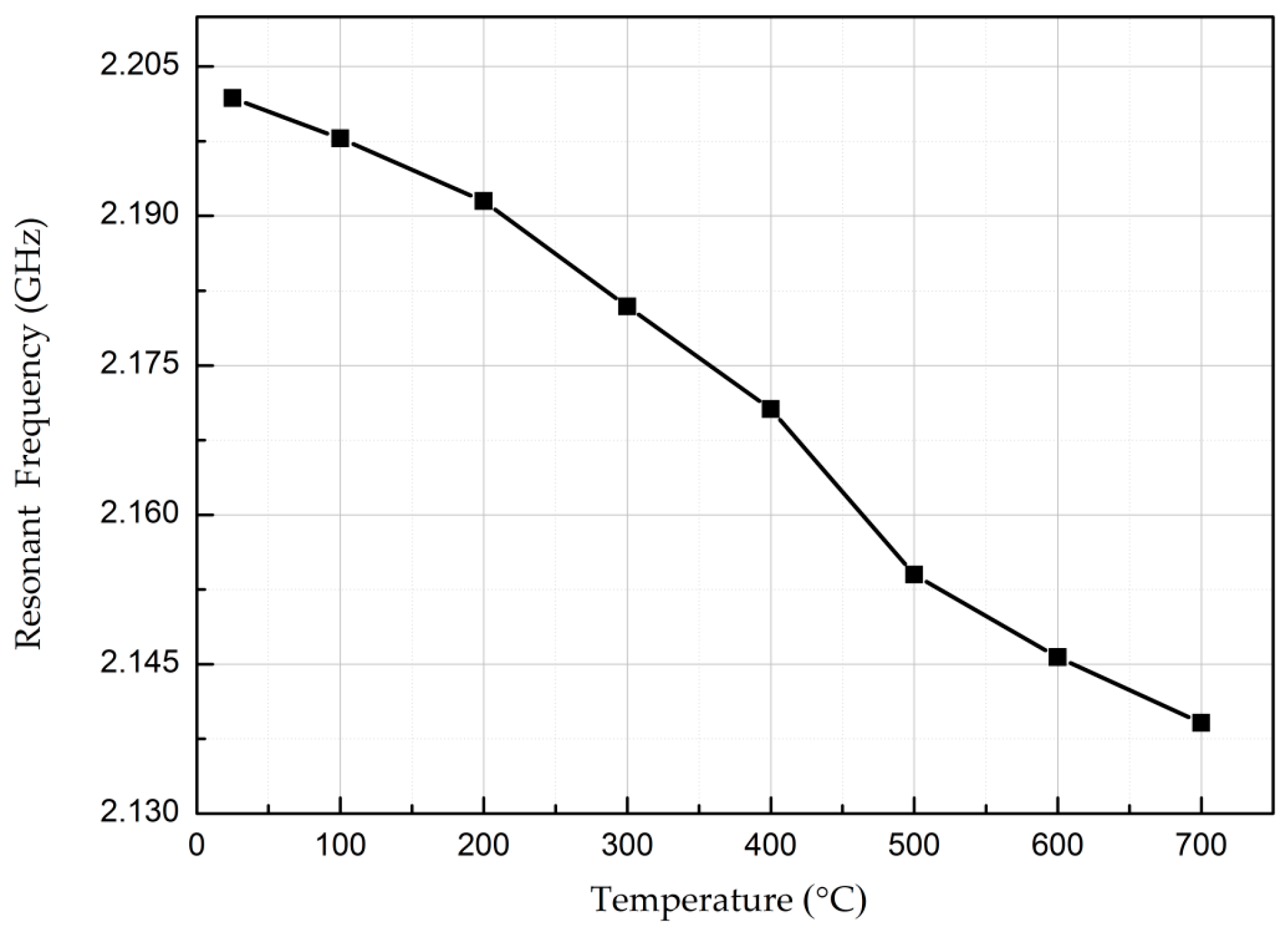
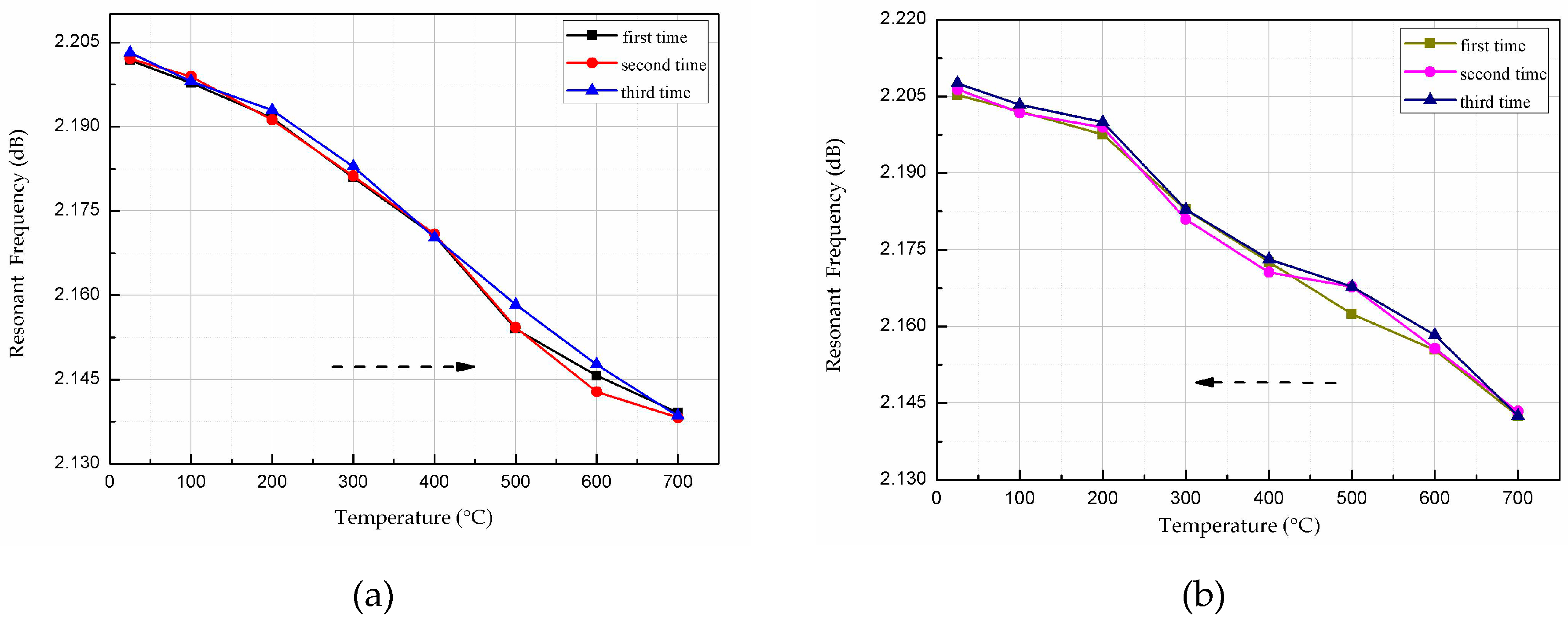
5. Measurement and Discussion
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- San, H.; Li, Y.; Song, Z.; Yu, Y.; Chen, X. Self-packaging fabrication of silicon–glass-based piezoresistive pressure sensor. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 2013, 34, 789–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Q.; Luo, T.; Wei, T.; Liu, J.; Lin, L.; Xiong, J. A wireless passive pressure and temperature sensor via a dual LC resonant circuit in harsh environments. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2017, 26, 351–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okojie, R.S.; Lukco, D.; Nguyen, V.; Savrun, E. 4H-SiC piezoresistive pressure sensors at 800 °C with observed sensitivity recovery. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 2015, 36, 17–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyce, M.P. Gas Turbine Engineering Handbook; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Saito, A.; Castanier, M.P.; Pierre, C. Effects of a cracked blade on mistunedturbine engine rotor vibration. J. Vib. Acoust. 2009, 131, 061006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib, Z.; Parthasarathy, R.; Gollahalli, S. Performance and emission characteristics of biofuel in a small-scale gas turbine engine. Appl. Energy. 2010, 87, 1701–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Childs, P.R.N.; Greenwood, J.R.; Long, C.A. Review of temperature measurement. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2000, 71, 2959–2978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machin, G.; Anhalt, K.; Edler, F.; Pearce, J.V.; Sadli, M.; Strnad, R.; Vuelban, E.M. HiTeMS: A project to solve high temperature measurement problems in industry. AIP Conference Proc. 2013, 1552, 958–963. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, H. Flexible wireless antenna sensor: A review. IEEE Sens. J. 2013, 13, 3865–3872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshmukh, S.; Huang, H. Wireless interrogation of passive antenna sensors. Measurement Sci. Tech. 2010, 21, 035201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Bednorz, T. Introducing S-parameters for ultrasound-based structural health monitoring. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Frequency Control 2014, 61, 1856–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Cunha, M.P.; Lad, R.J.; Davulis, P.; Canabal, A.; Moonlight, T.; Moulzolf, S.; Frankel, D.J.; Pollard, T.; McCann, D.; Dudzik, E.; et al. Wireless acoustic wave sensors and systems for harsh environment applications. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE Topical Conference on Wireless Sensors and Sensor Networks, Phoenix, AZ, USA, 16–19 January 2011; pp. 41–44. [Google Scholar]
- Luan, C.C.; Yao, X.H.; Chen, Q.Y.; Fu, J.Z. Research on transmission performance of a surface acoustic wave sensing system used in manufacturing environment monitoring. J. Zhejiang University-Science A 2017, 18, 443–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Guo, Y.; Tang, Y.; Zu, X.; Ma, J.; Wang, L.; Fu, Y.Q. Room-temperature ammonia sensor based on ZnO nanorods deposited on ST-cut quartz surface acoustic wave devices. Sensors 2017, 17, 1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binder, A.; Bruckner, G.; Schobernig, N.; Schmitt, D. Wireless surface acoustic wave pressure and temperature sensor with unique identification based on LiNbO3. IEEE Sens. J. 2013, 13, 1801–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reindl, L.M.; Shrena, I.M. Wireless measurement of temperature using surface acoustic waves sensors. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Frequency Control 2004, 51, 1457–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardong, J.; Aubert, T.; Naumenko, N.; Salzmann, S.; Reindl, L.M. Experimental and theoretical investigations of some useful langasite cuts for high-temperature SAW applications. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Frequency Control 2013, 60, 814–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knapp, M.; Lomonosov, A.M.; Warkentin, P.; Jager, P.M.; Ruile, W.; Kirschner, H.P.; Honal, M.; Bleyl, I.; Mayer, A.P.; Reindl, L.M. Accurate characterization of SiO2 thin films using surface acoustic waves. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Frequency Control 2015, 62, 736–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shu, L.; Peng, B.; Cui, Y.; Gong, D.; Yang, Z.; Liu, X.; Zhang, W. Effects of AlN coating layer on high temperature characteristics of langasite SAW sensors. Sensors 2016, 16, 1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Q.A.; Dong, L.; Wang, L.F. LC passive wireless sensors toward a wireless sensing platform: status, prospects, and challenges. J. Microelectromec. Syst. 2016, 25, 822–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sturesson, P.; Khaji, Z.; Klintberg, L.; Thornell, G. Ceramic pressure sensor for high temperatures–investigation of the effect of metallization on read range. IEEE Sens. J. 2016, 17, 2411–2421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Khan, H.; Shan, W.; Wang, Y.; Ou, J.Z.; Liu, Z.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; Li, Y. A novel wireless gas sensor based on LTCC technology. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 239, 711–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Q.Y.; Wang, L.F.; Huang, J.Q.; Zhang, C.; Huang, Q.A. Simultaneous remote sensing of temperature and humidity by LC-type passive wireless sensors. J. Microelectromech.l Syst. 2015, 24, 1117–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, D.; Dziedzic, A. LTCC package for high temperature applications. Microelectron. Reliability 2011, 51, 1241–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, P.; Lai, R.; Huff, D.; Wang, F.; Ngo, K.D.; Immanuel, V.D.; Karimi, K.J. SiC wirebond multichip phase-leg module packaging design and testing for harsh environment. IEEE Trans. Pow. Electron. 2010, 25, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoppe, J.; Boccard, J.M.; Aftab, T.; Yousaf, A.; Ojha, A.; Ostertag, T.; Reindl, L.M. Open parallel-plate dielectric resonator for passive torque sensing. In Proceedings of the 2014 11th International Multi-Conference on Systems, Signals & Devices (SSD), Castelldefels-Barcelona, Spain, 11–14 February 2014; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Aftab, T.; Yousaf, A.; Hoppe, J.; Stoecklin, S.; Ostertag, T.; Reindl, L. A parallel plate dielectric resonator as a wireless passive strain sensor. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Sensors Applications Symposium (SAS), Zadar, Croatia, 13–15 April 2015; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Boccard, J.M.; Aftab, T.; Hoppe, J.; Yousaf, A.; Hütter, R.; Reindl, L.M. High-resolution, far-field, and passive temperature sensing up to 700 °C using an isolated ZST microwave dielectric resonator. IEEE Sens. J. 2016, 16, 715–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Sanders, J.; Yao, J.; Huang, H. Patch antenna based temperature sensor. In Proceedings of the SPIE 9063, San Diego, CA, USA, 9–13 March 2014; p. 90631P-1. [Google Scholar]
- Sanders, J.W.; Yao, J.; Huang, H. Microstrip patch antenna temperature sensor. IEEE Sens. J. 2015, 15, 5312–5319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Tchafa, F.M.; Jain, A.; Tjuatja, S.; Huang, H. Far-field interrogation of microstrip patch antenna for temperature sensing without electronics. IEEE Sens. J. 2016, 16, 7053–7060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kairm, H.; Delfin, D.; Shuvo, M.A.; Chavez, L.A.; Garcia, C.R.; Barton, J.H.; Gaytan, S.M.; Cadena, M.A.; Rumpf, R.C.; Wicker, R.B.; et al. Concept and model of a metamaterial-based passive wireless temperature sensor for harsh environment applications. IEEE Sens. J. 2015, 15, 1445–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, S.; Peroulis, D. A capacitively-loaded MEMS slot element for wireless temperature sensing of up to 300. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE/MTT-S International Microwave Symposium, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2009; pp. 1161–1164. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, J.; Wu, G.; Tan, Q.; Wei, T.; Wu, D.; Shen, S.; Dong, H.; Zhang, W. Dielectrically-loaded cylindrical resonator-based wireless passive high-temperature sensor. Sensors 2016, 16, 2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, H.; Ebadi, S.; Gong, X. A Low-profile wireless passive temperature sensor using resonator/antenna integration up to 1000 °C. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2012, 11, 369–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Ebadi, S.; Ren, X.; Gong, X. Wireless passive high-temperature sensor based on multifunctional reflective patch antenna up to 1050 degrees centigrade. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2015, 222, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Wang, D.; Chen, H.; Guo, L. Normalized evaluation of thermal shock resistance for ceramic materials. J. Adv. Ceram. 2014, 3, 250–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, K.M.; Lenie, C. Some properties of aluminum nitride. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1960, 107, 308–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyashiro, F.; Iwase, N.; Tsuge, A.; Ueno, F.; Nakahashi, M.; Takahashi, T. High thermal conductivity aluminum nitride ceramic substrates and packages. IEEE Trans. Compon. Hybrids Manuf. Tech. 1990, 13, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurokawa, Y.; Utsumi, K.; Takamizawa, H.; Kamata, T.O.; Noguchi, S.H. AlN substrates with high thermal conductivity. IEEE Trans. Compon. Hybrids Manuf. Tech. 1985, 8, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, D.D. Materials for thermal conduction. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2001, 21, 1593–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.M.; Bharathi, K.; Kim, D.K. Processing and characterization of aluminum nitride ceramics for high thermal conductivity. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2014, 16, 655–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Q.; Wei, T.; Chen, X.; Luo, T.; Wu, G.; Li, C.; Xiong, J. Antenna-resonator integrated wireless passive temperature sensor based on low-temperature co-fired ceramic for harsh environment. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2015, 236, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Yuan, Y.; Ren, Z.; Tan, Q.; Xiong, J. High-Temperature Dielectric Properties of Aluminum Nitride Ceramic for Wireless Passive Sensing Applications. Sensors 2015, 15, 22660–22671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Constantine, A.B. Antenna Theory: Analysis and Design, 3rd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2005; pp. 819–820. [Google Scholar]







| Symbol | Parameter | Value (mm) |
|---|---|---|
| L | Patch length | 22.4 |
| W | Patch width | 34 |
| H | Substrate thickness | 1.0 |
| 2L | Substrate length | 44.8 |
| 2W | Substrate width | 68 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yan, D.; Yang, Y.; Hong, Y.; Liang, T.; Yao, Z.; Chen, X.; Xiong, J. AlN-Based Ceramic Patch Antenna-Type Wireless Passive High-Temperature Sensor. Micromachines 2017, 8, 301. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi8100301
Yan D, Yang Y, Hong Y, Liang T, Yao Z, Chen X, Xiong J. AlN-Based Ceramic Patch Antenna-Type Wireless Passive High-Temperature Sensor. Micromachines. 2017; 8(10):301. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi8100301
Chicago/Turabian StyleYan, Dan, Yong Yang, Yingping Hong, Ting Liang, Zong Yao, Xiaoyong Chen, and Jijun Xiong. 2017. "AlN-Based Ceramic Patch Antenna-Type Wireless Passive High-Temperature Sensor" Micromachines 8, no. 10: 301. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi8100301
APA StyleYan, D., Yang, Y., Hong, Y., Liang, T., Yao, Z., Chen, X., & Xiong, J. (2017). AlN-Based Ceramic Patch Antenna-Type Wireless Passive High-Temperature Sensor. Micromachines, 8(10), 301. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi8100301




