Research on Robust and Efficient Optimization Design Methods for Analog Integrated Circuits
Abstract
1. Introduction
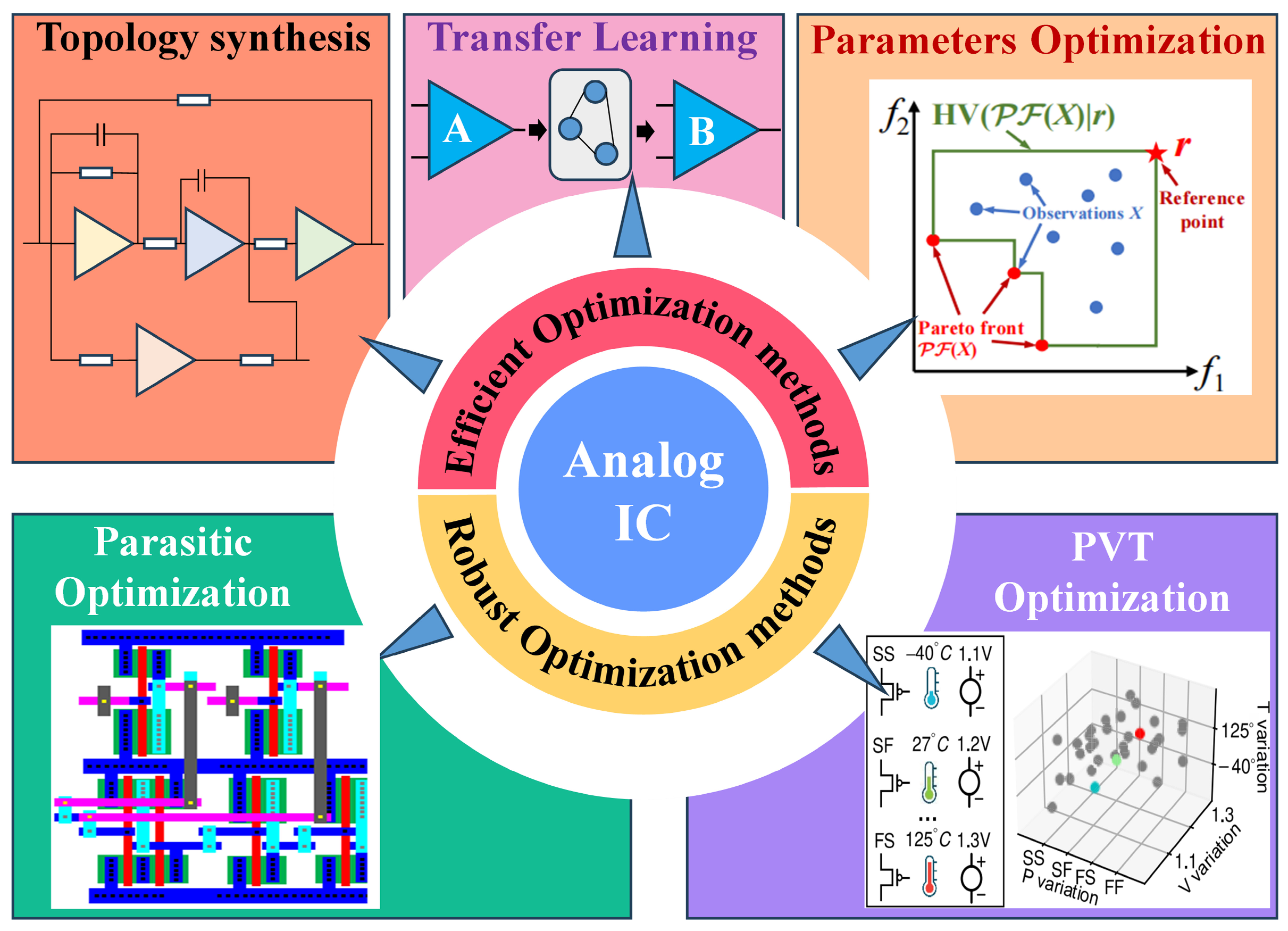
2. Efficient Optimization Design Methods for Analog ICs
2.1. Efficient Topology Synthesis Methods
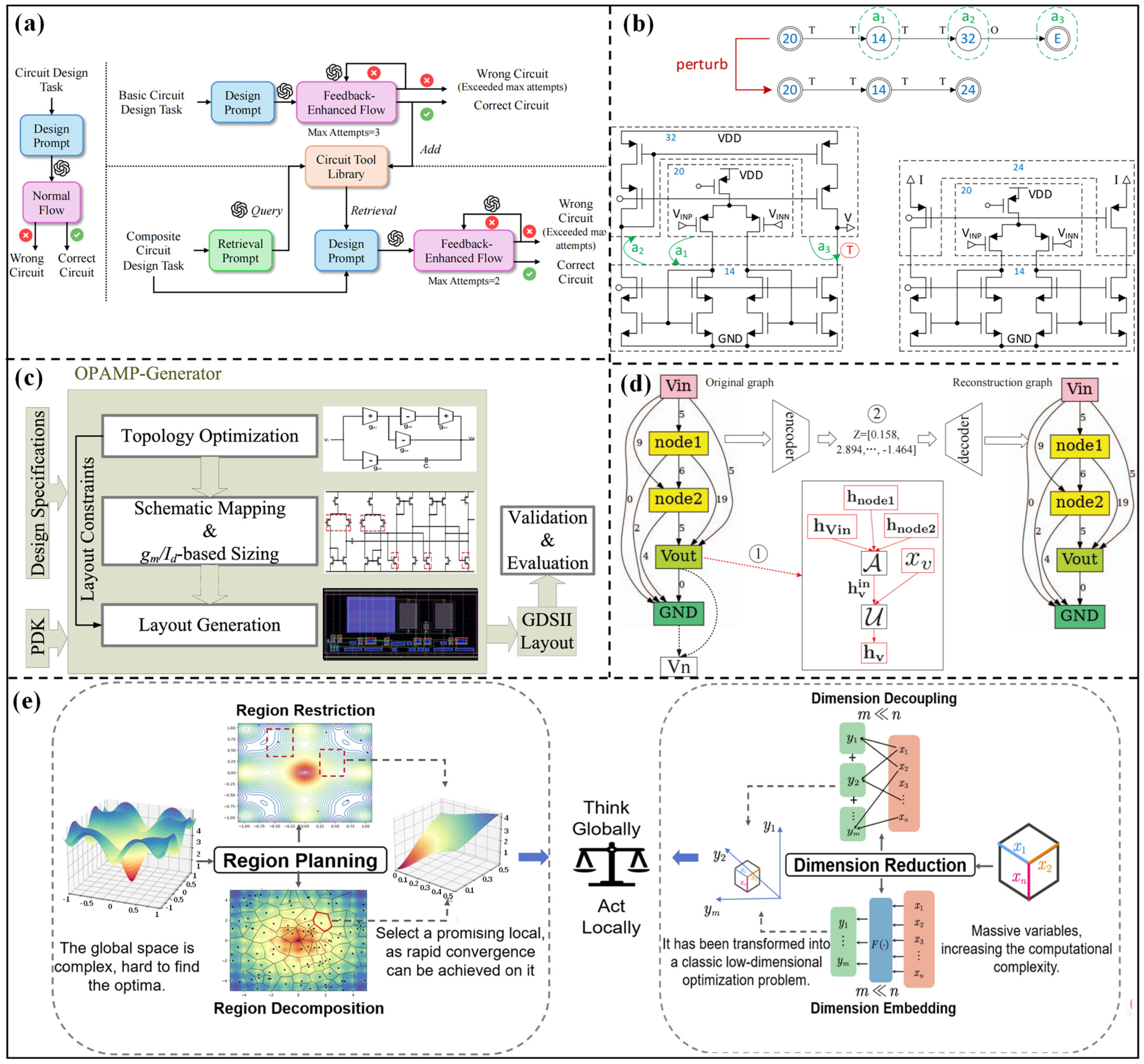
2.1.1. Topology Synthesis Method Based on Preset Modules
2.1.2. Topology Fine-Tuning Method Based on Known Structures
2.1.3. Topology Optimization Method Generated from Scratch
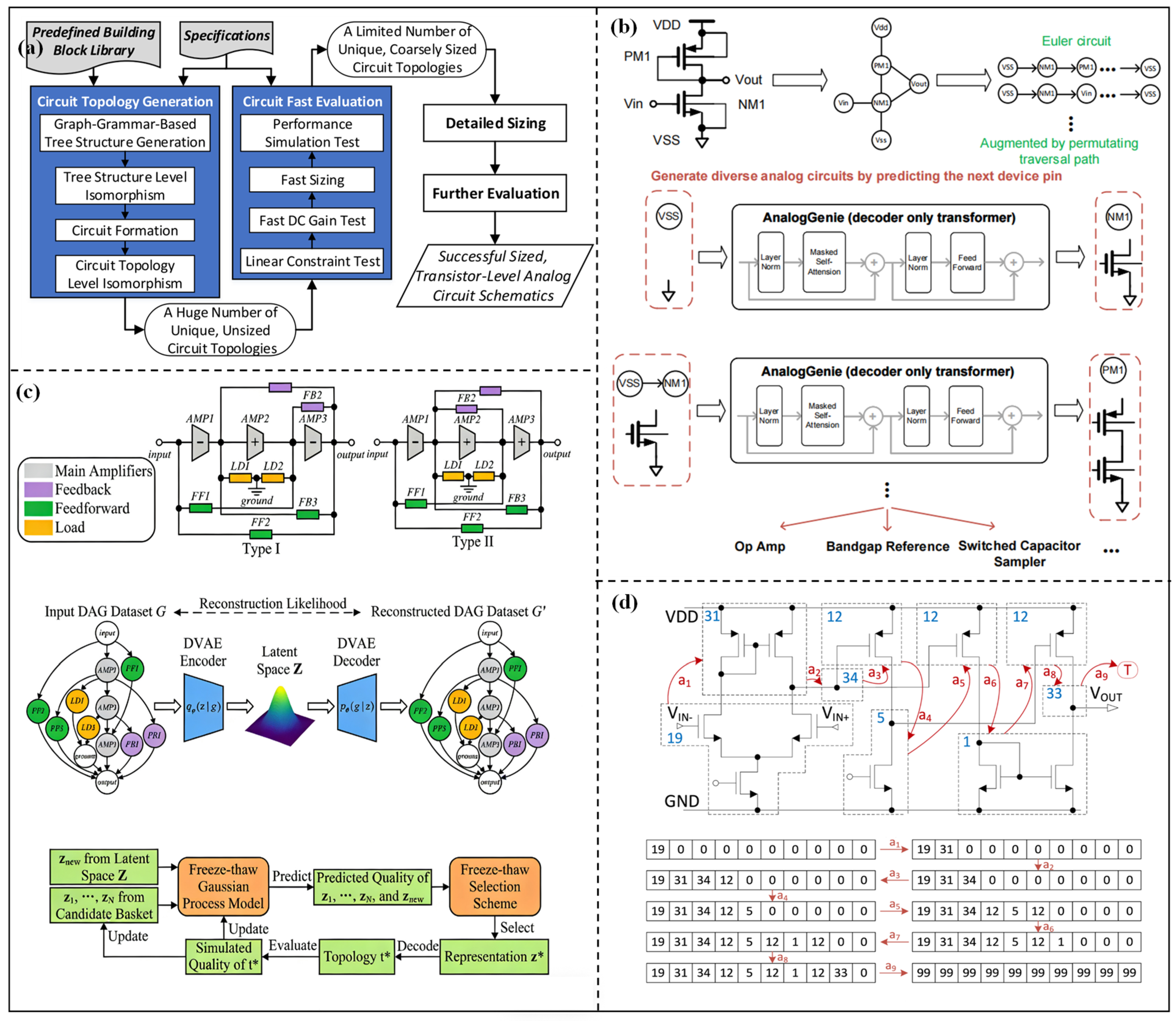
2.2. Efficient Parameter Optimization Methods
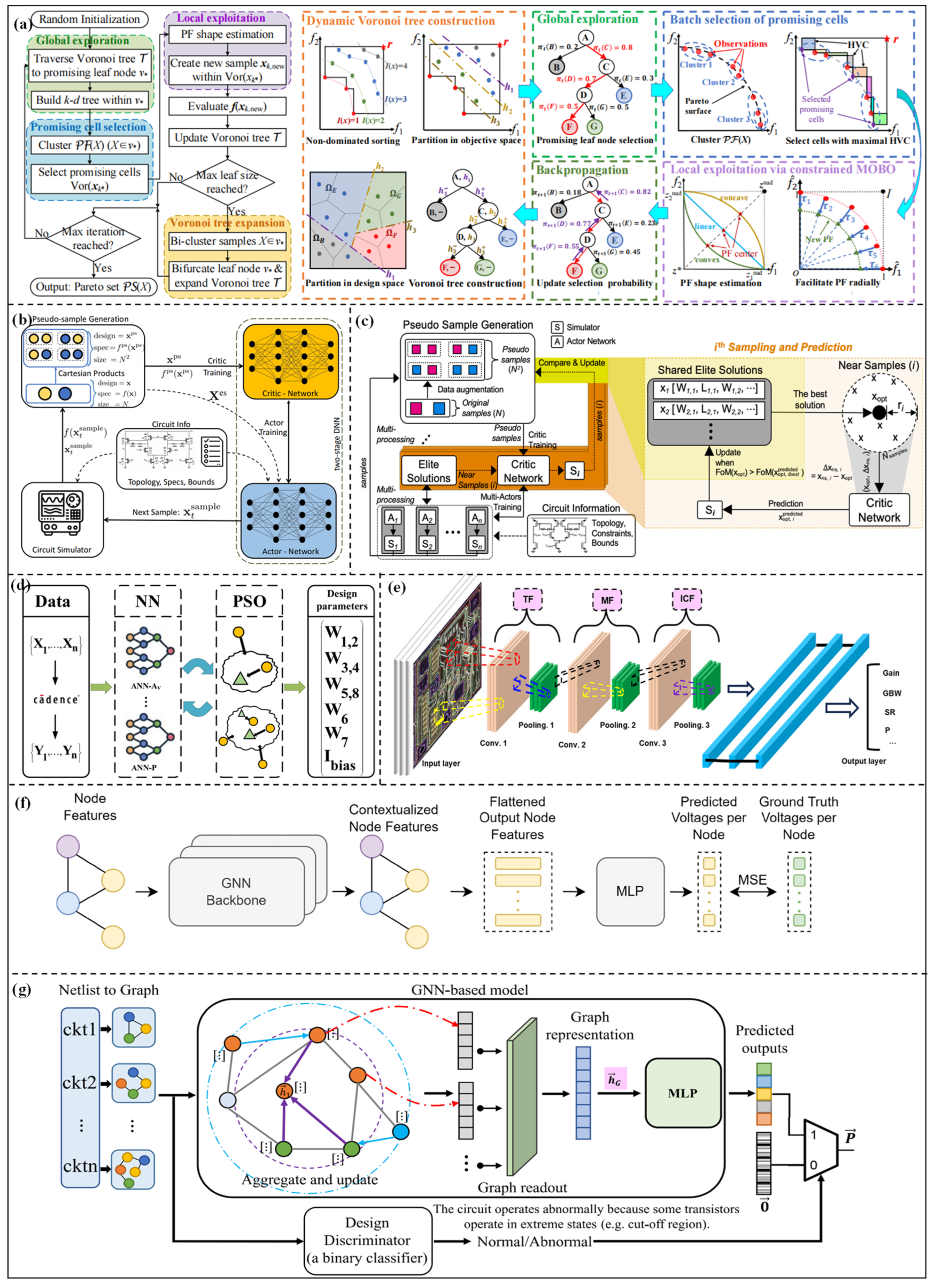
2.2.1. Parameter Optimization Methods Based on Intelligent Optimization Algorithms
2.2.2. Parameter Optimization Methods Based on Deep Learning Algorithms
2.3. General Transfer Learning Methods
2.3.1. Transfer Between Different Technology Nodes
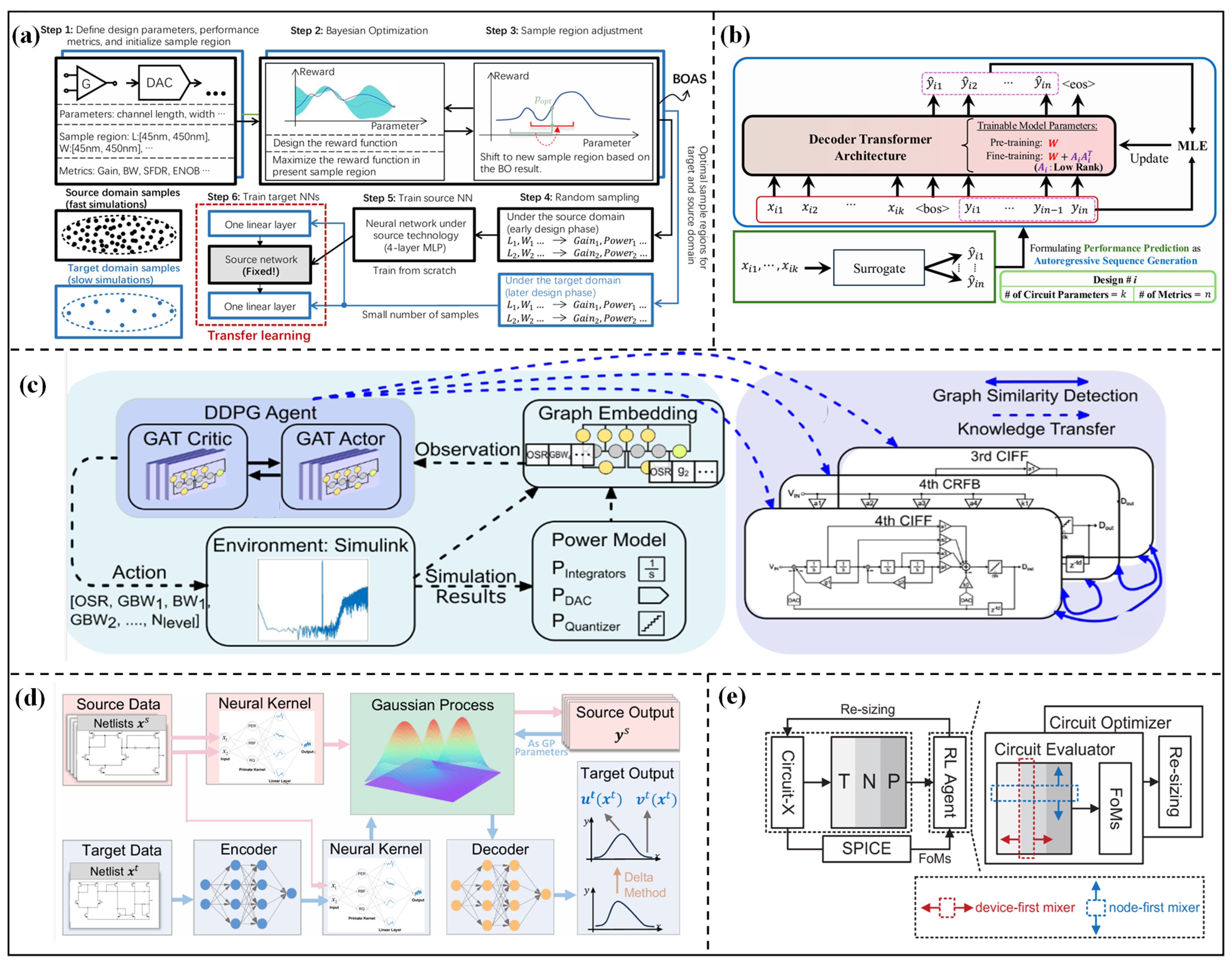
2.3.2. Transfer Between Different Topology Structures
2.4. Summary
3. Robust Optimization Design Methodology for High-Performance Analog ICs
3.1. Optimization Design Methods Considering PVT Corners
3.1.1. Robust Optimization Based on Reinforcement Learning
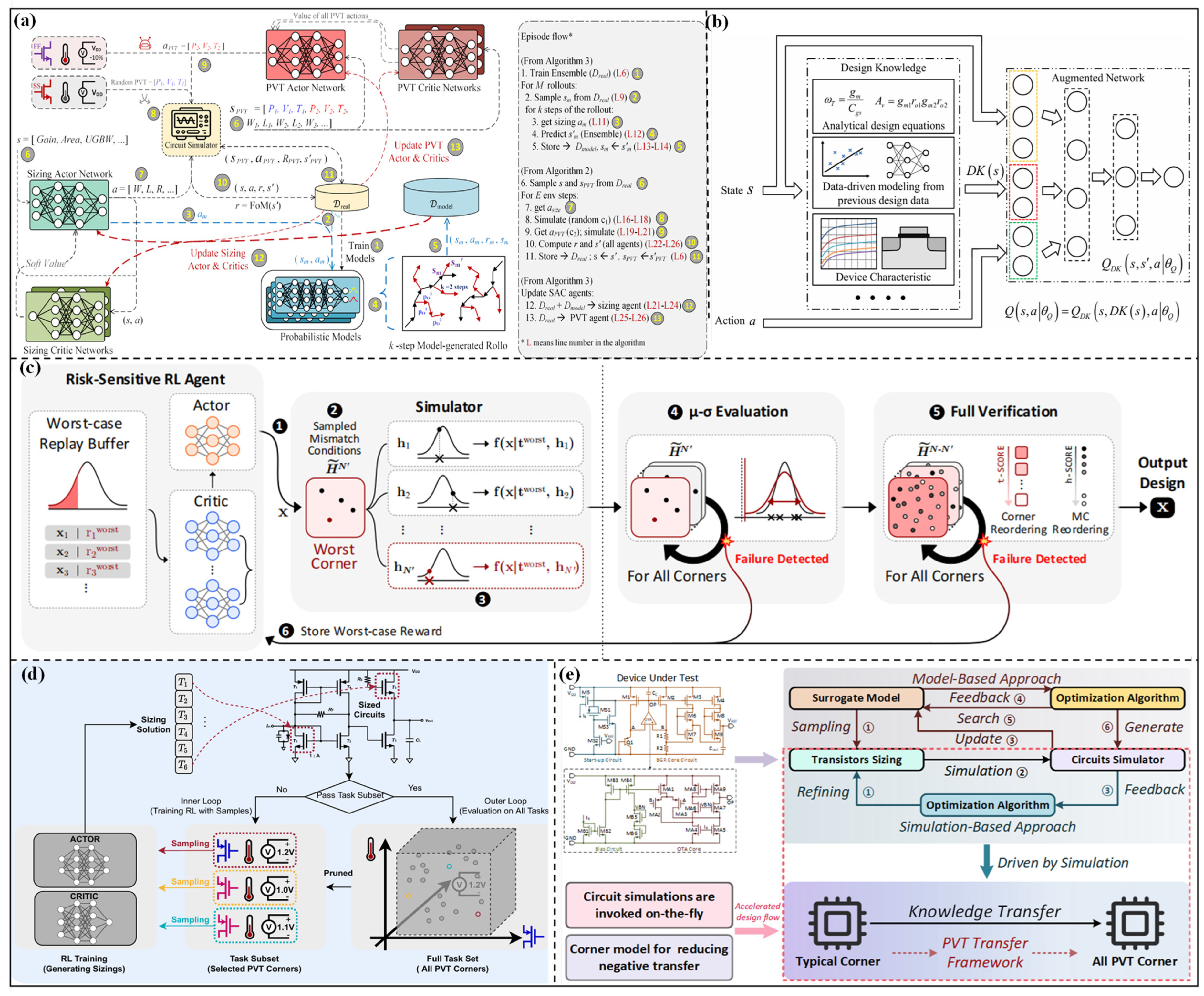
3.1.2. Robust Optimization Based on Multi-Task Learning
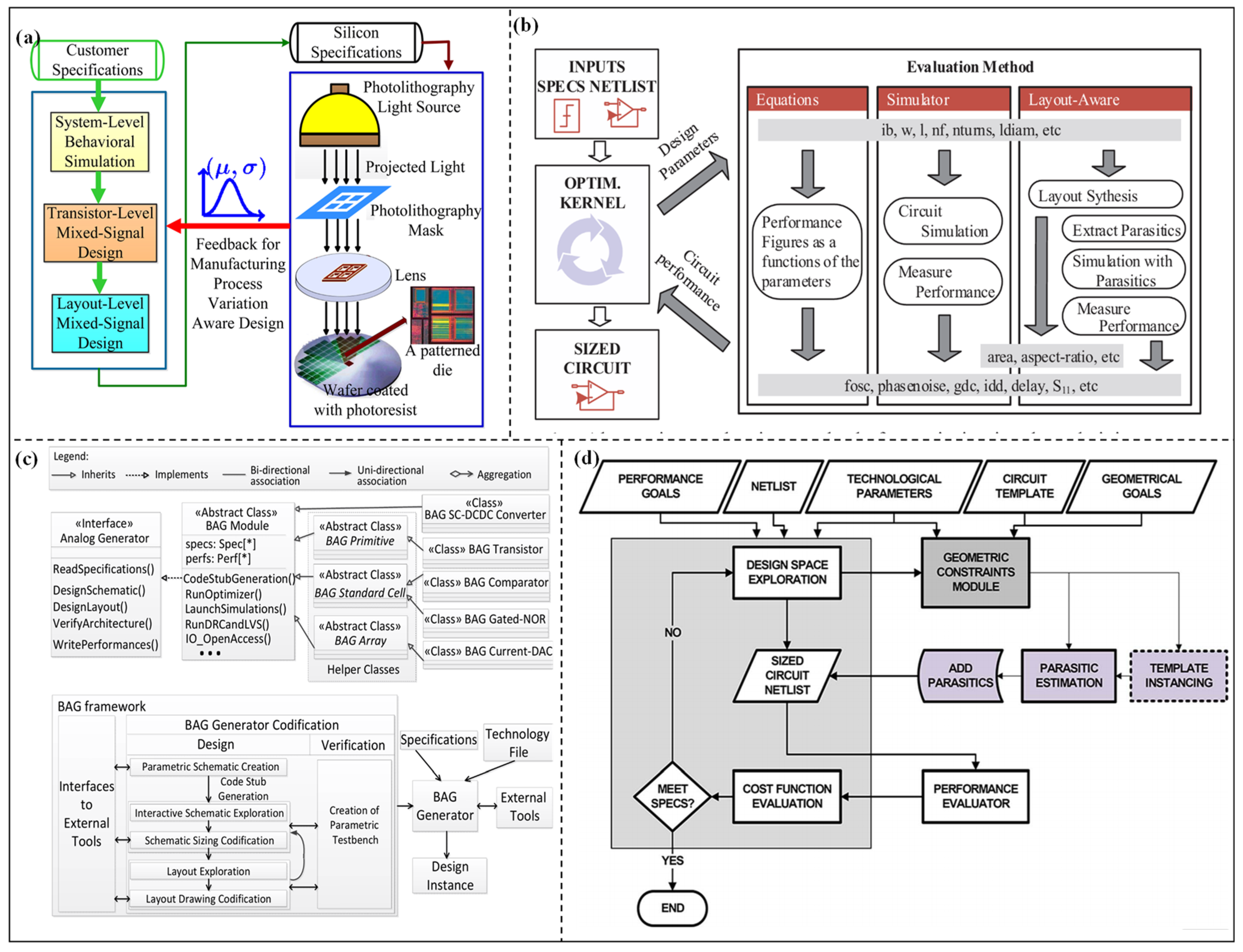
3.2. Optimization Design Methods Considering Post-Layout Parasitic Effect
3.2.1. Parasitic-Aware Optimization Methods Based on Approximate Parasitic Modeling
3.2.2. Parasitic-Aware Optimization Methods Based on Automatic Layout
3.3. Summary
4. Conclusions and Perspectives
4.1. Optimization Design Methods from Black Box Optimization to Physical Perception
4.2. Improvement of Model Generalization Ability for Different Applications
4.3. Full Process Optimization Design from Front-End to Post Simulation
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Av | Gain |
| BAG | Berkeley analog generator |
| BW | Bandwidth |
| CTSF | Circuit topology synthesis framework |
| CIFF | Cascade of integrators feed forward |
| CRFB | Cascade resonator feedback |
| CNN | Convolutional neural networks |
| DAC | Digital to analog converter |
| DAG | Directed acyclic graph |
| DDPG | Deep deterministic policy gradient |
| DL | Deep learning |
| DLL | Delay locked loop |
| DNN | Deep neural network |
| DVAE | Deep variational autoencoder |
| ES | Evolution strategy |
| FIA | Floating inverter amplifier |
| FoM | Figure of merit |
| GA | Genetic algorithm |
| GBW | Gain bandwidth |
| GCN | Graph convolutional network |
| GNN | Graph neuron network |
| GP | Gaussian process |
| IC | Integrated circuit |
| LDO | Low dropout |
| LLM | Large language model |
| MTL | Multi-task learning |
| MVAR | Multivariate value-at-risk |
| NSGA II | Non-dominated sorting genetic algorithm II |
| OCSA | Offset-compensation sense amplifier |
| PC | Power consumption |
| PM | Phase margin |
| PPO | Proximal policy optimization |
| PSRR | Power supply rejection ratio |
| PVT | Process, voltage, and temperature |
| RL | Reinforcement learning |
| SAR ADC | Successive approximation register analog to digital converter |
| ΔΣ ADC | Sigma-delta analog to digital converter |
| SR | Slew rate |
| TC | Temperature coefficient |
| TD3 | twin delayed deep deterministic policy gradient |
| TIA | Transimpedance amplifier |
| TL | Transfer learning |
| UGB | Unity gain bandwidth |
| VCO | Voltage controlled oscillator |
| VGAE | Variational graph autoencoder |
References
- Chen, K.; Li, D.; Chen, D.; Chai, C. An Improved MOS Self-Biased Ring Amplifier and Modified Auto-Zeroing Scheme. IEEE Trans. Very Large Scale Integr. (VLSI) Syst. 2023, 31, 606–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Wang, C.; Cui, X.; Chen, D.; Fei, C.; Yang, Y. Recent progress and development of interface integrated circuits for piezoelectric energy harvesting. Nano Energy 2022, 94, 106938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Cheng, W.; Cui, X.; Chen, D.; Fei, C.; Yang, Y. Echo Signal Receiving and Data Conversion Integrated Circuits for Portable High-Frequency Ultrasonic Imaging System. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 2022, 69, 1980–1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.; Li, R.; Xu, J.; Li, D.; Fei, C.; Yang, Y. Recent progress and development of radio frequency energy harvesting devices and circuits. Nano Energy 2023, 117, 108845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Yoo, H. Recent Progress in Thin-Film Transistors toward Digital, Analog, and Functional Circuits. Micromachines 2022, 13, 2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barraj, I.; Mestiri, H.; Masmoudi, M. Overview of Memristor-Based Design for Analog Applications. Micromachines 2024, 15, 505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Su, J.; Lai, X.; Chen, D.; Li, D.; Yang, Y. Recent Developments and Perspectives on Optimization Design Methods for Analog Integrated Circuits. Symmetry 2025, 17, 529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yin, Y.; Xu, N.; Jia, B. MCE-HGCN: Heterogeneous Graph Convolution Network for Analog IC Matching Constraints Extraction. Micromachines 2025, 16, 677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, J.; Yang, X.; Martins, R.P.; Zhu, Y.; Chan, C.-H. A 0.016 mm2 Active Area 4 GHz Fully Ring-Oscillator-Based Cascaded Fractional-N PLL With Burst-Mode Sampling. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2023, 70, 3792–3796. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Chen, D.; Wang, X.; Li, D.; Yang, Y. A High-Efficiency Codesign Method for Bandgap Circuit by Submodule Optimization. Int. J. Circuit Theory Appl. 2025, 53, 5141–5154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, L.; Chen, D.; Li, D.; Yng, Y. The High-Efficiency Lightweight Optimization Method for Analog-to-Digital Conversion System in IoT. IEEE Internet Things J. 2025, 12, 50928–50937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tegazzini, L.; Di Meo, G.; Strollo, A.G.M. High-Precision MUX-Based Digital Delay Interpolators Based on a Novel Transistor Sizing Algorithm. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2025, 72, 938–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poddar, S.; Budak, A.; Zhao, L.; Hsu, C.-H.; Maji, S.; Zhu, K. A Data-Driven Analog Circuit Synthesizer with Automatic Topology Selection and Sizing. In Proceedings of the 2024 Design, Automation & Test in Europe Conference & Exhibition (DATE), Düsseldorf, Germany, 18–22 March 2024. [Google Scholar]
- McConaghy, T.; Gielen, G.G.E. Template-Free Symbolic Performance Modeling of Analog Circuits via Canonical-Form Functions and Genetic Programming. IEEE Trans. Comput.-Aided Des. Integr. Circuits Syst. 2009, 28, 1162–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maji, S.; Budak, A.F.; Poddar, S.; Pan, D.Z. Toward End-to-End Analog Design Automation with ML and Data-Driven Approaches (Invited Paper). In Proceedings of the 2024 29th Asia and South Pacific Design Automation Conference (ASP-DAC), Incheon, Republic of Korea, 22–25 January 2024. [Google Scholar]
- McConaghy, T.; Palmers, P.; Steyaert, M.; Gielen, G.G.E. Variation-aware structural synthesis of analog circuits via hierarchical building blocks and structural homotopy. IEEE Trans. Comput.-Aided Des. Integr. Circuits Syst. 2009, 28, 1281–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Wang, H.; Liang, F.; Bäck, T.; Wang, H. A Multi-Form Optimization Framework for Analog Integrated Circuit Sizing. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2025, 72, 7095–7108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linán-Cembrano, G.; Lourenço, N.; Horta, N.; de la Rosa, J.M. Design Automation of Analog and Mixed-Signal Circuits Using Neural Networks—A Tutorial Brief. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2024, 71, 1677–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, S.; Tilwankar, G.; Zele, R. Automated Design of Analog Circuits using Machine Learning Techniques. In Proceedings of the 2021 25th International Symposium on VLSI Design and Test (VDAT), Surat, India, 16–18 September 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhou, R.; Lin, Z. An Artificial Neural Network Assisted Optimization System for Analog Design Space Exploration. IEEE Trans. Comput.-Aided Des. Integr. Circuits Syst. 2020, 39, 2640–2653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xu, J.; Jiang, S. Inverse Design of Tunable Lowpass Microstrip Filters Based on Generative Adversarial Network and Transfer Learning. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2024, 71, 2594–2598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, K.; Liu, Z.; Wei, Q.; Qiao, F.; Liu, X.; Yang, Y. Calibrating Process Variation at System Level with In-Situ Low-Precision Transfer Learning for Analog Neural Network Processors. In Proceedings of the 2018 55th ACM/ESDA/IEEE Design Automation Conference (DAC), San Francisco, CA, USA, 24–28 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Chu, C.; Mao, Y.; Wang, H. Transfer Learning Assisted Fast Design Migration Over Technology Nodes: A Study on Transformer Matching Network. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE/MTT-S International Microwave Symposium-IMS 2024, Washington, DC, USA, 16–21 June 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Costa, J.; Azevedo, F.; Martins, R. A Comparative Study on the Incorporation of PVT Corner Conditions within Reinforcement Learning-based Analog IC Sizing Approaches. In Proceedings of the 2025 21st International Conference on Synthesis, Modeling, Analysis and Simulation Methods, and Applications to Circuits Design (SMACD), Istanbul, Turkey, 7–10 July 2025. [Google Scholar]
- He, B.; Zhang, S.; Yang, F.; Yan, C.; Zhou, D.; Zeng, X. An Efficient Bayesian Optimization Approach for Analog Circuit Synthesis via Sparse Gaussian Process Modeling. In Proceedings of the 2020 Design, Automation & Test in Europe Conference & Exhibition (DATE), Grenoble, France, 9–13 March 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Z.; Wang, F.; Tao, J.; Su, Y.; Zeng, X.; Li, X. Correlated Bayesian Model Fusion: Efficient High-Dimensional Performance Modeling of Analog/RF Integrated Circuits Over Multiple Corners. IEEE Trans. Comput.-Aided Des. Integr. Circuits Syst. 2023, 42, 360–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutenbar, R.A.; Gielen, G.G.E.; Antao, B.A. Efficient Analog Circuit Synthesis with simultaneous Yield and Robustness Optimization. In Computer-Aided Design of Analog Integrated Circuits and Systems; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2002; pp. 699–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touloupas, K.; Sotiriadis, P.P. LoCoMOBO: A Local Constrained Multiobjective Bayesian Optimization for Analog Circuit Sizing. IEEE Trans. Comput.-Aided Des. Integr. Circuits Syst. 2022, 41, 2780–2793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Gu, J.; Ding, Y.; Li, Z.; Chong, F.T.; Pan, D.Z. QuantumNAT: Quantum noise-aware training with noise injection, quantization and normalization. In Proceedings of the 59th ACM/IEEE Design Automation Conference (DAC ‘22), New York, NY, USA, 10–14 July 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xu, B.; Li, P. ADO-LLM: Analog Design Bayesian Optimization with In-Context Learning of Large Language Models. In Proceedings of the 2024 ACM/IEEE International Conference on Computer Aided Design (ICCAD), Newark, NJ, USA, 27–31 October 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, T.; Zhang, L. Parasitic-aware gm/ID-based many-objective analog/RF circuit sizing. In Proceedings of the 2018 19th International Symposium on Quality Electronic Design (ISQED), Santa Clara, CA, USA, 13–14 March 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Zhu, H.; Bi, Z.; Yan, C.; Zhou, D.; Su, Y. Smart-MSP: A Self-Adaptive Multiple Starting Point Optimization Approach for Analog Circuit Synthesis. IEEE Trans. Comput.-Aided Des. Integr. Circuits Syst. 2018, 37, 531–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McConaghy, T.; Palmers, P.; Steyaert, M.; Gielen, G.G.E. Trustworthy Genetic Programming-Based Synthesis of Analog Circuit Topologies Using Hierarchical Domain-Specific Building Blocks. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 2011, 15, 557–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Y.; Lee, S.; Chen, G.; Poddar, S.; Hu, M.; Pan, D.Z.; Luo, P. AnalogCoder: Analog circuit design via training-free code generation. In Proceedings of the Thirty-Ninth AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Thirty-Seventh Conference on Innovative Applications of Artificial Intelligence and Fifteenth Symposium on Educational Advances in Artificial Intelligence, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 25 February–4 March 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Z.; Luo, J.; Liu, J.; Zhang, L. Signal-Division-Aware Analog Circuit Topology Synthesis Aided by Transfer Learning. IEEE Trans. Comput.-Aided Des. Integr. Circuits Syst. 2023, 42, 3481–3490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Lei, L.; Huang, J.; Yang, F.; Shang, L.; Zeng, X. Automatic Op-Amp Generation from Specification to Layout. IEEE Trans. Comput.-Aided Des. Integr. Circuits Syst. 2023, 42, 4378–4390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Lei, L.; Yang, F.; Shang, L.; Zeng, X. Topology Optimization of Operational Amplifier in Continuous Space via Graph Embedding. In Proceedings of the 2022 Design, Automation & Test in Europe Conference & Exhibition (DATE), Antwerp, Belgium, 14–23 March 2022; pp. 142–147. [Google Scholar]
- Lyu, R.; Meng, Y.; Zhao, A.; Bi, Z.; Zhu, K.; Yang, F.; Yan, C.; Zhou, D.; Zeng, X. A Study on Exploring and Exploiting the High-dimensional Design Space for Analog Circuit Design Automation. In Proceedings of the 2024 29th Asia and South Pacific Design Automation Conference (ASP-DAC), Incheon, Republic of Korea, 22–25 January 2024; pp. 671–678. [Google Scholar]
- Rojec, Ž.; Bűrmen, Á.; Fajfar, I. Analog circuit topology synthesis by means of evolutionary computation. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2019, 80, 48–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Yang, F.; Shang, L.; Yan, C.; Bi, Z.; Zhou, D. Topology Optimization of Operational Amplifiers using a Performance-Aware Representation. In Proceedings of the 2024 2nd International Symposium of Electronics Design Automation (ISEDA), Xi’an, China, 10–13 May 2024; pp. 166–170. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, J.; Lei, L.; Yang, F.; Yan, C.; Zeng, X. Automated Compensation Scheme Design for Operational Amplifier via Bayesian Optimization. In Proceedings of the 2021 58th ACM/IEEE Design Automation Conference (DAC), San Francisco, CA, USA, 5–9 December 2021; pp. 517–522. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Z.; Zhang, L. Efficient Performance Modeling for Automated CMOS Analog Circuit Synthesis. IEEE Trans. Very Large Scale Integr. (VLSI) Syst. 2021, 29, 1824–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.; Vemuri, R. A graph grammar based approach to automated multi-objective analog circuit design. In Proceedings of the 2009 Design, Automation & Test in Europe Conference & Exhibition, Nice, France, 20–24 April 2009; pp. 700–705. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Z.; Zhang, L. An Automated Topology Synthesis Framework for Analog Integrated Circuits. IEEE Trans. Comput.-Aided Des. Integr. Circuits Syst. 2020, 39, 4325–4337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Zhang, L. Analog Integrated Circuit Topology Synthesis with Deep Reinforcement Learning. IEEE Trans. Comput.-Aided Des. Integr. Circuits Syst. 2022, 41, 5138–5151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Meng, S.; Yang, F.; Shang, L.; Zeng, X. TOTAL: Topology Optimization of Operational Amplifier via Reinforcement Learning. In Proceedings of the 2023 24th International Symposium on Quality Electronic Design (ISQED), San Francisco, CA, USA, 5–7 April 2023; pp. 6–8. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, J.; Cao, W.; Yang, J.; Zhang, X. AnalogGenie: A Generative Engine for Automatic Discovery of Analog Circuit Topologies. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Representation Learning, Singapore, 24 April–28 April 2025; pp. 96496–96514. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, J.; Yang, F.; Shang, L.; Yan, C.; Bi, H.; Zhou, D.; Zeng, X. ATOM: An Automatic Topology Synthesis Framework for Operational Amplifiers. IEEE Trans. Comput.-Aided Des. Integr. Circuits Syst. 2025, 44, 1193–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meissner, M.; Hedrich, L. FEATS: Framework for Explorative Analog Topology Synthesis. IEEE Trans. Comput.-Aided Des. Integr. Circuits Syst. 2015, 34, 213–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Liu, J.; Zhao, W.-S.; Zhang, L. Automated Topology Synthesis of Analog Integrated Circuits with Frequency Compensation. IEEE Trans. Comput.-Aided Des. Integr. Circuits Syst. 2025, 44, 832–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harsha, M.V.; Harish, B.P. An Integrated MaxFit Genetic Algorithm-SPICE Framework for 2-stage Op-amp Design Automation. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Computer Society Annual Symposium on VLSI (ISVLSI), Hong Kong, China, 8–11 July 2018; pp. 170–174. [Google Scholar]
- Das, P.; Jajodia, B. Design Automation of Two-Stage Operational Amplifier Using Multi-Objective Genetic Algorithm and SPICE Framework. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Conference on Inventive Computation Technologies (ICICT), Lalitpur, Nepal, 20–22 July 2022; pp. 166–170. [Google Scholar]
- Rashid, R.; Nambath, N. Hybrid Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm for Area Minimization in 65 nm Technology. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS), Daegu, Republic of Korea, 22–28 May 2021; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Rashid, R.; Nambath, N. Area Optimisation of Two Stage Miller Compensated Op-Amp in 65 nm Using Hybrid PSO. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2022, 69, 199–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Chen, A.; Li, H.; Chen, Z.; Liang, F.; Wang, H. A Hybrid Multi-Population Algorithm for Efficient Analog Circuit Optimization. IEEE Trans. Comput.-Aided Des. Integr. Circuits Syst. 2025, 45, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sridhar, P.; Kittur, H.M.; Korantak, A.; Kumar, A. An Adaptive Multi-Objective Optimization on CMOS Two Stage Op-Amp Circuit Synthesis. In Proceedings of the 2024 28th International Symposium on VLSI Design and Test (VDAT), Vellore, India, 1–3 September 2024; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, T.; Li, W.; Zhao, A.; Bi, Z.; Li, X.; Yang, F.; Yan, C.; Hu, W.; Zhou, D.; Cui, T.; et al. BBGP-sDFO: Batch Bayesian and Gaussian Process Enhanced Subspace Derivative Free Optimization for High-Dimensional Analog Circuit Synthesis. IEEE Trans. Comput.-Aided Des. Integr. Circuits Syst. 2024, 43, 417–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, A.; Lyu, R.; Zhao, X.; Bi, Z.; Yang, F.; Yan, C.; Zhou, D.; Su, Y.; Zeng, X. VTSMOC: An Efficient Voronoi Tree Search Boosted Multi-objective Bayesian Optimization with Constraints for High-dimensional Analog Circuit Synthesis. IEEE Trans. Comput.-Aided Des. Integr. Circuits Syst. 2025, 44, 818–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budak, A.F.; Bhansali, P.; Liu, B.; Sun, N.; Pan, D.Z.; Kashyap, C.V. DNN-Opt: An RL Inspired Optimization for Analog Circuit Sizing using Deep Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 2021 58th ACM/IEEE Design Automation Conference (DAC), San Francisco, CA, USA, 5–9 December 2021; pp. 1219–1224. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, Y.; Choi, M.; Lee, K.; Kang, S. MA-Opt: Reinforcement Learning-Based Analog Circuit Optimization Using Multi-Actors. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2024, 71, 2045–2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Yin, X.; Chen, D.; Li, D.; Yang, Y. The High Efficiency Optimization Design Method for Two Stage Miller Compensated Operational Amplifier. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2024, 71, 2029–2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Yang, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, D.; Yang, Y. A high-efficiency modeling method for analog integrated circuits. Chip 2025, 4, 100135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakhamaneshi, K.; Nassar, M.; Phielipp, M.; Abbeel, P.; Stojanovic, V. Pretraining Graph Neural Networks for Few-Shot Analog Circuit Modeling and Design. IEEE Trans. Comput.-Aided Des. Integr. Circuits Syst. 2023, 42, 2163–2173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xin, J.; Fang, J.; Chen, X.; Liu, H.; Qin, Q.; Chai, C.; Lu, Y.; Hao, J.; Xiao, J.; et al. Topology Generic DC-Model for Accelerating Analog Circuit Optimization. In Proceedings of the 2023 International Symposium of Electronics Design Automation (ISEDA), Nanjing, China, 8–11 May 2023; pp. 65–70. [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto, K.; Takai, N. GNN-Curio: Transistor Sizing by Curiosity-Driven Reinforcement Learning with Graph Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 2024 6th International Conference on Circuits and Systems (ICCS), Chengdu, China, 20–23 September 2024; pp. 129–134. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, J.; Zhang, J.; Huang, Z.; Bi, Z.; Feng, X.; Zeng, X.; Lu, Y. Multiagent based Reinforcement Learning (MA-RL): An Automated Designer for Complex Analog Circuits. IEEE Trans. Comput.-Aided Des. Integr. Circuits Syst. 2024, 43, 4398–4411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajjadi, S.A.; Sadrossadat, S.A.; Moftakharzadeh, A.; Nabavi, M.; Sawan, M. DNN-Based Optimization to Significantly Speed Up and Increase the Accuracy of Electronic Circuit Design. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2024, 71, 1273–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budak, A.F.; Gandara, M.; Shi, W.; Pan, D.Z.; Sun, N.; Liu, B. An Efficient Analog Circuit Sizing Method Based on Machine Learning Assisted Global Optimization. IEEE Trans. Comput.-Aided Des. Integr. Circuits Syst. 2022, 41, 1209–1221. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.; Savidis, I. Circuit-GNN: A Graph Neural Network for Transistor-level Modeling of Analog Circuit Hierarchies. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS), Monterey, CA, USA, 21–25 May 2023; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.; Savidis, I. Transfer Learning for Reuse of Analog Circuit Sizing Models Across Technology Nodes. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS), Austin, TX, USA, 27 May–1 June 2022; pp. 1033–1037. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Hassanpourghadi, M.; Zhang, Q.; Su, S.; Chen, M.S.-W. Transfer Learning with Bayesian Optimization-Aided Sampling for Efficient AMS Circuit Modeling. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/ACM International Conference on Computer Aided Design (ICCAD), San Diego, CA, USA, 2–5 November 2020; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Su, S.; Madhusudan, M.; Hassanpourghadi, M.; Saunders, S.; Zhang, Q.; Rasul, R.; Li, Y.; Hu, J.; Sharma, A.K.; et al. From Specification to Silicon: Towards Analog/Mixed-Signal Design Automation using Surrogate NN Models with Transfer Learning. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/ACM International Conference on Computer Aided Design (ICCAD), Munich, Germany, 1–4 November 2021; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Poddar, S.; Oh, Y.; Lai, Y.; Zhu, H.; Hwang, B.; Pan, D.Z. INSIGHT: A Universal Neural Simulator Framework for Analog Circuits with Autoregressive Transformers. In Proceedings of the 2025 62nd ACM/IEEE Design Automation Conference (DAC), San Francisco, CA, USA, 22–25 June 2025; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Xing, W.W.; Fan, W.; Liu, Z.; Yao, Y.; Hu, Y. KATO: Knowledge Alignment and Transfer for Transistor Sizing of Different Design and Technology. In Proceedings of the 2025 61st ACM/IEEE Design Automation Conference (DAC), San Francisco, CA, USA, 23–27 June 2024; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Wang, K.; Yang, J.; Shen, L.; Sun, N.; Lee, H.-S.; Han, S. GCN-RL Circuit Designer: Transferable Transistor Sizing with Graph Neural Networks and Reinforcement Learning. In Proceedings of the 2020 57th ACM/IEEE Design Automation Conference (DAC), San Francisco, CA, USA, 20–24 July 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Gielen, G.G.E. ESAT-MICAS, KU Leuven, 3001 Leuven, Belgium Graph-Guided Transfer Learning to Boost the Efficiency of System-Level Optimization of Analog/Mixed-Signal Circuits. In Proceedings of the 2025 62nd ACM/IEEE Design Automation Conference (DAC), San Francisco, CA, USA, 22–25 June 2025; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.-J.; Lee, K.-J.; Choi, Y.; Lee, K.; Kang, S.; Sim, J.-Y. Trans-Net: Knowledge-Transferring Analog Circuit Optimizer with a Netlist-Based Circuit Representation. In Proceedings of the 2024 Design, Automation & Test in Europe Conference & Exhibition (DATE), Valencia, Spain, 25–27 March 2024; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Z.; Yan, A.; Huang, Z.; Cui, J.; Roh, B.-H.; Liu, G. Graph-Based Multitask Transfer Learning for Fault Detection and Diagnosis of Few-Shot Analog Circuits. IEEE Internet Things J. 2025, 12, 21264–21279. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmadzadeh, M.; Lappas, J.; Wehn, N.; Gielen, G. AnaCraft: Duel-Play Probabilistic-Model-based Reinforcement Learning for Sample-Efficient PVT-Robust Analog Circuit Sizing Optimization. IEEE Trans. Comput.-Aided Des. Integr. Circuits Syst. 2025, 45, 901–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Wang, Z.; Lee, S.; Oh, Y.; Zhu, H.; Kim, D.; Pan, D.Z. PPAAS: PVT and Pareto Aware Analog Sizing via Goal-conditioned Reinforcement Learning. In Proceedings of the 2025 IEEE/ACM International Conference on Computer Aided Design (ICCAD), Valencia, Spain, 26–30 October 2025; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Somayaji, N.K.; Hu, H.; Li, P. Prioritized Reinforcement Learning for Analog Circuit Optimization with Design Knowledge. In Proceedings of the 2021 58th ACM/IEEE Design Automation Conference (DAC), San Francisco, CA, USA, 5–9 December 2021; pp. 1231–1236. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, K.-E.; Tsai, C.-Y.; Shen, H.-H.; Chiang, C.-F.; Tsai, F.-M.; Wang, C.-A.; Ting, Y.; Yeh, C.-S.; Lai, C.-T. Trust-Region Method with Deep Reinforcement Learning in Analog Design Space Exploration. In Proceedings of the 2021 58th ACM/IEEE Design Automation Conference (DAC), San Francisco, CA, USA, 5–9 December 2021; pp. 1225–1230. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, D.; Park, J.; Shin, C.; Jung, J.; Shin, K.; Baek, S.; Heo, S.; Kim, W.; Jeong, I.; Cho, J.; et al. GLOVA: Global and Local Variation-Aware Analog Circuit Design with Risk-Sensitive Reinforcement Learning. In Proceedings of the 2025 62nd ACM/IEEE Design Automation Conference (DAC), San Francisco, CA, USA, 22–25 June 2025; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, W.; Wang, H.; Gu, J.; Liu, M.; Pan, D.Z.; Han, S.; Sun, N. RobustAnalog: Fast Variation-Aware Analog Circuit Design Via Multi-task RL. In Proceedings of the 2022 ACM/IEEE 4th Workshop on Machine Learning for CAD (MLCAD), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 12–13 September 2022; pp. 35–41. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Zhi, H.; Shan, W.; Li, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Li, Y. Multi-Task Evolutionary to PVT Knowledge Transfer for Analog Integrated Circuit Optimization. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE/ACM International Conference on Computer Aided Design (ICCAD), San Francisco, CA, USA, 28 October–2 November 2023; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Teh, Y.W.; Bapst, V.; Czarnecki, W.M.; Quan, J.; Kirkpatrick, J.; Hadsell, R.; Heess, N.; Pascanu, R. Distral: Robust Multitask Reinforcement Learning. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2017, 30, 4499–4509. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, Z.; Tang, X.; Shi, W.; Du, Y.; Lin, Y.; Wang, Y. PVTSizing: A TuRBO-RL-Based Batch-Sampling Optimization Framework for PVT-Robust Analog Circuit Synthesis. In Proceedings of the 61st ACM/IEEE Design Automation Conference (DAC ‘24); Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2024; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Garitselov, O.; Mohanty, S.P.; Kougianos, E. A Comparative Study of Metamodels for Fast and Accurate Simulation of Nano-CMOS Circuits. IEEE Trans. Semicond. Manuf. 2012, 25, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghai, D.; Mohanty, S.P.; Kougianos, E. Design of Parasitic and Process-Variation Aware Nano-CMOS RF Circuits: A VCO Case Study. IEEE Trans. Very Large Scale Integr. (VLSI) Syst. 2009, 17, 1339–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, S.P.; Kougianos, E. Incorporating Manufacturing Process Variation Awareness in Fast Design Optimization of Nanoscale CMOS VCOs. IEEE Trans. Semicond. Manuf. 2014, 27, 22–31. [Google Scholar]
- Habal, H.; Graeb, H. Constraint-Based Layout-Driven Sizing of Analog Circuits. IEEE Trans. Comput.-Aided Des. Integr. Circuits Syst. 2011, 30, 1089–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Tseng, I.-L.; Postula, A.; Jozwiak, L. Symbolic extraction for estimating analog layout parasitics in layout-aware synthesis. In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference Mixed Design of Integrated Circuits and Systems, Krakow, Poland, 22–25 June 2005; pp. 195–199. [Google Scholar]
- Lourenço, N.; Martins, R.; Horta, N. Layout-aware sizing of analog ICs using floorplan & routing estimates for parasitic extraction. In Proceedings of the 2015 Design, Automation & Test in Europe Conference & Exhibition (DATE), Grenoble, France, 9–13 March 2015; pp. 1156–1161. [Google Scholar]
- Daulton, S.; Cakmak, S.; Balandat, M.; Osborne, M.A.; Zhou, E.; Bakshy, E. Robust Multi-Objective Bayesian Optimization Under Input Noise. Proc. Mach. Learn. Res. 2022, 162, 4831–4866. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, H.; Kokai, G.F.; Turner, W.J.; Ku, T.-S. ParaGraph: Layout Parasitics and Device Parameter Prediction using Graph Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 57th ACM/EDAC/IEEE Design Automation Conference (DAC ‘20), Long Beach, CA, USA, 20–24 July 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Garitselov, O.; Mohanty, S.P.; Kougianos, E. Fast-Accurate Non-Polynomial Metamodeling for nano-CMOS PLL Design Optimization. In Proceedings of the 2012 25th International Conference on VLSI Design, Hyderabad, India, 7–11 January 2012; pp. 316–321. [Google Scholar]
- Crossley, J.; Puggelli, A.; Le, H.-P.; Yang, B.; Nancollas, R.; Jung, K.; Kong, L.; Narevsky, N.; Lu, Y.; Sutardja, N.; et al. BAG: A Designer-Oriented Integrated Framework for the Development of AMS Circuit Generators. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE/ACM International Conference on Computer-Aided Design (ICCAD), San Jose, CA, USA, 18–21 November 2013; pp. 74–81. [Google Scholar]
- Hakhamaneshi, K.; Werblun, N.; Abbeel, P.; Stojanović, V. BagNet: Berkeley Analog Generator with Layout Optimizer Boosted with Deep Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/ACM International Conference on Computer-Aided Design (ICCAD), Westminster, CO, USA, 4–7 November 2019; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Castro-Lopez, R.; Guerra, O.; Roca, E.; Fernandez, F.V. An Integrated Layout-Synthesis Approach for Analog ICs. IEEE Trans. Comput.-Aided Des. Integr. Circuits Syst. 2008, 27, 1179–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porrasmaa, S.; Lahtinen, V.; Heikkinen, A.; Boopathy, D.; Tamminen, A.; Kosunen, M. An Efficient Method for Analog Design Optimization with Layout Generators. Integr. Circuits Syst. 2025, 2, 217–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Methods | Refs. | Circuit | Topology Synthesis Methods | Evaluated Methods | Optimization Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Preset modules-based | [34] | Common source amplifier, three-stage amplifier, folded Cascode amplifier | AnalogCoder | PySpice | Common source amplifier: Av = 13.98 dB; Three-stage amplifier: Av = 44.13 dB; Folded Cascode amplifier: Av = 13.98 dB |
| Known structure-based | [39] | Voltage reference | NSGA-II | NgSpice | PC = 1.8 μW, PSRR = 89 dB, generations = 1610, time ≈ 35 h |
| [41] | Three Novel amplifiers with compensation | Bi-level BO | Cadence | Run1: Av = 90.34 dB, PM = 56°, GBW = 3.3 MHz, PC = 69.44 μW; Run2: Av = 90.5 dB, PM = 47°, GBW = 3.1 MHz, PC = 102.6 μW; Run3: Av = 87.2 dB, PM = 45.4°, GBW = 3.4 MHz, PC = 91.7 μW; Generations ≈ 8000; Running time ≈ 9 h | |
| Generate from scratch | [43] | Novel amplifier, voltage Controlled Oscillator (VCO) | Graph Grammar Based Approach | HSpice | Novel amplifier: Av = 42.15 dB, UGB = 9.2 GHz, PM = 56°, generation = 100; VCO: Oscillation frequency = 4.17 GHz, tuning range = 0.12 GHz, generate = 50 |
| [44] | Novel multistage amplifiers | GCTG | Cadence | Av = 70.31 dB, BW = 66.48 MHz, generate 388 tree structures within 0.06 s | |
| [45] | High-Av amplifiers, high-BW amplifiers, novel amplifiers | PGNN + NSGA-II | Cadence | High-gain Opamps: Av > 100 dB, PM = 60°, UGB = 10 MHz; High-BW Opamps: Av = 60 dB, PM = 60°, UGB > 1 GHz; Novel Opamps: Av > 100 dB, generations = 800–2000; Running time = 2–9 h | |
| [48] | Three-stage amplifiers | ATOM | HSpice | FOM = 356.56 × 103, Av = 106.7 dB, UGF = 1.62 MHz, PM = 62.9°, PC = 45.4 μW, generations = 1600, running time ≈ 20 min |
| Refs. | Circuit | Optimization Methods | Technology Node | Optimization Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [51] | Two-stage amplifier | MaxFit GA | 180 nm | Av = 76.3 dB, PM = 68.8°, UGF = 11.65 MHz, SR = 9.83 V/μs, PC = 0.166 mW |
| [52] | Two-stage amplifier | MOGA | 180 nm | Av = 75.6dB, PM = 62°, UGF = 16.8MHz, SR = 15.8 V/μs, PC = 220 μW |
| [53] | Two-stage amplifier | Hybrid PSO | 65 nm | Av = 12.1 dB, PM = 104°, UGF = 84.8 MHz, SR = 104 V/μs, PC = 76.1 μW |
| [17] | Two-stage amplifier | MFO + EA/NSGA-II/BO | 180 nm | Av = 36.7 dB, UGF = 20.6 MHz, Iq = 400–800 μA, generations = 50, runtime = 2717 s |
| [57] | VCO, charge pump, amplifier | BBGP-sDFO | 40 nm/180 nm | VCO: FoM = 4.083, k_min = 339.37 MHz/V, R_min = 0.998, generations = 452, runtime = 2.8 h; Charge pump: FoM = 4.74 (±0.31), diff = 8.103 μA, generations = 452, runtime = 3.2 h; OTA: Iq = 10.211 μA, Av= 130.985 dB, UGF = 505.5 MHz, PM = 63.34°, generations = 1390, runtime = 6.8 h |
| [59] | Folded Cascode amplifier, strong latch comparator | DNN-opt | 180 nm | Folded Cascode amplifier: Average PC = 0.71 mW, PM > 60°, UGB > 30 MHz, setting time < 30 ns, generations = 132, runtime = 3.3 h Strong latch comparator: Average PC= 2.65 μW, set delay < 10 ns, reset delay < 6.5 ns, area < 26 μm2 generations = 330, runtime = 3.9 h |
| [60] | Two-stage amplifier, three-stage amplifier, LDO | MA-opt | 180 nm | Two-stage amplifier: PC = 0.608 mW, FoM = −2.93, generations = 200, runtime = 0.83 h Three-stage amplifier: PC = 0.129 mW, FoM = −3.57, generations = 200, runtime = 0.86 h LDO: Iq = 0.216 mA, FoM = −3.13, generations = 200, runtime = 1.13 h |
| [61] | Two-stage amplifier | ANN + PSO | 65 nm | Av = 20.4 dB, UGF = 100.4 MHz, PM = 62.51°, SR =162.2 V/μs, PC=72.1 μW generations = 100, runtime = 208 s |
| Refs. | Circuit | Optimization Methods | Transfer Range | Transfer Effect |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [70] | Two-stage amplifier | TL with frozen layers | 180 nm → 65 nm | Transferred two-stage amplifier: PC = 398 μW, Av = 50.3 dB, PM = 51°, GBW = 128 MHz, SR = 2.21 V/μs; Samples can be decreased by 90% |
| [71] | Inverter, folded Cascode amplifier, ∆Σ DAC | TL + BOAS + MLP | 45 nm → 32 nm | Transferred inverter: Samples can be decreased by 19×; Transferred folded Cascode amplifier: Samples can be decreased by 17×; Transferred ∆Σ DAC: Samples can be decreased by 150x; |
| [74] | Two-stage amplifier, three-stage amplifier, bandgap reference | KATO | 180 nm → 40 nm | Transferred two-stage amplifier: PC = 254.05 μW, Av = 50.29 dB, PM = 83.72°, GBW = 15.05 MHz; Transferred three-stage amplifier: PC = 118.47 μW, Av = 74.41 dB, PM = 71.84°, GBW = 2.65 MHz; Transferred bandgap reference: Temperature coefficient (TC) = 9.66 ppm/°C, Iq = 5.42 μA, PSRR = 61.99 dB; Iterations can be decreased by 2.52× |
| [75] | Two-TIA, three-TIA, voltage amplifier, LDO | GCN-RL | 180nm → 250/130/65/45 nm Two-TIA ↔ Three-TIA | 250 nm: FoM is increased by 84%; 180 nm: FoM is increased by 98%; 65 nm: FoM is increased by 118%; 45 nm: FoM is increased by 100%; Two-TIA → Three-TIA: FoM is increased by 24%; Three-TIA → Two-TIA: FoM is increased by 3.4% |
| [76] | CT∆Σ ADC | Graph-guided TL + RL | Fourth-order CIFF ↔ Fourth-order CRFB; Third-order CIFF → Fourth-order CIFF | Fourth-order CIFF → Fourth-order CRFB: Simulation efficiency increased 11×, PC = 45.52 mW; Fourth-order CRFB → Fourth-order CIFF: Simulation efficiency increased 2.2×, PC = 42.43 mW; Third-order CIFF → Fourth-order CIFF: Simulation efficiency increased 1.7×, PC increased 5.6% |
| Refs. | Circuit | Optimization Methods | Technology Node | Robust Optimization Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [80] | Two-stage amplifier, Cascode amplifier, LDO | PPAAS | GF180MCU/SKY130 | Samples are decreased by 1.6×; Simulation efficiency is increased by 4.1×; PVT deviation is decreased |
| [82] | Two-stage amplifier | Trust-Region Method+RL | 45 nm | Average generations are 36; 9 PVT angle validations are completed in 72.6 iterations; Optimization efficiency is increased by 4× |
| [83] | Strongarm latch; floating inverter amplifier (FIA); offset-compensation sense amplifier (OCSA) | GLOVA | 28 nm | Sample efficiency is increased by 80.5×; Simulation time is decreased by 76.0×; 30 PVT corners can be simulated |
| [84] | Two-stage amplifier; folded-Cascode amplifier, strongarm latch | RobustAnalog | 45 nm/180 nm | Two-stage amplifier: Simulation times is decreased by 26×; Folded-Cascode amplifier: Simulation times is decreased by 14×; Strongarm Latch: Simulation times is decreased by 30×; All circuits pass all PVT corner verification under different random seeds |
| [85] | Voltage reference circuit | PVT-Transfer | 180 nm | FoM is increased by 7.8×; Simulation times are decreased by 60%; Total runtime is 1.8~2.8 h; All PVT conners are verified |
| [87] | Folded-Cascode amplifier; strongarm latch; BGR; FIA | PVTSizing | 28 nm/180 nm | Sample efficiency is increased by 8.8×; Optimization time is decreased by 9.8×; All PVT conners are verified |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2026 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Yang, Y.; Fang, J.; Dong, H.; Lai, X.; Chen, D.; Li, D.; Yang, Y. Research on Robust and Efficient Optimization Design Methods for Analog Integrated Circuits. Micromachines 2026, 17, 184. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi17020184
Yang Y, Fang J, Dong H, Lai X, Chen D, Li D, Yang Y. Research on Robust and Efficient Optimization Design Methods for Analog Integrated Circuits. Micromachines. 2026; 17(2):184. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi17020184
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Yunqi, Jiayuan Fang, Huachen Dong, Xiaoran Lai, Dongdong Chen, Di Li, and Yintang Yang. 2026. "Research on Robust and Efficient Optimization Design Methods for Analog Integrated Circuits" Micromachines 17, no. 2: 184. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi17020184
APA StyleYang, Y., Fang, J., Dong, H., Lai, X., Chen, D., Li, D., & Yang, Y. (2026). Research on Robust and Efficient Optimization Design Methods for Analog Integrated Circuits. Micromachines, 17(2), 184. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi17020184








