Multi-Objective Optimization of Surface Roughness, Cutting Force, and Temperature in Ultrasonic-Vibration-Assisted Milling of Titanium Alloy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The Mechanism of UAM and Experimental Equipment
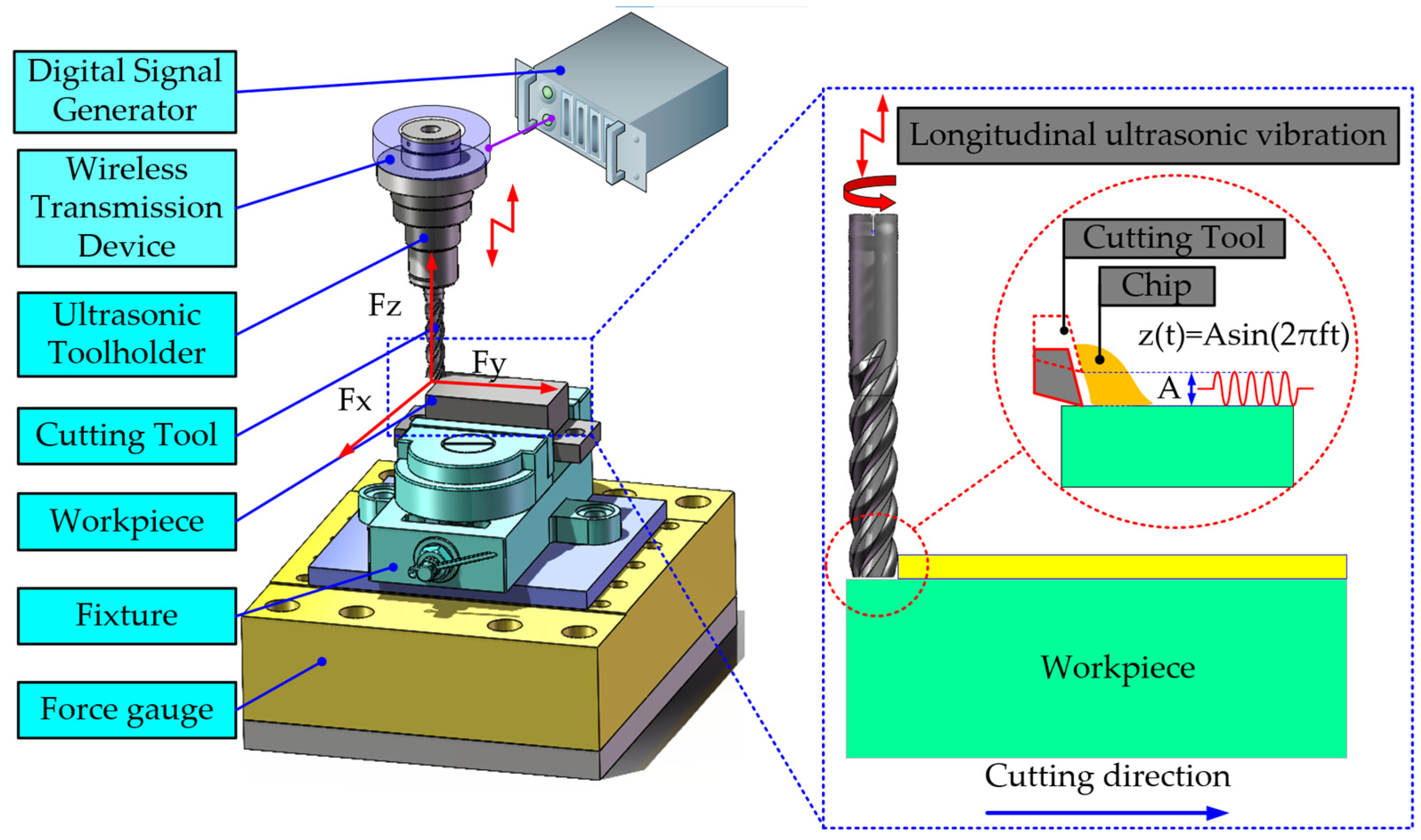
2.1. The Mechanism of UAM
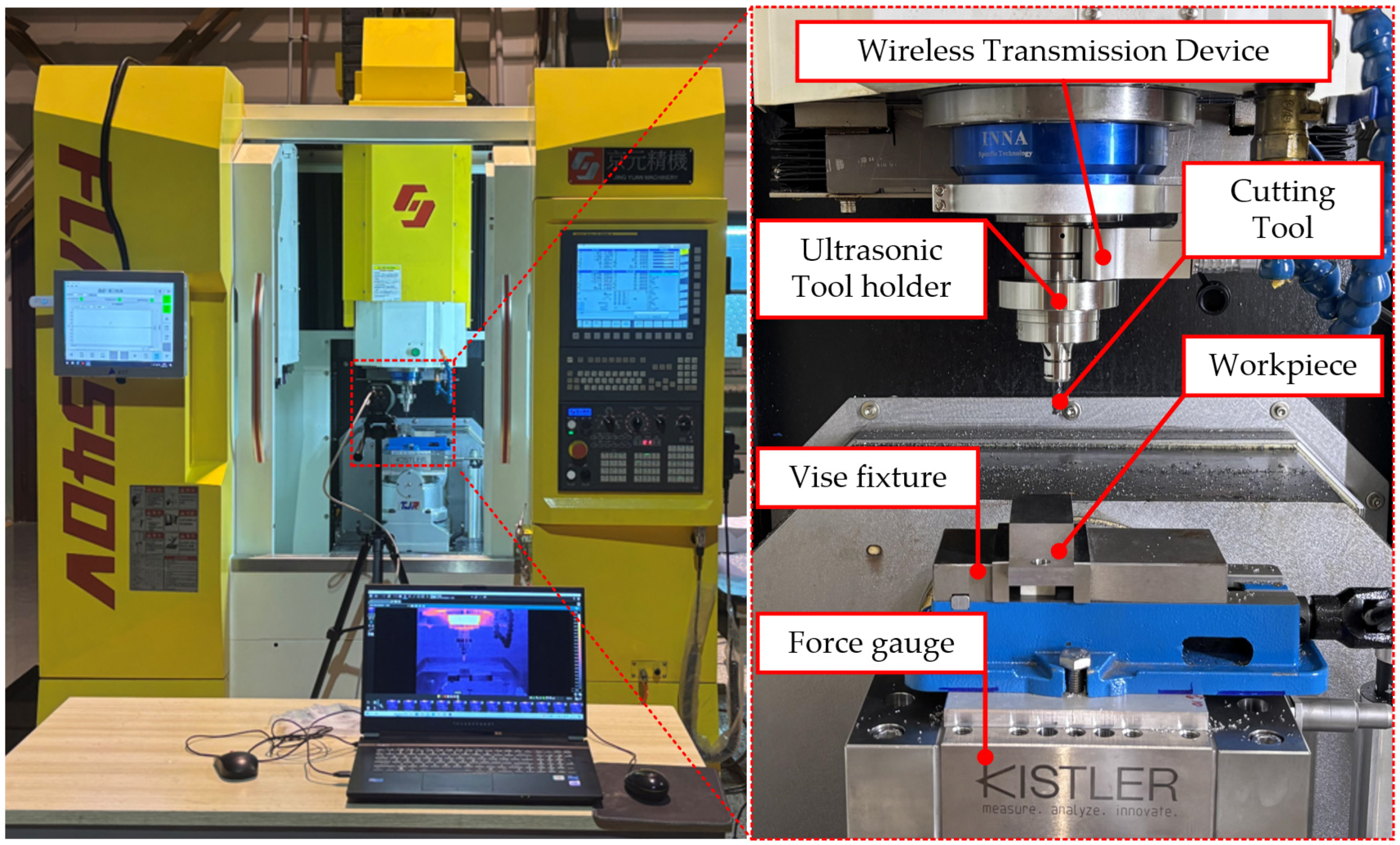
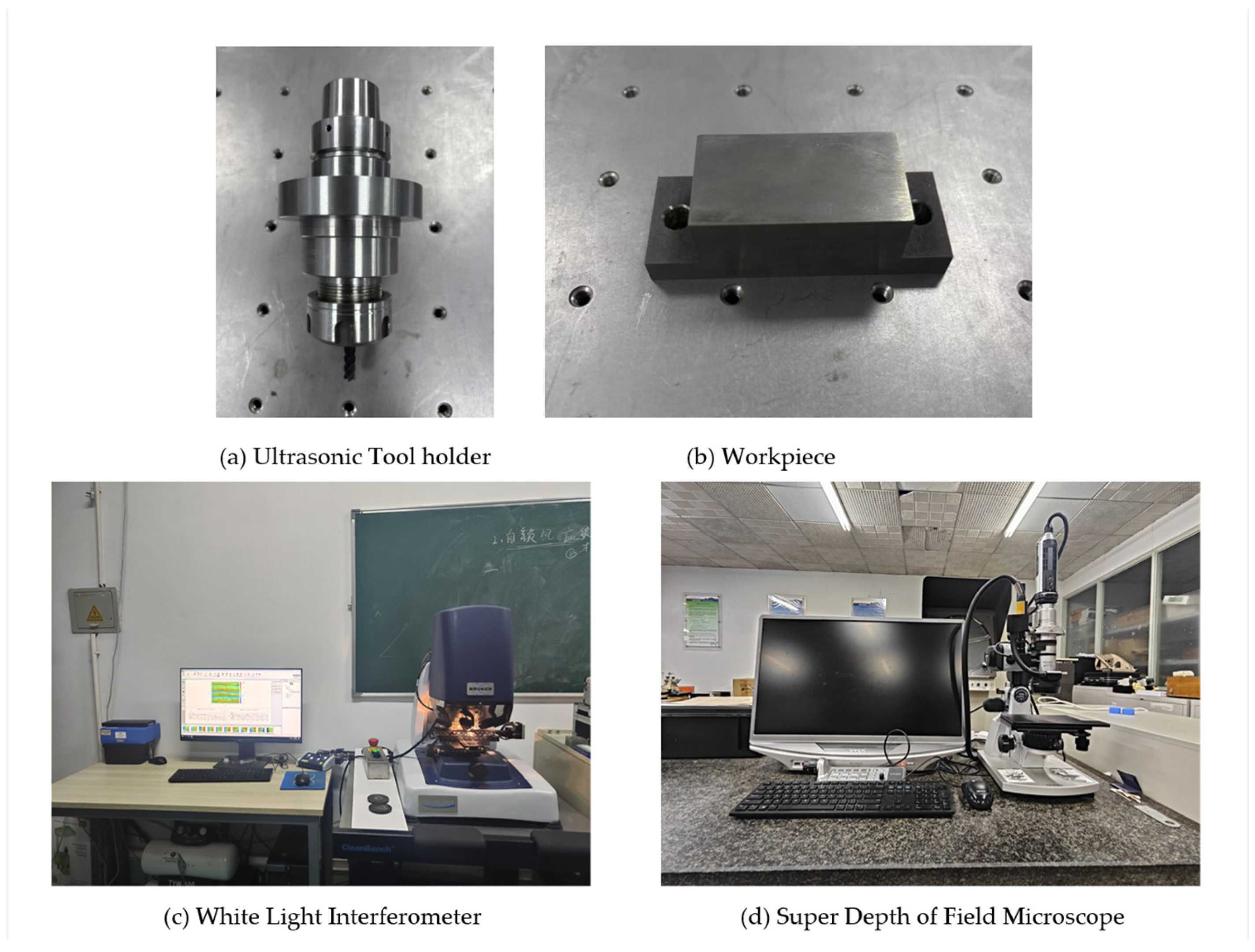
2.2. Experimental Equipment and Materials
3. Experimental Arrangement and Results Analysis
3.1. Experimental Arrangement and Results
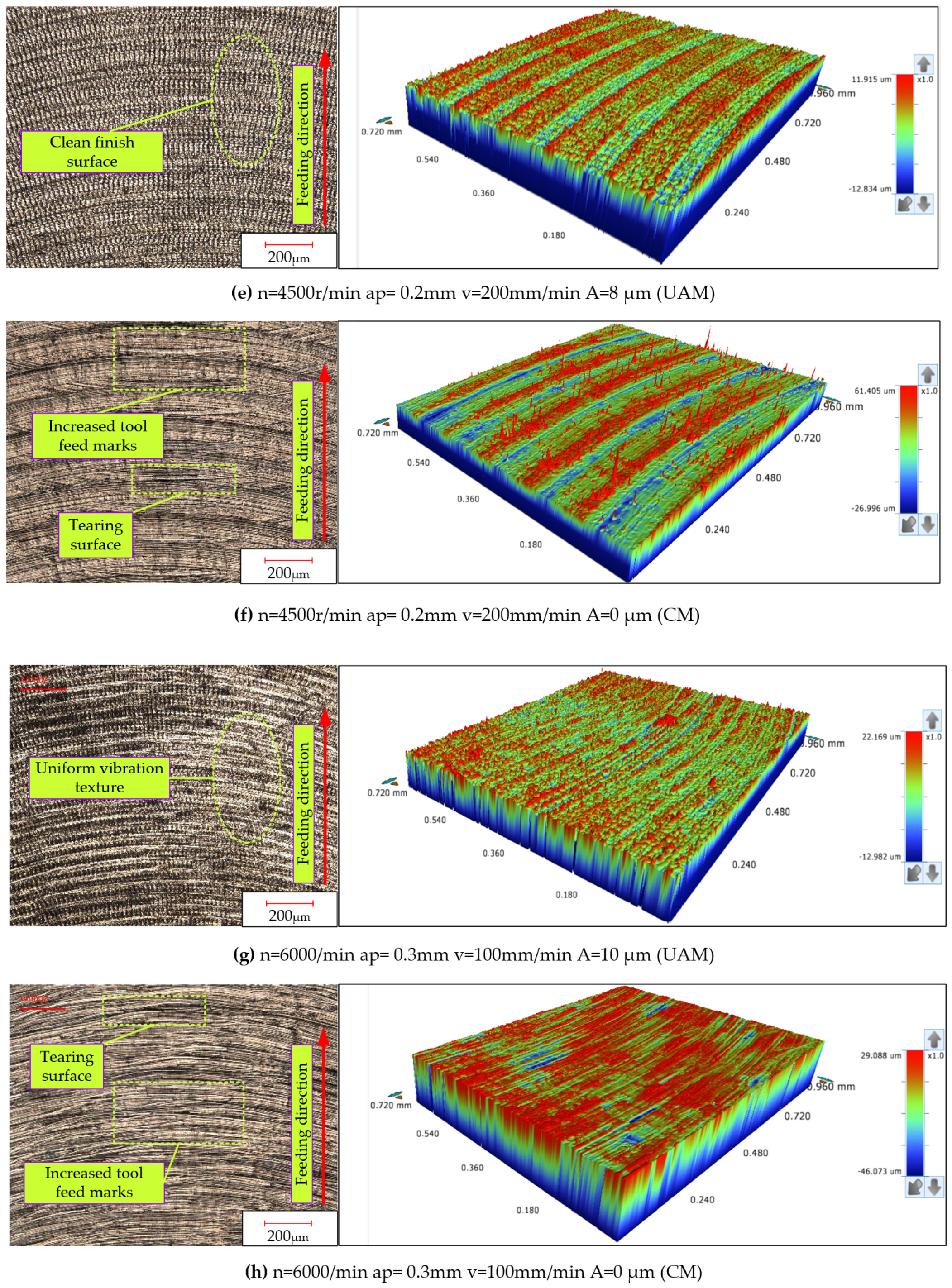
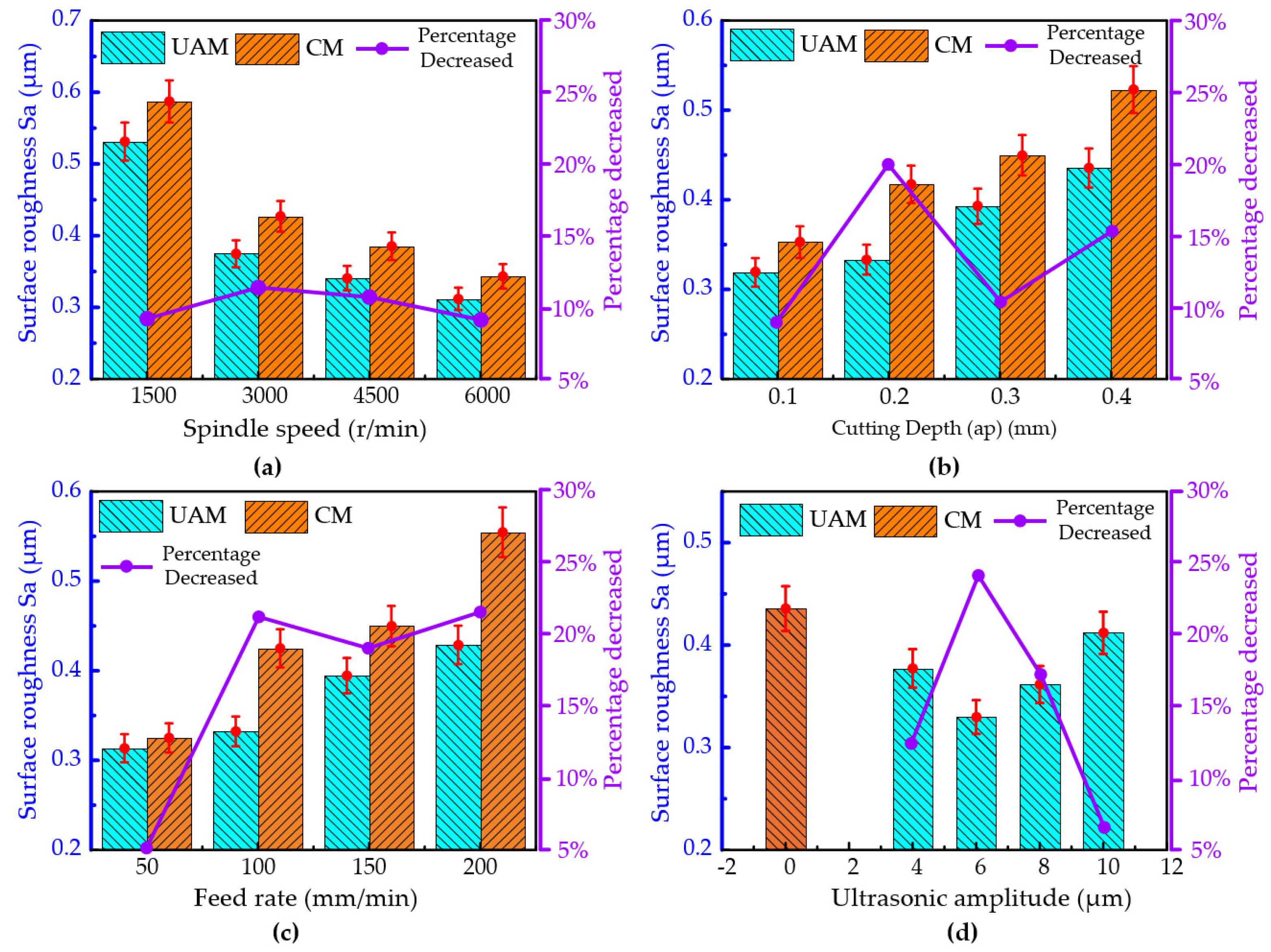
3.2. The Effect of the Process Parameters on the Surface Roughness
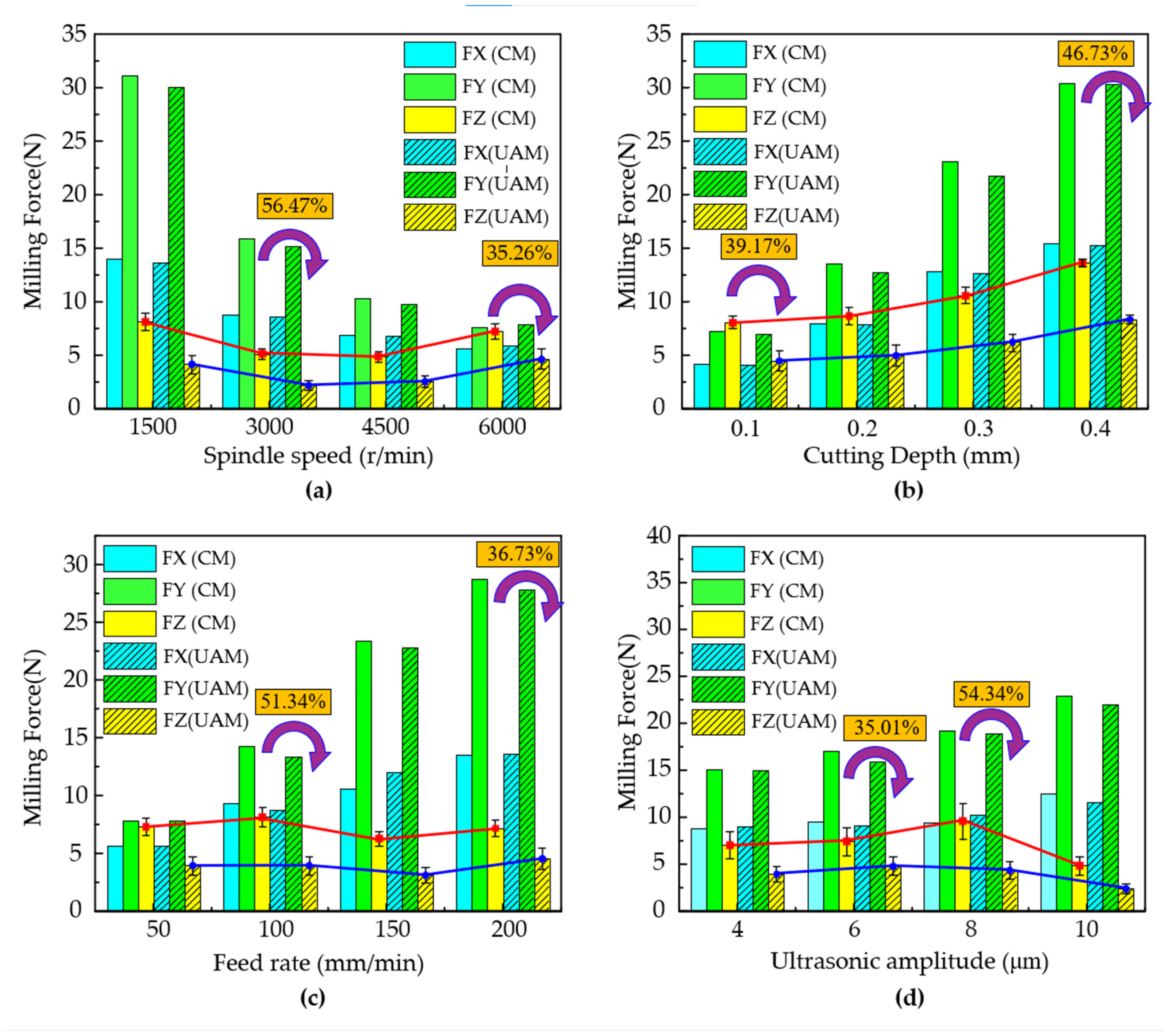
3.3. The Effect of the Process Parameters on the Cutting Force
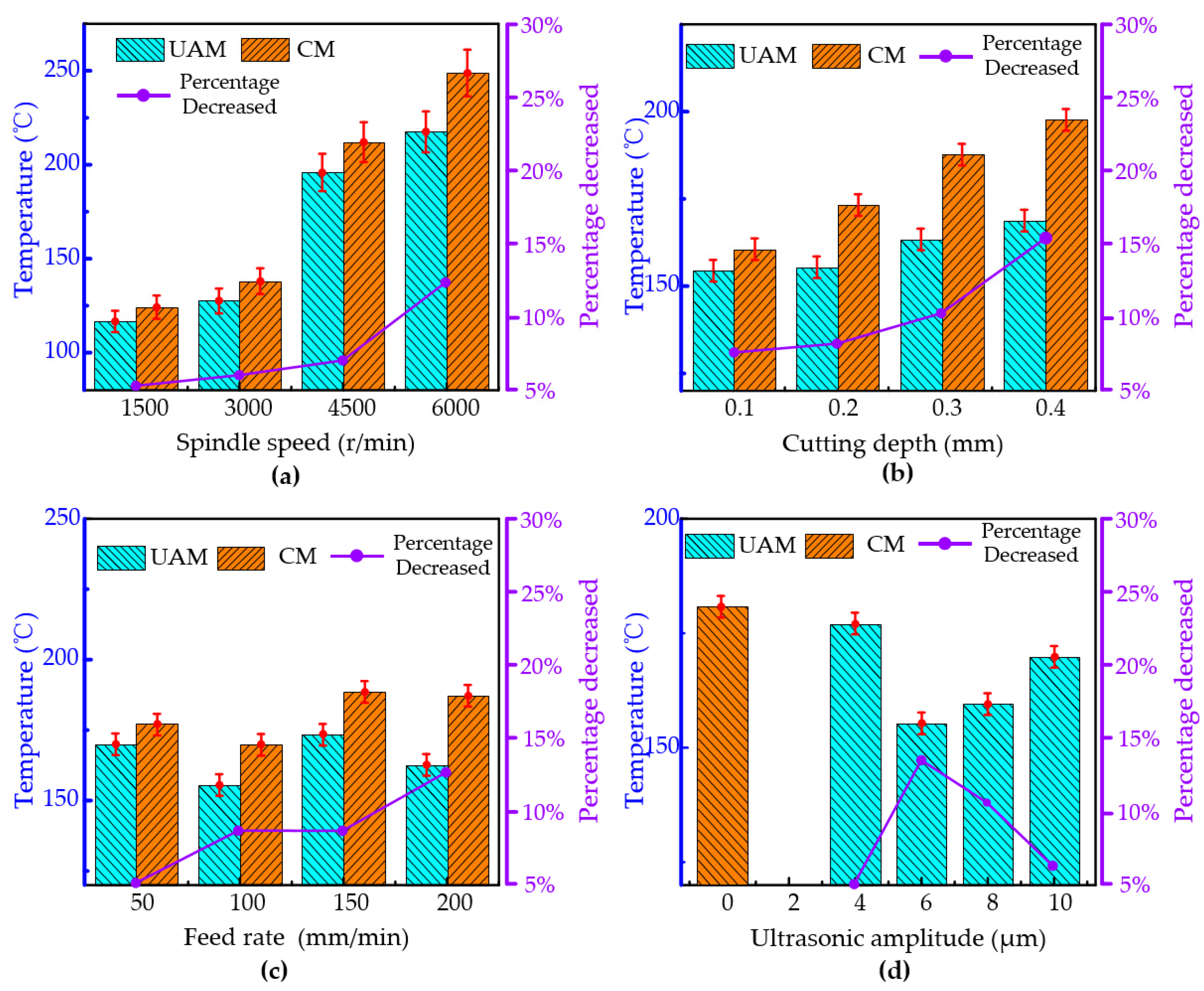
3.4. The Effect of the Process Parameters on the Cutting Temperature
4. Grey Correlation Analysis
4.1. Data Standardization Processing
4.2. Grey Correlation Coefficient and Grey Correlation Degree
4.3. Grey Relational Coefficient and Grey Relational Grade
4.4. Experimental Validation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hu, R.; Zhang, K.W.; Zou, H.; Gao, Z.T.; Luo, X.; Liu, X.X.; Wu, Z.Y. Research progress on Ti2AlNb-based alloys and composites for aerospace applications. J. Alloys Compd. 2025, 1021, 179701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razzak, A.; Wang, S.X.; Xue, W.H.; Gao, S.Y.; Duan, D.L. Study on fretting wear behavior of titanium alloys sliding against various friction pair materials at room temperature for aero-engine applications. J. Bio- Tribo-Corros. 2025, 11, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.M.; Qiao, H.Y.; Yang, M.Y.; Zhang, Y.M. Research on milling characteristics of titanium alloy TC4 with variable helical end milling cutter. Machines 2022, 10, 537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celaya, A.; Lopez de Lacalle, L.N.; Norberto, L.L.; Javier, C.F.; Lamikiz, A. Ultrasonic Assisted Turning of mild steels. Int. J. Mater. Prod. Technol. 2010, 37, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celaya, A.; López de Lacalle, L.N.; Norberto, L.L.; Javier, C.F.; Lamikiz, A. Application of ultrasonics as assistance in machining operations. In Ultrasonics: Theory, Techniques and Practical Applications; Ayabito, H., Katsukawa, M., Eds.; Nova Science Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 159–172. ISBN 978-1-62257-685-2. [Google Scholar]
- Chern, G.L.; Chang, Y.C. Using two-dimensional vibration cutting for micro-milling. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2006, 46, 659–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Ibrahim, R.; Cheng, K.; Chen, S.J. Experimental study on machinability improvement of hardened tool steel using two-dimensional vibration-assisted micro-end-milling. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2010, 50, 1115–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Zou, Y.H.; Qin, X.D.; Liu, J.; Feng, Q.; Ren, C.Z. Geometrical texture and surface integrity in helical milling and ultrasonic vibration helical milling of Ti-6Al-4V alloy. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2019, 278, 116494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, G.F.; Lu, Y.J.; Zhou, S.M.; Zhang, M.; He, X.; Zhang, F.H.; Chen, G.J. Experimental Study on Surface Integrity of Nickel-Based Superalloy in Ultrasonic Elliptical Vibration Cutting. Micromachines 2025, 16, 728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamoto, E.; Suzuki, N. Ultrasonic vibration diamond cutting and ultrasonic elliptical vibration cutting. Compr. Mater. Process. 2014, 11, 405–454. [Google Scholar]
- Tong, J.L.; Feng, Z.B.; Jiao, F.; Zhao, B. Study on tool wear characteristics in ultrasonic longitudinal-torsional composite milling of titanium alloy. Surf. Technol. 2019, 48, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suárez, A.; Veiga, F.; López de Lacalle, L.N.; Polvorosa, R.; Lutze, S.; Wretland, A. Effects of ultrasonics-assisted face milling on surface integrity and fatigue life of Ni-Alloy 718. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2016, 25, 5076–5086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Li, P.T.; Zhang, C.Y.; Wang, X.B. Influence of ultrasonic vibration direction on milling characteristics of TC4 titanium alloy. Acta Aeronaut. Astronaut. Sin. 2020, 41, 39–49. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, A.; He, Q.; Wang, X.; Zhao, B.; Ding, W.; Khan, A.M.; Hussain, S. Unraveling the influence of vibrations on material removal and surface quality in longitudinal ultrasonic vibration–assisted milling of Ti2AlNb intermetallic alloy. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2025, 136, 2507–2525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Huang, X.F.; Fu, Y.; Wang, Q.Y.; Tao, G.B.; Cao, H.J. Design and surface analysis in large-amplitude longitudinal ultrasonic vibration-assisted milling of TC4 titanium alloy under dry conditions. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2024, 133, 289–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, M.; Rodriguez, A.; Pereira, O.; Celaya, A.; Norberto, L.L.; Esparta, M. Axial-compliant tools for adaptive chamfering of sharp-edges: Characterisation and modelling. Eng. Sci. Technol.-Int. J.-Jestech. 2023, 41, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, C.H.; Li, C.C.; Li, C.P. Analysis of chip adhesion characteristics and optimization of process parameters in milling of Ti-6Al-4V titanium alloy. Tool Technol. 2025, 59, 7–11. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, X.; Li, L.; Li, L.L.; Zhao, J.H.; Sutherland, J.W. Parameter optimization of titanium alloy considering energy efficiency and tool wear based on RBFNN-MOPSO algorithm in milling. J. Manuf. Process. 2024, 122, 97–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.P.; Liu, C.F.; Tong, H.; Wang, D.H. Optimization of process parameters for minimizing the temperature field of high-speed milling of titanium alloy thin-walled parts. Int. J. Interact. Des. Manuf. (IJIDeM) 2024, 19, 2415–2430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.Y.; Ren, X.X. Analysis of milling force and optimization of cutting parameters for titanium alloy based on high-speed machining. J. Liaoning Inst. Sci. Technol. 2024, 26, 28–33. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.Q.Y.; Guo, H.; Qin, H. Optimization and application of milling process parameters for titanium alloy based on orthogonal experiment method. Tool Technol. 2023, 57, 126–129. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, M.H.; Li, S.C.; Hu, Y.T.; Li, Y.Q.; Popov, E. Study on parameter optimization of noise-vibration-force-metal removal rate in TC4 titanium alloy milling. J. Vib. Control. 2023, 29, 5698–5712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.J.; Yang, J.T.; Jiao, F.; Wang, X.B.; Liu, H.L.; Lv, Y.W. Mechanical force modeling and experimental verification of ultrasonic vibration assisted milling of high volume fraction SiCp/Al. J. Alloys Compd. 2025, 1016, 178870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Z.W.; Shan, C.W.; Zhang, M.H.; Liu, W.G.; Cui, M.C.; Luo, M. Machinability of elliptical ultrasonic vibration milling γ-TiAl: Chip formation, edge breakage, and subsurface layer deformation. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2025, 38, 103096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.Y.; Zou, P.; Zhou, L.; Wang, X. Research on the machining mechanism of AISI 304 ultrasonic vibration assisted grinding. Appl. Acoust. 2023, 214, 109712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.J.; Jiang, X.G.; Han, X.; Gao, Z.; Zhang, D.Y. Effects of rotary ultrasonic elliptical machining for side milling on the surface integrity of Ti-6Al-4V. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2019, 101, 1451–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.D.; Liu, X.F. PCD Tool Ultrasonic Vibration-Assisted Milling of TC4 Titanium Alloy: Simulation and Experiment. Manuf. Technol. Mach. Tools 2024, 9, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.H.; Wang, Y.N.; Chen, Z. Study on high-quality and high-efficiency milling collaborative optimization based on response surface modeling and fuzzy grey relational analysis. Mach. Des. 2023, 40, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tibakh, I.; Yallese, M.A.; Belhadi, S.; Kaddeche, M. Multi-response optimisation during face milling of polyoxymethylene copolymer using grey relational analysis and data envelopment analysis based ranking coupled with the Taguchi approach. Adv. Mater. Process. Technol. 2025, 11, 681–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, P.; Wins, K.L.D.; Dhas, D.S.E.J.; Beatrice, B.A.; George, P. A grey relational-Taguchi analysis on high-speed milling of duplex and super duplex stainless steels used in chemical tankers. Int. J. Interact. Des. Manuf. (IJIDeM) 2024, 19, 5153–5170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Element | Ti | Al | V | Fe | C | N | H | O |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wt (%) | 51.75 | 17 | 5.15 | 2.93 | 1.07 | 0.45 | 0.042 | 0.21 |
| Property | Elastic Modulus (GPa) | Poisson’s Ratio | Hardness (HV) | Yield Strength (MPa) | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Elongation (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TC4 | 110 | 0.34 | 310 | 830 | 895 | 10 |
| Level | Spindle Speed n (r/min) | Cutting Depth ap (mm) | Feed Rate vf (mm/min) | Amplitude A (μm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1500 | 0.1 | 50 | 4 |
| 2 | 3000 | 0.2 | 100 | 6 |
| 3 | 4500 | 0.3 | 150 | 8 |
| 4 | 6000 | 0.4 | 200 | 10 |
| No. | Experimental Parameters | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spindle Speed n (r/min) | Cutting Depth ap (mm) | Feed Rate vf mm/min | Amplitude A (μm) | |
| k1 | 0.48 | 0.32 | 0.32 | 0.38 |
| k2 | 0.37 | 0.33 | 0.33 | 0.33 |
| k3 | 0.32 | 0.39 | 0.43 | 0.36 |
| k4 | 0.31 | 0.44 | 0.39 | 0.41 |
| r | −0.18 | −0.12 | −0.1 | −0.08 |
| No. | Experimental Parameters | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spindle Speed n (r/min) | Cutting Depth ap (mm) | Feed Rate vf mm/min | Amplitude A (μm) | |
| k1 | 4.777 | 4.518 | 3.963 | 3.974 |
| k2 | 2.559 | 5.012 | 3.981 | 4.842 |
| k3 | 2.969 | 4.103 | 3.149 | 4.391 |
| k4 | 5.350 | 2.022 | 4.562 | 2.449 |
| r | 2.791 | 2.990 | 1.413 | 2.393 |
| No. | Experimental Parameters | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spindle Speed n (r/min) | Cutting Depth ap (mm) | Feed Rate vf mm/min | Amplitude A (μm) | |
| k1 | 113.36 | 159.6 | 170.01 | 169.82 |
| k2 | 132.03 | 193.07 | 155.54 | 177.03 |
| k3 | 198.83 | 145.86 | 173.5 | 155.34 |
| k4 | 217.5 | 163.18 | 162.66 | 159.52 |
| r | −104.14 | −47.21 | −17.97 | −21.68 |
| Serial Number | Comparison Sequence | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sa | Temperature | FX | FY | FZ | |
| 1 | 0.73512 | 1.00000 | 0.95634 | 0.96269 | 0.42962 |
| 2 | 0.61905 | 0.83564 | 0.70895 | 0.75363 | 0.00000 |
| 3 | 0.00000 | 0.84609 | 0.29172 | 0.35213 | 0.44076 |
| 4 | 0.10119 | 0.71560 | 0.00000 | 0.00000 | 0.80306 |
| 5 | 0.85417 | 0.72661 | 0.97404 | 0.98024 | 0.60245 |
| 6 | 0.91369 | 0.50400 | 0.94585 | 0.99563 | 0.73892 |
| 7 | 0.67560 | 0.83442 | 0.55698 | 0.66132 | 0.41787 |
| 8 | 0.30952 | 0.08090 | 0.46189 | 0.58507 | 1.00000 |
| 9 | 0.82738 | 0.43836 | 0.96011 | 0.98141 | 0.67650 |
| 10 | 0.74107 | 0.55731 | 0.74670 | 0.85084 | 0.46610 |
| 11 | 0.98214 | 0.42848 | 0.87610 | 0.98105 | 0.55006 |
| 12 | 0.90476 | 0.36458 | 0.69129 | 0.82824 | 0.86585 |
| 13 | 1.00000 | 0.36208 | 1.00000 | 1.00000 | 0.09155 |
| 14 | 0.97321 | 0.00000 | 0.86041 | 0.92942 | 0.35337 |
| 15 | 0.88095 | 0.67664 | 0.73822 | 0.92732 | 0.59486 |
| 16 | 0.64881 | 0.39855 | 0.86041 | 0.92942 | 0.35337 |
| Serial Number | Difference Series | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sa | Temperature | FX | FY | FZ | |
| 1 | 0.265 | 0.000 | 0.042 | 0.037 | 0.570 |
| 2 | 0.309 | 0.167 | 0.207 | 0.234 | 0.000 |
| 3 | 0.000 | 0.153 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.439 |
| 4 | 0.051 | 0.285 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.803 |
| 5 | 0.427 | 0.274 | 0.286 | 0.302 | 0.600 |
| 6 | 0.456 | 0.500 | 0.268 | 0.324 | 0.737 |
| 7 | 0.338 | 0.166 | 0.171 | 0.160 | 0.417 |
| 8 | 0.155 | 0.721 | 0.113 | 0.138 | 0.997 |
| 9 | 0.413 | 0.000 | 0.303 | 0.308 | 0.674 |
| 10 | 0.371 | 0.400 | 0.218 | 0.249 | 0.465 |
| 11 | 0.492 | 0.000 | 0.244 | 0.243 | 0.549 |
| 12 | 0.453 | 0.000 | 0.183 | 0.172 | 0.863 |
| 13 | 0.505 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.091 |
| 14 | 0.486 | 0.000 | 0.251 | 0.245 | 0.354 |
| 15 | 0.440 | 0.326 | 0.228 | 0.244 | 0.594 |
| 16 | 0.324 | 0.000 | 0.251 | 0.245 | 0.354 |
| Serial Number | Grey Correlation Coefficient | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sa | Temp | FX | FY | FZ | Relatedness | Rank | |
| 1 | 0.653 | 1.000 | 0.922 | 0.931 | 0.467 | 0.795 | 3 |
| 2 | 0.617 | 0.749 | 0.707 | 0.681 | 1.000 | 0.751 | 5 |
| 3 | 1.000 | 0.765 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.531 | 0.859 | 2 |
| 4 | 0.907 | 0.636 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.383 | 0.785 | 4 |
| 5 | 0.539 | 0.645 | 0.635 | 0.623 | 0.454 | 0.579 | 15 |
| 6 | 0.522 | 0.499 | 0.65 | 0.606 | 0.404 | 0.536 | 16 |
| 7 | 0.596 | 0.75 | 0.745 | 0.757 | 0.544 | 0.678 | 8 |
| 8 | 0.763 | 0.409 | 0.815 | 0.783 | 0.333 | 0.621 | 12 |
| 9 | 0.547 | 1.000 | 0.622 | 0.618 | 0.425 | 0.642 | 11 |
| 10 | 0.573 | 0.555 | 0.696 | 0.667 | 0.518 | 0.602 | 13 |
| 11 | 0.503 | 1.000 | 0.671 | 0.672 | 0.476 | 0.664 | 10 |
| 12 | 0.524 | 1.000 | 0.731 | 0.744 | 0.366 | 0.673 | 8 |
| 13 | 0.497 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.846 | 0.869 | 1 |
| 14 | 0.506 | 1.000 | 0.665 | 0.67 | 0.585 | 0.685 | 7 |
| 15 | 0.531 | 0.605 | 0.686 | 0.671 | 0.456 | 0.590 | 14 |
| 16 | 0.606 | 1.000 | 0.665 | 0.670 | 0.585 | 0.705 | 6 |
| Spindle Speed n (r/min) | Cutting Depth ap (mm) | Feed Rate vf (mm/min) | Amplitude A (μm) | Surface Roughness Sa(μm) | Cutting Temperature (°C) | FX (N) | FY (N) | FZ (N) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6000 | 0.2 | 200 | 6 | 0.268 | 255.39 | 5.2 | 7.9 | 6.4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, G.; Lu, Y.; Zhou, S.; He, X.; Zhang, F.; Zhu, P.; Wang, M.; Tan, T.; Chen, G. Multi-Objective Optimization of Surface Roughness, Cutting Force, and Temperature in Ultrasonic-Vibration-Assisted Milling of Titanium Alloy. Micromachines 2025, 16, 936. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16080936
Hu G, Lu Y, Zhou S, He X, Zhang F, Zhu P, Wang M, Tan T, Chen G. Multi-Objective Optimization of Surface Roughness, Cutting Force, and Temperature in Ultrasonic-Vibration-Assisted Milling of Titanium Alloy. Micromachines. 2025; 16(8):936. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16080936
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Gaofeng, Yanjie Lu, Shengming Zhou, Xin He, Fenghui Zhang, Pengchao Zhu, Mingshang Wang, Taowei Tan, and Guangjun Chen. 2025. "Multi-Objective Optimization of Surface Roughness, Cutting Force, and Temperature in Ultrasonic-Vibration-Assisted Milling of Titanium Alloy" Micromachines 16, no. 8: 936. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16080936
APA StyleHu, G., Lu, Y., Zhou, S., He, X., Zhang, F., Zhu, P., Wang, M., Tan, T., & Chen, G. (2025). Multi-Objective Optimization of Surface Roughness, Cutting Force, and Temperature in Ultrasonic-Vibration-Assisted Milling of Titanium Alloy. Micromachines, 16(8), 936. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16080936






