Study of the Sensitivity of DC Arc Temperature Field, Pressure Field, and Potential to Process Parameters
Abstract
1. Introduction
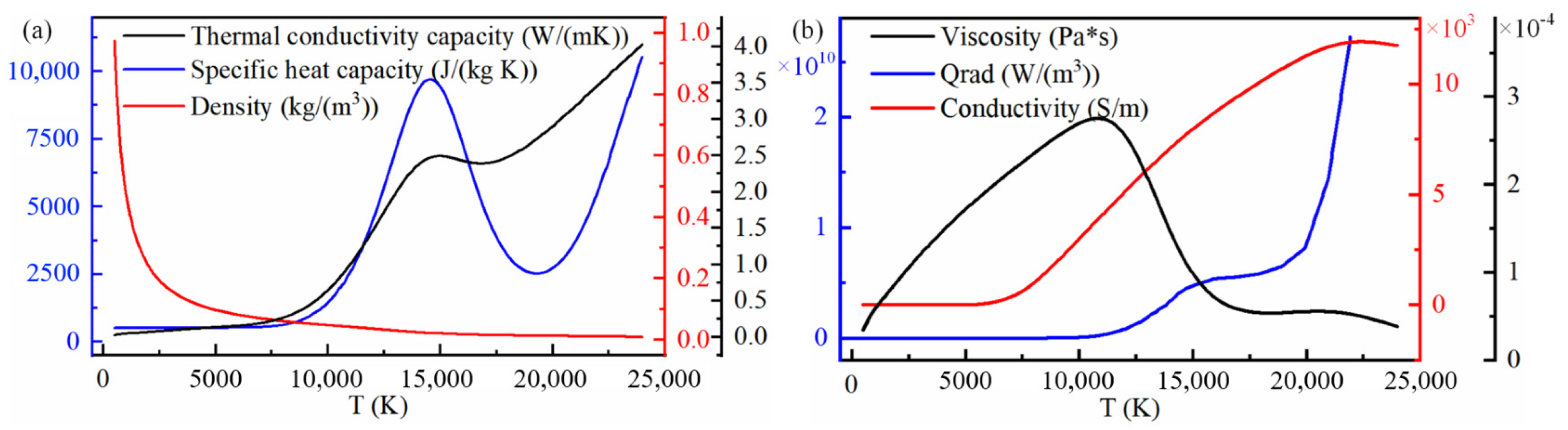
2. Numerical Model
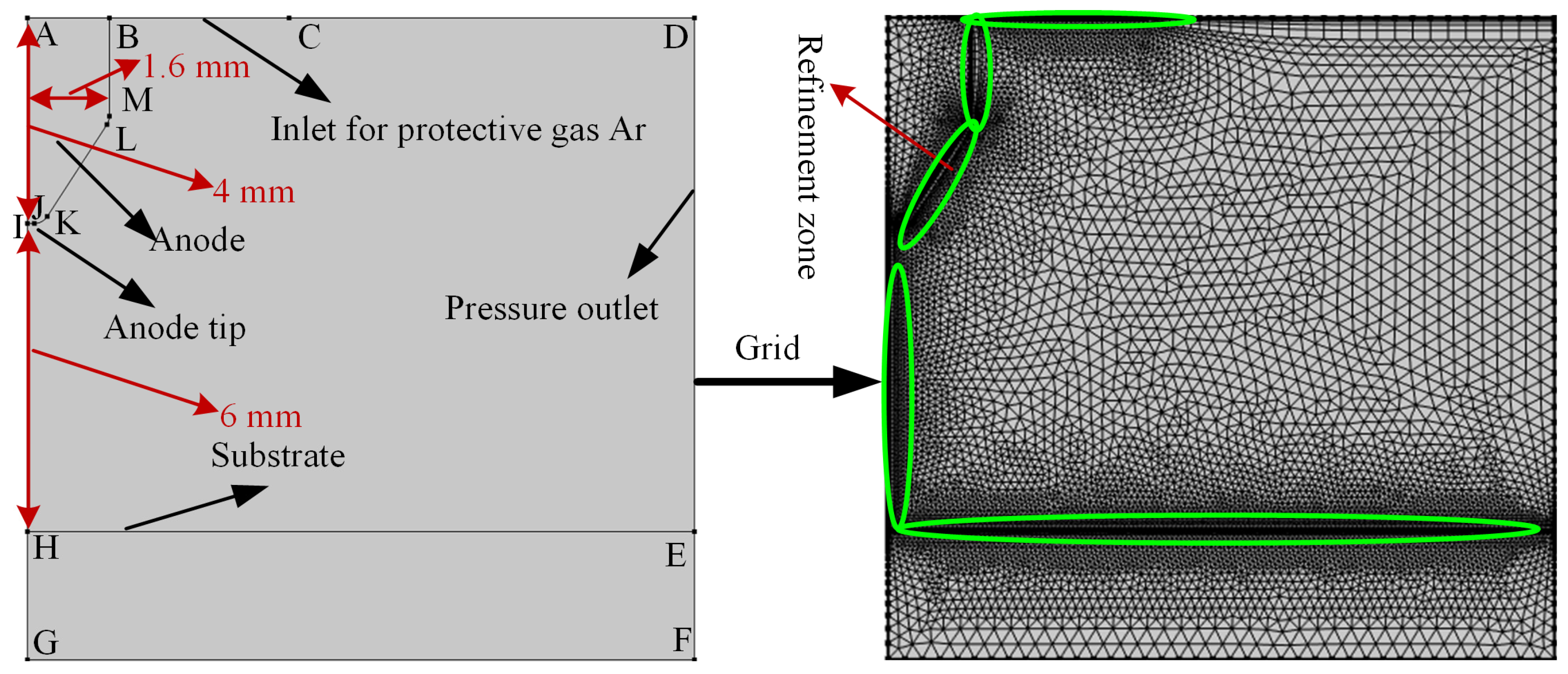
2.1. Modelling and Assumptions
- (1)
- The arc is in a steady state and is two-dimensional axisymmetric;
- (2)
- The effect of the anode surface state on the arc is not considered;
- (3)
- The arc space plasma is locally in thermal equilibrium;
- (4)
- The arc iso-discrete flow state is laminar;
- (5)
- The external environment is standard atmospheric pressure, argon each physical property is only a function of temperature;
- (6)
- The tungsten electrode tip current density is uniformly distributed.
2.2. Control Equations
2.3. Boundary Condition
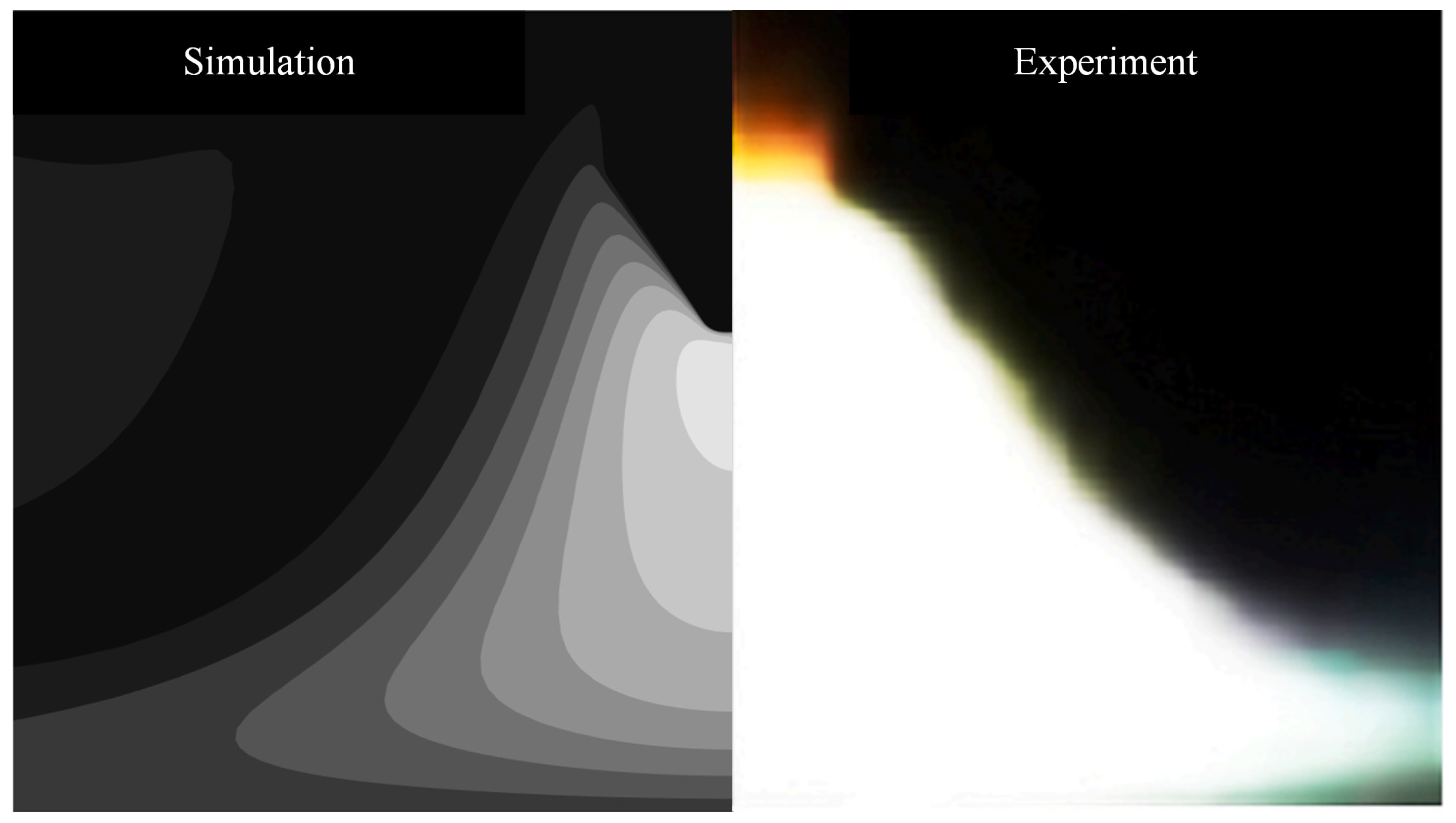
3. Empirical Verification
4. Arc Numerical Calculation Results
4.1. Characterisation of the Effect of Current on Potential, Temperature and Voltage Fields
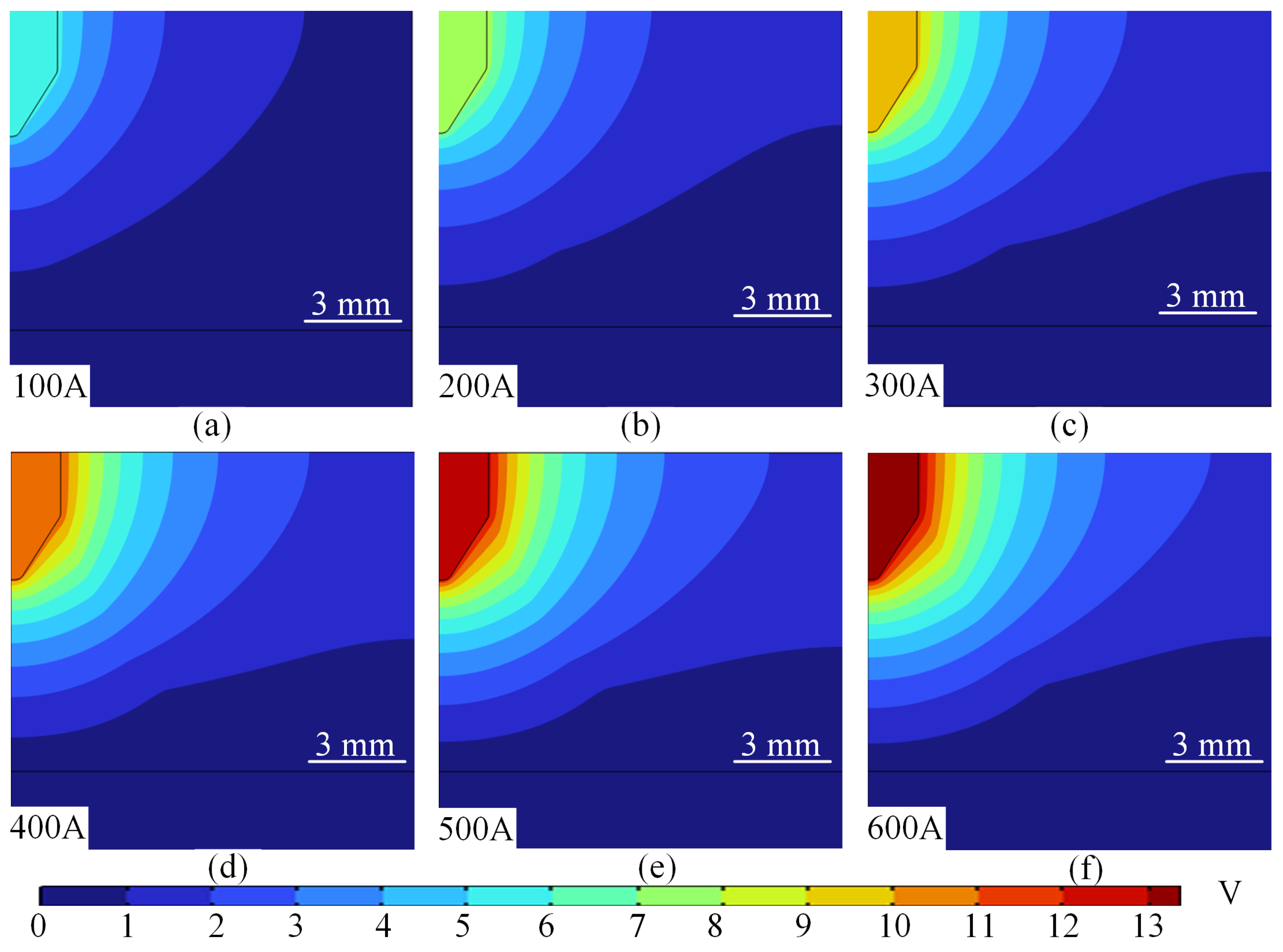
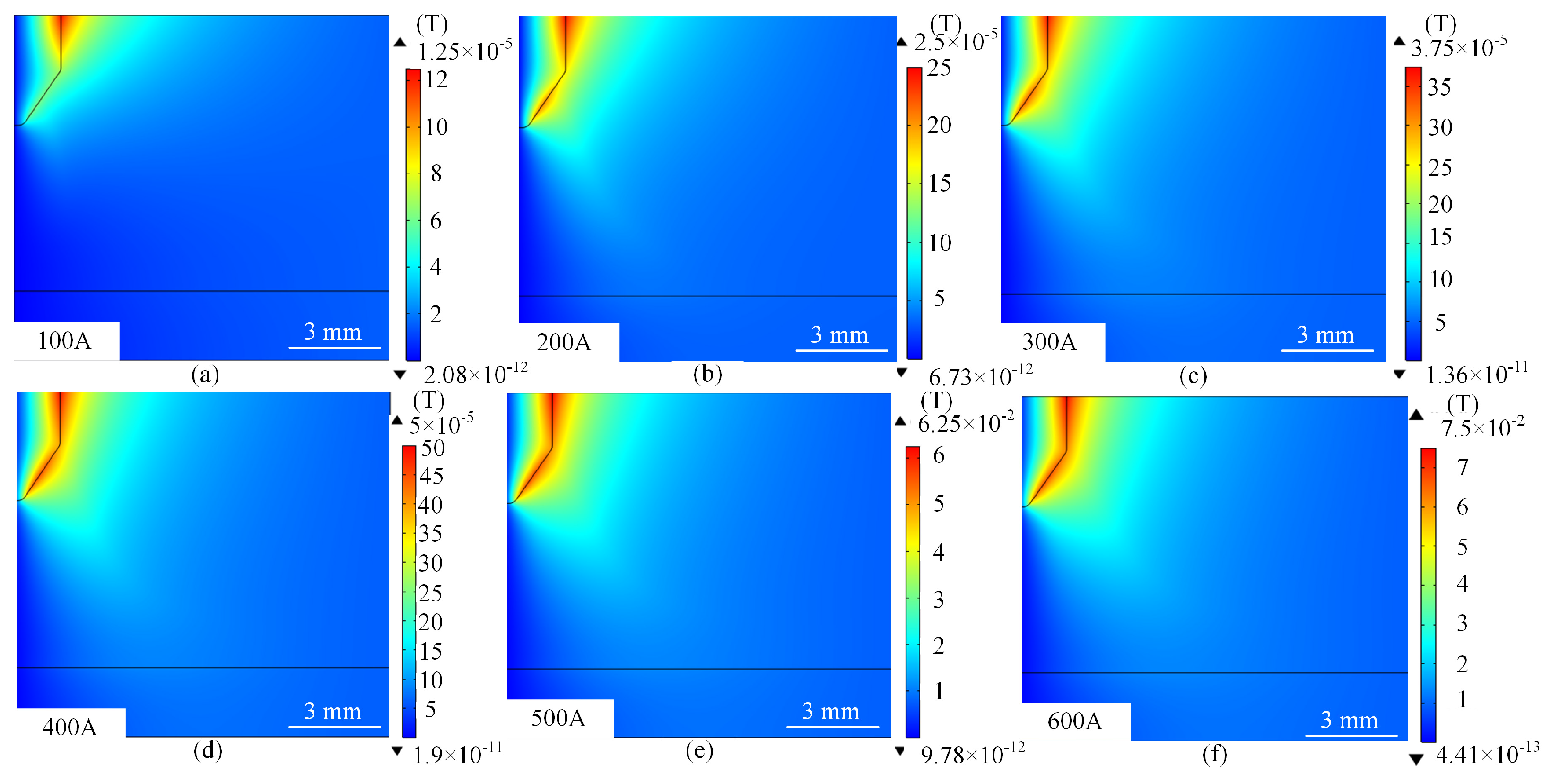
4.1.1. Characterisation of the Effect of Current on the Distribution of the Potential Field
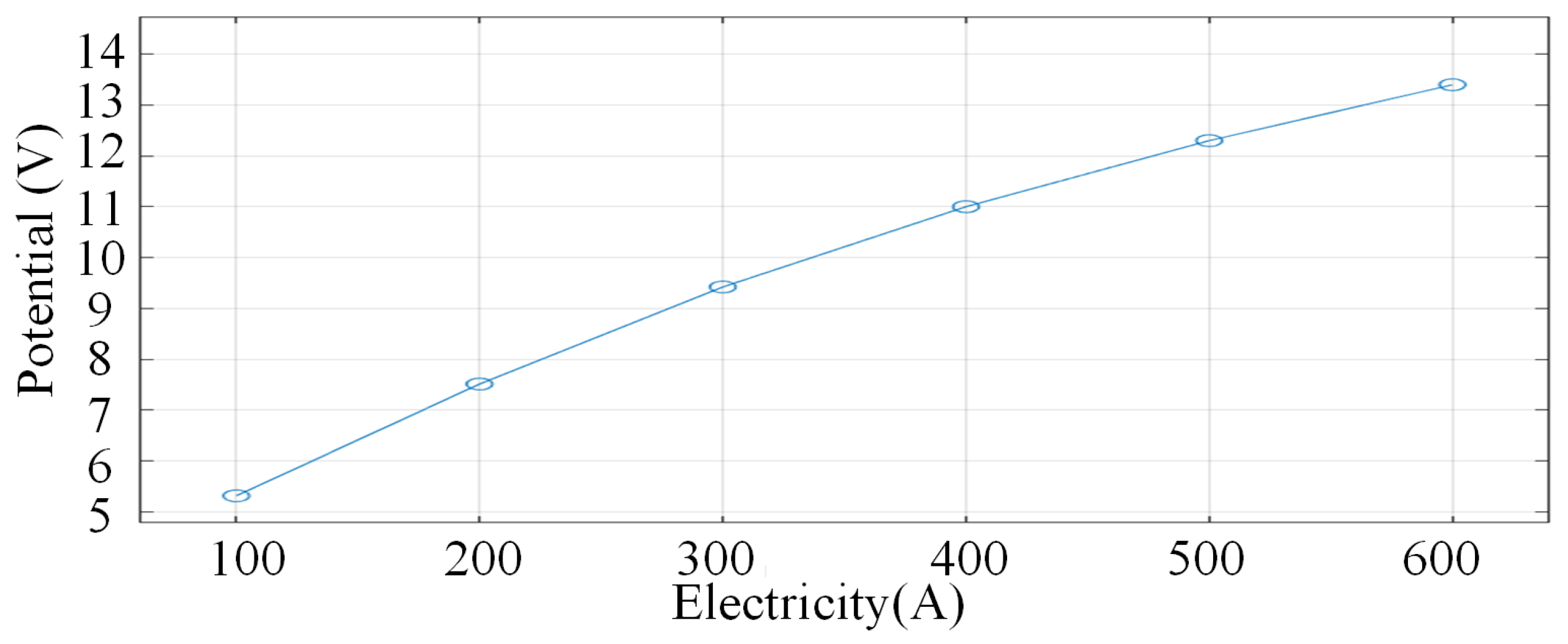
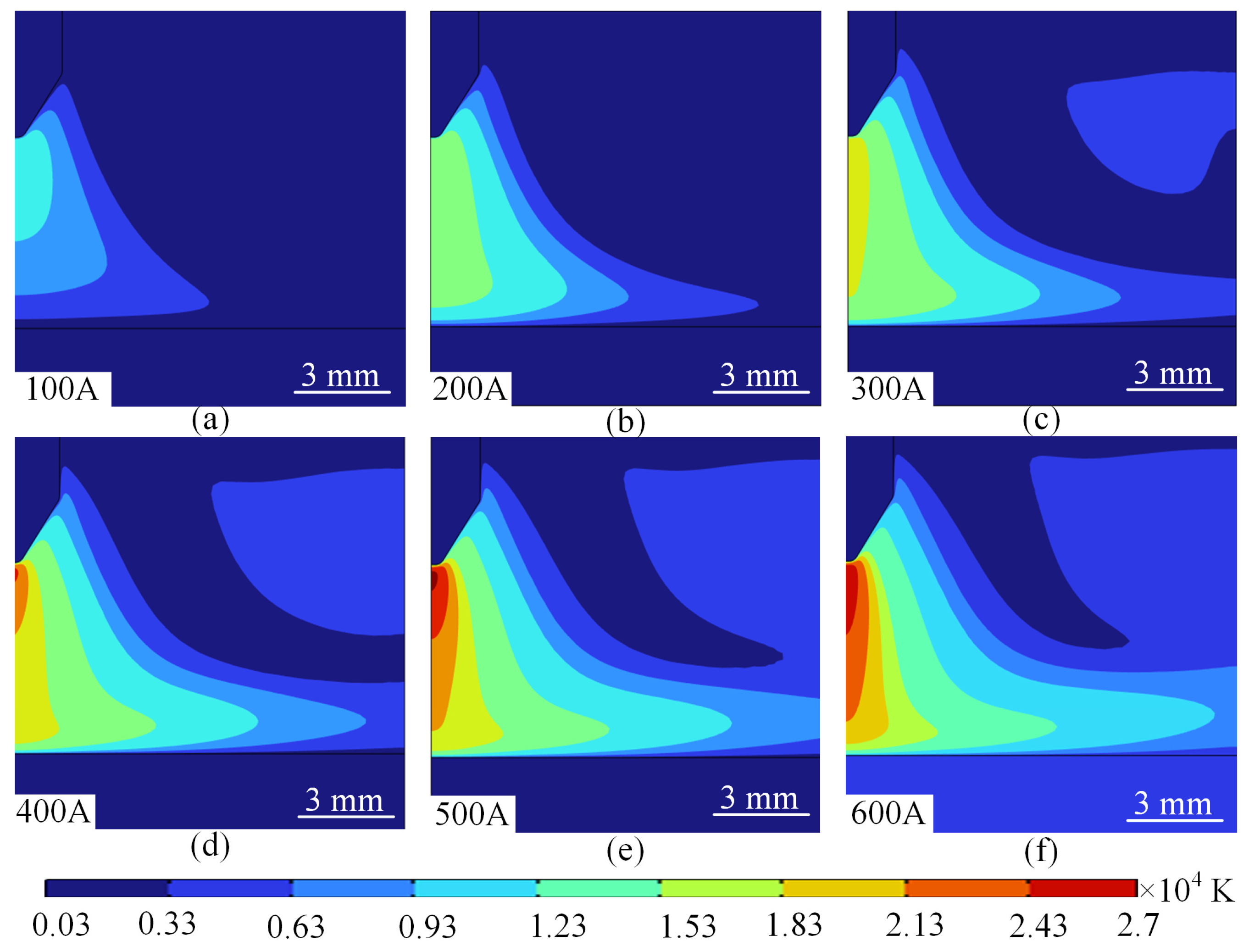
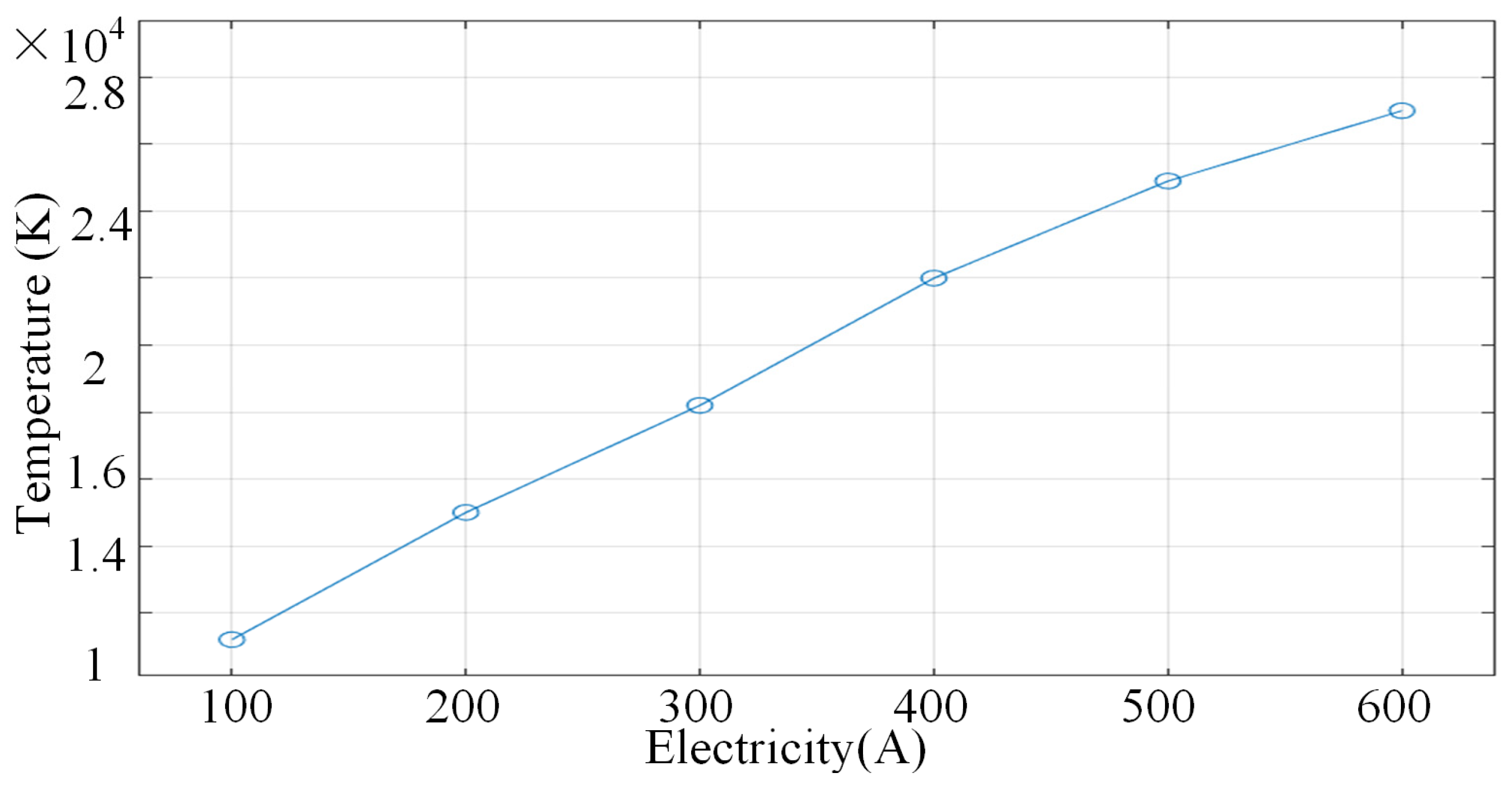
4.1.2. Characterisation of the Effect of Current on the Temperature Field Distribution
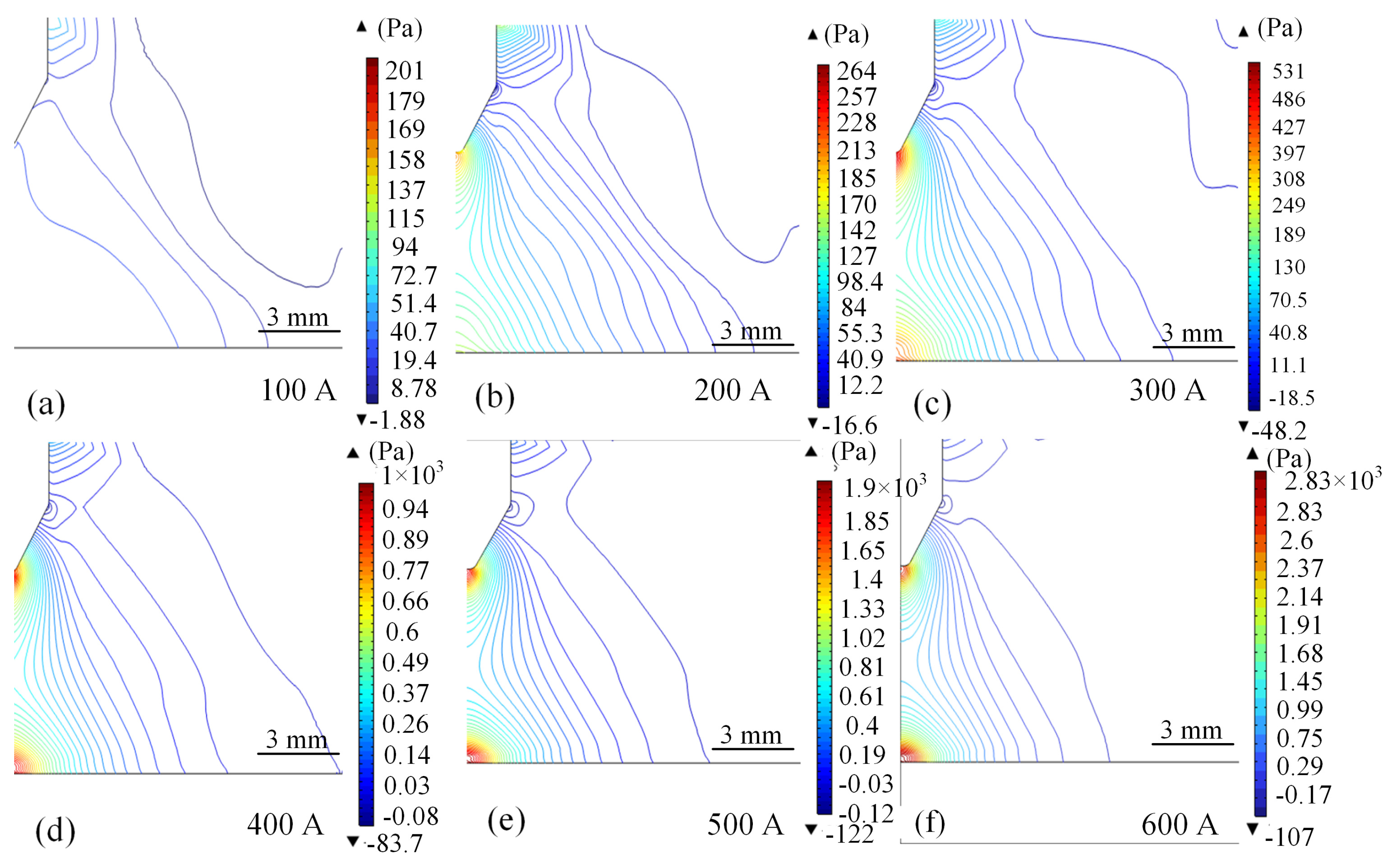
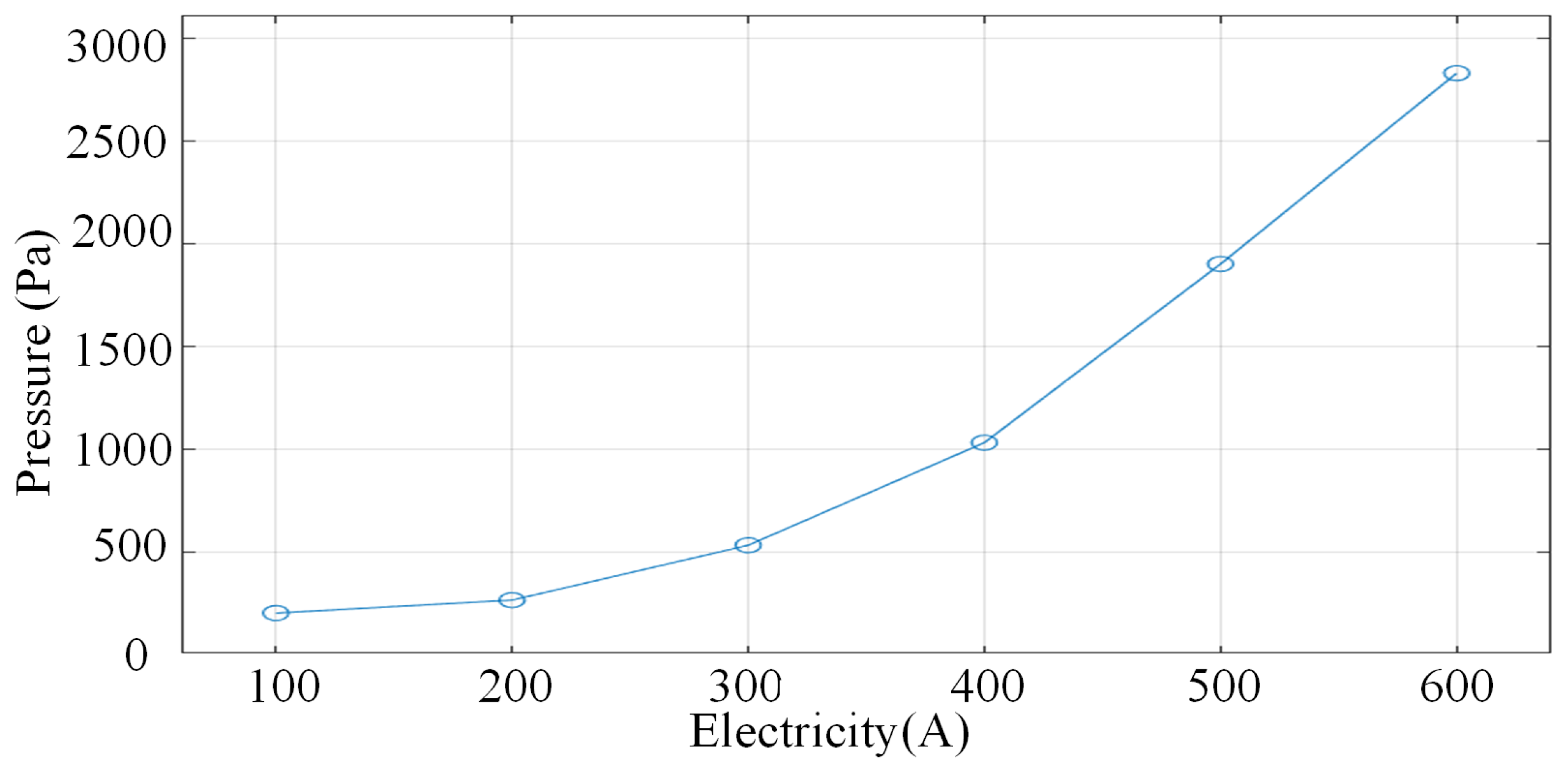
4.1.3. Characterisation of the Effect of Current on the Pressure Field Distribution
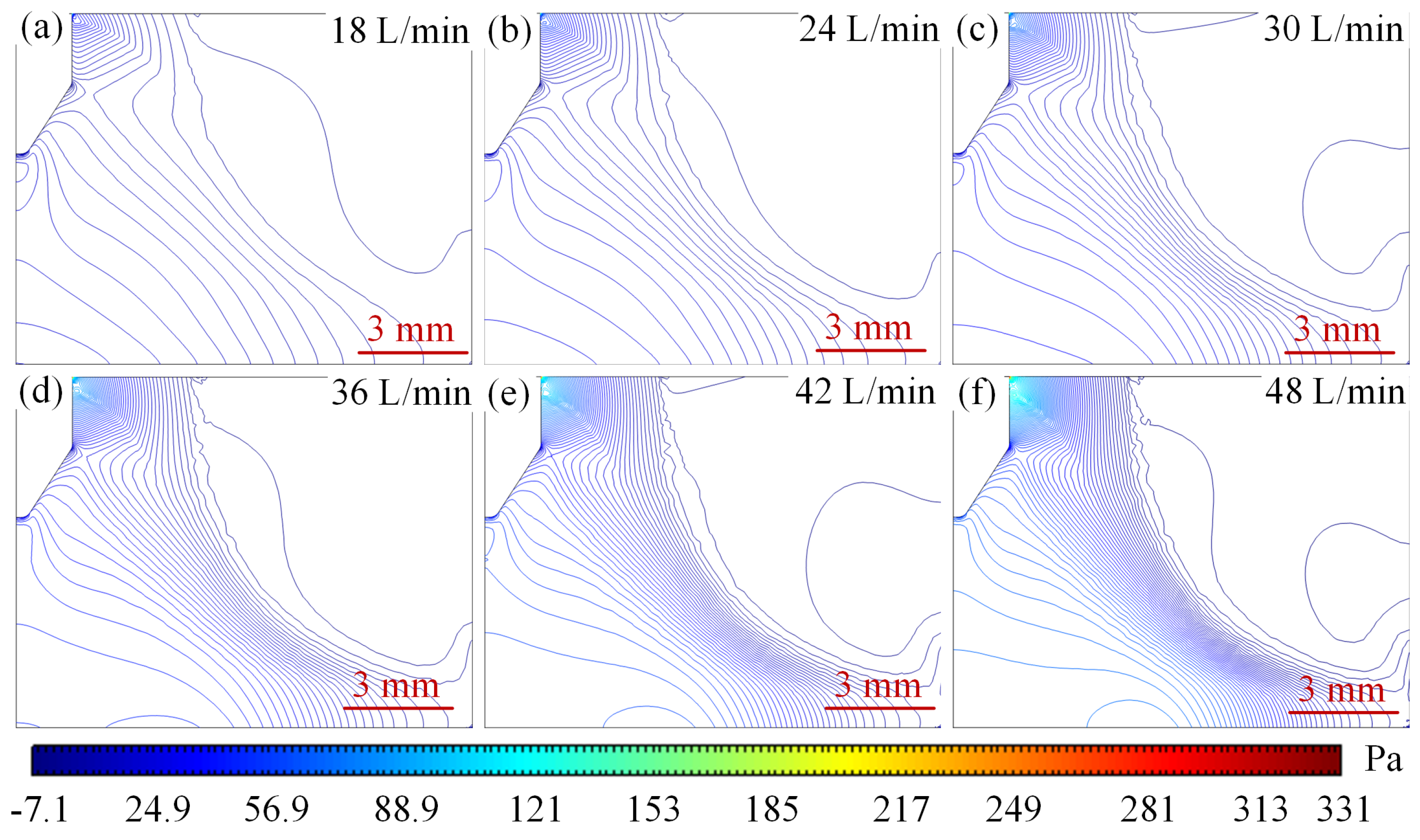
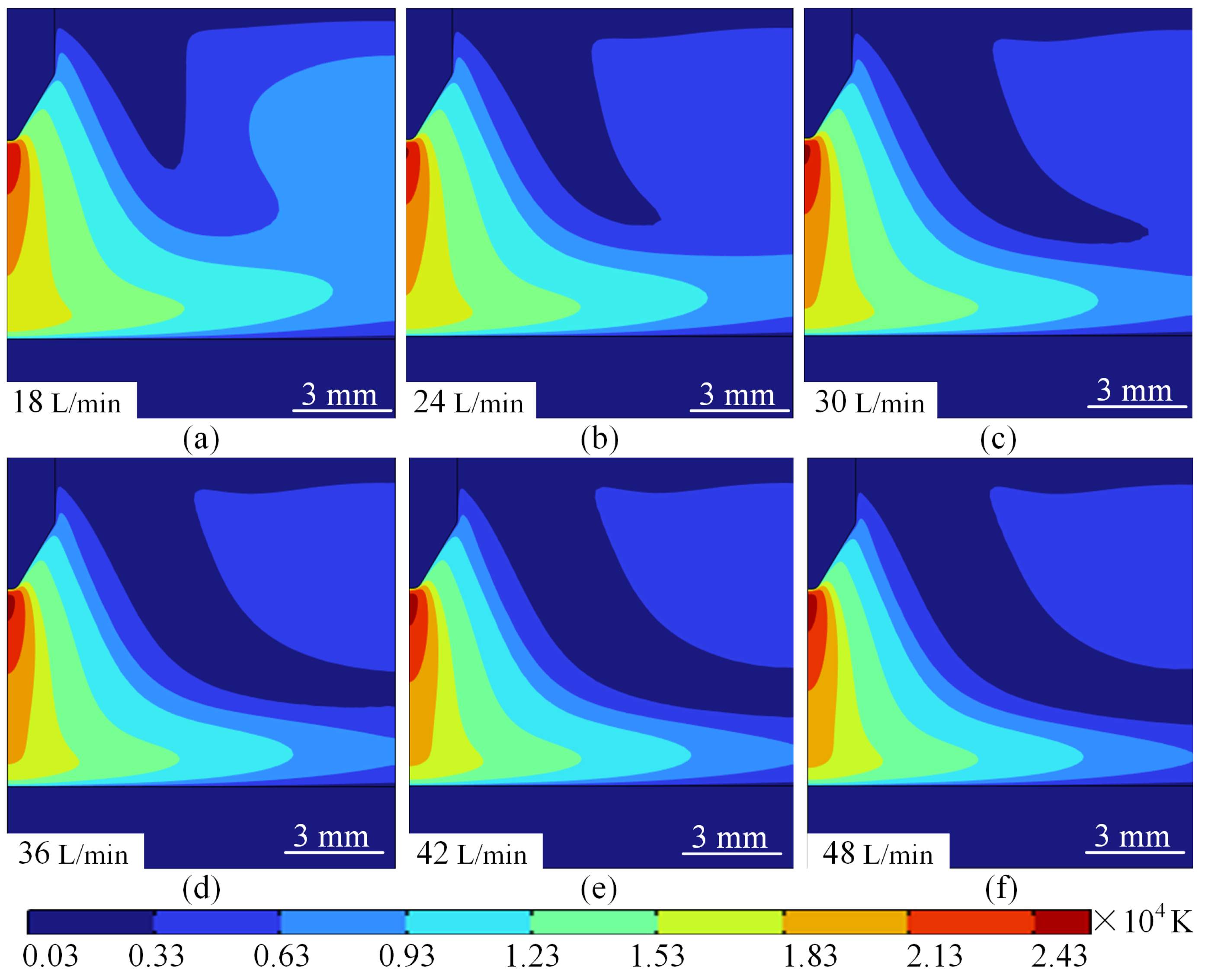
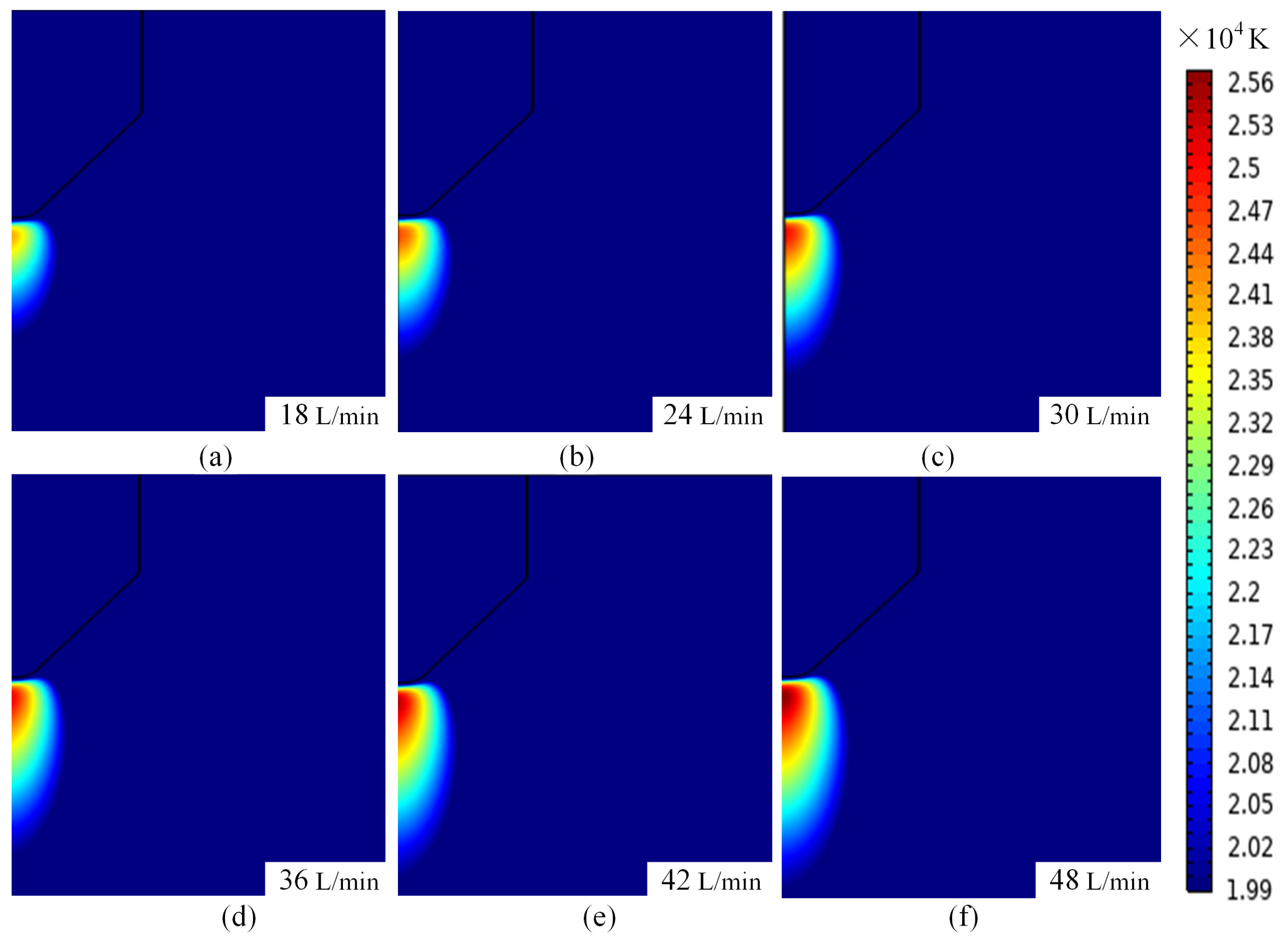
4.2. Characterisation of the Effect of Argon Flow Rate on the Physical Field Distribution
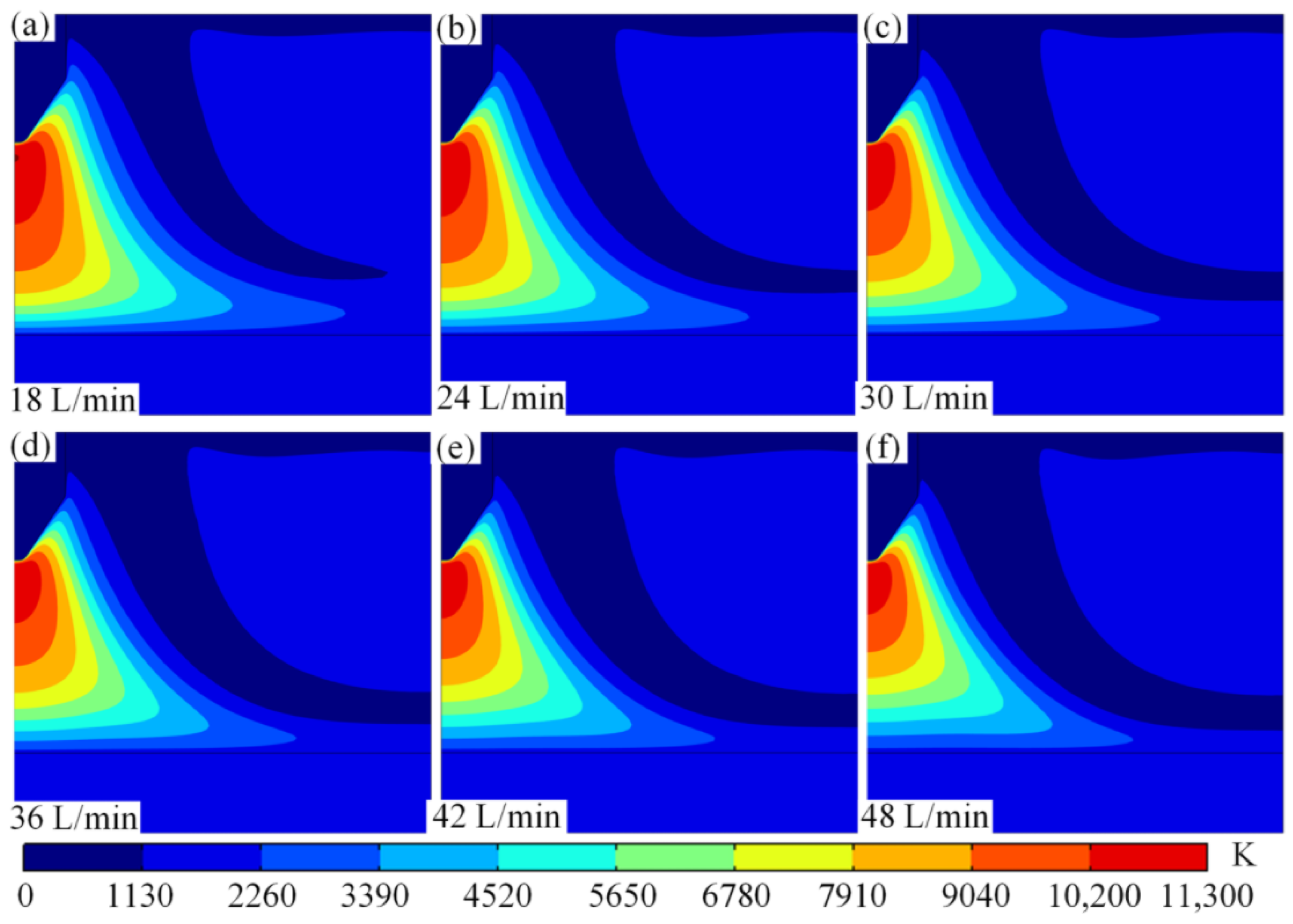
4.2.1. Effect of Argon Flow Rate on Temperature Field Distribution
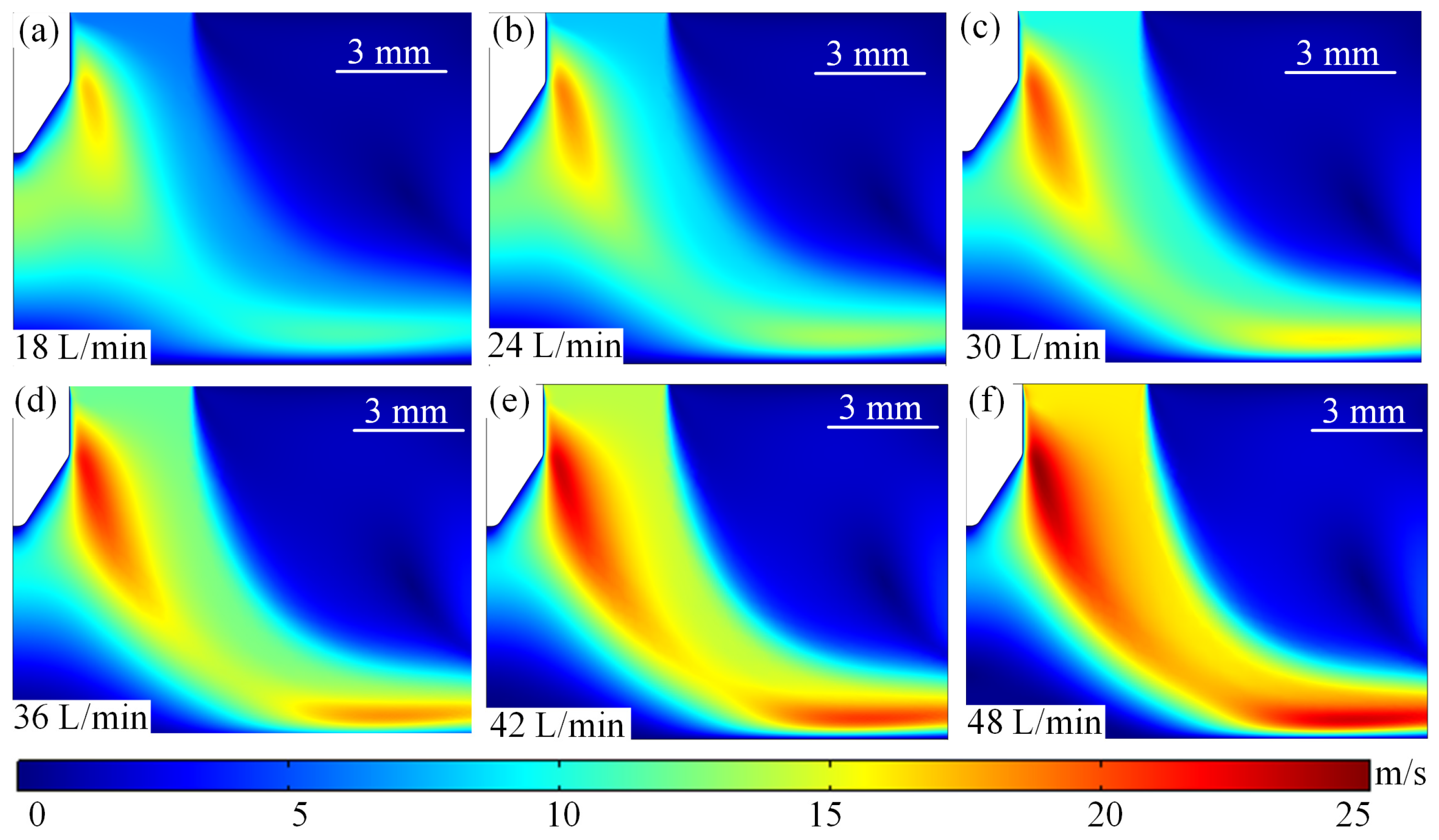
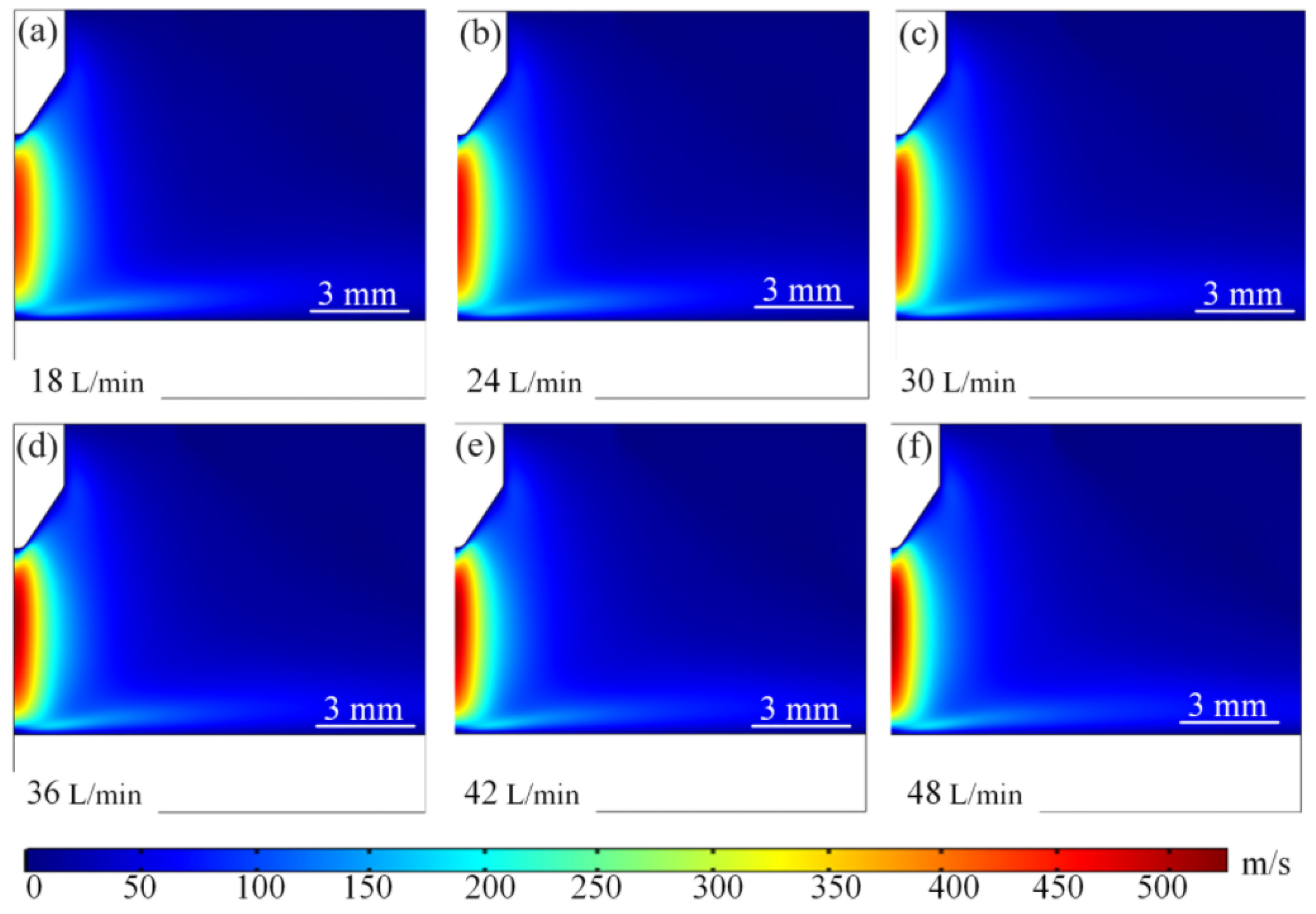
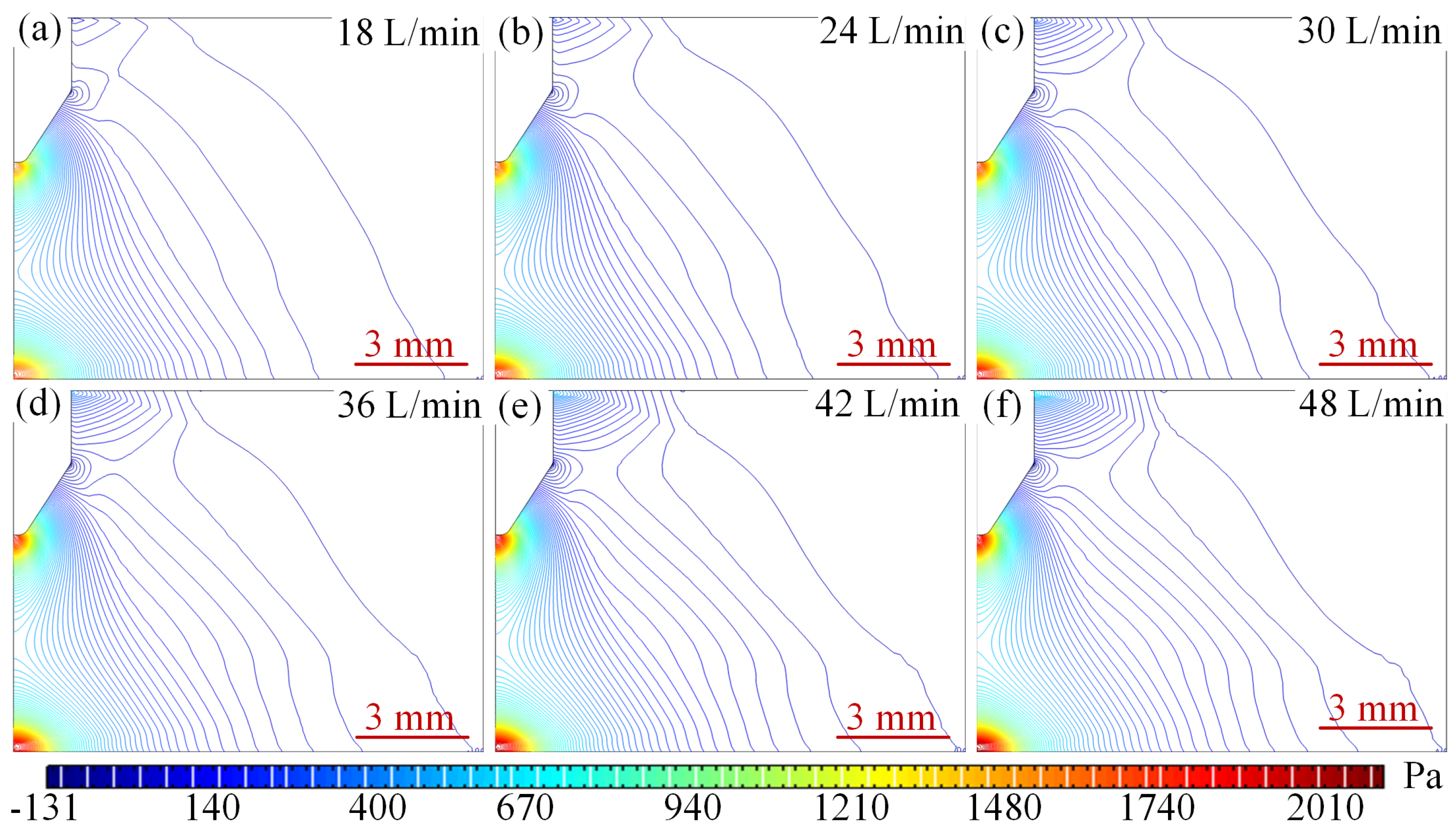
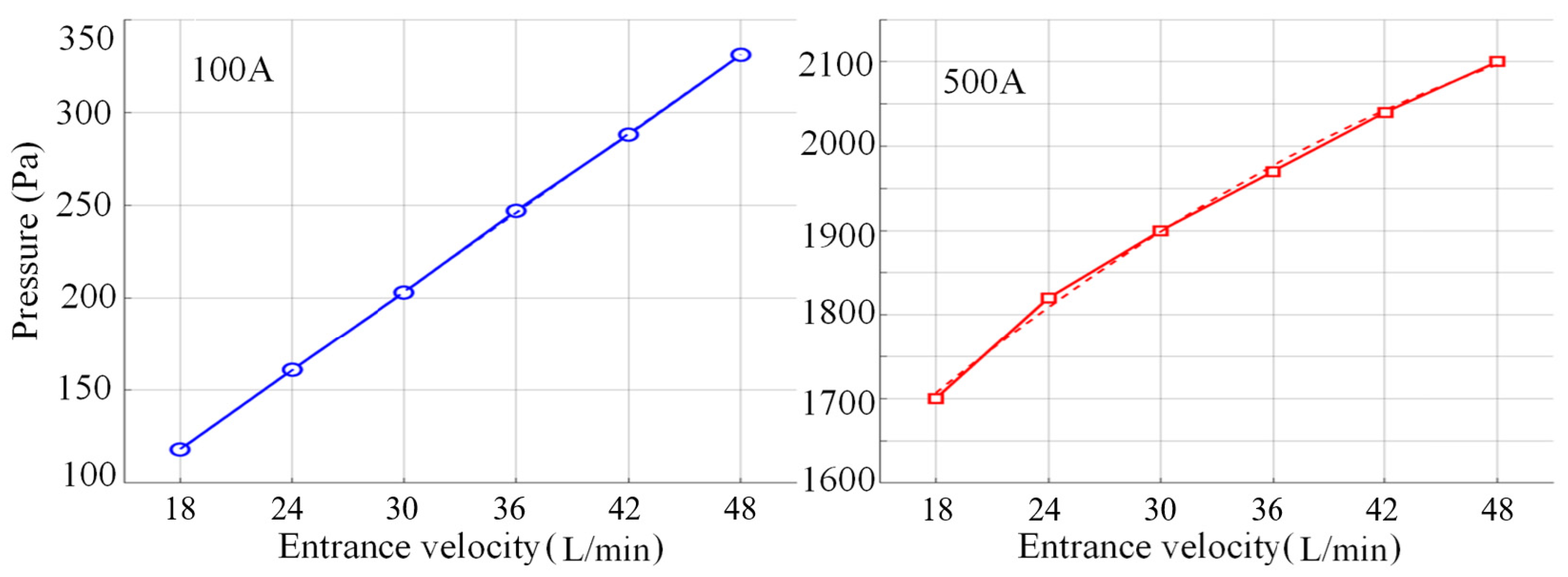
4.2.2. Effect of Argon Flow Rate on Pressure Field Distribution
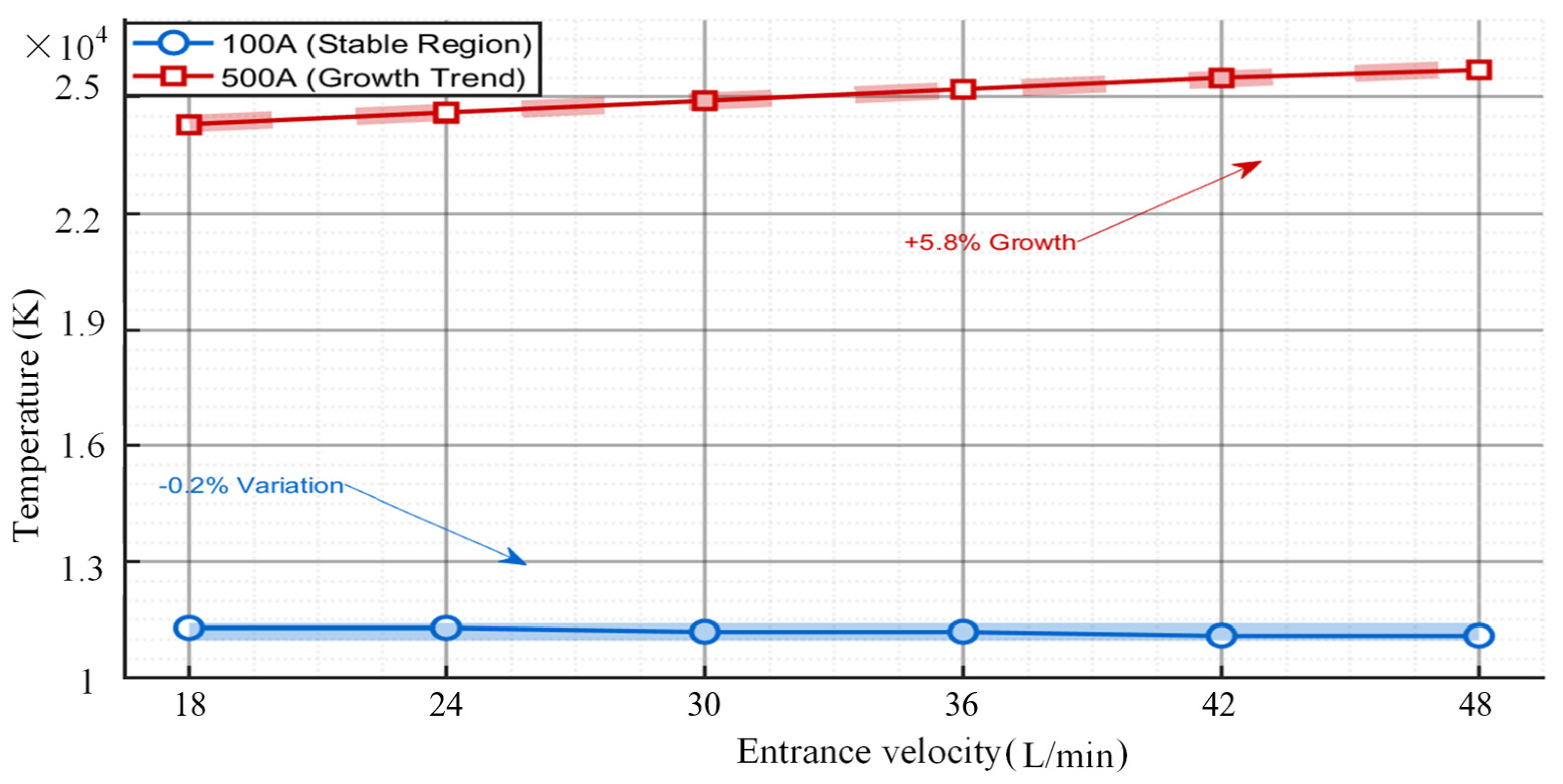
4.3. Comparison of Flow Velocity Sensitivity Under Different Currents and Its Guidance for Practical Applications
4.3.1. Effect of Flow Rate Sensitivity on Temperature Field Distribution Characteristics at Different Current Intensities
4.3.2. Flow Velocity Sensitivity to Pressure Field Distribution Characteristics at Different Current Intensities
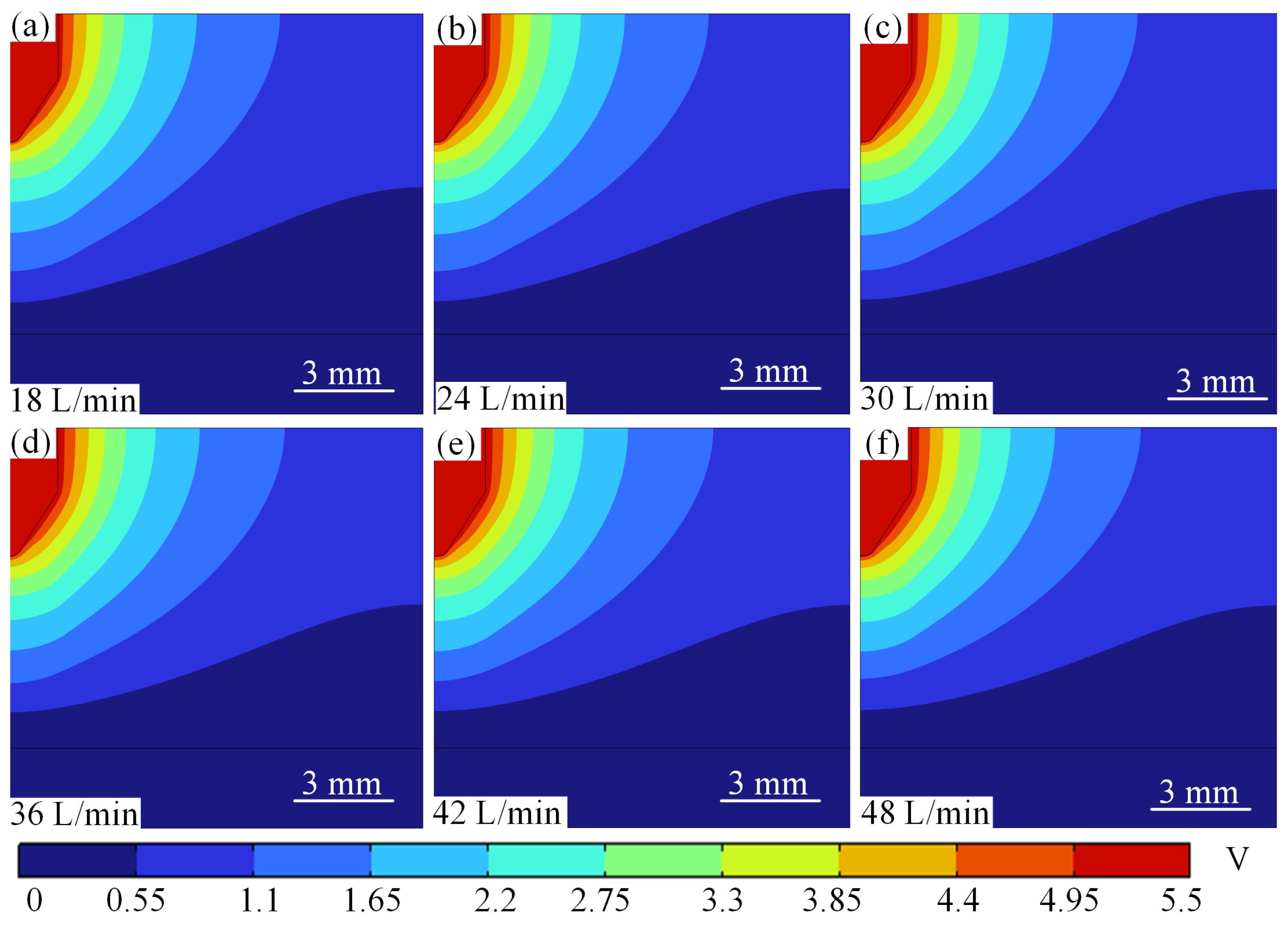
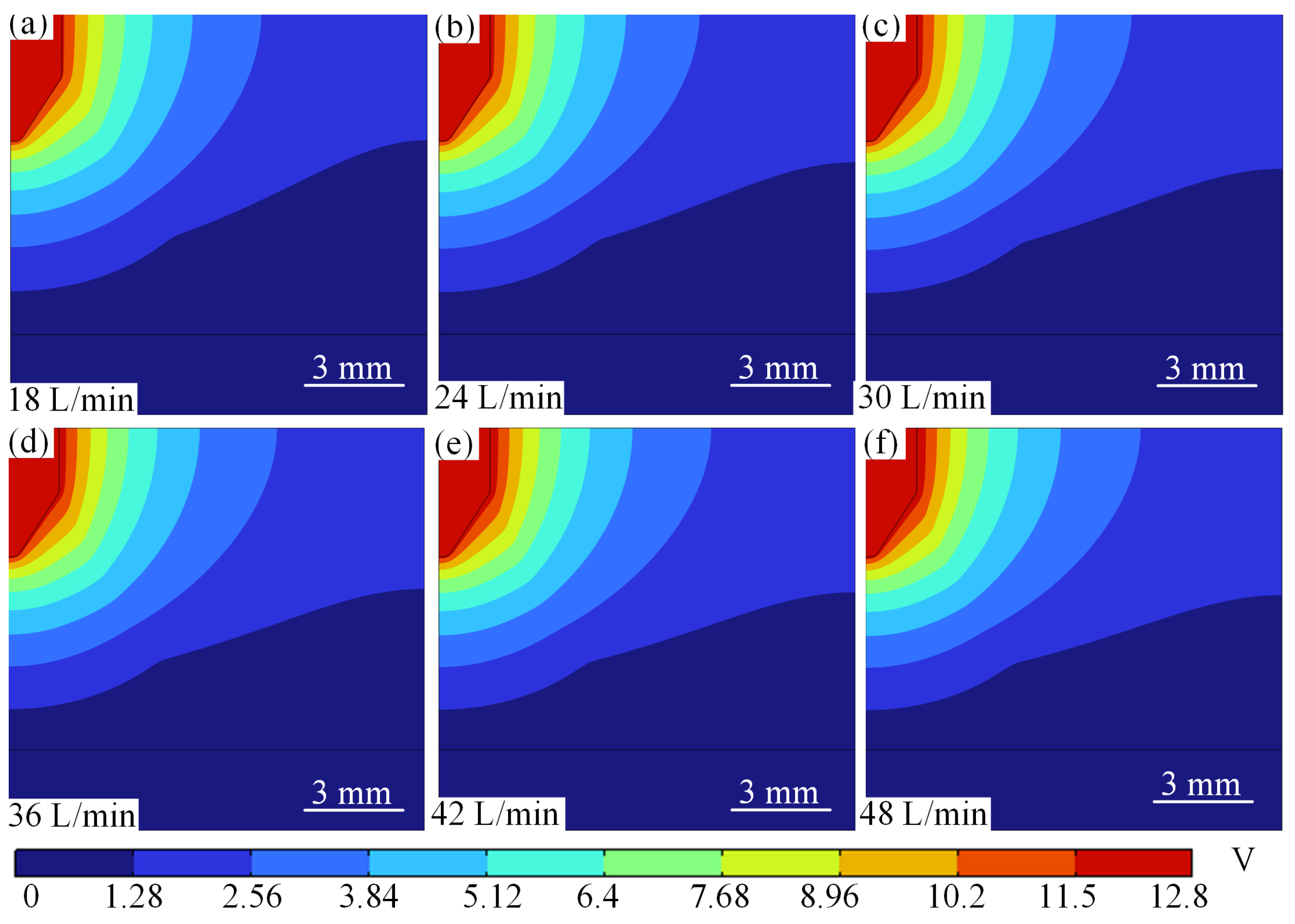
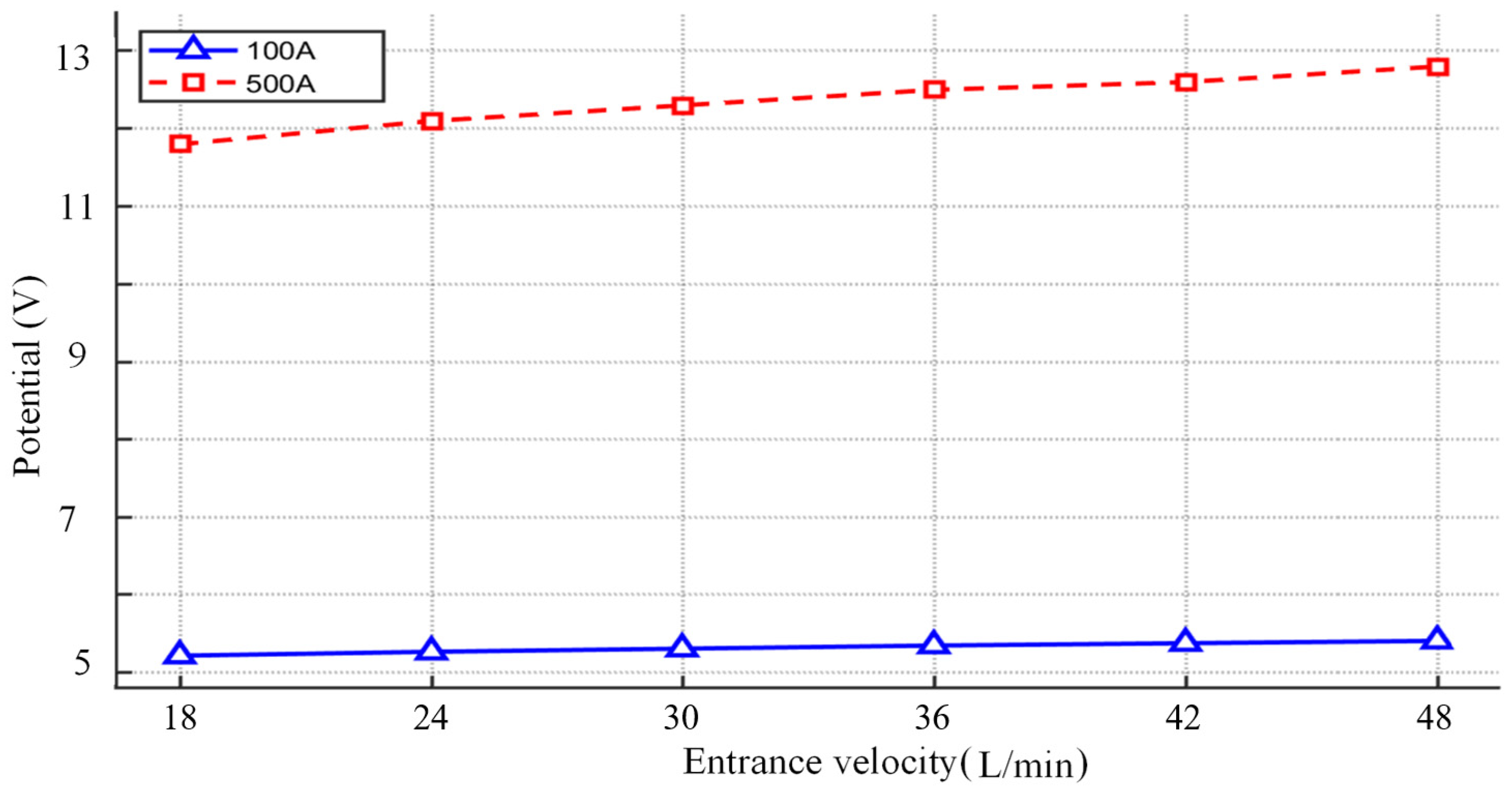
4.3.3. Flow Velocity Sensitivity to Potential Field Distribution Properties at Different Current Intensities
4.3.4. Guidance on Numerical Calculations for Practical Applications
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chaurasia, P.K.; Barik, B.K.; Das, A.; De, A. Evaluating porosity formation in gas metal arc directed energy deposition of an aluminium alloy. Sci. Technol. Weld. Join. 2025, 30, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Wen, C.F.; Chen, H.; Xiong, J. Arc behavior and droplet transfer characteristics in double-electrode arc-directed energy deposition. Int. J. Heat Mass Tran. 2025, 247, 127115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, J.W.; Li, F.; Shen, C.; Wang, L.; Zhou, W.L.; Zhang, D.Q.; Zhang, Y.L.; Wu, D.S.; Hua, X.M. Modifying microstructure and mechanical properties of twin-wire directed energy deposition-arc (TW-DED-arc) fabricated Ti-48Al-2Cr-2Nb alloy via ultra-high frequency pulsed (UHFP) current. Mater. Des. 2025, 254, 114029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.Z.; Ding, H.F.; Luo, J.; Bair, D.; Xu, X.L.; Chang, Y.L. Numerical and experimental study of TIG welding arc in high frequency longitudinal magnetic field. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 33, 5253–5262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becerra, M.; Nilsson, J.; Franke, S.; Breitkopf, C.; André, P. Spectral and electric diagnostics of low-current arc plasmas in CO2 with N2 and H2O admixtures. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2024, 57, 015202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, K.S.; Arivazhagan, N. Arc-welded armour steel: A tailored and comparative study of its microstructure and mechanical properties. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part L J. Mater. Des. Appl. 2024, 238, 1557–1584. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, Z.; Liang, Y.; Liu, H.B.; Wang, F.; Yang, J.; Song, Y.B. Research on Process Characteristics and Properties in Deep-Penetration Variable-Polarity Tungsten Inert Gas Welding of AA7075 Aluminum Alloy. Metals 2024, 14, 1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.K.; Hao, K.D.; Xu, L.Y.; Han, Y.D.; Zhao, L.; Ren, W.J.; Jing, H.Y. Microstructure homogeneity and mechanical properties of laser-arc hybrid welded AZ31B magnesium alloy. J. Magnes. Alloy. 2024, 12, 1986–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.Y.; Yu, P.X.; Wan, Y.X.; Zhou, B.W.; Zhou, H.X.; Yang, X.F.; Tang, P.Q.; Zhang, C.Z.; Huang, M.; Wei, H.L.; et al. Study on the plasma characteristics in the extraction region of hybrid negative ion source. Fusion Eng. Des. 2025, 216, 115094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, C.G.; An, T.Y.; Luo, B.W.; Yao, X.F.; Zhang, P.; Liu, H.; Zhang, B.H. An Improved Black-Box Model for Low-Current AC Arcs in Vacuum Interrupters. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2024, 31, 1030–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.J.; Kawabata, T.; Kyouno, S.; Li, X.X.; Uranaka, S.; Maeda, D. Influence of welding methods on the microstructure of nickel-based weld metal for liquid hydrogen tanks. J. Mater. Sci. 2024, 59, 22310–22326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Nasser, M.; Barati, H.; Redl, C.; Ishmurzin, A.; Voller, N.; Hackl, G.; Leuchtenmüller, M.; Wu, M.H.; Kharicha, A. Effect of compressibility on industrial DC electric arcs. Results Eng. 2023, 19, 101312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baeva, M. Reversal of the electric field and the anode fall in DC arcs in air during contact opening. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2024, 57, 39LT01. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, J.Y.; Li, Y.W.; Zhao, H.L.; Zhang, S.Y.; Gong, Q.L.; Chang, Y.L. Study of CO2 welding arc with and without external magnetic field. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. 2024, 46, 681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.J.; Hu, R.Z.; Chen, Z.; Wang, Z.W. Particle-in-cell/Monte Carlo collision simulation on gap breakdown characteristics of under the conditions of hot-electrode and high-temperature gas medium in low-voltage circuit breaker chamber. Phys. Fluids 2024, 36, 033614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.J.; Wang, X.Y.; Chen, J.L.; Luo, M.; Xie, Y.D.; Wang, H.J. Numerical simulation of CuCr alloys vacuum arc under conditions of arc contraction, deflection, and anode vapor. Phys. Plasmas 2024, 31, 123501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F.; Peng, S.; Zhang, G.K.; Xu, B.; Cai, X.Y.; Chen, S.J.; Zhang, P.T. Investigation of arc behavior and welding formation for a novel vector gas regulated plasma arc welding. J. Manuf. Process. 2024, 119, 768–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.J.; Zhu, X.Y.; Jiang, Y.P.; Peng, X.; Li, Q.H.; Huang, X.L. Characteristics and Control of High Current Vacuum Arc Deflection Under the Impact of Lateral Magnetic Field. IEEE Access 2025, 13, 2571–2580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.L.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, Y.S.; Luo, C.F.; Hu, Q.X. Impact of welding current on arc physical characteristics in single-power, double-wire, single-arc gas metal arc welding. Weld. World 2025, 69, 2657–2668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, D.; Wang, Y.Z.; Zhang, C.; Huang, J.K.; Li, D.Q. Numerical analysis of arc-droplet-pool coupling behavior in magnetically controlled high current MIG welding. J. Manuf. Process. 2024, 126, 402–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.M.; Xiu, S.X.; Liu, Z.X.; Guo, M.Q.; Zhu, D.J. Numerical Simulation and Experimental Investigation of the Influence of Gap Distance on Vacuum Arc Characteristics Between TMF Contacts. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 2024, 52, 951–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.Y.; Wei, Y.H.; Xu, G.X.; Liu, X.B.; Yan, D.J. Numerical investigation of arc characteristics and metal properties in ELAMF-assisted WAAM with wire retraction. Vacuum 2024, 230, 113689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.B.; Zhou, H.; Fei, F.; Chen, Q. Numerical simulation study on the characteristics of TIG welding arc with an external longitudinal magnetic field. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Material Science and Technology, Macao, China, 10–12 January 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, L.; Zhang, Y.S.; Cao, T.; Xue, R.R.; Zhang, J.J.; Zhang, J. Investigation of the effect of electrode materials on Arc Discharge Machining of 40% SiCp/Al composites. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Tech. 2025, 137, 455–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, K.P.; Cao, J.L.; Yang, Y. Weight function method for stress intensity factors of semi-elliptical surface cracks on functionally graded plates subjected to non-uniform stresses. Materials 2020, 13, 3155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Y.; Li, G.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Z. Study of the Sensitivity of DC Arc Temperature Field, Pressure Field, and Potential to Process Parameters. Micromachines 2025, 16, 919. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16080919
Liu Y, Li G, Zhang S, Wang Z. Study of the Sensitivity of DC Arc Temperature Field, Pressure Field, and Potential to Process Parameters. Micromachines. 2025; 16(8):919. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16080919
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Yongjun, Gaosong Li, Shuai Zhang, and Zhenya Wang. 2025. "Study of the Sensitivity of DC Arc Temperature Field, Pressure Field, and Potential to Process Parameters" Micromachines 16, no. 8: 919. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16080919
APA StyleLiu, Y., Li, G., Zhang, S., & Wang, Z. (2025). Study of the Sensitivity of DC Arc Temperature Field, Pressure Field, and Potential to Process Parameters. Micromachines, 16(8), 919. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16080919





