A Novel Triboelectric–Electromagnetic Hybrid Generator with a Multi-Layered Structure for Wind Energy Harvesting and Wind Vector Monitoring
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. The Fabrication of the TEHG
2.2. Electrical Measurements and Simulations
3. Results and Discussion
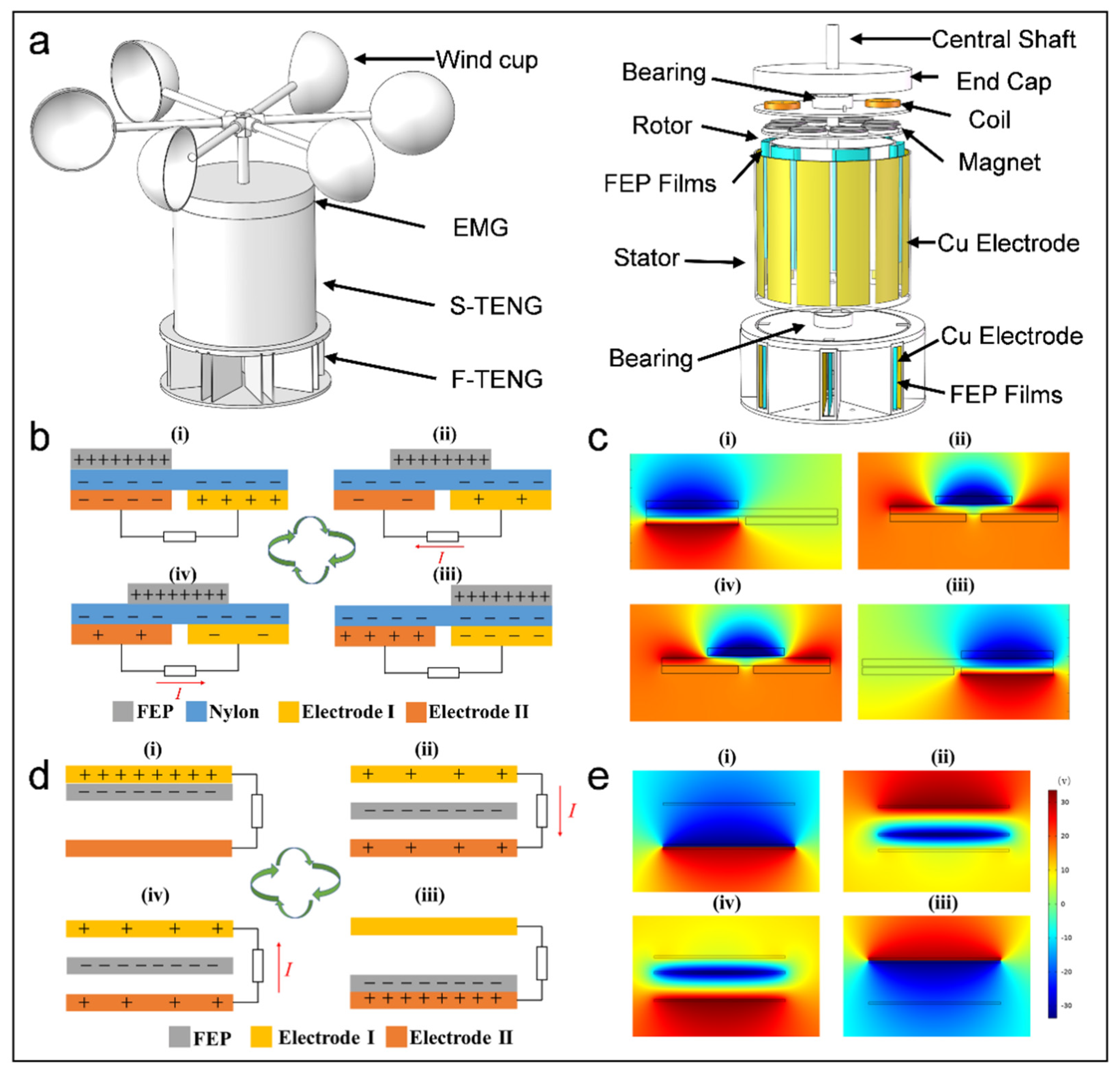
3.1. Composition and Working Principle of TEHG
3.2. Optimization of Output Characteristics for TEHG
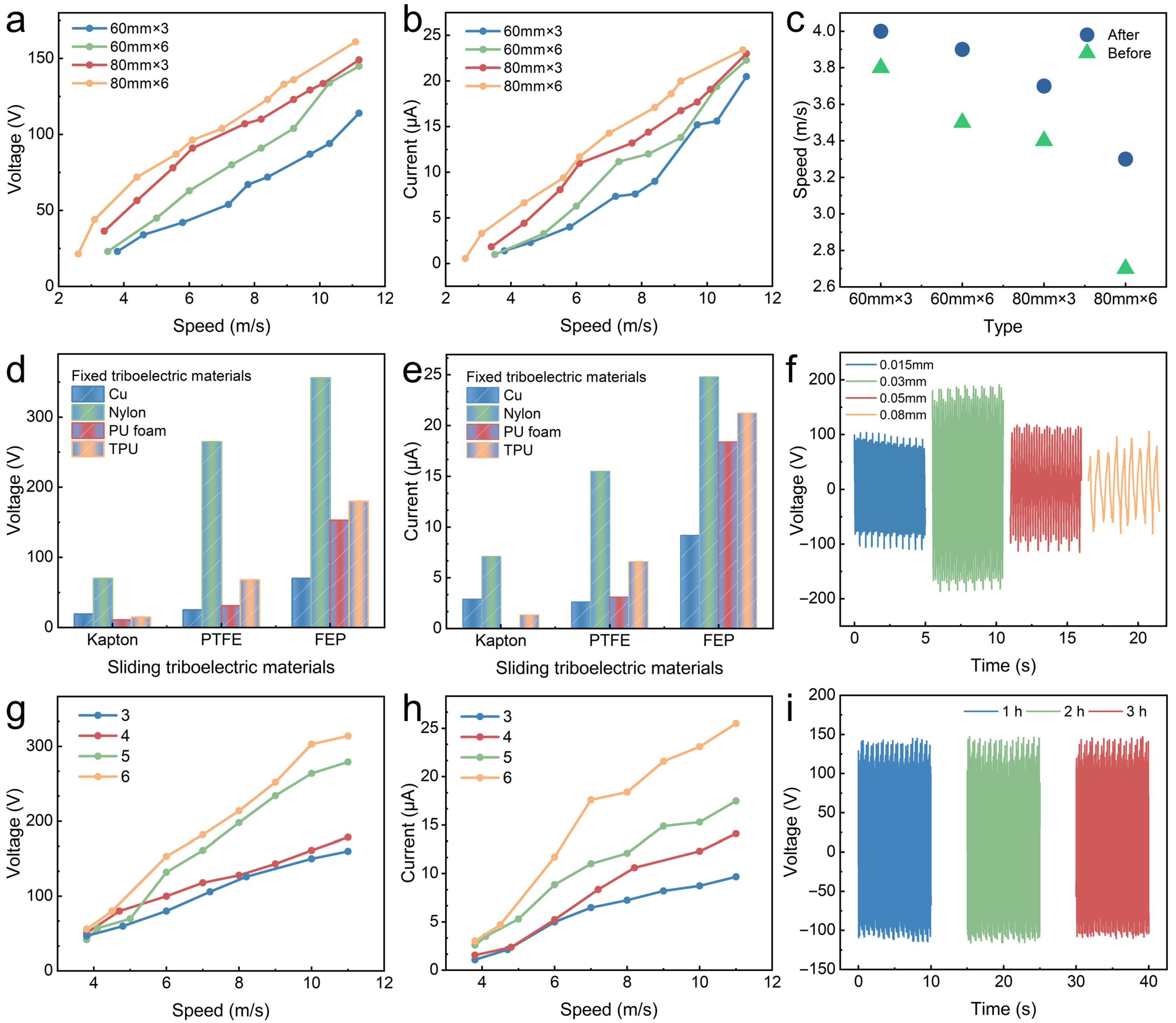
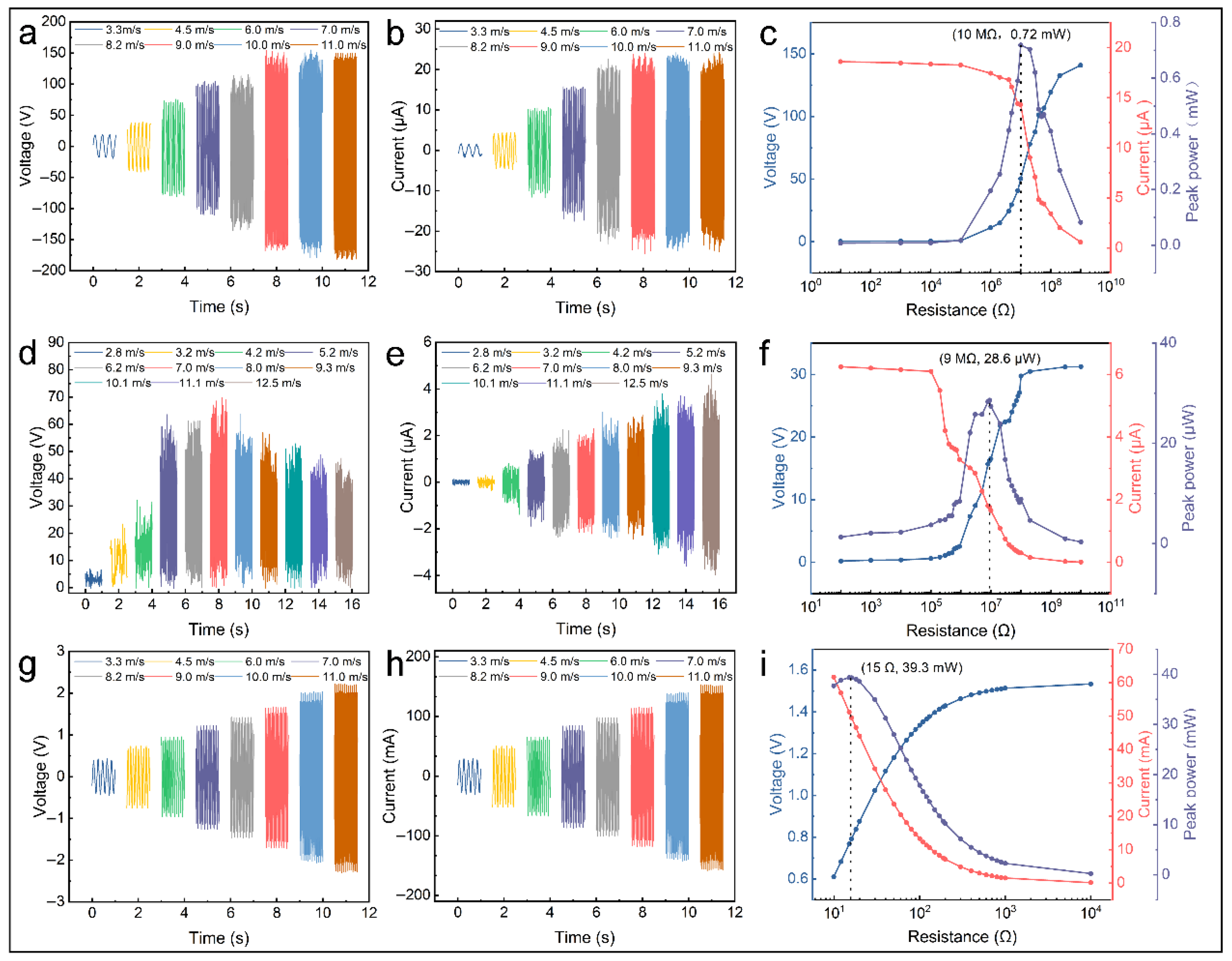
3.2.1. Output Characteristics of S-TENG
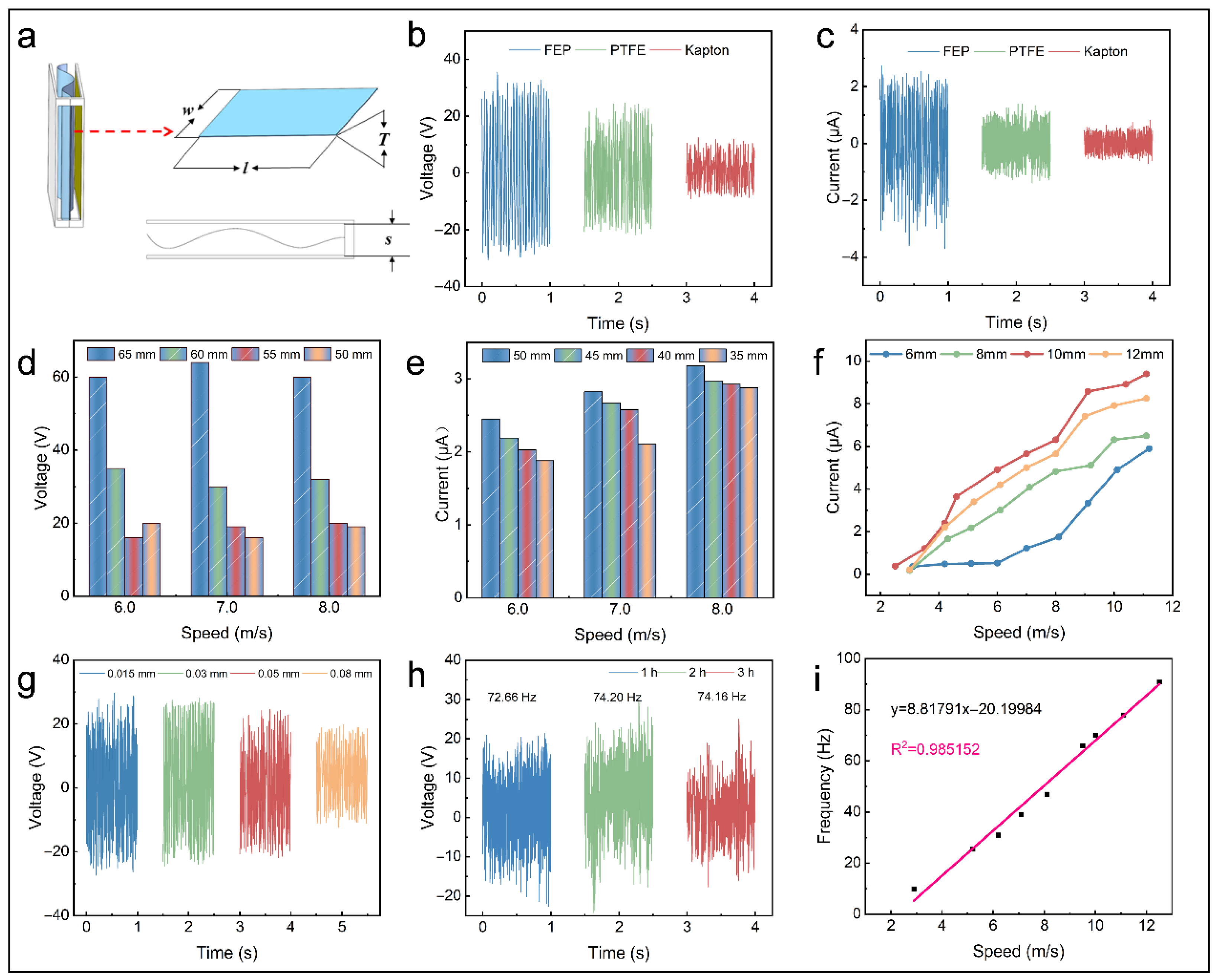
3.2.2. Electrical Characteristics of F-TENG
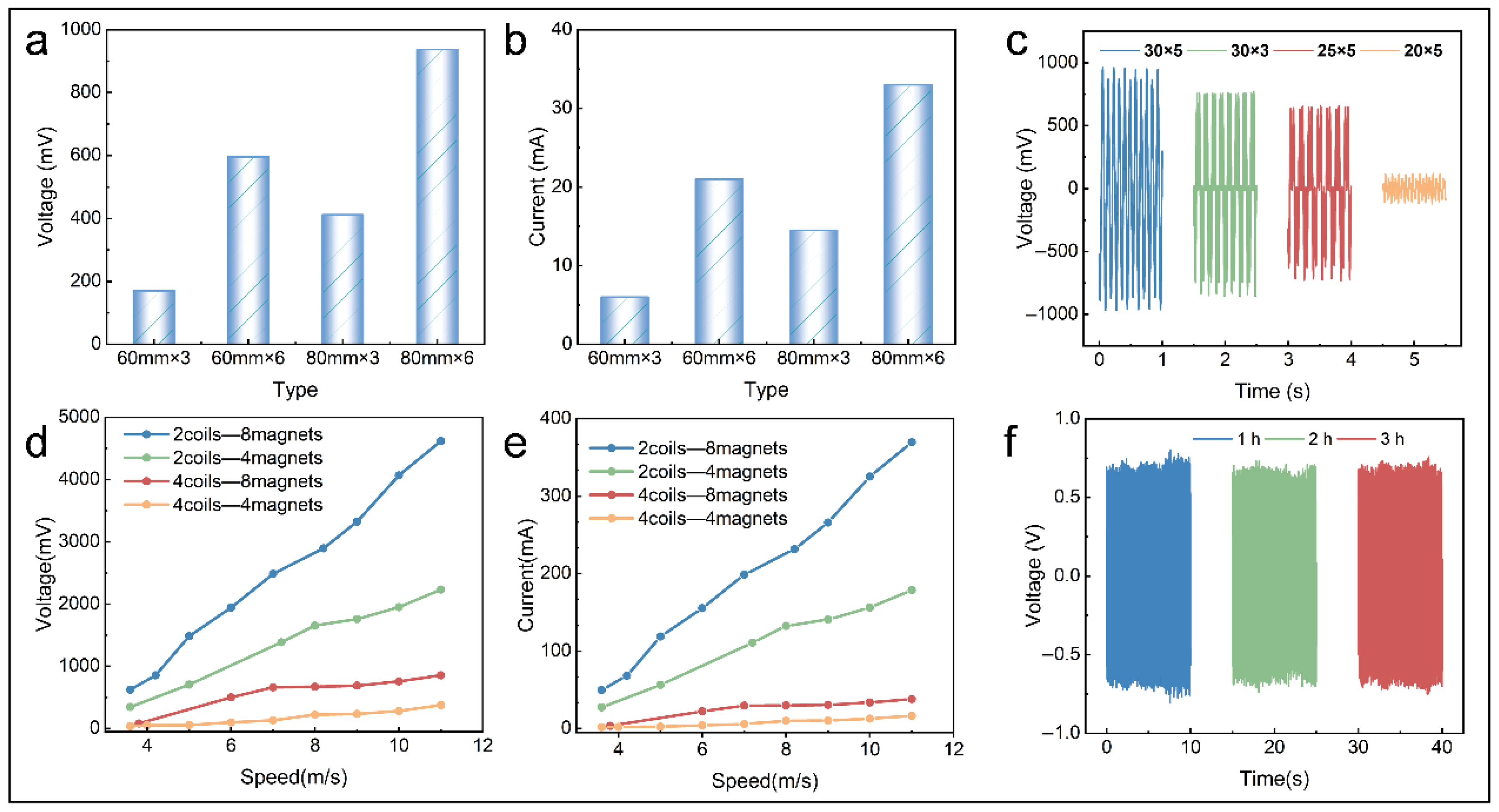
3.2.3. Output Characteristics of EMG
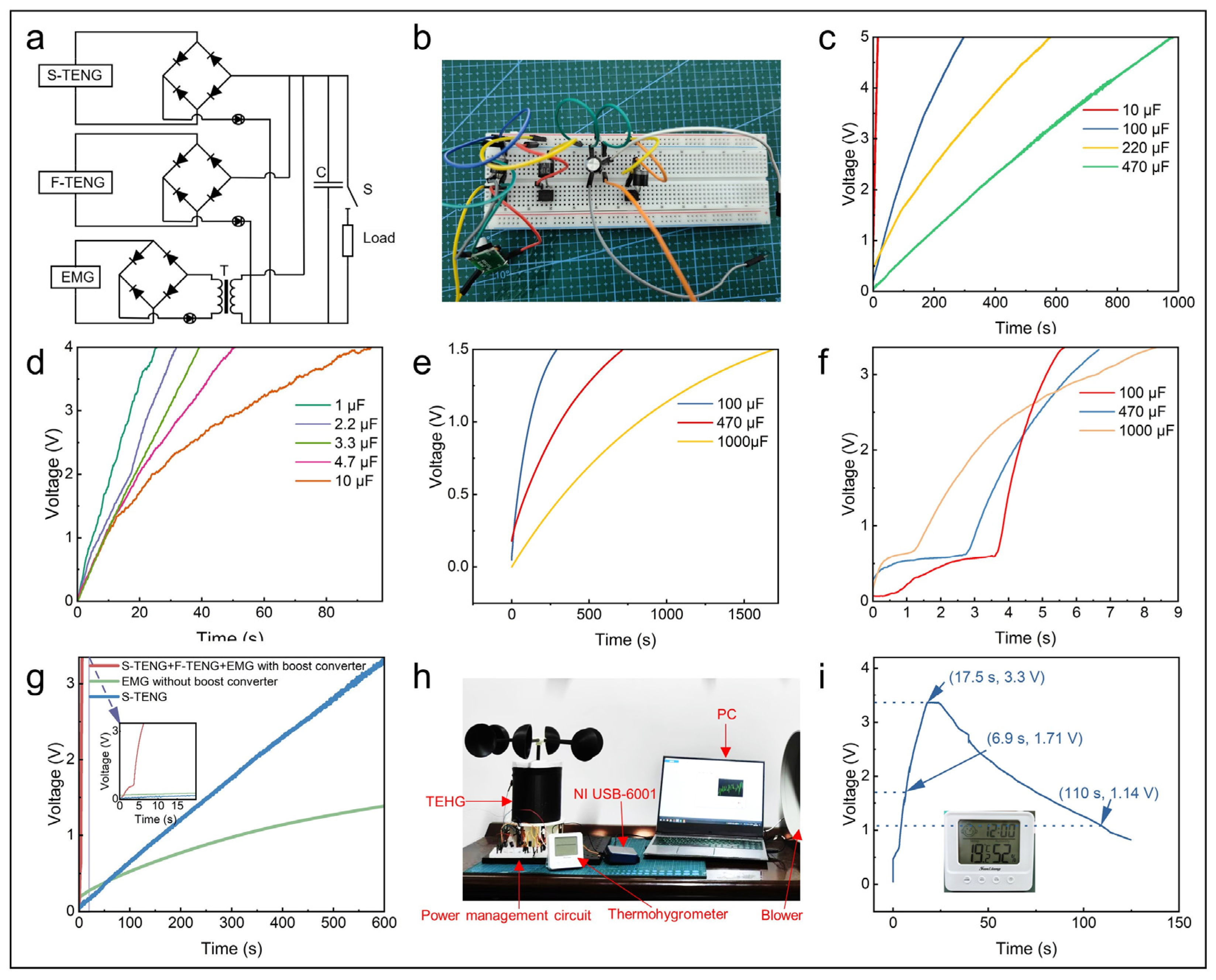
3.3. The Electrical Output Characteristics of the TEHG
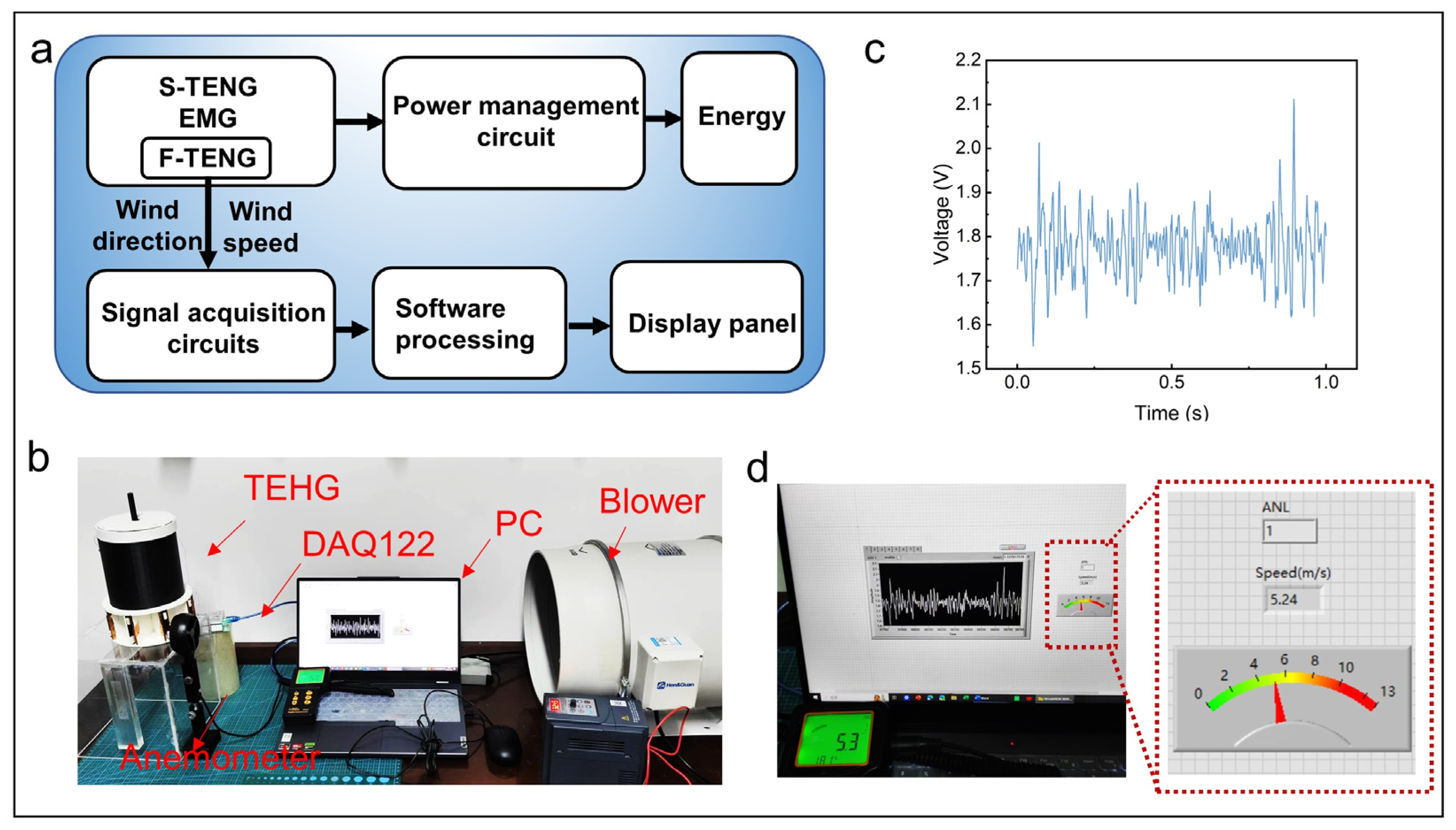
3.4. Demonstrations
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, X.; Gao, Q.; Cao, Y.; Yang, Y.; Liu, S.; Wang, Z.L.; Cheng, T. Optimization Strategy of Wind Energy Harvesting via Triboelectric-Electromagnetic Flexible Cooperation. Appl. Energy 2022, 307, 118311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.; Wang, X.; Zhang, H.; Ye, J.; Li, X. Various Energy Harvesting Strategies and Innovative Applications of Triboelectric-Electromagnetic Hybrid Nanogenerators. J. Alloys Compd. 2024, 1009, 176941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, S.; Majumdar, A. Opportunities and Challenges for a Sustainable Energy Future. Nature 2012, 488, 294–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.-F.; Gao, J. Wind Energy Harvesting Based on Flow-Induced-Vibration and Impact. Microelectron. Eng. 2013, 111, 82–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, B.; Wang, Q.; Su, H.; Li, J.; Xie, B.; Wang, P.; Qiu, J.; Wu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, X.; et al. Progress in Recent Research on the Design and Use of Triboelectric Nanogenerators for Harvesting Wind Energy. Nano Energy 2023, 116, 108789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, B.; Yang, O.; Yuan, W.; He, L.; Wei, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, Z.L. Harvesting Wind Energy by a Triboelectric Nanogenerator for an Intelligent High-Speed Train System. ACS Energy Lett. 2021, 6, 1490–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joselin Herbert, G.M.; Iniyan, S.; Sreevalsan, E.; Rajapandian, S. A Review of Wind Energy Technologies. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2007, 11, 1117–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Lu, P.; Zhou, X.; Bai, J.; An, S.; Liu, S.; Pu, X. Triboelectric Wind Sensors: Fundamentals, Progress, and Perspectives. Nano Energy 2024, 131, 110209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.; Wu, L.; Pang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Yang, R. Strategies for Effectively Harvesting Wind Energy Based on Triboelectric Nanogenerators. Nano Energy 2022, 100, 107522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Divya, S.; Hajra, S.; Panda, S.; Vivekananthan, V.; Mistewicz, K.; Kim, H.J.; Oh, T.H. A Review on the next Generation of Healing: Exploring the Use of Triboelectric Nanogenerators in Wound Care. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2023, 826, 140648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.; Gong, X.; Lu, T.; Zheng, L.; Li, H. Self-Powered Wind Detection and Positioning System for Hot Air Balloon Based on Multi-Module Triboelectric Nanogenerator. Nano Energy 2023, 116, 108791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Wu, Y.; Dai, X.; Han, J.; Dong, B.; Huang, L.-B. Calliopsis Structure-Based Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Harvesting Wind Energy and Self-Powerd Wind Speed/Direction Sensor. Mater. Des. 2022, 221, 111005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.L. On the First Principle Theory of Nanogenerators from Maxwell’s Equations. Nano Energy 2020, 68, 104272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, S.; Liu, Y.; Wang, S.; Lin, L.; Zhou, Y.S.; Hu, Y.; Wang, Z.L. Theoretical Investigation and Structural Optimization of Single-Electrode Triboelectric Nanogenerators. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 3332–3340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; He, J.; Gao, Y.; Xu, B.; Li, J.; Liu, K.; Nie, S.; Wang, S.; Duan, Q.; Liang, D. Efficient Output and Stability Triboelectric Materials Enabled by High Deep Trap Density. Nano Lett. 2025, 25, 410–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Chen, J.; Tang, Q.; Feng, L.; Yang, H.; Li, J.; Xi, Y.; Wang, X.; Hu, C. Wireless Electric Energy Transmission through Various Isolated Solid Media Based on Triboelectric Nanogenerator. Adv. Energy Mater. 2018, 8, 1703086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Jiang, L.; Wang, Z.L.; Zhu, J.; Cheng, T. Triboelectric-Electromagnetic Hybrid Generator with Swing-Blade Structures for Effectively Harvesting Distributed Wind Energy in Urban Environments. Nano Res. 2023, 16, 11621–11629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, J.; Chen, P.; Wang, Z.; Berbille, A.; Pang, H.; Jiang, Y.; Jiang, T.; Wang, Z.L. Biomimetic Hairy Whiskers for Robotic Skin Tactility. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2101891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Huang, H.; Zhu, W.; Zhao, X.; Yang, Y. Arc-Shaped Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Wind Energy Harvesting. Energy Technol. 2022, 10, 2101156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.A.M.; Zhu, W.; Bowen, C.R.; Wang, Z.L.; Yang, Y. Triboelectric Nanogenerators for Wind Energy Harvesting. Nat. Rev. Electr. Eng. 2024, 1, 453–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Pu, X.; Du, C.; Li, L.; Jiang, C.; Hu, W.; Wang, Z.L. Freestanding Flag-Type Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Harvesting High-Altitude Wind Energy from Arbitrary Directions. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 1780–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Wen, J.; Ou, Z.; Su, E.; Xing, F.; Yang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Wang, Z.L.; Chen, B. Leaf-Like TENGs for Harvesting Gentle Wind Energy at An Air Velocity as Low as 0.2 m S−1. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2212207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Wang, S.; Lin, L.; Jing, Q.; Lin, Z.-H.; Niu, S.; Wu, Z.; Wang, Z.L. Rotary Triboelectric Nanogenerator Based on a Hybridized Mechanism for Harvesting Wind Energy. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 7119–7125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, X.; Fan, H.; Wang, C.; Ma, J.; Li, H.; Zhang, M.; Lei, S.; Wang, W. Wind Energy Harvester Based on Coaxial Rotatory Freestanding Triboelectric Nanogenerators for Self-Powered Water Splitting. Nano Energy 2018, 50, 562–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, B.; Yang, O.; Yuan, W.; Zhou, L.; Zhao, Z.; Wu, Z.; Wang, J.; Wang, Z.L. A Dual-Mode Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Wind Energy Harvesting and Self-Powered Wind Speed Monitoring. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 6244–6254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Wang, Y.-C.; Zhang, S.L.; Ding, W.; Cheng, J.; He, X.; Zhang, P.; Wang, Z.; Pan, X.; Wang, Z.L. An Aeroelastic Flutter Based Triboelectric Nanogenerator as a Self-Powered Active Wind Speed Sensor in Harsh Environment. Extrem. Mech. Lett. 2017, 15, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Wei, H.; Wang, J.; Luo, X.; Wang, R.; Chen, Y.; Xiang, M.; Chen, X.; Xie, H.; Feng, S. Self-Powered System by a Suspension Structure-Based Triboelectric-Electromagnetic-Piezoelectric Hybrid Generator for Unifying Wind Energy and Vibration Harvesting with Vibration Attenuation Function. Nano Energy 2024, 122, 109323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, J.; Zou, J.; Song, J.; He, J.; Hou, X.; Yu, J.; Han, X.; Feng, C.; He, H.; Chou, X. Hybrid Enhancement Effect of Structural and Material Properties of the Triboelectric Generator on Its Performance in Integrated Energy Harvester. Energy Convers. Manag. 2022, 254, 115151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Zhou, H.; Zhou, Y.; Hu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Z.L.; Sun, Q. High Performance Rotary-Structured Triboelectric-Electromagnetic Hybrid Nanogenerator for Ocean Wind Energy Harvesting. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2023, 8, 2300327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Q.; Gan, C.-Z.; Zhou, T.; Du, Z.-C.; Wang, J.-H.; Wang, Q.; Wei, K.-X.; Zou, H.-X. A Triboelectric-Piezoelectric-Electromagnetic Hybrid Wind Energy Harvester Based on a Snap-through Bistable Mechanism. Energy Convers. Manag. 2024, 306, 118323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.; Wu, H.; Shan, C.; Li, K.; He, W.; Li, Q.; Yu, X.; Du, S.; Li, G.; Hu, C. Ultra-Durable and High-Output Triboelectric Nanogenerator Based on Coupling of Soft-Soft Contact and Volume Effect. Nano Energy 2023, 116, 108850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Cao, Y.; Yu, X.; Xu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Liu, S.; Cheng, T.; Wang, Z.L. Breeze-Driven Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Wind Energy Harvesting and Application in Smart Agriculture. Appl. Energy 2022, 306, 117977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, Y.; Guo, H.; Zi, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, J.; Deng, J.; Li, S.; Hu, C.; Cao, X.; Wang, Z.L. Multifunctional TENG for Blue Energy Scavenging and Self-Powered Wind-Speed Sensor. Adv. Energy Mater. 2017, 7, 1602397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; An, J.; Shu, S.; Cheng, R.; Nie, J.; Jiang, T.; Wang, Z.L. Super-Durable, Low-Wear, and High-Performance Fur-Brush Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Wind and Water Energy Harvesting for Smart Agriculture. Adv. Energy Mater. 2021, 11, 2003066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Wang, R.; Wei, H.; Luo, X.; Zhang, J.; Chen, X. Three-Terminal High-Output Triboelectric Nanogenerator to Achieve Alternating Current/Direct Current Collaborative Output by Coupling Three-Dimensional Porous Structure, Triboelectrification and Corona Discharge. Nano Energy 2024, 129, 110070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Yu, X.; Zhu, J.; Shen, P.; Wang, Z.L.; Cheng, T. Driving-Torque Self-Adjusted Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Effective Harvesting of Random Wind Energy. Nano Energy 2022, 99, 107389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.T.; Salauddin, M.; Maharjan, P.; Rasel, M.S.; Cho, H.; Park, J.Y. Natural Wind-Driven Ultra-Compact and Highly Efficient Hybridized Nanogenerator for Self-Sustained Wireless Environmental Monitoring System. Nano Energy 2019, 57, 256–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khandelwal, G.; Maria Joseph Raj, N.P.; Kim, S.-J. Materials Beyond Conventional Triboelectric Series for Fabrication and Applications of Triboelectric Nanogenerators. Adv. Energy Mater. 2021, 11, 2101170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Luo, X.; Wei, H.; Wang, R.; Chen, X.; Zhang, J. Wind-Driven Suspended Triboelectric-Electromagnetic Hybrid Generator with Vibration Elimination for Environmental Monitoring in the High-Voltage Power Transmission Line. Nano Energy 2024, 128, 109831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Yu, X.; Wang, J.; Gao, Q.; Wang, Z.; Cheng, T.; Wang, Z.L. A Standard for Normalizing the Outputs of Triboelectric Nanogenerators in Various Modes. Energy Environ. Sci. 2022, 15, 3901–3911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Zeng, X.; Chen, X.; Liao, T.; Wang, R.; Chen, Y.; Wei, H.; Luo, X.; Feng, S. Self-Powered System for Environment and Aeolian Vibration Monitoring in the High-Voltage Transmission System by Multi-Directional Wind-Driven Triboelectric Nanogenerator. Nano Energy 2023, 117, 108911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Yang, Z.; Yang, Y.; Yang, B.; Song, Y.; Cheng, X.; Lai, Z.; Zhao, H.; Ji, L.; Zhu, Z.; et al. A Remote Monitoring System for Wind Speed and Direction Based on Non-Contact Triboelectric Nanogenerator. Nano Energy 2025, 133, 110453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Wen, Z.; Zi, Y.; Yeh, M.-H.; Wang, J.; Zhu, L.; Hu, C.; Wang, Z.L. A Water-Proof Triboelectric–Electromagnetic Hybrid Generator for Energy Harvesting in Harsh Environments. Adv. Energy Mater. 2016, 6, 1501593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Xie, Y.; Niu, S.; Lin, L.; Wang, Z.L. Freestanding Triboelectric-Layer-Based Nanogenerators for Harvesting Energy from a Moving Object or Human Motion in Contact and Non-Contact Modes. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 2818–2824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Wu, X.; Wu, H.; Pan, Y.; Luo, D.; Azam, A.; Zhang, Z. A Hybrid Self-Powered System Based on Wind Energy Harvesting for Low-Power Sensors on Canyon Bridges. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf.-Green Technol. 2023, 10, 167–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; He, J.; Mu, J.; Qian, J.; Zhang, N.; Yang, C.; Hou, X.; Geng, W.; Wang, X.; Chou, X. Triboelectric-Electromagnetic Hybrid Nanogenerator Driven by Wind for Self-Powered Wireless Transmission in Internet of Things and Self-Powered Wind Speed Sensor. Nano Energy 2020, 68, 104319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayfidinov, K.; Cezan, S.D.; Baytekin, B.; Baytekin, H.T. Minimizing Friction, Wear, and Energy Losses by Eliminating Contact Charging. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, eaau3808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, S.; Lai, L.; Xin, J.; Qu, Z.; Li, B.; Dai, Y. Hybrid Triboelectric-Electromagnetic-Piezoelectric Wind Energy Harvester toward Wide-Scale IoT Self-Powered Sensing. Small 2024, 20, 2307282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Hou, W.; Zheng, Q.; Fang, L.; Zhu, R.; Zheng, L. Self-Powered Wind Sensor Based on Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Detecting Breeze Vibration on Electric Transmission Lines. Nano Energy 2022, 99, 107412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, E.; Chen, T.; Wang, J.; Hu, Z.; Mi, J.; Pan, X.; Xu, M. A Novel Humidity Resisting and Wind Direction Adapting Flag-Type Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Wind Energy Harvesting and Speed Sensing. Nano Energy 2020, 78, 105279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, P.; Zhu, H.; Lu, H.; Zeng, Y.; Zheng, N.; Wang, Z.L.; Cao, X. Design of Biodegradable Wheat-Straw Based Triboelectric Nanogenerator as Self-Powered Sensor for Wind Detection. Nano Energy 2021, 86, 106032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Fu, S.; Zuo, X.; Zeng, J.; Shan, C.; He, W.; Li, W.; Hu, C. Moisture Resistant and Stable Wireless Wind Speed Sensing System Based on Triboelectric Nanogenerator with Charge-Excitation Strategy. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2207498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, H.-X.; Zhao, L.-C.; Wang, Q.; Gao, Q.-H.; Yan, G.; Wei, K.-X.; Zhang, W.-M. A Self-Regulation Strategy for Triboelectric Nanogenerator and Self-Powered Wind-Speed Sensor. Nano Energy 2022, 95, 106990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Ding, W.; Pan, L.; Wu, C.; Yu, H.; Yang, L.; Liao, R.; Wang, Z.L. Self-Powered Wind Sensor System for Detecting Wind Speed and Direction Based on a Triboelectric Nanogenerator. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 3954–3963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, W.; Ni, Q.; Zhu, R.; Fu, X.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, C.; Liao, L. Triboelectric-Electromagnetic Hybrid Wind Energy Harvesting and Multifunctional Sensing Device for Self-Powered Smart Agricultural Monitoring. Nano Energy 2024, 131, 110272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, L.; Fang, L.; Wang, F.; Li, Z.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Z.; He, W.; Rasheed, A.; Fan, K.; et al. Wind Speed Adaptive Triboelectric Nanogenerator with Low Start-up Wind Speed, Enhanced Durability and High Power Density via the Synergistic Mechanism of Magnetic and Centrifugal Forces for Intelligent Street Lamp System. Nano Energy 2025, 133, 110487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Reference | Mechanism | Cut-In Wind Speed | Diameter | Number |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [32] | TENG | 3.3 m/s | 50 mm | 6 |
| [36] | TENG | 5 m/s | 50 mm | 6 |
| [37] | TENG + PEG + EMG | 3 m/s | 35 mm | 3 |
| [1] | TENG + EMG | 4 m/s | - | 6 |
| [30] | TENG + PEG + EMG | 3 m/s | 60 mm | 6 |
| [28] | TENG + EMG | 4.3 m/s | - | 3 |
| This work | TENG + EMG | 3.3 m/s | 80 mm | 6 |
| Reference | Mechanism | Wind Speed | Power |
|---|---|---|---|
| [30] | TENG + PEG + EMG | 5 m/s | 0.65 mW |
| [32] | TENG | 4 m/s | 2.81 mW |
| [45] | PEG + EMG | 6.5 m/s | 19.24 mW |
| [46] | TENG + EMG | 9 m/s | 18.96 mW |
| [47] | TENG + EMG | 4 m/s | 0.32 mW |
| [48] | TENG + PEG + EMG | 3 m/s | 11.83 mW |
| This work | TENG + EMG | 8 m/s | 40.05 mW |
| Energy | Power | Power Density |
|---|---|---|
| 32.67 mJ | 1.87 W | 11.2 W/m3 |
| Reference | Wind Speed Range | Wind Direction |
|---|---|---|
| [25] | 3.77~11.91 | × |
| [26] | 3.1~10.8 | × |
| [49] | 1.7~6.7 | √ |
| [50] | 3.0~7.5 | √ |
| [51] | 2.9~4.5 | × |
| [52] | 2.0~12.0 | × |
| [53] | 2.0~12.0 | × |
| [54] | 2.7~8 | √ |
| [33] | 4.5~12.5 | × |
| [55] | 3~5 | √ |
| [56] | 1.6~9.4 | × |
| This work | 2.8~12.5 | √ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Niu, J.; Hu, R.; Li, M.; Zhang, L.; Xu, B.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, Y.; Ding, J.; Duan, Q. A Novel Triboelectric–Electromagnetic Hybrid Generator with a Multi-Layered Structure for Wind Energy Harvesting and Wind Vector Monitoring. Micromachines 2025, 16, 795. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16070795
Niu J, Hu R, Li M, Zhang L, Xu B, Zhang Y, Luo Y, Ding J, Duan Q. A Novel Triboelectric–Electromagnetic Hybrid Generator with a Multi-Layered Structure for Wind Energy Harvesting and Wind Vector Monitoring. Micromachines. 2025; 16(7):795. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16070795
Chicago/Turabian StyleNiu, Jiaqing, Ribin Hu, Ming Li, Luying Zhang, Bei Xu, Yaqi Zhang, Yi Luo, Jiang Ding, and Qingshan Duan. 2025. "A Novel Triboelectric–Electromagnetic Hybrid Generator with a Multi-Layered Structure for Wind Energy Harvesting and Wind Vector Monitoring" Micromachines 16, no. 7: 795. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16070795
APA StyleNiu, J., Hu, R., Li, M., Zhang, L., Xu, B., Zhang, Y., Luo, Y., Ding, J., & Duan, Q. (2025). A Novel Triboelectric–Electromagnetic Hybrid Generator with a Multi-Layered Structure for Wind Energy Harvesting and Wind Vector Monitoring. Micromachines, 16(7), 795. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16070795






