Towards Novel Spintronic Materials: Mg-Based d0-d Heusler (Nowotny–Juza) Compounds
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Structural Properties
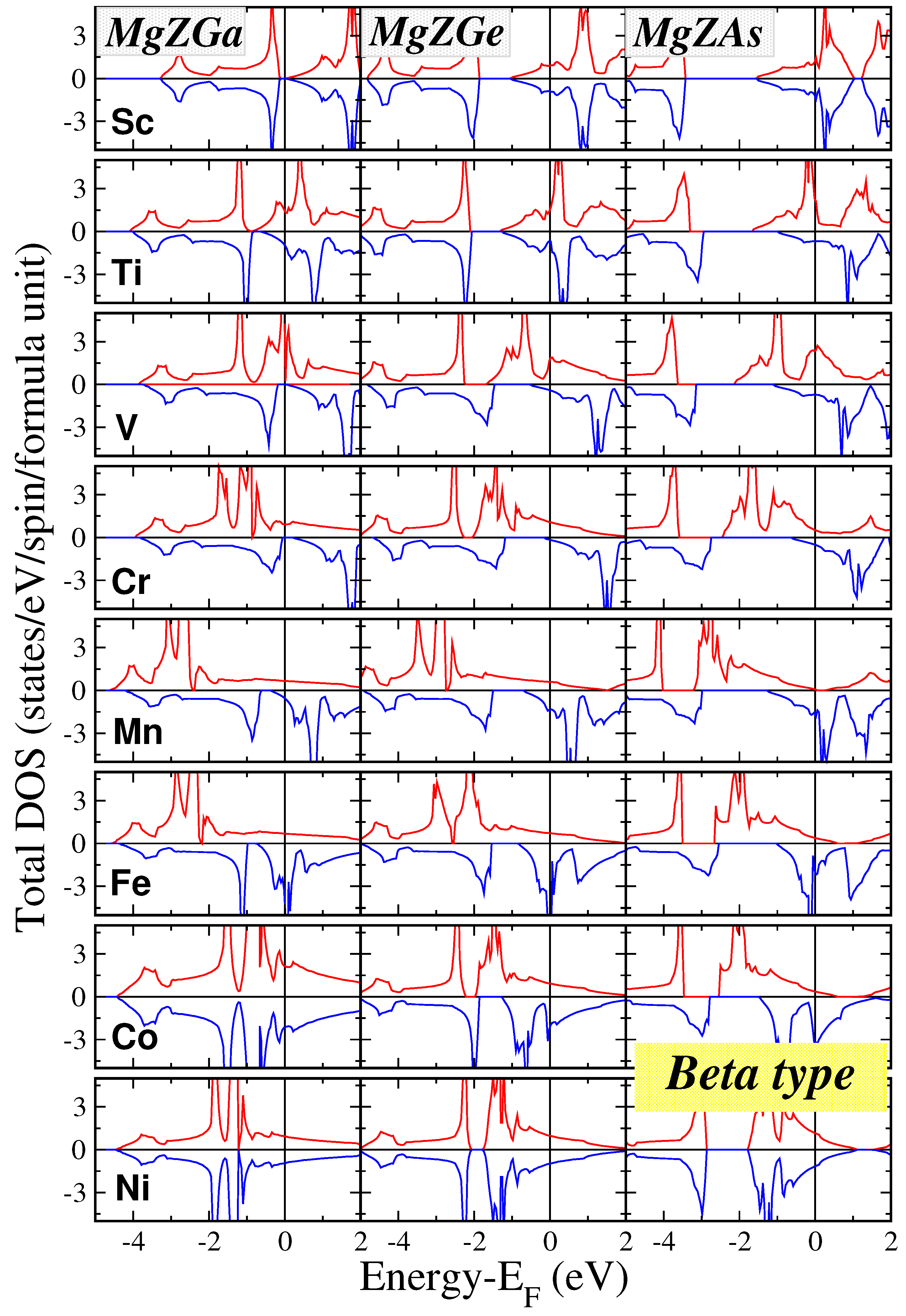
3.2. Electronic Properties
- : This triply degenerate set hybridizes with the p orbitals of Ga/Ge/As, forming delocalized bonding states across both the transition metal and the pnictogen atoms.
- : This doubly degenerate set remains localized on the transition metal atom due to symmetry restrictions and does not participate in significant hybridization.
3.3. Magnetic Properties
4. Summary and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DOS | Density of States |
| f.u. | formula unit |
| FPLO | Full-potential nonorthogonal local-orbital minimum- basis band structure approach |
| GGA | Generalized gradient approximation |
| PBE | Perdew Burke Ernzerhof |
References
- Nowotny, H.; Sibert, W.Z. Ternäre Valenzverbindungen in den Systemen Kupfer(Silber)-Arsen(Antimon,Wismut)-Magnesium. Z. Metallkd 1941, 33, 391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juza, R.; Hund, F. Die Kristallstrukturen Li Mg N, Li Zn N, Li3 Al N2 und Li3 Ga N2. Naturwissenschaften 1946, 33, 121–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castelliz, L. Eine ferromagnetische phase im system nickel-mangan-antimon. Monatshefte Chem. Verwandte Teile Anderer Wiss. 1951, 82, 1059–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heusler, F. Über magnetische manganlegierungen. Verh. Dtsch. Phys. Ges. 1903, 12, 219. [Google Scholar]
- Heusler, F.; Take, E. The nature of the Heusler alloys. Phys. Z. 1912, 13, 897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, P.J.; Ziebeck, K.R.A. Alloys and Compounds of d-Elements with Main Group Elements. Part 2. In Landolt-Börnstein, New Series, Group III, vol 19c; Wijn, H.R.J., Ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1988; pp. 75–184. [Google Scholar]
- Ziebeck, K.R.A.; Neumann, K.-U. Magnetic Properties of Metals. In Landolt-Börnstein, New Series, Group III, vol 32/c; Wijn, H.R.J., Ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2001; pp. 64–414. [Google Scholar]
- Kawasaki, J.K.; Chatterjee, S.; Canfield, P.C. Full and half-Heusler compounds. MRS Bull. 2022, 47, 555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graf, T.; Felser, C.; Parkin, S.S.P. Simple rules for the understanding of Heusler compounds. Prog. Solid State Chem. 2011, 39, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachagha, T.; Sunol, J.-J. All-d-Metal Heusler Alloys: A Review. Metals 2023, 13, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Paula, V.G.; Reis, M.S. All-d-Metal Full Heusler Alloys: A Novel Class of Functional Materials. Chem. Mater. 2021, 33, 5483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tas, M.; Özdoğan, K.; Şaşıoğlu, E.; Galanakis, I. High Spin Magnetic Moments in All-3d-Metallic Co-Based Full Heusler Compounds. Materials 2023, 16, 7543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortunato, N.M.; Li, X.; Schönecker, S.; Xie, R.; Aubel, A.; Scheibel, F.; Opahle, I.; Gutfleisch, O.; Zhang, H. High-Throughput Screening of All-d-Metal Heusler Alloys for Magnetocaloric Applications. Chem. Mater. 2024, 36, 6765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galanakis, I. Slater-Pauling Behavior in Half-Metallic Heusler Compounds. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsnelson, M.I.; Irkhin, V.Y.; Chioncel, L.; Lichtenstein, A.I.; de Groot, R.A. Half-metallic ferromagnets: From band structure to many-body effects. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2008, 80, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirohata, A.; Yamada, K.; Nakatani, Y.; Prejbeanu, I.-L.; Diény, B.; Pirro, P.; Hillebrands, B.K. Review on Spintronics: Principles and device applications. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2020, 509, 166711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirohata, A.; Takanashi, K. Perspectives of Heusler compounds. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2014, 47, 193001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spintronics. From Materials to Devices; Felser, C., Fecher, G.H., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Fong, C.Y.; Pask, J.E.; Yang, L.H. Half-metallic Materials and Their Properties. In Series on Materials for Engineering, vol. 2; Fong, C.Y., Pask, J.E., Yang, L.H., Eds.; Imperial College Press: London, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Heusler Alloys. Properties, Growth, Applications. In Springer Series in Materials Science; Felser, C., Hirohata, A., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; Volume 222. [Google Scholar]
- Galanakis, I.; Özdoğan, K.; Şaşıoğlu, E. Spin-filter and spin-gapless semiconductors: The case of Heusler compounds. AIP Adv. 2016, 6, 055606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilleßen, M.; Dronskowski, R. A combinatorial study of full Heusler alloys by first-principles computational methods. J. Comput. Chem. 2009, 30, 1290–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilleßen, M.; Dronskowski, R. A combinatorial study of inverse Heusler alloys by first-principles computational methods. J. Comput. Chem. 2010, 31, 612–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Hegde, V.I.; Munira, K.; Xie, Y.; Keshavarz, S.; Mildebrath, D.T.; Wolverton, C.; Ghosh, A.W.; Butler, W.H. Computational investigation of half-Heusler compounds for spintronics applications. Phys. Rev. B 2017, 95, 024411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanvito, S.; Oses, C.; Xue, J.; Tiwari, A.; Zic, M.; Archer, T.; Tozman, P.; Venkatesan, M.; Coey, M.; Curtarolo, S. Accelerated discovery of new magnets in the Heusler alloy family. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, e1602241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faleev, S.V.; Ferrante, Y.; Jeong, J.; Samant, M.G.; Jones, B.; Parkin, S.S.P. Unified explanation of chemical ordering, the Slater-Pauling rule, and half-metallicity in full Heusler compounds. Phys. Rev. B 2017, 95, 045140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faleev, S.V.; Ferrante, Y.; Jeong, J.; Samant, M.G.; Jones, B.; Parkin, S.S.P. Heusler compounds with perpendicular magnetic anisotropy and large tunneling magnetoresistance. Phys. Rev. Mater. 2017, 1, 024402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Rabe, K.M.; Wolverton, C. Computationally accelerated discovery of functional and structural Heusler materials. MRS Bull. 2022, 47, 559–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damewood, L.; Busemeyer, B.; Shaughnessy, M.; Fong, C.Y.; Yang, L.H.; Felser, C. Stabilizing and increasing the magnetic moment of half-metals: The role of Li in half-Heusler LiMnZ (Z=N,P,Si). Phys. Rev. B 2015, 91, 064409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehghan, A.; Davatolhagh, S. d0-d half-Heusler alloys: A potential class of advanced spintronic materials. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 773, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakil, M.; Kousar, M.; Gillani, S.S.A.; Rizwan, M.; Arshad, H.; Rafique, M.; Zafar, M. First principle computation of half metallicity and mechanical properties of a new series of half Heusler alloys KMnZ (Z = B, Si, Ge, As) for spintronics. Ind. J. Phys. 2022, 96, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehghan, A.; Davatolhagh, S. First principles study of d0-d half-Heusler alloys containing group-IV, -V, and -VI sp atoms as prospective half-metals for real spintronic applications. Mat. Chem. Phys. 2021, 273, 125064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özdoğan, K.; Galanakis, I. Interplay between Structural, Electronic, and Magnetic Properties in the p0-d Semi-Heusler Compounds: The Case of Li-Based Compounds. Crystals 2024, 14, 693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özdoğan, K.; Galanakis, I. Interplay between Structural, Electronic, and Magnetic Properties in the d0-d Semi-Heusler Compounds: The Case of K-Based Compounds. Solids 2024, 5, 533–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koepernik, K.; Eschrig, H. Full-potential nonorthogonal local-orbital minimum-basis band-structure scheme. Phys. Rev. B 1999, 59, 1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopernik, K. Full Potential Local Orbital Minimum Basis Bandstructure Scheme User’s Manual. Available online: https://www.fplo.de/ (accessed on 20 April 2025).
- Perdew, J.P.; Burke, K.; Ernzerhof, M. Generalized Gradient Approximation Made Simple. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1996, 77, 3865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meinert, M. Modified Becke-Johnson potential investigation of half-metallic Heusler compounds. Phys. Rev. B 2013, 87, 045103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hlukhyy, V.; Siggelkow, L.; Fässler, T.F. From One to Three Dimensions: Corrugated ∞1[NiGe] Ribbons as a Building Block in Alkaline Earth Metal Ae/Ni/Ge Phases with Crystal Structure and Chemical Bonding in AeNiGe (Ae = Mg, Sr, Ba). Inorg. Chem. 2013, 52, 6905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dascoulidou, A.; Müller, P.; Bronger, W. Ternäre Mangan-Verbindungen AMnX (A Mg, Ca, Sr oder Ba; X Si, Ge oder Sn): Neutronenbeugungsuntersuchungen zur Charakterisierung der magnetischen Eigenschaften. Z. Anorg. Allg. Chemie 1998, 624, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Matsuishi, S.; Fujitsu, S.; Hosono, H. MgFeGe as an isoelectronic and isostructural analog of the superconductor LiFeAs. Phys. Rev. B 2012, 85, 104403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hlukhyy, V.; Chumalo, N.; Zaremba, V.; Fässler, T.F. Syntheses and Structures of the Germanides CaNiGe and MgCoGe as well as Chemical Bonding in CaNiGe and CaNi2Ge2. Z. Anorg. Allg. Chemie 2008, 634, 1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, W.A. Electronic Structure and the Properties of Solids. The Physics of the Chemical Bond; Courier Corporation: North Chelmsford, MA, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Matyunina, M.; Baigutlin, D.; Sokolovskiy, V.; Buchelnikov, V. Systematic study of d0-d KYZ (Y = Sc, Ti, V, Cr, Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu, Z = Al, Ga, In, Si, Ge, Sn, Pb, P, As, Sb, Bi, S, Se, Te) Heusler alloys. Phys. B Condens. Matter 2025, 697, 416701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Compound | Lattice Constant a in Å | Energy Difference in eV | Most Stable | Least Stable | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| -Type | -Type | -Type | Type | Type | ||||
| MgScGa | 6.47 | 6.49 | 6.64 | −1.129 | −1.532 | −0.403 | ||
| MgTiGa | 6.27 | 6.24 | 6.36 | −1.275 | −1.000 | 0.275 | ||
| MgVGa | 6.26 | 6.18 | 6.24 | −1.186 | −0.838 | 0.348 | ||
| MgCrGa | 6.30 | 6.17 | 6.23 | −0.993 | −0.520 | 0.473 | ||
| MgMnGa | 6.28 | 6.19 | 6.16 | −1.012 | −0.290 | 0.723 | ||
| MgFeGa | 6.14 | 6.04 | 6.03 | −1.060 | 0.137 | 1.197 | ||
| MgCoGa | 5.99 | 5.88 | 5.86 | −1.123 | 0.443 | 1.566 | ||
| MgNiGa | 6.02 | 5.93 | 5.90 | −0.886 | 0.602 | 1.487 | ||
| MgScGe | 6.39 | 6.41 | 6.55 | −1.358 | −1.203 | 0.155 | ||
| MgTiGe | 6.29 | 6.19 | 6.29 | −1.482 | −0.796 | 0.686 | ||
| MgVGe | 6.24 | 6.18 | 6.19 | −1.321 | −0.787 | 0.534 | ||
| MgCrGe | 6.27 | 6.22 | 6.17 | −1.101 | −0.483 | 0.618 | ||
| MgMnGe | 6.25 | 6.19 | 6.12 | −1.174 | −0.167 | 1.007 | ||
| MgFeGe | 6.12 | 6.01 | 5.95 | −1.271 | 0.178 | 1.449 | ||
| MgCoGe | 6.01 | 5.89 | 5.80 | −1.266 | 0.521 | 1.787 | ||
| MgNiGe | 6.00 | 5.92 | 5.84 | −1.058 | 0.641 | 1.699 | ||
| MgScAs | 6.47 | 6.37 | 6.57 | −1.432 | −0.668 | 0.764 | ||
| MgTiAs | 6.37 | 6.23 | 6.31 | −1.584 | −0.759 | 0.824 | ||
| MgVAs | 6.29 | 6.14 | 6.19 | −1.194 | −0.413 | 0.781 | ||
| MgCrAs | 6.34 | 6.26 | 6.19 | −1.017 | −0.253 | 0.764 | ||
| MgMnAs | 6.26 | 6.14 | 6.11 | −1.163 | −0.116 | 1.047 | ||
| MgFeAs | 6.15 | 6.01 | 5.94 | −1.406 | −0.021 | 1.385 | ||
| MgCoAs | 6.06 | 5.93 | 5.77 | −1.227 | 0.360 | 1.587 | ||
| MgNiAs | 5.99 | 5.91 | 5.81 | −1.172 | 0.531 | 1.702 | ||
| MgZGa | MgZGe | MgZAs | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Z | ( ) | ( ) | ( ) | |||||||||||||
| Sc | Metal | 8 (0) | Metal | 9 (1) | Metal | 10 (2) | ||||||||||
| Gapless Semiconductor | 8 (0) | Metal | 9 (1) | Metal | 10 (2) | |||||||||||
| Metal | 8 (0) | Metal | 9 (1) | Metal | 10 (2) | |||||||||||
| Ti | 0.05 | 0.83 | −0.13 | 0.76 | 9 (1) | 0.17 | 1.90 | −0.25 | 1.82 | 10 (2) | 0.44 | 2.56 | −0.18 | 2.82 | 11 (3) | |
| −0.01 | 0.58 | −0.05 | 0.53 | 9 (1) | 0.00 | 0.18 | −0.02 | 0.16 | 10 (2) | 0.19 | 1.95 | −0.05 | 2.10 | 11 (3) | ||
| Metal | 9 (1) | Metal | 10 (2) | 0.09 | 1.37 | −0.15 | 1.31 | 11 (3) | ||||||||
| V | 0.00 | 2.85 | −0.37 | 2.49 | 10 (2) | 0.12 | 3.30 | −0.40 | 3.02 | 11 (3) | 0.34 | 3.81 | −0.21 | 3.94 | 12 (4) | |
| −0.11 | 2.41 | −0.31 | 2.00 | 10 (2) | 0.06 | 3.01 | −0.30 | 2.77 | 11 (3) | 0.08 | 3.00 | −0.14 | 2.93 | 12 (4) | ||
| −0.06 | 2.21 | −0.26 | 1.89 | 10 (2) | 0.06 | 2.74 | −0.38 | 2.42 | 11 (3) | 0.08 | 2.90 | −0.30 | 2.69 | 12 (4) | ||
| Cr | −0.14 | 4.21 | −0.46 | 3.62 | 11 (3) | 0.01 | 4.49 | −0.48 | 4.02 | 12 (4) | 0.23 | 4.88 | −0.16 | 4.95 | 13 (5) | |
| −0.22 | 3.73 | −0.51 | 3.00 | 11 (3) | 0.06 | 4.32 | −0.40 | 3.97 | 12 (4) | 0.14 | 4.65 | −0.15 | 4.65 | 13 (5) | ||
| −0.17 | 3.83 | −0.41 | 3.25 | 11 (3) | 0.03 | 3.92 | −0.50 | 3.45 | 12 (4) | 0.09 | 4.18 | −0.32 | 3.96 | 13 (5) | ||
| Mn | −0.11 | 4.31 | −0.31 | 3.90 | 12 (4) | 0.01 | 4.41 | −0.17 | 4.26 | 13 (5) | −0.02 | 4.35 | 0.03 | 4.36 | 14 (6) | |
| −0.11 | 4.23 | −0.31 | 3.81 | 12 (4) | −0.06 | 4.32 | −0.08 | 4.19 | 13 (5) | −0.18 | 4.10 | 0.07 | 4.0 | 14 (6) | ||
| −0.15 | 3.75 | −0.38 | 3.23 | 12 (4) | −0.03 | 3.85 | −0.27 | 3.55 | 13 (5) | −0.07 | 3.89 | −0.03 | 3.79 | 14 (6) | ||
| Fe | −0.14 | 3.04 | −0.17 | 2.73 | 13 (5) | −0.08 | 3.03 | −0.13 | 2.81 | 14 (6) | −0.09 | 3.13 | 0.13 | 3.17 | 15 (7) | |
| −0.11 | 2.93 | −0.20 | 2.62 | 13 (5) | −0.07 | 2.77 | −0.15 | 2.56 | 14 (6) | −0.10 | 2.82 | 0.03 | 2.75 | 15 (7) | ||
| −0.12 | 2.54 | −0.21 | 2.21 | 13 (5) | −0.06 | 2.40 | −0.16 | 2.18 | 14 (6) | −0.07 | 2.53 | 0.02 | 2.48 | 15 (7) | ||
| Co | −0.09 | 0.95 | −0.12 | 0.74 | 14 (6) | −0.05 | 1.40 | −0.17 | 1.18 | 15 (7) | −0.01 | 1.86 | 0.08 | 1.92 | 16 (8) | |
| Metal | 14 (6) | −0.01 | 1.05 | −0.03 | 1.01 | 15 (7) | −0.05 | 1.69 | 0.14 | 1.77 | 16 (8) | |||||
| Metal | 14 (6) | Metal | 15 (7) | Metal | 16 (8) | |||||||||||
| Ni | Metal | 15 (7) | Metal | 16 (8) | Metal | 17 (9) | ||||||||||
| Metal | 15 (7) | Metal | 16 (8) | Metal | 17 (9) | |||||||||||
| Metal | 15 (7) | Metal | 16 (8) | Metal | 17 (9) | |||||||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Özdoğan, K.; Galanakis, I. Towards Novel Spintronic Materials: Mg-Based d0-d Heusler (Nowotny–Juza) Compounds. Micromachines 2025, 16, 674. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16060674
Özdoğan K, Galanakis I. Towards Novel Spintronic Materials: Mg-Based d0-d Heusler (Nowotny–Juza) Compounds. Micromachines. 2025; 16(6):674. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16060674
Chicago/Turabian StyleÖzdoğan, Kemal, and Iosif Galanakis. 2025. "Towards Novel Spintronic Materials: Mg-Based d0-d Heusler (Nowotny–Juza) Compounds" Micromachines 16, no. 6: 674. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16060674
APA StyleÖzdoğan, K., & Galanakis, I. (2025). Towards Novel Spintronic Materials: Mg-Based d0-d Heusler (Nowotny–Juza) Compounds. Micromachines, 16(6), 674. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16060674






