Laser Fabrication and Comparative Study of Planoconcave and Planoconvex Microlenses on Fused Silica and Sapphire
Abstract
1. Introduction
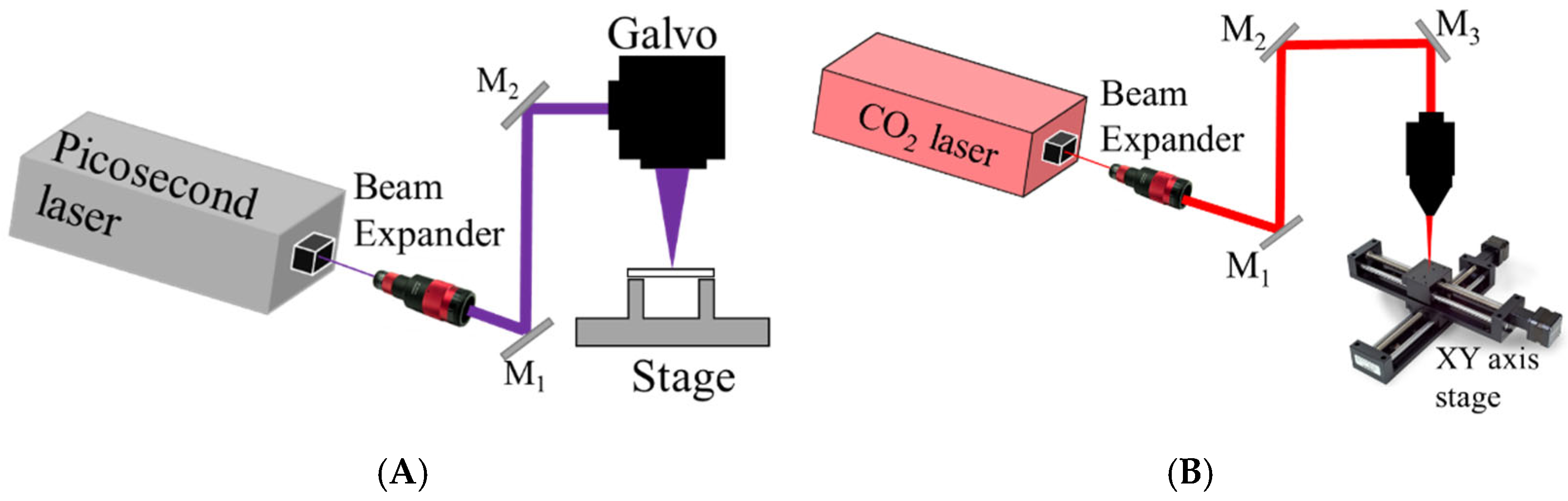
2. Experimental
3. Results
3.1. Design of MLAs
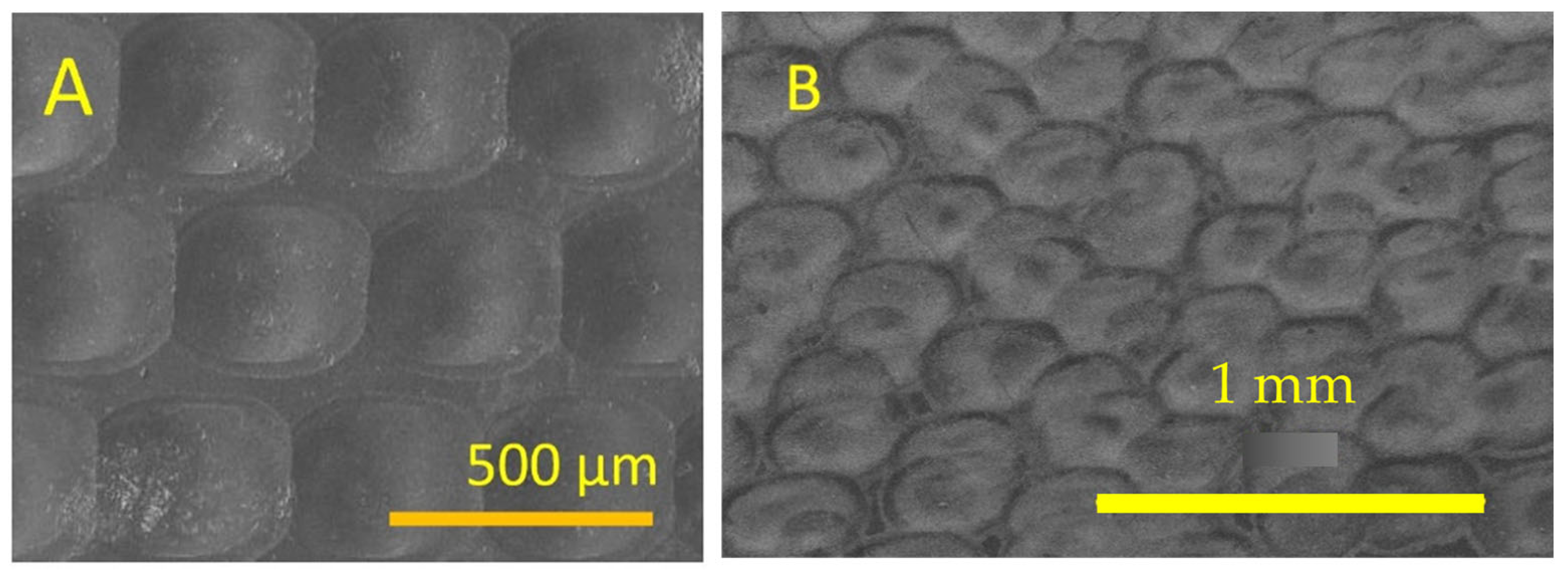
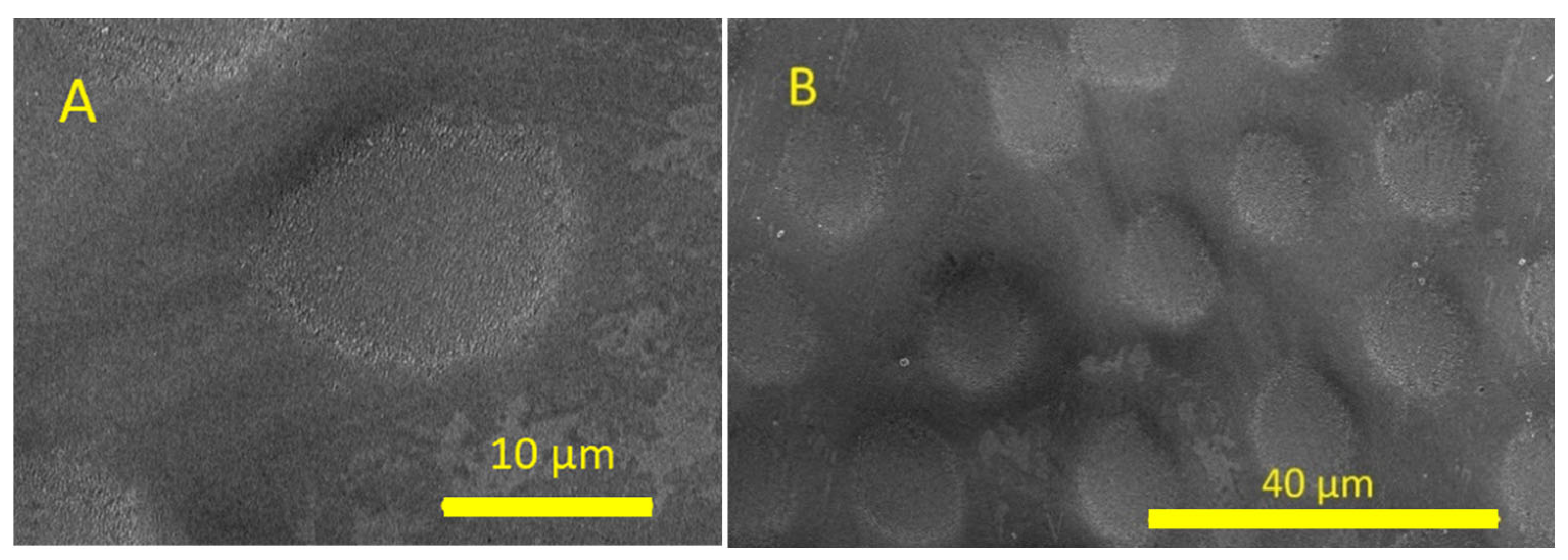
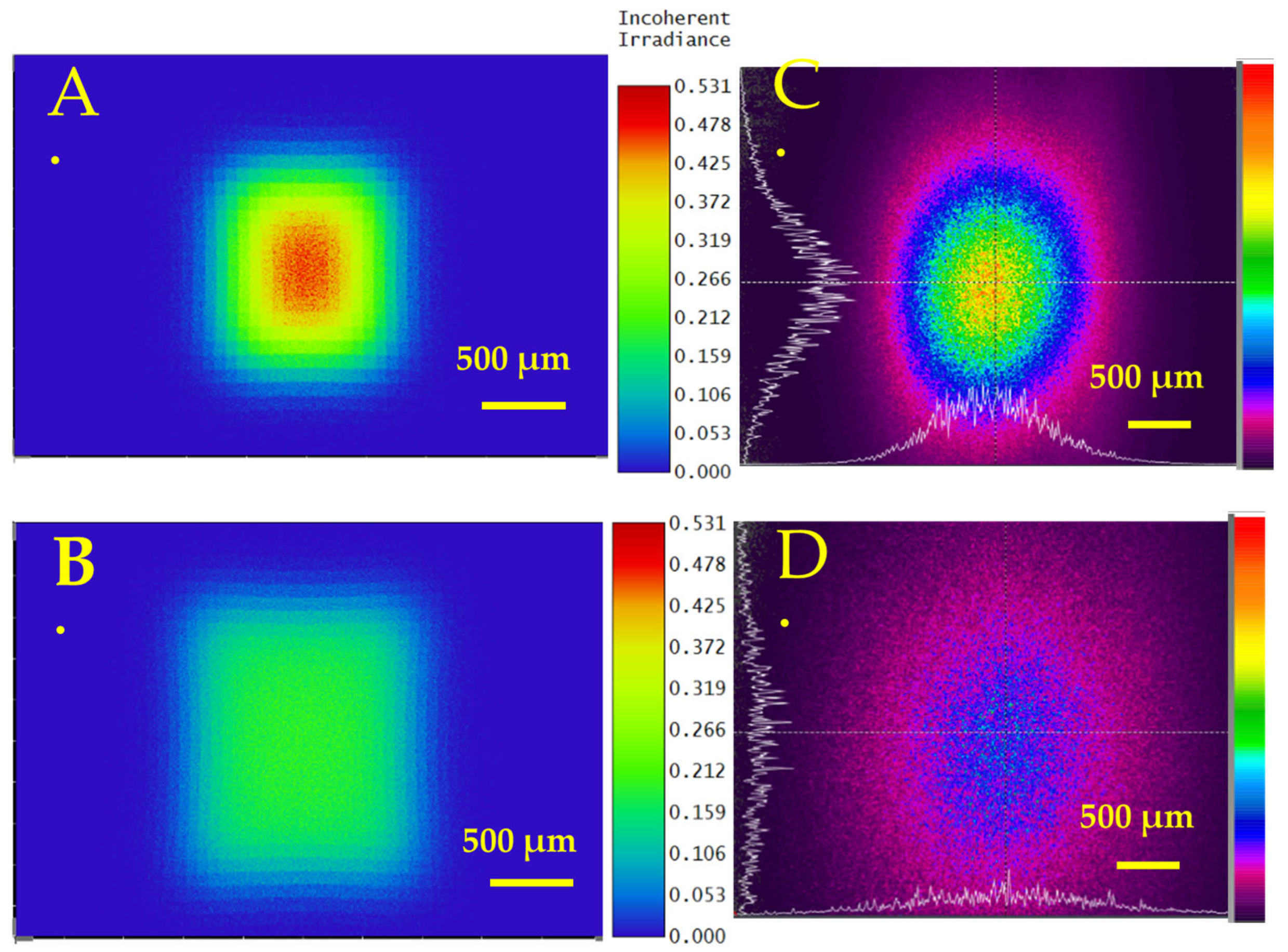
3.2. Concave Lens Fabrication on Fused Silica by CO2 Laser
3.3. Concave Lens Fabrication on Fused Silica by Picosecond Laser
3.4. Cylindrical Lens Fabrication on Fused Silica by Combining Picosecond and CO2 Lasers
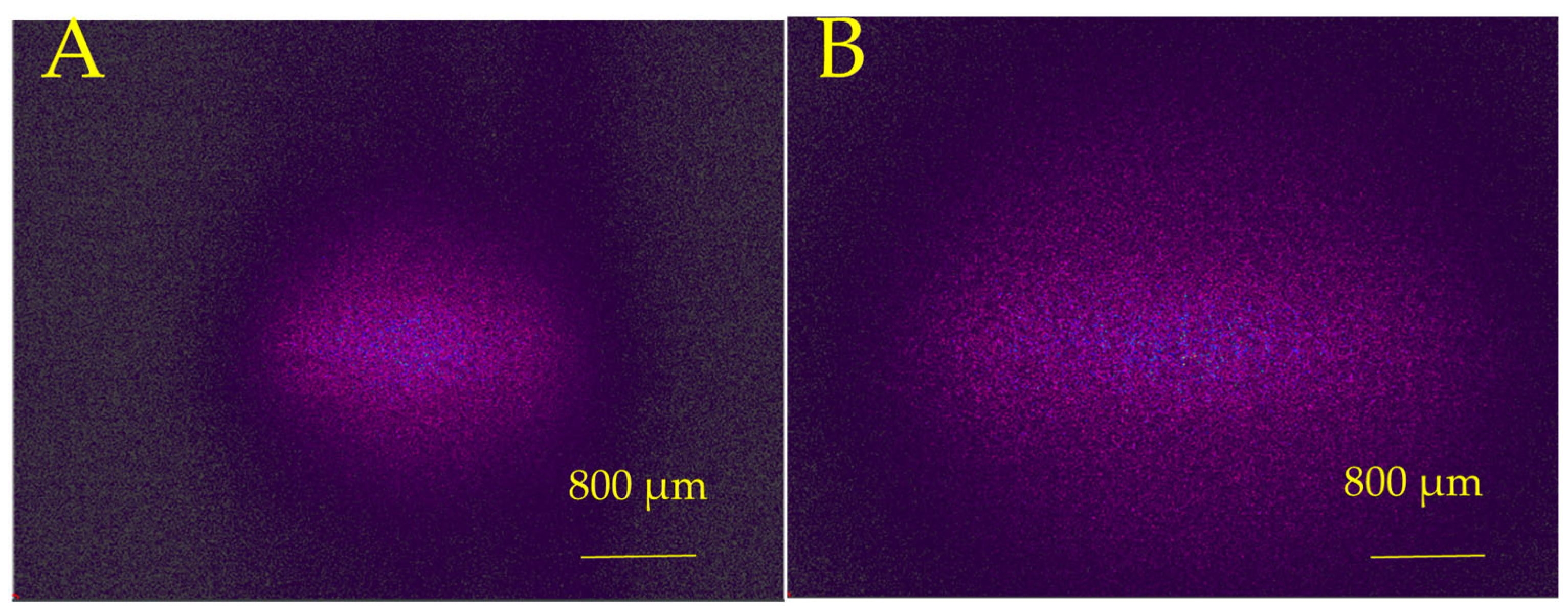
3.5. Convex Lens Fabrication on Fused Silica by Combining CO2 and Picosecond Laser
3.6. Concave Lens Fabrication on Sapphire by Picosecond Laser
3.7. Commercially Available MLA
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Al-Hamdani, A.H.; Rashid, H.G.; Ghayib, Z.R. Improvement of laser to fiber coupling efficiency using microlens technique. ARPN J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 2014, 9, 2286–2291. [Google Scholar]
- Harder, I.; Lano, M.; Lindlein, N.; Schwider, J. Homogenization and beam shaping with microlens arrays. Proc. SPIE 2004, 5456, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Hassan, A.; Jiang, Y. Freeform microlens array homogenizer for excimer laser beam shaping. Opt. Express 2016, 24, 24846–24858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Yi, A.Y. Design and fabrication of a freeform microlens array for uniform beam shaping. Microsyst. Technol. 2011, 17, 1713–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Kim, M.; Lee, G.; Yoo, Y.J.; Song, Y. Large area fabrication of engineered microlens array with low sag height for light-field imaging. Opt. Express 2019, 27, 4435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, X.-H.; Moreno, I.; Sun, C.-C. High-performance LED street lighting using microlens arrays. Opt. Express 2013, 21, 10612–10621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu-yan, P.; Xiong-tu, Z.; Yong-ai, Z.; Lan, Y.; Tai-liang, G. Design and Simulation of Curved Microlens Array for Integral Imaging 3D Display. Acta Photonica Sin. 2016, 45, 322002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.T.; Weng, Y.L.; Peng, Y.Y.; Chen, G.; Lin, J.P.; Yan, Q.; Zhang, Y.A.; Guo, T.L. Design and Fabrication of Square Micro-lens Array for Integral Imaging 3D Display. Opt. Int. J. Light Electron Opt. 2017, 157, 532–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Liu, X.; Cheng, Q.; Liang, Z. Long-term photovoltaic performance of thin-film solar cells with diffractive microlens arrays on glass substrates. Results Phys. 2021, 21, 103841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hamdani, A. Experimental and theoretical design for a new array micro-lenses silicon solar cell concentrator. ARPN J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 2013, 8, 169–172. [Google Scholar]
- Sinha, A.; Gupta, M.C. Microscale patterning of semiconductor c-Si by selective laser-heating induced KOH etching. Semicond. Sci. Technol. 2021, 36, 85002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, A.; Soman, A.; Das, U.; Hegedus, S.; Gupta, M.C. Nanosecond Pulsed Laser Patterning of Interdigitated Back Contact Heterojunction Silicon Solar Cells. IEEE J. Photovolt. 2020, 10, 1648–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wypych, G. 2—Fillers—Origin, Chemical Composition, Properties, and Morphology, 4th ed.; ChemTec Publishing: Toronto, ON, Canada, 2016; pp. 13–266. ISBN 978-1-895198-91-1. [Google Scholar]
- Bae, S.-I.; Kim, K.; Yang, S.; Jang, K.; Jeong, K.-H. Multifocal microlens arrays using multilayer photolithography. Opt. Express 2020, 28, 9082–9088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.-H.; Park, C.; Whitesides, G.M. Fabrication of Arrays of Microlenses with Controlled Profiles Using Gray-Scale Microlens Projection Photolithography. Langmuir 2002, 18, 9312–9318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nussbaum, P.; Völkel, R.; Herzig, H.P.; Eisner, M.; Haselbeck, S. Design, fabrication and testing of microlens arrays for sensors and microsystems. Pure Appl. Opt. J. Eur. Opt. Soc. Part A 1997, 6, 617–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stankevičius, E.; Daugnoraitė, E.; Ignatjev, I.; Kuodis, Z.; Niaura, G.; Račiukaitis, G. Concentric microring structures containing gold nanoparticles for SERS-based applications. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 497, 143752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stankevičius, E.; Garliauskas, M.; Raciukaitis, G. Bessel-like Beam Array Generation Using Round-tip Micro-structures and Their Use in the Material Treatment. J. Laser Micro Nanoeng. 2016, 11, 352–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kim, K.-R.; Chang, S.; Oh, K. Refractive microlens on fiber using UV-curable fluorinated acrylate polymer by surface-tension. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 2003, 15, 1100–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, D.; Zhang, H.; Shu, X.; Xiao, J. Fabrication of polymer micro-lens array with pneumatically diaphragm-driven drop-on-demand inkjet technology. Opt. Express 2012, 20, 15186–15195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Yuan, X.-C.; Ngo, N.Q.; Bu, J.; Tao, S.H. Single-step fabrication of a microlens array in sol–gel material by direct laser writing and its application in optical coupling. J. Opt. A Pure Appl. Opt. 2003, 6, 94–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Qin, Y.; Tu, P.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, M.; Yang, Z. High fill factor microlens array fabrication using direct laser writing and its application in wavefront detection. Opt. Lett. 2020, 45, 4460–4463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsutsumi, N.; Hirota, J.; Kinashi, K.; Sakai, W. Direct laser writing for micro-optical devices using a negative photoresist. Opt. Express 2017, 25, 31539–31551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smuk, A.Y.; Lawandy, N.M. Direct laser fabrication of dense microlens arrays in semiconductor-doped glass. J. Appl. Phys. 2000, 87, 4026–4030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Li, M.; Shen, L.; Qiu, J.; Zhou, Y. Fabrication of high quality aspheric microlens array by dose-modulated lithography and surface thermal reflow. Opt. Laser Technol. 2018, 100, 298–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigaliūnas, V.; Lazauskas, A.; Jucius, D.; Viržonis, D.; Abakevičienė, B.; Smetona, S.; Tamulevičius, S. Microlens fabrication by 3D electron beam lithography combined with thermal reflow technique. Microelectron. Eng. 2016, 164, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Chao, C.-K.; Wei, M.-K.; Lin, C.-P. High fill-factor microlens array mold insert fabrication using a thermal reflow process. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2004, 14, 1197–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Peng, K.; Cao, X.; Wang, W.; Chen, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhao, J.; Li, B. CO2 laser thermal reflow shaped convex glass microlens array after Bessel picosecond laser inscribing and hydrofluoric acid processing. Appl. Opt. 2020, 59, 1099–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.Y.; Yang, S.Y.; Sheh, J.L. A roller embossing process for rapid fabrication of microlens arrays on glass substrates. Microsyst. Technol. 2006, 12, 754–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, P.; Deng, Y.; Hao, P.; Fan, J.; Chi, M.; Wu, Y. Polymeric microlens array fabricated with PDMS mold-based hot embossing. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2014, 24, 95028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, C.T.; Wu, T.T.; Chen, M.F.; Chang, Y.C.; Lee, C.J.; Huang, J.C. Hot embossing of micro-lens array on bulk metallic glass. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2008, 141, 422–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, N.S.; Koh, Y.H.; Fu, Y.Q. Microlens array produced using hot embossing process. Microelectron. Eng. 2002, 60, 365–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Liu, H.; Yang, Q.; Wang, X.; Hou, C.; Bian, H.; Liang, W.; Si, J.; Hou, X. Maskless fabrication of concave microlens arrays on silica glasses by a femtosecond-laser-enhanced local wet etching method. Opt. Express 2010, 18, 20334–20343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Yang, Q.; Chen, F.; Bian, H.; Deng, Z.; Du, G.; Si, J.; Yun, F.; Hou, X. Cost-efficient and flexible fabrication of rectangular-shaped microlens arrays with controllable aspect ratio and spherical morphology. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 292, 285–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.-W.; Chen, Q.-D.; Zhang, L.; Tian, Z.-N.; Li, Q.-K.; Wang, L.; Juodkazis, S.; Sun, H.-B. Single-pulse writing of a concave microlens array. Opt. Lett. 2018, 43, 831–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Li, M.; Qiu, J.; Ye, H. Fabrication of high fill-factor aspheric microlens array by dose-modulated lithography and low temperature thermal reflow. Microsyst. Technol. 2019, 25, 1235–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Zhu, L.; Chen, H.; Yang, M.; Zhang, W. Fabrication of multi-scale micro-lens arrays on hydrophobic surfaces using a drop-on-demand droplet generator. Opt. Laser Technol. 2015, 66, 156–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forest, C.R.; Saez, M.A.; Hunter, I.W. Microforging technique for rapid, low-cost fabrication of lens array molds. Appl. Opt. 2007, 46, 8668–8673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, H.; Choi, D.-Y.; Gai, X.; Luther-Davies, B.; Zhang, B. CMOS compatible fabrication of micro, nano convex silicon lens arrays by conformal chemical vapor deposition. Opt. Express 2017, 25, 3069–3076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado, T.; Nieto, D.; Flores-Arias, M.T. Soda-lime glass microlens arrays fabricated by laser: Comparison between a nanosecond and a femtosecond IR pulsed laser. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2016, 86, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado, T.; Nieto, D.; Flores-Arias, M.T. Fabrication of microlens arrays on soda-lime glass using a laser direct-write technique and a thermal treatment assisted by a CO2 laser. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2015, 73, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.-K.; Ahsan, M.S.; Yoo, D.; Sohn, I.-B.; Noh, Y.-C.; Kim, J.-T.; Jung, D.; Kim, J.; Kang, H.-M. Formation of cylindrical micro-lens array on fused silica glass surface using CO2 laser assisted reshaping technique. Opt. Laser Technol. 2015, 75, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.-K.; Ryu, J.; Kim, C.; Noh, Y.-C.; Sohn, I.-B.; Kim, J.-T. Formation of Micro-lens Array using Femtosecond and CO2 lasers. J. Laser Micro Nanoeng. 2016, 11, 341. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, C.; Sohn, I.-B.; Lee, Y.J.; Byeon, C.C.; Kim, S.Y.; Park, H.; Lee, H. Fabrication of a fused silica based mold for the microlenticular lens array using a femtosecond laser and a CO2 laser. Opt. Mater. Express 2014, 4, 2233–2240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, P.; Wei, H.; Fan, W.; Li, X.; Zhu, J. Numerical and Experimental Investigation of Morphological Modification on Fused Silica Using CO2 Laser Ablation. Materials 2019, 12, 4109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakaki, M.; Komachi, Y.; Kanai, G. Microlenses and microlens arrays formed on a glass plate by use of a CO2 laser. Appl. Opt. 1998, 37, 627–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, S.; Rung, S.; Esen, C.; Hellmann, R. Fabrication of a high-quality axicon by femtosecond laser ablation and CO2 laser polishing for quasi-Bessel beam generation. Opt. Express 2018, 26, 23287–23294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, S.; Rung, S.; Esen, C.; Hellmann, R. Rapid fabrication of precise glass axicon arrays by an all laser-based manufacturing technology. J. Laser Appl. 2019, 32, 12001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Cheng, J.; Yin, Z.; Yang, H.; Liu, Q.; Tan, C.; Liao, W.; Chen, M.; Yuan, X. Rapid CO2 laser processing technique for fabrication of micro-optics and micro-structures on fused silica materials. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part B J. Eng. Manuf. 2020, 236, 100–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohn, I.-B.; Yoo, D.; Noh, Y.-C.; Sung, J.-H.; Lee, S.-K.; Choi, H.-K.; Ahsan, M.S. Formation of a plano-convex micro-lens array in fused silica glass by using a CO2 laser-assisted reshaping technique. J. Korean Phys. Soc. 2016, 69, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, T.; Conrad, D. Micro lens arrays made by CO2-laser radiation. In Proceedings of the Seventh European Seminar on Precision Optics Manufacturing, Teisnach, Germany, 31 March–1 April 2020; Haberl, A., Fütterer, G., Fähnle, O.W., Rascher, R., Eds.; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2020; Volume 11478, p. 39. [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz, S.; Götzendorfer, B.; Rung, S.; Esen, C.; Hellmann, R. Compact Beam Homogenizer Module with Laser-Fabricated Lens-Arrays. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Büttner, S.; Pfeifer, M.; Weissmantel, S. Manufacturing of Cylindrical Micro Lenses and Micro Lens Arrays in Fused Silica and Borosilicate Glass using F2-Laser Microstructuring. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Photonics, Optics and Laser Technology, Prague, Czech Republic, 25–27 February 2019. [Google Scholar]




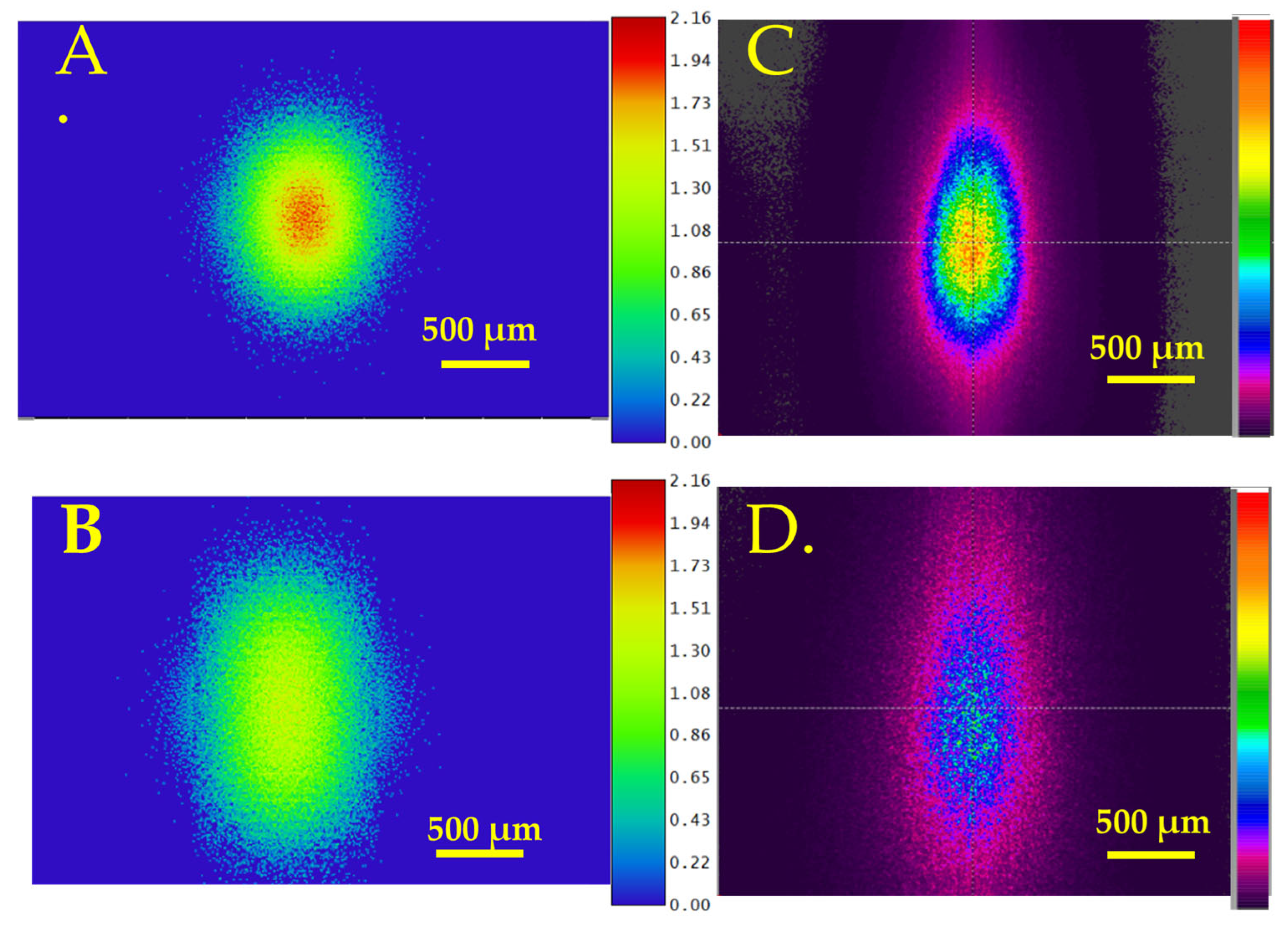
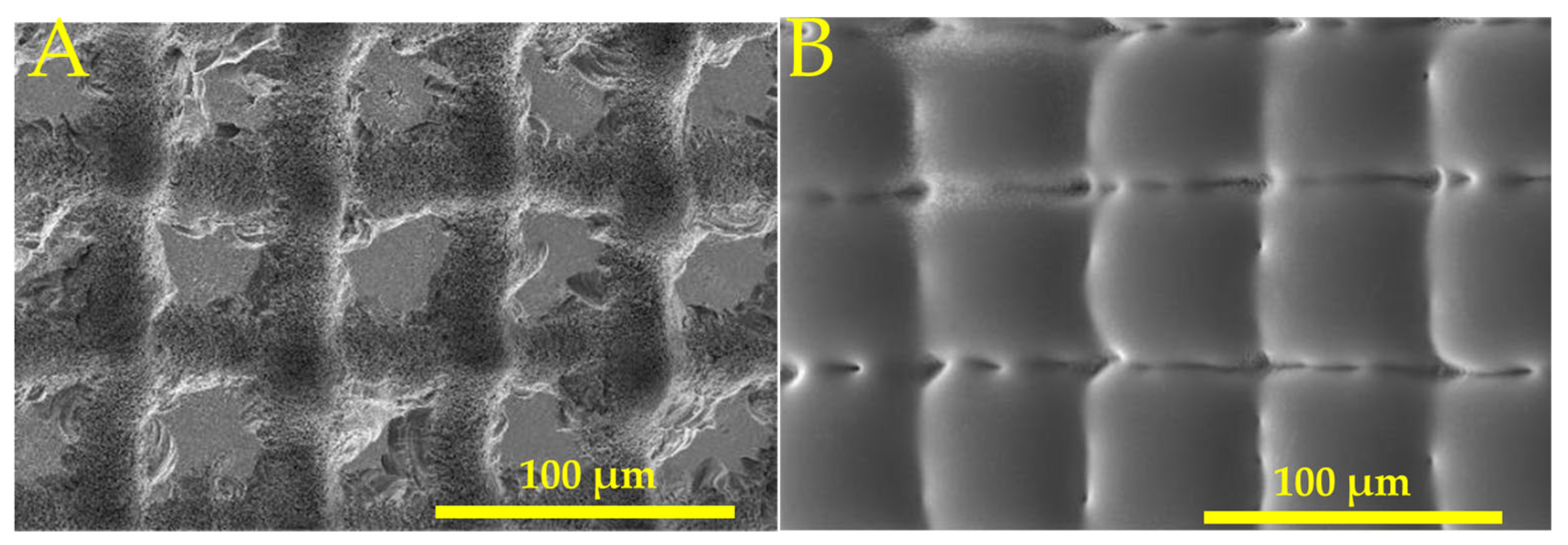
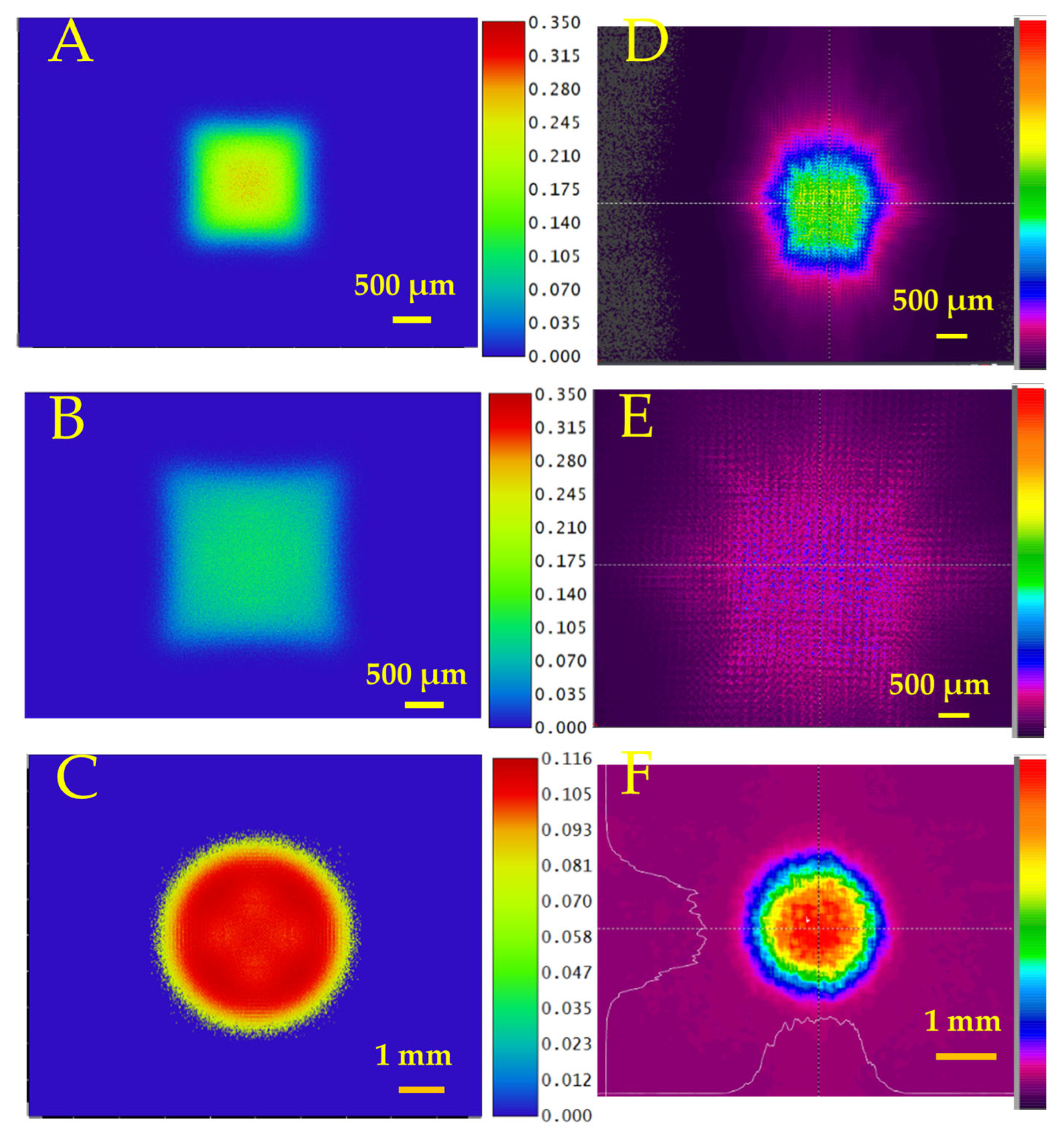
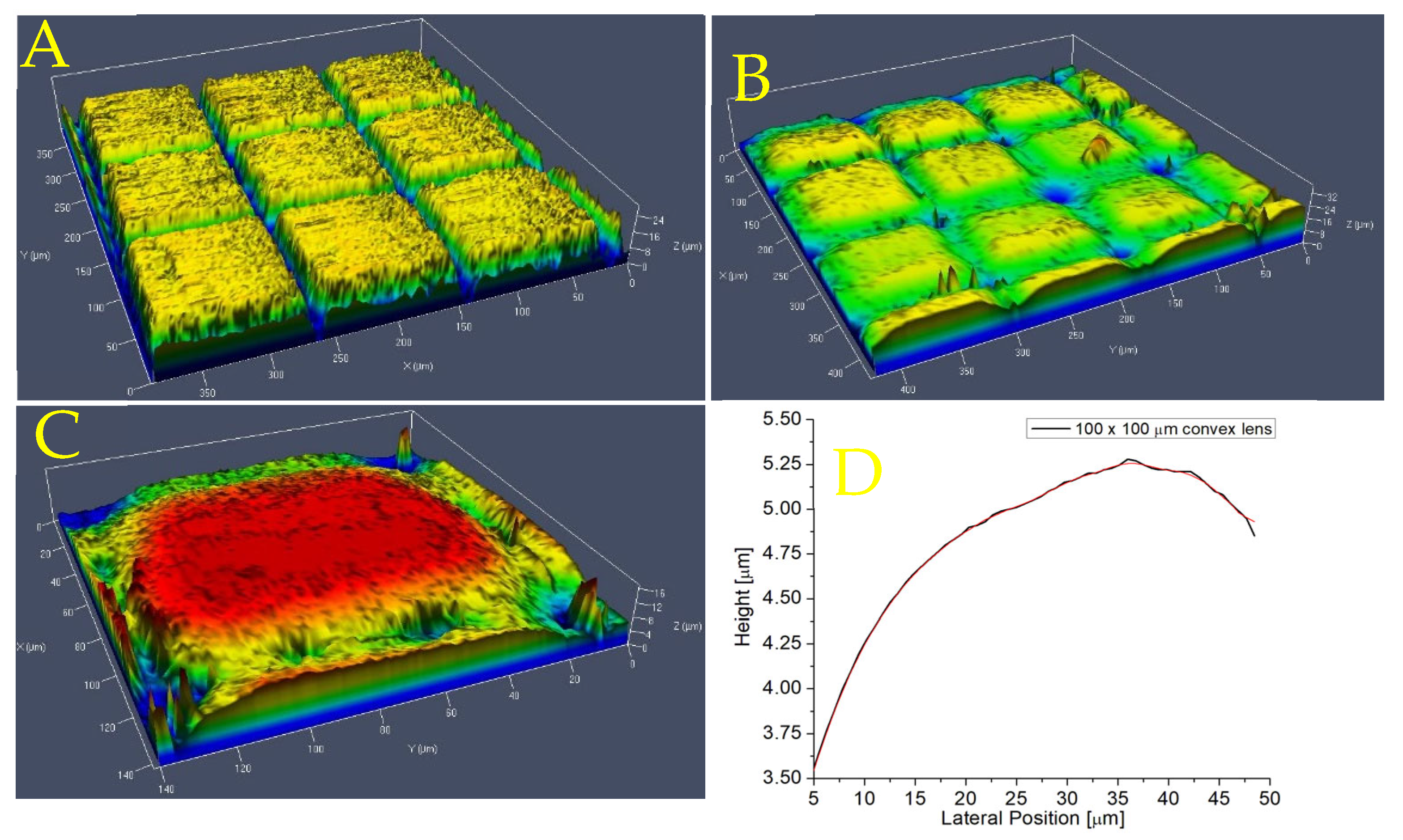




| Paper | Type of Lens | Pulse Width, Wavelength | T | R (nm) | FL | Thermal Treatment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| This study | Concave, Convex, and Cylindrical | 355 nm ps, and 10.6 µm, CW | >94% | 75 | 180 µm | No thermal treatment |
| [40] | Convex | 1030 nm fs, 1064 nm ns, 10.6 µm, CW | - | 3.90 | 1 mm | 500 °C |
| [41] | Convex | 1064 nm ns, 10.6 µm, CW | - | 9.6 | 1 mm | 500 °C |
| [42] | Cylindrical lenses | 1030 nm fs, 10.6 µm, CW | - | - | 18 µm | No thermal treatment |
| [43] | Convex and Cylindrical lenses | 1030 nm fs, 10.6 µm, CW | - | 783 | 125 µm | No thermal treatment |
| [44] | Cylindrical lenses | 1030 nm fs, 10.6 µm, CW | - | 10 | 125 µm | No thermal treatment |
| [45] | Concave lens | 10.6 µm, CW | - | 475 | - | No thermal treatment |
| [46] | Concave lens | 10.6 µm, CW | - | - | 181 µm | Not provided |
| [47] | Axicon | 1030 nm fs, 10.6 µm, CW | - | 34 | 2 mm | No thermal treatment |
| [49] | Concave | 10.6 µm, CW | - | 78 | - | No thermal treatment |
| Parameter | ps Laser Fabrication (Concave Lens) | CO2 Laser Fabrication (Concave Lens) | ps + CO2 Laser Fabrication (Convex Lens) | ps + CO2 Laser Fabrication (Cylindrical Lens) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wavelength | 355 nm | 10.6 µm | 355 nm + 10.6 µm | 355 nm + 10.6 µm |
| Pulse width | 10 ps | CW | 6 ps +CW | 6 ps +CW |
| Power/energy density | 4.7 J/cm2 | 43.6 kW/cm2 | 4.7 J/cm2 + 25.2 kW/cm2 | 4.7 J/cm2 + 25.2 kW/cm2 |
| Repetition rate | 350 kHz | Continuous | 350 kHz + CW | 350 kHz + CW |
| Scan speed (mm/s) | 1000 | 100 | 1000 + 100 | 1000 + 100 |
| µ-lens height (µm) | 6.14 | 27.4 | 6.5 | 3.1 |
| Simulated focal length (µm) | −262.5 | −2251.6 | 156.5 | 34.8 |
| Measured focal length (µm) | −145.64 | −1796.7 | 177.49 | 55.69 |
| Transmission efficiency (before ARC) | 85.2% | 90.8% | 84.3% | 86.7% |
| Transmission efficiency (after ARC) | 92.1% | 94.5% | 93.4% | Not coated |
| Simulated beam divergence (degrees) | X: 8.56 Y: 11.4 | X: 2.56 Y: 4.58 | X: 8.56 Y: 10.00 | X: 2.86 Y: 11.4 |
| Measured beam divergence (degrees) | X: 11.99 Y: 15.09 | X: 6.13 Y: 8.04 | X: 13.35 Y: 15.56 | X: 5.55 Y: 11.33 |
| Fabrication time for 1-inch MLA | 2 min | 1 min | 4 min | 4 min |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gottumukkala, N.R.; Barnes, C.; Gupta, M.C. Laser Fabrication and Comparative Study of Planoconcave and Planoconvex Microlenses on Fused Silica and Sapphire. Micromachines 2025, 16, 608. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16060608
Gottumukkala NR, Barnes C, Gupta MC. Laser Fabrication and Comparative Study of Planoconcave and Planoconvex Microlenses on Fused Silica and Sapphire. Micromachines. 2025; 16(6):608. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16060608
Chicago/Turabian StyleGottumukkala, Narayana R., Caleb Barnes, and Mool C. Gupta. 2025. "Laser Fabrication and Comparative Study of Planoconcave and Planoconvex Microlenses on Fused Silica and Sapphire" Micromachines 16, no. 6: 608. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16060608
APA StyleGottumukkala, N. R., Barnes, C., & Gupta, M. C. (2025). Laser Fabrication and Comparative Study of Planoconcave and Planoconvex Microlenses on Fused Silica and Sapphire. Micromachines, 16(6), 608. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16060608







