Advances in Magnetically Controlled Medical Robotics: A Review of Actuation Systems, Continuum Designs, and Clinical Prospects for Minimally Invasive Therapies
Abstract
1. Introduction
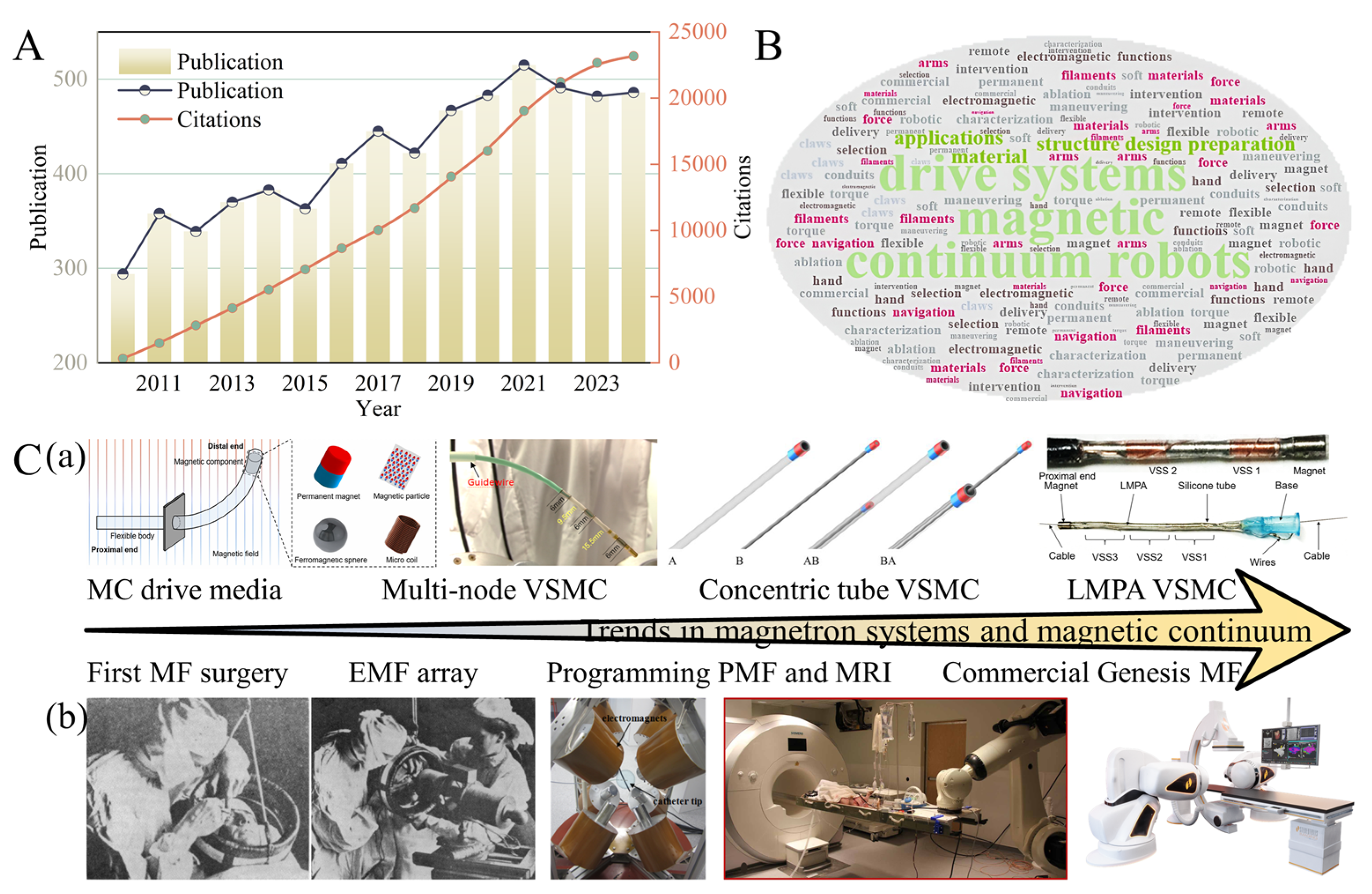
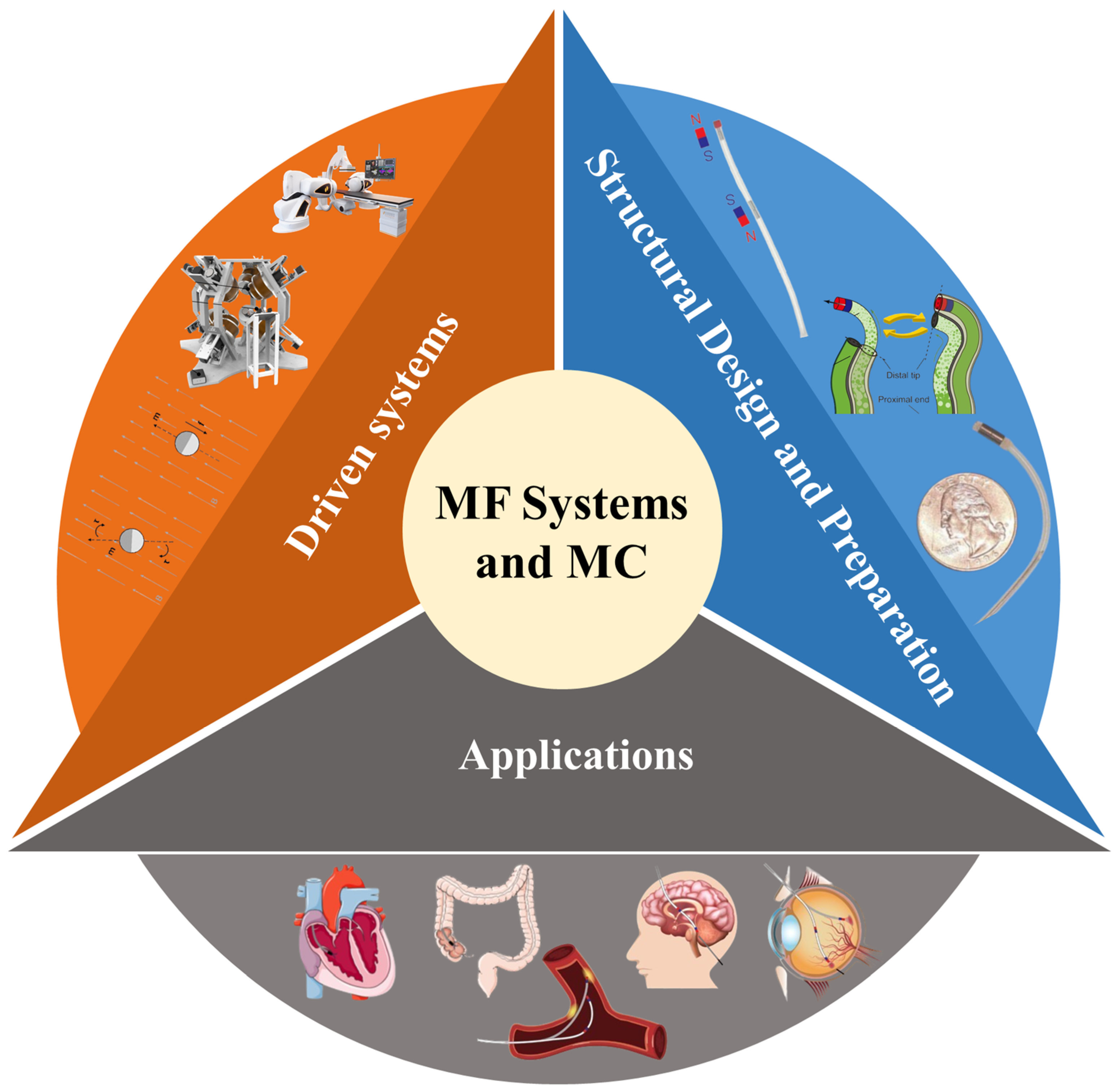
2. Driven Systems
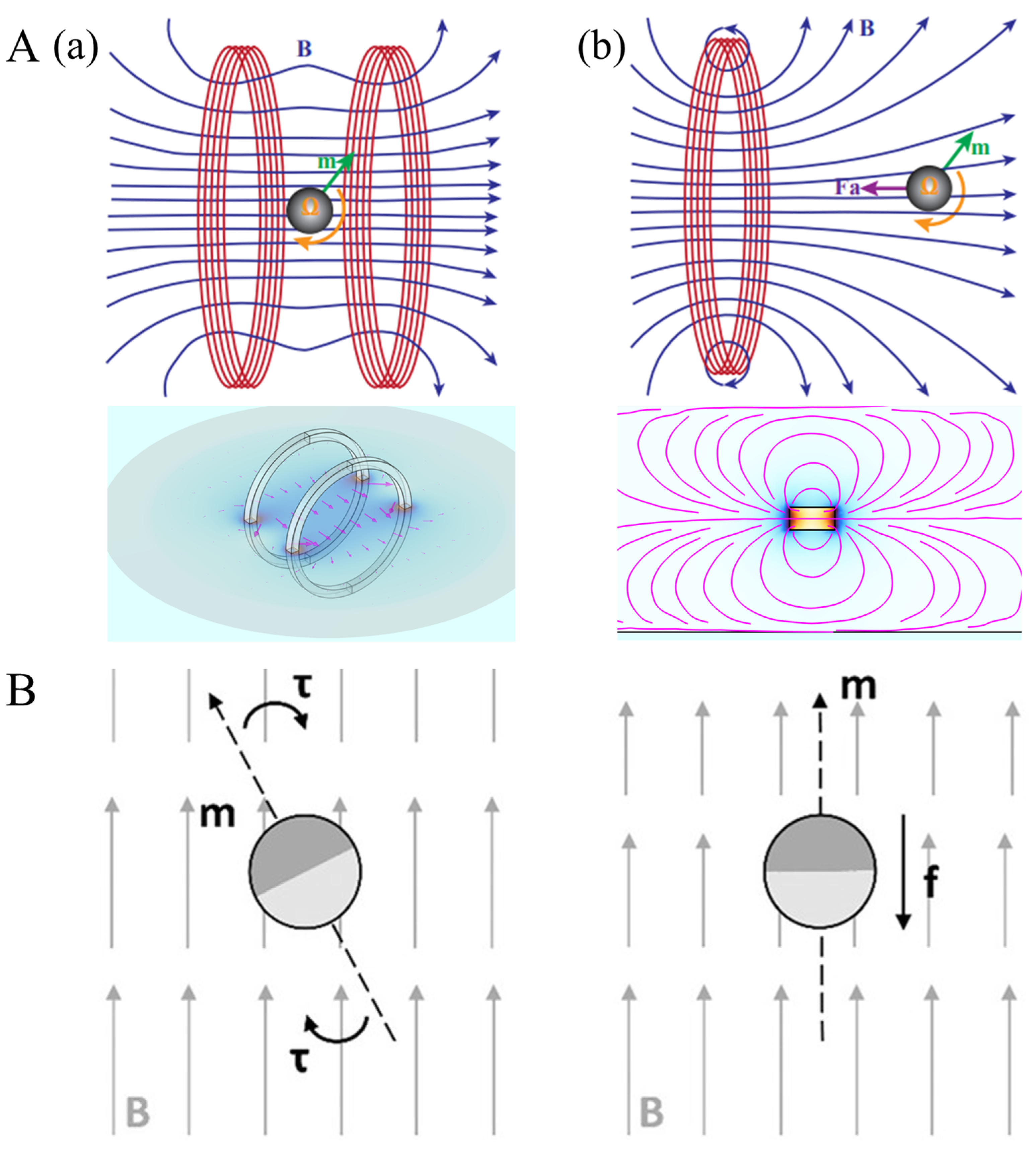
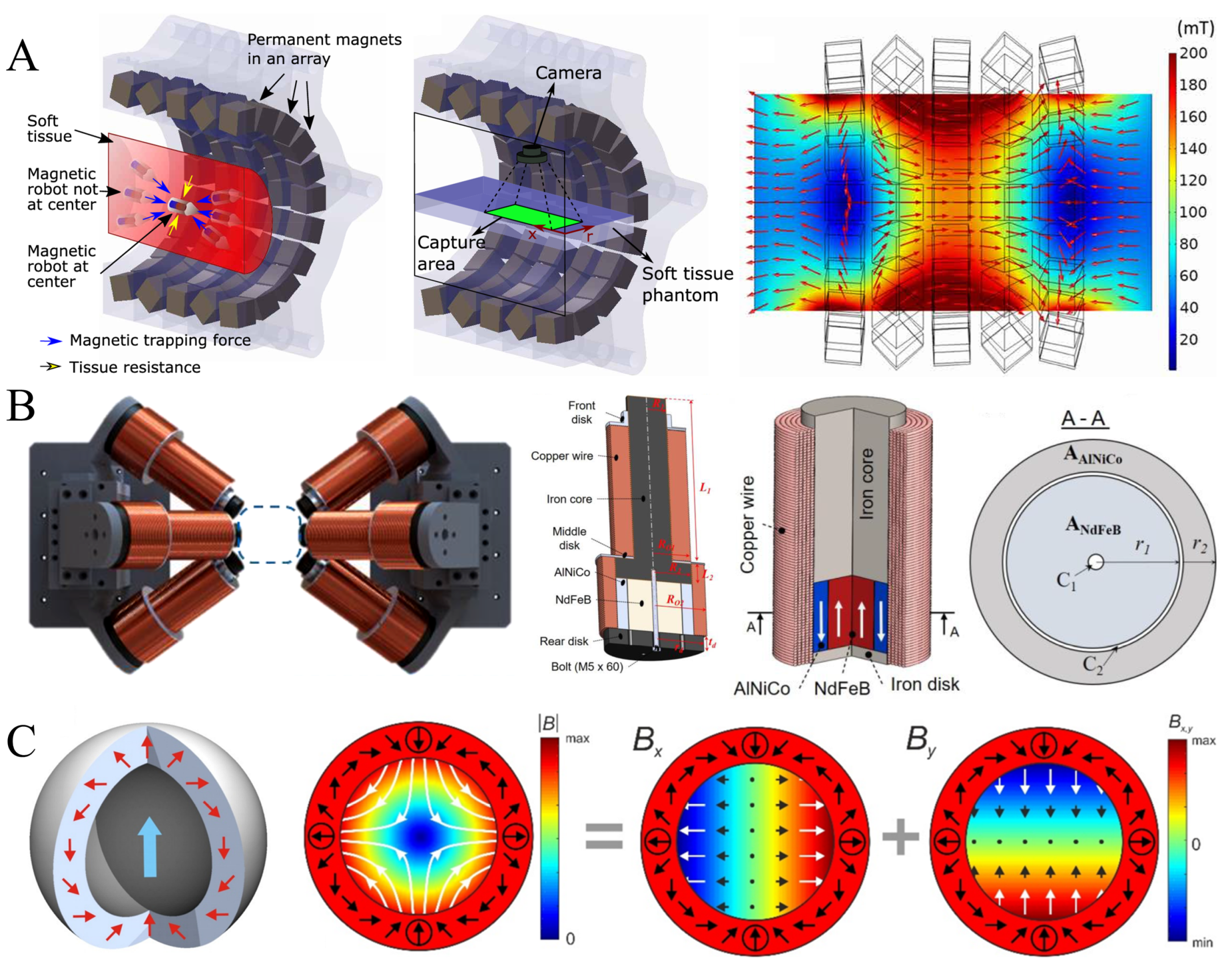
2.1. Permanent Magnet Control System
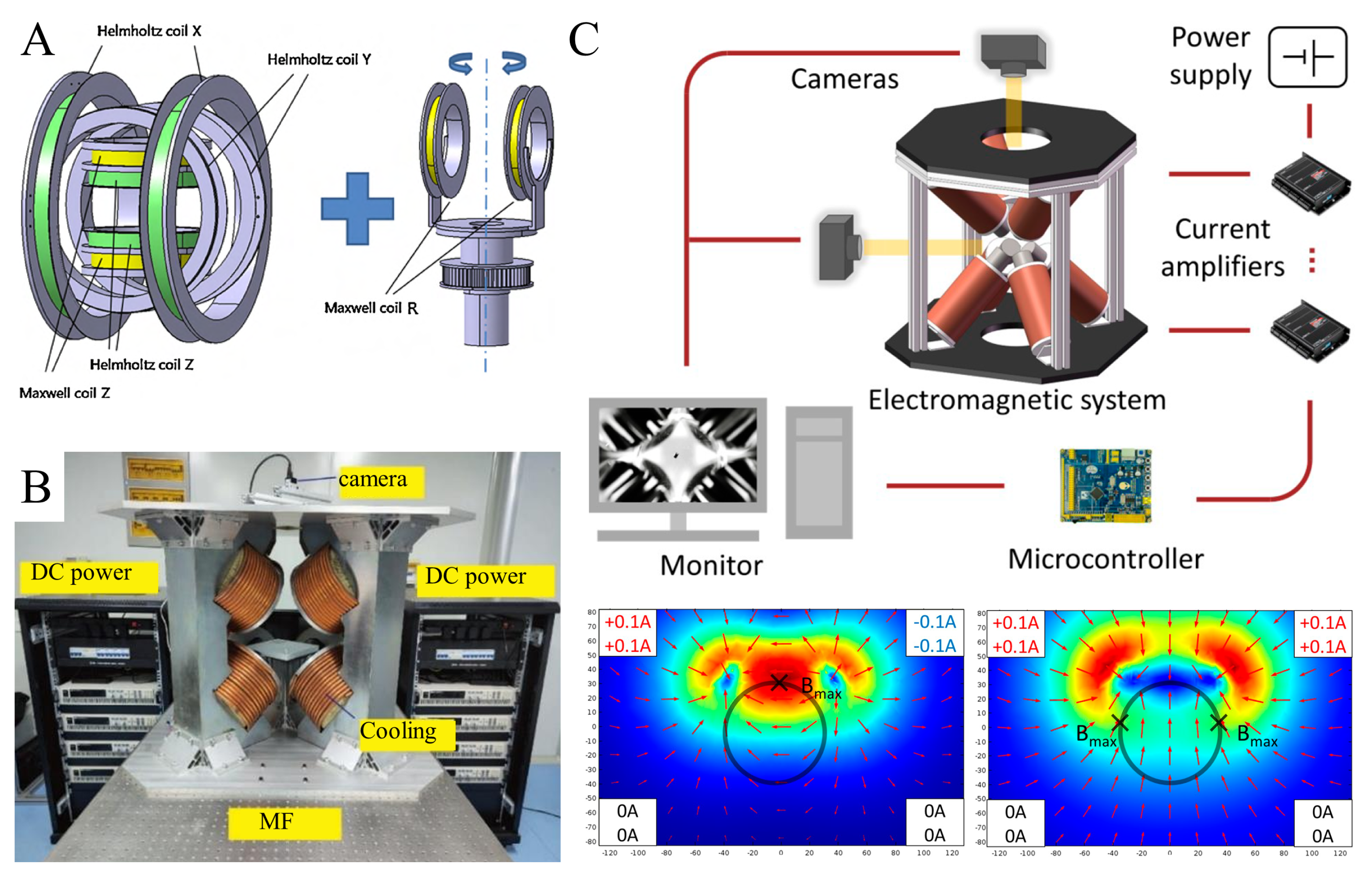
2.2. Electromagnet Control System
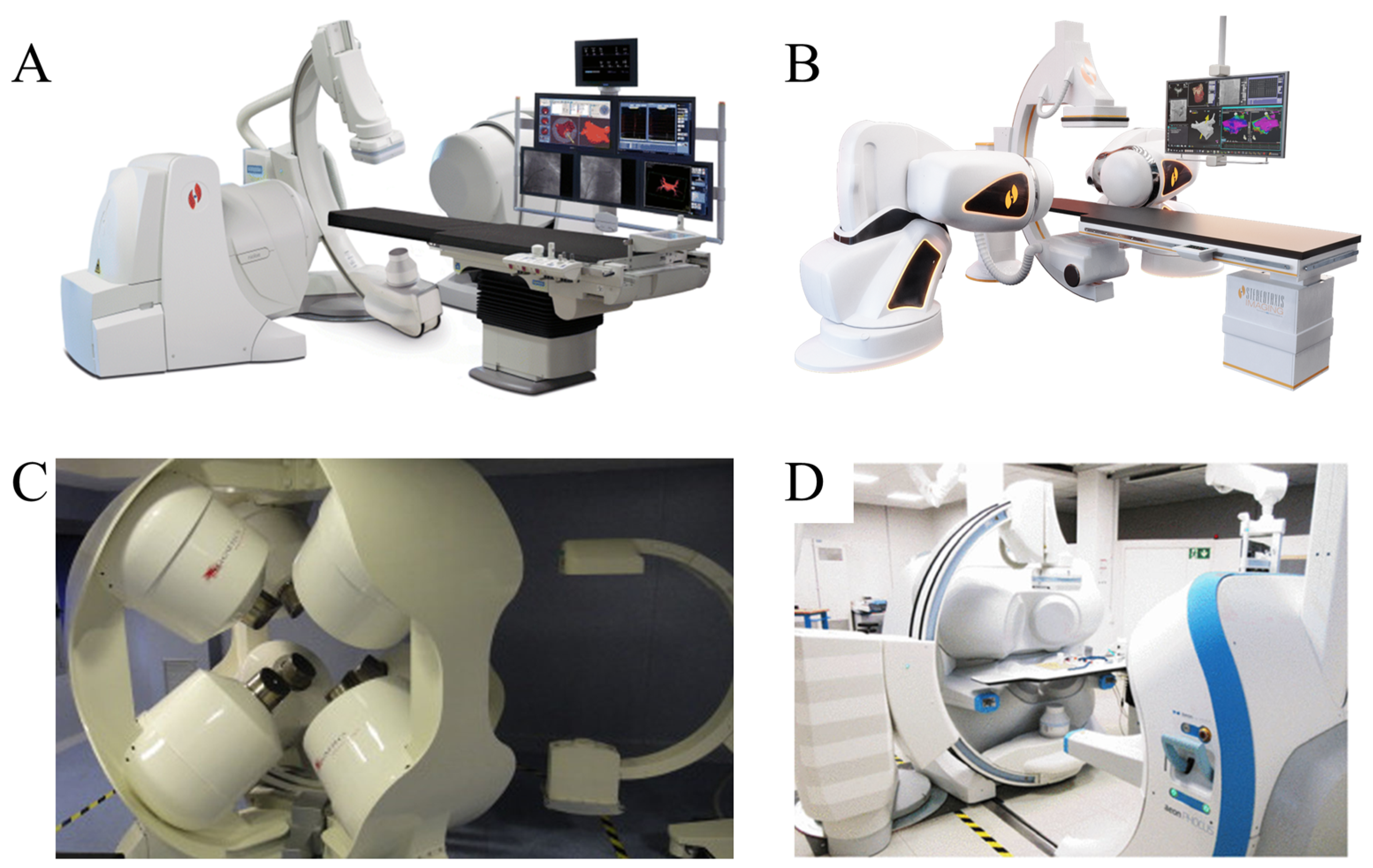
2.3. Commercial Magnetic Control Systems
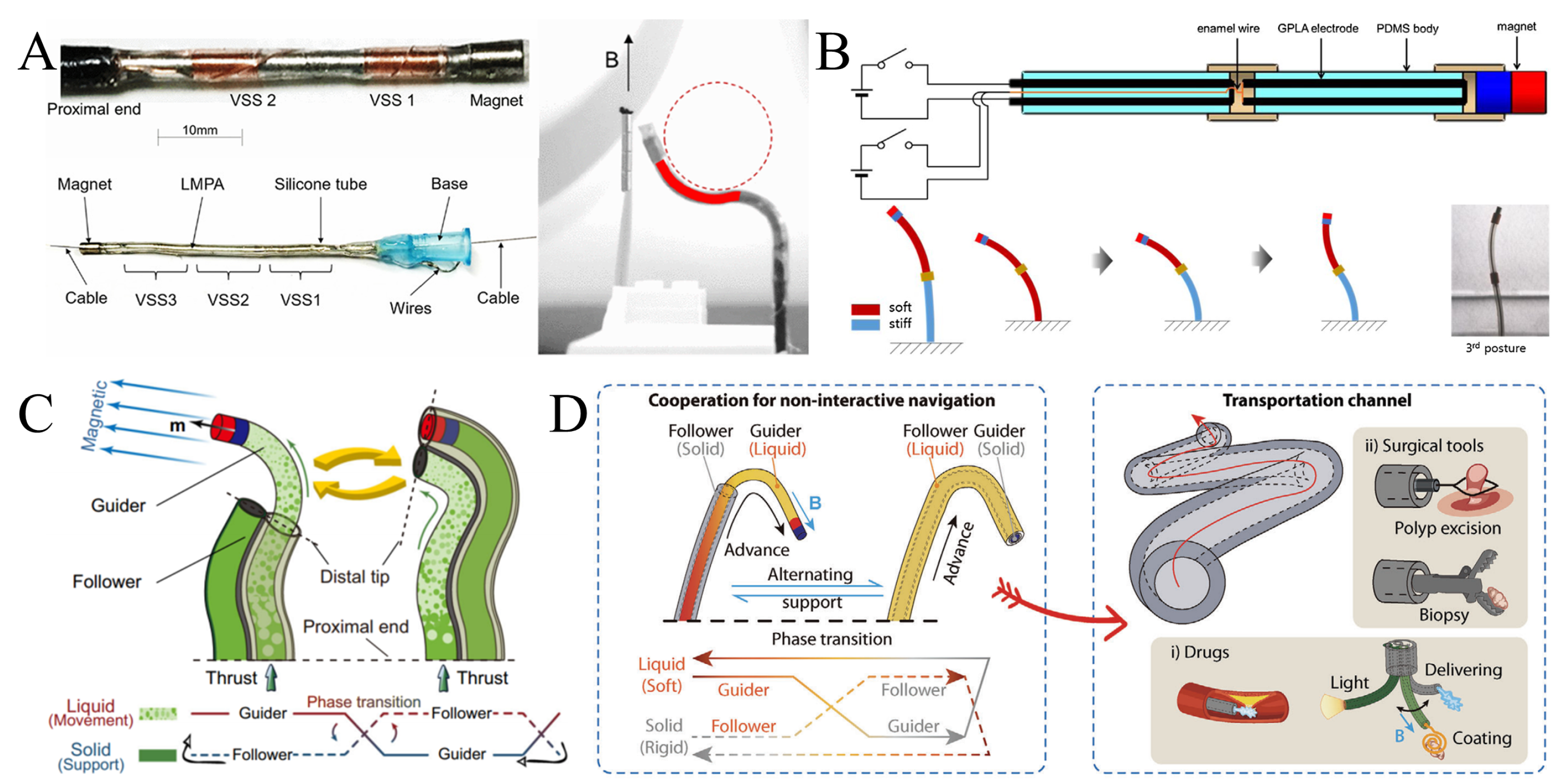
3. Structural Design and Preparation of Magnetic Continua
3.1. Continuum of Magnetically Guided Wires and Magnetic Conduits
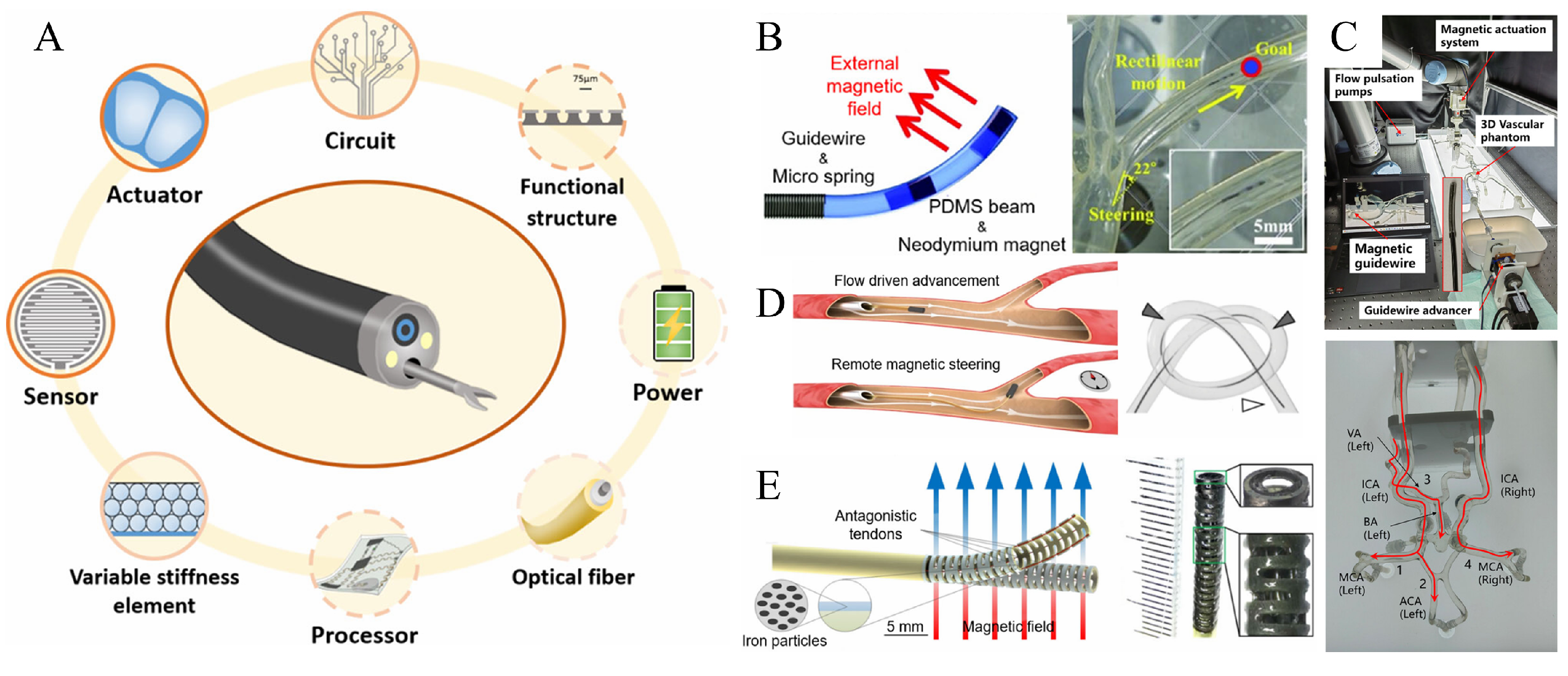
3.2. Variable Stiffness Magnetic Continuum Based on Low Melting Point Alloys
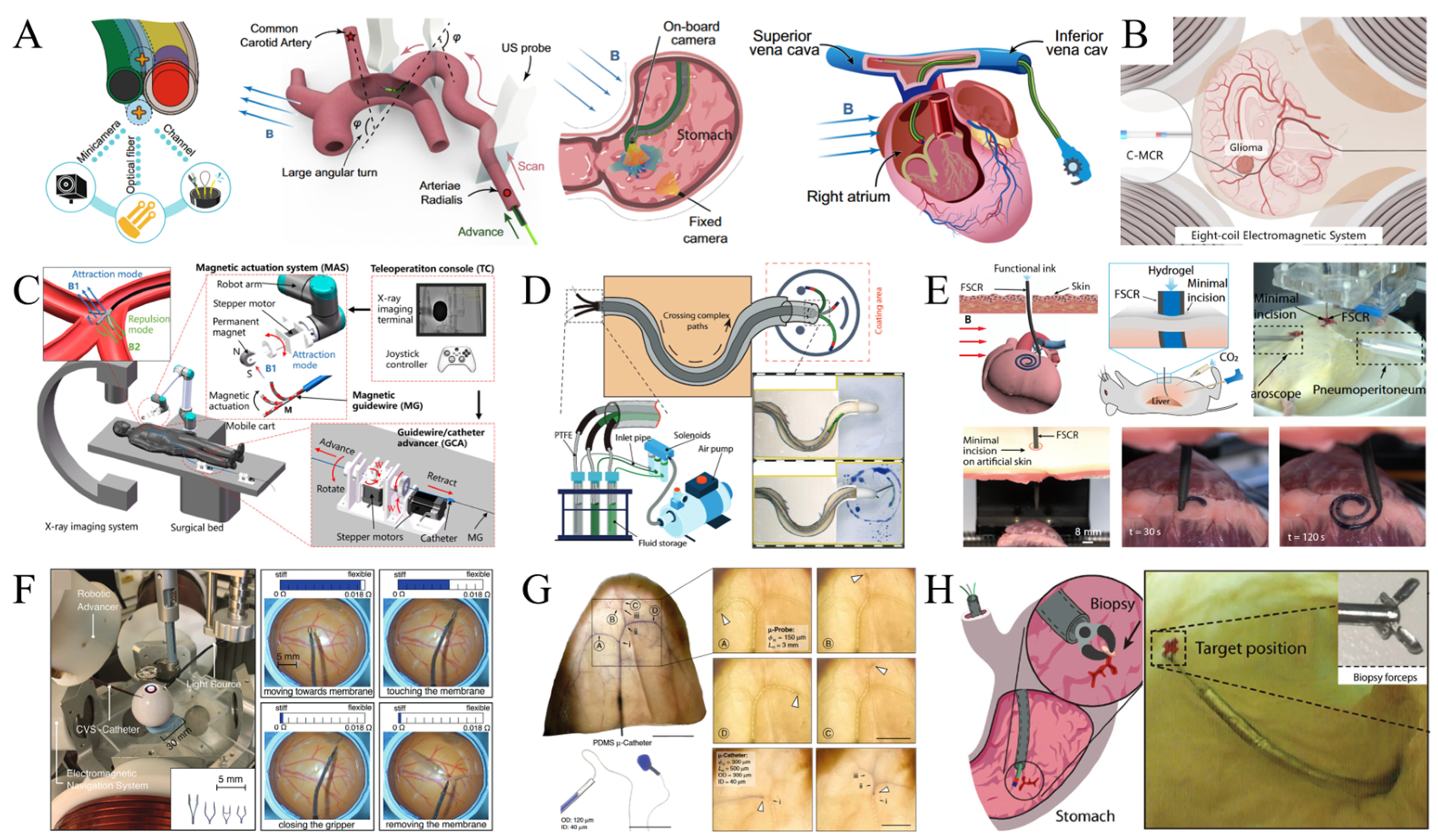
4. Applications
5. Conclusions, Current Challenges and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jiao, Z.; Zhou, H.; Han, X.; Han, D.; Zhang, Y. Photothermal responsive slippery surfaces based on laser-structured graphene@PVDF composites. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2023, 629, 582–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, N.; Ding, L.; Liu, Y.; Wang, K.; Zhang, B.; Yin, R.; Zhou, W.; Bi, Z.; Zhang, W. Development of 3D-Printed Magnetic Micro-Nanorobots for Targeted Therapeutics: The State of Art. Adv. NanoBiomed Res. 2023, 3, 2300018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.-N.; Ma, B.; Wang, Z.-X.; Song, P.; Han, D.-D.; Zhang, Y.-L. Multiresponsive MXene Actuators with Asymmetric Quantum-Confined Superfluidic Structures. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 34, 2308317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Lin, D.; Zhou, Y.; Jiao, N.; Tung, S.; Liu, L. Multistimuli-Responsive Hydroplaning Superhydrophobic Microrobots with Programmable Motion and Multifunctional Applications. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 14895–14906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Li, L.; Zhang, W.; Ren, Z.; Liu, J.; Qiu, C.; Chang, L.; Hu, Y.; Wu, Y. MXene-Based Soft Actuators with Multiresponse and Diverse Applications by a Simple Method. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2023, 308, 2300200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Liu, J.; Shi, F.; Li, T.; Zhang, H.; Yang, D.; Li, Y.; Tian, Z.; Zhou, N. A novel bidirectional fast self-responsive PVA-PNIPAM/LimCsnWO3 composite hydrogel for smart window applications. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 431, 133353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, F.; Li, T.; Yu, S.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, L. Propulsion Gait Analysis and Fluidic Trapping of Swinging Flexible Nanomotors. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 5118–5128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kochergin, Y.S.; Villa, K.; Novotný, F.; Plutnar, J.; Bojdys, M.J.; Pumera, M. Multifunctional Visible-Light Powered Micromotors Based on Semiconducting Sulfur- and Nitrogen-Containing Donor–Acceptor Polymer. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 2002701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.B.; Guo, Q.h.; Wang, W.h.; Yu, T.; Yuan, Z.; Ge, Z.x.; Yang, W.g. A review of magnetically driven swimming microrobots: Material selection, structure design, control method, and applications. Rev. Adv. Mater. Sci. 2023, 62, 20230119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Liu, Y.; Huang, W.; Bi, K.; Zhu, Y.; Fan, Q. Robust Control Strategy of Gradient Magnetic Drive for Microrobots Based on Extended State Observer. Cyborg Bionic Syst. 2022, 2022, 9835014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Yu, S.; Liao, J.; Qing, X.; Sun, D.; Ji, F.; Song, W.; Wang, L.; Li, T. A Robot Platform for Highly Efficient Pollutant Purification. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 903219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, L.; Liao, P.; Mo, H.; Li, D.; Sun, D. Preformation Characterization of a Torque-Driven Magnetic Microswimmer with Multi-Segment Structure. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 29279–29292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Cui, H.; Xu, T.; Huang, C.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Xu, Y.; Wu, X. Reconfiguration, Camouflage, and Color-Shifting for Bioinspired Adaptive Hydrogel-Based Millirobots. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 1909202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Go, G.; Yoo, A.; Nguyen, K.T.; Nan, M.; Darmawan, B.A.; Zheng, S.; Kang, B.; Kim, C.-S.; Bang, D.; Lee, S.; et al. Multifunctional microrobot with real-time visualization and magnetic resonance imaging for chemoembolization therapy of liver cancer. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, 8545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Ma, Z.-C.; Zhang, Y.-L.; Zhu, L.; Fan, H.; Bai, B.; Chen, Q.-D.; Yang, G.-Z.; Sun, H.-B. Reprogrammable Soft Robot Actuation by Synergistic Magnetic and Light Fields. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2110997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Wang, H.; Fu, R.; Wang, X.; Yu, J.; Zhang, S.; Huang, Q.; Sun, Y.; Fukuda, T. A review on microrobots driven by optical and magnetic fields. Lab A Chip 2023, 23, 848–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Chen, L.; Ma, Y.; Weng, D.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J. Multi-physics coupling simulation and design of magnetic field-driven soft microrobots in liquid environments. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2024, 272, 109136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Qiao, Z.; Teng, X.; Yu, H.; Yuan, Z.; Yang, W. A Powerful Dual-Responsive Hand Claw Structured by a Photothermal Double Layer Based on Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) and Carbon Nanotubes. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2024, 6, 3150–3159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peyron, Q.; Rabenorosoa, K.; Andreff, N.; Renaud, P. A numerical framework for the stability and cardinality analysis of concentric tube robots: Introduction and application to the follow-the-leader deployment. Mech. Mach. Theory 2019, 132, 176–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayorga-Martinez, C.C.; Zelenka, J.; Pribyl, T.; Lopez Marzo, A.; Zivotsky, O.; Ruml, T.; Pumera, M. Programming self-assembling magnetic microrobots with multiple physical and chemical intelligence. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 488, 150625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ofridam, F.; Tarhini, M.; Lebaz, N.; Gagnière, É.; Mangin, D.; Elaissari, A. pH-sensitive polymers: Classification and some fine potential applications. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2021, 32, 1455–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, C.J.; Otto, C.M. Prevention and management of paravalvular regurgitation after transcatheter aortic valve implantation. Eur. Heart J. 2023, 44, 1340–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- del Val, D.; Panagides, V.; Mestres Carlos, A.; Miró José, M.; Rodés-Cabau, J. Infective Endocarditis After Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2023, 81, 394–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, M.; Zhu, Y.; Xin, G.; Wang, Y.; Li, F.; Li, S.; Dong, Y.; Zhang, K.; Feng, L.; Tang, L.; et al. Multi-enzyme mimetic iridium nanozymes-based thrombus microenvironment-modulated nanoplatform for enhanced thrombolytic therapy. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 470, 144156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, V.N.T.; Nguyen, N.H.; Alameh, K.; Weerasooriya, R.; Pratten, P. Accurate modeling and positioning of a magnetically controlled catheter tip. Med. Phys. 2016, 43, 650–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizi, A.; Tremblay, C.C.; Gagné, K.; Martel, S. Using the fringe field of a clinical MRI scanner enables robotic navigation of tethered instruments in deeper vascular regions. Sci. Robot. 2019, 4, 7342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, B.J.; Gervasoni, S.; Chiu, P.W.Y.; Zhang, L.; Zemmar, A. Magnetically Actuated Medical Robots: An in vivo Perspective. Proc. IEEE 2022, 110, 1028–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, L.; Jin, D.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Pan, C.; Jiang, S.; Yang, H.; Yang, Z.; Wang, X.; Xia, N.; et al. Modularized microrobot with lock-and-detachable modules for targeted cell delivery in bile duct. Sci. Adv. 2023, 9, 0883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Chen, Q.; Chen, X.; Han, F.; Chen, Z.; Wang, Y. The blood–brain barrier: Structure, regulation, and drug delivery. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceresoli, M.; Pisano, M.; Abu-Zidan, F.; Allievi, N.; Gurusamy, K.; Biffl, W.L.; Tebala, G.D.; Catena, F.; Ansaloni, L.; Sartelli, M.; et al. Minimally invasive surgery in emergency surgery: A WSES survey. World J. Emerg. Surg. 2022, 17, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chautems, C.; Tonazzini, A.; Boehler, Q.; Jeong, S.H.; Floreano, D.; Nelson, B.J. Magnetic Continuum Device with Variable Stiffness for Minimally Invasive Surgery. Adv. Intell. Syst. 2020, 2, 1900086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davierwala, P.M.; Verevkin, A.; Bergien, L.; von Aspern, K.; Deo, S.V.; Misfeld, M.; Holzhey, D.; Borger, M.A. Twenty-year outcomes of minimally invasive direct coronary artery bypass surgery: The Leipzig experience. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2023, 165, 115–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Sayed Ahmad, A.; Bayram, A.; Salamate, S.; Sirat, S.; Amer, M.; Bakhtiary, F. Percutaneous versus surgical femoral access in minimally invasive cardiac operations. Eur. J. Cardio-Thorac. Surg. 2022, 61, 1348–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Guo, Y.; Yang, Y.; Tang, Y.; Wang, B.; Yan, Q.; Chen, X.; Cai, J.; Fang, L.; Xiong, Z.; et al. Magnetically Manipulated Optoelectronic Hybrid Microrobots for Optically Targeted Non-Genetic Neuromodulation. Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, 2305632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardi, G.; Ceron, S.; Wang, W.; Petersen, K.; Sitti, M. Microrobot collectives with reconfigurable morphologies, behaviors, and functions. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gozzo, C.; Caruana, G.; Cannella, R.; Farina, A.; Giambelluca, D.; Dinoto, E.; Vernuccio, F.; Basile, A.; Midiri, M. CT angiography for the assessment of EVAR complications: A pictorial review. Insights Into Imaging 2022, 13, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, H.; Möckli, M.; Ehmke, C.; Kim, M.; Wieland, M.; Moser, S.; Bechinger, C.; Boehler, Q.; Nelson, B.J. Self-folding soft-robotic chains with reconfigurable shapes and functionalities. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Yang, H.; Cao, Y.; Cui, Y.; Zhang, L. Magnetically Actuated Continuum Medical Robots: A Review. Adv. Intell. Syst. 2023, 5, 2200416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, B.; Liu, H.; Fen, X.; Gao, Z.; Ge, Z.; Yang, W. Design, optimization, and validation of a magnetic mother-child robot system for targeted drug delivery. Mater. Des. 2025, 253, 113827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Lin, D.; Wu, J.; Gan, Q.; Hu, X.; Jiao, N. Novel Concentric Magnetic Continuum Robot with Multiple Stiffness Modes for Potential Delivery of Nanomedicine. Magnetochemistry 2023, 9, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwok, K.W.; Wurdemann, H.; Arezzo, A.; Menciassi, A.; Althoefer, K. Soft Robot-Assisted Minimally Invasive Surgery and Interventions: Advances and Outlook. Proc. IEEE 2022, 110, 871–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Wu, J.; Lin, D.; Yang, J.; Jiao, N.; Wang, Y.; Liu, L. A diatom-based biohybrid microrobot with a high drug-loading capacity and pH-sensitive drug release for target therapy. Acta Biomater. 2022, 154, 443–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, N.; Fei, P.; Tous, C.; Rezaei Adariani, M.; Hautot, M.-L.; Ouedraogo, I.; Hadjadj, A.; Dimov, I.P.; Zhang, Q.; Lessard, S.; et al. Human-scale navigation of magnetic microrobots in hepatic arteries. Sci. Robot. 2024, 9, 8702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasanshahi, B.; Cao, L.; Song, K.-Y.; Zhang, W. Design of Soft Robots: A Review of Methods and Future Opportunities for Research. Machines 2024, 12, 527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Yu, S.; Sun, B.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Pan, Y.; Song, C.; Ren, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Grattan, K.T.V.; et al. Bioinspired claw-engaged and biolubricated swimming microrobots creating active retention in blood vessels. Sci. Adv. 2023, 9, 4501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.; Chen, W.; He, K.; Jiao, N.; Wang, Z.; Liu, L. Position and Orientation Control of Multisection Magnetic Soft Microcatheters. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2023, 28, 907–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.; Jiao, N.; Wang, Z.; Liu, L. A Magnetic Continuum Robot With Multi-Mode Control Using Opposite-Magnetized Magnets. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2021, 6, 2485–2492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.; Li, N.; Jiao, N.; Wang, Z.; Liu, L. Kinematic Analysis of Multi-Section Opposite Magnetic Catheter Robots With Solution Multiplicity. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2024, 21, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linghu, E.; Ji, Y. A new stage of surgical treatment: Super minimally invasive surgery. Chin. Med. J. 2022, 135, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Liu, X.; Huang, Q.; Arai, T. Recent Progress of Magnetically Actuated DNA Micro/Nanorobots. Cyborg Bionic Syst. 2022, 2022, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lussi, J.; Mattmann, M.; Sevim, S.; Grigis, F.; De Marco, C.; Chautems, C.; Pané, S.; Puigmartí-Luis, J.; Boehler, Q.; Nelson, B.J. A Submillimeter Continuous Variable Stiffness Catheter for Compliance Control. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, 2101290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattmann, M.; De Marco, C.; Briatico, F.; Tagliabue, S.; Colusso, A.; Chen, X.-Z.; Lussi, J.; Chautems, C.; Pané, S.; Nelson, B. Thermoset Shape Memory Polymer Variable Stiffness 4D Robotic Catheters. Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, 2103277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pangal, D.J.; Cote, D.J.; Ruzevick, J.; Yarovinsky, B.; Kugener, G.; Wrobel, B.; Ference, E.H.; Swanson, M.; Hung, A.J.; Donoho, D.A.; et al. Robotic and robot-assisted skull base neurosurgery: Systematic review of current applications and future directions. Neurosurg. Focus 2022, 52, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shamilyan, O.; Kabin, I.; Dyka, Z.; Sudakov, O.; Cherninskyi, A.; Brzozowski, M.; Langendoerfer, P. Intelligence and motion models of continuum robots: An overview. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 60988–61003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamilyan, O.; Kabin, I.; Dyka, Z.; Langendoerfer, P. Resilient Movement Planning for Continuum Robots. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2404.06178. [Google Scholar]
- Shamilyan, O.; Kabin, I.; Dyka, Z.; Langendoerfer, P. Distributed Artificial Intelligence as a Means to Achieve Self-X-Functions for Increasing Resilience: The First Steps. In Proceedings of the 2022 11th Mediterranean Conference on Embedded Computing (MECO), Budva, Montenegro, 7–10 June 2022; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyka, Z.; Vogel, E.; Kabin, I.; Klann, D.; Shamilyan, O.; Langendörfer, P. No Resilience Without Security. In Proceedings of the 2020 9th Mediterranean Conference on Embedded Computing (MECO), Budva, Montenegro, 8–11 June 2020; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soon, R.H.; Yin, Z.; Dogan, M.A.; Dogan, N.O.; Tiryaki, M.E.; Karacakol, A.C.; Aydin, A.; Esmaeili-Dokht, P.; Sitti, M. Pangolin-inspired untethered magnetic robot for on-demand biomedical heating applications. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 3320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Liu, C.; Yang, X.; Ji, F.; Song, W.; Zhang, G.; Wang, L.; Zhu, Y.; Yu, S.; Zhang, W.; et al. Multimode microdimer robot for crossing tissue morphological barrier. iScience 2023, 26, 108320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, J.J.; Diller, E.; Petruska, A.J. Magnetic Methods in Robotics. Annu. Rev. Control Robot. Auton. Syst. 2020, 3, 57–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wang, L.; Xiang, Y.; Liao, F.; Li, N.; Li, J.; Wang, J.; Wu, Q.; Zhou, C.; Yang, Y.; et al. Magnetic soft microfiberbots for robotic embolization. Sci. Robot. 2024, 9, eadh2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacchetti, A.; Lloyd, P.; Taccola, S.; Fakhoury, E.; Cochran, S.; Harris, R.A.; Valdastri, P.; Chandler, J.H. Optimization and fabrication of programmable domains for soft magnetic robots: A review. Front. Robot. AI 2022, 9, 1040984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Yang, Z.; Hao, B.; Wang, X.; Cai, M.; Qi, Z.; Sun, B.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, L. Magnetic Continuum Robot with Intraoperative Magnetic Moment Programming. Soft Robot. 2023, 10, 1209–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, H.; Choi, J.; Jeong, S.; Yu, C.; Park, J.-o.; Park, S. Two-dimensional locomotion of a microrobot with a novel stationary electromagnetic actuation system. Smart Mater. Struct. 2009, 18, 115017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, W.; Zhong, G.; Cao, J.; Shi, Z.; Peng, B.; Jiang, L. Soft Robotic Manipulators: Designs, Actuation, Stiffness Tuning, and Sensing. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2021, 6, 2100018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edelmann, J.; Petruska, A.J.; Nelson, B.J. Magnetic control of continuum devices. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2017, 36, 68–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Yi, B.; Liu, D. An overview of stiffening approaches for continuum robots. Robot. Comput.-Integr. Manuf. 2024, 90, 102811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Zhang, L. Magnetic Actuation Systems for Miniature Robots: A Review. Adv. Intell. Syst. 2020, 2, 2000082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Ju, F.; Cao, Y.; Qi, F.; Bai, D.; Wang, Y.; Chen, B. Continuum robot shape estimation using permanent magnets and magnetic sensors. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2019, 285, 519–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Gao, J.; Lv, Y.; Liu, J. Low Melting Point Alloys Enabled Stiffness Tunable Advanced Materials. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2201942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Liu, J.; Chen, J.; Dai, S.; Wang, J.; Zhang, B.; Liao, H. A Miniaturized Variable Stiffness Soft Manipulator With a Customizable LMPA Pattern. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2023, 8, 5704–5711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.; Kim, J.-Y.; Choi, H. A review of magnetic actuation systems and magnetically actuated guidewire- and catheter-based microrobots for vascular interventions. Intell. Serv. Robot. 2020, 13, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, D.; Ugurlu, M.C.; Sitti, M. Permanent magnet array–driven navigation of wireless millirobots inside soft tissues. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabi8932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, K.T.; Lee, H.-S.; Kim, J.; Choi, E.; Park, J.-O.; Kim, C.-S. A composite electro-permanent magnetic actuator for microrobot manipulation. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2022, 229, 107516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blümler, P. Magnetic Guiding with Permanent Magnets: Concept, Realization and Applications to Nanoparticles and Cells. Cells 2021, 10, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilami, M.; Ahmed, R.J.; Petras, A.; Beigzadeh, B.; Marvi, H. Magnetic Needle Steering in Soft Phantom Tissue. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 2500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahoney, A.W.; Abbott, J.J. Control of untethered magnetically actuated tools with localization uncertainty using a rotating permanent magnet. In Proceedings of the 2012 4th IEEE RAS & EMBS International Conference on Biomedical Robotics and Biomechatronics (BioRob), Rome, Italy, 24–27 June 2012; pp. 1632–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmanipour, S.; Diller, E. Eight-Degrees-of-Freedom Remote Actuation of Small Magnetic Mechanisms. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Brisbane, QLD, Australia, 21–25 May 2018; 2018, pp. 3608–3613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pittiglio, G.; Chandler, J.H.; Richter, M.; Venkiteswaran, V.K.; Misra, S.; Valdastri, P. Dual-Arm Control for Enhanced Magnetic Manipulation. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 24 October–24 January 2021; pp. 7211–7218. [Google Scholar]
- Pittiglio, G.; Barducci, L.; Martin, J.W.; Norton, J.C.; Avizzano, C.A.; Obstein, K.L.; Valdastri, P. Magnetic Levitation for Soft-Tethered Capsule Colonoscopy Actuated With a Single Permanent Magnet: A Dynamic Control Approach. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2019, 4, 1224–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pittiglio, G.; Brockdorff, M.; Veiga, T.d.; Davy, J.; Chandler, J.H.; Valdastri, P. Collaborative Magnetic Manipulation via Two Robotically Actuated Permanent Magnets. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2023, 39, 1407–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, P.; Diller, E. Magnetic Actuation for Full Dexterity Microrobotic Control Using Rotating Permanent Magnets. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2017, 33, 1398–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Chu, X.; Hu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Li, N.; Li, J. Variable stiffness methods for robots: A review. Smart Mater. Struct. 2024, 33, 063002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limpabandhu, C.; Hu, Y.; Ren, H.; Song, W.; Tse, Z.T.H. Magnetically steerable catheters: State of the art review. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part H J. Eng. Med. 2023, 237, 297–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.; Song, S.; Wang, J. Variable stiffness methods of flexible robots for minimally invasive surgery: A review. Biomim. Intell. Robot. 2024, 4, 100168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.; Wang, J.; Song, S.; Li, B.; Meng, M.Q.H. A Modular Lockable Mechanism for Tendon-Driven Robots: Design, Modeling and Characterization. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2022, 7, 2023–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, H.; Wang, Y.; Sheng, Y.; Zhu, H.; Zhu, S.; Yu, J.; Zhang, Q. Water-Induced Shape-Locking Magnetic Robots. Adv. Sci. 2024, 11, 2405021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahoney, A.W.; Abbott, J.J. Generating Rotating Magnetic Fields With a Single Permanent Magnet for Propulsion of Untethered Magnetic Devices in a Lumen. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2014, 30, 411–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Kim, J.; Choi, H.; Choi, J.; Jeong, S.; Cha, K.; Park, J.-o.; Park, S. Novel electromagnetic actuation system for three-dimensional locomotion and drilling of intravascular microrobot. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2010, 161, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, S.; Choi, H.; Ko, S.Y.; Park, J.O.; Park, S. Remote controlled micro-robots using electromagnetic actuation (EMA) systems. In Proceedings of the 2012 4th IEEE RAS & EMBS International Conference on Biomedical Robotics and Biomechatronics (BioRob), Rome, Italy, 24–27 June 2012; pp. 482–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Folio, D. Electromagnetic Actuation Microrobotic Systems. Curr. Robot. Rep. 2022, 3, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, H.; Cui, J.; Shi, Q.; Zheng, Z.; Sun, T.; Huang, Q.; Fukuda, T. Magnetic Micromachine Using Nickel Nanoparticles for Propelling and Releasing in Indirect Assembly of Cell-Laden Micromodules. Micromachines 2019, 10, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Genevriere, E.; Harker, P.; Choe, J.; Balicki, M.; Regenhardt, R.W.; Vranic, J.E.; Dmytriw, A.A.; Patel, A.B.; Zhao, X. Telerobotic neurovascular interventions with magnetic manipulation. Sci. Robot. 2022, 7, eabg9907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.; Xu, C.; Cui, B.; Zhang, T.; Liang, B.; Yuan, W.; Ren, H. Motor-free telerobotic endomicroscopy for steerable and programmable imaging in complex curved and localized areas. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 7680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, C.; Morimoto, T.K. Permanent Magnet-Based Localization for Growing Robots in Medical Applications. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2020, 5, 2666–2673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scali, M.; Breedveld, P.; Dodou, D. Experimental evaluation of a self-propelling bio-inspired needle in single- and multi-layered phantoms. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 19988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, H.; Dong, L.; Pei, C.; Jin, Z.; Sun, Y.; Liu, T. Variable stiffness soft robotic gripper: Design, development, and prospects. Bioinspir. Biomim. 2023, 19, 011001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armacost, M.P.; Adair, J.; Munger, T.; Viswanathan, R.R.; Creighton, F.M.; Curd, D.T.; Sehra, R. Accurate and Reproducible Target Navigation with the Stereotaxis Niobe® Magnetic Navigation System. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2007, 18, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chautems, C.; Tonazzini, A.; Floreano, D.; Nelson, B.J. A variable stiffness catheter controlled with an external magnetic field. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 24–28 September 2017; pp. 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zheng, D.; Harker, P.; Patel, A.B.; Guo, C.F.; Zhao, X. Evolutionary design of magnetic soft continuum robots. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, 922118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Ugurlu, H.; Yan, Y.; Li, M.; Li, M.; Wild, A.-M.; Yildiz, E.; Schneider, M.; Sheehan, D.; Hu, W.; et al. Adaptive wireless millirobotic locomotion into distal vasculature. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 4465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Fang, Q.; Liu, L.; Jin, R.; Xiang, P.; Xiong, R.; Wang, Y.; Lu, H. Design and Stiffness Control of a Variable-Length Continuum Robot for Endoscopic Surgery. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2024, 2024, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Q.; Deng, R.; Pan, Y.; Liu, R.; Chen, Y.; Gong, G.; Zou, J.; Yang, H.; Han, D. Robotic wireless capsule endoscopy: Recent advances and upcoming technologies. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 4597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhao, S.; Zhou, X.; Jing, X.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, D.; et al. A Magnetic-Driven Multi-motion Robot with Position/Orientation Sensing Capability. Research 2023, 6, 0177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhang, Z.; Yi, X.; Jin, S.; Chen, Y. Control of Self-Winding Microrobot Using an Electromagnetic Drive System: Integration of Movable Electromagnetic Coil and Permanent Magnet. Micromachines 2024, 15, 438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Weng, D.; Li, Z.; Chen, L.; Ma, Y.; Wang, J. A Magnetic-Controlled Flexible Continuum Robot with Different Deformation Modes for Vascular Interventional Navigation Surgery. Actuators 2023, 12, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Geng, S.; Walker, I.; Branson, D.T.; Liu, J.; Dai, J.S.; Kang, R. Geometric constraint-based modeling and analysis of a novel continuum robot with shape memory alloy initiated variable stiffness. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2020, 39, 1620–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Cao, L.; Luo, Y.; Chen, A.; Zhang, E.; Zhang, W.J. A Novel Methodology for Comprehensive Modeling of the Kinetic Behavior of Steerable Catheters. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2019, 24, 1785–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, N.; Ding, L.; Wang, A.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, B.; Yin, R. Comprehensive modeling of corkscrew motion in micro-/nano-robots with general helical structures. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 7399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Li, Y.; Chen, Y. Principles and methods for stiffness modulation in soft robot design and development. Bio-Des. Manuf. 2018, 1, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Li, Z.; Gao, X.; Liu, J.; Jiao, Z.; Kang, J.; Wang, P.; Yang, W.; Liu, M. PolymerLMPA for manufacturing deformable structure by coaxial printing. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2023, 140, e54554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Lyu, L.; Xu, Y.; Liang, H.; Zhang, X.; Ding, H.; Wu, Z. Intelligent Soft Surgical Robots for Next-Generation Minimally Invasive Surgery. Adv. Intell. Syst. 2021, 3, 2100011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Parada, G.A.; Liu, S.; Zhao, X. Ferromagnetic soft continuum robots. Sci. Robot. 2019, 4, 7329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Yang, L.; Zhang, M.; Wang, Q.; Yu, S.C.H.; Zhang, L. Magnetic Control of a Steerable Guidewire Under Ultrasound Guidance Using Mobile Electromagnets. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2021, 6, 1280–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.; Chen, B.; Li, D.; Han, J.; Xu, S.; Wang, S.; Huang, C.; Qiu, M.; Cheng, S.; Wu, X.; et al. A Magnetically Controlled Guidewire Robot System with Steering and Propulsion Capabilities for Vascular Interventional Surgery. Adv. Intell. Syst. 2023, 5, 2300267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pancaldi, L.; Dirix, P.; Fanelli, A.; Lima, A.M.; Stergiopulos, N.; Mosimann, P.J.; Ghezzi, D.; Sakar, M.S. Flow driven robotic navigation of microengineered endovascular probes. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 6356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Yang, L.; Yang, X.; Tan, R.; Lu, H.; Shen, Y. Millimeter-Scale Soft Continuum Robots for Large-Angle and High-Precision Manipulation by Hybrid Actuation. Adv. Intell. Syst. 2021, 3, 2000189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peyron, Q.; Boehler, Q.; Rougeot, P.; Roux, P.; Nelson, B.J.; Andreff, N.; Rabenorosoa, K.; Renaud, P. Magnetic concentric tube robots: Introduction and analysis. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2022, 41, 418–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, S.; Hoshiar, A.K.; Kim, K.; Lee, S.; Kim, E.; Lee, S.; Kim, J.-y.; Nelson, B.J.; Cha, H.-J.; Yi, B.-J.; et al. A Magnetically Controlled Soft Microrobot Steering a Guidewire in a Three-Dimensional Phantom Vascular Network. Soft Robot. 2018, 6, 54–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lloyd, P.; Hoshiar, A.K.; Veiga, T.D.; Attanasio, A.; Marahrens, N.; Chandler, J.H.; Valdastri, P. A Learnt Approach for the Design of Magnetically Actuated Shape Forming Soft Tentacle Robots. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2020, 5, 3937–3944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piskarev, Y.; Sun, Y.; Righi, M.; Boehler, Q.; Chautems, C.; Fischer, C.; Nelson, B.J.; Shintake, J.; Floreano, D. Fast-Response Variable-Stiffness Magnetic Catheters for Minimally Invasive Surgery. Adv. Sci. 2024, 11, 2305537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreyfus, R.; Boehler, Q.; Lyttle, S.; Gruber, P.; Lussi, J.; Chautems, C.; Gervasoni, S.; Berberat, J.; Seibold, D.; Ochsenbein-Kölble, N.; et al. Dexterous helical magnetic robot for improved endovascular access. Sci. Robot. 2024, 9, eadh0298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Mao, L.; Tian, C.; Meng, X.; Xie, H. A Cooperative and Multifunctional Magnetic Continuum Robot for Noninteractive Access, Dexterous Navigation, and Versatile Manipulation. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2024, 35, 2412543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zi, P.; Xu, K.; Tian, Y.; Ding, X. A mechanical adhesive gripper inspired by beetle claw for a rock climbing robot. Mech. Mach. Theory 2023, 181, 105168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Wang, H.; Dong, L.; Shi, Q.; Li, J.; Sun, T.; Huang, Q.; Fukuda, T. Ionic shape-morphing microrobotic end-effectors for environmentally adaptive targeting, releasing, and sampling. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Lee, H.; Kee, H.; Park, S. Magnetically steerable manipulator with variable stiffness using graphene polylactic acid for minimally invasive surgery. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2020, 309, 112032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, L.; Yang, P.; Tian, C.; Shen, X.; Wang, F.; Zhang, H.; Meng, X.; Xie, H. Magnetic steering continuum robot for transluminal procedures with programmable shape and functionalities. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 3759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Lu, J.; Wang, W.; Wang, D. Synergistically photothermal Au Nanoprisms@MXene enable adaptive solar modulation of HA-PNIPAM hydrogels for smart window. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 457, 141299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Yan, B.; Zhang, S.; Fan, P.; Zeng, P.; Shi, S.; Yang, F. Development of a Novel Biomimetic Mechanical Hand Based on Physical Characteristics of Apples. Agriculture 2022, 12, 1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Chen, G.; Weng, S.; Hou, L.; Ye, D.; Jiang, X. Thermo-Responsive Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)/Hydroxypropylmethyl Cellulose Hydrogel with High Luminous Transmittance and Solar Modulation for Smart Windows. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 4385–4397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiryaki, M.E.; Elmacıoğlu, Y.G.; Sitti, M. Magnetic guidewire steering at ultrahigh magnetic fields. Sci. Adv. 2023, 9, eadg6438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Tang, Y.; Qian, C.; Kim, B.J.; Liao, Y.; Yu, D.-G. Electrospinning spinneret: A bridge between the visible world and the invisible nanostructures. Innovation 2023, 4, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Urso, M.; Ussia, M.; Pumera, M. Shape-Controlled Self-Assembly of Light-Powered Microrobots into Ordered Microchains for Cells Transport and Water Remediation. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 7615–7625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, W.; Xu, S.; Wu, J.; Bo, R.; Jin, T.; Xiao, Y.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, F.; Cheng, X.; Bai, K.; et al. A soft microrobot with highly deformable 3D actuators for climbing and transitioning complex surfaces. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2215028119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.; Tabassian, R.; Thangasamy, P.; Mahato, M.; Nguyen, V.H.; Nam, S.; Huapeng, Z.; Oh, I.-K. Cooling-Accelerated Nanowire-Nitinol Hybrid Muscle for Versatile Prosthetic Hand and Biomimetic Retractable Claw. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2111145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, J.-W.; Han, D.-D.; Zhou, H.; Sun, H.-B.; Zhang, Y.-L. Bioinspired Superhydrophobic Swimming Robots with Embedded Microfluidic Networks and Photothermal Switch for Controllable Marangoni Propulsion. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2208677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Liu, D.; Hu, Y.; Su, Z.; Zhang, X.; Guo, R.; Li, D.; Lu, Y. Soft Magnetic Microrobot Doped with Porous Silica for Stability-Enhanced Multimodal Locomotion in a Nonideal Environment. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 10856–10874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, D.-D.; Chen, Z.-D.; Li, J.-C.; Mao, J.-W.; Jiao, Z.-Z.; Wang, W.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Y.-L.; Sun, H.-B. Airflow Enhanced Solar Evaporation Based on Janus Graphene Membranes with Stable Interfacial Floatability. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 25435–25443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, C.; Yang, Y.; Wang, J.; Wu, Q.; Gu, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, X.; Yang, Y.; Tang, H.; Ling, Q.; et al. Ferromagnetic soft catheter robots for minimally invasive bioprinting. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 5072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, M.; Yang, S.; Jiang, J.; Zhang, L. Horizontal and Vertical Coalescent Microrobotic Collectives Using Ferrofluid Droplets. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, 2300521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Type | Strength | Manipulation | Scenes | Disadvantages | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PMF | Strong | Robotic arm programming | Open Run Scenarios | Safety of magnetic field arrays | [103] |
| EMF | Weak | Current Signal Programming | Coil surround area | Weak field strength, little operating space | [104] |
| CMF | Medium | Electromagnetic and permanent magnet systems work together | Semi-open operating table | Control algorithms for permanent–electromagnetic hybrid drive systems | [105] |
| Type | Stiffness | Scenes | Advantages | Disadvantages | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MW | Low | Cardiovascular stenosis or curvature | Flexibility and mobility | Simple functionality, unable to realize complex operations | [131] |
| MC | High | Digestive gastrointestinal area | Support, conveying capacity | Prone to jamming and compression of lumen | [40] |
| VSM | Variable | Vascular and digestive | Shaping and precise manipulation | Complex design, preparation and assembly of variable stiffness layers | [102] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kong, T.; Zheng, Q.; Sun, J.; Wang, C.; Liu, H.; Gao, Z.; Qiao, Z.; Yang, W. Advances in Magnetically Controlled Medical Robotics: A Review of Actuation Systems, Continuum Designs, and Clinical Prospects for Minimally Invasive Therapies. Micromachines 2025, 16, 561. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16050561
Kong T, Zheng Q, Sun J, Wang C, Liu H, Gao Z, Qiao Z, Yang W. Advances in Magnetically Controlled Medical Robotics: A Review of Actuation Systems, Continuum Designs, and Clinical Prospects for Minimally Invasive Therapies. Micromachines. 2025; 16(5):561. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16050561
Chicago/Turabian StyleKong, Tiantian, Qitong Zheng, Jiarong Sun, Chunxiao Wang, Huibin Liu, Zhizheng Gao, Zezheng Qiao, and Wenguang Yang. 2025. "Advances in Magnetically Controlled Medical Robotics: A Review of Actuation Systems, Continuum Designs, and Clinical Prospects for Minimally Invasive Therapies" Micromachines 16, no. 5: 561. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16050561
APA StyleKong, T., Zheng, Q., Sun, J., Wang, C., Liu, H., Gao, Z., Qiao, Z., & Yang, W. (2025). Advances in Magnetically Controlled Medical Robotics: A Review of Actuation Systems, Continuum Designs, and Clinical Prospects for Minimally Invasive Therapies. Micromachines, 16(5), 561. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16050561






