Kinetostatic Modeling and Workspace Analysis of Redundant Actuated n-4R Compliant Parallel Pointing Mechanism
Abstract
1. Introduction
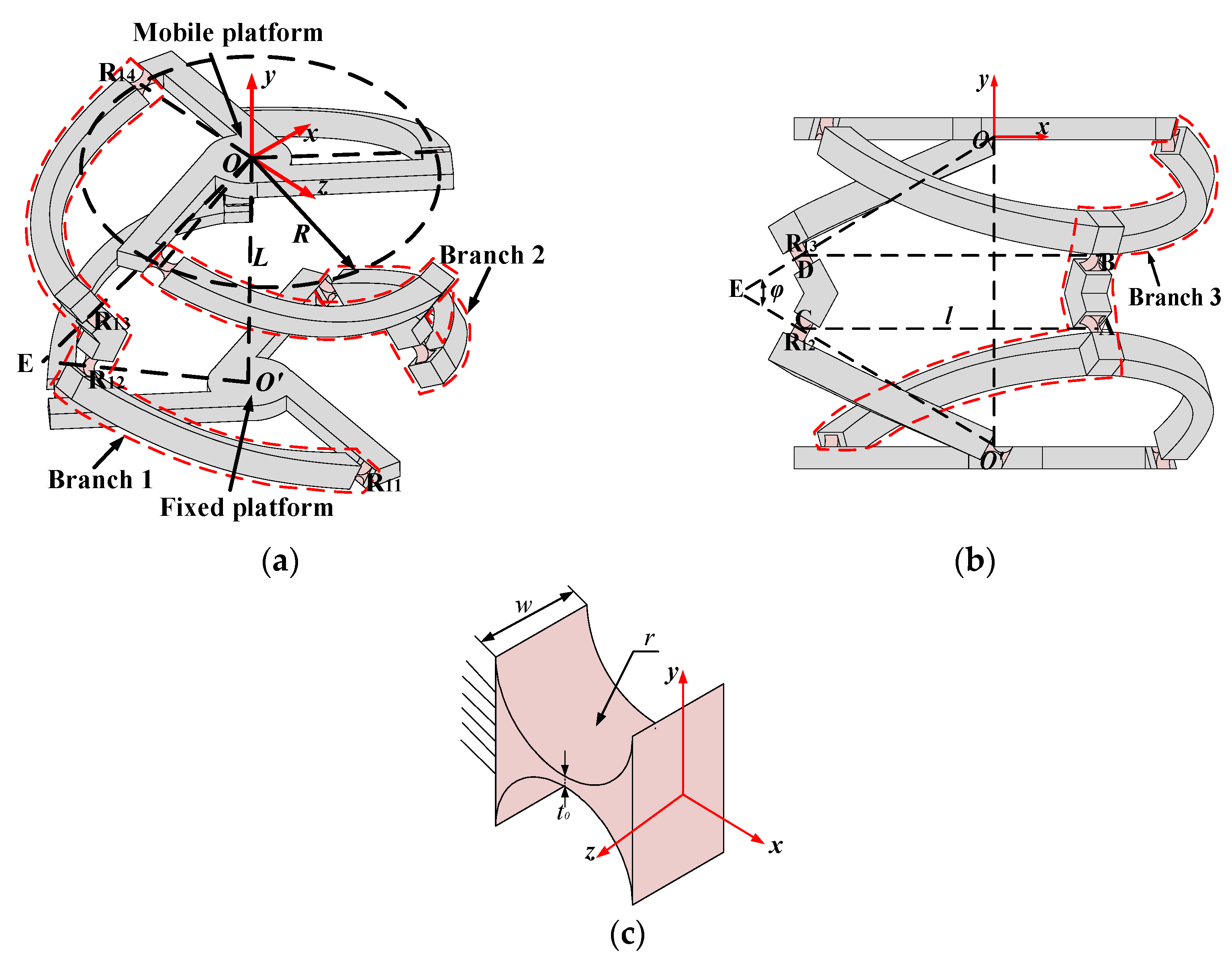
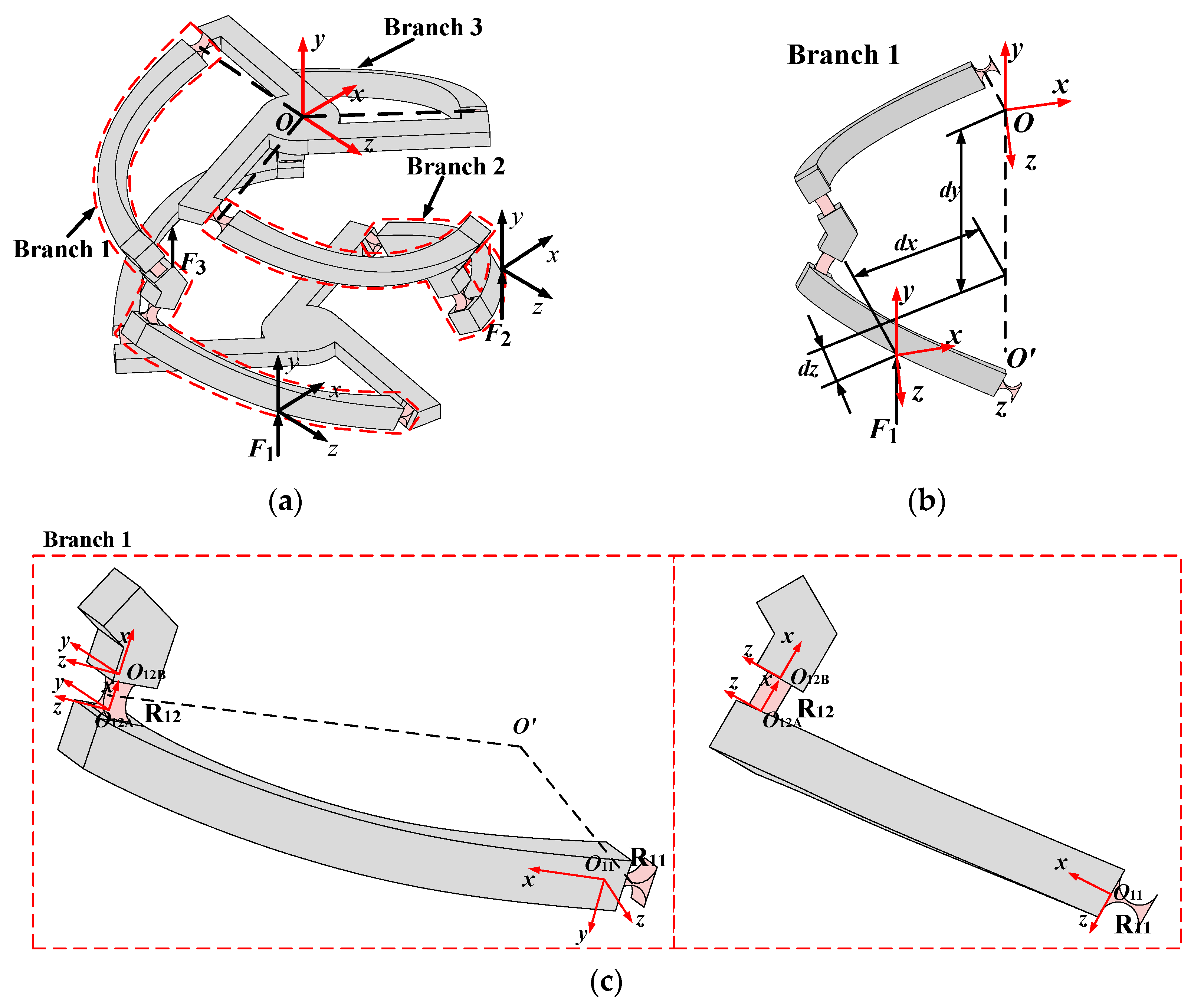
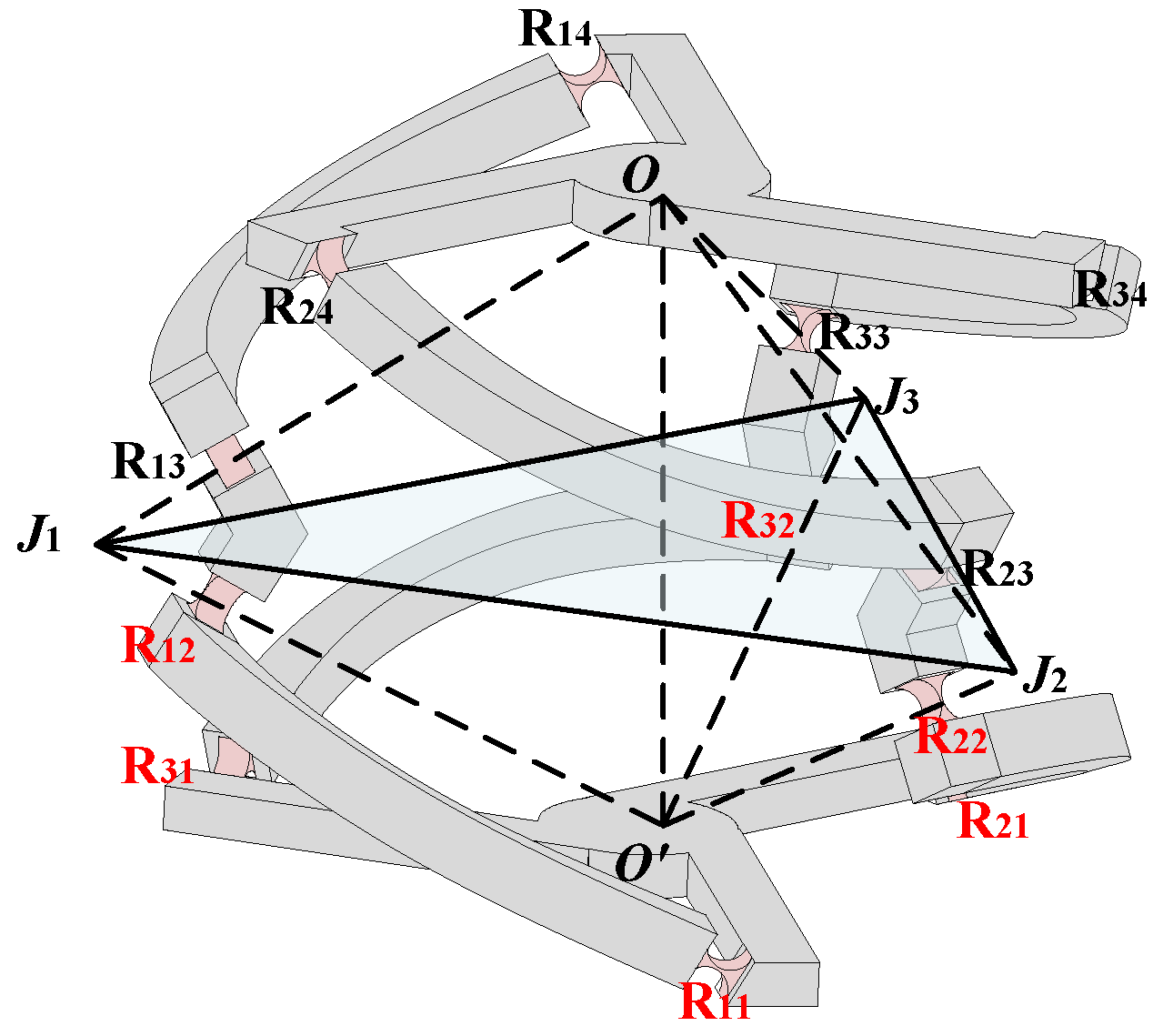
2. Structure Description of the n-4R CPPM
3. Kinetostatic Modeling of the Redundant Actuated n-4R CPPM
3.1. Kinetostatic Model of Redundant Actuated 3-4R CPPM
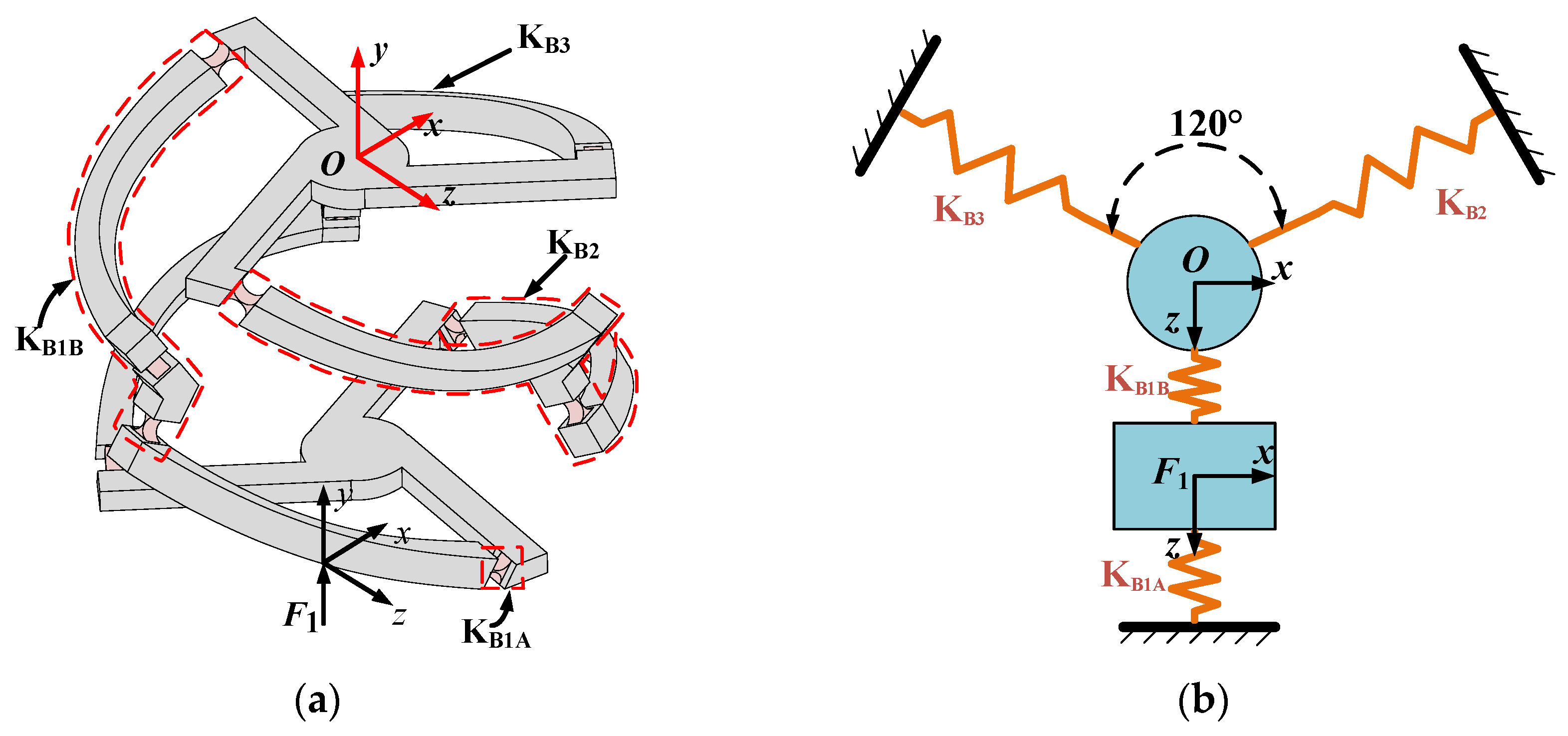
3.1.1. The Relationship Between Input Force and Output Displacement
3.1.2. The Relationship Between Input Displacement and Output Displacement
3.2. Kinetostatic Model of Redundant Actuated n-4R CPPM
4. The Workspace of the Redundant Actuated n-4R CPPM
4.1. The Constraints of the Workspace
4.2. The Flexible Hinge Displacement Model of the Redundant Actuated 3-4R CPPM
4.3. The Flexible Hinge Displacement Model of the Redundant Actuated n-4R CPPM
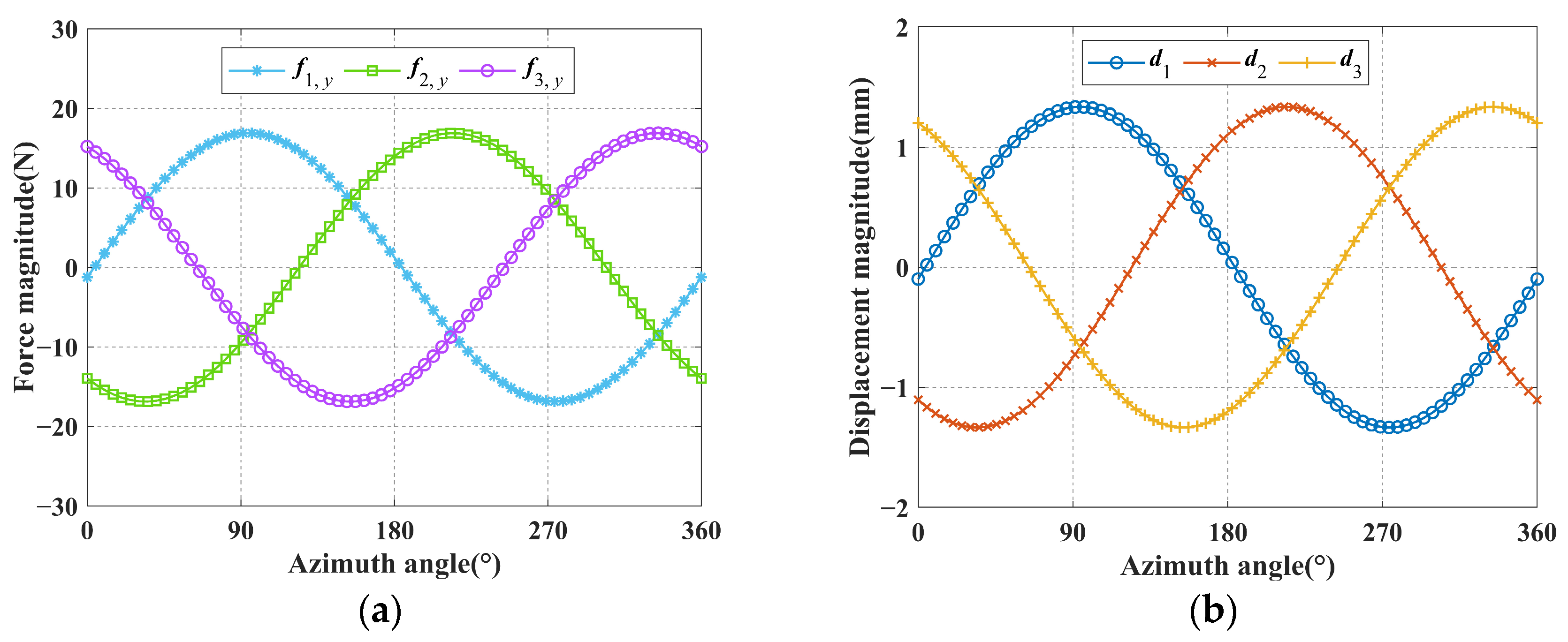
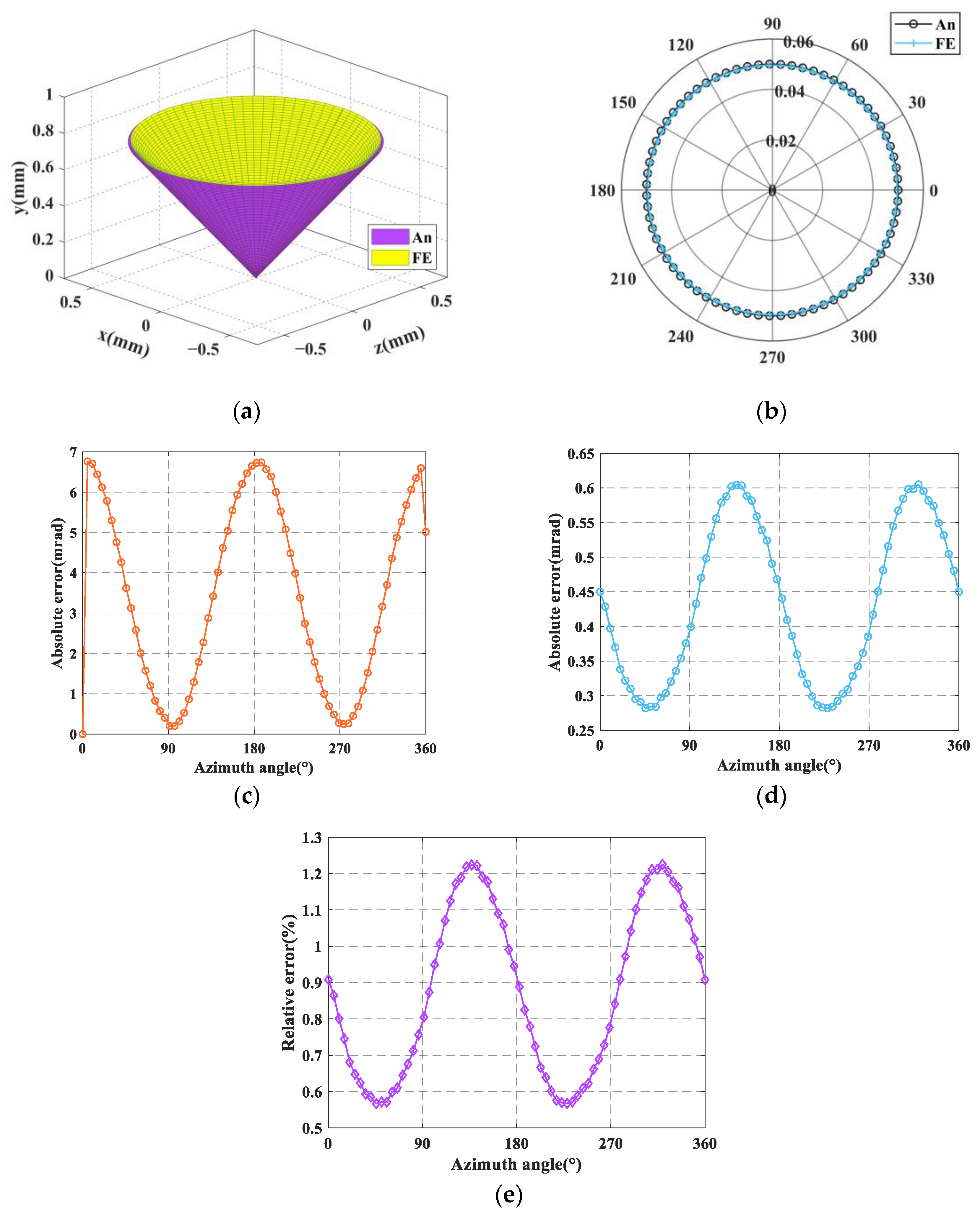
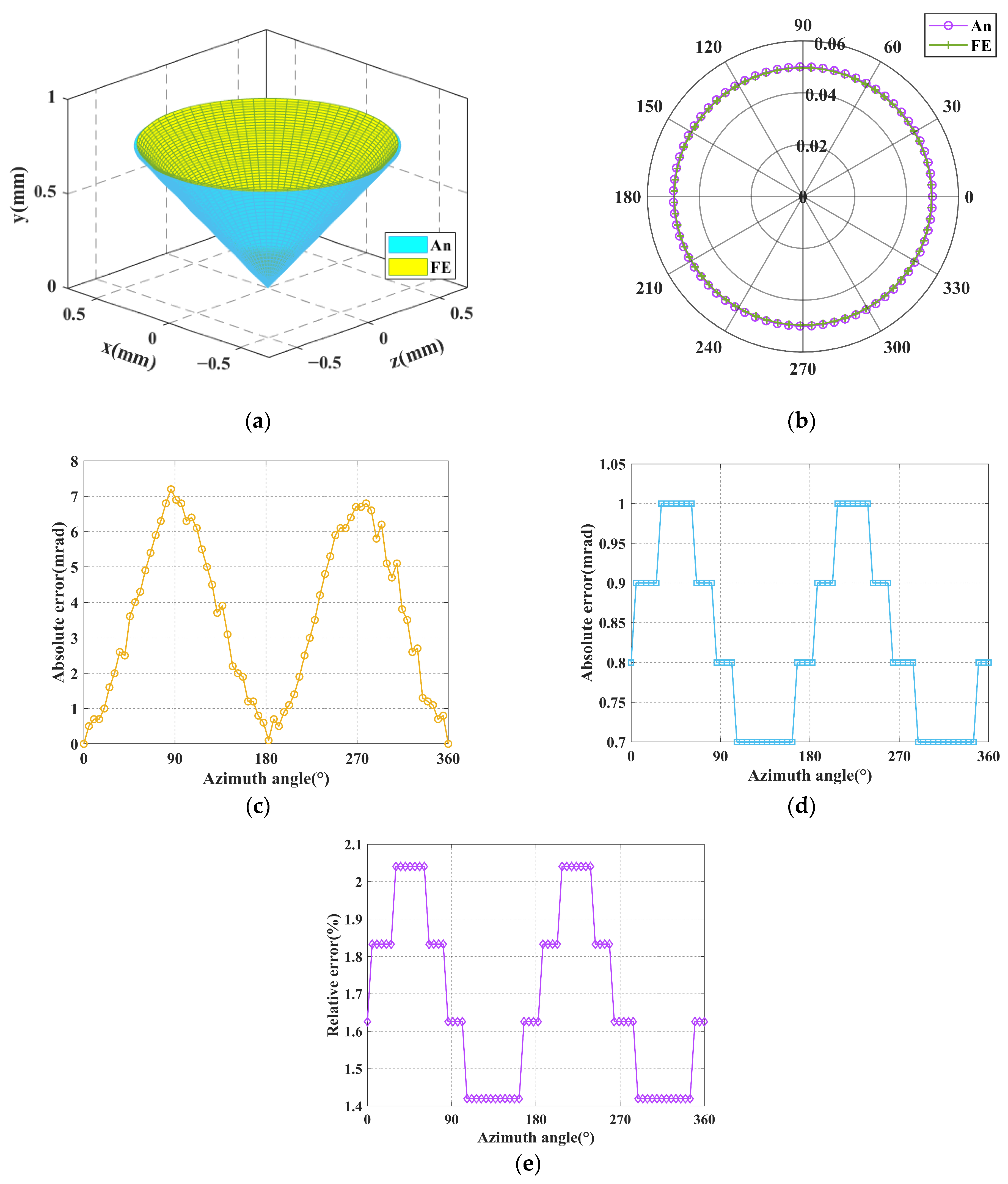
5. Validation, Calculation and Analysis
5.1. Validation of the Kinetostatic Model
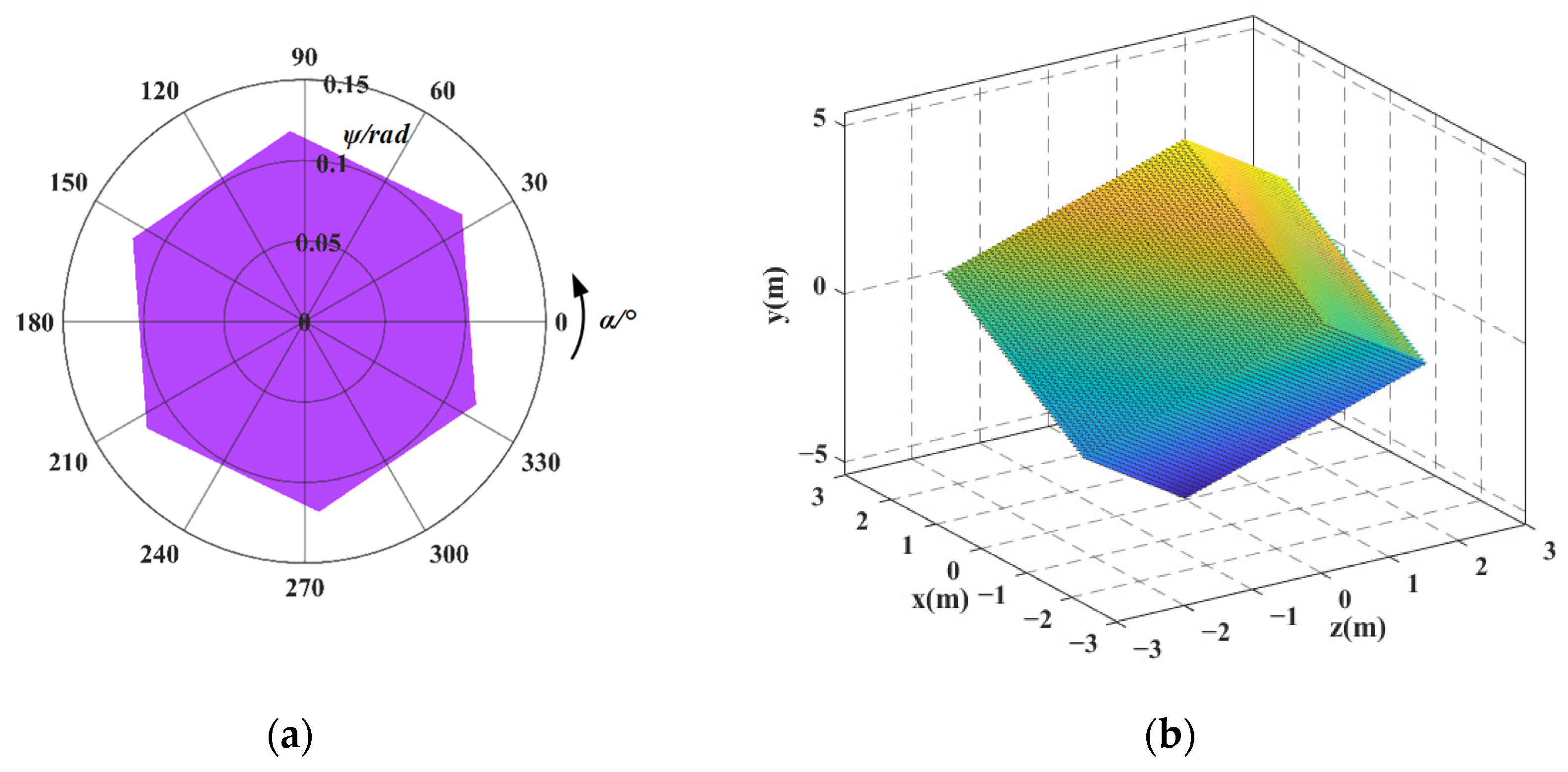
5.2. Calculation of Workspace
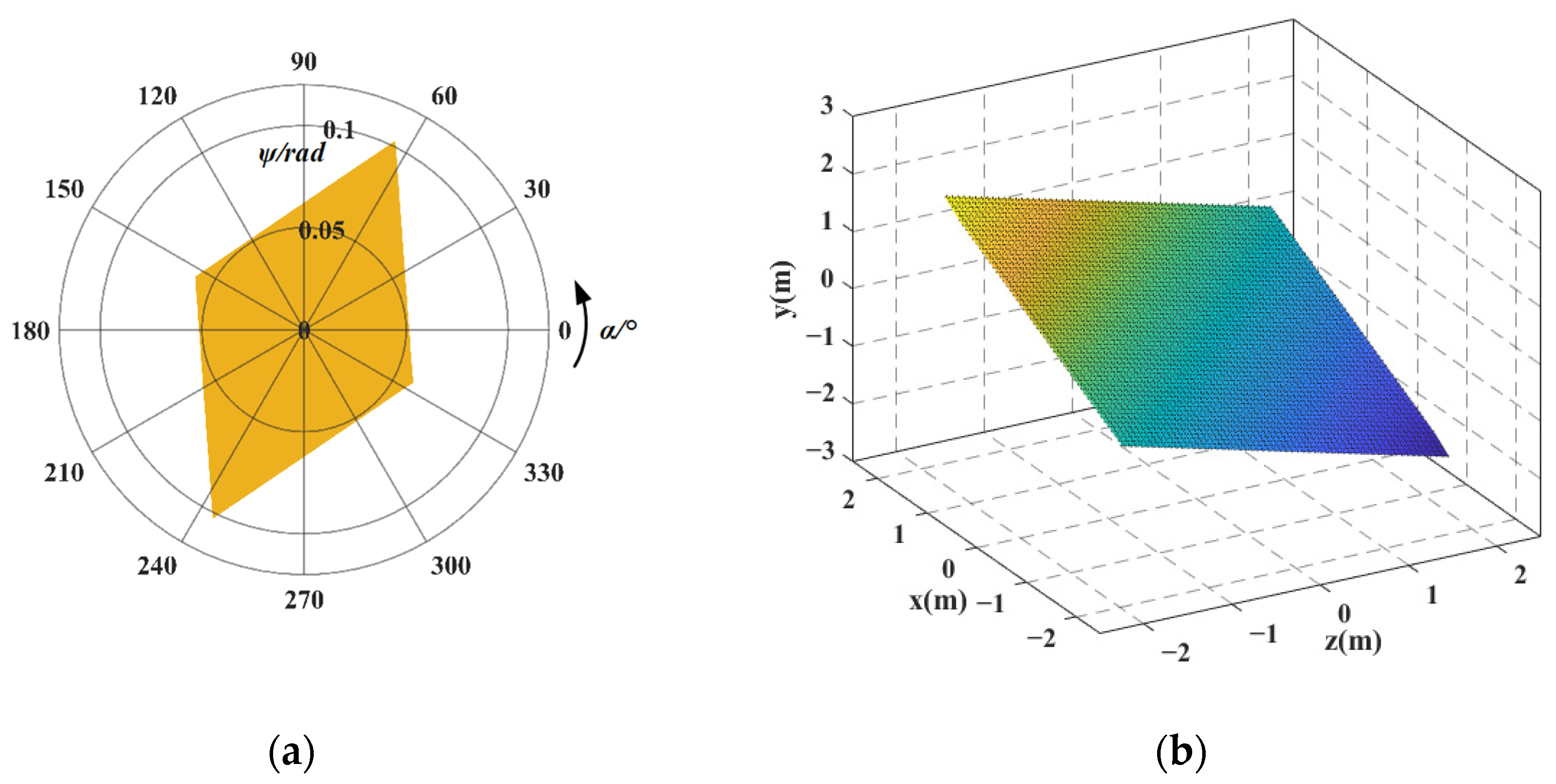
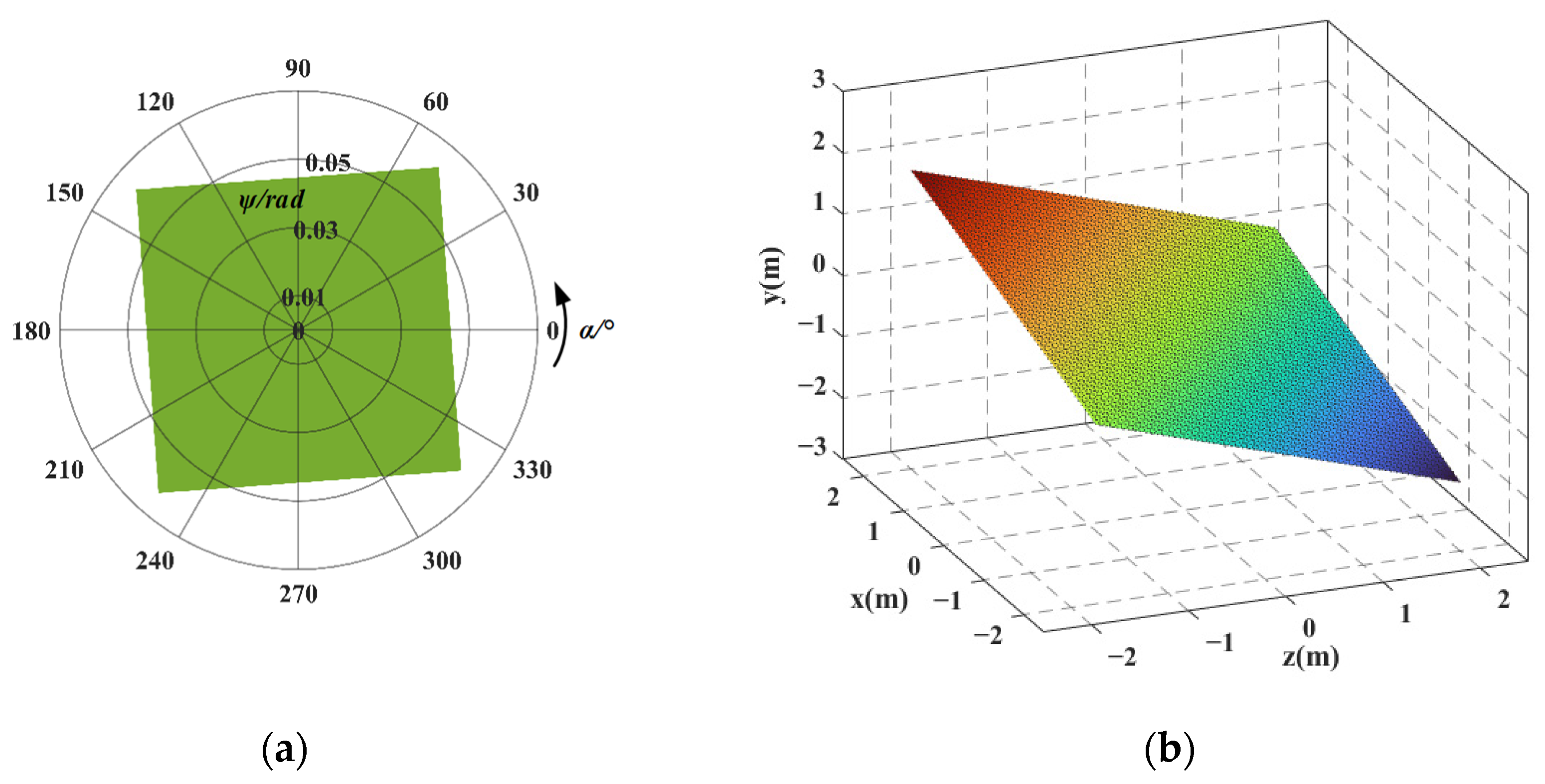
5.3. Analysis of Workspace
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pham, M.T.; Yeo, S.H.; Teo, T.J.; Wang, P.; Nai, M.L.S. A Decoupled 6-DOF Compliant Parallel Mechanism with Optimized Dynamic Characteristics Using Cellular Structure. Machines 2021, 9, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, Z.; Xu, Q. Design of a New XY Compliant Parallel Manipulator Based on Deployable Spatial Monolithic Structure. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2024, 29, 3762–3773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.Q.; Zhang, J.W.; Zhang, D.; Tang, H.Y. Modeling and Analysis of a Novel 3R Parallel Compliant Mechanism. Machines 2023, 11, 375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.Y.; Zhang, D.; Zou, Q.; Ye, W.; Kong, L.Y. Analysis and design method of a class of reconfigurable parallel mechanisms by using reconfigurable platform. Mech. Mach. Theory 2023, 181, 105215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, W.; Chai, X.X.; Zhang, K.T. Kinematic modeling and optimization of a new reconfigurable parallel mechanism. Mech. Mach. Theory 2020, 149, 103850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MA, L.; XIE, W.; LIU, B.; SUN, L. Design of micro-positioning stage with flexure hinge. Opt. Precis. Eng. 2014, 22, 338–345. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.; Xu, Q. Design and Precision Position/Force Control of a Piezo-Driven Microinjection System. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2017, 22, 1744–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komati, B.; Clévy, C.; Lutz, P. High Bandwidth Microgripper With Integrated Force Sensors and Position Estimation for the Grasp of Multistiffness Microcomponents. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2016, 21, 2039–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.H.; Yang, Q.; Dong, H.M. A Monolithic Compliant Piezoelectric-Driven Microgripper: Design, Modeling, and Testing. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2013, 18, 138–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Huo, Z.; Liang, C.; Shi, B.; Tian, Y.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, D. A Novel Actuator-Internal Micro/Nano Positioning Stage With an Arch-Shape Bridge-Type Amplifier. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2019, 66, 9161–9172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleming, A.J.; Aphale, S.S.; Moheimani, S.O.R. A New Method for Robust Damping and Tracking Control of Scanning Probe Microscope Positioning Stages. IEEE Trans. Nanotechnol. 2010, 9, 438–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, Y.A.; Li, Y.M. Design and analysis of a novel 6-DOF redundant actuated parallel robot with compliant hinges for high precision positioning. Nonlinear Dyn. 2010, 61, 829–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, K.Y.; Liu, P.B.; Lu, S.S.; Yan, P. Design and modeling of a piezo-driven three-dimensional bridge-type amplification mechanism with input/output guiding constraint. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2022, 93, 025005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.L.; Zhang, X.M.; Fatikow, S. Design, modeling and test of a novel compliant orthogonal displacement amplification mechanism for the compact micro-grasping system. Microsyst. Technol.-Micro-Nanosyst.-Inf. Storage Process. Syst. 2017, 23, 2485–2498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, M.X.; Yuan, L.; Luo, Z.H.; Huang, T.; Zhang, X.M. Enhancing Dynamic Bandwidth of Amplified Piezoelectric Actuators by a Hybrid Lever and Bridge-Type Compliant Mechanism. Actuators 2022, 11, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Xie, Z.; Tan, H.; Tai, K. Design and mechanical modeling of high-magnification and low-parasitic displacement microgripper with three-stage displacement amplification. Mech. Mach. Theory 2023, 190, 105463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, Y.; Li, Y.M. Optimal design of a 3-PUPU parallel robot with compliant hinges for micromanipulation in a cubic workspace. Robot. Comput.-Integr. Manuf. 2011, 27, 977–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Lan, A.J. Compliance Modeling and Kinetostatic Analysis of a Generalized 3-PSS Compliant Parallel Micro-Motion Platform. Micromachines 2024, 15, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Sun, M.; Wu, Z.; Li, J.; Long, Y. Design of a redundant actuated 4-PPR planar 3-DOF compliant nanopositioning stage. Precis. Eng. 2023, 82, 68–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.F.; Wan, B.; Liu, Y.; Chen, R.; Yao, J.T.; Zhao, Y.S. Kinematic Performance Analysis and Dimensional Optimization of New Symmetric Parallel Mechanism 6RPS With Multi-Redundant Actuations. J. Mech. Robot.-Trans. ASME 2024, 16, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.; Che, J.J.; Liu, J.Y.; Yang, D. Performance evaluation and dimensional optimization design of planar 6R redundant actuation parallel mechanism. Robotica 2024, 42, 1649–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, D.B.; Song, Z.M.; Guo, H.W.; Liu, R.Q.; Kou, Z.M. Workspace analysis and size optimization of planar 3-DOF redundantly actuated parallel mechanism. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2024, 38, 957–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Li, Y.; Weng, S.F.; Wan, H.; Luo, D.B. Design and Simulation of a Novel 6-DOF Hybrid Mechanism Motion Platform for Pose Adjustment of Heavy Equipment. Iran. J. Sci. Technol.-Trans. Mech. Eng. 2023, 47, 1055–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Li, Q. Analysis of Compliance and Kinetostatic of a Novel Class of n-4R Compliant Parallel Micro Pointing Mechanism. Micromachines 2022, 13, 1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.H.; Chen, S.S.; Qu, J.L.; Chen, W.J. A large-range compliant remote center of motion stage with input/output decoupling. Precis. Eng. J. Int. Soc. Precis. Eng. Nanotechnol. 2018, 51, 468–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Yang, D.; Wu, C.; Fei, F. Workspace Analysis of a Novel Six DOFs Parallel Mechanism with Micro Displacement. Mech. Sci. Technol. Aerosp. Eng. 2019, 38, 433–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; He, W. Kinematics and Workspace Analysis of 3-PSS Flexible Parallel Micromanipulator. Mach. Des. Manuf. 2022, 382, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arredondo-Soto, M.; Cuan-Urquizo, E.; Gómez-Espinosa, A. The compliance matrix method for the kinetostatic analysis of flexure-based compliant parallel mechanisms: Conventions and general force–displacement cases. Mech. Mach. Theory 2022, 168, 104583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Jiang, H. Compliance and Kinetostatics of a Novel 2PRS-2PSS Compliant Parallel Micromanipulator: Modeling and Analysis. Micromachines 2024, 15, 526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| x | y | z | θx | θy | θz | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R | 0 | 0 | ||||
| 0 | 0 |
| Hinge Parameters | Values | Structural Parameters | Values |
|---|---|---|---|
| E/pa | 2.06 × 1011 | l/mm | 66.6 |
| μ | 0.3 | φ/° | 60° |
| t0/mm | 0.5 | R/mm | 66 |
| r/mm | 3.75 | dx/mm | 41.006 |
| w/mm | 5 | dy/mm | 88.308 |
| dz/mm | 59 | ||
| L/mm | 100 |
| Maximum angular displacement | (rad) | (rad) | (rad) |
| 0.0124 | 0.00562 | 0.0253 | |
| Maximum line displacement | (mm) | (mm) | (mm) |
| 7.962 × 10−3 | 9.671 × 10−2 | 3.136 × 10−2 |
| Name of the CPPM | 3-4R | 4-4R | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Actuation Case | Redundant | Non-Redundant | Redundant | Non-Redundant |
| ψmax/rad | 0.118 | 0.103 | 0.126 | 0.063 |
| ψa/rad | 0.102 | 0.051 | 0.088 | 0.044 |
| xd/mm | −2.7~2.7 | −2.27~2.27 | −2.34~2.34 | −2.07~2.07 |
| yd/mm | −0.54~0.54 | −0.27~0.27 | −0.5~0.5 | −0.25~0.25 |
| zd/mm | −2.7~2.7 | −2.53~2.53 | −2.34~2.34 | −2.05~2.05 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ren, J.; Shu, Y.; Lin, Y. Kinetostatic Modeling and Workspace Analysis of Redundant Actuated n-4R Compliant Parallel Pointing Mechanism. Micromachines 2025, 16, 478. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16040478
Ren J, Shu Y, Lin Y. Kinetostatic Modeling and Workspace Analysis of Redundant Actuated n-4R Compliant Parallel Pointing Mechanism. Micromachines. 2025; 16(4):478. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16040478
Chicago/Turabian StyleRen, Jun, Yikang Shu, and Youwei Lin. 2025. "Kinetostatic Modeling and Workspace Analysis of Redundant Actuated n-4R Compliant Parallel Pointing Mechanism" Micromachines 16, no. 4: 478. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16040478
APA StyleRen, J., Shu, Y., & Lin, Y. (2025). Kinetostatic Modeling and Workspace Analysis of Redundant Actuated n-4R Compliant Parallel Pointing Mechanism. Micromachines, 16(4), 478. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16040478







