Multistage Cyclic Dielectrophoresis for High-Resolution Sorting of Submicron Particles
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
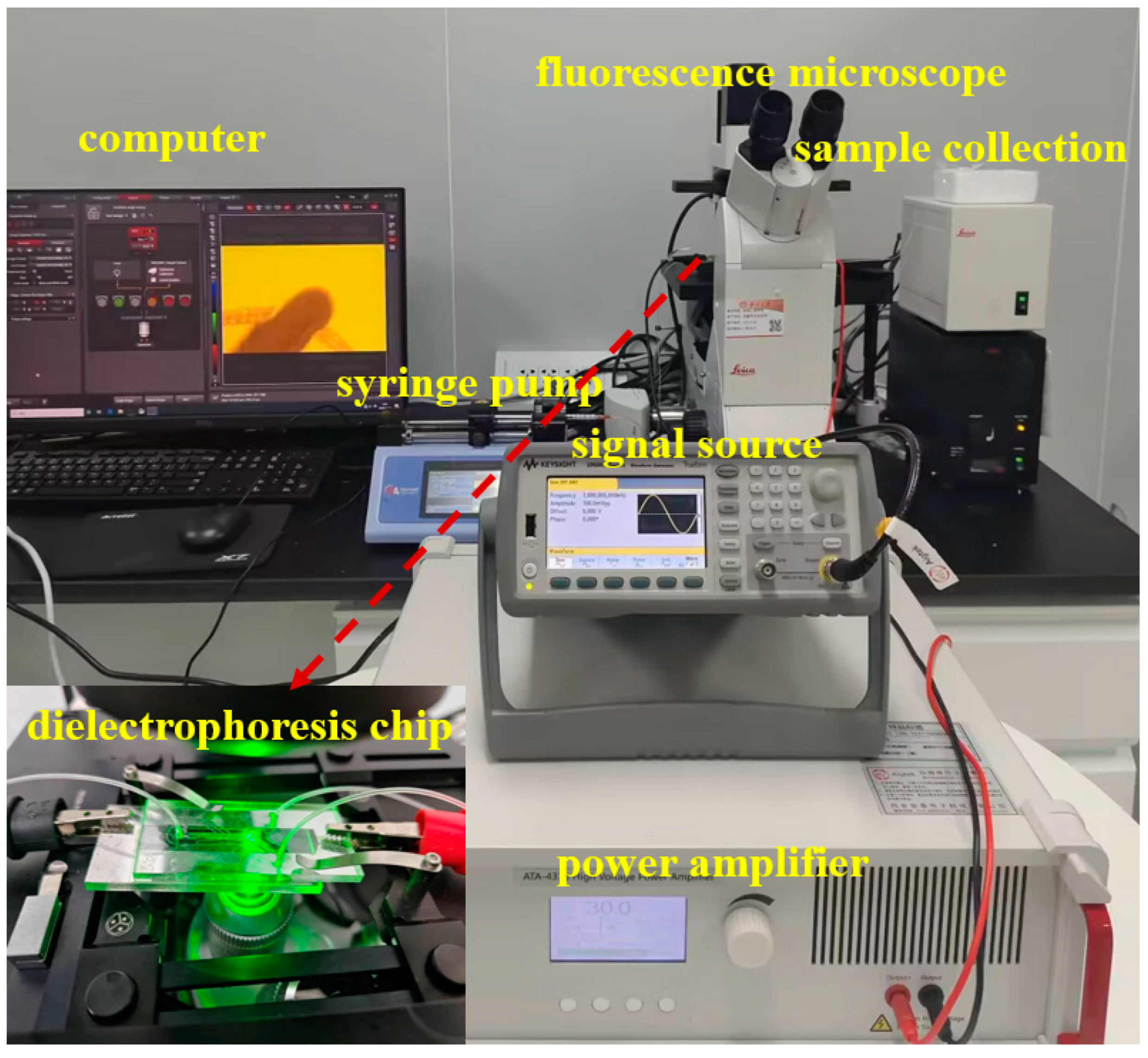
2.1. Multistage Cyclic Dielectrophoresis Sorting System
2.2. Materials and Structures of Dielectrophoretic Chips
2.3. Multistage Cyclic Dielectrophoresis Sorting Mechanism
3. Results and Discussion
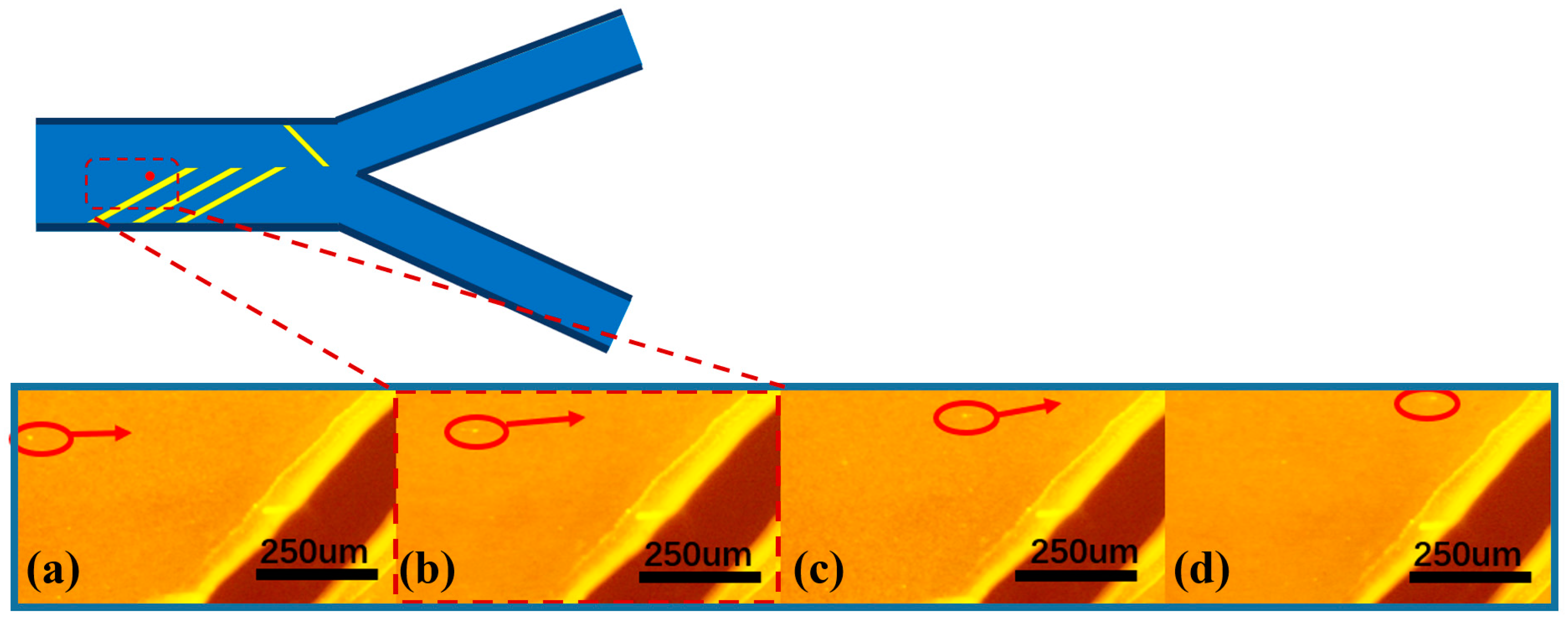
3.1. Submicron Microsphere Focusing
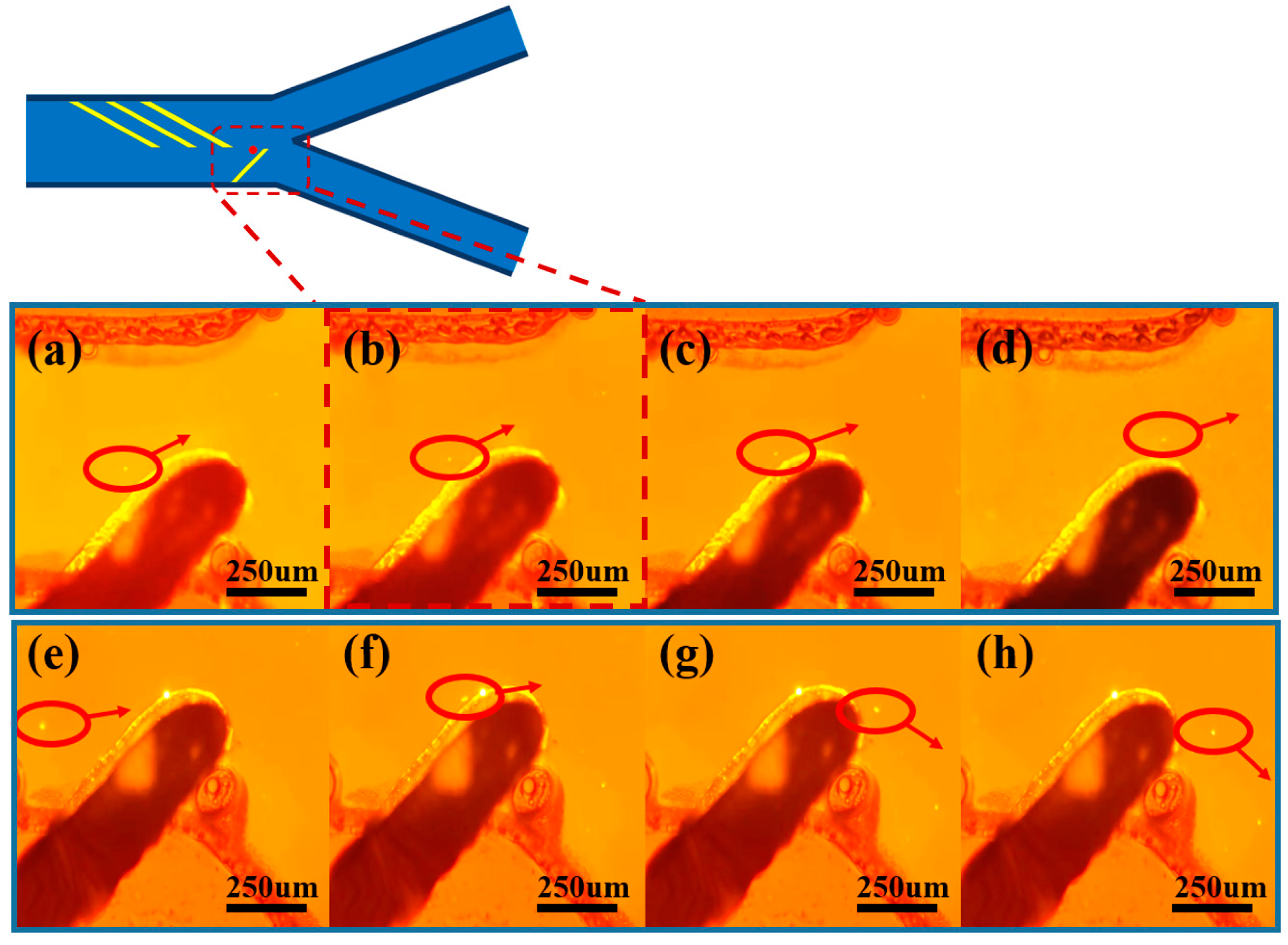
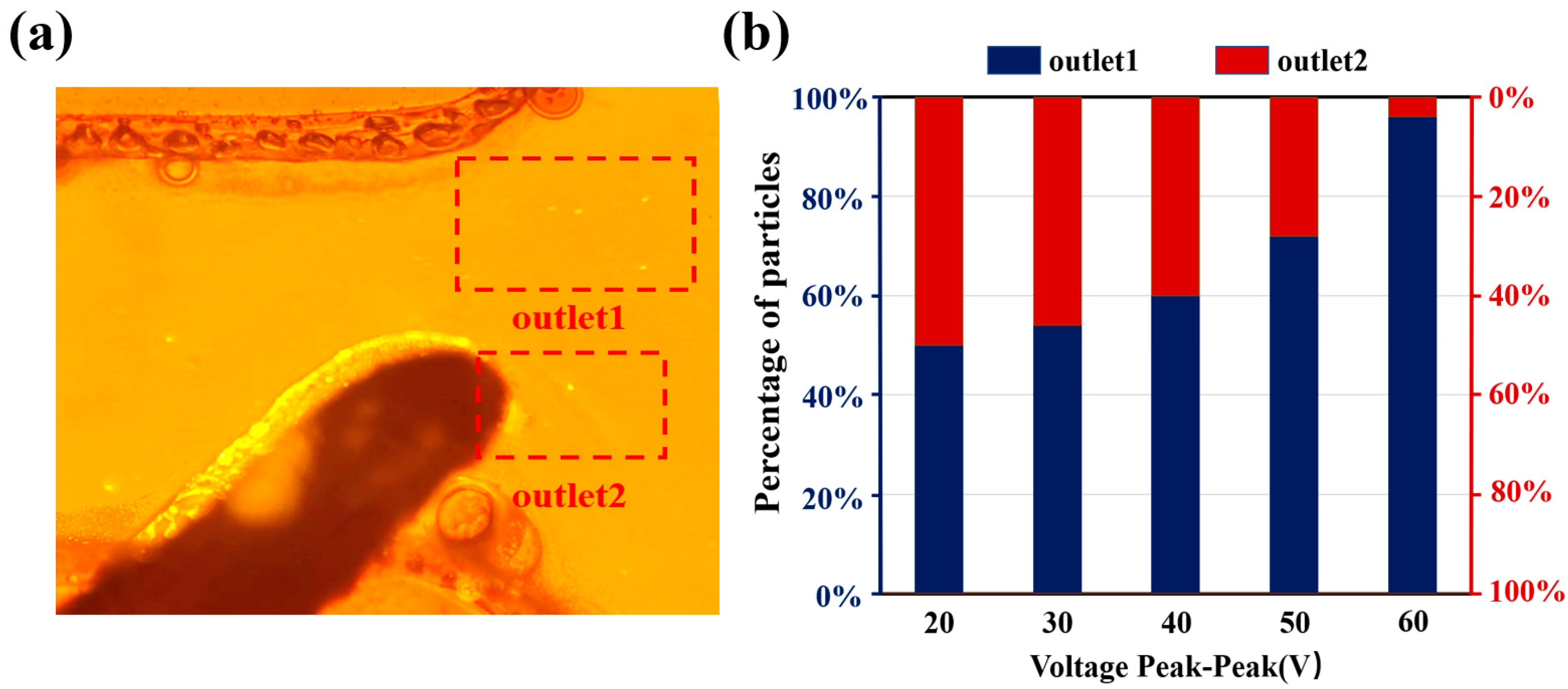
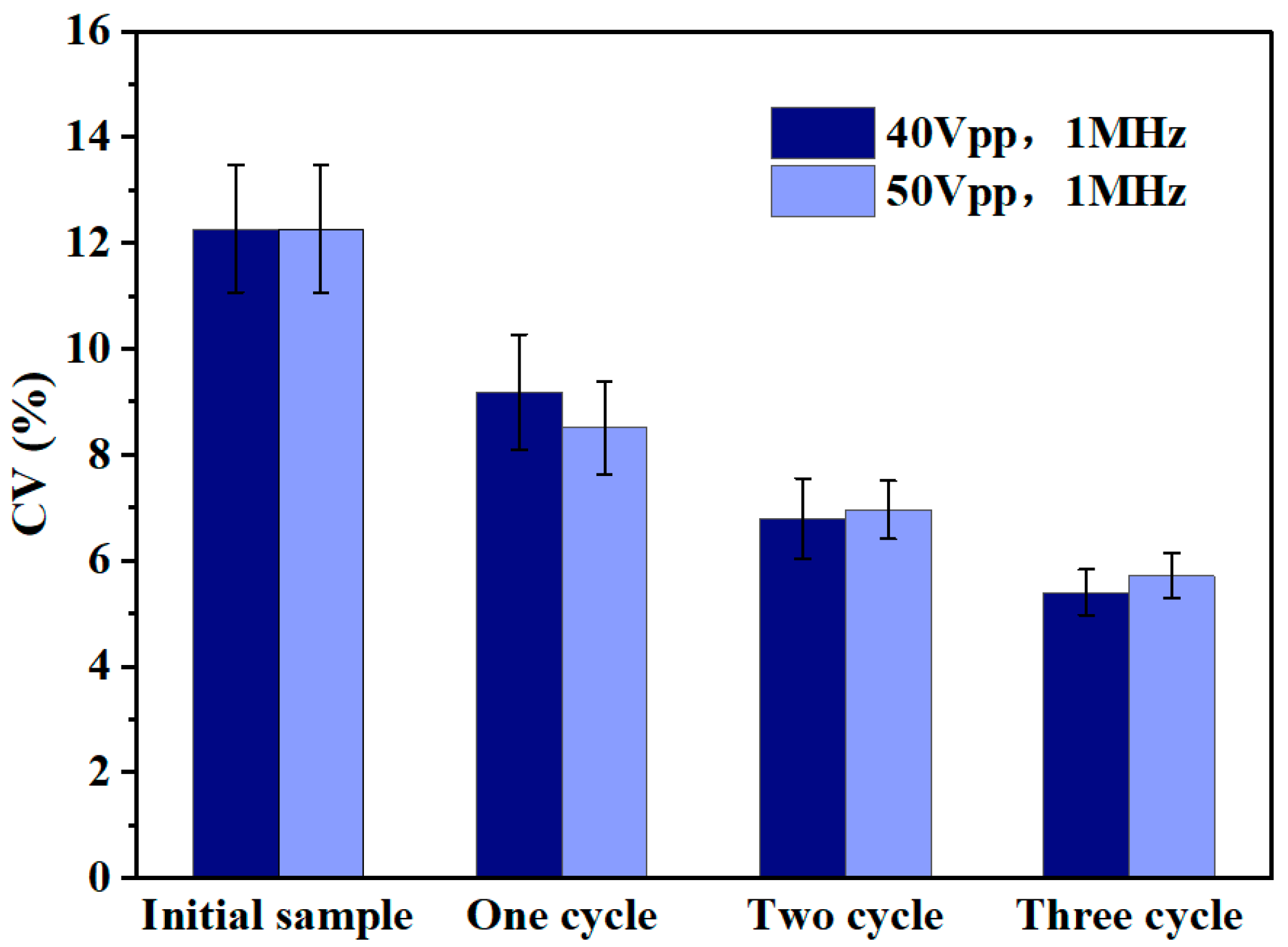
3.2. Submicron Microsphere Sorting
3.3. Particle Size Optimization of Submicron Microspheres by MC-DEP
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, T.; Hong, Z.Y.; Tang, S.Y.; Li, W.; Inglis, D.W.; Hosokawa, Y.; Yalikun, Y.; Li, M. Focusing of sub-micrometer particles in microfluidic devices. Lab Chip 2020, 20, 35–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Y.; Liu, D.; Sun, Q.; Duan, M.; Fan, B. PLGA submicron particles containing chlorhexidine, calcium and phosphorus inhibit Enterococcus faecalis infection and improve the microhardness of dentin. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2019, 30, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, L.; Li, H.; Su, S.; Wen, X.; Yan, R.; Tao, C. Study on the structure and properties of Fe3O4@HMPDA@HA magnetic hollow mesoporous submicron drug-carrying system. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2022, 330, 111582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahradeh, K.; Saievar-Iranizad, E.; Bayat, A. Electrophoretically deposited carbon micro and nanospheres thin films as superhydrophobic coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2017, 319, 318–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, G.; Chen, F.; Zhao, B.; Zhang, X.; Zussman, E.; Rojas, O. Self-Assembled Nanorods and Microspheres for Functional Photonics: Retroreflector Meets Microlens Array. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2021, 9, 2002258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reese, C.; Guerrero, C.; Weissman, J.; Lee, K.; Asher, S. Synthesis of Highly Charged, Monodisperse Polystyrene Colloidal Particles for the Fabrication of Photonic Crystals. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2000, 232, 76–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allard, M.; Sargent, E. Impact of polydispersity on light propagation in colloidal photonic crystals. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2004, 85, 5887–5889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Ma, Z.; Tayebi, M.; Ai, Y. Submicron Particle Focusing and Exosome Sorting by Wavy Microchannel Structures within Viscoelastic Fluids. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 4577–4584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, H.; Lee, S.; Shin, J.; Song, K.; Ahn, N.; Park, J. Elasto-inertial microfluidic separation of microspheres with submicron resolution at high-throughput. Microsyst. Nanoeng. 2024, 10, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.; Song, S.; Choi, C.; Park, J.-K. Hydrophoretic Sorting of Micrometer and Submicrometer Particles Using Anisotropic Microfluidic Obstacles. Anal. Chem. 2008, 81, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sehgal, P.; Kirby, B. Separation of 300 and 100 nm Particles in Fabry–Perot Acoustofluidic Resonators. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 12192–12200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arosio, P.; Müller, T.; Mahadevan, L.; Knowles, T. Density-Gradient-Free Microfluidic Centrifugation for Analytical and Preparative Separation of Nanoparticles. Nano Lett. 2014, 14, 2365–2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tayebi, M.; Yang, D.; Collins, D.; Ai, Y. Deterministic Sorting of Submicrometer Particles and Extracellular Vesicles Using a Combined Electric and Acoustic Field. Nano Lett. 2021, 21, 6835–6842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cottet, J.; Kehren, A.; Lasli, S.; van Lintel, H.; Buret, F.; Frénéa-Robin, M.; Renaud, P. Dielectrophoresis-assisted creation of cell aggregates under flow conditions using planar electrodes. Electrophoresis 2019, 40, 1498–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chuang, H.-S.; Chung, T.-Y.; Li, Y. Compact and tunable size-based dielectrophoretic flow fractionation. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2014, 24, 125016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezanoor, M.; Dutta, P. Combined AC electroosmosis and dielectrophoresis for controlled rotation of microparticles. Biomicrofluidics 2016, 10, 024101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.; Rufo, J.; Zhong, R.; Rich, J.; Li, P.; Leong, K.W.; Huang, T.J. Microfluidic Isolation and Enrichment of Nanoparticles. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 16220–16240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Wang, H.; Yu, C.; Xie, D. Diffusion characteristics of the industrial submicron particle under Brownian motion and turbulent diffusion. Indoor Built Environ. 2021, 31, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kushigbor, S.; Tang, Z.; Bu, Y.; Yobas, L. Electrokinetic oscillation, railing, and enrichment of submicron particles along 3D microelectrode tracks. Microfluid. Nanofluidics 2021, 25, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viefhues, M.; Eichhorn, R.; Fredrich, E.; Regtmeier, J.; Anselmetti, D. Continuous and reversible mixing or demixing of nanoparticles by dielectrophoresis. Lab Chip 2012, 12, 485–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soong, W.-J.; Wang, C.-H.; Chen, C.; Lee, G.-B. Nanoscale sorting of extracellular vesicles via optically-induced dielectrophoresis on an integrated microfluidic system. Lab Chip 2024, 24, 1965–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tasci, T.; Johnson, W.; Fernandez, D.; Manangon, E.; Gale, B. Biased Cyclical Electrical Field Flow Fractionation for Separation of Sub 50 nm Particles. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 11225–11232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dürr, M.; Kentsch, J.; Müller, T.; Schnelle, T.; Stelzle, M. Microdevices for manipulation and accumulation of micro- and nanoparticles by dielectrophoresis. Electrophoresis 2003, 24, 722–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C.; Chen, B.; Yan, B.; Wu, J. A new method for particle manipulation by combination of dielectrophoresis and field-modulated electroosmotic vortex. Appl. Math. Mech. 2017, 39, 409–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luo, W.; Zheng, C.; Sun, C.; Li, Z.; You, H. Multistage Cyclic Dielectrophoresis for High-Resolution Sorting of Submicron Particles. Micromachines 2025, 16, 404. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16040404
Luo W, Zheng C, Sun C, Li Z, You H. Multistage Cyclic Dielectrophoresis for High-Resolution Sorting of Submicron Particles. Micromachines. 2025; 16(4):404. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16040404
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuo, Wenshen, Chaowen Zheng, Cuimin Sun, Zekun Li, and Hui You. 2025. "Multistage Cyclic Dielectrophoresis for High-Resolution Sorting of Submicron Particles" Micromachines 16, no. 4: 404. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16040404
APA StyleLuo, W., Zheng, C., Sun, C., Li, Z., & You, H. (2025). Multistage Cyclic Dielectrophoresis for High-Resolution Sorting of Submicron Particles. Micromachines, 16(4), 404. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16040404






