Polarity-Dependent Driving Scheme for Suppressing Oil Film Splitting in Electrowetting Displays
Abstract
1. Introduction
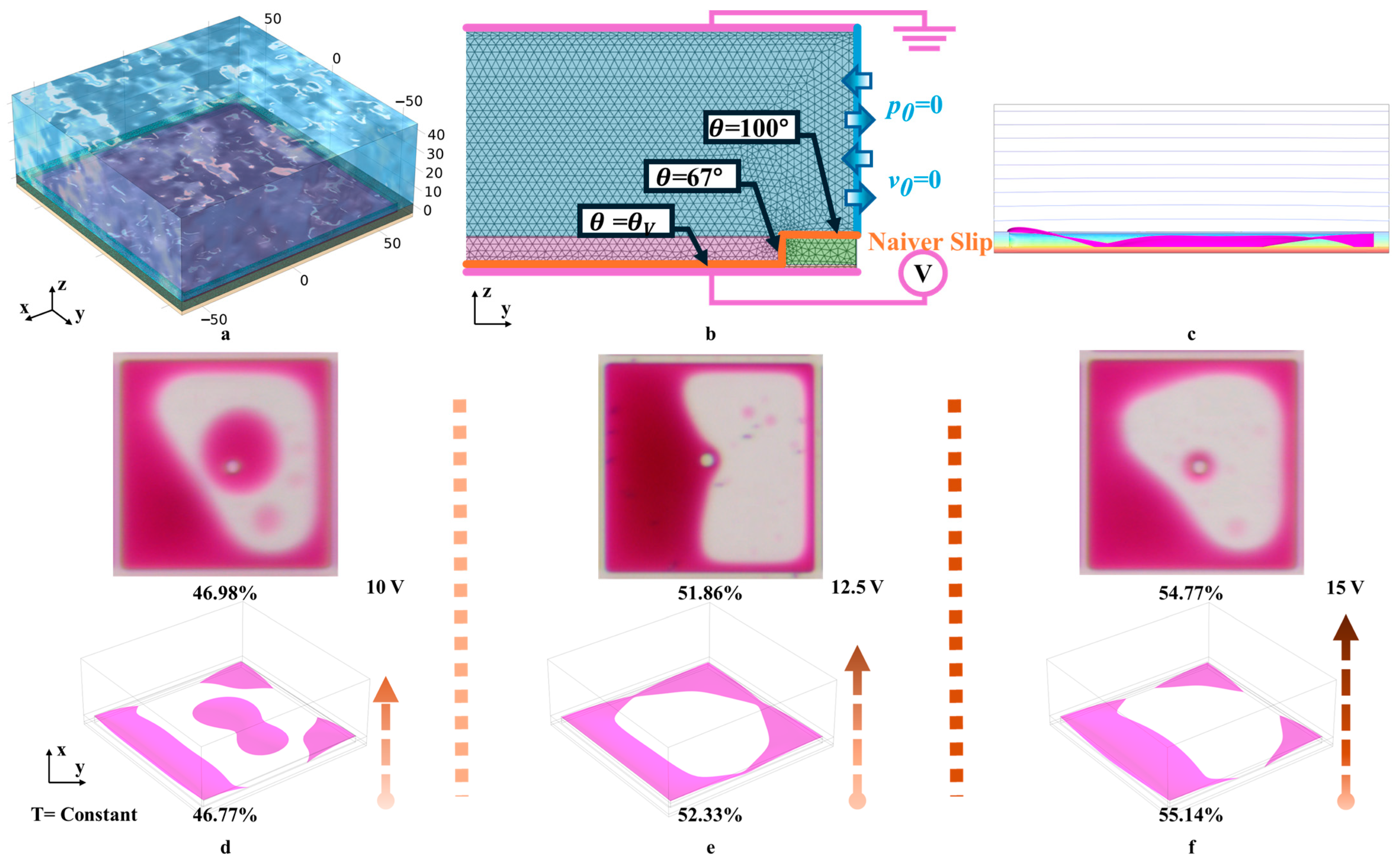
2. EWDs Principles and Simulation Methods
2.1. EWDs Principles
2.2. Simulation Methods
3. Oil Film Splitting Simulation
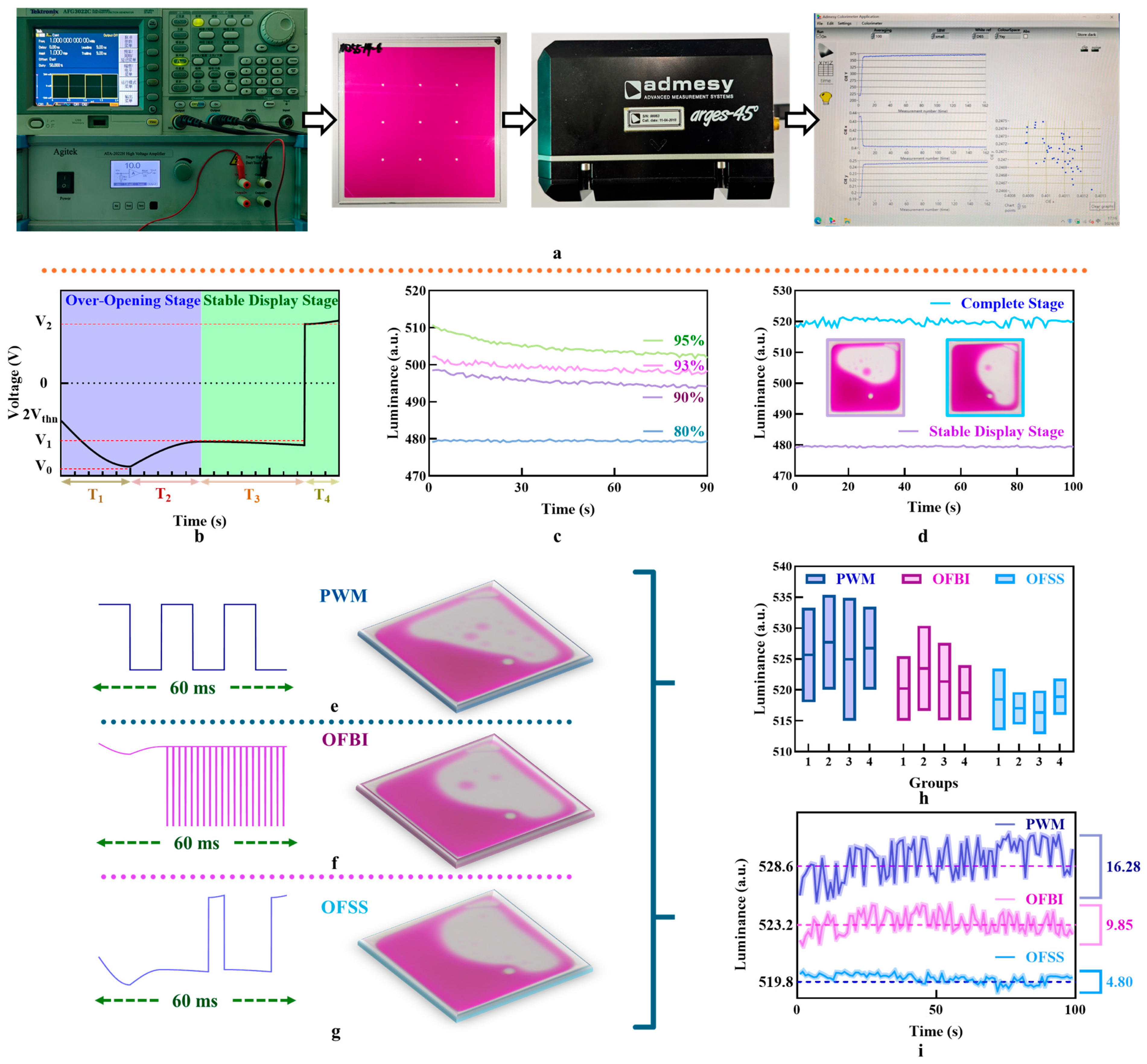
4. Driving Scheme
5. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rogers, J.A. Toward paperlike displays. Science 2001, 291, 1502–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kao, W.; Tsai, J. Driving method of three-particle electrophoretic displays. IEEE Trans. Electron. Devices 2018, 65, 1023–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, R.A.; Feenstra, B.J. Video-speed electronic paper based on electrowetting. Nature 2003, 425, 383–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Battat, S.; Weitz, D.A.; Whitesides, G.M. An outlook on microfluidics: The promise and the challenge. Lab. Chip 2022, 22, 530–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Q.; Yu, W.; Bao, G.; Ge, J. Electrically responsive photonic crystals with bistable states for low-power electrophoretic color displays. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 7007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raissi, M.; Yazdani, A.; Karniadakis, G.E. Hidden fluid mechanics: Learning velocity and pressure fields from flow visualizations. Science 2020, 367, 1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Fan, J.; Xu, J.; Zhou, G.; Liu, S. A novel driving scheme for oil-splitting suppression in electrowetting display. Opt. Rev. 2020, 27, 339–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Yi, Z.; Long, Z.; Zhang, H.; Jiang, J.; Liu, L.; Chi, F.; Tan, D.; Wang, H. Stability study of multi-level grayscales based on driving waveforms for electrowetting displays. Micromachines 2023, 14, 1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, S.; Feng, H.; Deng, Y.; Xie, S.; Yi, Z.; Jin, M.; Zhou, G.; Mulvaney, P.; Shui, L. A reflective display based on the electro-microfluidic assembly of particles within suppressed water-in-oil droplet array. Light Sci. Appl. 2023, 12, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Qian, R.; Yang, T.; Guo, Y.; Yuan, D.; Tang, B.; Zhou, R.; Li, H.; Zhou, G. Inkjet-printed dielectric layer for the enhancement of electrowetting display devices. Nanomaterials 2024, 14, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, S.; Tian, L.; Shen, S.; Yuan, D.; Tang, B. An arc multi-electrode pixel structure for improving the response speed of electrowetting displays. Front. Phys. 2022, 10, 706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.; Yang, J.; Shu, C.; Liang, Q.; Han, J.; Wu, Y.; Chen, M.; Cao, Y.; Ju, X.; Sun, H.; et al. Self-powered colorful dynamic electrowetting display systems based on triboelectricity. Small 2024, 20, 2310359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Li, S.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Li, Z.; Xiao, B.; Guo, W.; Liu, L.; Bai, P.-F. Design of multi-dc overdriving waveform of electrowetting displays for gray scale consistency. Micromachines 2023, 14, 684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Wang, L.; Heinzen, A. A multi waveform adaptive driving scheme for reducing hysteresis effect of electrowetting display. Front. Phys. 2020, 8, 618811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Zhuang, L.; Feng, H.; Zhong, B.; Henzen, A.; Groenewold, J.; Liu, F.; Deng, Y.; Tang, B.; Zhou, G. Programmable control of two-phase fluid interface relative motion in electrowetting device. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 8, 2101086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Guo, Y.; Ye, D.; Chen, W.; Zhou, G. Design and synthesis of a terrylene diimide-based stable cyan dye for printable electrofluidic display. Mater. Adv. 2023, 4, 2831–2838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Tang, B.; Yang, G.; Guo, Y.; Liu, L.; Henzen, A. Progress in advanced properties of electrowetting displays. Micromachines 2021, 12, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Wu, J.; Gao, G.; Zeng, Y.; Liu, S.; Zheng, H. Universal droplet propulsion by dynamic surface-charge wetting. Microsyst. Nanoeng. 2024, 10, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Chen, X.; Wang, Z.L. Contact electrification at the liquid–solid interface. Chem. Rev. 2022, 122, 5209–5232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, J.; Ren, Z.; Xu, L.; Lin, S.; Zhan, F.; Chen, X.; Wang, Z.L. Probing contact-electrification-induced electron and ion transfers at a liquid–solid interface. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 1905696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Li, S.; Ye, D.; Jiang, H.; Tang, B.; Zhou, G. Synthesis and a photo-stability study of organic dyes for electro-fluidic display. Micromachines 2020, 11, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Ye, D.; Guo, Y.; Zhou, G.; Jiang, H. Multi-chromophore dyes for improving light stability of electro-fluidic displays. Front. Phys. 2021, 9, 737205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Jiang, L. Wettability by ionic liquids. Small 2016, 12, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Z.; Yi, Z.; Zhang, H.; Liu, L.; Shui, L. Toward suppressing charge trapping based on a combined driving waveform with an AC reset signal for electro-fluidic displays. Membranes 2022, 12, 1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Zhuang, Z.; Qin, Z.; Wen, B. Movable and Focus-Tunable Lens Based on Electrically Controllable Liquid: A Lattice Boltzmann Study. Entropy 2022, 24, 1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massard, R.; Mans, J.; Adityaputra, A.; Leguijt, R.; Staats, C.; Giraldo, A. Colored oil electrowetting displays. J. Inf. Disp. 2013, 14, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heikemfed, J.; Zhou, K.; Kreit, E.; Raj, B.; Yang, S.; Sun, B.; Milarcik, A.; Clapp, L.; Schwartz, R. Electrofluidic displays using. Young–Laplace transposition of brilliant pigment dispersions. Nat. Photonics 2009, 3, 292–296. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, F.; Nestler, B. Multi-component electro-hydro-thermodynamic model with phase-field method. I. Dielectric. J. Comput. Phys. 2024, 505, 112907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Nestler, B. Wetting and contact-angle hysteresis: Density asymmetry and van der waals force. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2024, 132, 126202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ratschow, A.D.; Hardt, S.; Butt, H.-J. Surface charge deposition by moving drops reduces contact angles. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2023, 131, 228201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yi, Z.; Jiang, M.; Xu, W.; Long, Z.; Wan, Q.; Liu, L.; Chi, F. Driving waveform optimization of electrowetting displays based on pixel’s 2-D model for reducing oil reflux. Opt. Express 2024, 32, 28536–28551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Parameters | Values | Units |
|---|---|---|
| Oil Film Density | 0.880 | g/cm3 |
| Water Density | 0.998 | g/cm3 |
| Oil Film Dynamic Viscosity | 0.004 | s |
| Water Dynamic Viscosity | 0.001 | s |
| Oil Film Relative Dielectric Constant | 4.1 | 1 |
| Water Relative Dielectric Constant | 79 | 1 |
| HIC Layer Dielectric Constant | 1.3 | 1 |
| Photoresist Wall Dielectric Constant | 3.3 | 1 |
| Pixel Total Height | 50 | |
| Oil Film Height | 6 | |
| Water Height | 42 | |
| HIC Layer Height | 2 | |
| Photoresist Wall Height | 6 | |
| Photoresist Wall Width | 15 | |
| Pixel Total Area | 160 |
| Driving Scheme | PWM | OFBI | OFSS |
|---|---|---|---|
| Min Luminance | 518.28 | 515.44 | 514.15 |
| Average Luminance | 528.06 | 520.39 | 516.93 |
| Max Luminance | 534.28 | 526.87 | 521.20 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, J.; Wu, X.; Lin, Y.; Yi, Z.; Jiang, M.; Rui, Y.; Li, L.; Wang, L.; Li, X.; Liu, L.; et al. Polarity-Dependent Driving Scheme for Suppressing Oil Film Splitting in Electrowetting Displays. Micromachines 2025, 16, 338. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16030338
Wang J, Wu X, Lin Y, Yi Z, Jiang M, Rui Y, Li L, Wang L, Li X, Liu L, et al. Polarity-Dependent Driving Scheme for Suppressing Oil Film Splitting in Electrowetting Displays. Micromachines. 2025; 16(3):338. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16030338
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Jiashuai, Xianyue Wu, Yibin Lin, Zichuan Yi, Mouhua Jiang, Yiting Rui, Liangyu Li, Li Wang, Xiuxiu Li, Liming Liu, and et al. 2025. "Polarity-Dependent Driving Scheme for Suppressing Oil Film Splitting in Electrowetting Displays" Micromachines 16, no. 3: 338. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16030338
APA StyleWang, J., Wu, X., Lin, Y., Yi, Z., Jiang, M., Rui, Y., Li, L., Wang, L., Li, X., Liu, L., & Zhou, G. (2025). Polarity-Dependent Driving Scheme for Suppressing Oil Film Splitting in Electrowetting Displays. Micromachines, 16(3), 338. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16030338







