Advances in Triboelectric Nanogenerators for Microbial Disinfection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Working Principle and Materials of TENG
2.1. Working Mechanism of TENG
2.2. Advanced Triboelectric Materials for High-Performance TENG
2.2.1. High-Dielectric Composite
2.2.2. Functional Group Modification
2.2.3. Micro/Nano-Patterned Surface
2.2.4. Ultrasound Vibration Control
3. TENG for Microbial Disinfection
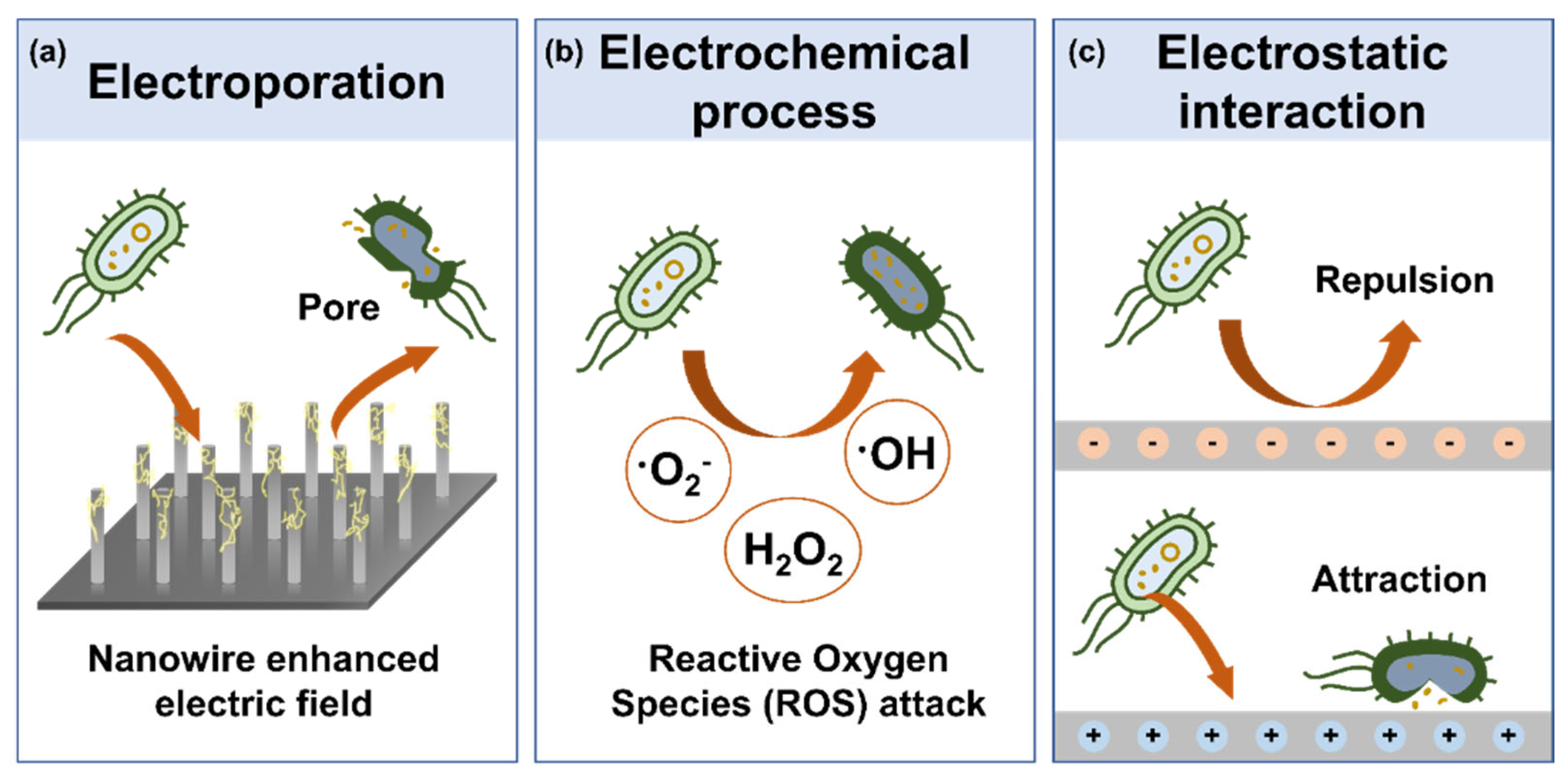
3.1. Mechanism of Microbial Disinfection via TENG
3.2. Water Disinfection
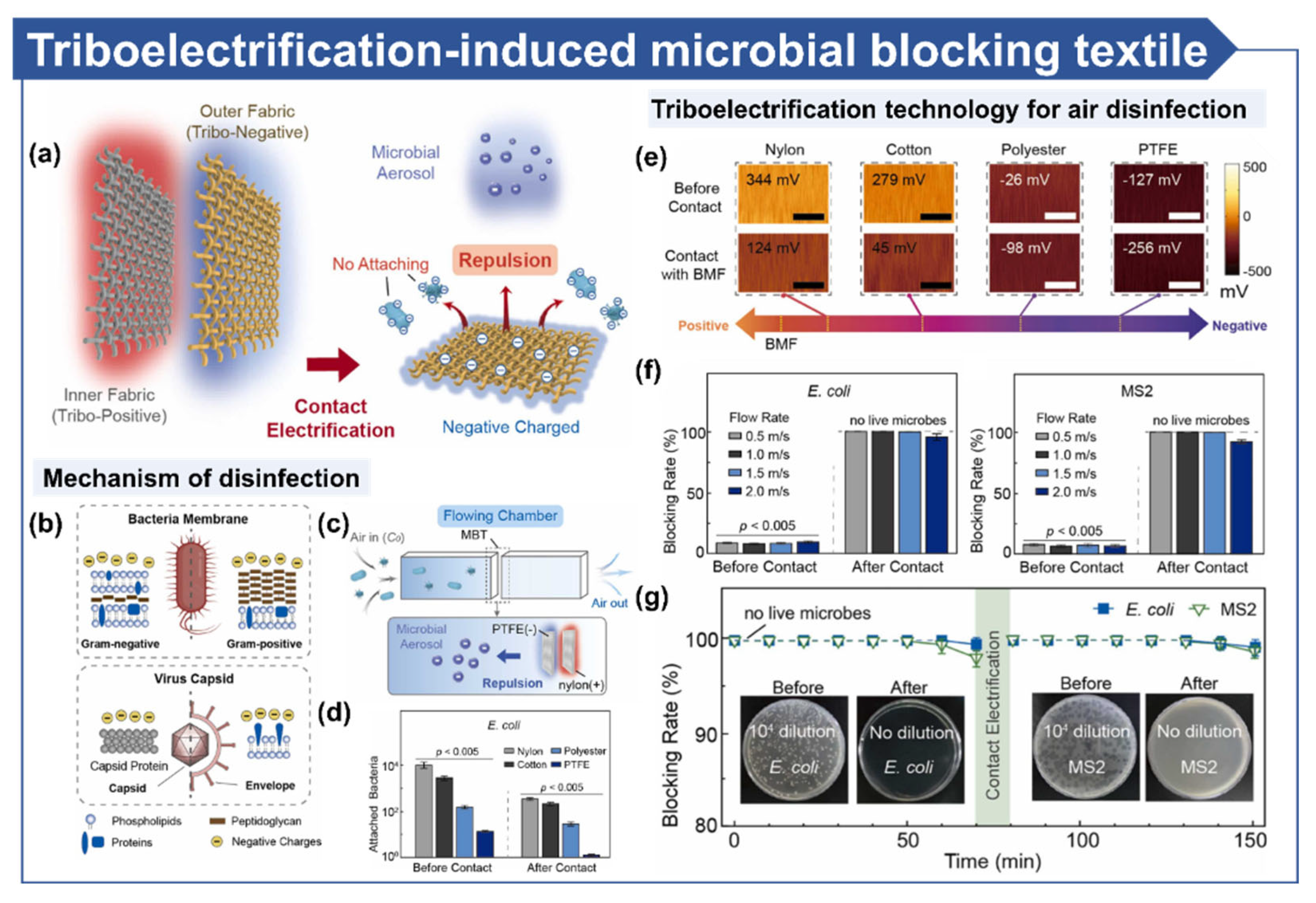
3.3. Air Disinfection
3.4. Surface Disinfection
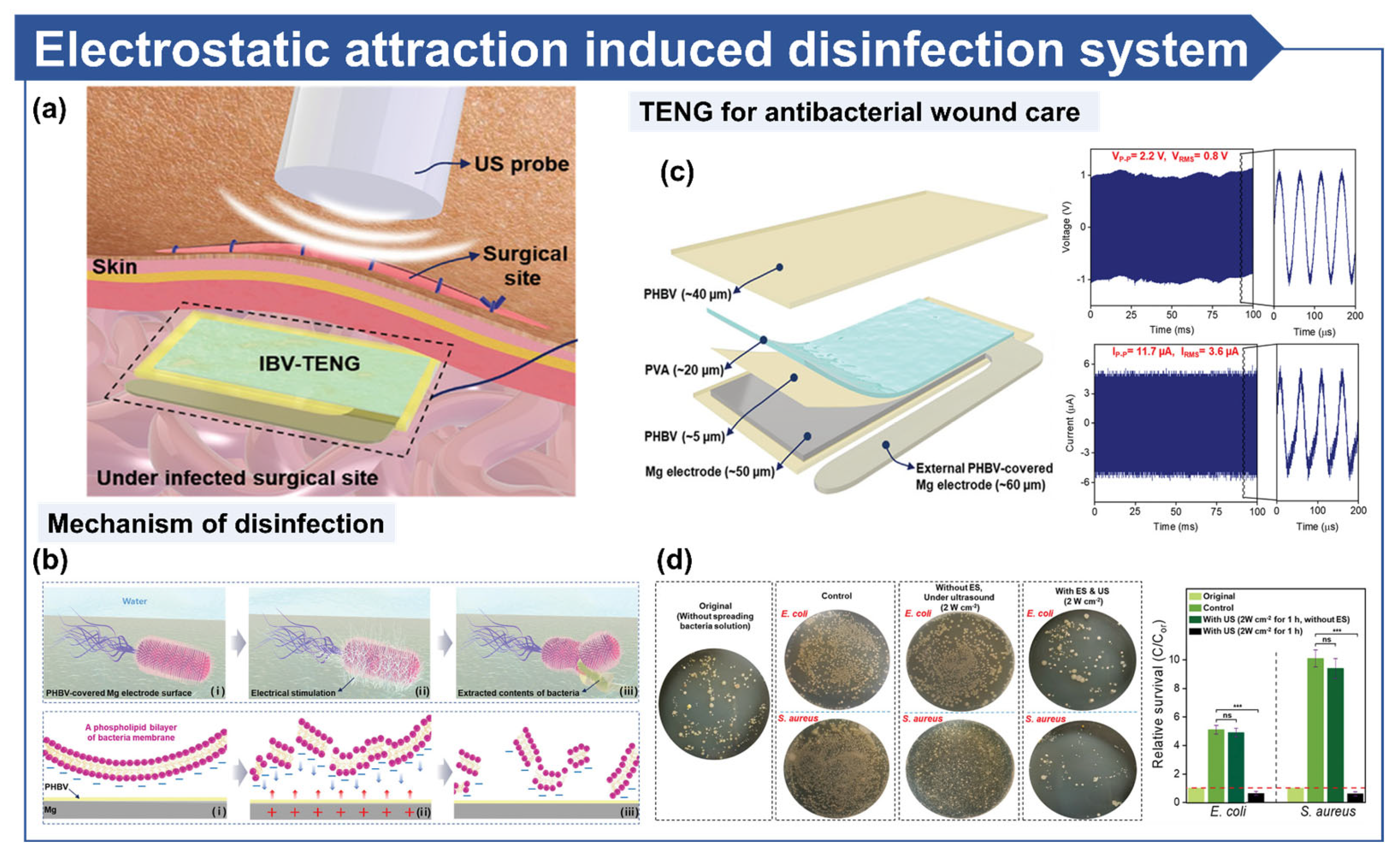
3.5. Antibacterial Wound Care
4. Challenges and Perspective
4.1. Development of Durable TENG
4.2. High-Efficiency Microbial Disinfection
4.3. Expanding Applications to In Vivo
4.4. Integrating Monitoring Systems
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Raymenants, J.; Geenen, C.; Budts, L.; Thibaut, J.; Thijssen, M.; De Mulder, H.; Gorissen, S.; Craessaerts, B.; Laenen, L.; Beuselinck, K.; et al. Indoor air surveillance and factors associated with respiratory pathogen detection in community settings in Belgium. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moritz, S.; Gottschick, C.; Horn, J.; Popp, M.; Langer, S.; Klee, B.; Purschke, O.; Gekle, M.; Ihling, A.; Zimmermann, F.D.L.; et al. The risk of indoor sports and culture events for the transmission of COVID-19. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 5096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, X.; Suh, I.-Y.; Xiao, X.; Pang, F.; Jeon, J.; Cho, D.S.; Kwon, Y.H.; Kim, S.-W. Triboelectric and piezoelectric technologies for self-powered microbial disinfection. Nano Energy 2024, 127, 109716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Sun, Z.; Guo, Y.; Qiang, Z.; Ben, W. Virus inactivation by sequential ultraviolet-chlorine disinfection: Synergistic effect and mechanism. Chemosphere 2023, 314, 137632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedlak, D.L.; von Gunten, U. The Chlorine Dilemma. Science 2011, 331, 42–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albolafio, S.; Marín, A.; Allende, A.; García, F.; Simón-Andreu, P.J.; Abellán Soler, M.; Gil, M.I. Strategies for mitigating chlorinated disinfection byproducts in wastewater treatment plants. Chemosphere 2022, 288, 132583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.-J.; Nguyen, T.T.M.; Yoon, J.; Lee, C. Role of Reactive Oxygen Species in Escherichia coli Inactivation by Cupric Ion. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 11299–11304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, I.-Y.; Huo, Z.-Y.; Jung, J.-H.; Kang, D.; Lee, D.-M.; Kim, Y.-J.; Kim, B.; Jeon, J.; Zhao, P.; Shin, J.; et al. Highly efficient microbial inactivation enabled by tunneling charges injected through two-dimensional electronics. Sci. Adv. 2024, 10, eadl5067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, H.; Park, H.-M.; Kim, M.-K.; Kim, B.; Myoung, H.S.; Kim, T.Y.; Yoon, H.-J.; Kwak, S.S.; Kim, J.; Hwang, T.H.; et al. Self-rechargeable cardiac pacemaker system with triboelectric nanogenerators. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, B.; Yang, O.; Yuan, W.; Zhou, L.; Zhao, Z.; Wu, Z.; Wang, J.; Wang, Z.L. A Dual-Mode Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Wind Energy Harvesting and Self-Powered Wind Speed Monitoring. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 6244–6254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Liu, S.; Yang, H.; Jiang, T. Triboelectric Nanogenerators for Ocean Wave Energy Harvesting: Unit Integration and Network Construction. Electronics 2023, 12, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinchet, R.; Yoon, H.-J.; Ryu, H.; Kim, M.-K.; Choi, E.-K.; Kim, D.-S.; Kim, S.-W. Transcutaneous ultrasound energy harvesting using capacitive triboelectric technology. Science 2019, 365, 491–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, J.; Feng, H.; Yan, L.; Yu, M.; Ouyang, H.; Li, H.; Jiang, W.; Jin, Y.; Zhu, G.; Li, Z.; et al. A self-powered sterilization system with both instant and sustainable anti-bacterial ability. Nano Energy 2017, 36, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, Z.-Y.; Yang, Y.; Jeong, J.-M.; Wang, X.; Zhang, H.; Wei, M.; Dai, K.; Xiong, P.; Kim, S.-W. Self-Powered Disinfection Using Triboelectric, Conductive Wires of Metal–Organic Frameworks. Nano Lett. 2023, 23, 3090–3097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, Z.-Y.; Kim, Y.-J.; Suh, I.-Y.; Lee, D.-M.; Lee, J.H.; Du, Y.; Wang, S.; Yoon, H.-J.; Kim, S.-W. Triboelectrification induced self-powered microbial disinfection using nanowire-enhanced localized electric field. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 3693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, I.-Y.; Kim, Y.-J.; Zhao, P.; Cho, D.S.; Kang, M.; Huo, Z.-Y.; Kim, S.-W. Self-powered microbial blocking textile driven by triboelectric charges. Nano Energy 2023, 110, 108343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imani, I.M.; Kim, B.; Xiao, X.; Rubab, N.; Park, B.-J.; Kim, Y.-J.; Zhao, P.; Kang, M.; Kim, S.-W. Ultrasound-Driven On-Demand Transient Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Subcutaneous Antibacterial Activity. Adv. Sci. 2022, 10, 2204801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, D.; Hwang, J.-H.; Kim, Y.-J.; Zhao, P.; Lee, H.Y.; Kim, J.; Shin, M.S.; Jeon, S.; Kim, S.; Kim, S.-W. Contact electrification controlled by material deformation-induced electronic structure changes. Mater. Today 2024, 72, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, D.; Lee, H.Y.; Hwang, J.-H.; Jeon, S.; Kim, D.; Kim, S.; Kim, S.-W. Deformation-contributed negative triboelectric property of polytetrafluoroethylene: A density functional theory calculation. Nano Energy 2022, 100, 107531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, H.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, L.; Wang, P.; He, X.; Dai, G.; Zheng, H.; Chen, C.; Wang, A.C.; Xu, C.; et al. Quantifying the triboelectric series. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kang, D.; Lee, H.-K.; Hwang, J.-H.; Lee, H.Y.; Jeon, S.; Kim, D.; Kim, S.; Kim, S.-W. Design Principles to Maximize Non-Bonding States for Highly Tribopositive Behavior. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2209648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seol, M.; Kim, S.; Cho, Y.; Byun, K.-E.; Kim, H.; Kim, J.; Kim, S.K.; Kim, S.-W.; Shin, H.-J.; Park, S. Triboelectric Series of 2D Layered Materials. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1801210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, K.; Liu, J.; Li, W.; Jiao, P.; He, Z.; Wei, Y.; Qu, F.; Xu, Z.; Wang, L.; Ren, X.; et al. A self-powered bridge health monitoring system driven by elastic origami triboelectric nanogenerator. Nano Energy 2023, 105, 107974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, K.; Miao, X.; Zhang, W.; Huang, X.; Zhang, H.; Kim, S.-W. Robust Displacement Sensing by Direct-Current Triboelectric Nanogenerator Via Intelligent Waveform Recognition. Adv. Sci. 2022, 10, 2204694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.; Yun, Y.; Jang, S.; Ra, Y.; Choi, J.H.; Hwang, H.J.; Choi, D.; Choi, D. Universal biomechanical energy harvesting from joint movements using a direction-switchable triboelectric nanogenerator. Nano Energy 2020, 71, 104584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-J.; Lee, J.; Hwang, J.-H.; Chung, Y.; Park, B.-J.; Kim, J.; Kim, S.-H.; Mun, J.; Yoon, H.-J.; Park, S.-M.; et al. High-Performing and Capacitive-Matched Triboelectric Implants Driven by Ultrasound. Adv. Mater. 2023, 36, 2307194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, G.; Ma, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Fan, K.; Liu, J.; Zhou, B.; Wang, G.; You, Z.; et al. An ultrasound-driven implantable wireless energy harvesting system using a triboelectric transducer. Matter 2022, 5, 4315–4331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, Y.; Yuan, H.; Wang, Z.; Jeong, J.-M.; Park, B.-J.; Hwang, J.-H.; Suh, S.-J.; Choi, B.-O.; Park, H.-M.; Kim, Y.-J.; et al. Acoustic Tunable Battery-Free Implants Based on Sustainable Triboelectric Nanogenerators with Metal-Polymer Intermixing Layers. Adv. Energy Mater. 2024, 15, 2403712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, Z.-Y.; Li, G.-Q.; Yu, T.; Feng, C.; Lu, Y.; Wu, Y.-H.; Yu, C.; Xie, X.; Hu, H.-Y. Cell Transport Prompts the Performance of Low-Voltage Electroporation for Cell Inactivation. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 15832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Yang, D.; Li, S.; Yang, L.; Yan, W.; Xu, H. Advances on electrochemical disinfection research: Mechanisms, influencing factors and applications. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 912, 169043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seung, W.; Yoon, H.-J.; Kim, T.Y.; Ryu, H.; Kim, J.; Lee, J.-H.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, S.; Park, Y.K.; Park, Y.J.; et al. Boosting Power-Generating Performance of Triboelectric Nanogenerators via Artificial Control of Ferroelectric Polarization and Dielectric Properties. Adv. Energy Mater. 2016, 7, 1600988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Ryu, H.; Lee, J.H.; Khan, U.; Kwak, S.S.; Yoon, H.-J.; Kim, S.-W. High Permittivity CaCu3Ti4O12 Particle-Induced Internal Polarization Amplification for High Performance Triboelectric Nanogenerators. Adv. Energy Mater. 2020, 10, 1903524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, S.S.; Kim, S.M.; Ryu, H.; Kim, J.; Khan, U.; Yoon, H.-J.; Jeong, Y.H.; Kim, S.-W. Butylated melamine formaldehyde as a durable and highly positive friction layer for stable, high output triboelectric nanogenerators. Energy Environ. Sci. 2019, 12, 3156–3163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, V.-T.; Zhou, Q.; Kim, J.-N.; Oh, J.-H.; Han, K.-W.; Choi, H.-S.; Kim, S.-W.; Oh, I.-K. Treefrog Toe Pad-Inspired Micropatterning for High-Power Triboelectric Nanogenerator. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1901638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, B.-G.; Lee, C.; Kim, Y.-J.; Park, J.; Kim, H.; Jung, Y.; Ko, J.S.; Kim, S.-W.; Lee, J.-H.; Cho, H. Toxic micro/nano particles removal in water via triboelectric nanogenerator. Nano Energy 2022, 100, 107433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Hinchet, R.; Kim, S.K.; Kim, S.; Kim, S.-W. Shape memory polymer-based self-healing triboelectric nanogenerator. Energy Environ. Sci. 2015, 8, 3605–3613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seung, W.; Gupta, M.K.; Lee, K.Y.; Shin, K.-S.; Lee, J.-H.; Kim, T.Y.; Kim, S.; Lin, J.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, S.-W. Nanopatterned Textile-Based Wearable Triboelectric Nanogenerator. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 3501–3509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, Y.; Jeong, J.-M.; Hwang, J.-H.; Kim, Y.-J.; Park, B.-J.; Cho, D.S.; Cho, Y.; Suh, S.-J.; Choi, B.-O.; Park, H.-M.; et al. Gigantic triboelectric power generation overcoming acoustic energy barrier using metal-liquid coupling. Joule 2024, 8, 2681–2695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.; Yoon, H.-J.; Kim, Y.-J.; Park, B.-J.; Jung, J.-H.; Kim, S.-W. Ultrasound-Driven Triboelectric Nanogenerator with Biocompatible 2-Hydroxyethyl Methacrylate. ACS Energy Lett. 2023, 8, 3412–3419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, W.; Zhou, J.; Cheng, J.; Wang, Z.; Guo, H.; Wu, C.; Xu, S.; Wu, Z.; Xie, X.; Wang, Z.L. TriboPump: A Low-Cost, Hand-Powered Water Disinfection System. Adv. Energy Mater. 2019, 9, 1901320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghatak, B.; Banerjee, S.; Ali, S.B.; Bandyopadhyay, R.; Das, N.; Mandal, D.; Tudu, B. Design of a self-powered triboelectric face mask. Nano Energy 2021, 79, 105387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sim, M.T.; Ee, Z.Y.; Lim, Y.H.; Sia, T.S.; Ong, D.T.K.; Koay, J.S.C.; Goh, B.T.; Yong, Y.S.; Aw, K.C.; Tan, S.T.; et al. Instant Disinfecting Face Masks Utilizing Electroporation Powered by Respiration-Driven Triboelectric Nanogenerators. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2410062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, Z.-Y.; Liu, H.; Wang, W.-L.; Wang, Y.-H.; Wu, Y.-H.; Xie, X.; Hu, H.-Y. Low-voltage alternating current powered polydopamine-protected copper phosphide nanowire for electroporation-disinfection in water. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 7347–7354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Xie, X.; Zhao, W.; Yao, J.; Kong, D.; Boehm, A.B.; Cui, Y. Static Electricity Powered Copper Oxide Nanowire Microbicidal Electroporation for Water Disinfection. Nano Lett. 2014, 14, 5603–5608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellal, M.S.; Hemdan, B.A.; Youssef, M.; El-Taweel, G.E.; AbouTaleb, E.M. Novel electro-oxidation unit for electro-disinfection of E. coli and some waterborne pathogens during wastewater treatment: Batch and continuous experiments. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 16417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Feng, H.; Hu, L.; Jin, W.; Hao, Q.; Gao, A.; Peng, X.; Li, W.; Wong, K.-Y.; Wang, H.; et al. An antibacterial platform based on capacitive carbon-doped TiO2 nanotubes after direct or alternating current charging. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-J.; Kim, H.T.; Lee, J.H.; Suh, I.-Y.; Kim, S.-W. Self-Powered Fine Dust Filtration Using Triboelectrification-Induced Electric Field. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2022, 17, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.X.; Kuang, S.Y.; Chen, Y.H.; Wang, Z.L.; Li, C.; Zhu, G. In Situ Active Poling of Nanofiber Networks for Gigantically Enhanced Particulate Filtration. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 24332–24338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Han, C.B.; He, C.; Gu, G.Q.; Nie, J.H.; Shao, J.J.; Xiao, T.X.; Deng, C.R.; Wang, Z.L. Washable Multilayer Triboelectric Air Filter for Efficient Particulate Matter PM2.5 Removal. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1706680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, Z.-Y.; Lee, D.-M.; Jeong, J.-M.; Kim, Y.-J.; Kim, J.; Suh, I.-Y.; Xiong, P.; Kim, S.-W. Microbial Disinfection with Supercoiling Capacitive Triboelectric Nanogenerator. Adv. Energy Mater. 2022, 12, 2103680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.; Hanif, Z.; Yun, Y.; Khan, Z.A.; Jang, S.; Ra, Y.; Lin, Z.-H.; La, M.; Park, S.J.; Choi, D. Triboelectrification-driven microbial inactivation in a conductive cellulose filter for affordable, portable, and efficient water sterilization. Nano Energy 2021, 88, 106228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Huang, H.; Zhang, W.; Hu, Z.; Li, X.; Liu, J.; Xu, G.; Yang, C. Self-powered triboelectric nanogenerator driven nanowires electrode array system for the urine sterilization. Nano Energy 2022, 96, 107111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-J.; Huo, Z.-Y.; Wang, X.; Dai, H.; Lee, D.-M.; Suh, I.-Y.; Hwang, J.-H.; Chung, Y.; Lee, H.Y.; Du, Y.; et al. Walking-induced electrostatic charges enable in situ electroporated disinfection in portable water bottles. Nat. Water 2024, 2, 360–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.-L.; Song, W.-Z.; Sun, D.-J.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, J.; Chen, Y.-Q.; Ramakrishna, S.; Long, Y.-Z. A self-priming air filtration system based on triboelectric nanogenerator for active air purification. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 452, 139428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.; Son, Y.; Ahn, J.; Lim, H.; Ahn, S.; Lee, J.; Bae, P.K.; Kim, I.-D. Multifunctional Filter Membranes Based on Self-Assembled Core–Shell Biodegradable Nanofibers for Persistent Electrostatic Filtration through the Triboelectric Effect. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 19451–19463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, M.; Jang, N.-Y.; Kim, Y.-J.; Ro, H.-J.; Kim, D.; Kim, Y.; Kim, H.T.; Kwon, H.M.; Ahn, J.-H.; Choi, B.-O.; et al. Virus blocking textile for SARS-CoV-2 using human body triboelectric energy harvesting. Cell Rep. Phys. Sci. 2022, 3, 100813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Dong, K.; Ye, C.; Jiang, Y.; Zhai, S.; Cheng, R.; Liu, D.; Gao, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, Z.L. A breathable, biodegradable, antibacterial, and self-powered electronic skin based on all-nanofiber triboelectric nanogenerators. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaba9624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barman, S.R.; Chan, S.-W.; Kao, F.-C.; Ho, H.-Y.; Khan, I.; Pal, A.; Huang, C.-C.; Lin, Z.-H. A self-powered multifunctional dressing for active infection prevention and accelerated wound healing. Sci. Adv. 2023, 9, eadc8758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Li, H.; Song, Y.; Zhang, D.; Wang, Z.; Yi, X.; Qi, B.; Zhang, X.; Jiang, P.; Yu, A. Drug-Free “Triboelectric Immunotherapy” Activating Immunity for Osteomyelitis Treatment and Recurrence Prevention. Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, 2408473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, Z.-Y.; Winter, L.R.; Wang, X.-X.; Du, Y.; Wu, Y.-H.; Hübner, U.; Hu, H.-Y.; Elimelech, M. Synergistic Nanowire-Enhanced Electroporation and Electrochlorination for Highly Efficient Water Disinfection. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 10925–10934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, Z.-Y.; Lee, D.-M.; Wang, S.; Kim, Y.-J.; Kim, S.-W. Emerging Energy Harvesting Materials and Devices for Self-Powered Water Disinfection. Small Methods 2021, 5, 2100093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Sun, Y.; Cui, A.; Xia, Y.; Yan, Q.; Song, Y.; Wang, L.; Shan, G.; Wang, X. Electrothermal sterilization and self-powered real-time respiratory monitoring of reusable mask based on Ag micro-mesh films. Nano Energy 2023, 105, 107987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, D.; Wu, J.; Zi, Y.; Pan, C.; Cui, H.; Li, X. Self-Powered Sterilization System for Wearable Devices Based on Biocompatible Materials and Triboelectric Nanogenerator. ACS Appl. Electron. Mater. 2023, 5, 2819–2828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Shi, Y. Boosting the Durability of Triboelectric Nanogenerators: A Critical Review and Prospect. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2213407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Luo, N.; Liu, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, D. A New Self-Healing Triboelectric Nanogenerator Based on Polyurethane Coating and Its Application for Self-Powered Cathodic Protection. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 10498–10507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; Zhai, N.; Liu, Y.; Wen, Z.; Sun, X. Hybrid Triboelectric Nanogenerators: From Energy Complementation to Integration. Research 2021, 2021, 9143762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Materials/Structure | Performance | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Non poled poly(vinylidenefluoride-co-trifluoroethylene) (P(VDF-TrFE)) | 30 V | [31] |
| Poled P(VDF-TrFE):BaTiO3 (BTO) | 1130 V | [31] |
| Butylated melamine formaldehyde (BMF):CaCu3Ti4O₁2 (CCTO) | 268 V | [32] |
| Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) | 90 V | [33] |
| BMF | 210 V | [33] |
| Flat polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) | 200 V | [34] |
| Micropatterned PDMS | 490 V | [34] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jeon, J.; Kang, D.; Kim, S.-W. Advances in Triboelectric Nanogenerators for Microbial Disinfection. Micromachines 2025, 16, 281. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16030281
Jeon J, Kang D, Kim S-W. Advances in Triboelectric Nanogenerators for Microbial Disinfection. Micromachines. 2025; 16(3):281. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16030281
Chicago/Turabian StyleJeon, Jinyoung, Donghyeon Kang, and Sang-Woo Kim. 2025. "Advances in Triboelectric Nanogenerators for Microbial Disinfection" Micromachines 16, no. 3: 281. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16030281
APA StyleJeon, J., Kang, D., & Kim, S.-W. (2025). Advances in Triboelectric Nanogenerators for Microbial Disinfection. Micromachines, 16(3), 281. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16030281









