Investigation into Laser-Vibration-Assisted Cutting of Single-Crystal Silicon by Molecular Dynamics Simulation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Simulation Method
3. Results and Discussion
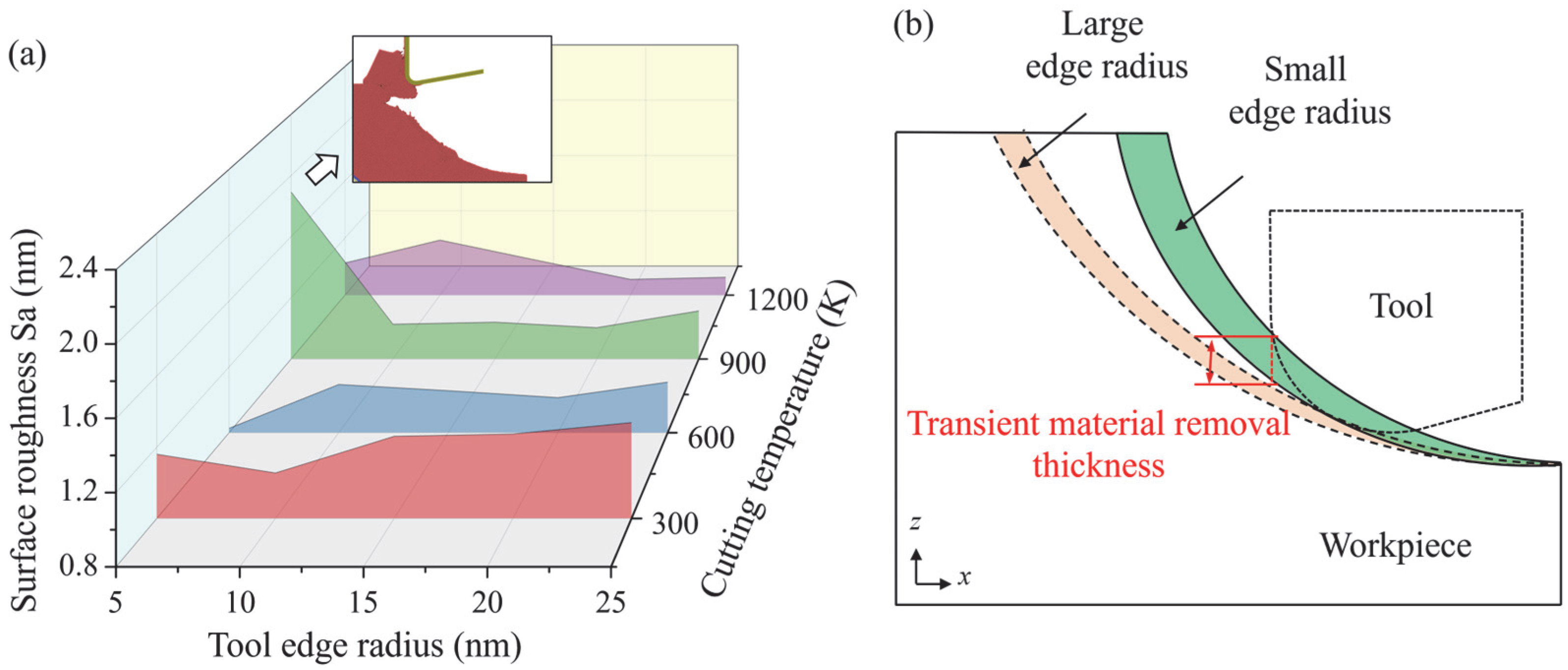
3.1. Surface Morphology
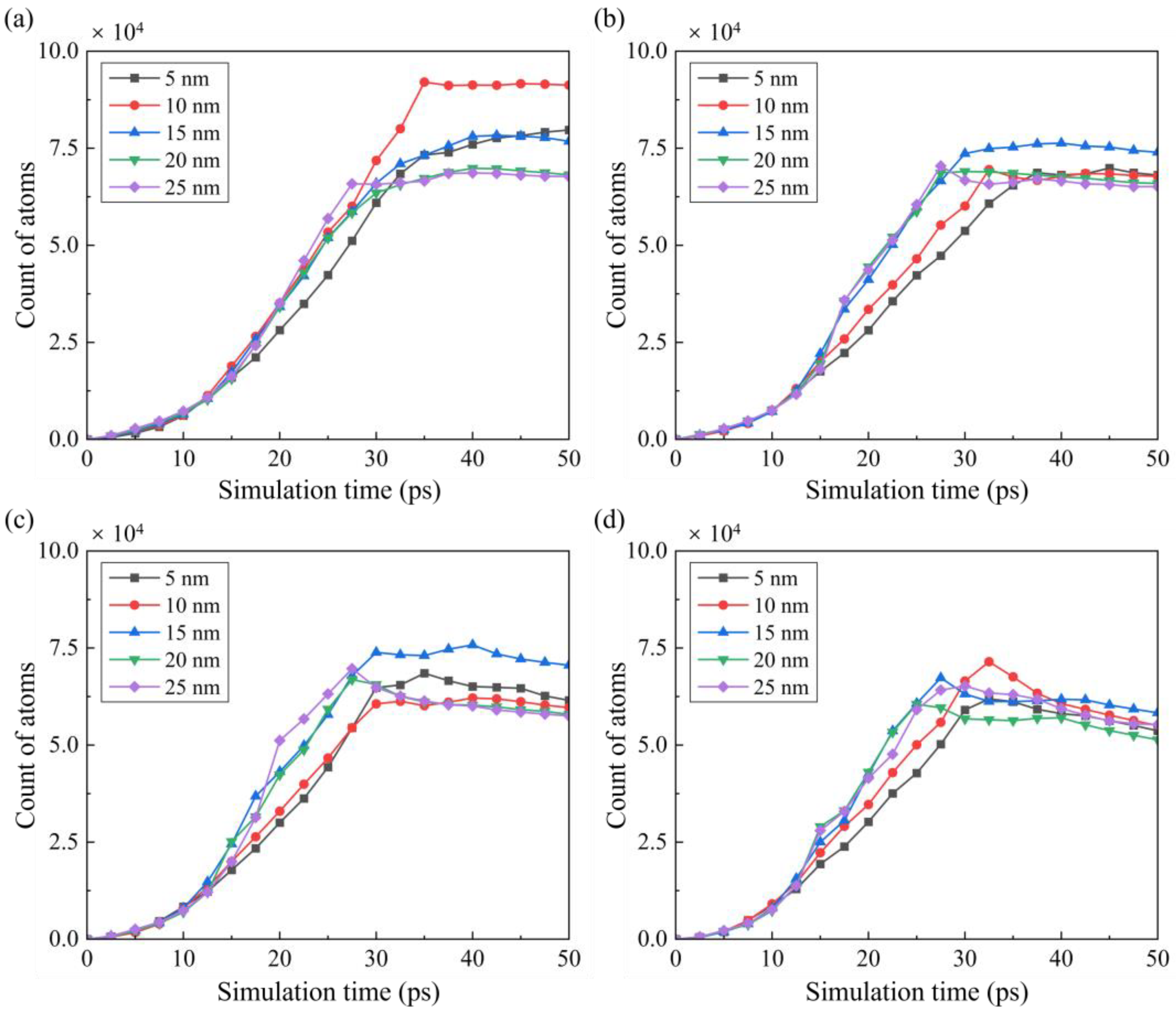
3.2. Material Removal Behavior
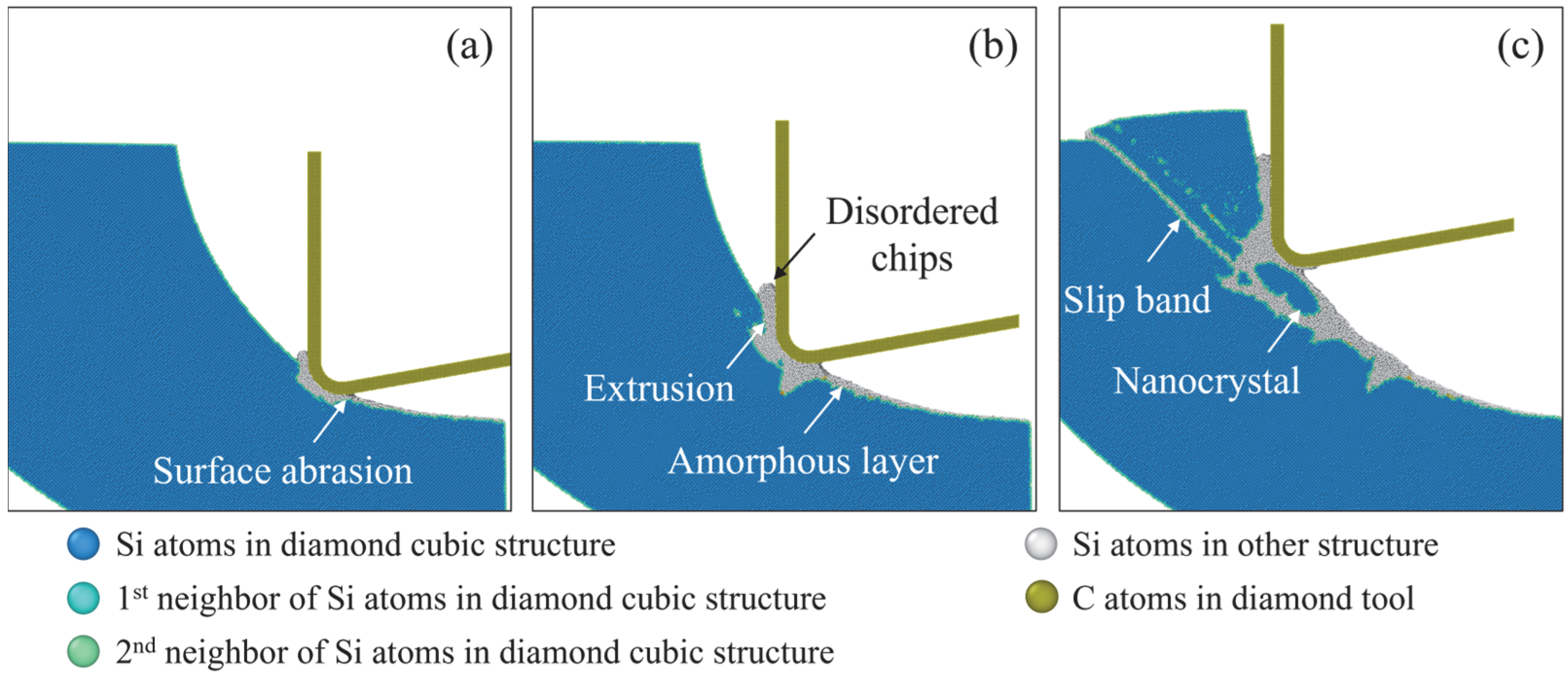
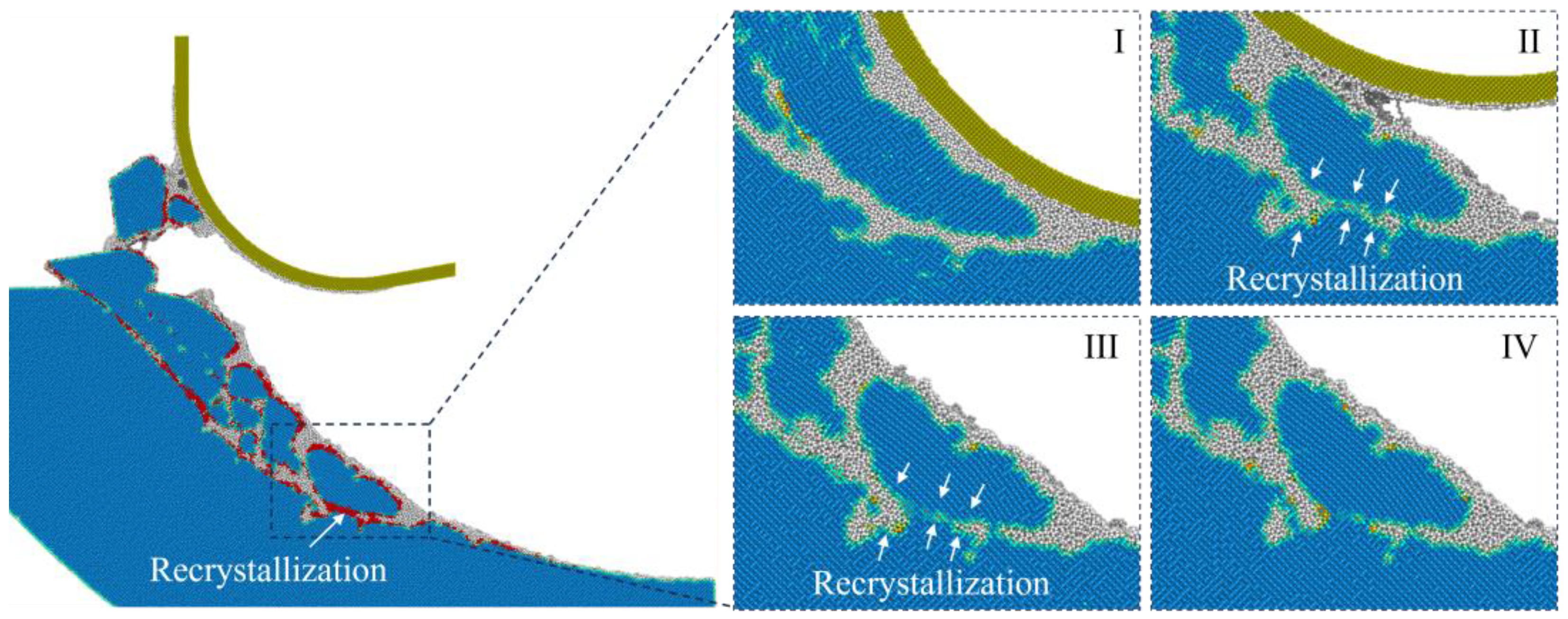
3.3. Crystal Defects
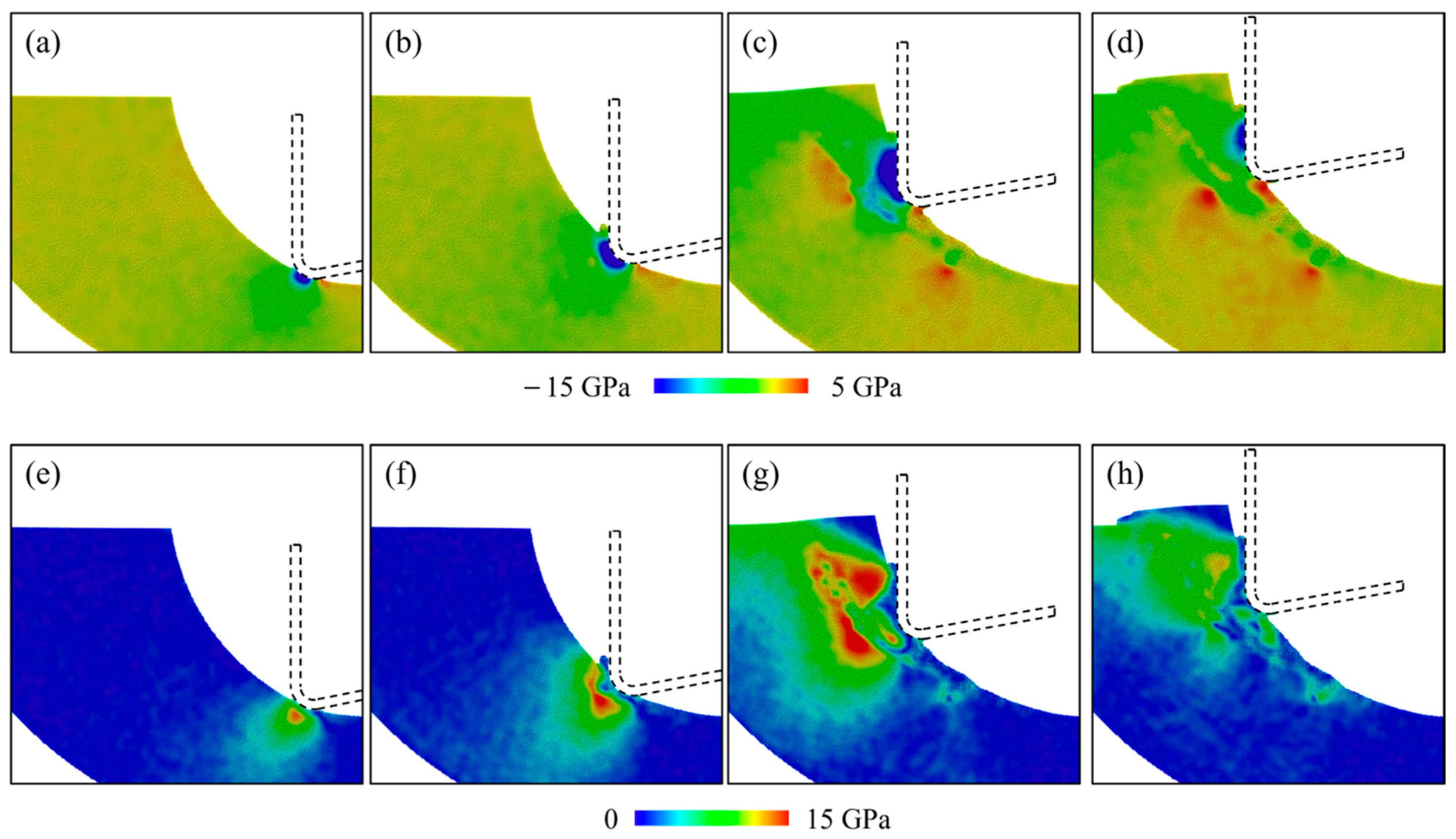
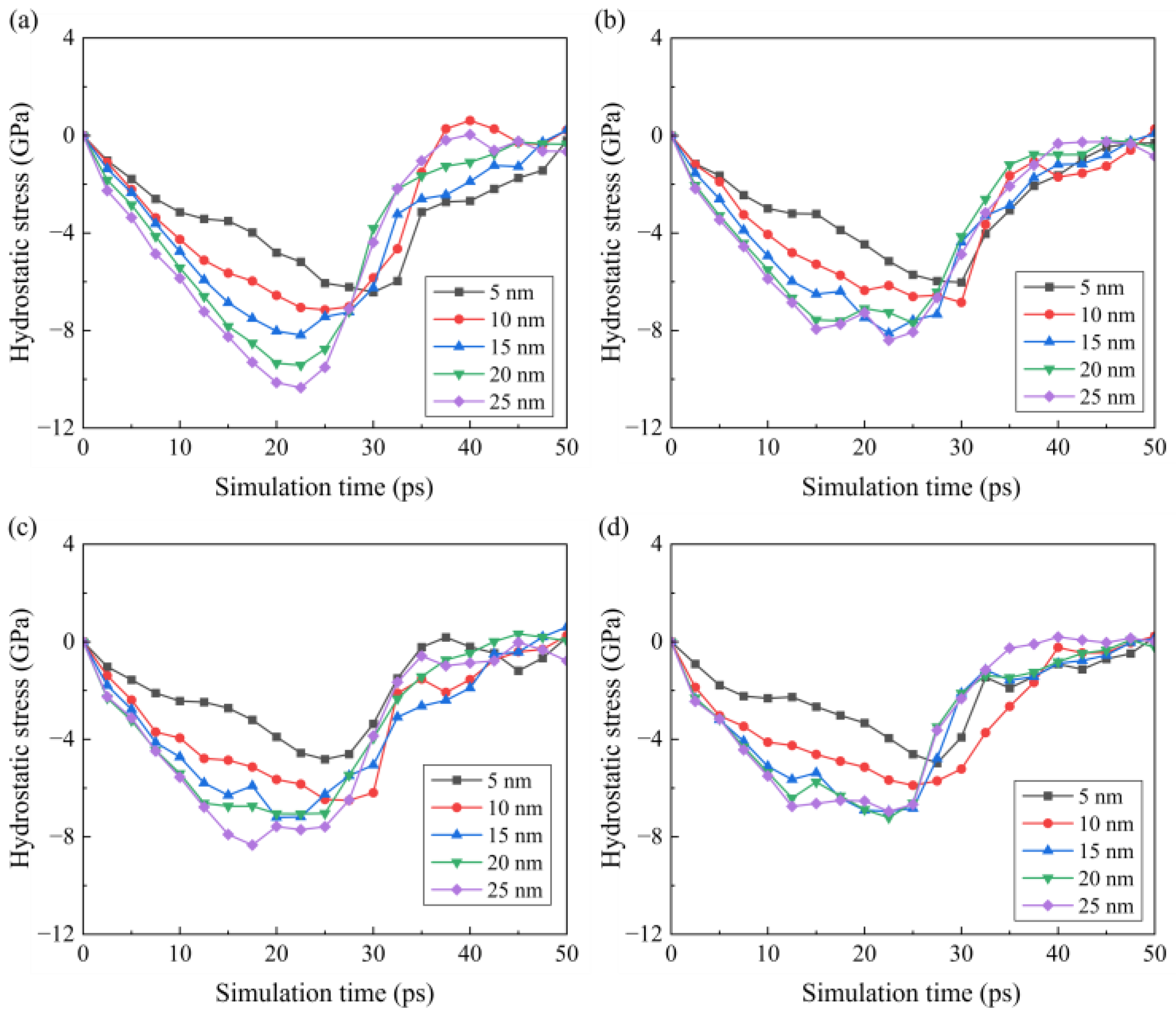
3.4. Stress Analysis
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- In one vibration cycle, surface swelling gradually becomes obvious after the initial contact due to the rise in material removal thickness, while it becomes less apparent at the end of the contact stage. When cutting at room temperature, the surface swelling is more obvious, and the surface roughness is increased when tools with a large edge radius are adopted. As the cutting temperature increases, a decrease in surface roughness is observed when the tool edge radius is increased.
- (2)
- As the tool edge radius increases, more surface abrasion and extrusion removal can be observed during the cutting stage. As the cutting temperature increases, the plastic deformation in the subsurface workpiece is promoted. In the surface abrasion and extrusion stage, obvious plastic deformation patterns are observed. During the shear stage, more slip bands are observed with voids formed in the subsurface workpiece.
- (3)
- With increasing tool edge radius, more disordered atoms are generated on the machined surface since the surface abrasion and extrusion stage is prolonged. As the temperature increases, the amorphous layer becomes inapparent, and more grains are left on the machined surface, which can be attributed to the enhanced dislocation-induced plastic deformation. Furthermore, recrystallization is promoted by raising the cutting temperature and tool edge radius.
- (4)
- As the cutting temperature increases, both hydrostatic stress and von Mises stress show an apparent decrease owing to the thermal softening of the workpiece material. For workpieces machined by a blunt tool, an increase in internal stress is observed, and the internal stress reaches a maximum earlier. While this phenomenon becomes less apparent when the cutting temperature increases, since the enhanced plastic deformability facilitates the detachment of the crystal grains.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, K.S.; Seo, S.; Kwon, J.; Lee, D.; Kim, C.; Ryu, J.E.; Kim, J.; Suh, J.M.; Jung, H.G.; Jo, Y.; et al. Growth-based monolithic 3D integration of single-crystal 2D semiconductors. Nature 2024, 636, 615–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priolo, F.; Gregorkiewicz, T.; Galli, M.; Krauss, T.F. Silicon nanostructures for photonics and photovoltaics. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2014, 9, 19–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, H.; Zhao, D.; Liu, C.; Chen, H.; To, S. Laser-assisted slow tool servo diamond turning of single-crystal silicon for fabricating micro-lens arrays. J. Manuf. Process. 2024, 127, 174–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wang, K.; Zakharov, O.; Cui, H.; Wu, M.; Zhao, T.; Yan, Y.; Geng, Y. Damage evolution mechanism and low-damage grinding technology of silicon carbide ceramics. Int. J. Extrem. Manuf. 2025, 7, 022015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Cheung, C.F.; Zang, Y.; Wang, C.; Liu, C. Material removal rate optimization with bayesian optimized differential evolution based on deep learning in robotic polishing. J. Manuf. Syst. 2025, 78, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Chen, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, J.; Chu, J.; Xiao, J.; Xu, J. Molecular dynamic simulation of tool groove wear in nanoscale cutting of silicon. AIP Adv. 2020, 10, 015327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Liu, C.; Ke, J.; Zhang, J.; Shu, X.; Xu, J. Subsurface damage and phase transformation in laser-assisted nanometric cutting of single crystal silicon. Mater. Des. 2020, 190, 108524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, J.; Chen, X.; Liu, C.; Zhang, J.; Yang, H.; Xu, J. Enhancing the ductile machinability of single-crystal silicon by laser-assisted diamond cutting. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2022, 118, 3265–3282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skelton, R.C. Turning with an oscillating tool. Int. J. Mach. Tool Des. Res. 1968, 8, 239–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamoto, E.; Moriwaki, T. Study on Elliptical Vibration Cutting. CIRP Ann. 1994, 43, 35–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriwaki, T.; Shamoto, E. Ultrasonic Elliptical Vibration Cutting. CIRP Ann. Manuf. Technol. 1995, 44, 31–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, J.; Liu, C.; Chen, X.; Xiao, J.; Xu, J. Machinability of single crystal calcium fluoride by applying elliptical vibration diamond cutting. Precis. Eng. 2020, 66, 306–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yip, W.S.; To, S. An application of eddy current damping effect on single point diamond turning of titanium alloys. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2017, 50, 435002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatefi, S.; Abou-El-Hossein, K. Review of magnetic-assisted single-point diamond turning for ultra-high-precision optical component manufacturing. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2022, 120, 1591–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yin, T.; Li, D.; Sun, Z.; Xue, C.; Yip, W.S.; To, S. Magnetic and ultrasonic vibration dual-field assisted ultra-precision diamond cutting of high-entropy alloys. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2024, 202, 104208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, J.; Zhang, J.; Chen, X.; Liu, C.; Long, G.; Sun, H.; Xu, J. Investigation on the material removal mechanism in ion implantation-assisted elliptical vibration cutting of hard and brittle material. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2024, 203, 104220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, X.; Ma, S.; Lu, Y.; Tian, H.; Xiao, J.; Xu, J. High efficiency fabrication of Si microlenses by applying in-situ laser and ultrasonic vibration hybrid diamond cutting. Precis. Eng. 2025, 93, 324–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, F.; Geng, Y.; Meng, B. Molecular dynamics simulation of laser assisted grinding of GaN crystals. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2023, 239, 107856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; To, S.; Sheng, X.; Xu, J. Molecular dynamics simulation on crystal defects of single-crystal silicon during elliptical vibration cutting. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2023, 244, 108072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, X.; Fang, F. Molecular dynamics study on nanometric cutting of ion implanted silicon. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2016, 117, 240–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, H.; Li, S.; Chen, G. Comparison of subsurface damages on mono-crystalline silicon between traditional nanoscale machining and laser-assisted nanoscale machining via molecular dynamics simulation. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B Beam Interact. Mater. At. 2018, 414, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Ke, J.; Yin, T.; Yip, W.S.; Zhang, J.; To, S.; Xu, J. Cutting mechanism of reaction-bonded silicon carbide in laser-assisted ultra-precision machining. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2024, 203, 104219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, J.; Chen, X.; Xiao, J.; Xu, J. A simulation investigation on elliptical vibration cutting of single-crystal silicon. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2020, 108, 2231–2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, J.; Chu, J.; Chen, X.; Xiao, J.; Xu, J. Numerical investigation on material removal mechanism in elliptical vibration cutting of single-crystal silicon. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2021, 134, 106019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; He, W.; Chu, J.; Zhang, J.; Chen, X.; Xiao, J.; Xu, J. Molecular Dynamics Simulation on Cutting Mechanism in the Hybrid Machining Process of Single-Crystal Silicon. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2021, 16, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plimpton, S. Fast parallel algorithms for short-range molecular dynamics. J. Comput. Phys. 1995, 117, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stukowski, A. Visualization and analysis of atomistic simulation data with OVITO–the Open Visualization Tool. Model. Simul. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2010, 18, 015012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Chu, J.; Chen, X.; Xiao, J.; Xu, J. Molecular dynamics simulation on structure evolution of silica glass in nano-cutting at high temperature. Mol. Simul. 2020, 46, 957–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Yip, W.S.; To, S.; Chen, B.; Xu, J. Numerical Investigation on the Effects of Grain Size and Grinding Depth on Nano-Grinding of Cadmium Telluride Using Molecular Dynamics Simulation. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 2670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erhart, P.; Albe, K. Analytical potential for atomistic simulations of silicon, carbon, and silicon carbide. Phys. Rev. B 2005, 71, 035211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Li, Q.; Liu, T.; Zhai, C.; Kang, R.; Jin, Z. Molecular dynamics study on the thickness of damage layer in multiple grinding of monocrystalline silicon. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2016, 51, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, H.; Chen, G.; Zhou, C.; Fang, Q.; Fei, X. A numerical study of ultraprecision machining of monocrystalline silicon with laser nano-structured diamond tools by atomistic simulation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 393, 405–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, M.B.; Li, X.P.; Rahman, M. Characteristics of “dynamic hard particles” in nanoscale ductile mode cutting of monocrystalline silicon with diamond tools in relation to tool groove wear. Wear 2007, 263, 1459–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Chu, J.; Zhu, Z.; Liu, C. Effect of temperature on surface morphology of single-crystal silicon in nanometric cutting. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2025, 684, 161957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Chu, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, J.; Chen, X.; Xiao, J.; Xu, J. Effect of tool rake angle on the material removal mechanism transition of single-crystal silicon: A molecular dynamics study. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2021, 115, 3631–3644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maras, E.; Trushin, O.; Stukowski, A.; Ala-Nissila, T.; Jónsson, H. Global transition path search for dislocation formation in Ge on Si(001). Comput. Phys. Commun. 2016, 205, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Yip, W.S.; Chen, J.; Wang, R.; Xu, J.; To, S. Atomic simulation of the temperature effect on fabrication mechanism of micro-structured surface on single-crystal silicon. J. Manuf. Process. 2025, 133, 238–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Xu, W.; Zhang, J.; Xiao, J.; Chen, X.; Xu, J. Numerical investigation on the temperature effect in nanometric cutting of polycrystalline silicon. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2022, 220, 107172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Chen, X.; Ke, J.; She, Z.; Zhang, J.; Xiao, J.; Xu, J. Numerical investigation on subsurface damage in nanometric cutting of single-crystal silicon at elevated temperatures. J. Manuf. Process. 2021, 68, 1060–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goel, S.; Luo, X.; Agrawal, A.; Reuben, R.L. Diamond machining of silicon: A review of advances in molecular dynamics simulation. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2015, 88, 131–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

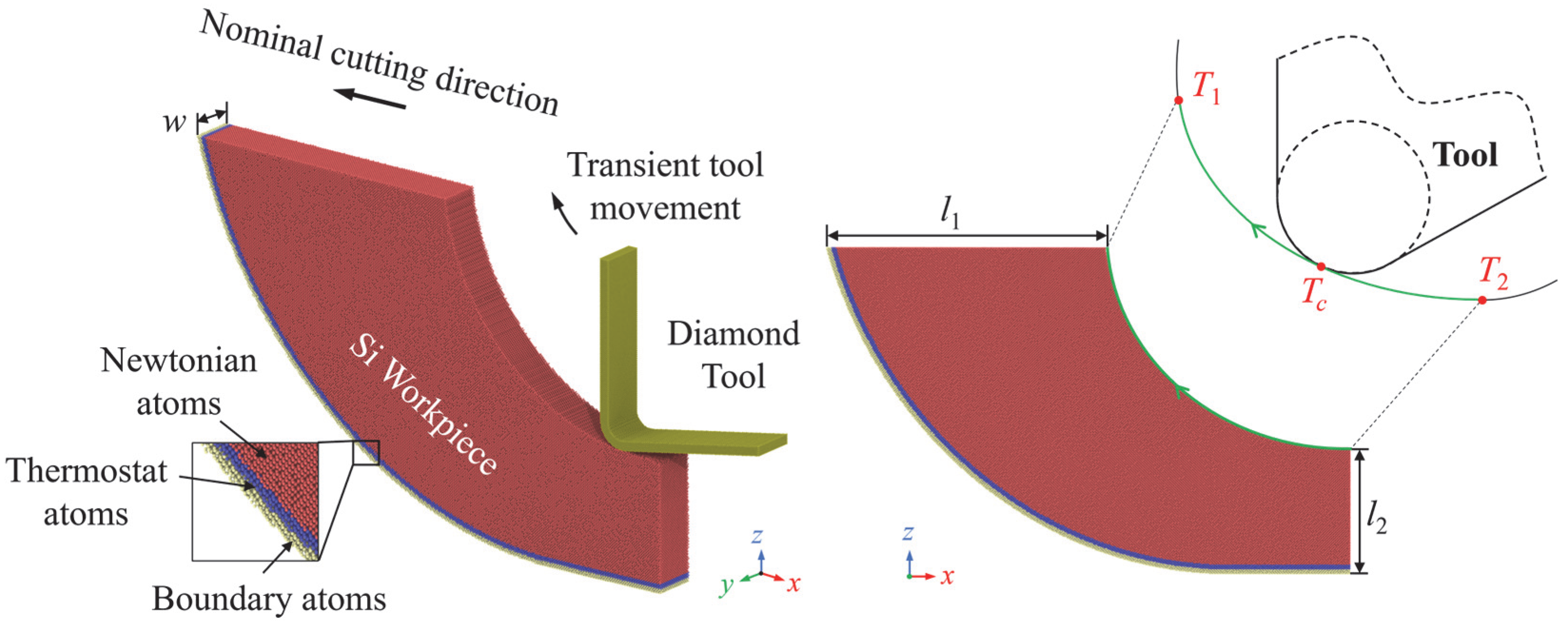





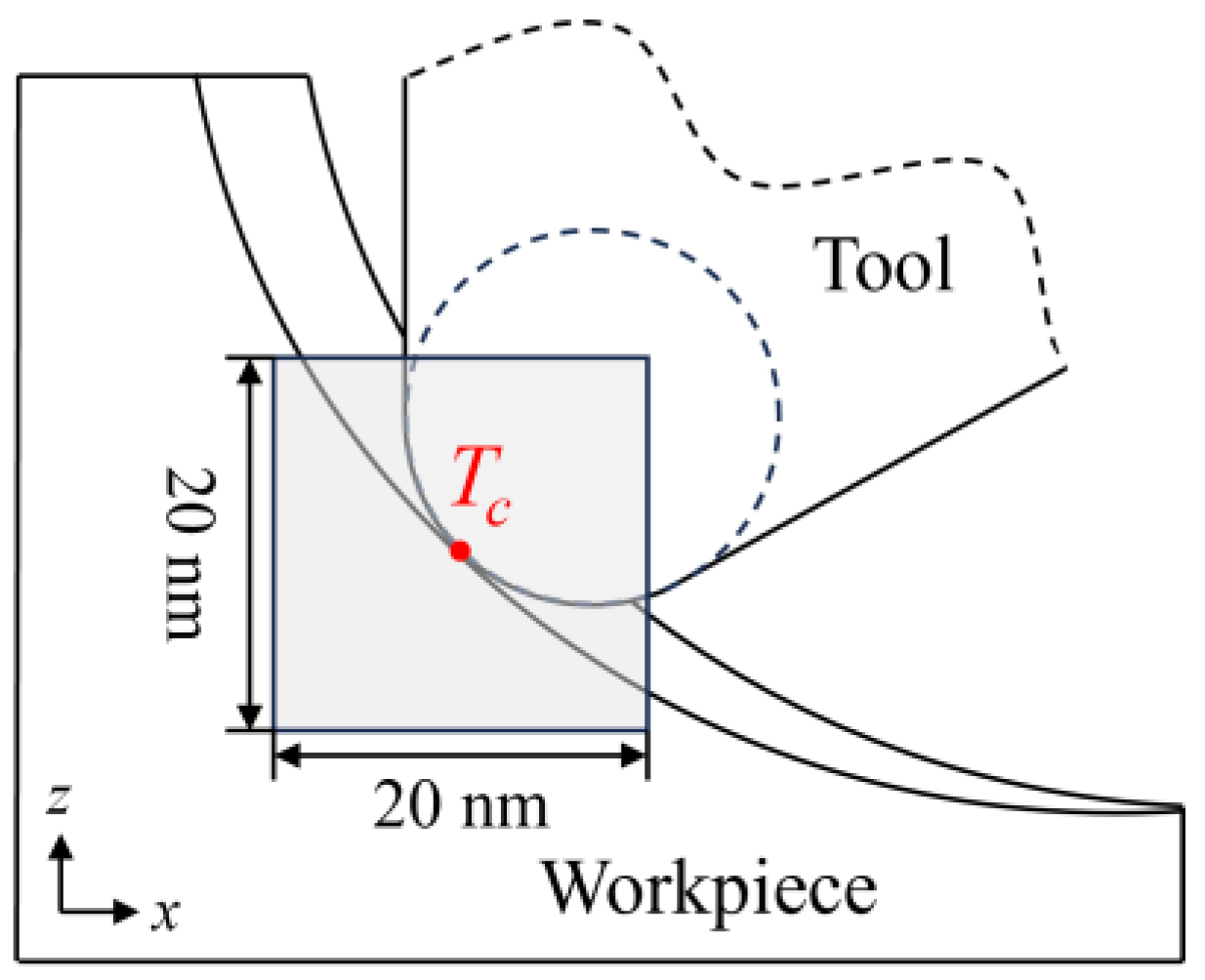

| Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| Size of workpiece (l1/l2/w) | 50 nm/15 nm/8.7 nm |
| Crystal orientation | x:(001)[100]; y:(001)[010] (workpiece and tool) |
| Total atoms | Approximately 1.9–2.1 million |
| Cutting temperature | 300 K, 600 K, 900 K, 1200 K |
| Vibration frequency (f) | 500 MHz |
| Phase difference (φ) | 90° |
| Vibration amplitude (Ax/Ad) | 40 nm/40 nm |
| Nominal depth of cut | 40 nm |
| Tool edge radius | 5 nm, 10 nm, 15 nm, 20 nm, 25 nm |
| Nominal cutting speed | 3 m/s |
| Timestep | 1 fs |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chu, J.; Yang, Y.; Zang, Y.; Ke, J.; Wang, Z.; Chen, C.; He, J.; Xu, A.; She, Z. Investigation into Laser-Vibration-Assisted Cutting of Single-Crystal Silicon by Molecular Dynamics Simulation. Micromachines 2025, 16, 1411. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16121411
Chu J, Yang Y, Zang Y, Ke J, Wang Z, Chen C, He J, Xu A, She Z. Investigation into Laser-Vibration-Assisted Cutting of Single-Crystal Silicon by Molecular Dynamics Simulation. Micromachines. 2025; 16(12):1411. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16121411
Chicago/Turabian StyleChu, Jianning, Yichen Yang, Yikai Zang, Jinyang Ke, Ziyue Wang, Chen Chen, Jifei He, Aijiang Xu, and Zhongdi She. 2025. "Investigation into Laser-Vibration-Assisted Cutting of Single-Crystal Silicon by Molecular Dynamics Simulation" Micromachines 16, no. 12: 1411. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16121411
APA StyleChu, J., Yang, Y., Zang, Y., Ke, J., Wang, Z., Chen, C., He, J., Xu, A., & She, Z. (2025). Investigation into Laser-Vibration-Assisted Cutting of Single-Crystal Silicon by Molecular Dynamics Simulation. Micromachines, 16(12), 1411. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16121411





